Lab 4 phylum platyhelminthes and body symmetry
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
body symmetry
bilateral
acoelomate body structure
no true body cavity (coelum)
platyhelminthe digestive system
incomplete, gastrovascular cavity
class turbellaria
free living flatworms (non parasitic) less than 5mm long
class turbellaria ecology
found in water
oral opening of class turbellaria
midventrally, opens into the gut via a pharynx that extends out through the mouth for feeding
class turbellaria digestion
both extracellular and intracellular (can range from simple sac to complex branched intestine)
auricles
earlike, chemosensory lobes that are "ear-like"
eyespots
black pigment that serves as light detectors to help orient the organism
class trematoda
liver flukes, endo and ectoparasites of both vertebrates and non vertebrates
what type of attachments do trematodes have
1 or more ventral suckers
one host
simple life cycle
multiple hosts
complex life cycle
tegument
living outer layer of the epidermis (the neodermis)
opisthorchis
the chinese liver fluke, of class tremetoda
primary/definitive host of opisthorchis
humans and domestic animals
miracidium
a free swimming ciliated larva that resembles a protozoan (so it will get eaten by its host)
first imediate host of opisthorchis
an aquatic snail
sporocyst
stage in the opisthorchis life cycle that contains many rediae
redia
stage in the opisthorchis life cycle that contains many cercaria
cercaria
escapes into the water from the redia to attach to the next host (a fish)
second intermediate host of opisthorchis
