A&P Spring 2025
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
5 types of bones
Short, long, flat, sesamoid, irregular
ventral
Towards the front (belly)
Dorsal
Towards the back (spine)
Anterior
Toward ventral side
Posterior
Towards dorsal side
Superior
Above
Inferior
Below
Medial
Towards the midline |
Lateral
Away from the midline
Proximal
Closer to point of attachment
Distal
Further from point of attachment
Superficial
Closer to the surface of the body
Deep
Further from the surface of body
Osteoblasts
Cells that synthesize bone tissue and are responsible for bone formation.
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells that maintain bone tissue and function in the regulation of bone density.
Lacunae
cavities within bone that house osteocytes.
Canaliculi
Microscopic channels in the bone connect lacunae and help communication and nutrient exchange between osteocytes.
Osteoclasts
bone cells that break down bone tissue
Bony joints
immovable joints formed when bones fuse together, providing stability and strength.
Fibrous joints
joints connected by dense connective tissue, allowing for little to no movement.
cartilaginous joints
joints connected by cartilage, allowing for limited movement between bones.
Synovial joints
joints characterized by a fluid-filled cavity, allowing for a wide range of motion.
ball on socket joint
type of synovial joint, spherical head fits into a cup-like socket of another bone, allowing for rotational movement in multiple directions.
Condylar joint
type of synovial joint, oval-shaped end of one bone fits into a similarly shaped hollow of another bone, allowing movement in two planes.
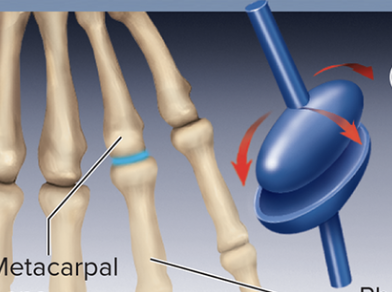
Saddle joint
type of synovial joint, opposing surfaces are shaped like a saddle, allowing for movement in two planes, such as flexion, extension, and opposition.
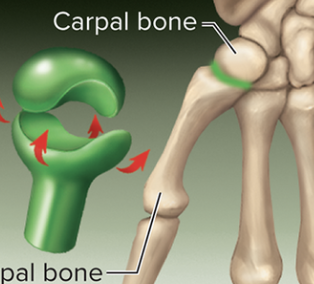
Plane joint
joint type where flat or slightly curved surfaces glide over one another, allowing for limited movement in multiple directions.
Hinge joint
type of synovial joint where the cylindrical end of one bone fits into a trough-shaped surface of another bone, allowing movement primarily in one plane, such as flexion and extension.
Pivot joint
type of synovial joint where a rounded end of one bone rotates within a ring formed by another bone and ligament, allowing for rotational movement.
Endomysium
a thin layer of connective tissue that surrounds each muscle fiber
perimysium
a connective tissue sheath that surrounds groups of muscle fibers, or fascicles
Epimhsium
a connective tissue layer that surrounds an entire muscle
Fascia
a sheet of connective tissue that encloses muscles and other organs
myeloid tissue
a type of connective tissue that produces blood cells, primarily found in the bone marrow.
Epiphysis
the end part of a long bone, initially separated from the main bone by a growth plate.
metaphysis
the region between the diaphysis and epiphysis of a long bone, where growth occurs during development.
Sarcomere
z disc
the functional unit of a muscle fiber, responsible for muscle contraction.
ends of sacromere
aponeuroses
broad, flat tendons that connect muscles to the parts they move.
transverse formania
openings in the cervical vertebrae that allow for the passage of the vertebral arteries and veins. of
formania
are openings in bones that allow for the passage of nerves or blood vessels.
amphiathrosis
slightly moveable joint
diarthrosis
freely moving joint
Synovial fluid
fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints reduces friction between the articular cartilages during movement.
gomphosis
joint between a tooth and the mandible
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle
Slow oxidative
muscle fibers that have long endurance contract slowly, and are aerboic
Fast oxidative
muscle fibers that contract quickly have moderate endurance, both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism.
Fast glycolic
muscle fibers that contract quickly, have low endurance, and primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism.