VLSM and Route Summarization
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Variable Length Subnet Mask
VLSM stands for:
VLSM
It is the process of “subnetting a subnet” and using different subnet masks for different networks in your IP plan.
What you have to remember is that you need to make sure that there is no overlap in any of the addresses.
Also known as route aggregation
It allows routing protocols to advertise many networks as one address
Eventual collapse of IPv4 address space
Ability to route traffic
The Internet has experienced 2 major scaling issues as it has struggled to provide continuous and interrupted growth.
Internet Protocol version 6
Also known as IP Next Generation (IPng)
Tested and implemented on the 6Bone network.
6Bone Network
It is an informal joint project covering North America, Europe, and Japan.
Subnets
Allows to take one larger network and break it into a bunch of smaller networks by borrowing bits from host or node addresses.
Network Address Translation
NAT stands for:
NAT
It is used to slow the depletion of available IP address space by allowing many private IP addresses to be represented by some smaller number of public IP addresses.
It is a useful tool for network migrations and mergers, server load sharing, and creating “virtual servers”.
Classless-based IP addressing
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
Solutions to Internet Scaling Problems:
CIDR
It is a method that ISPs (Internet Service Providers) use to allocate a number of addresses to a company, a home — a customer.
Classless-Based IP Addressing Scheme
This is where network can be in any size (no defined class).
Classful-Based IP Addressing Scheme
This is where network size is defined by network classes (A, B, C, D, E)
decimal dotted notation
In Classful-Based IP Addressing Scheme, it uses fixed network portion — ___________________.
static
Once the subnetting design has been established, it remains ____________.
It locks the organization into a fixed-number of fixed-sized subnets.
Traditional Subnetting
The same or fixed number of host addresses is allocated for each subnet.
2
Subnets that require fewer addresses have unused (wasted) addresses.
Example, WAN links only need __ addresses.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DHCP stands for:
Addresses for Clients
It is usually assigned using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
IPv6
It is designed to be the successor to IPv4
Depletion of IPv4 address space has been the motivating factor for moving to this version
Regional Internet Registries
Projections show that all five ____________________________ (RIRs) will run out of IPv4 addresses between 2015 and 2020.
Network Address Translation
NAT stands for:
ICMPv6
IPv6 fixes the limitations of IPv4 and include additional enhancements such as ____________.
Internet Control Message Protocol version 6
ICMPv6 stands for:
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
The ______________________________ (IANA) divided the available IPv6 addresses into 8 equal segments based on the 3 leading bits of the addresses.
000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111
What are the three leading bits of the addresses?
Internet Engineering Task Force
IETF stands for:
Regional Internet Registry
This organization manages the allocation and registration of Internet number resources worldwide.
AfriNIC, ARIN, APNIC, LACNIC, RIPE NCC
The Regional Internet Registry has evolved over time to divide the world into five areas or RIRs, these five RIRs are:
African Network Information Centre
AfriNIC stands for:
American Registry for Internet Numbers
ARIN
Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre
APNIC stands for:
Latin America and Caribbean Network Information Centre
LACNIC
Reseaux IP Europeens Network Coordination Centre
RIPE NCC
Dual-Stack
Tunnelling
Translation
What are the IPv4 to IPv6 Migration Techniques?
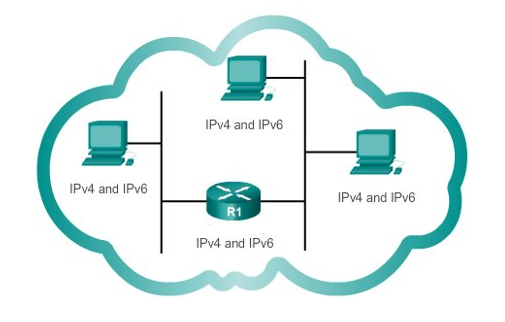
Dual-Stack
This migration technique allows IPv4 and IPv6 to coexist on the same network.
Devices run both IPv4 and IPv6 protocol stacks simultaneously.
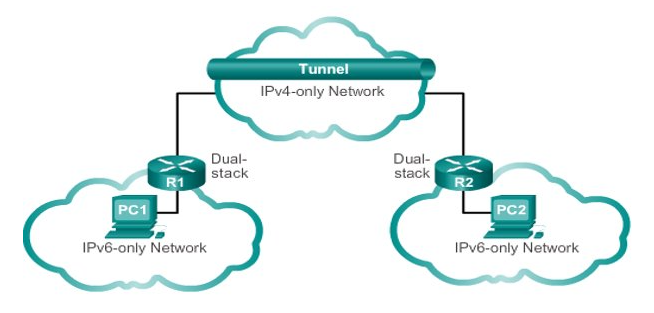
Tunnelling
This is a method of transporting an IPv6 packet over an IPv4 network.