fish
metacercaria
cercaria boring into the fish host and form cysts
body plan of cercaria
larva have a tail and oral and ventral suckers to attach onto the gills of fish
host cycle of opisthorchis
water, free swimming miracidia enter snail, larvae develop in snails body, cercariae break out into water, attach to fish gills, infected fish eaten by humans, eggs released in feces eventually makes it back to the water
life cycle of opisthorchis
miracidium breaks out of capsule, into sporocyst, into rediae, into cercariae, into metacercarial cysts, into adult fluke which produce eggs in the capsules
what is the difference between the 2 trematoda parasites, opisthorchis and schistosoma?
schistosoma skips the first snail host stage
what long term disease can schistosoma cause
bladder cancer
what is class cestoda
tape worms
cestoda digestive system
no mouth or digestive tract as they are absorbing digested nutrients
scolex
head of the tapeworm
strobila
body of the tape worm, composed of numerous proglottids
proglottid
segments of a tapeworm
cysticercus stage of cestoda
the larval stage, found in muscle of tapeworms intermediate host
life cycle of beef tapeworm
eggs with larvae in grass, beef eats it, scolex attachs worm into muscle tissue, beef is eaten by humans
cephalization
brain and sensory information gathered in the anterior "head" region
dugesia tigrina
the flatworm we used in the experiment
how does dugesia tigrina react to light
negatively phototactic
eyespots
A
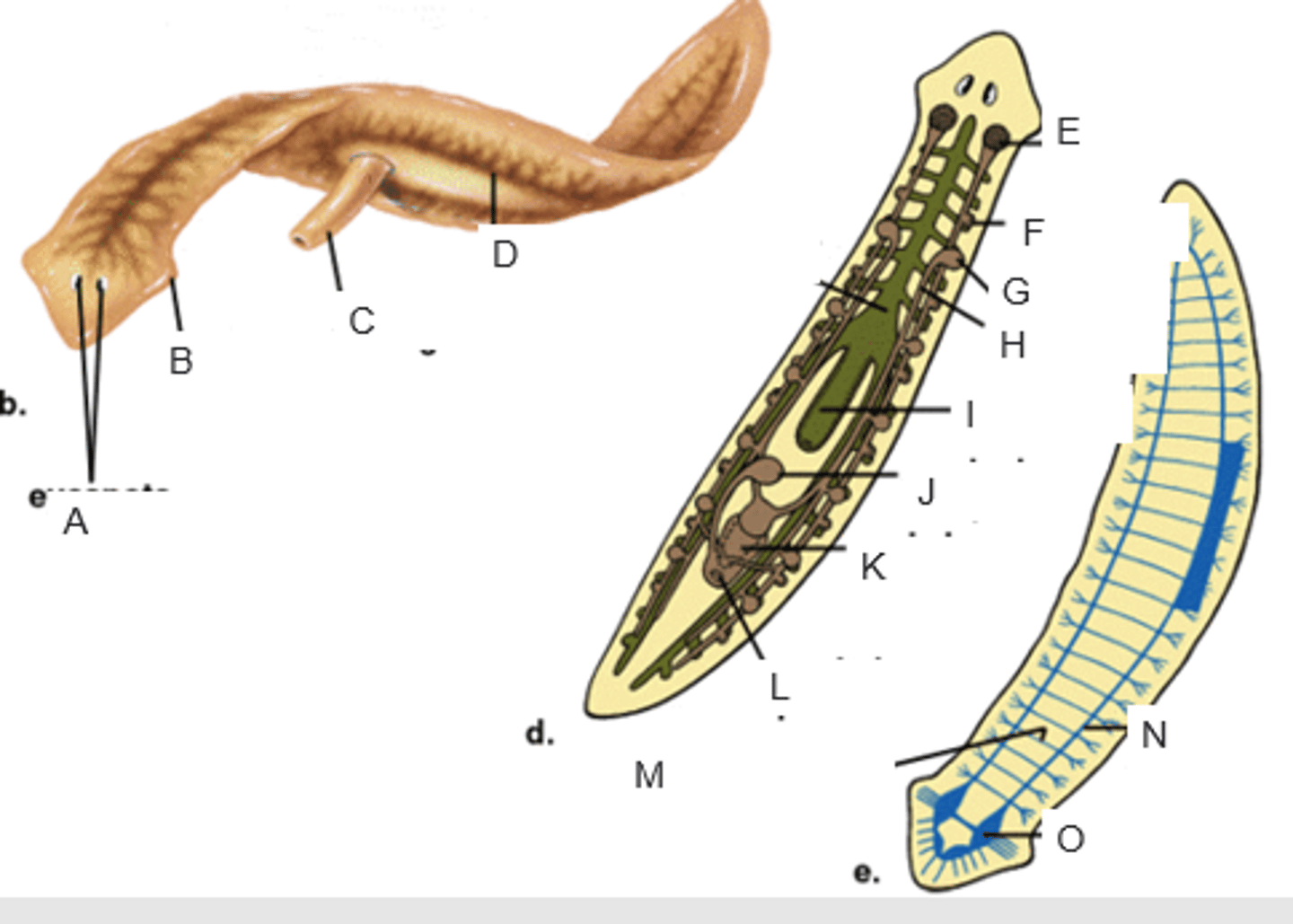
auricle
B
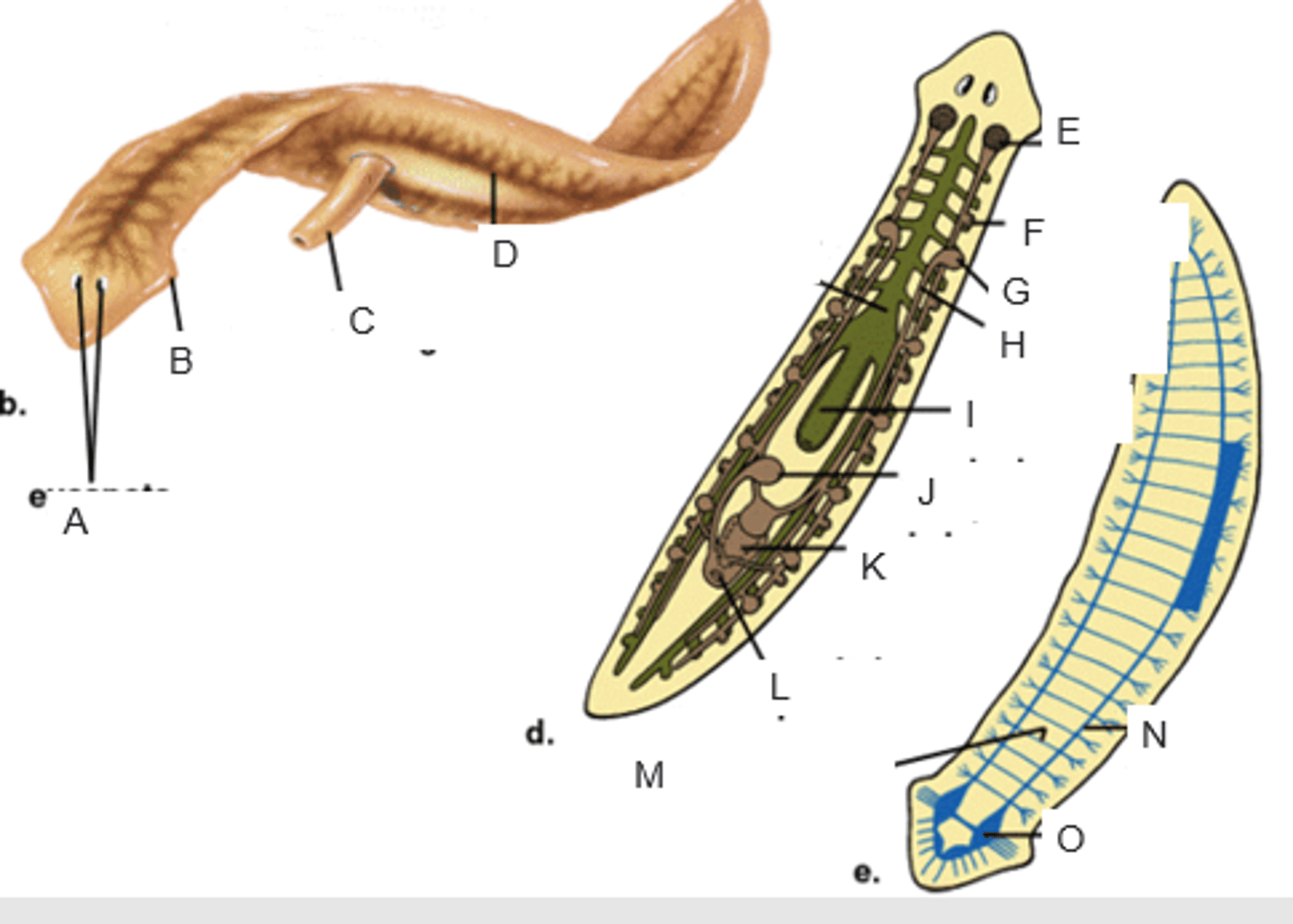
