World geography unit 1 vocab
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Physical geography
the natural world, weather climate, physical features, waterway, etc.
Human geography
studies the distribution of humans and their activities on the surface of the earth and the processes that generate these distributions (Ex: culture, settlement, politics, agriculture, cites)
Toblers 1st law of geography
“Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things.”
Scale analysis
this is the level of representation, expirience, and organization of the geographical events + process
Absolute location
exact location on the earth using latitude and longitude (ex: a grid system or an address)
Relative location
the location of a place by comparing it to another location (cardinal direction, distance, time and landmarks)
physical
natural characteristics (ex: climate, vegetation, wildlife and topography)
human
Man-made characteristics ( ex:agriculture, architecture, reliving and economics )
Region
grouping of places that have something in common and can be given a name based on a similar features ( climate, geographic, political, economic, cultural and physical region )
Formal / uniform
An area defined by a limited number of related characteristics (ex: city, state and country)
Functional
areas created by movement around a central hub or node, must have movement (ex:subway system in New York)
Perceptual
How people perceive a region. It exists in someone’s mind meaning the boundaries and characteristics are different depending on the individuals perception. (Ex: south and Midwest)
Depend
to get essential resources, humans DEPEND on the environment/nature for survival (ex: water, and soil for agriculture)
Adapt
humans can change / adapt to various environmental conditions for survival and to meet their needs (ex: clothing like shorts during summer and jackets during winter)
Modify
any change in the physical environment by humans (ex:building a bridge)
movement
how people and places are linked by the flow of communication and the movement of people, goods and ideas (goods, energy, disease, ideas and people)
Migration
the act of owing from one place, country or location to another
Refugees
