Chapter 6 - General Physiology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:46 PM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
The fluid compartment surrounding cells is considered the \_________________ environment.
extracellular
2
New cards
True or false: Most of the fluid in the body is located within the extracellular compartment.
False
3
New cards
Extracellular matrix is comprised of:
ground substance
blood plasma
collagen fibers
elastin fibers
ground substance
blood plasma
collagen fibers
elastin fibers
ground substance
collagen fibers
elastin fibers
collagen fibers
elastin fibers
4
New cards
The largest percentage of total body water is found in the \______________________ fluid or compartment.
intracellular
5
New cards
Molecules that are \______ are lipid-soluble and can easily cross a plasma membrane, while \______ molecules cannot.
non-polar; polar
6
New cards
The \______ is comprised of protein fibers and a gel-like ground substance.
extracellular matrix
7
New cards
An increased temperature of a solution is likely \_____________________________.
to increase the rate of diffusion
8
New cards
In a solution, fluid water is known as the \______________ in which molecules may dissolve.
solvent
9
New cards
\_______________ is the specific term referring to the net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
Osmosis
10
New cards
Identify the substances that can easily diffuse through the plasma membrane:
Steroid hormones
Lipids
Proteins
Sodium ions
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Steroid hormones
Lipids
Proteins
Sodium ions
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Steroid hormones
Lipids
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Lipids
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
11
New cards
For osmosis to occur:
- the membrane must be relatively impermeable to the solute.
- the membrane must have numerous microvilli.
- the membrane must be selectively permeable.
- the membrane must be lacking channel proteins.
- there must be difference in the concentration of a solute on both sides of a membrane.
- the membrane must be relatively impermeable to the solute.
- the membrane must have numerous microvilli.
- the membrane must be selectively permeable.
- the membrane must be lacking channel proteins.
- there must be difference in the concentration of a solute on both sides of a membrane.
the membrane must be relatively impermeable to the solute.
the membrane must be selectively permeable.
there must be difference in the concentration of a solute on both sides of a membrane
the membrane must be selectively permeable.
there must be difference in the concentration of a solute on both sides of a membrane
12
New cards
The \______ of diffusion is dependent upon the surface area and permeability of the membrane, temperature and steepness of the concentration gradient.
rate
13
New cards
The pressure needed to stop osmosis is:
osmotic pressure
14
New cards
The \____________ of a solution takes into account all of the solutes in the solution.
osmolality
15
New cards
True or false: Tonicity describes the effect of a solution on the movement of water.
True
16
New cards
\______________ pressure is the pressure required to halt the process of osmosis.
Osmotic
17
New cards
A solution that will not induce osmosis to occur is \______.
isotonic
18
New cards
\_______ cannot function properly if osmolality is disrupted.
Neurons
19
New cards
Transport of molecules from high to low concentration across a membrane carrier is termed \____________ diffusion.
facilitated
20
New cards
Primary active transport is directly achieved by hydrolysis of \_______.
ATP
21
New cards
Which of the following substances will only cross a plasma membrane using facilitated diffusion?
Glucose
Lipids
Water
Glucose
Lipids
Water
Glucose
22
New cards
Diffusion and osmosis occurring between the spaces of epithelial cells are termed \_______________ transport.
paracellular
23
New cards
Paracellular transport is the movement of substances:
across a membrane in two different directions
between adjacent cells
directly through the cytoplasm of a cell
across a cell in a vesicle
across a membrane in two different directions
between adjacent cells
directly through the cytoplasm of a cell
across a cell in a vesicle
between adjacent cells
24
New cards
The membrane potential is \______.
the observation that cells appear negative inside relative to the outside
the observation that cells appear positive inside relative to the outside
the voltage of the fluid outside the cell
the observation that cells appear negative inside relative to the outside
the observation that cells appear positive inside relative to the outside
the voltage of the fluid outside the cell
the observation that cells appear negative inside relative to the outside
25
New cards
The charge difference between the inside and outside of a cell that is not sending any impulses is known as its \____________ \_______________ \_____________.
resting membrane potential
26
New cards
In the broadest definition, cells can communicate with other tissue types via \______.
hormones
gap junctions
extracellular secretions
neurotransmitters
hormones
gap junctions
extracellular secretions
neurotransmitters
extracellular secretions
27
New cards
Under normal circumstances, which of the following plays the major role in determining membrane potential?
The membrane's permeability to potassium.
The concentration gradient of sodium.
The membrane's permeability to proteins.
The concentration gradient of phosphate ions.
The membrane's permeability to potassium.
The concentration gradient of sodium.
The membrane's permeability to proteins.
The concentration gradient of phosphate ions.
The membrane's permeability to potassium.
28
New cards
Polar molecules that bind to receptors, but do not enter a cell, use \______________ \___________________ to change the activities of the cell.
secondary messengers
29
New cards
\____________________ are molecules that initially respond to polar regulatory molecules by opening/closing membrane ion channels or by activating enzymes, such as those that produce cyclic AMP.
G-proteins
30
New cards
Some cells can communicate directly with each other through \______, where signaling molecules diffuse through the cytoplasm of adjacent cells.
gap junctions
31
New cards
1. Active transport requires \________.
both ATP and a carrier protein
water
carrier protein
ATP
both ATP and a carrier protein
water
carrier protein
ATP
both ATP and a carrier protein
32
New cards
2. The binding of ATP to the carrier protein causes \________.
the channel to close
the carrier to change its shape
All of the choices are correct
any molecule to bind to the carrier
the channel to close
the carrier to change its shape
All of the choices are correct
any molecule to bind to the carrier
the carrier to change its shape
33
New cards
3. The movement of substances across the plasma membrane will continue until the ATP is used up. True or false
True
34
New cards
1. The directional movement of ions by facilitated diffusion through protein channels is determined by \__________________.