The IPv6 packet is encapsulated inside an IPv4 packet.
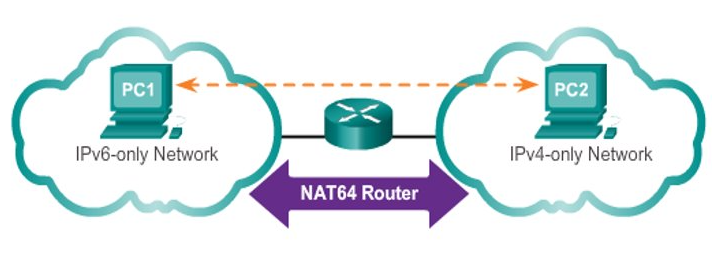
Network Address Translation 64
NAT64 stands for:
Translation
In this migration technique, the NAT64 allows IPv6-enabled devices to communicate with IPv4-enabled devices using a translation technique similar to NAT for IPv4.
An IPv6 packet is translated to an IPv4 packet, and vice versa.
Hexadecimal
It is a base 16 system
0 to 9, A to F
Base 16 numbering system uses the numbers __________ and the letters __________.
half byte or nibble
4 bits, _______________, can be represented with a single hexadecimal value.
4-bits
In IPv6, __________ represents a single hexadecimal digit.
HEXTET
It is used to refer to a segment of 16 bits of four hexadecimals.
Double Colon (::)
It can be only used once within an address otherwise the address will be ambiguous.
Unicast
Multicast
Anycast
What are the 3 general types of IPv6 addresses?
Unicast
These addresses identifies a unique interface on an IPv6 device.
one-to-one connection
A Unicast address is a ______________________ between a source and destination.
Multicast
These addresses is used to send a single packet to multiple (one-to-many) destinations simultaneously.
Anycast
These addresses are described as a one-to-nearest or one-to-one-of-many packet delivery.
broadcast address
IPv6 does not have _________________.
True
IPv6 does not use the dotted-decimal subnet mask notation.
IPv6 address /prefix length
Prefix length can range from 0 to 128
Typical prefix length is /64
Prefix length indicates the network portion of an IPv6 address using the following format:
unicast address
A packet sent to a ________________ is received by the interface that is assigned to that address.
Global Unicast
Link-Local
Loopback
Unspecified Address
Unique Local
Embedded IPv4
What are the 6 types of IPv6 Unicast Addresses?
Global Unicast
They are a type of unicast addresses that are used to uniquely identify a specific interface on a host and can be used as a public address on the internet (globally routable).
Address Range: 2000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/3 to 3FFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF/3
Link-Local Unicast
A unicast addresses that are limited to a point-to-point connection within a local network (other devices on the same local link).
Address Range: FE80:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/10 to FEBF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF/10
Loopback Unicast
A unicast addresses that is used by a host to send a packet to itself and cannot be assigned to a physical interface
Ping an IPv6 loopback address to test the configuration of TCP/IP on the local host
All 0s except for the last bit, represented as ::1/128 or just ::1
127.0.0.1
Loopback Unicast operates the same as the IPv4 ________________ loopback address.
Unspecified Unicast
This unicast address is only used as a source address to indicate the absence of an actual address and it cannot be assigned to an interface
It is an all 0s unicast address represented as ::/128 or just ::
Unique Local Unicast
A unicast address that is roughly the same (similar) as IPv4 private addresses.
It is used for local addressing within a site or between a limited number of sites.
Address Range: FE80:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/10 to FEBF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF/10
IPv4 Embedded
A unicast addresses that are IPv6 addresses with an IPv4 address embedded in the low-order 32-bits
It is used to help transition from IPv4 to IPv6
Address Range: FE80:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/10 to FEBF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF/10
IPv6 Link-Local Unicast Addresses
This enables a device to communicate with other IPv6-enabled devices on the same link and only on that link (subnet).
IPv6 Internet
IPv6 global unicast addresses are globally unique and routable on the _______________.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers
ICANN stands for:
ICANN
This corporation allocates IPv6 address blocks to the 5 RIRs.
Global Routing Prefix
Subnet ID
Interface ID
A global unicast address has 3 parts: