Physics Class 6 - Light, Mirrors and Lenses, Quantum Physics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is electromagnetic radiation?
Transverse wave composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields
Propagates without medium (unlike all other waves)
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
c = 3 × 108 m/s
What is the visible light spectrum?
Wavelengths of 700nm(red) - 400 nm (violet)
What is the order of electromagnetic waves, from longest to shortest?
Radio, Micro, Infrared, Visible Light, Ultraviolet, X-Rays
What is energy of a sound wave?
Like sound waves, proportional to square of wave amplitude
Amplitude with electromagnetic waves is electric field strength
What does light do when it hits the interface of two media?
Reflection: bounces back
Transmission: continues through, but refracts
What is the angle of refraction?
Angle of incidence = angle of refraction
Angle measured relative to surface normal (perpendicular)(not the surface)
What is the index of refraction?
How much slower light travels through a medium than a vacuum
n = c/vmedium
n >/= 1
nvacuum = nair = 1
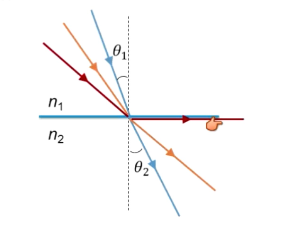
What is Snell’s law?
Tells us angle of refraction
n1 sin(theta1) = n2 sin (theta2)
For angles between 0 and 90, as theta increases, so does sin theta
As n gets larger, theta decreases
What is the equation of lens power?
P = 1/f
f = focal length in centimeters
In diopters
What do glasses with a negative diopter value do?
They form an image of a far away thing f centimeters from the lens or your eye
How do you fix nearsightedness?
A diverging lens
Negative diopter value
How do you fix farsightedness?
Converging lens
Positive diopter
What is total internal reflectance?
Happens when light transmits to a medium of lower refractive index
As you increase the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction increases faster
What is the critical angle?
thetac = critical angle
Angle of incidence that creates a 90 degree angle of refractance
sin thetac = n2/n1
When theta is greater than the critical angle, you get all energy reflected
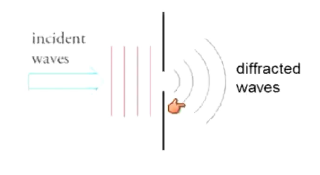
What is diffraction?
When waves encounter an obstacle/aperture about the same size of their wavelength, the waves will spread out
What is dispersion?
Effect that allows prisms to split white light into ROYGBV colors → rainbows
First rule of waves (speed depends on medium alone, not frequency) is untrue for light
Higher frequencies have higher indexes of refraction
What is polarization?
One direction of oscillation is privileged over another (usually, light waves have electric fields that oscillate in all directions equally)
Via reflection or transmission through a special fiber/material
What is plane polarization?
Removal of all electric field oscillations except those along one plane parallel to the direction of propagation
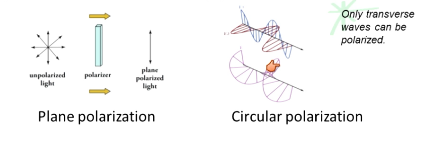
What is circular polarization?
Two perpendicular electric field components oscillate 90 degrees out of phase with each other
Vector of the sum of these components creates a field that rotates in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation
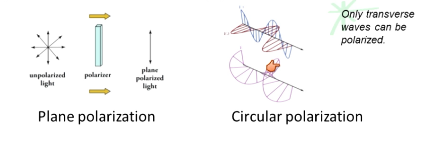
What waves can be polarized?
Transverse waves
What are the mirror equations?
1/f = 1/o + 1/i
m = -i/o
f = focal length (intrinsic property)
o = object distance; object distance from lens/mirror (almost always positive)
i = image distance; distance from lens/mirror that image is formed
m = magnification (size of image compared to object)
What does a negative magnification mean?
The image is inverted relative to the object
What is the sign of f for a concave mirror, convex mirror, concave lens, and convex lens?
Concave mirror: +
Convex mirror: -
Concave lens: -
Convex lens: +
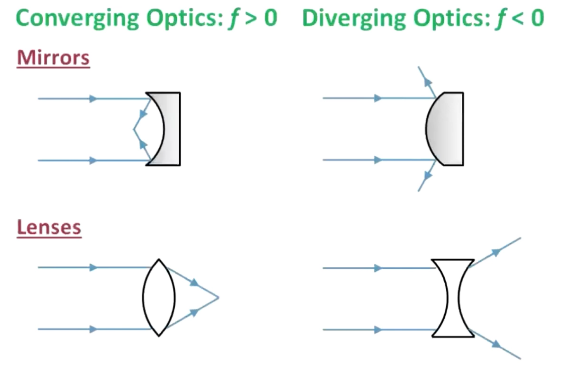
Where is the image located in a mirror with positive/negative f? Lens?
Mirror with positive f: same side of mirror as the object
Mirror with negative f: opposite side of mirror as object
Lens with positive f: opposite side of lens as object
Lens with negative f: same side of lens as object
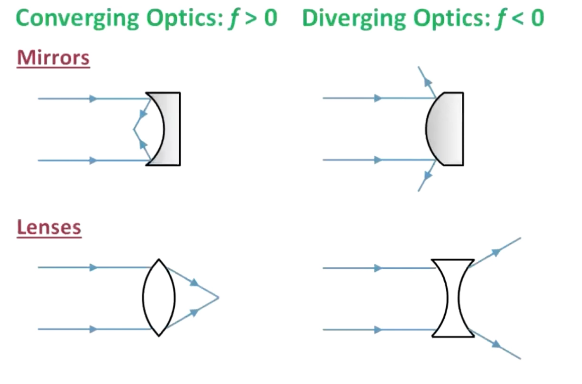
When is image distance positive?
Positive where light actually goes (on opposite side of lens) (on same side of mirror)
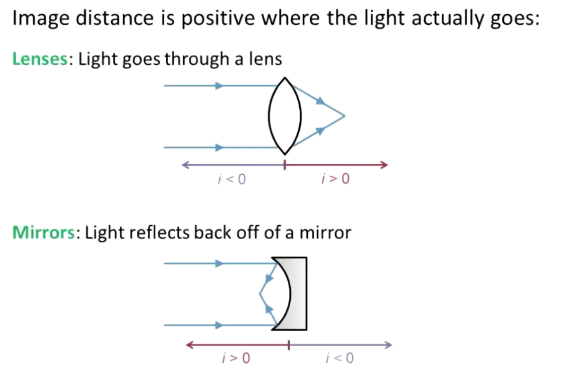
What is a real image?
Light rays converge
i > o → m = -1/o < o
Inverted image
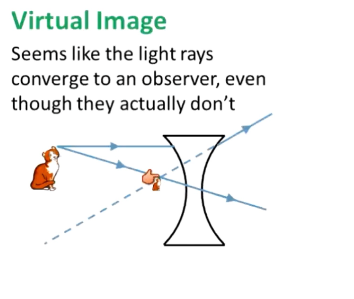
What is a virtual image?
To the observer, the light rays converge → they do not actually
Eye traces them back to where they intersect and tricks you
i < o → m = -1/o > o
Upright image
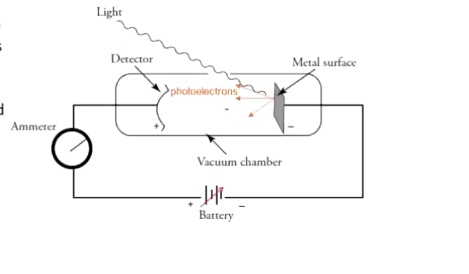
How is the photoelectric experiment set up?
Light shines on metal surface → energy to metal → loosest bound electrons ejected → captured by high potential detector → register as current in ammeter
What do you expect from the photoelectric experiment?
If light is a wave, in terms of brighter vs dimmer light of any color
Brighter: higher intensity → liberate more electrons → higher current
Dimmer: lower intensity → fewer liberated electrons → lower current
What do you expect from the photoelectric experiment?
If light is a wave, in terms of how long it takes to see a current
Delayed
What do you expect from the photoelectric experiment?
If light is a wave, if the polarity of battery is flipped and voltage is increased, what do we need to do to the light to see current flow?
As detector becomes more negative (it was positive, normally), more and more electrons are repelled → eventually you get no current
The potential of the detector at which you get no current will depend on intensity of the light
What is the result from the photoelectric experiment?
In terms of brighter vs dimmer light of any color
Brighter light meant more current only for short wavelengths
Some show no current, regardless of brightness
What results did they get from the photoelectric experiment?
In terms of how long it takes to see a current
Current was instantaneous, no delay
What results did they get from the photoelectric experiment?
If the polarity of battery is flipped and voltage is increased, what do we need to do to the light to see current flow?
The potential at which the current stops flowing depends on wavelength, not intensity
Why were the results of the photoelectric experiment weird?
Electromagnetic energy is quantized as particles, photons, containing energy E = hf (aka E = hc/wavelength)
h = planck’s constant
f = frequency
Each photon delivers energy to a single electron → ejected photoelectrons have energy KEmax = hf - phi
phi = work function (binding energy) of the metal target
Because delta KE = - delta PE = -eV for electron striking detector, -eVstop = KEmax
What is the Heisenberg uncertainty principle?
Light behaves as a particle when it interacts with matter
Particles of matter, like electrons, show wave properties (interference and diffraction) under the right conditions
No particle behaves solely as a particle, and no wave solely as a wave
Waves are spread out. If you create a wave with a specific location (central peak with no spread), it is caused by the interference of an infinite number of different wavelengths
Uncertainty in position and momentum (function of frequency) due to waviness of matter is characterized by delta x * delta p >/= h/2pi
delta x = uncertainty from measuring position
delta p = uncertainty from measuring momentum
h = planck’s constant