APHG final (all units) pt. 1
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/149
Last updated 5:15 PM on 4/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
1
New cards
What are the 5 themes of geography?
Location, Human environment interaction, place, movement, and regions
2
New cards
Define hearth
where an idea originates
3
New cards
define globalization of culture
globalization due to interchanging beliefs and customs
4
New cards
define globalization of economy
globalization due to business
5
New cards
define reference maps
regular maps showing cities, boundaries, mountains, or roads
6
New cards
define thematic maps
maps highlighting a particular feature or a single variable such as temperature, city, size, or extra information
7
New cards
define isoline maps
topographic maps, that show lines that connect points of equal value.
8
New cards
define choropleth maps
maps that show the level of some variable within predefined regions, such as counties, states, or countries
9
New cards
define dot maps
maps that use a dot to represent the occurrence of some phenomenon in order to depict variation in density in a given area
10
New cards
define cartograms
maps that have distorted population
11
New cards
define resolution
the amount of details or depth of a maps
12
New cards
define scale
the relationship between the portion of earth being studied and earth as a whole, specifically the relationship between the size of an object on a map and the size of the actual feature of earths surface
13
New cards
what are the 3 types of scale
Ratio (fraction, ex: 1:24,000), bar, and written
14
New cards
define small scale
depicts a large area but with less detail
15
New cards
define large scale
depicts a small area but with great detail
16
New cards
define cartography
the science of making maps
17
New cards
define projection
the system used to transfer locations from earths surface to a flat map
18
New cards
Maps that project the entire world can distort..
shape, distance, relative size, and direction
19
New cards
define Robinson projection
a compromise map projection showing the poles as lines rather than points and more accurately portraying high latitude lands and water to land ratio.
20
New cards
define Mercator projection
the oldest of the map projections; a cylindrical map projection It became the standard map projection for navigation because it is unique in representing north as up and south as down; it is distorted near the poles.
21
New cards
define Toponym
The name given to a portion of earths surface. Has to be natural feature
22
New cards
define site
the physical characteristics of a place
23
New cards
define situation
the location of a place relative to other places
24
New cards
define meridian. The 2 main meridians?
an arc is drawn on a map between the North and South poles (longitude)
Prime Merdian and International dateline
Prime Merdian and International dateline
25
New cards
define parallel
a circle drawn around the globe parallel to the equator and at the right angle to the meridians (latitude)
26
New cards
How many time zones are there in the US? what is it based on and why? where do time zones occur?
4, Eastern, Central, Mountain, and Pacific.
Greenwich England, was the most powerful country when established
every 15 degrees longitude
Greenwich England, was the most powerful country when established
every 15 degrees longitude
27
New cards
define Greenwich mean time
the time in that time zone encompassing the prime meridian, or zero degrees longitude
28
New cards
define the international date line
Arc 180 degrees longitude, when passing east (near America) clock moves back a day. when you move west (toward Asia) moves ahead a day
29
New cards
define spatial association
the distribution of one phenomenon that is related to another phenomenon. (why 2 places are located there, related is to be closer)
30
New cards
define spatial distribution
The arrangement of phenomenon across earths surface
31
New cards
define environmental determinism
19th and early 20th century approach that argued physical terrain of world dictates of humans survive.
32
New cards
define possibilism
theory that people can overcome the physical problems/features-( humans conquer land instead of land conquering humans)
33
New cards
define distribution
the 3 types?
the 3 types?
the arrangement of something across earths surface
density, concentration, pattern
density, concentration, pattern
34
New cards
define density
the frequency with which somethings exists within a given unit of area. Does not tell you where something is, just numbers
35
New cards
define arithmetic density
the total # of people divided by total land area
36
New cards
define physiological density
the total # of people divided by all arable land
37
New cards
define agricultural density
the total # of farmers divided by arable land
38
New cards
define diffusion
the spreading of a feature or trend from one place to another overtime
39
New cards
define relocation diffusion
the spread of a feature of tend through physical movement of people from one place to another. Does not have to grow in #s
40
New cards
define expansion diffusion. The 3 types?
the spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another in a snowballing process. Involves growing #s
Hierarchical, Contagious, stimulus
Hierarchical, Contagious, stimulus
41
New cards
define Hierarchical diffusion
the spread of a feature or tend from one key person or node of authority or power to other people or places
42
New cards
define Contagious diffusion
the rapid widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population
43
New cards
define stimulus diffusion
the spread of an underlying principle or thought process, even though a specific characteristic is rejected
44
New cards
define a formal region
uniform, everyone shares a distinct characteristic
45
New cards
define a functional region
nodal, area organized around a focal point
46
New cards
define a vernacular region
perceptual region, beliefs and cultural identify
47
New cards
Define culture
Customary beliefs, social, forms, and material traits of a group of people in tradition
48
New cards
define acculturation
the spread of cultural traits from one society to another
49
New cards
define overpopulation
too many people, to little resources
50
New cards
define carrying capacity
the largest number of people that the environment of a particular area can support
51
New cards
define doubling time
the time it takes for a population to double
52
New cards
what are the 4 most over populated regions in the world?