the availability of ATP
the formation of a secretory vesicle
the electrochemical gradient of the ion being transported
the availability of ATP
the formation of a secretory vesicle
the electrochemical gradient of the ion being transported
the electrochemical gradient of the ion being transported
35
New cards
2. Simple and facilitated diffusion differ because \_____________.
ions being transported by simple diffusion move along their electrochemical gradients, while ions being transported by facilitated diffusion move against their electrochemical gradients
ions being transported by simple diffusion move against their electrochemical gradients, while ions being transported by facilitated diffusion move along their electrochemical gradients
facilitated diffusion requires the presence of a transport protein within the plasma membrane, while simple diffusion does not
simple diffusion requires the presence of a transport protein within the plasma membrane, while facilitated diffusion does not
ions being transported by simple diffusion move along their electrochemical gradients, while ions being transported by facilitated diffusion move against their electrochemical gradients
ions being transported by simple diffusion move against their electrochemical gradients, while ions being transported by facilitated diffusion move along their electrochemical gradients
facilitated diffusion requires the presence of a transport protein within the plasma membrane, while simple diffusion does not
simple diffusion requires the presence of a transport protein within the plasma membrane, while facilitated diffusion does not
facilitated diffusion requires the presence of a transport protein within the plasma membrane, while simple diffusion does not
36
New cards
3. Changes in the membrane potential trigger the opening or closing of \____________________.
voltage-gated channels
ligand-gated channels
mechanically-gated channels
voltage-gated channels
ligand-gated channels
mechanically-gated channels
voltage-gated channels
37
New cards
Glucose is passively transported across the \______________ membrane through facilitated diffusion.
hepatocyte
38
New cards
1. The \____________________ determines if glucose moves into or out of the hepatocyte.
mount of intracellular ATP available
amount of intracellular ATP versus intracellular glucose
oxygen concentration between the intracellular and extracellular fluid
glucose concentration between the intracellular and extracellular fluid
mount of intracellular ATP available
amount of intracellular ATP versus intracellular glucose
oxygen concentration between the intracellular and extracellular fluid
glucose concentration between the intracellular and extracellular fluid
glucose concentration between the intracellular and extracellular fluid
39
New cards
2. A reduction in the number of glucose carrier proteins within the plasma membrane \_____________ the rate of glucose diffusion.
decreases
40
New cards
Physiological saline is a solution containing 0.9% NaCl. A cell in 1.5% NaCl is in a(n) \___________________ solution.
hypotonic
hypertonic
isotonic
hypotonic
hypertonic
isotonic
hypertonic
41
New cards
2. The movement of water by osmosis is always from a \_____________.
low to high water concentration
high to low water concentration
high to low solute concentration
low to high water concentration
high to low water concentration
high to low solute concentration
high to low water concentration
42
New cards
1. Water you drink is absorbed into the blood from the digestive tract. An increase in water intake causes a(n) \___________________ in the plasma osmolarity.
decrease
increase
decrease
increase
decrease
43
New cards
2. An IV solution of 0.45% NaCl is \________________ and induces the movement of water \________________.
hypertonic; out of cells
hypertonic; into cells
hypotonic; into cells
hypotonic; out of cells
hypertonic; out of cells
hypertonic; into cells
hypotonic; into cells
hypotonic; out of cells
hypotonic; into cells
0.9% NaCl is isotonic
0.9% NaCl is isotonic
44
New cards
2. The Na+/K+ ATPase moves sodium in the \_________________ direction compared with the direction it travels through sodium leakage channels.
opposite
45
New cards
1. The sodium-iodide symporter plays a role in the accumulation of iodide in the thyroid gland. Here, one iodide gets converted to one iodine, which is utilized for the formation of either of the two types of thyroid hormones, T3 and T4. T3 and T4 are named after the number of iodines found in each of these hormones. To produce a single molecule of T3, a total of \____________ sodium ions must move down their concentration gradients by secondary active transport. The movement of iodide ions occurs in the \_________________ direction as sodium ions.
six, same
46
New cards
2. Phagocyosis and pinocytosis differ in that \_____________.
- one is a type of exocytosis, and one is a type of endocytosis
- almost all cells are capable of phagocytosis, while few select cell types are capable of pinocytosis
- phagocytosis allows for the transport of larger particles than pinocytosis
- pinocytosis is more selective than phagocytosis
- one is a type of exocytosis, and one is a type of endocytosis
- almost all cells are capable of phagocytosis, while few select cell types are capable of pinocytosis
- phagocytosis allows for the transport of larger particles than pinocytosis
- pinocytosis is more selective than phagocytosis
phagocytosis allows for the transport of larger particles than pinocytosis
47
New cards
1. An individual displaying a larger than normal number of LDL receptors is \_____________ likely to develop artherosclerosis.
more
less
more
less
less
48
New cards
The extracellular matrix includes \________.
cytoplasm
blood plasma
collagen
red blood cells.
cytoplasm
blood plasma
collagen
red blood cells.
collagen
49
New cards
Simple diffusion is defined as the movement of \________.
- molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
- molecules from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration
- water molecules across a membrane
- gas molecules across a membrane
- gas or water molecules across a membrane
- molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
- molecules from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration
- water molecules across a membrane
- gas molecules across a membrane
- gas or water molecules across a membrane
molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
50
New cards
Osmosis is best defined as the movement of \__________.
- water molecules from an area of high solute concentration to an area of lower solute concentration
- water molecules from an area of low solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration
- solute molecules across a membrane from an area of low water to an area of higher water concentration
- solute molecules across a membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of lower water concentration
- water molecules inside a container
- water molecules from an area of high solute concentration to an area of lower solute concentration
- water molecules from an area of low solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration
- solute molecules across a membrane from an area of low water to an area of higher water concentration
- solute molecules across a membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of lower water concentration
- water molecules inside a container
water molecules from an area of low solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration
51
New cards
The osmolality of a red blood cell is \__________ mOsmoles.
300 mOsmoles
52
New cards
Edema occurs when:
- There is excessive albumin production
- Blood osmolality is too high
- Tissue osmolality is too high
- There is decreased fibrinogen production
- There is excessive albumin production
- Blood osmolality is too high
- Tissue osmolality is too high
- There is decreased fibrinogen production
Tissue osmotically is too high
53
New cards
Which of the following would be used to reduce cerebral edema?
- Normal saline
- Ringer's lactate
- Mannitol
- 5% dextrose
- Normal saline
- Ringer's lactate
- Mannitol
- 5% dextrose
Mannitol
54
New cards
What does the hydrolysis of ATP do in a Ca2+ pump or Na+/K+ pump?
- Returns the carrier to its initial shape
- Allows the ion to bind to the inside of the carrier
- Activates ATPase
- Temporarily blocks both exits of the carrier
- Returns the carrier to its initial shape
- Allows the ion to bind to the inside of the carrier
- Activates ATPase
- Temporarily blocks both exits of the carrier
Temporarily blocks both exits of the carrier
55
New cards
Facilitated diffusion occurs \__________.
- into the cell only
out of the cell only
- in either direction depending on the temperature
- in either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule
- in either direction depending on the size of the molecule
- into the cell only
out of the cell only
- in either direction depending on the temperature
- in either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule
- in either direction depending on the size of the molecule
in either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule
56
New cards
Facilitated diffusion is used to transport \__________.
sugars
57
New cards
Choose the statement that correctly describes a ligand.
- A small molecule that binds to the alpha subunit of the G-protein
- A small molecule that binds to a membrane-bound receptor
- A large molecule that binds to the alpha subunit of the G-protein
- A large molecule that binds to a membrane-bound receptor
- A small molecule that binds to a G-protein
- A small molecule that binds to the alpha subunit of the G-protein
- A small molecule that binds to a membrane-bound receptor
- A large molecule that binds to the alpha subunit of the G-protein
- A large molecule that binds to a membrane-bound receptor
- A small molecule that binds to a G-protein
A small molecule that binds to a membrane-bound receptor
58
New cards
\___% of our water is within cells in the intracellular compartment.
__% is in the extracellular compartment
__% is in the blood plasm
__% makes up what is called tissue fluid, or interstitial fluid which connects the intracellular compartment with the blood plasma.
__% is in the extracellular compartment
__% is in the blood plasm
__% makes up what is called tissue fluid, or interstitial fluid which connects the intracellular compartment with the blood plasma.
67
33
20
80
33
20
80
59
New cards
Extracellular Matrix
What are the three things it contains?
What are the three things it contains?
protein fibers of collagen and elastin, and a gel-like ground substance
60
New cards
Extracellular Matrix
Protein fibers provide \_____________ support
Ground substance is composed of \______________ and \_______________
What are integrins?
Protein fibers provide \_____________ support
Ground substance is composed of \______________ and \_______________
What are integrins?
structural
glycoproteins (composed of proteins and sugars) and proteoglycans (composed of polysaccharides)
Integrins are glycoproteins that extend from the cell cytoskeleton and bind to components of the extracellular matrix
glycoproteins (composed of proteins and sugars) and proteoglycans (composed of polysaccharides)
Integrins are glycoproteins that extend from the cell cytoskeleton and bind to components of the extracellular matrix
61
New cards
Extracellular Matrix
Functions of Integrins
Affect adhesion and \_____________
Relay \_______ between compartments
Impart a \________ to cells
Affect \_________________
Functions of Integrins
Affect adhesion and \_____________
Relay \_______ between compartments
Impart a \________ to cells
Affect \_________________
motility
signals
polarity
proliferation
signals
polarity
proliferation
62
New cards
Plasma membrane is generally permeable to \___________ and \__________.
Some ions are transported creating \_______________________________ currents in certain cells
Some ions are transported creating \_______________________________ currents in certain cells
nutrients, waste
electrochemical
electrochemical
63
New cards
What are the two categories of membrane transport?
Carrier-mediated transport and non-carrier-mediated transport
64
New cards
What are the three types of carrier-mediated transport?
Facilitated diffusion, active transport, and secondary active transport
65
New cards
Passive transport moves molecules from \______to \______ concentration without utilizing metabolic energy.
Active transport moves molecules from \______to \______ concentration utilizing ATP and specific carrier pumps.
Active transport moves molecules from \______to \______ concentration utilizing ATP and specific carrier pumps.
higher; lower
lower; higher (against concentration gradient)
lower; higher (against concentration gradient)
66
New cards
- Simple diffusion of ions through \_____________ \______________ proteins
- Facilitated diffusion of glucose or other small organic molecules that bind to a specific \___________ \_____________ which undergoes a conformational change to release the molecule on the other side of the membrane
- Facilitated diffusion of glucose or other small organic molecules that bind to a specific \___________ \_____________ which undergoes a conformational change to release the molecule on the other side of the membrane
membrane channel
carrier protein
carrier protein
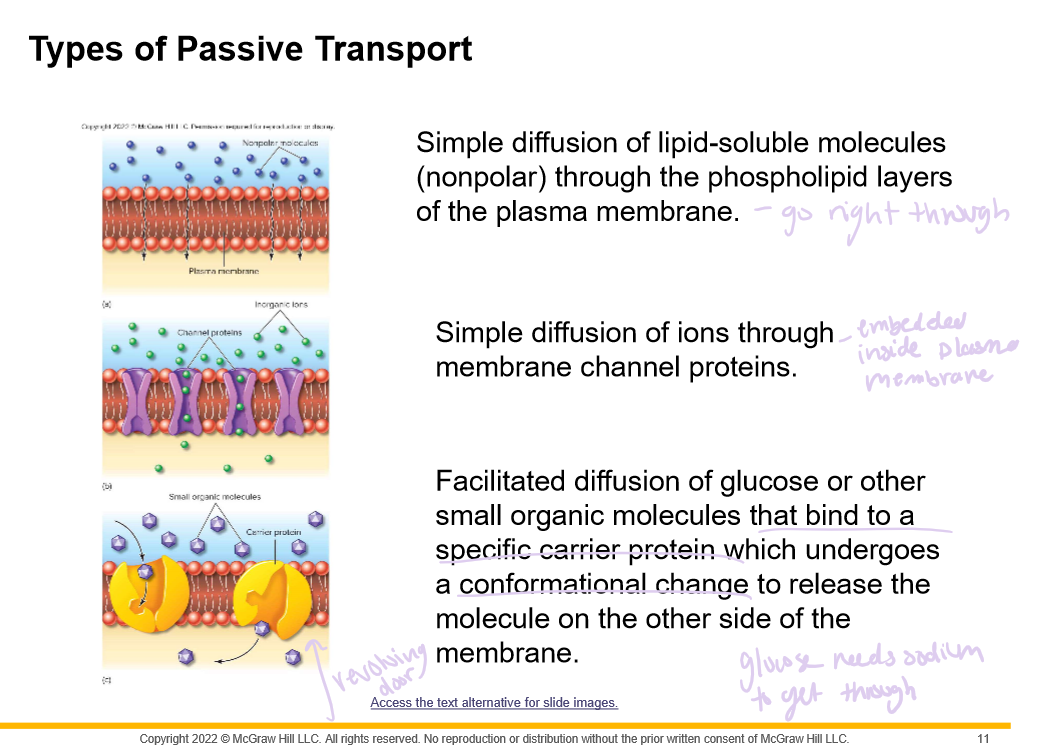
67
New cards
Molecules in a solution are in a \_______ state of motion.
If there is a concentration difference between two regions, \______ motion will establish equilibrium via \______________.
Obeys the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - diffusion increases \___________
If there is a concentration difference between two regions, \______ motion will establish equilibrium via \______________.
Obeys the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - diffusion increases \___________
constant
diffusion
entropy
diffusion
entropy
68
New cards
Diffusion will occur \_________ a physical separation or across a permeable membrane
Net diffusion - due to random movement, the net direction of diffusion is from \_____ to \_____ solute concentration
Mean diffusion time - the average time it takes for a solution to \________
\_________ with the square of the distance the solute must travel
Net diffusion - due to random movement, the net direction of diffusion is from \_____ to \_____ solute concentration
Mean diffusion time - the average time it takes for a solution to \________
\_________ with the square of the distance the solute must travel
without
high; low
diffuse
increases (less distance, faster, distances beyond 100 um, diffusion time is too long to be effective)
high; low
diffuse
increases (less distance, faster, distances beyond 100 um, diffusion time is too long to be effective)
69
New cards
Gas exchange: net diffusion of O2 into cells and C02 out of cells due to concentration gradients (Opposite in \_________)
lungs
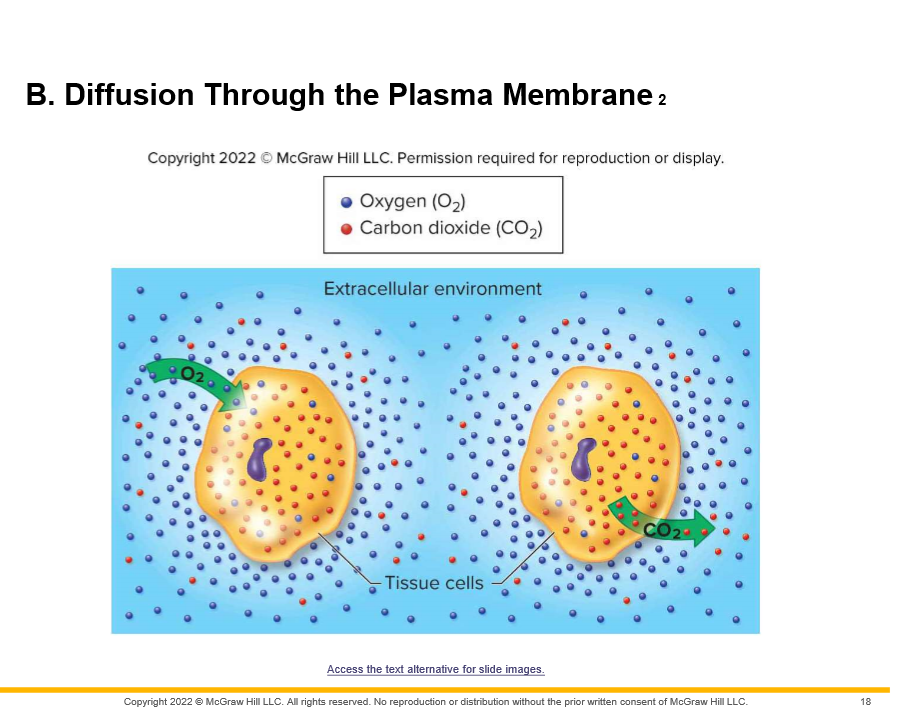
70
New cards
Rate of Diffusion
Measured by the number of diffusing particles per unit of time
Depends on:
Magnitude of concentration difference - the \__________ \__________ for diffusion
Permeability of membrane to the molecules
Temp of the solution; higher temp increases rate
Surface area of the membrane; increased by \_________
Measured by the number of diffusing particles per unit of time
Depends on:
Magnitude of concentration difference - the \__________ \__________ for diffusion
Permeability of membrane to the molecules
Temp of the solution; higher temp increases rate
Surface area of the membrane; increased by \_________
driving force
microvilli
microvilli
71
New cards
Osmosis Requirements
- Must be a \____ concentration difference on either side of a membrane permeable to water
- The membrane must be \___________ to the solute, or the concentration difference will not be maintained
Solutes that cannot cross and permit osmosis are called \_______________ \________
- Must be a \____ concentration difference on either side of a membrane permeable to water
- The membrane must be \___________ to the solute, or the concentration difference will not be maintained
Solutes that cannot cross and permit osmosis are called \_______________ \________
solute
impermeable
osmotically active
impermeable
osmotically active
72
New cards
Osmotic \_________ is the force surrounding a cell required to stop osmosis.
Higher solute concentration has a \________ osmotic pressure
Higher solute concentration has a \________ osmotic pressure
pressure
higher (Pure water has an osmotic pressure of zero)
higher (Pure water has an osmotic pressure of zero)
73
New cards
Explain difference between Molarity (M) and Molality (m)
Which do we like to use better?
Which do we like to use better?
Molarity \= moles solute/liter solution
Molality \= moles solute/kg solvent
Molality since the amount of water never changes, we can compare the solute concentrations to predict the direction of osmosis
Molality \= moles solute/kg solvent
Molality since the amount of water never changes, we can compare the solute concentrations to predict the direction of osmosis
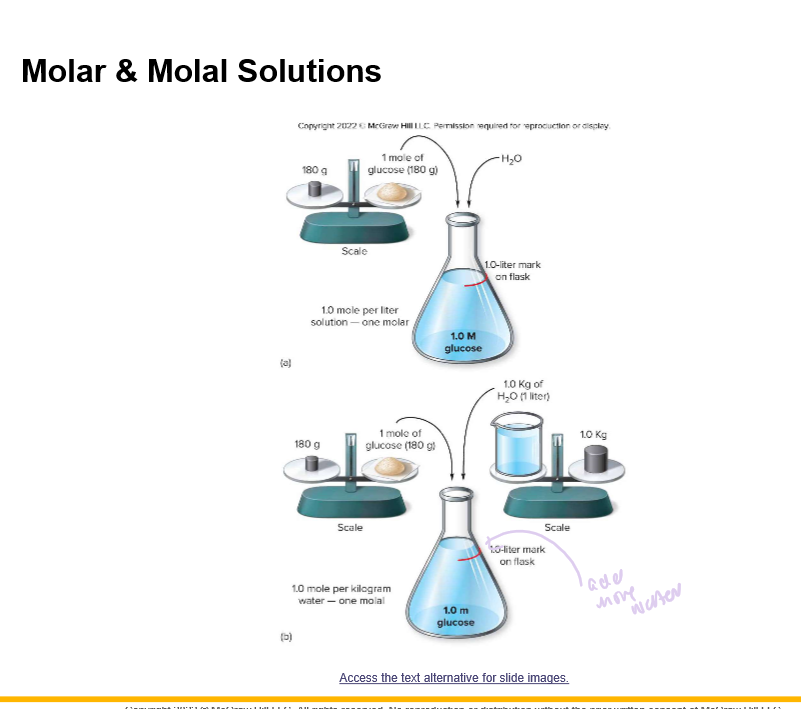
74
New cards
Osmolality is the \_______ molality of a solution when you combine all of the molecules within it
How can it be measured?
How can it be measured?
total
Freezing point depression - how much the freezing point is lowered depends on the number of particles present in the solution
Freezing point depression - how much the freezing point is lowered depends on the number of particles present in the solution
75
New cards
Tonicity is the effect of a solute concentration on the \________ of water
Takes into account the \_____________ of the membranes of the solutes
Takes into account the \_____________ of the membranes of the solutes
osmosis
permeability
permeability
76
New cards
\___________________ in the hypothalamus detect increases in osmolality (due to dehydration) which triggers:
- thirst
- decreased excretion of water in urine through release of \_________ \___________ which is also known as vasopressin
- thirst
- decreased excretion of water in urine through release of \_________ \___________ which is also known as vasopressin
Osmoreceptors
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
77
New cards
Molecules that are too large or polar cannot diffuse across the membrane and instead need \________ \____________.
Characteristics
- are specific to a given molecule
- may be \_____________ for similar carriers or molecules
- \_______________ - the number of carriers is limited
Characteristics
- are specific to a given molecule
- may be \_____________ for similar carriers or molecules
- \_______________ - the number of carriers is limited
carrier proteins
competition
Saturation
competition
Saturation
78
New cards
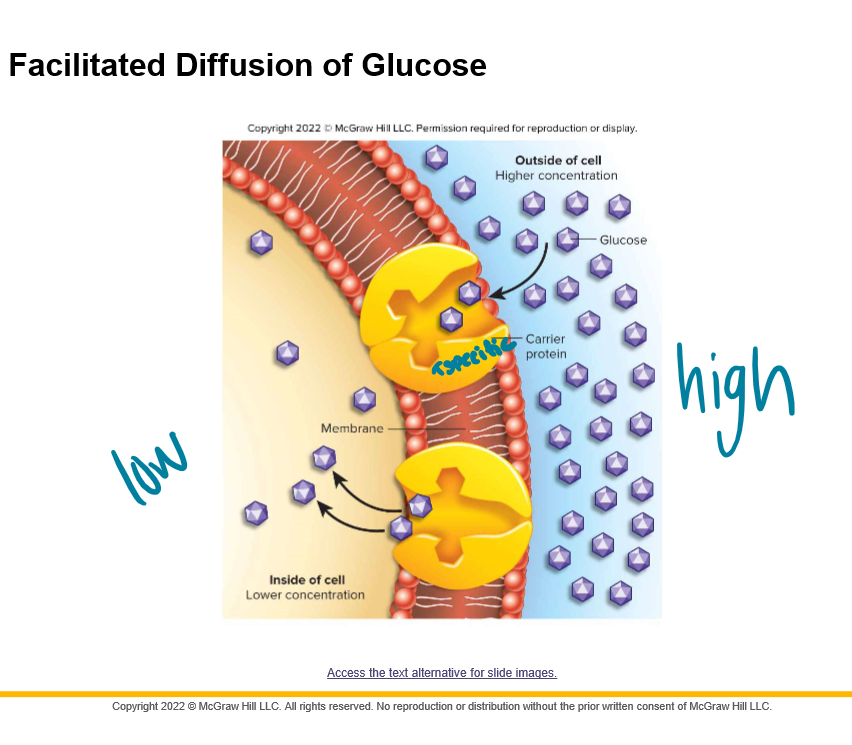
Facilitated Diffusion is powered by the \____ movement of molecules
Is ATP needed?
Net movement from \______ to \_____ concentration
Requires specific \_____________-\__________ proteins
Transport proteins may always exist in the plasma membrane or be \____________ when needed
Is ATP needed?
Net movement from \______ to \_____ concentration
Requires specific \_____________-\__________ proteins
Transport proteins may always exist in the plasma membrane or be \____________ when needed
random
No
high; low
carrier-mediated
inserted
No
high; low
carrier-mediated
inserted
79
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose
What are transport carriers for glucose designated as?
GLUT1 - \_______
GLUT2 - \_______
GLUT 3 - \_______
GLUT 4 - \_______
What are transport carriers for glucose designated as?
GLUT1 - \_______
GLUT2 - \_______
GLUT 3 - \_______
GLUT 4 - \_______
GLUT followed by the number of the isoform
CNS
pancreatic beta cells & hepatocytes
neurons
adipose tissue & skeletal muscle
CNS
pancreatic beta cells & hepatocytes
neurons
adipose tissue & skeletal muscle
80
New cards
Primary active transport occurs when the hydrolysis of ATP is \______ responsible for the carrier protein function
What is the transport protein also?
Pump is activated by \_______________ using a Pi from ATP
What is the transport protein also?
Pump is activated by \_______________ using a Pi from ATP
directly
an ATPase enzyme that will hydrolyze ATP (cleave ATP)
phosphorylation
an ATPase enzyme that will hydrolyze ATP (cleave ATP)
phosphorylation
81
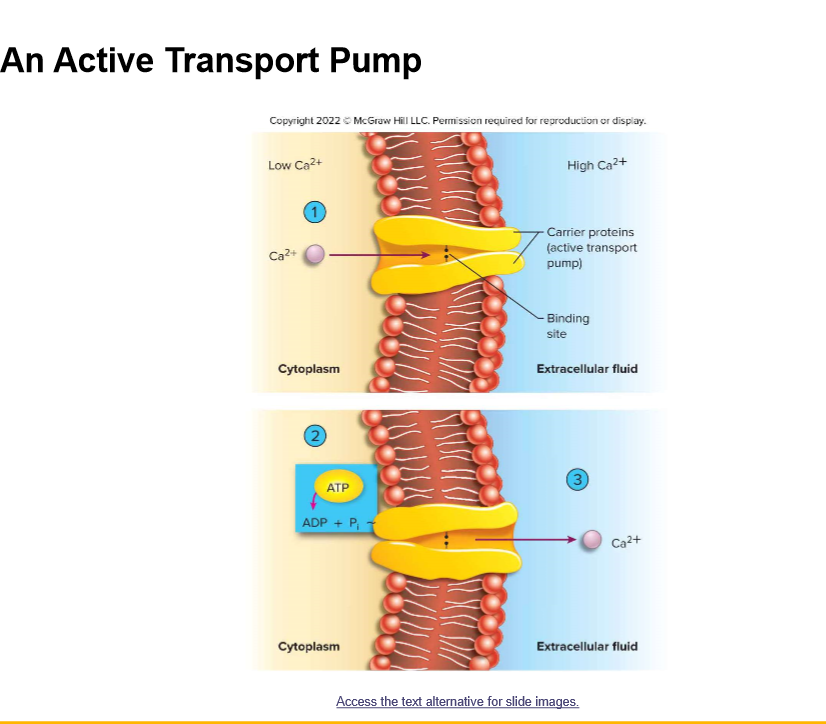
New cards
Ca2+ pump is what type of active transport?
Removes Ca2+ from the cytoplasm by pumping it into the extracellular fluid or \____________ of the ER
Removes Ca2+ from the cytoplasm by pumping it into the extracellular fluid or \____________ of the ER
Primary active transport
cisternae
cisternae
82
New cards
Na+/K+ Pump
Serves three functions:
1. Provides energy for \_________ transport of other molecule
2. Produces \____________ impulses in neuron and muscle cells
3. Maintains \_______________
Serves three functions:
1. Provides energy for \_________ transport of other molecule
2. Produces \____________ impulses in neuron and muscle cells
3. Maintains \_______________
coupled
electrochemical
osmolality
3Na+ out/2 K+ in
electrochemical
osmolality
3Na+ out/2 K+ in
83
New cards
Steps of the Na+/K+ pump:
1. 3 Na+ from the cytoplasm move into the pump and \_____
2. \________ activated to hydrolyze ATP to ADP and Pi which blocks both openings
3. ADP released causing a \_______ change that allows 3 Na+ to exit pump to outside cell
4. 2 K+ enter carrier from the outside, releasing the Pi
5. Pump returns to original shape and releases 2K+ to the inside
1. 3 Na+ from the cytoplasm move into the pump and \_____
2. \________ activated to hydrolyze ATP to ADP and Pi which blocks both openings
3. ADP released causing a \_______ change that allows 3 Na+ to exit pump to outside cell
4. 2 K+ enter carrier from the outside, releasing the Pi
5. Pump returns to original shape and releases 2K+ to the inside
bind
ATPase
shape
ATPase
shape
84
New cards
Secondary active transport is also called what?
The energy needed to move molecules across their concentration gradient is acquired by moving \________ back into the cell
Since the sodium was originally pumped out of the cell using ATP, this is considered active transport.
The energy needed to move molecules across their concentration gradient is acquired by moving \________ back into the cell
Since the sodium was originally pumped out of the cell using ATP, this is considered active transport.
Coupled transport
sodium
sodium
85
New cards
Transport Across Epithelial Membranes
- Involves \______________ transport: movement of molecules through the cytoplasm of the epithelial cells
- May also involve \____________ transport: movement across the tiny gaps between cells
- Involves \______________ transport: movement of molecules through the cytoplasm of the epithelial cells
- May also involve \____________ transport: movement across the tiny gaps between cells
transcellular
paracellular
paracellular
86
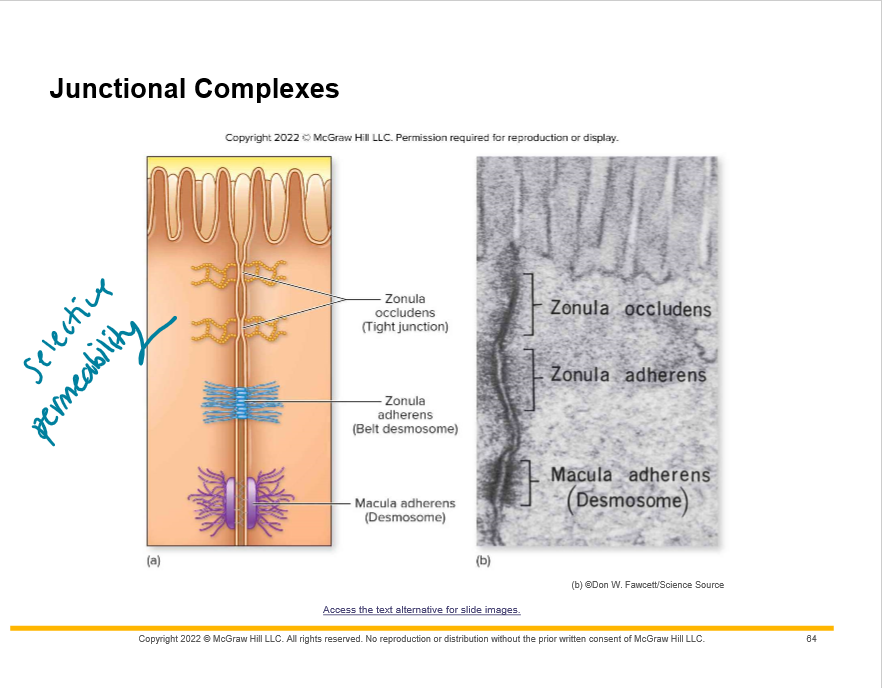
New cards
What is paracellular transport limited by?
1. Zonula occludens: tight junctions
2. Zonula adherens: \_______ desmosomes
3. Macula adherens: \________________
1. Zonula occludens: tight junctions
2. Zonula adherens: \_______ desmosomes
3. Macula adherens: \________________
Junctional complexes
belt
desmosomes
belt
desmosomes
87
New cards
Does bulk transport require ATP?
Which large molecules use exocytosis and endocytosis?
Which large molecules use exocytosis and endocytosis?
Yes since need moto proteins to make sure reaches membranes
Exo: proteins, hormones, and neurotransmitters
Endo: cholesterol (large molecules)
Exo: proteins, hormones, and neurotransmitters
Endo: cholesterol (large molecules)
88
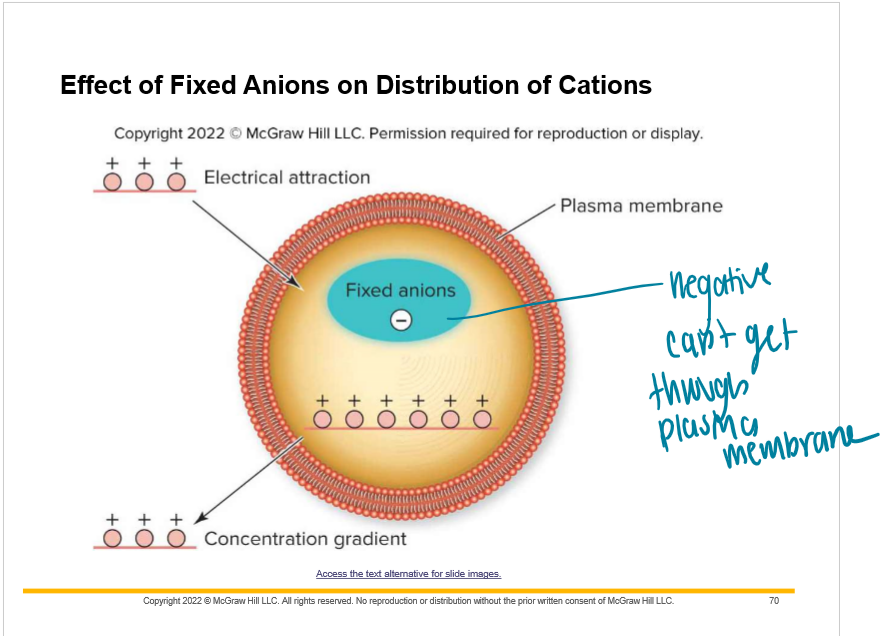
New cards
What makes the inside of the cell more negative compared to the outside?
Potential difference: difference in charge on each side of the plasma membrane
89
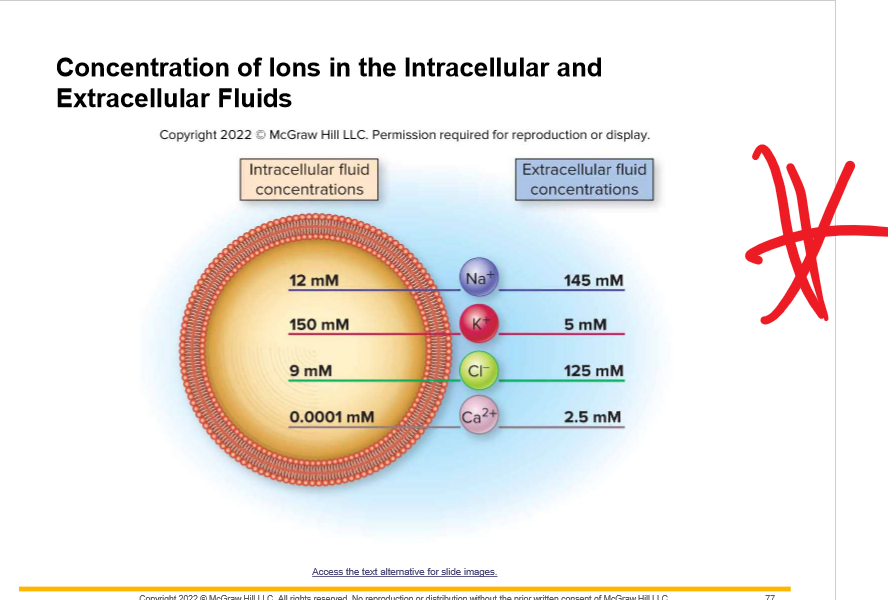
New cards
Since the membrane is so permeable to \____, this potential difference is usually maintained by \___ concentration gradient
The inside has a voltage of \________ lower than the outside
The inside has a voltage of \________ lower than the outside
K+, K+
-90mV
-90mV
90
New cards
What equation is used to calculate equilibrium potentials and is based on ion concentrations?
Nerst equation

91
New cards
In most cells, the resting potential is between \________ and \_________
Neurons are usually at \________
Neurons are usually at \________
-65, -85 mV
-70 mV
-70 mV
92
New cards
Cell signaling
What are gap junctions?
Paracrine signaling?
What are gap junctions?
Paracrine signaling?
Allow adjacent cells to pass ions and regulatory molecules through a channel between the cells (no extracellular space)
Cells within an organ secrete molecules that diffuse across the extracellular space to nearby target cells - also called local signaling (extracellular space)
Cells within an organ secrete molecules that diffuse across the extracellular space to nearby target cells - also called local signaling (extracellular space)
93
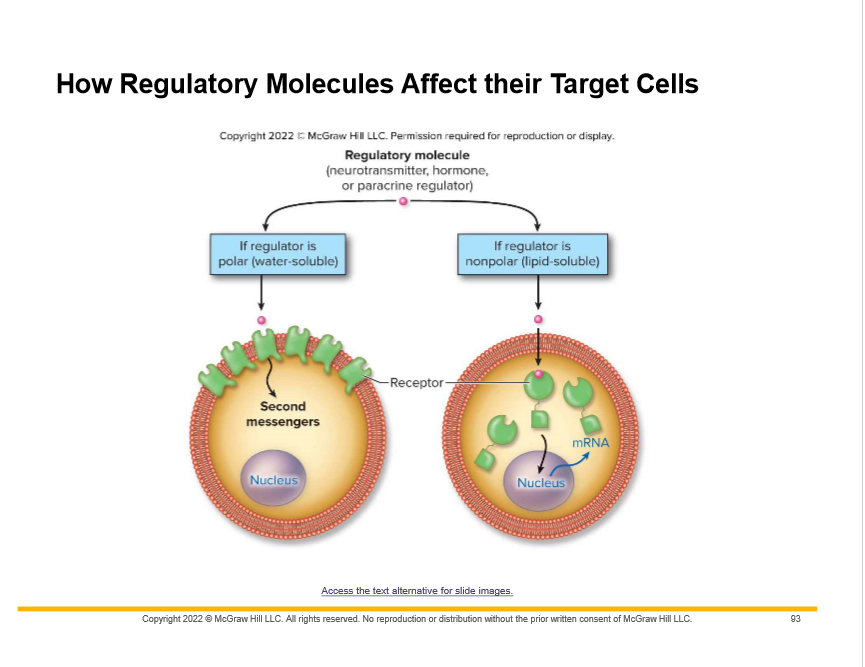
New cards
Polar or large signal molecules bind to receptors on the cell surface. What are the intermediates called and examples?
Second messengers
May be ions (Ca2+) or molecules
May be ions (Ca2+) or molecules
94
New cards
cAMP is a common second messenger
Steps to activate:
1. A signaling molecules binds to a \___________.
2. This activates an enzyme that produces cAMP from \____.
3. cAMP activates other enzymes in the cytoplasm.
4. Cell activities change in response.
Steps to activate:
1. A signaling molecules binds to a \___________.
2. This activates an enzyme that produces cAMP from \____.
3. cAMP activates other enzymes in the cytoplasm.
4. Cell activities change in response.
receptor
ATP
ATP
95
New cards
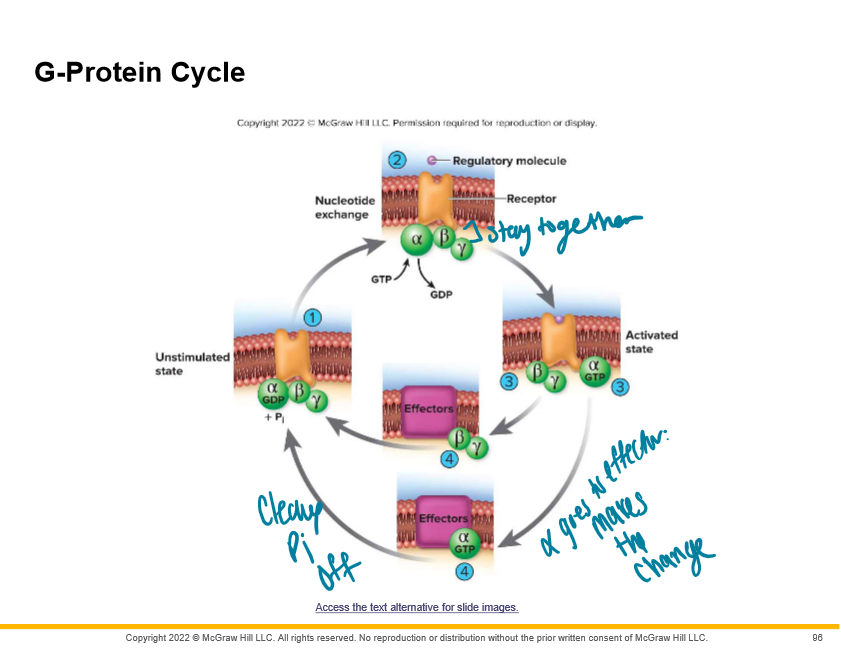
G-proteins are there to shuttle the receptor protein and enzyme proteins and are made up of 3 subunits which are?
alpha, beta, and gamma
96
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a function of integrins?
- Glue components of the matrix
- Allow diffusion to occur through the plasma membrane
- Establish cell polarity
- Communicate between the intracellular and extracellular compartments
- Glue components of the matrix
- Allow diffusion to occur through the plasma membrane
- Establish cell polarity
- Communicate between the intracellular and extracellular compartments
Allow diffusion to occur through the plasma membrane
97
New cards
Where is the receptor for a nonpolar, lipid-soluble regulatory molecule?
- Embedded in the outer surface of the plasma membrane
- Embedded in the inner surface of the plasma membrane
- In the cytoplasm or nucleus of the cell
- All of the choices are correct.
- Embedded in the outer surface of the plasma membrane
- Embedded in the inner surface of the plasma membrane
- In the cytoplasm or nucleus of the cell
- All of the choices are correct.
In the cytoplasm or nucleus of the cell
98
New cards
Regardless of solubility, a cell signaling molecule could not affect a target cell without \________.
- being attached to another cell
- a second messenger in the plasma membrane
- specific receptor proteins within the cell or in the plasma membrane
- All of the choices are correct.
- being attached to another cell
- a second messenger in the plasma membrane
- specific receptor proteins within the cell or in the plasma membrane
- All of the choices are correct.
specific receptor proteins within the cell or in the plasma membrane
99
New cards
Which of the following is NOT true of cyclic AMP?
- It is found on the outside of a plasma membrane
- It is a second messenger for polar regulatory molecules.
- It is made from ATP.I
- t activates enzymes inside a cell to produce the desired effect.
- It is found on the outside of a plasma membrane
- It is a second messenger for polar regulatory molecules.
- It is made from ATP.I
- t activates enzymes inside a cell to produce the desired effect.
It is found on the outside of a plasma membrane.
100
New cards
Clinical Application
What family of enzymes can break down extracellular matrix proteins?
What disease has a CFTR protein and had salty sweat, and in the pancreas and lungs can result in dense, vicious mucus that promotes pancreatic and pulmonary disorders?
What family of enzymes can break down extracellular matrix proteins?
What disease has a CFTR protein and had salty sweat, and in the pancreas and lungs can result in dense, vicious mucus that promotes pancreatic and pulmonary disorders?
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) because of their need for a zinc ion cofactor
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis