Cerebral Cortex (Ch. 5: Neuroanatomy)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
rostral means…
towards the head
caudal means…
towards the tail
ipsilateral means…
same side
contralateral means…
opposite side
unilateral means…
one side
bilateral means…
both sides
medial means…
closer to the midline
lateral means…
away from the midline
the CNS is composed of… (2)
the brain and the spinal cord
the PNS is composed of… (3)
31 pairs of spinal nerves, 12 pairs of cranial nerves, & peripheral autonomic and sensory ganglia
what are the 4 major divisions of the CNS?
cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brainstem, cerebellum
what 3 things make up the diencephalon?
thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus
what 3 things make up the brainstem?
midbrain, pons, medulla
the cerebral hemispheres are also known as what? (2)
telencephalon, endbrain
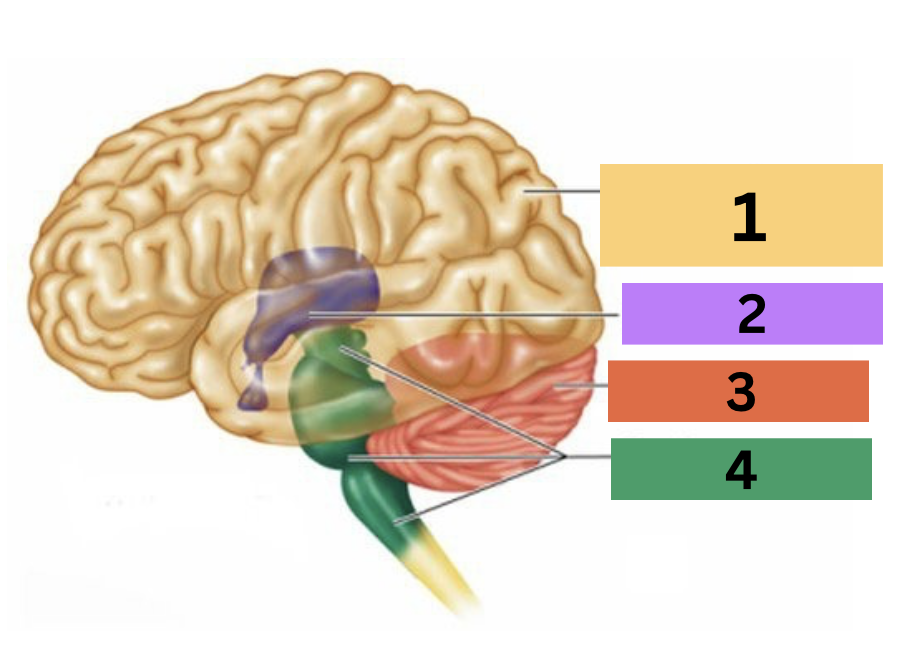
label the major divisions of the brain
1: cerebral hemisphere
2: diencephalon
3: cerebellum
4: brainstem
the cerebral cortex is the ____. it is responsible for…..
surface of the brain. responsible for the planning and execution of actions & interpretation and moderation of sensation
the cerebral cortex is divided into __ lobes. name them
frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital
which hemisphere is most responsible for speech?
left
the frontal lobe is responsible for….
higher thinking, executive function and motor planning. center for consciousness
Broca’s area is found in what lobe? What Broadmann number?
frontal. 44 and 45
Broca’s aphasia results in ____ speech production but _____ auditory comprehension
impaired speech, preserved comprehension
the temporal lobe in responsible for…
auditory processing and comprehension
Wernicke’s area is found in what lobe? What Broadmann number is it?
temporal. 22
Wernicke’s aphasia results in ____ speech production but _____ auditory comprehension
fluent speech, impaired comprehension
the parietal lobe is responsible for…
most sensory info
the occipital lobe is responsible for…
visual processing, including reading and writing
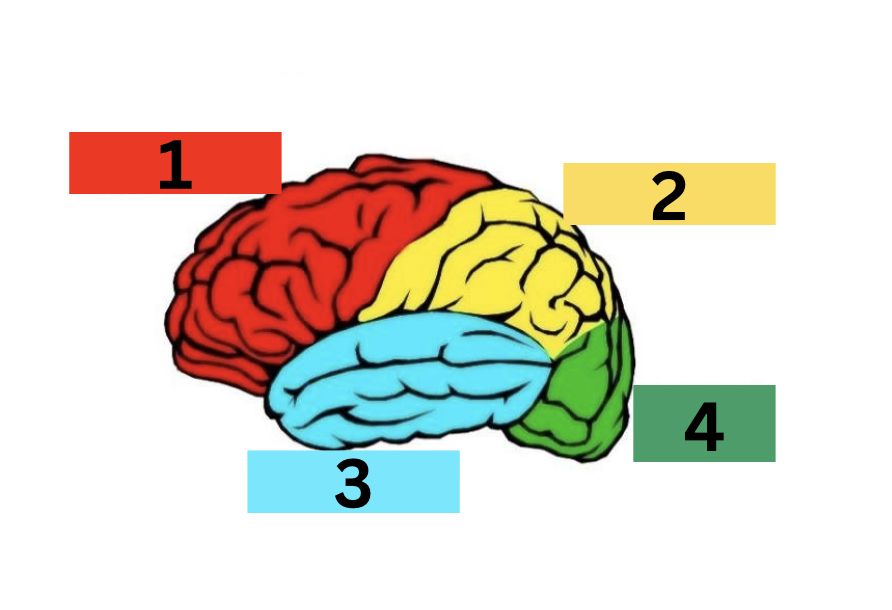
label the 4 lobes of the cerebral hemisphere
1: frontal
2: parietal
3: temporal
4: occipital
what is the 5th lobe called? what is it responsible for?
the limbic lobe. responsible for sensory and motor functions. related to speech/language but not well understood
sulci are….
the grooves or valleys
really deep sulci are called….
fissures
gyri are….
ridges or bumps
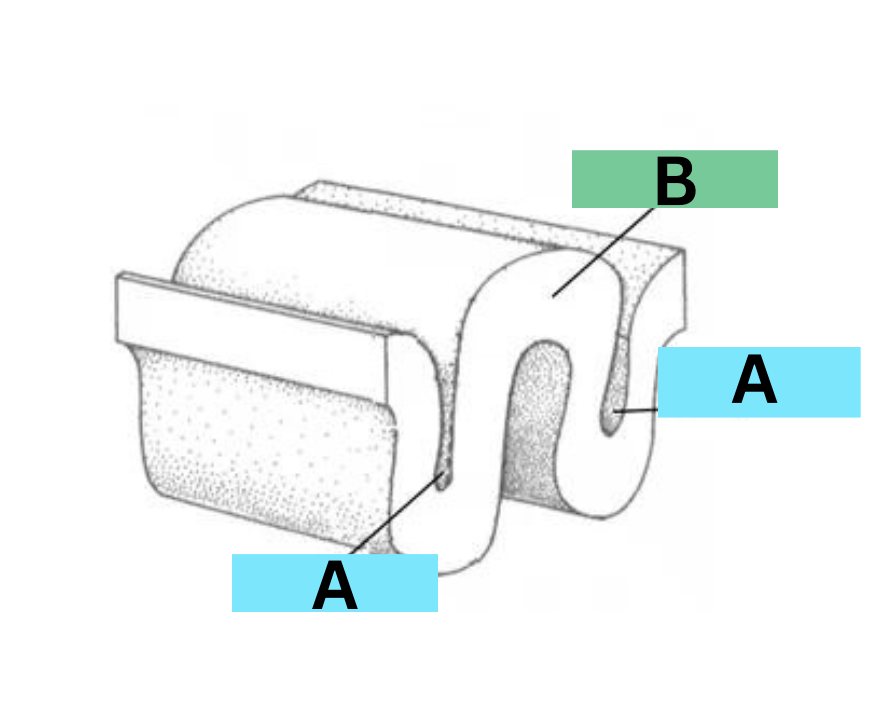
label
A: sulcus
B: gyrus
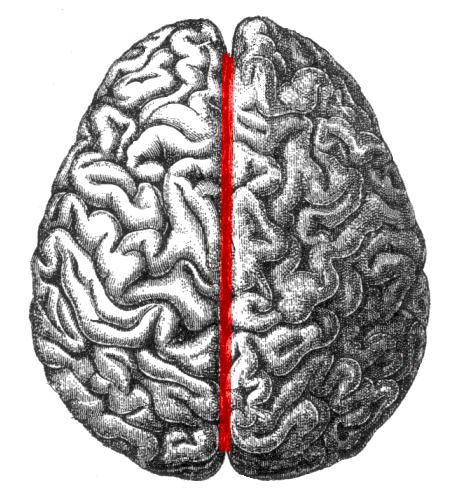
the medial/longitudinal fissure does what?
separates the brain into left and right hemispheres
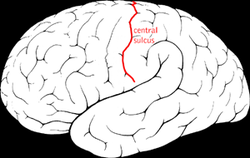
what does the central sulcus do?
separates the frontal and parietal lobes
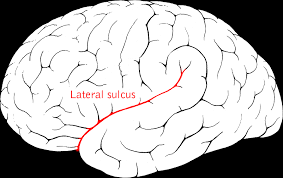
what does the lateral sulcus do? what is it known as?
separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes. aka sylvian fissure
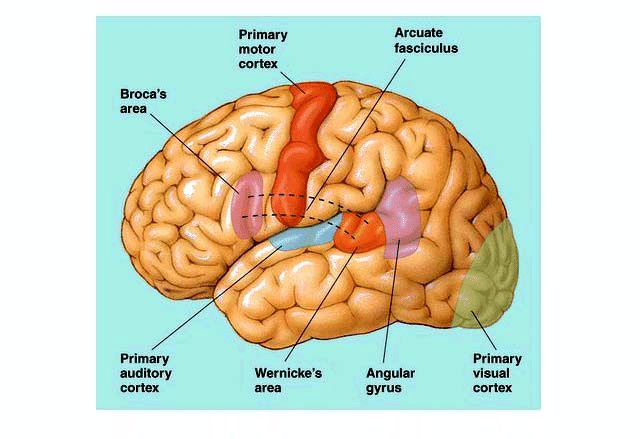
what are the perisylvian regions? what are they responsible for?
fibers running throughout the lobes around the sylvian fissure. important for language comprehension and production
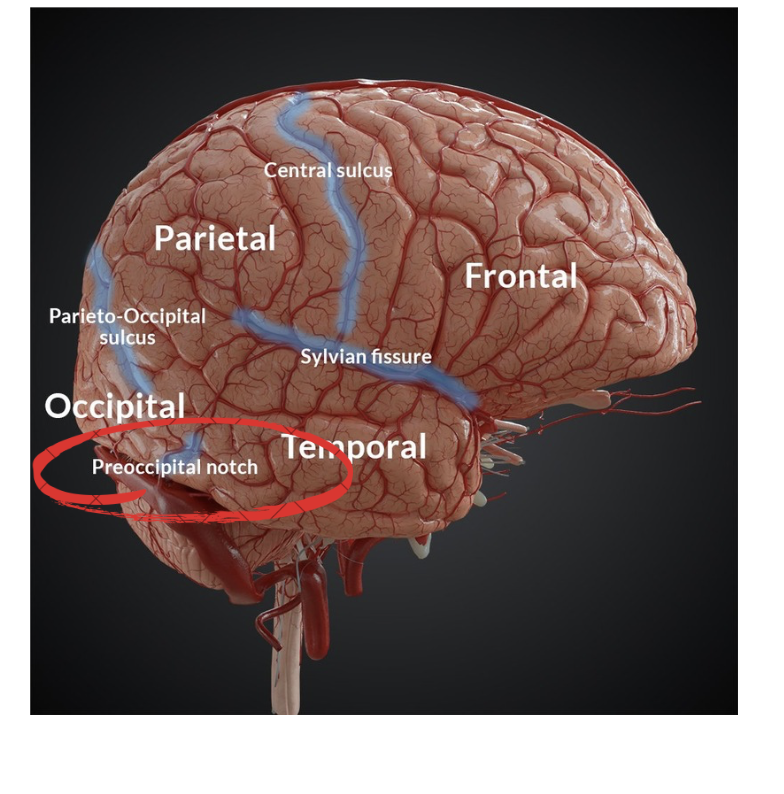
the preoccipital notch does what?
separates the occipital lobe from the temporal lobe
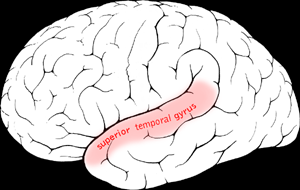
the superior temporal gyrus does what? where is it located?
contains primary auditory cortex and wernicke’s area. associated more closely with language input than language output. directly below the lateral sulcus
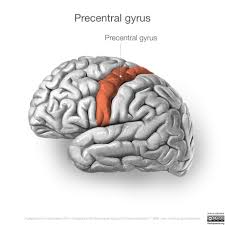
what does the precentral gyrus do? where is it located?
primary motor cortex - controls body movement. located anterior to the central sulcus
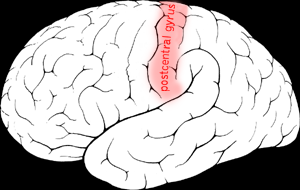
what does the postcentral gyrus do? where is it located?
primary sensory cortex - process bodily sensations. located posterior to central sulcus
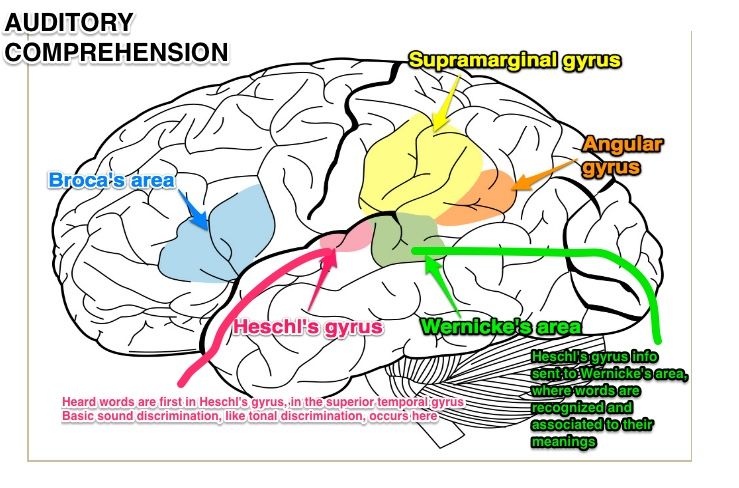
what does heschl’s gyrus do? where is it found?
responsible for the reception of auditory stimuli including frequency, location, intensity. found in primary auditory cortex (broadmann 41 & 42)
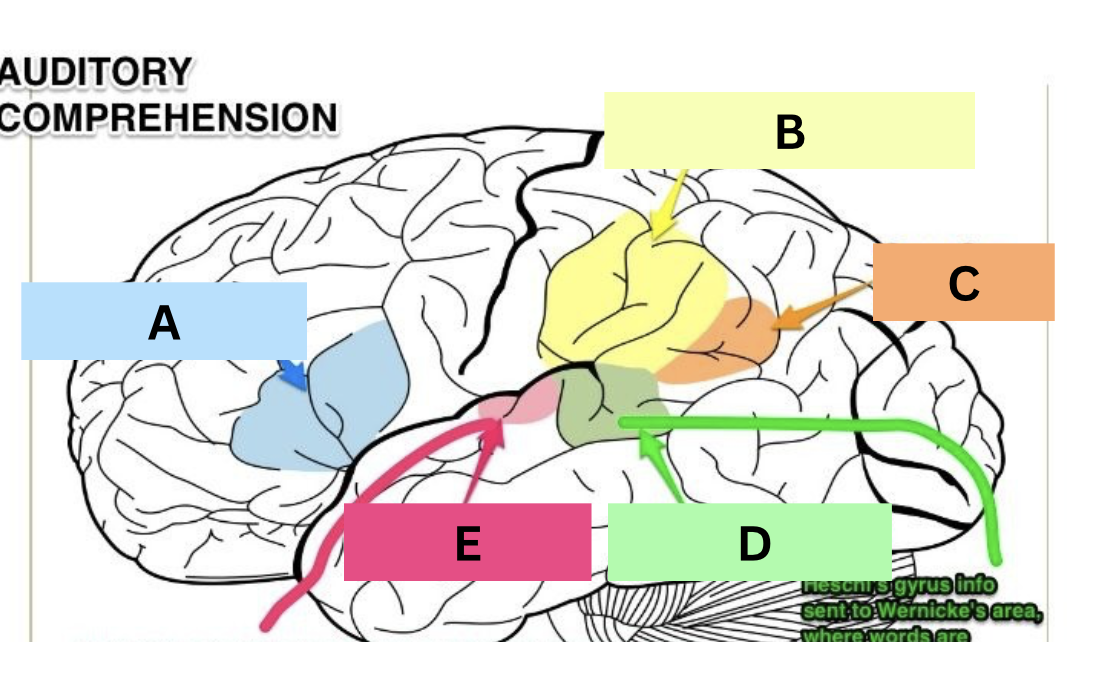
label
A: broca’s area
B: supramarginal gyrus
C: angular gyrus
D: wernicke’s area
E: heschl’s gyrus
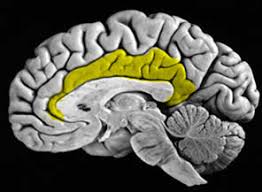
what does the cingulate gyrus do? where is it found?
limbic lobe - involved in emotional processing and behavior regulation. arc shaped structure lying above the corpus callosum
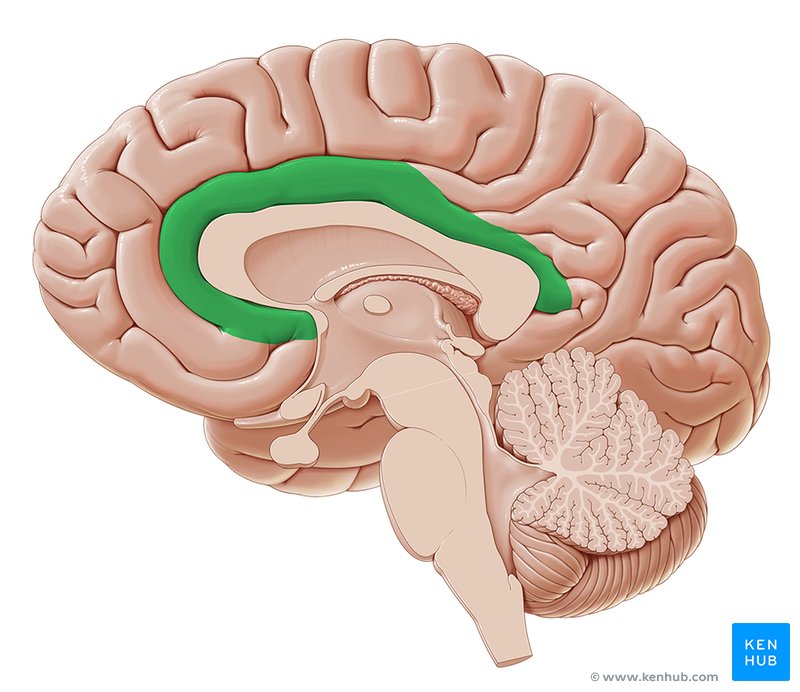
label the part
cingulate gyrus
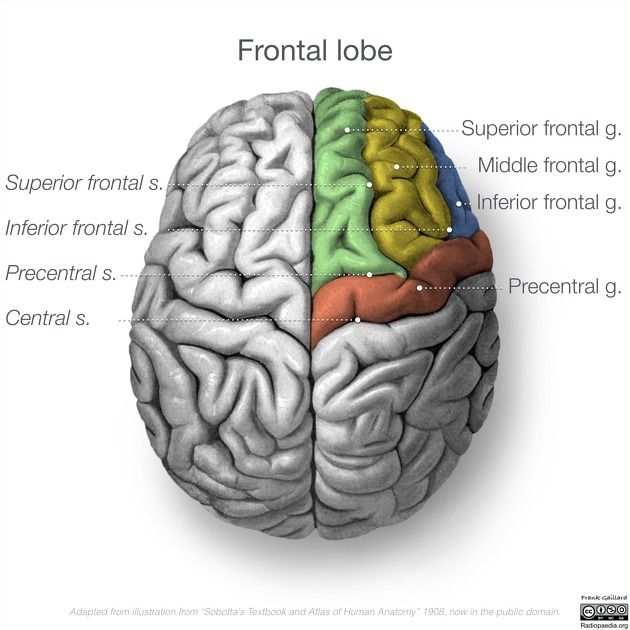
what are the functions of the superior, middle, and inferior frontal gyri?
critical for higher cognitive functions, like judgement, planning, decision making, executive function, reasoning
the inferior frontal gyrus includes what important area for speech?
Broca’s area
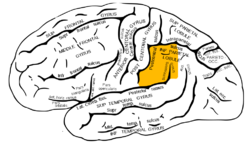
what is the function of the supramarginal gyrus? where is it located?
broad range of language formulation including semantic and phonologic processing. curves around the end of the lateral sulcus
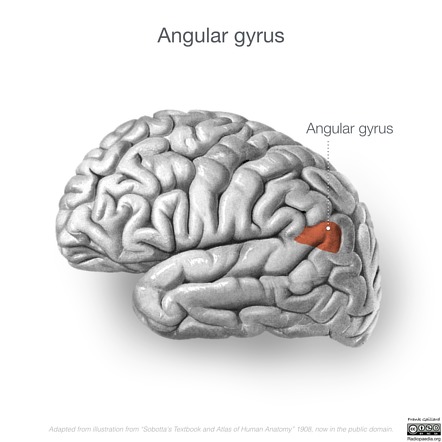
what is the function of the angular gyrus? where is it located?
semantic processing, repetition, metaphor comprehension. located posterior to the supramarginal gyrus
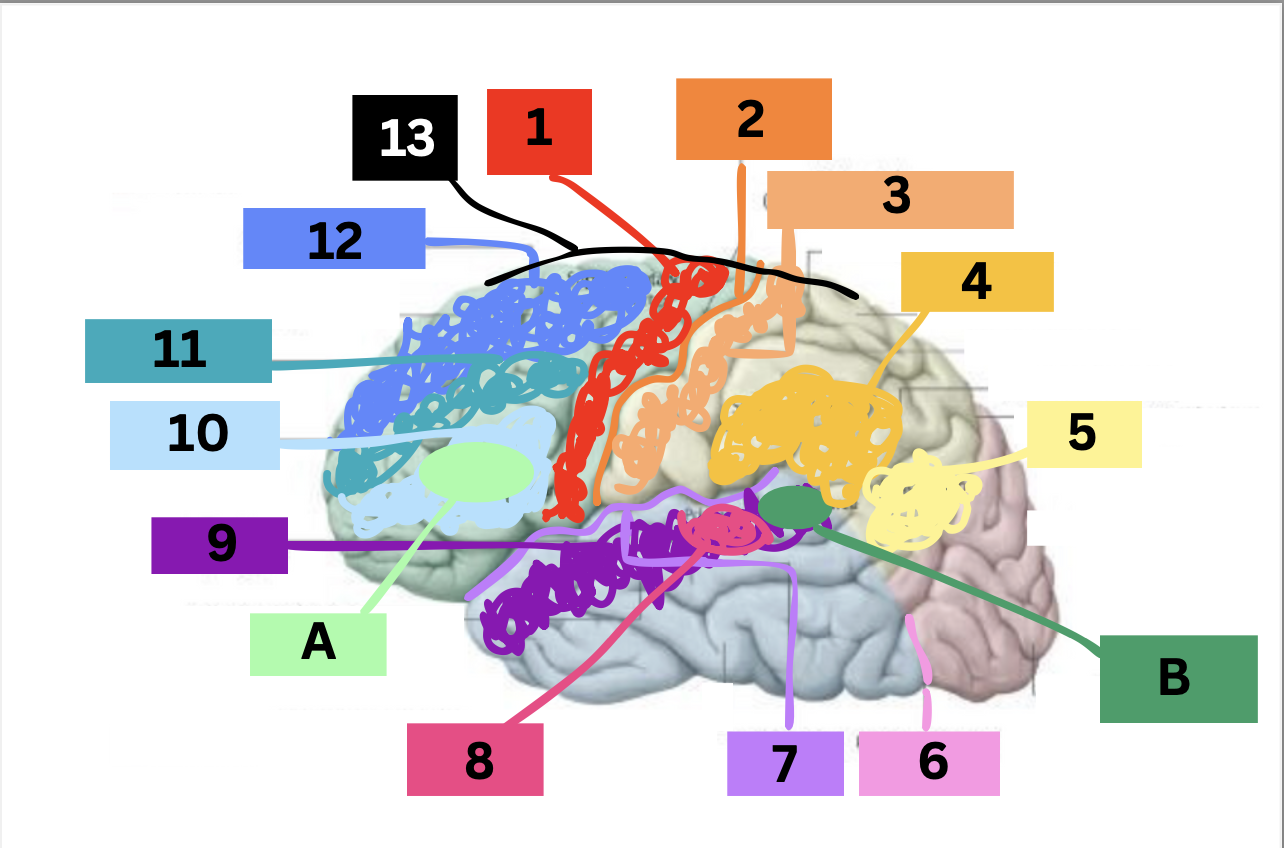
label
1: precentral gyrus
2: central sulcus
3: postcentral gyrus
4: supramarginal gyrus
5: angular gyrus
6: pre-occipital notch
7: lateral sulcus
8: heschl’s/transverse gyrus
9: superior temporal gyrus
10: inferior frontal gyrus
11: middle frontal gyrus
12: superior frontal gyrus
13: medial/longitudinal fissure
A: broca’s area
B: wernicke’s area