dinosaurs final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/214
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:56 AM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
215 Terms
1
New cards
what are the two types of fossils?
body and trace
2
New cards
example of a body fossil
bone
3
New cards
example of a trace fossil
footprints
4
New cards
why is the dinosaur record so bad?
dinosaurs were terrestrial, therefore their fossils were not preserved as well as subigneous organisms
5
New cards
absolute dating
actual numerical age
6
New cards
relative dating
comparison between two aged things
7
New cards
what types of rocks are used for absolute dating?
igneous
8
New cards
law of superposition
relative ages; oldest rock is at the bottom, youngest is at the top
9
New cards
parts of the mesozoic from oldest to youngest
triassic, jurassic, cretaceous
10
New cards
point of evidence for plate tectonics
the continents fit together almost perfectly, especially south america and africa
11
New cards
paleomagnetism
magnetic fields cause reverse polarity, making pattern of rock across ocean ridges
12
New cards
what defines the chordates as a clade?
they possess a notochord, a dorsal nerve cord
13
New cards
what defines the tetrapoda as a clade?
1. adaptation to live on land and facilitate locomotion (legs, four digits on feet, etc)
2. amniotic egg
14
New cards
what is the defining character of amniotes?
amniotic egg, allowing for the laying of eggs on land and independently of water
15
New cards
why are amniotic eggs important in an evolutionary sense?
they allowed the early amniotes to become more independent of the water and eventually led to full independence from water.
16
New cards
fenestrae
holes in the skull
17
New cards
why are fenestrae important?
increase the area and improve alignments for attachment of muscles, leading to stronger muscle attachments and a lighter skull
18
New cards
anapsid
no holes in the head
19
New cards
example of an anapsid
turtle
20
New cards
synapsid
one hole in the skull
21
New cards
example of synapsid
humans and all mammals
22
New cards
diapsid
two holes in the skull
23
New cards
example of diapsid
dinosauria
24
New cards
what clade is the ancestor to crocodiles, dinosaurs, and pterosaurs?
archosauria
25
New cards
are pterosaurs part of dinosauria?
no
26
New cards
are pterosaurs part of archosauria?
yes
27
New cards
carrier’s constraint
inability to run and breath at the same time in a sprawling stance
28
New cards
how did dinosaurs get around carrier’s constraint?
development of an erect stance
29
New cards
open acetabulum
hole in the hip
30
New cards
what caused the open acetabulum?
erect stance
31
New cards
what is the defining character of dinosaurs?
open acetabulum
32
New cards
what are the two groups of dinosaurs?
ornithischian and saurischian
33
New cards
which group of dinosaurs has a rear-facing pubis?
ornithischian
34
New cards
which group of dinosaurs has a front-facing pubis?
saurischian
35
New cards
when did dinosaurs first appear?
around 228 mya
36
New cards
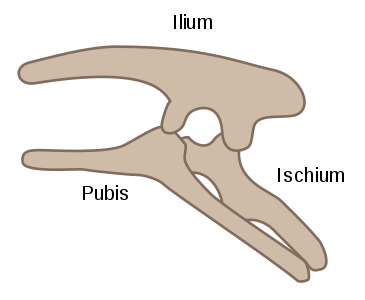
pelvis of…
ornithischian pelvis
37
New cards
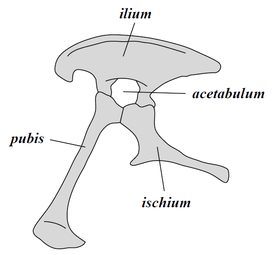
pelvis of…
saurischian pelvis
38
New cards
how did the end triassic mass extinction benefit the dinosaurs?
opened ecological niches, allowing dinosaurs to become dominant over synapsids and archosaurs and more well adapted
39
New cards
what is the main feature that defines the saurischians as a group?
front-facing pubis
40
New cards
another defining feature of saurischians
hinge of jaw is on one plane, scissor-like
41
New cards
what is sexual dimorphism?
male and female of a species have distinguishing and different features including size and appearance
42
New cards
what are pneumatic bones?
light bones, connected to the respiratory system
43
New cards
what were pneumatic bones used for?
moving faster and reducing energy spent when moving
44
New cards
were theropods bipedal or quadripedal?
obligate bipeds
45
New cards
what is unique about theropod hands?
large and grasping, made of low-density bones
46
New cards
what do theropod teeth and jaw structure suggest?
that they were meat-eaters; for slicing NOT chewing
47
New cards
theropod teeth were…
curved, pointed, and serrated
48
New cards
theropod jaw was…
scissor-like
49
New cards
what do orinthomimsaurs and oviraptors have in common?
no teeth
50
New cards
what is the encephalization quotient?
brain-mass to body-mass ratio
51
New cards
what do we know about the senses of theropods?
they had strong vision, large eyes, and enlarged ear cavity
52
New cards
did dinosaurs lay eggs or live birth?
layed eggs
53
New cards
what would be convincing evidence for pack hunting in theropods?
small dinosaur skeletons found near large ones, seeing as they couldn’t have taken down a large dinosaur alone
54
New cards
what do fossils found in hunting/fighting positions suggest?
pack hunting
55
New cards
what helped us determine what theropods ate?
gut contents, jaw structure, teeth structure, tooth marks on prey
56
New cards
what are gastroliths?
trace fossils of stomach stones
57
New cards
were feathers common or uncommon in theropods?
common
58
New cards
evidence of t-rex predation
* healed bite wounds
* pointy teeth
* strong teeth
* bite force very strong
* not that slow
* large olfactory
* pointy teeth
* strong teeth
* bite force very strong
* not that slow
* large olfactory
59
New cards
evidence of t-rex scavenging
* large olfactory
* small arms
* small optic nerve
* poor eyesight
* femur/tibia similar - slow
* teeth in bone beds
* small arms
* small optic nerve
* poor eyesight
* femur/tibia similar - slow
* teeth in bone beds
60
New cards
what is science?
a reliable method for learning about the natural world.
* must be testable and repeatable
* never prove anything
* used all the time
* must be testable and repeatable
* never prove anything
* used all the time
61
New cards
What as the climate like during the jurassic?
* no polar ice caps
* high sea level
* warm, equitable climates
* less seasonality due to high global sea levels
climate indicators:
* stable isotopes, tropical vegetation in polar regions
* high sea level
* warm, equitable climates
* less seasonality due to high global sea levels
climate indicators:
* stable isotopes, tropical vegetation in polar regions
62
New cards
what was the climate like during the cretaceous?
1st half:
* warm equitable; polar free of ice
* global tectonic activity
* higher sea level
* oceanic spreading
2nd half:
* deterioration of equitable climate
* high seasonslity
* polar to equator gradient much like today
* warm equitable; polar free of ice
* global tectonic activity
* higher sea level
* oceanic spreading
2nd half:
* deterioration of equitable climate
* high seasonslity
* polar to equator gradient much like today
63
New cards
how is climate different than weather?
climate is the analysis of weather conditions/patterns over time in a specific area, while weather is only a short period of time.
64
New cards
how did CO2 levels compare to today? should we be worried?
fluctuated but were generally higher than they are today. our levels are increasing at a much higher rate due to climate change, and we should be concerned about the human effects.
65
New cards
did darwin propose evolution? what did he do?
not the first person to propose evolution, but he discussed it at length, proposing it and natural selection and adding decent with modification he helped it to be understood better.
66
New cards
define cladistics
modern way to organize life based on shared characters
67
New cards
what are used to make cladograms?
characters
68
New cards
character
an isolated feature of an organism that is distributed among a group of organisms
69
New cards
what are the two types of characters?
derived and primitive
70
New cards
derived characters
specific; diagnostic of smaller groups
71
New cards
primitive characters
ancestral; general; distinguishes larger groups
72
New cards
_____ anatomical structures that can be traced back to a single structure in a common ancestor.
homologues
73
New cards
what is convergent evolution?
similar characters evolve separately in two independent lineages; can be adaptions to similar environments
74
New cards
why are transitional fossils important?
help “bridge gaps” and explain better ancestry between organisms; can help explain evolution and its process
75
New cards
what are a few features that make cynodonts a transitional fossil between reptiles and animals?
2 jaw hinges, erect hind limbs/sprawling front limbs, and partially developed 2nd palate
76
New cards
what are the two groups of dinosaurs?
saurischian and ornithischian
77
New cards
how do we differentiate between the two groups of dinosaurs?
pubis direction
* saurischian: forward facing
* ornithischian: rear facing
* saurischian: forward facing
* ornithischian: rear facing
78
New cards
what are two features that all ornithischians share?
predentary bone and rear-facing pubis
79
New cards
what is the reason behind a posterior facing pubis?
to make room for the large gut cavity needed to digest plant matter
80
New cards
what is the feature shared by genasauria?
muscular cheeks
81
New cards
name the five main members of the ornithischian
stegosaurs, ankylosaurs, ornithopods, pachycephalosaurs, and ceratopsians
82
New cards
what feature is necessary for chewing?
cheeks
83
New cards
what do ornithischians eat?
plant matter
84
New cards
which group of ornithischian was likely the best at eating?
ornithopods due to pluerokinesis and dental battery
85
New cards
what is pluerokinesis?
complex muscle jointing that allowed more movement in jaw for chewing; top jaw is mobilized
86
New cards
what group was likely the worst at eating?
stegosaurus or ankylosaurus due to weak, small teeth and extensive need for fermentation due to body size
87
New cards
what is the shared character of thyreophora?
osteoderms (bone embedded in the skin)
88
New cards
what are the two members of thyreophora?
stegosaurus and ankylosaurus
89
New cards
what does stegosaurus posture suggest about movement and feeding?
very slow due to long back legs and short front legs; too slow to chase prey, meaning that they were low-grazing herbivores
90
New cards
what is the main benefit of having a large gut cavity?
easier digestion of plant matter
91
New cards
did stegosaurs have a second brain?
it was once thought that they did because the sacrum was enlarged, but they do not.
92
New cards
what is the likely function of stegosaur spines? plates?
defense, display (intra- and interspecific) and thermoregulation
93
New cards
what are some lines of evidence that support stegosaur plates for defense?
* spikes on tail could wack a predator
* most likely hard structures; could take blunt force
* most likely hard structures; could take blunt force
94
New cards
what are some lines of evidence that support stegosaur plates for display?
* species specification: difference among species
* large plates = intimidate predators
* large plates = intimidate predators
95
New cards
what are some lines of evidence that support stegosaur plates for thermoregulation?
* blood vessels in the plates
96
New cards
what do we know about ankylosaur feeding based on hyoid bone, teeth, and large gut?
herbivores due to low head, tooth wear, gut for fermentation, etc.
97
New cards
what modern day animal has an enlarged hyoid bone analogous to that of the ankylosaur, and what does this allow for?
giraffe; long, flexible tongue
98
New cards
can we assume ankylosaurs were fast moving and nimble? why or why not?
no; due to round/broad body shape, smaller flocculus, etc. they were all about defense, not speed
99
New cards
at what time were stegosaurs most abundant? ankylosaurs?
stegosaurs: jurassic
ankylosaurs: cretaceous
ankylosaurs: cretaceous
100
New cards
what two forms of protection did ankylosaurs have against predation? are there any lines of evidence that would support that these functioned as protection?
* tail club
* force generated by club tail confirm use
* armor (osteoderms)
* biomechanics confirm durability
* force generated by club tail confirm use
* armor (osteoderms)
* biomechanics confirm durability