People are fleeing armed conflicts or persecution
Migrants
choose to move to improve their lives
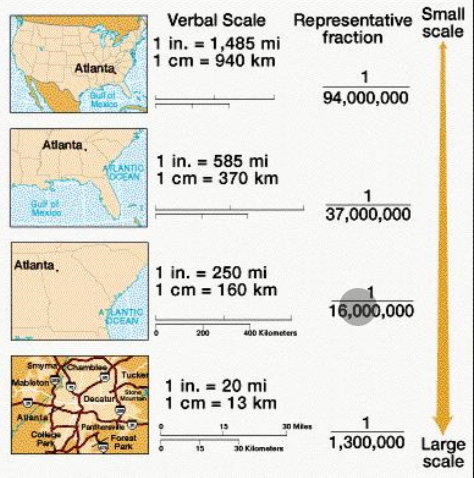
Map scale
distance on a map relative to the distance on earth
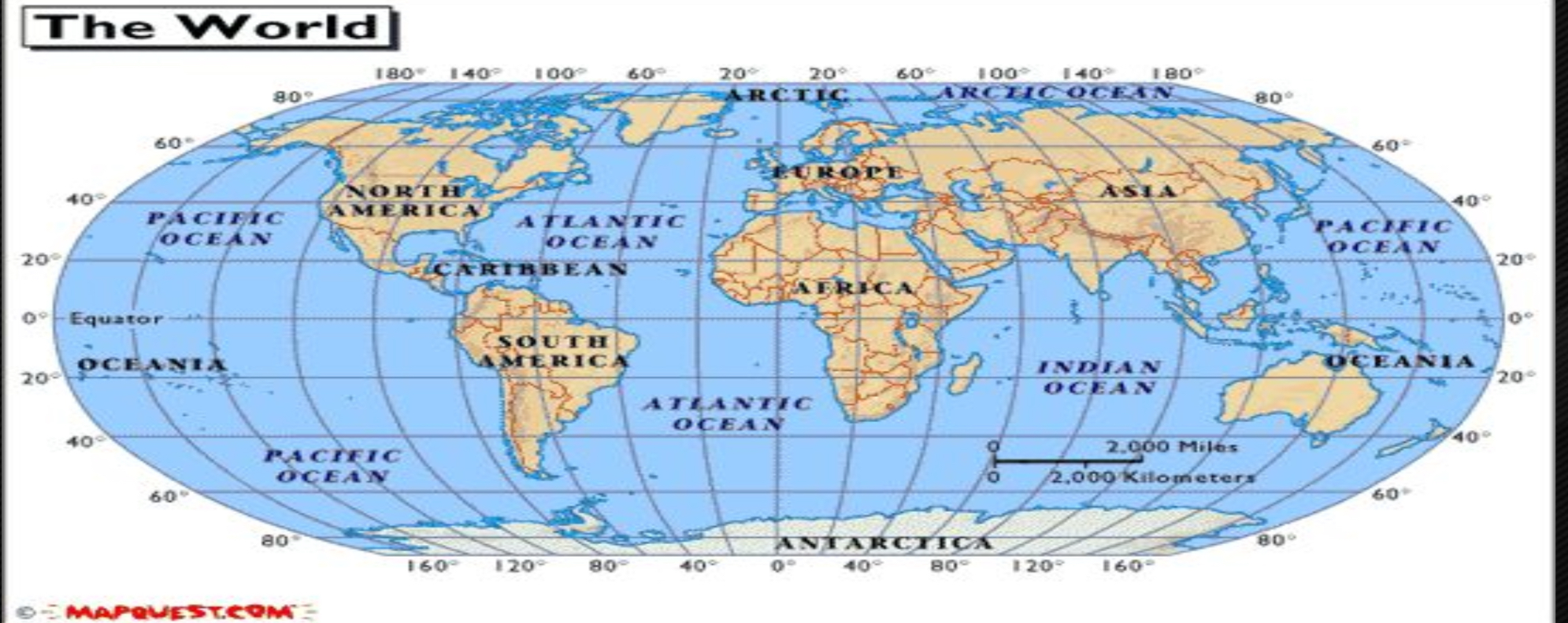
Small scale map
Show large areas in less detail
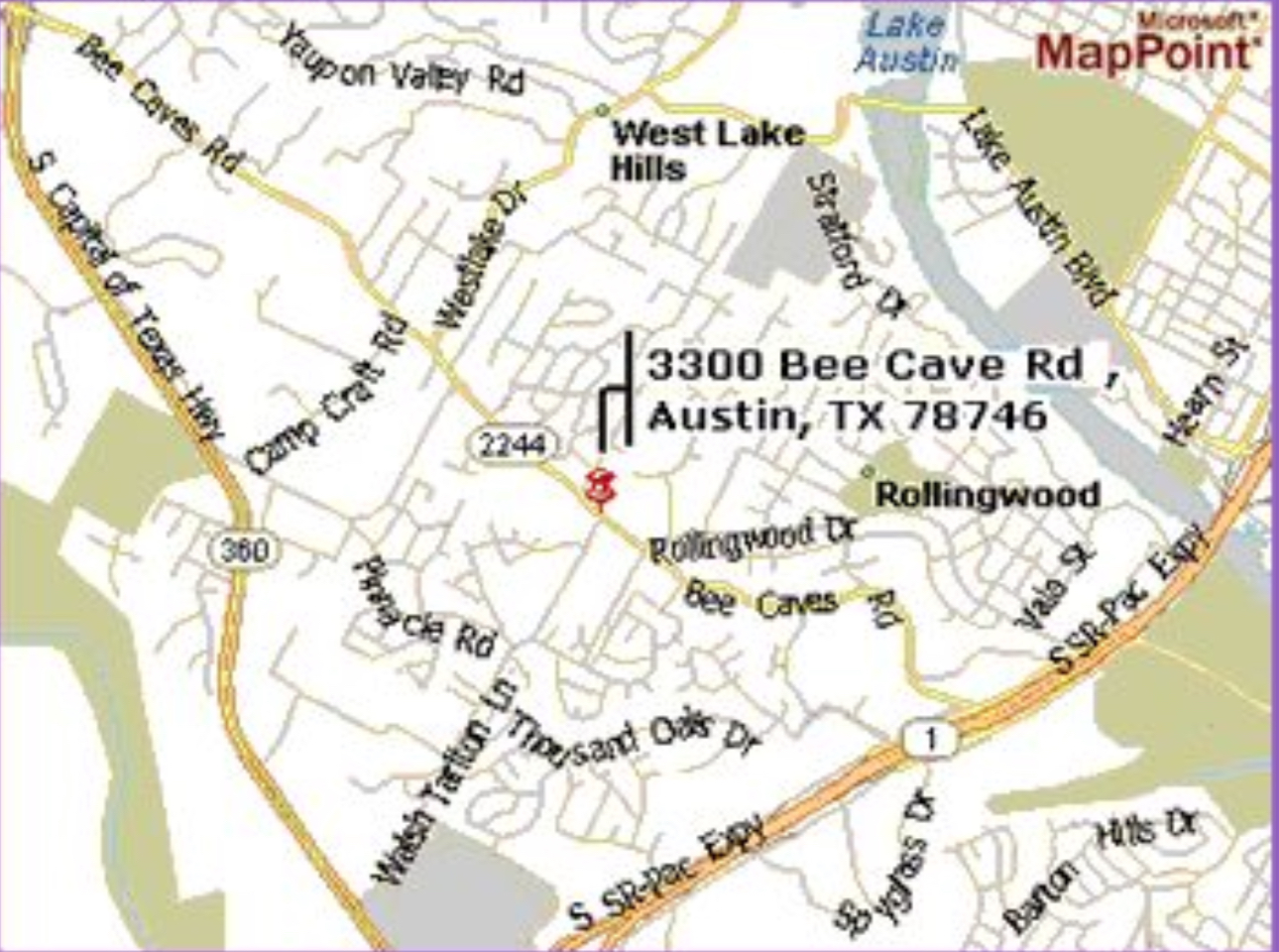
Large scale map
Shows small areas in greater detail
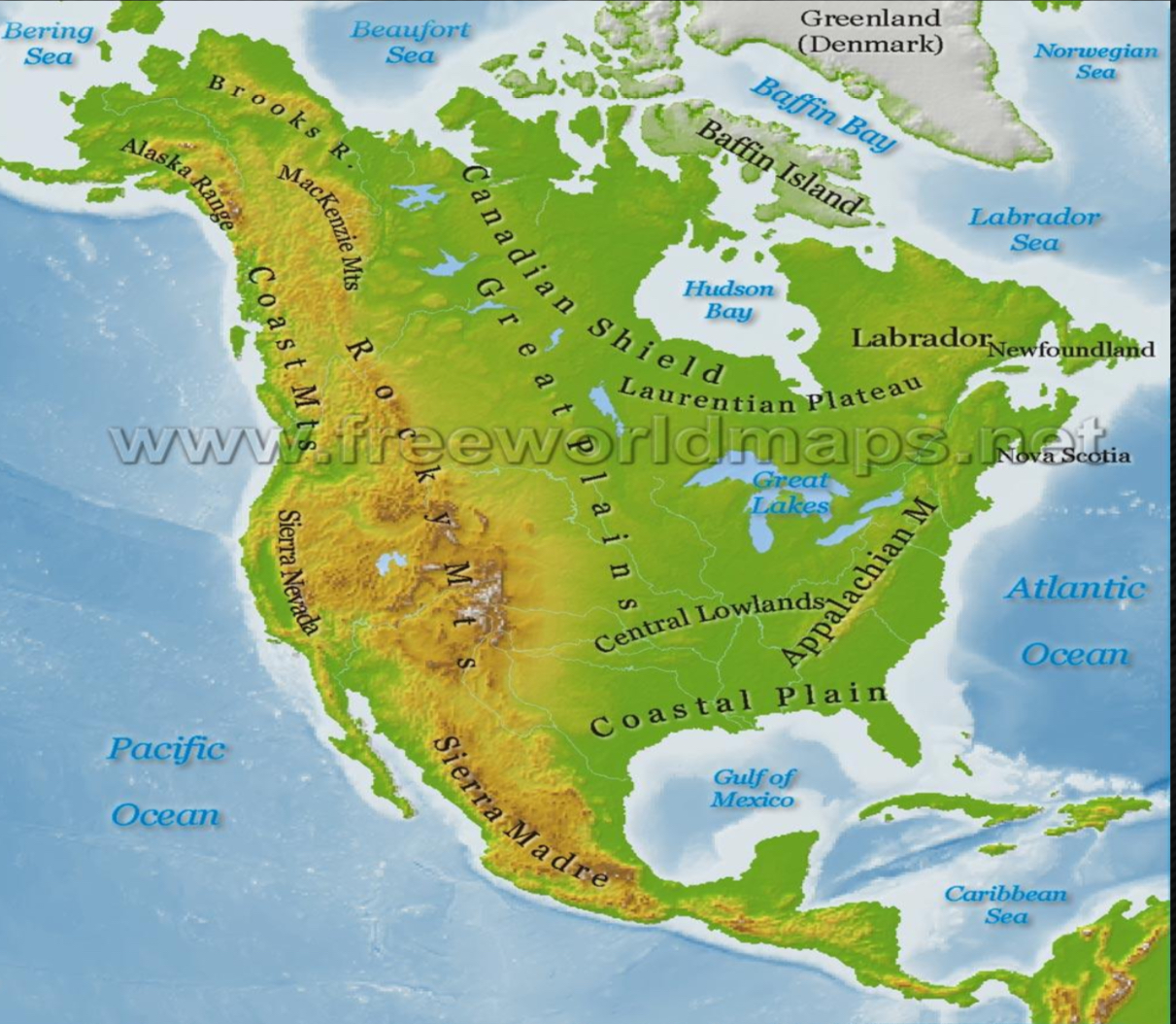
Physical map
highlight naturally occurring features
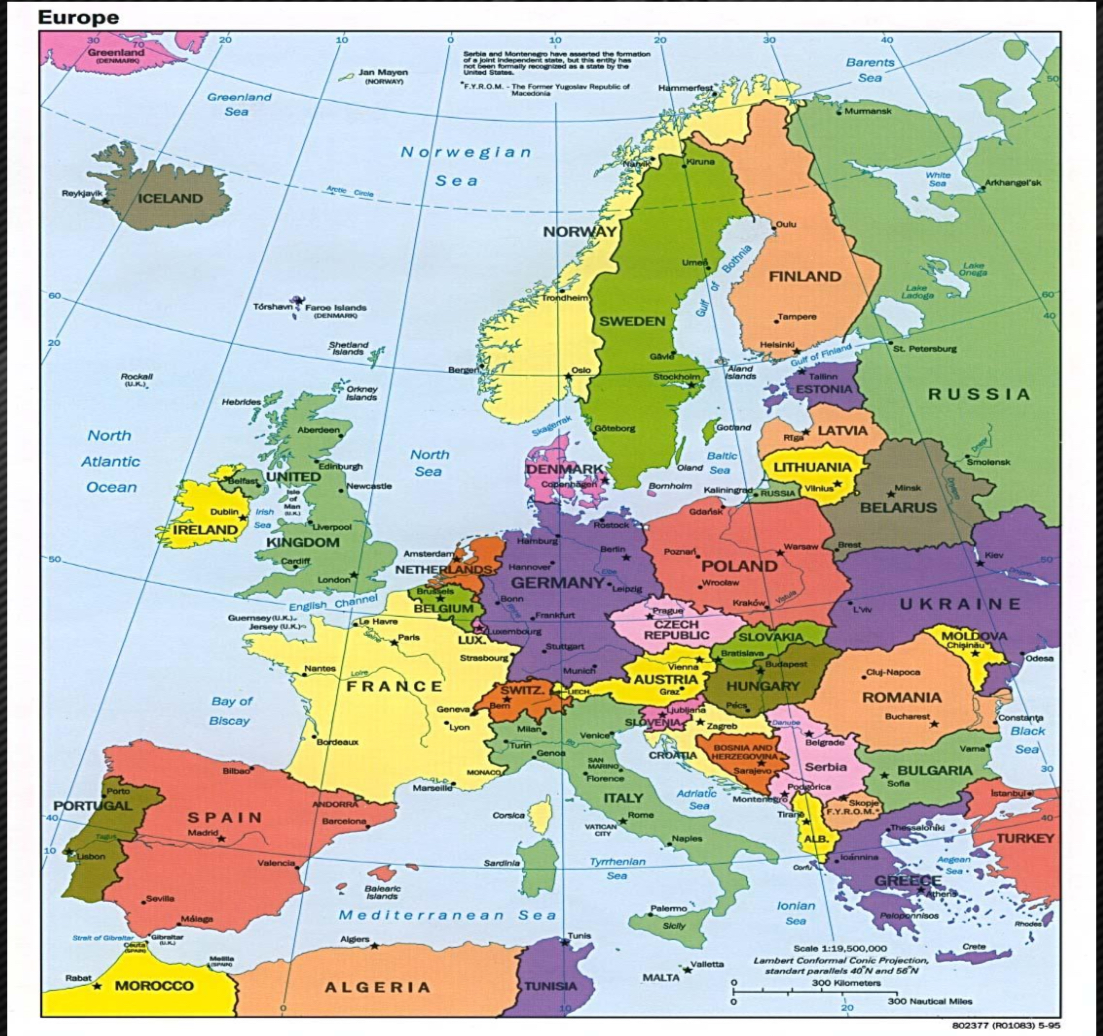
Political map
highlight human-made features
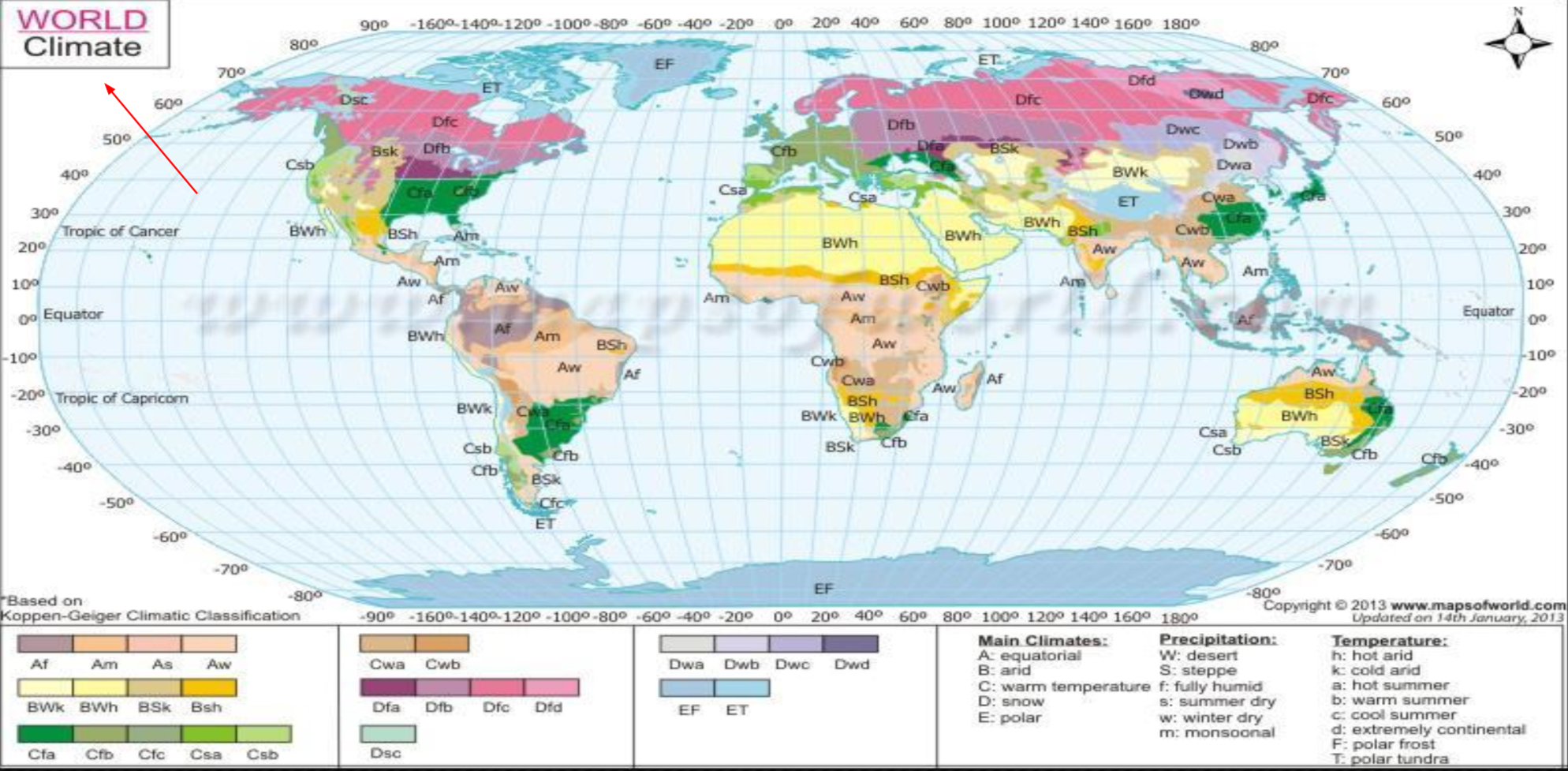
Thematic map
show one theme
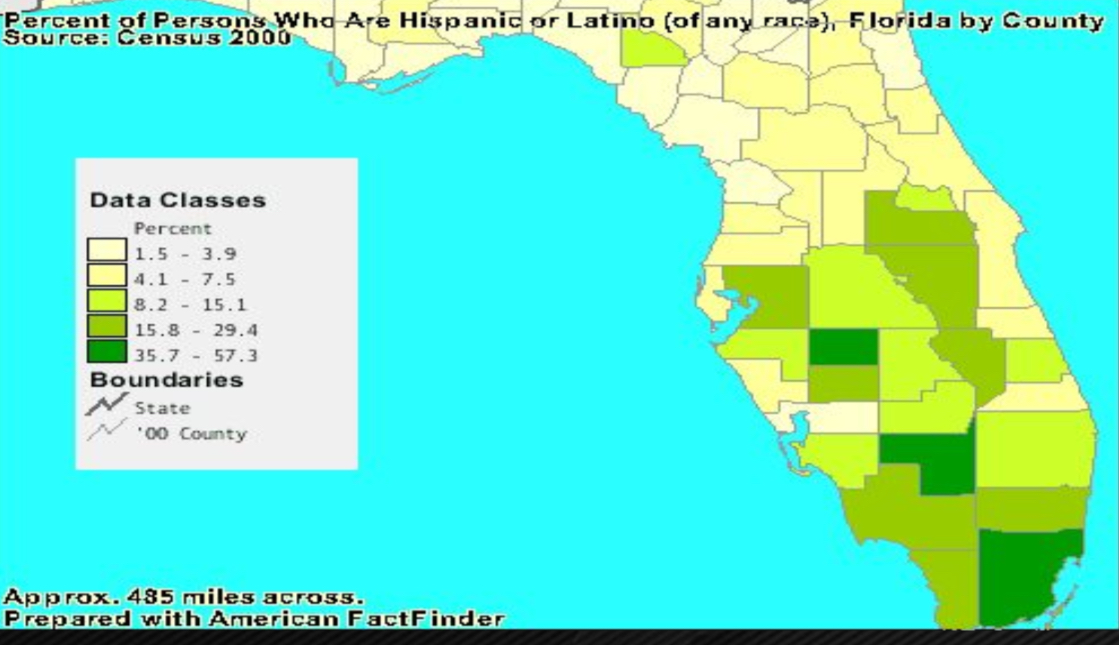
Choropleth map
uses shading to show different levels of data
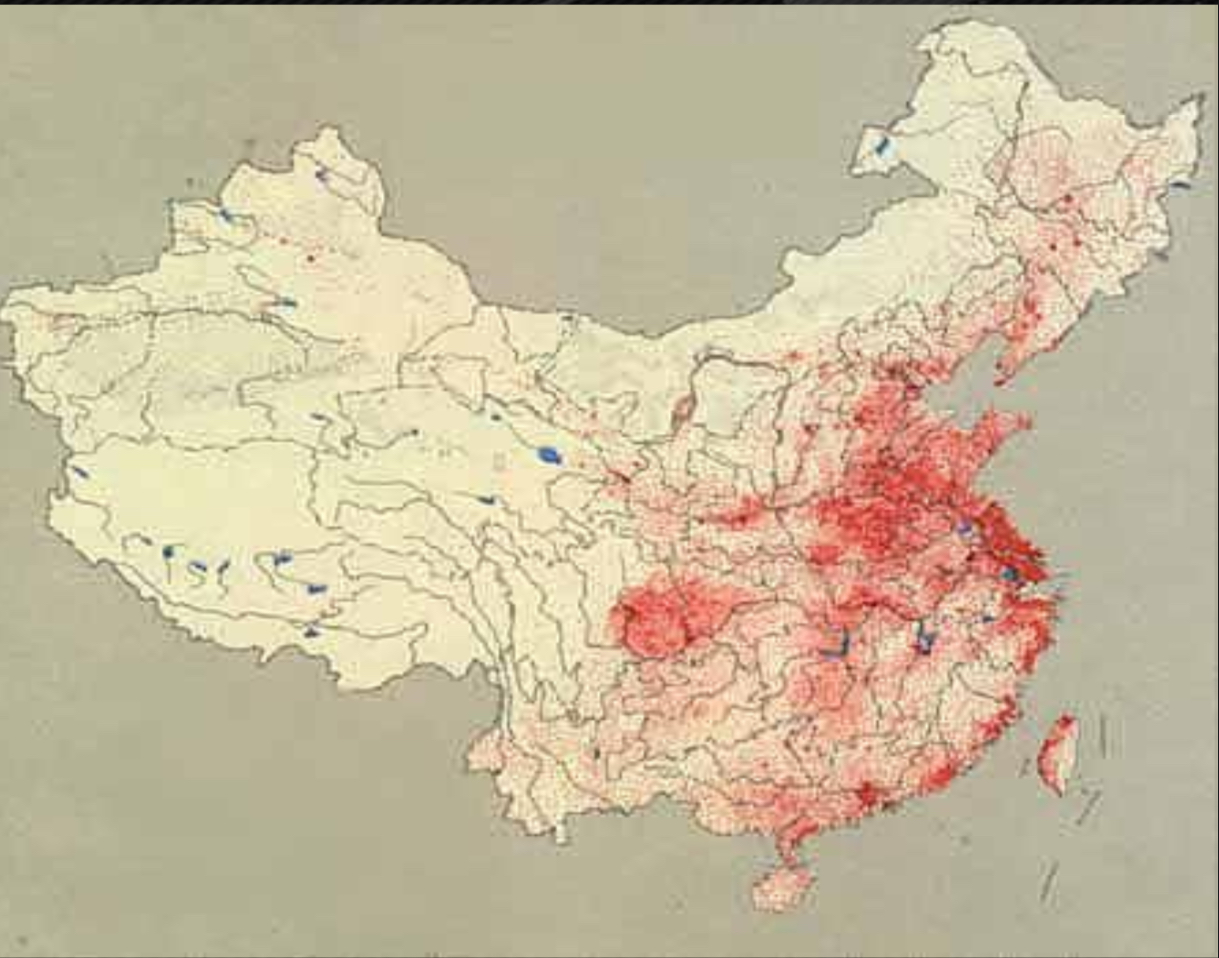
Dot / Pin dot map
each dot represents a number of occurrences
the closer the dots are together, the higher the occurrence
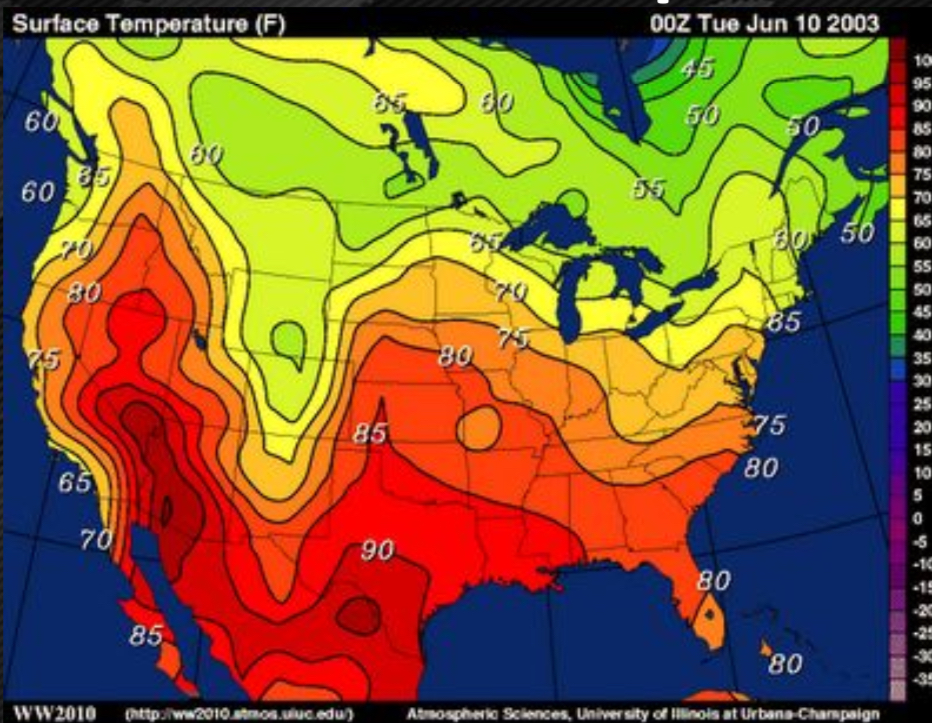
Isoline map
connects points of equal value to make lines on a map ( ex:topographic / contour map )
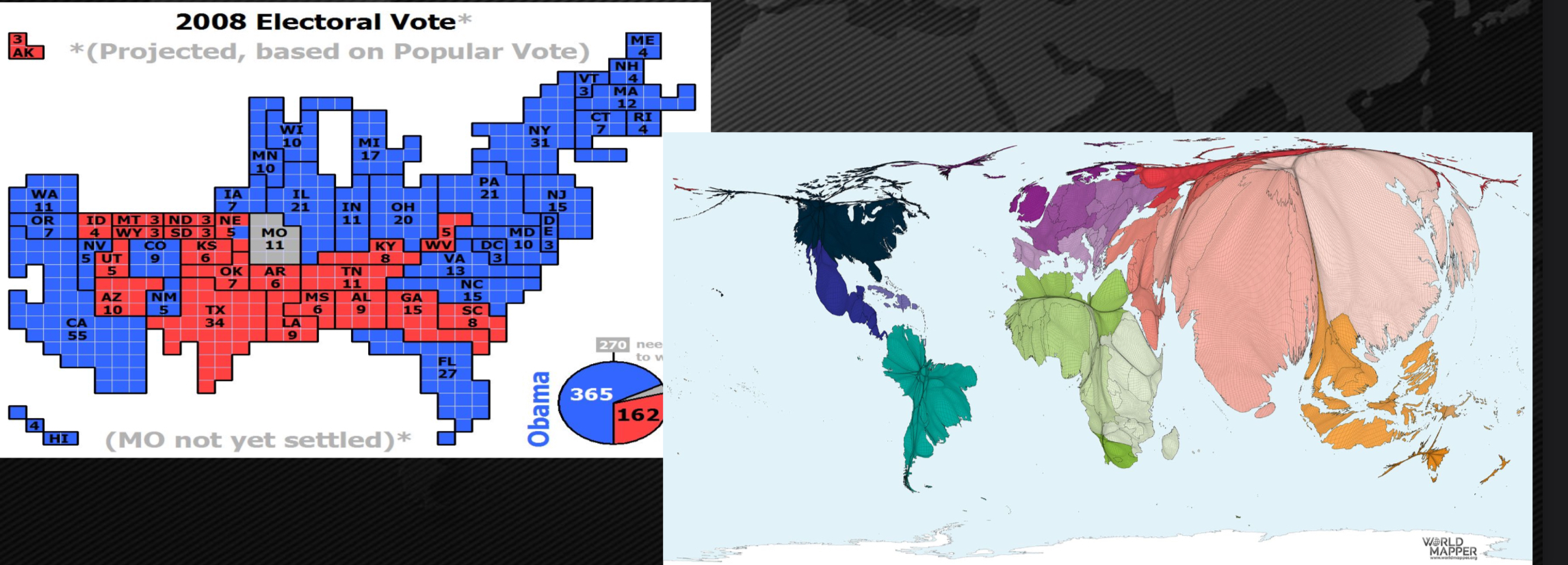
Cartogram
show size using data other than area
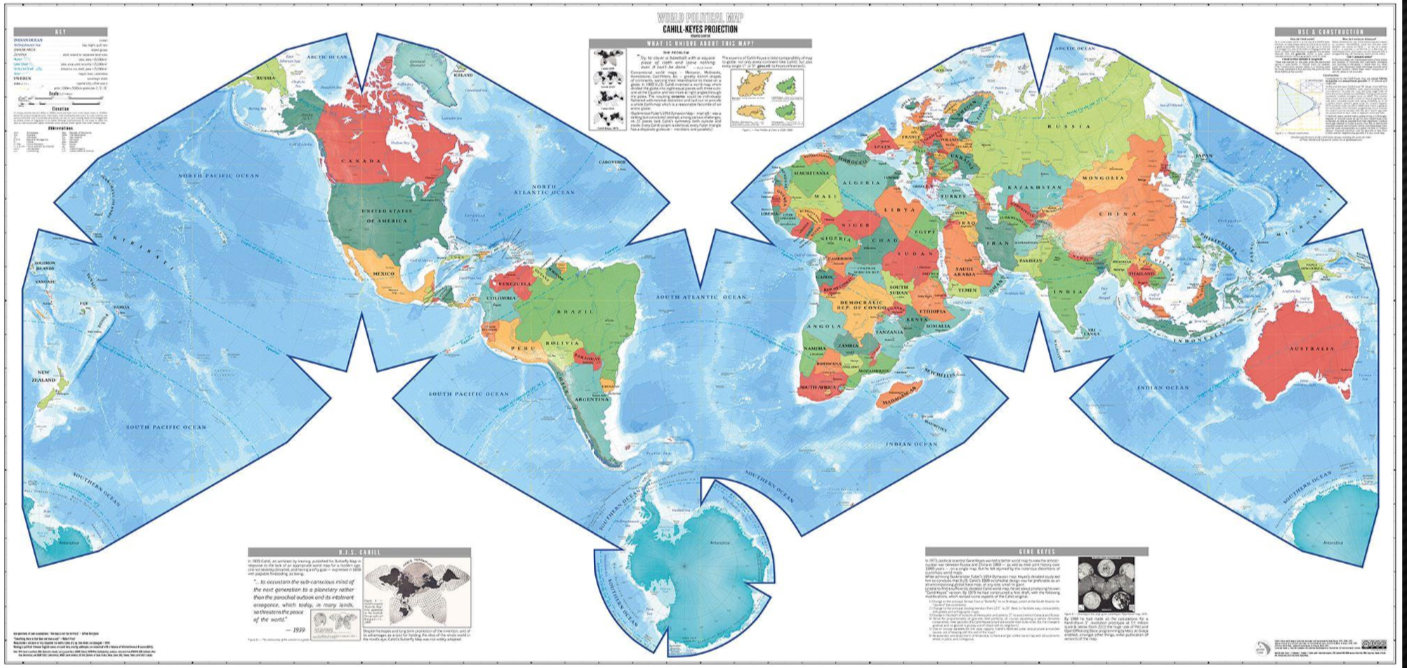
Map projection
a way to make a flat representation of the earth
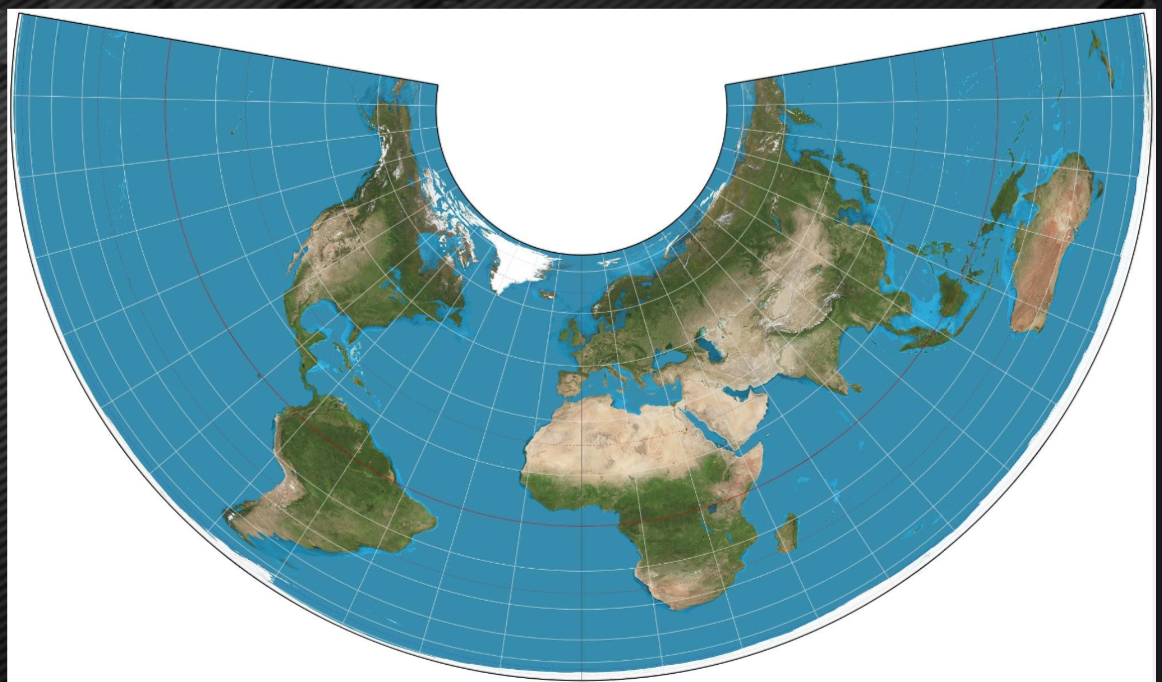
Distortions
Every map MUST have distortions that result from making a 2D representation of a 3D sphere
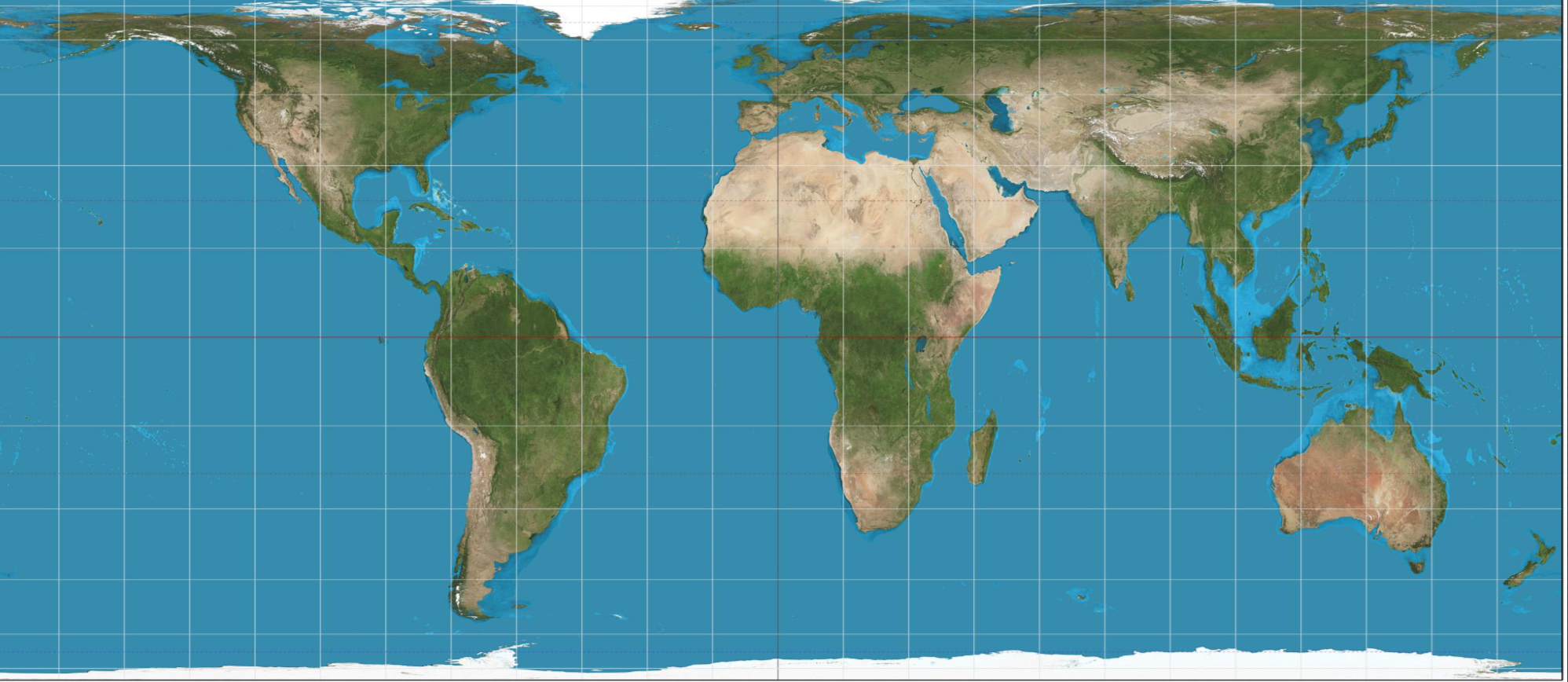
Gall-peters projection
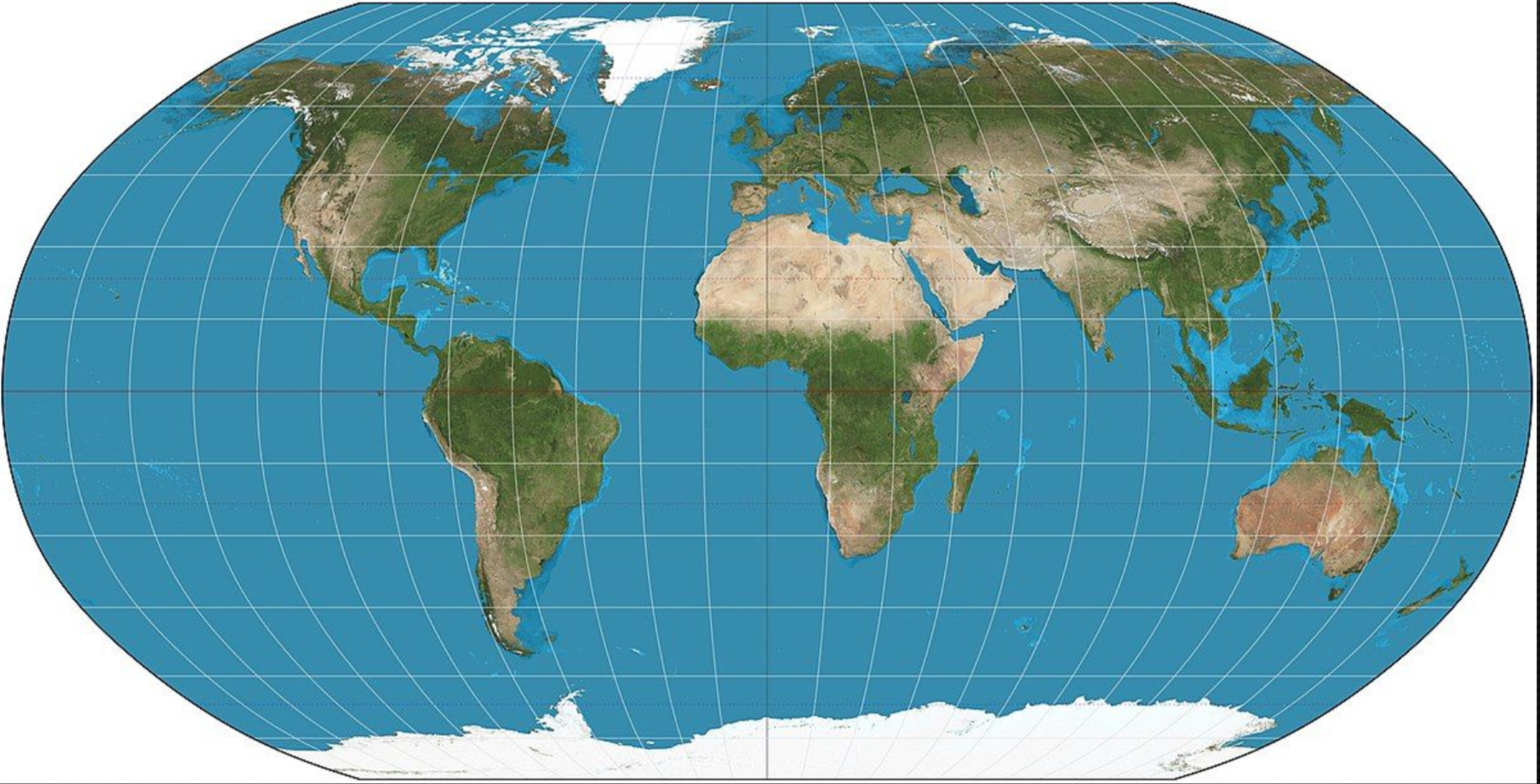
Robinson projection
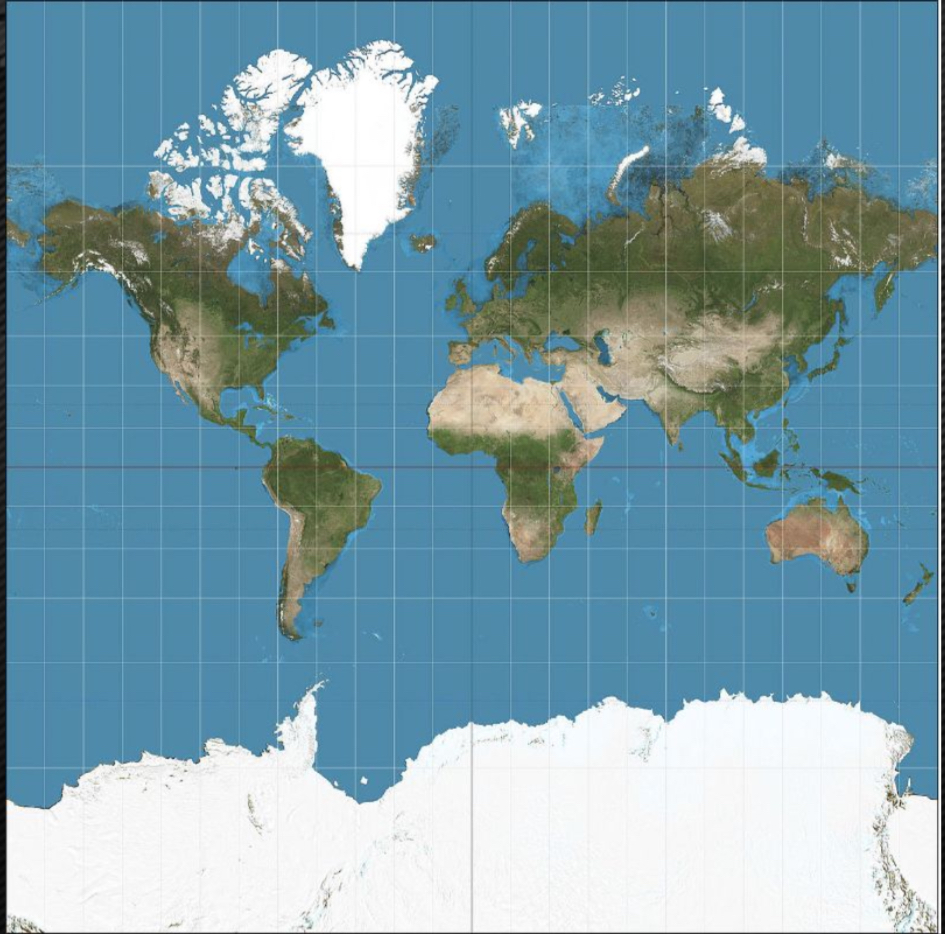
Mercator / cylindrical projection
Globe
THREE dimensional representation of the earth
Maps
TWO dimensional representations of selected parts of the earth surface
Remote sensing
gathering information on the earths surface from distance by using airplanes but mainly satellites
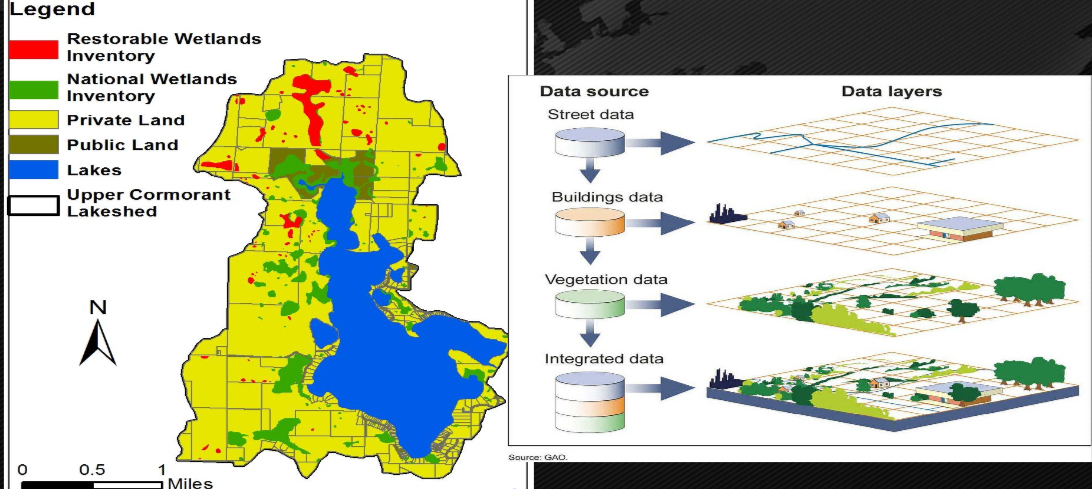
Geographic information system
the GIS is a database geographers use to create maps with “data layers”
These maps allow geographers to look at phenomena and data spatially
Satellite navigation systems
utilization of multicultural GPS points to guide navigation or track movements
Global Positioning System (GPS)
satellite based system for the determining the absolute location of places or geographic features