East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Western Europe
53
New cards
what are the 4 sparsely populated regions?
dry, wet, cold, and high lands
54
New cards
define characteristics for dry lands
* too dry for farming
* cover about 20% of earths land surface
* deserts, lack water.
* largest desert is the Sahara
* cover about 20% of earths land surface
* deserts, lack water.
* largest desert is the Sahara
55
New cards
define characteristics for wet lands
* receive high levels of precipitation
* unfavorable for human life
* combination of rain and heat depletes nutrients from soil, prevents growing crops
* unfavorable for human life
* combination of rain and heat depletes nutrients from soil, prevents growing crops
56
New cards
define characteristics for cold lands
* covered w/ ice or frozen to ground permanently
* have less perception then some deserts
* unsuitable for crops and animals
* have less perception then some deserts
* unsuitable for crops and animals
57
New cards
define characteristics for high lands
* few people live at high elevations
* mountains are steep, snowy, and sparsely settled
* mountains are steep, snowy, and sparsely settled
58
New cards
define total fertility rate
the average number of children a woman will have during her childbearing years
59
New cards
define infant mortality rate
the annual number of deaths of infants under 1 year old
60
New cards
define life expectancy
measure the numbers of years a newborn is expected to live
61
New cards
define Crude birth rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,00 people alive in the society
62
New cards
define Crude death rate (CDR)
the total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 population
63
New cards
Define natural increase (NIR). Does it include migration?
the percentage by which a population grows in a year. Find by CBR minus CDR divided by 10
No.
No.
64
New cards
How many people are added to the worlds population each year? When was the historic high and how many people were added?
80 million.
1989 w/ 87 million people
1989 w/ 87 million people
65
New cards
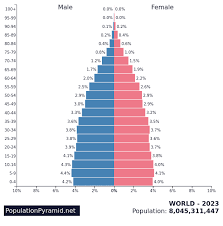
define a population pyramid
a bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
Can be used for demographics of a certain area and can be used to indicate development in a certain area
Can be used for demographics of a certain area and can be used to indicate development in a certain area
66
New cards
How many stages are there to the demographic transition model? are they low, moderate, or high growth?
Stage 1: low
Stage 2: high
Stage 3: moderate
Stage 4: low
\*\*\* possible stage 5: very low, zero population growth
Stage 2: high
Stage 3: moderate
Stage 4: low
\*\*\* possible stage 5: very low, zero population growth
67
New cards
define the characteristics Demographic transition model
Stage 1: \*Low growth \n High but fluctuating CDR and CBR. Low NIR. Population composition is youth dependencyStage 2: \*high growth \n CBR remains high. CDR plummets due to improved nutrient, sanitation, and medication. NIR rapidly grows. Population composition on youth. \n \*MDS enters industrial revolution and 150 yrs later LDCs enter Medical revolution \n Stage 3: \*moderate growth \n CBR falling, CDR falling slowly, NIR increase slows, population composition, mostly youth-people surviving longer \n Stage 4: \* low growth \n CBR low, CDR low, NIR falls and stays at low growth, population composition, shifts to elderly \n \*women education-less babies
68
New cards
what is the demographic transition model used for?
analyze and predict trends in populations
69
New cards
what country is closet to stage 5 Demographic transition model? other examples
Japan
Germany and Russia
Germany and Russia
70
New cards
What is the Malthus theory?
States that the world will get wiped out by over population, starvation, and disease (mainly food)
71
New cards
What do neo-Malthusians claim?
* Point out that the amount of farmland is decreasing while the population is increasing
* global warming could interfere with food production
* both extensification and intensification of agriculture will lead to land degradation
* global warming could interfere with food production
* both extensification and intensification of agriculture will lead to land degradation
72
New cards
What are criticisms on the Malthus theory?
1) factors that have slowed population growth
* birth control (contraceptives)
* education and advancement of women
2) factors that increased efficiency of farming
* mechanized farming
* hybrid seeds
* chemical fertilizers
* birth control (contraceptives)
* education and advancement of women
2) factors that increased efficiency of farming
* mechanized farming
* hybrid seeds
* chemical fertilizers
73
New cards
define demography
the scientific study of population characteristics
74
New cards
define census
the complete counting of a population
75
New cards
Define dependency ratio
the number if people under the age 15 and over age 64, compared to the number of people in the active labor force
76
New cards
what is Boserups claim?
food supply is impacted by population growth.
population increases= new development in technologies and increase production of food supply
population increases= new development in technologies and increase production of food supply
77
New cards
What were the causes of death of each stage in the Epidemologic transition model?
stage 1: infectious diseases (cholera, tuberculosis), pandemics/epidemics, animal attacks and accidents, malnutrition
stage 2: receding pandemics due to medical advancements, etc. (industrial revolution)
stage 3: degenerative and human-made diseases (cancer, aging lifestyle choices, heart diseases)
stage 4: delayed degenerative diseases (medical advancements, Alzheimer’s)
Stage 5: reemergence of infectious diseases. (covid, ebola)
stage 2: receding pandemics due to medical advancements, etc. (industrial revolution)
stage 3: degenerative and human-made diseases (cancer, aging lifestyle choices, heart diseases)
stage 4: delayed degenerative diseases (medical advancements, Alzheimer’s)
Stage 5: reemergence of infectious diseases. (covid, ebola)
78
New cards
what is the epidemiologic transition?
distinctive causes of death in each stage of the demographic transition
79
New cards
define epidemiology
branch of medical science concerned with the incidence, distribution, and control of diseases that affect large numbers of people
80
New cards
define ecumene
the portion of earths surface occupied by permanent human settlement
81
New cards
define the industrial revolution
a series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods
82
New cards
what are the 4 stages of the industrial revolution? describe each
First: before the 1870s
\-Mechanical production, railroads, steam, power
2nd: 1870s-first half on 20th century
\-development of standardized production process and mechanized assembly lines, reducing work to simple steps
3rd: last half of 20th century
\-Automated production, electronics, and computers
4th: now
\-artificial intelligence, big data, robotics, and more to come
\-Mechanical production, railroads, steam, power
2nd: 1870s-first half on 20th century
\-development of standardized production process and mechanized assembly lines, reducing work to simple steps
3rd: last half of 20th century
\-Automated production, electronics, and computers
4th: now
\-artificial intelligence, big data, robotics, and more to come
83
New cards
What are the 3 largest automakers in the US and Canada?
General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler
84
New cards
define the Medical revolution
medical technology invented in Europe and North America that is diffused to the poorer countries of Latin America, Asia, and Africa. Enabled people to live longer and healthier
85
New cards
define a sex ratio
the number of males per 100 females in a population
86
New cards
define migration
form of relocation diffusion involving permanent movement to a new location
87
New cards
define mobility
all types of movement from one location to another
88
New cards
define circulation
constant, short term, repetitive movements by an individual
89
New cards
define emigration
migration away from a country
90
New cards
define net migration
the difference between the number of immigrants and the number of emigrants. Net in and net out migration
91
New cards
define counterurbanization
net migration from urban to rural areas in MDCs
92
New cards
what are the reasons for migration? examples?
due to push and pull factors of..
economic: (push:low wages, pull job opportunities)
political: (push:war, discrimination,repressive laws, pull: peace, asylum)
social/ demographic:( push: racism, gender roles, slavery pull: more freedom, less prejudice, familiarity/kindness
natural: (push: natural disaster, crop failure, pull: desirable climate and landscape)
economic: (push:low wages, pull job opportunities)
political: (push:war, discrimination,repressive laws, pull: peace, asylum)
social/ demographic:( push: racism, gender roles, slavery pull: more freedom, less prejudice, familiarity/kindness
natural: (push: natural disaster, crop failure, pull: desirable climate and landscape)
93
New cards
what are push factors?
negative events that push people to move away
94
New cards
what are pull factors?
positive conditions of a location encourging others to move there.
95
New cards
define intervening obstacle
barriers that hold back migrants back from continuing to travel
96
New cards
define intervening opportunity
opportunity that causes migrants to voluntarily to sop traveling
97
New cards
define asylum
political migrants that move due to fear of oppressions and may be in danger due to political views and are granted protection in accepting countries
98
New cards
define brain drain
large scale emigration by talented people
99
New cards
Define internal migration. The 2 types?
the permanent movement from one country to another.
Interregional migration and Intraregional migration
Interregional migration and Intraregional migration
100
New cards
define international migration. The 2 types?
the permanent movement with a particular country
voluntary and forced migration.
voluntary and forced migration.