pharynx extended through the mouth
C
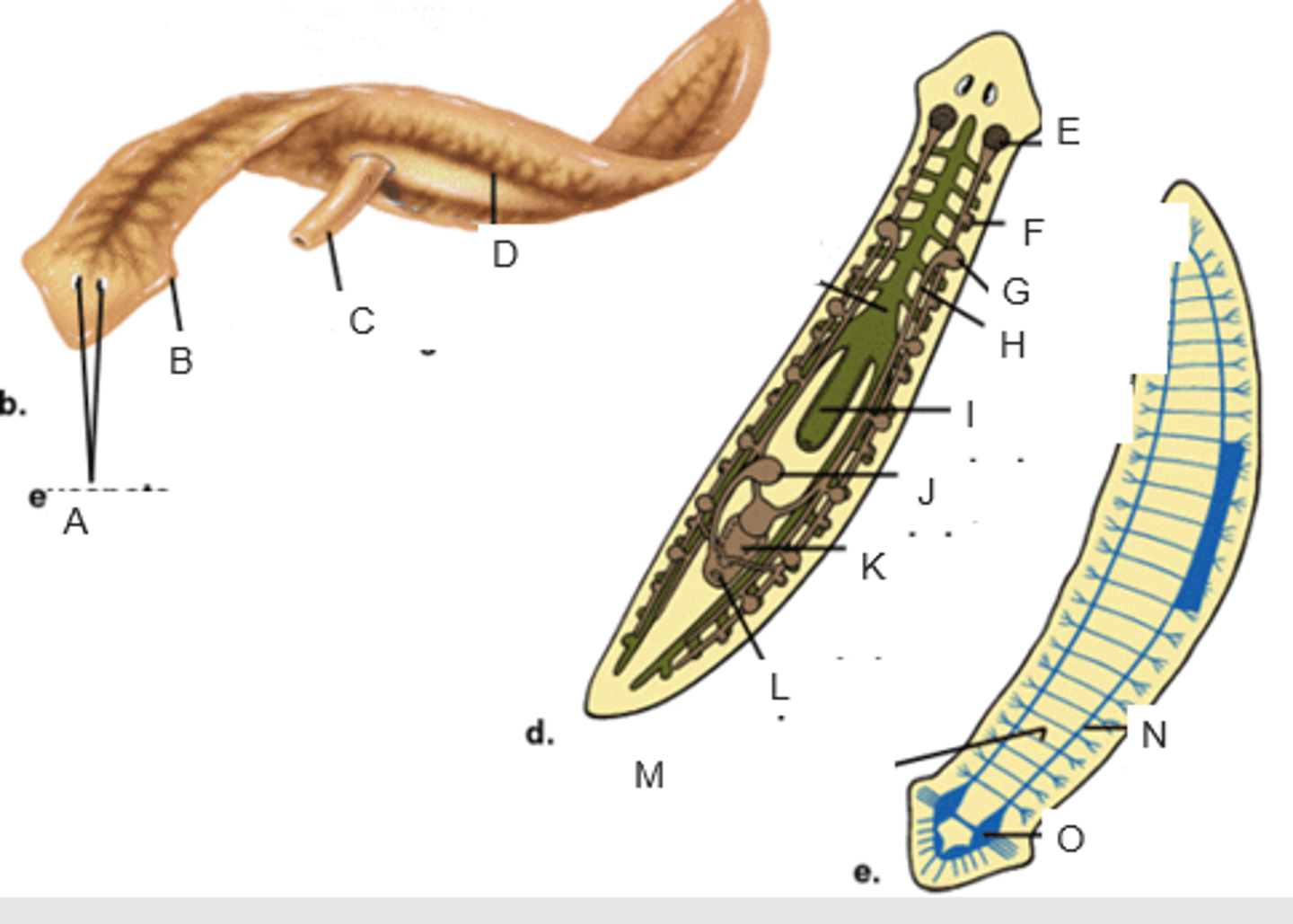
gastrovascular cavity
D
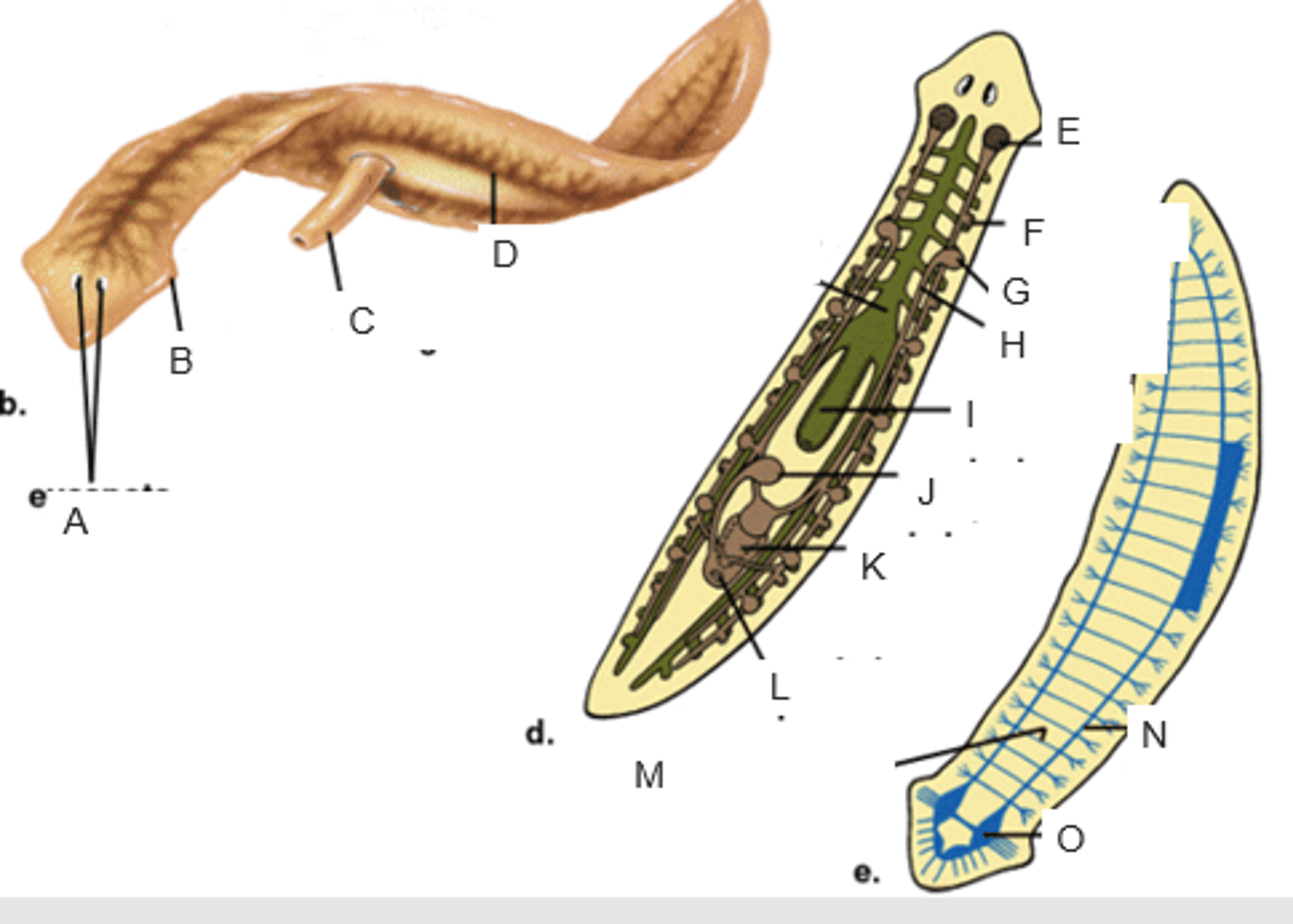
ovary
E
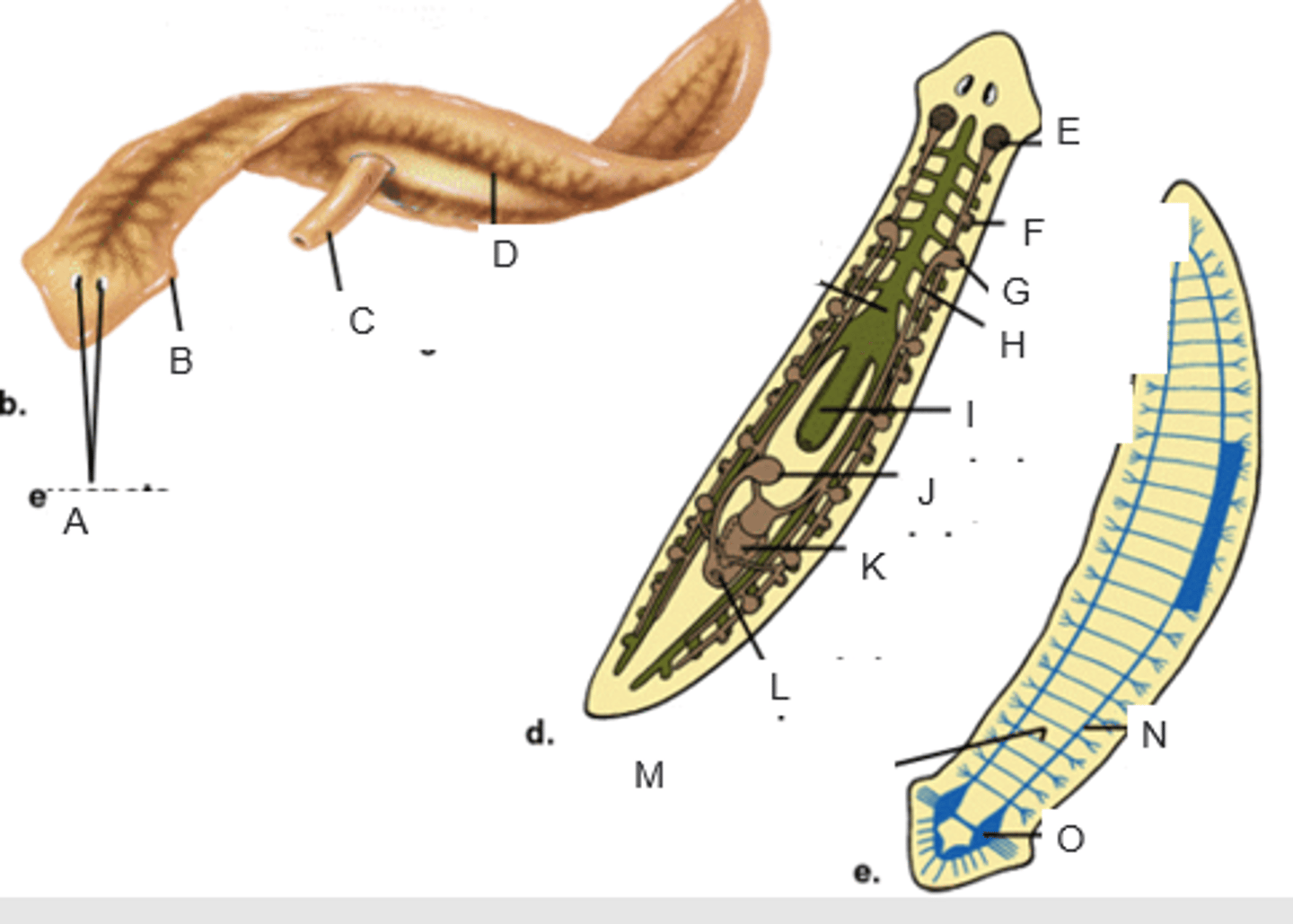
yolk gland
F
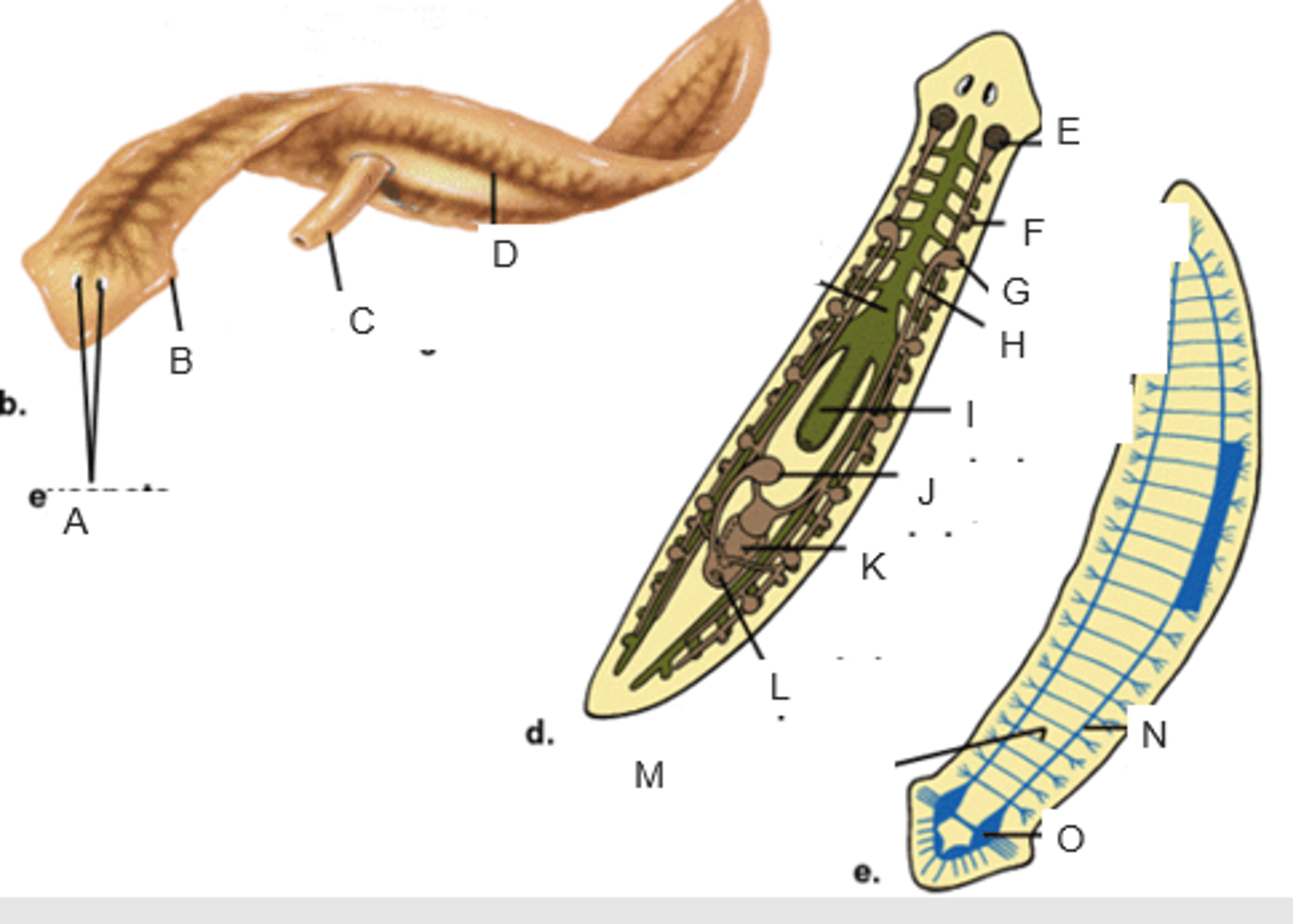
testis
G
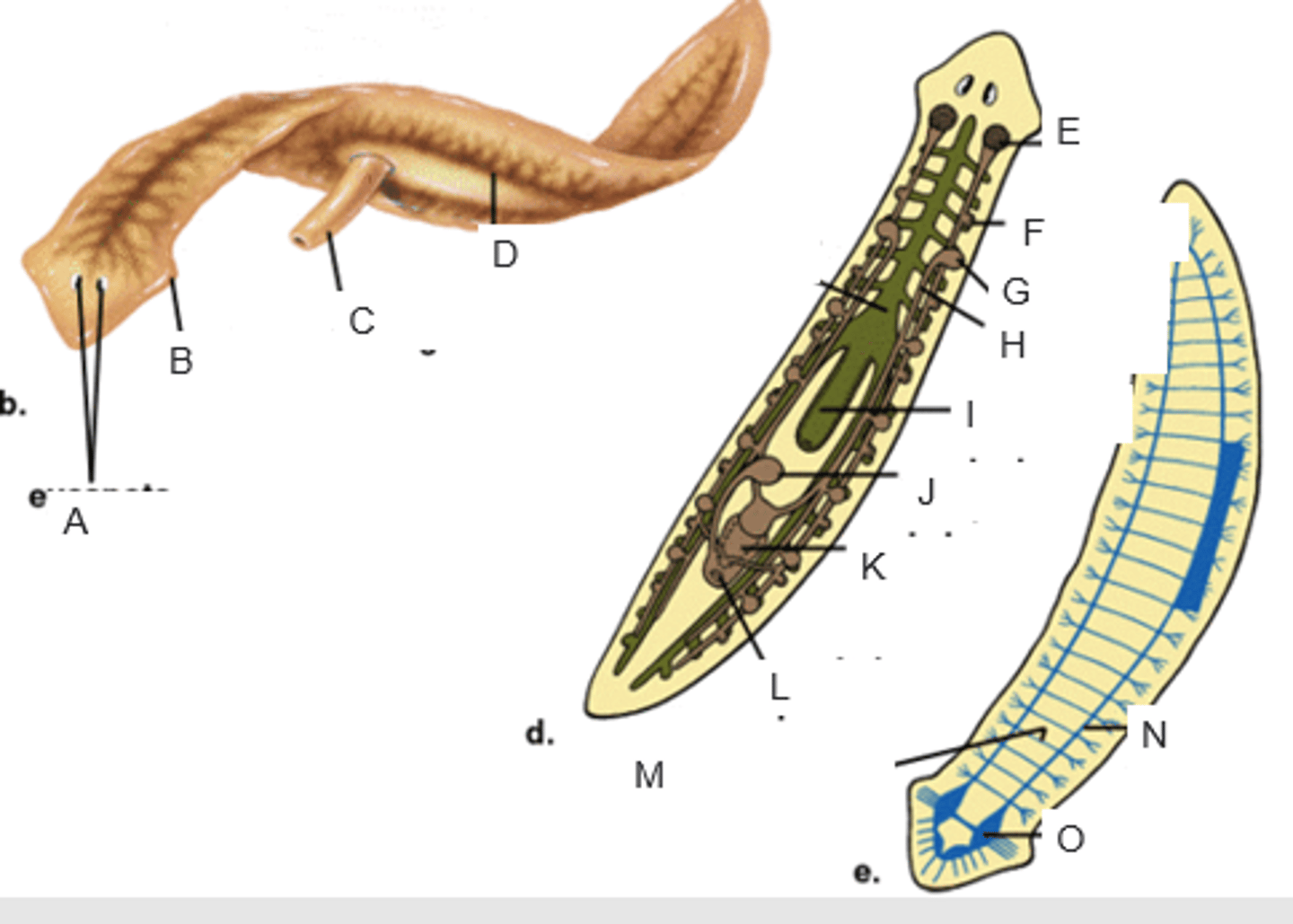
sperm duct
H
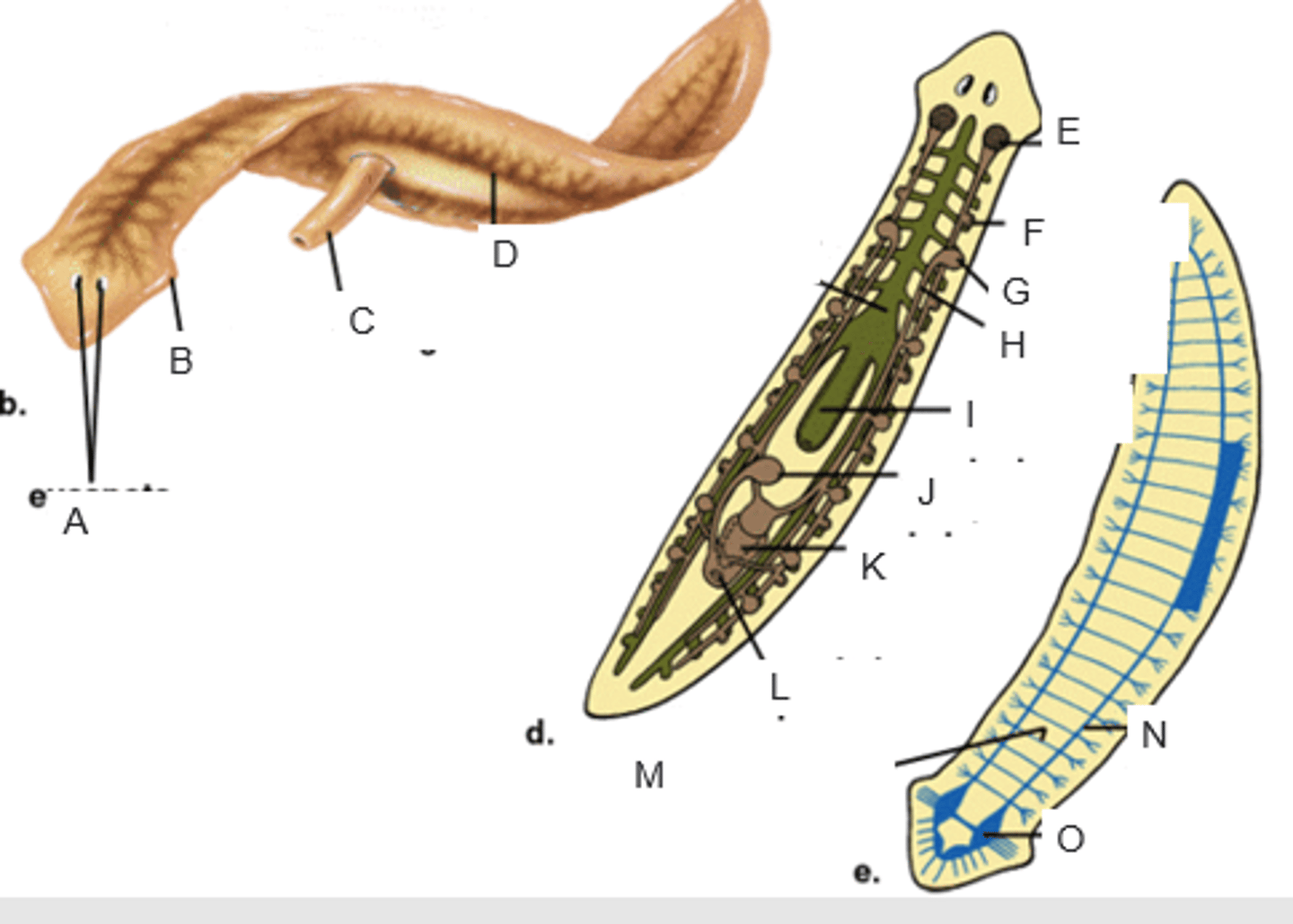
pharynx
I
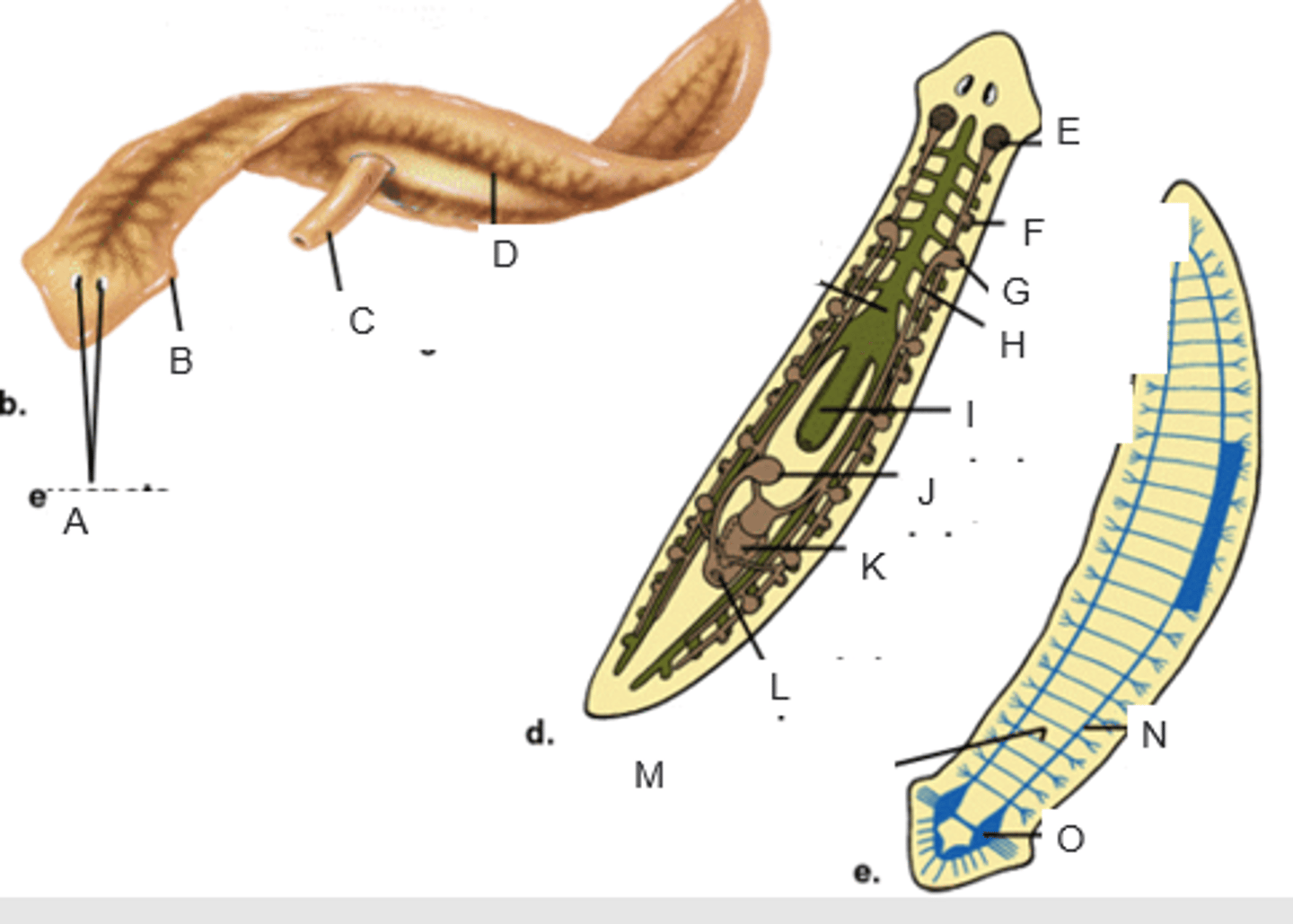
seminal receptacle
J
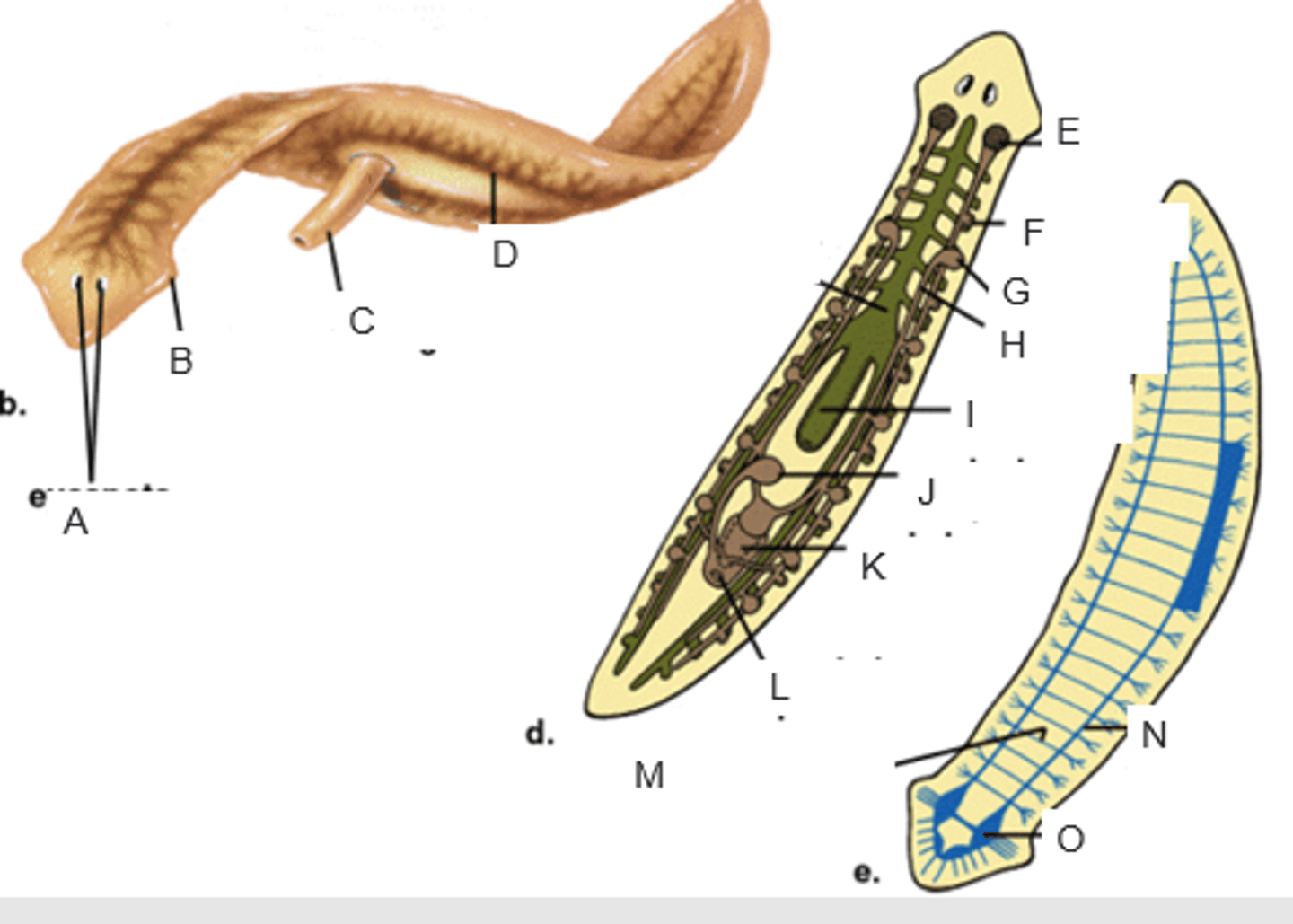
penis in genital chamber
K
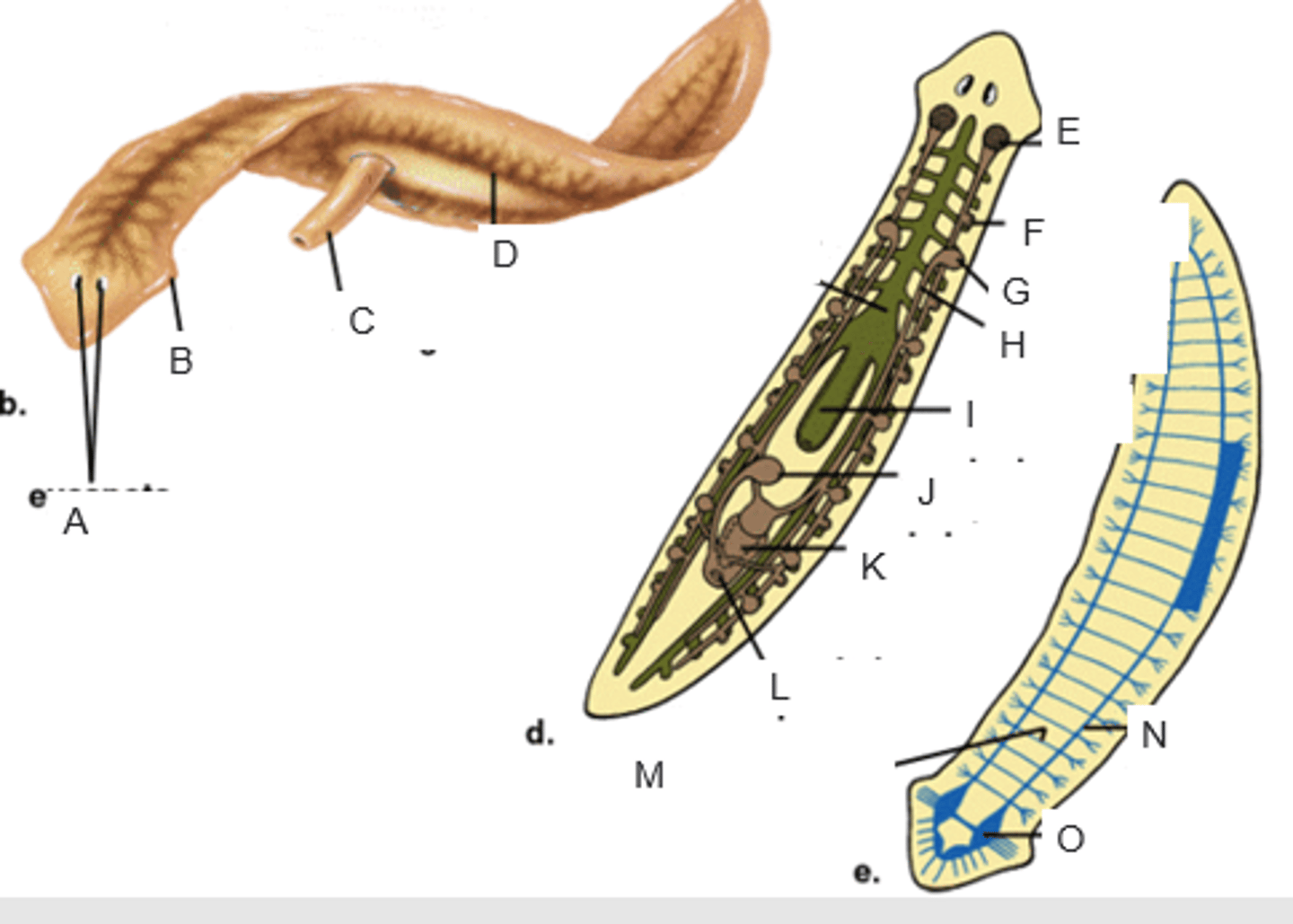
genital pore
L
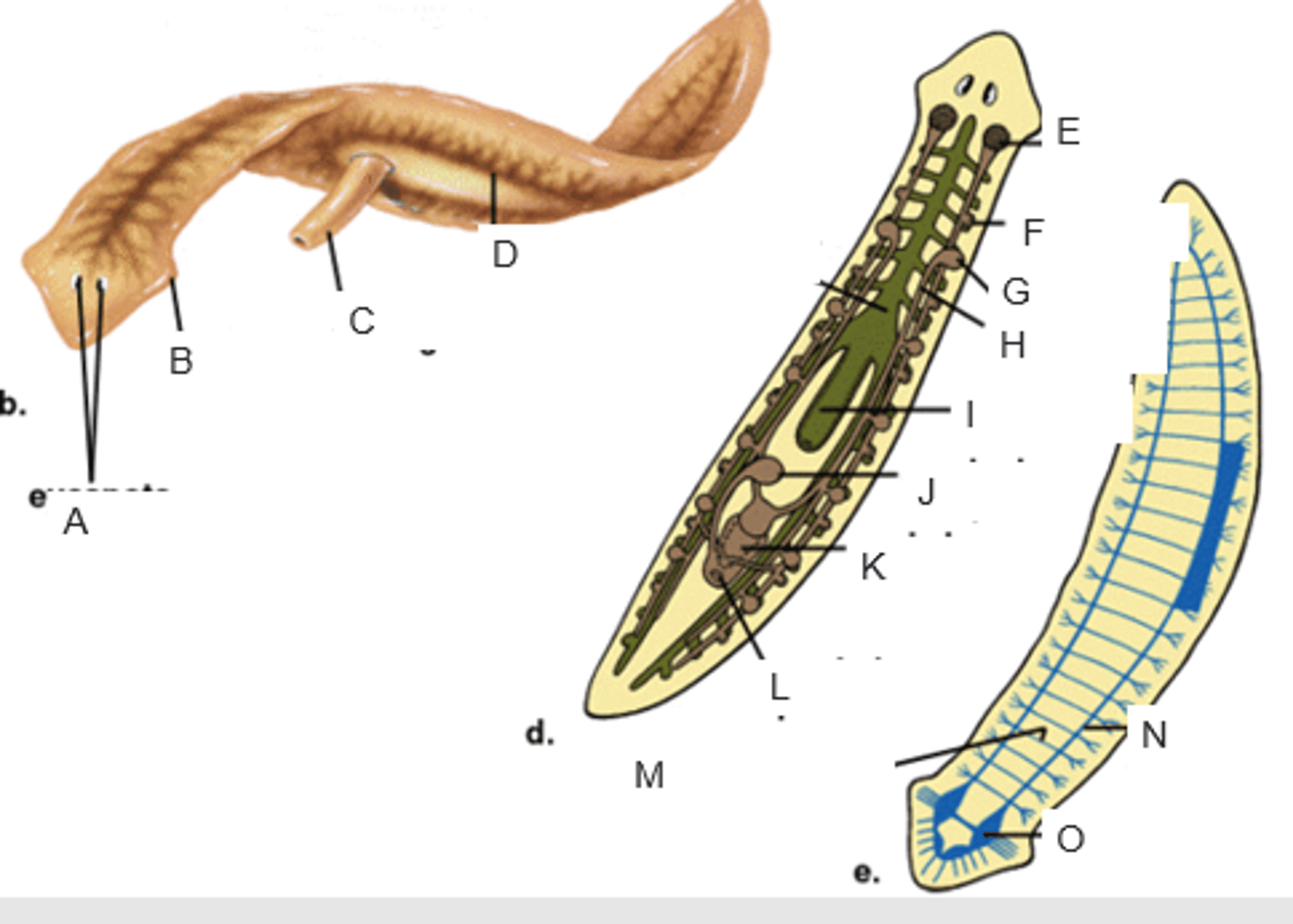
transverse nerve
M
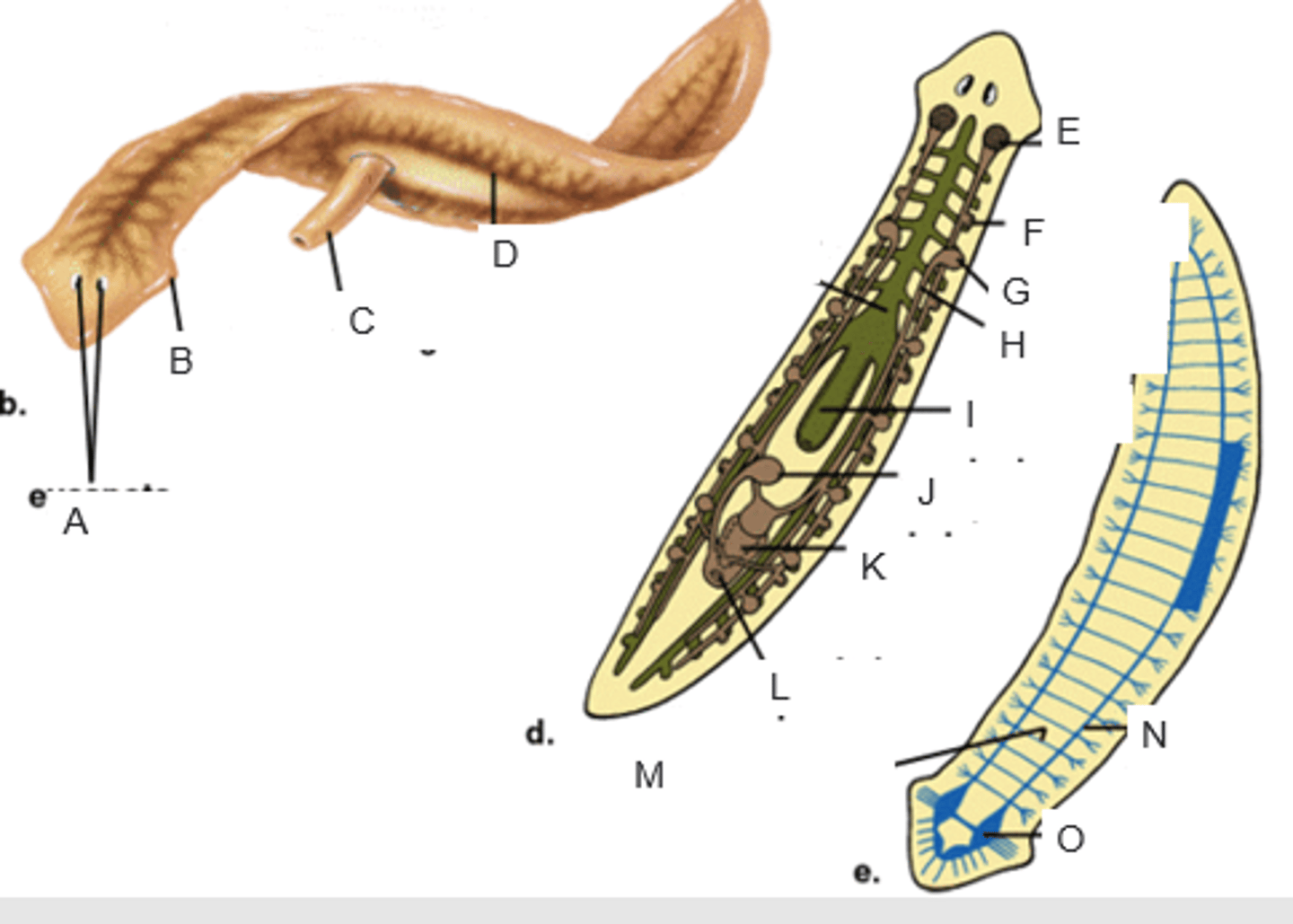
ventricle nerve cord
N
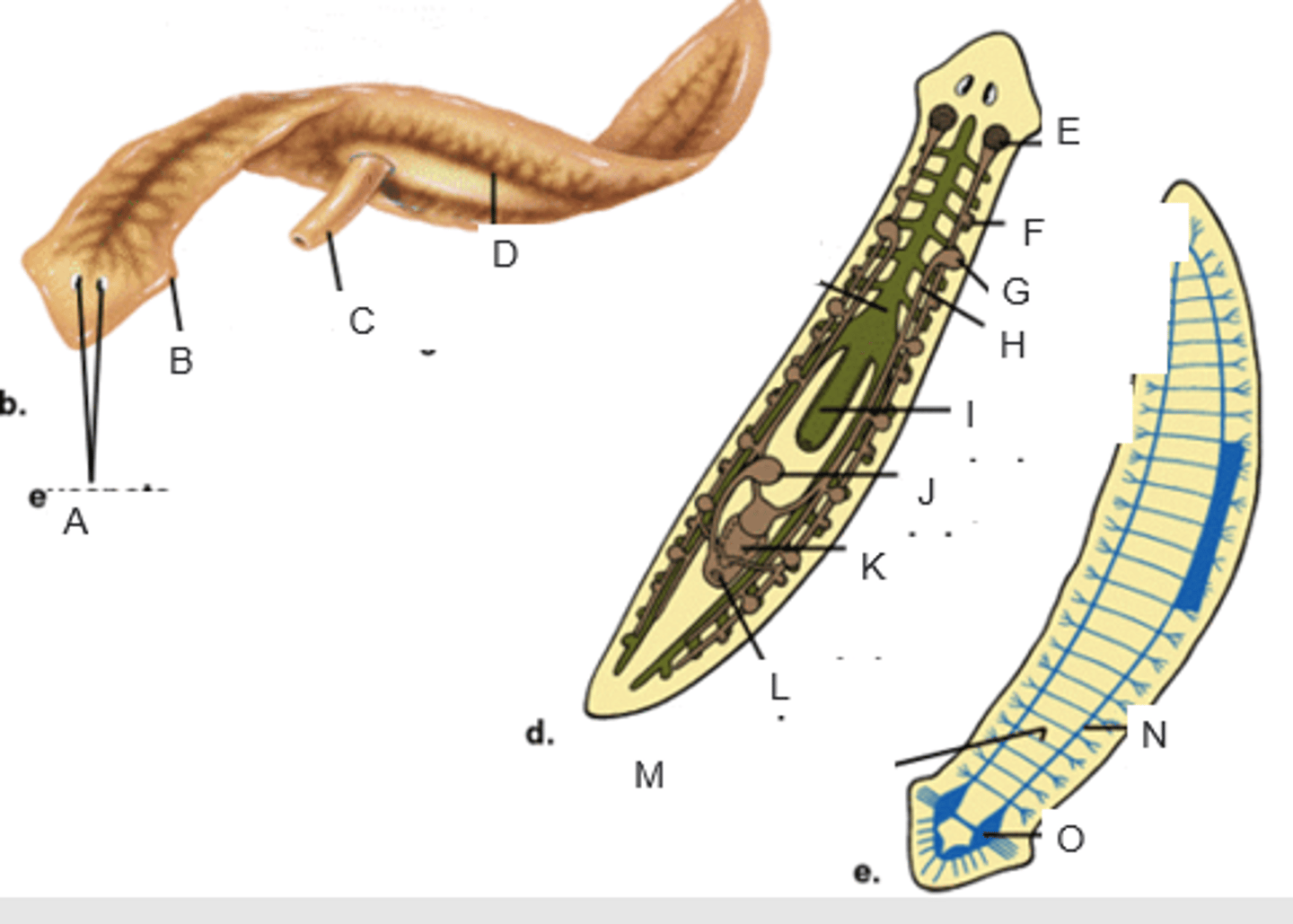
brain
O
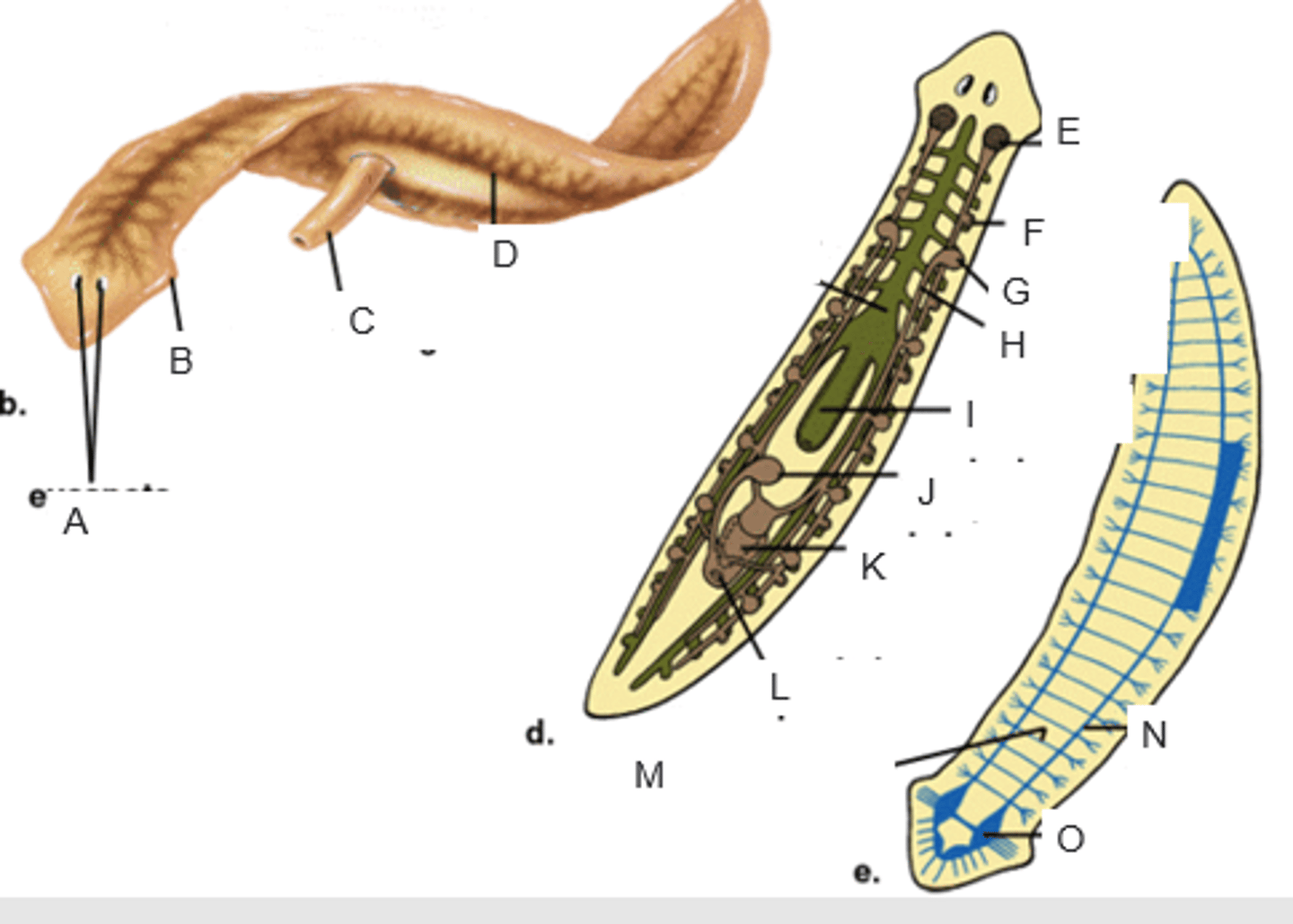
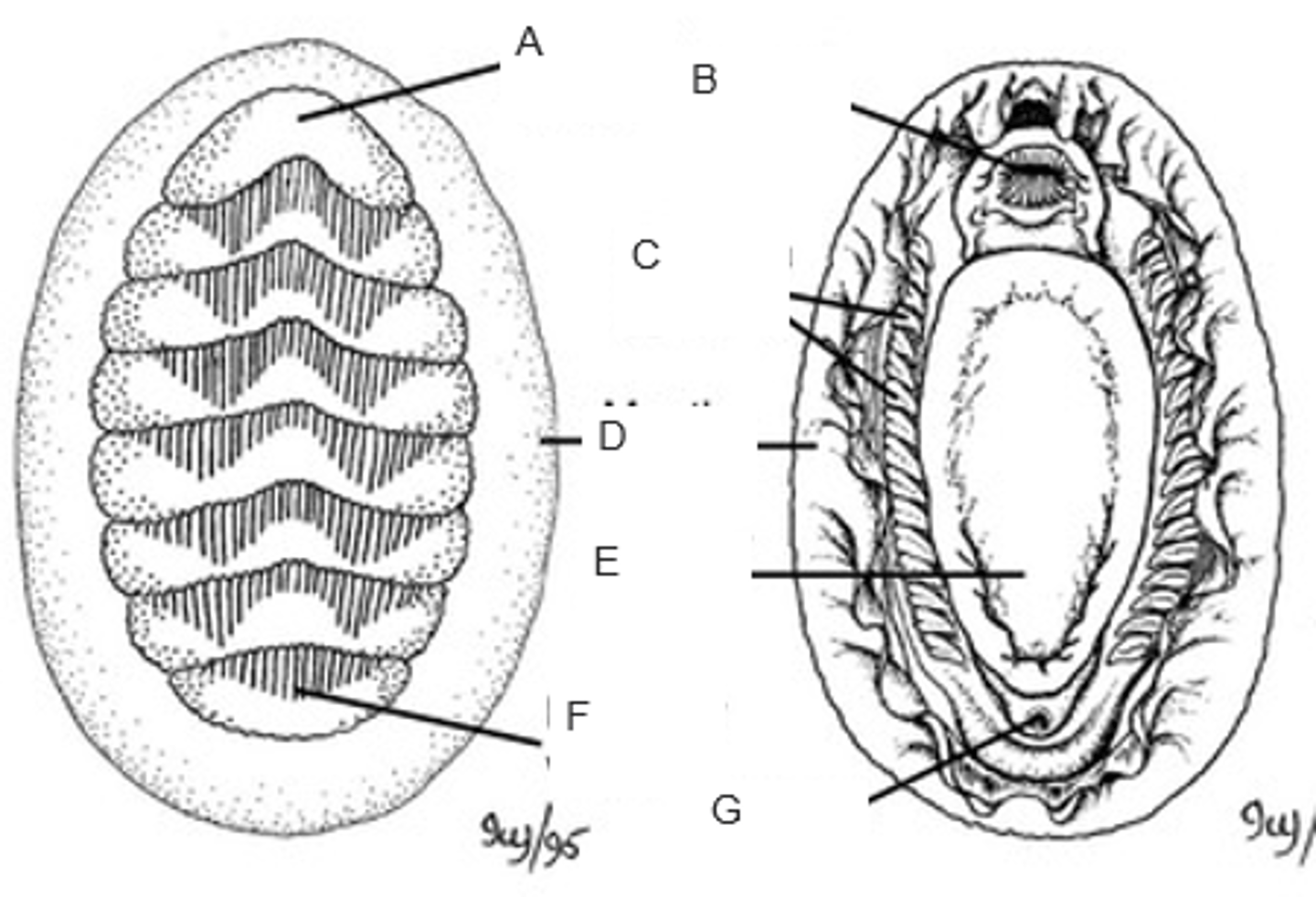
anterior valve
A
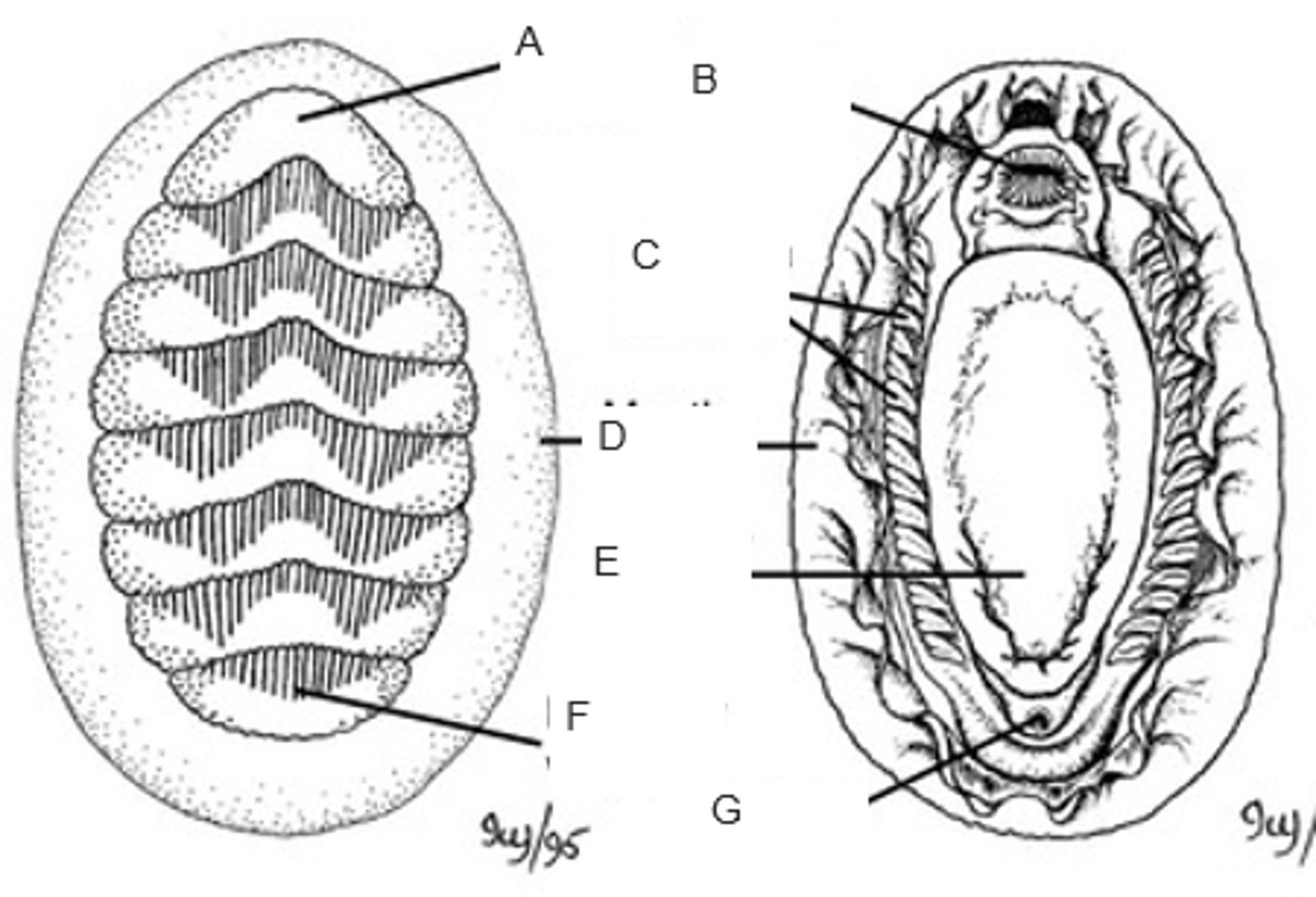
mouth
B
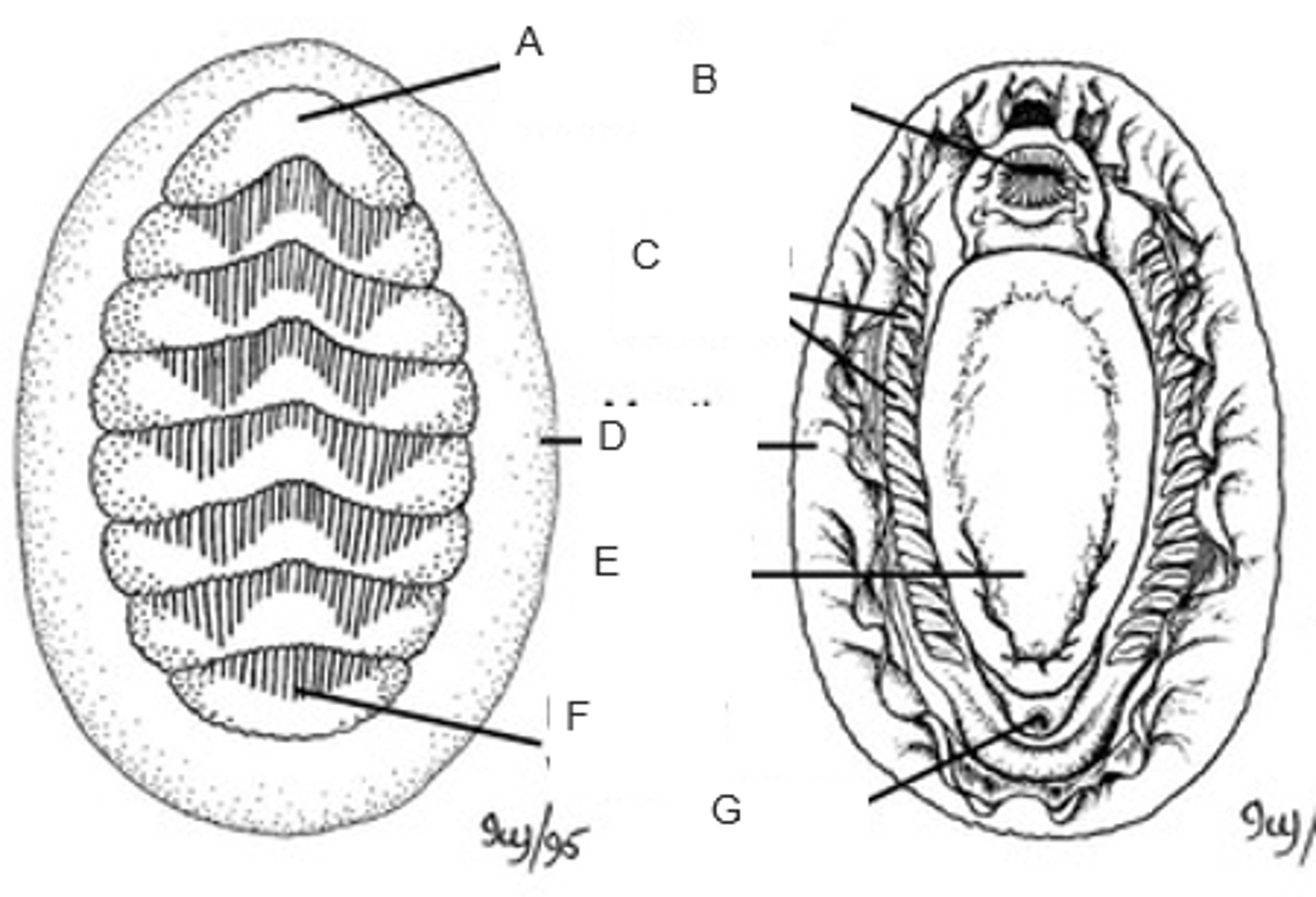
ctenidia (gills)
C
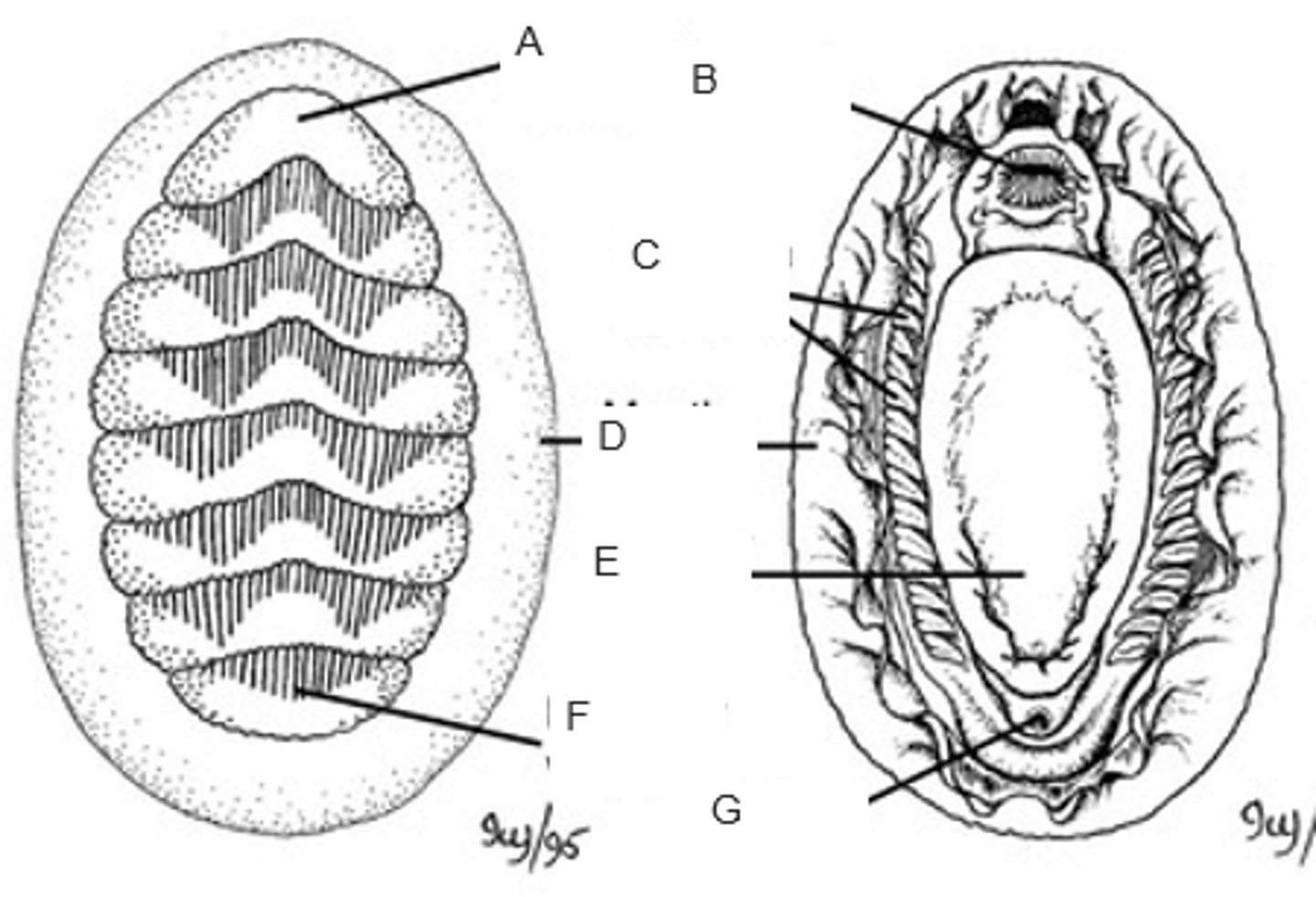
mantle (girdle)
D
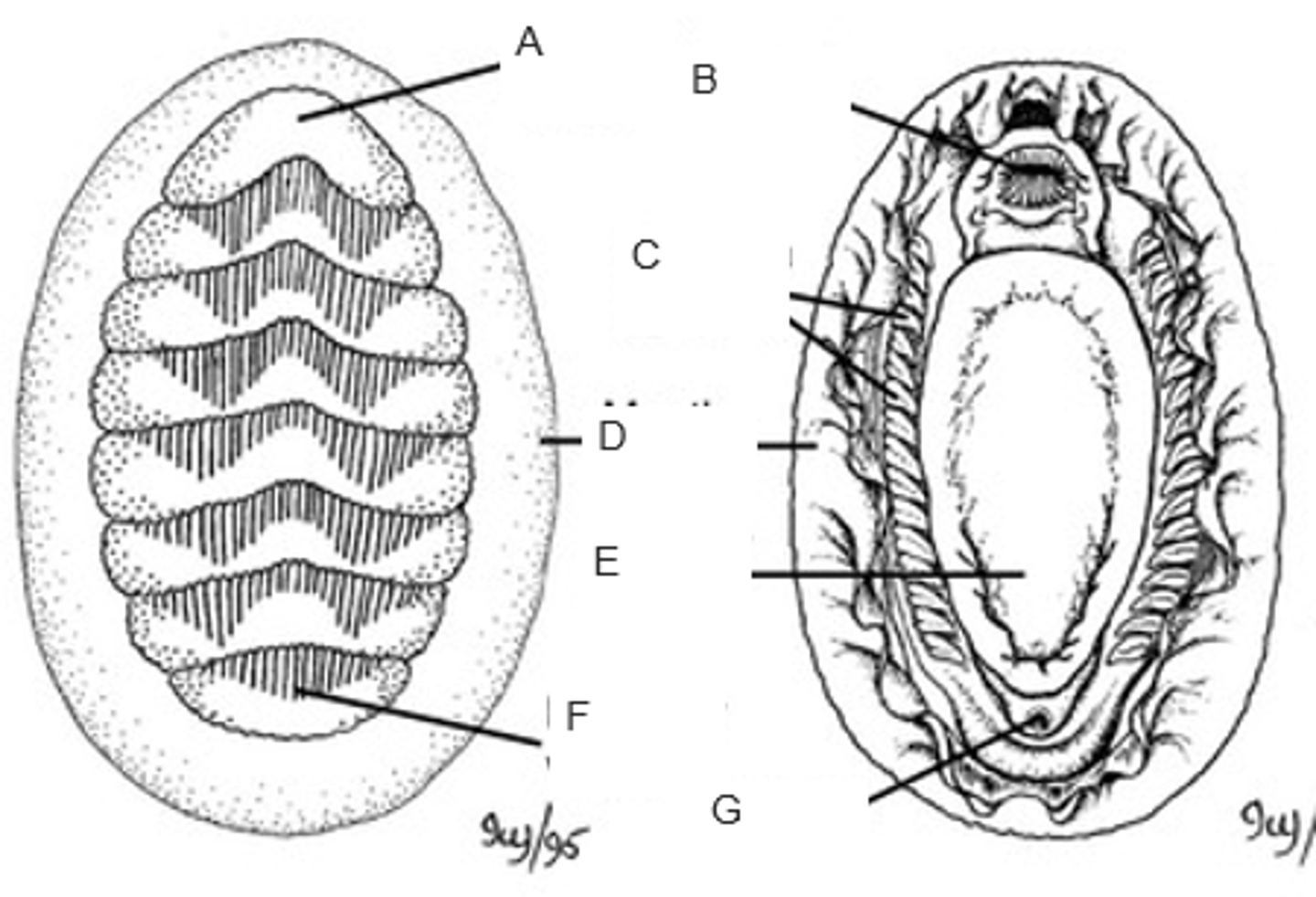
foot
E
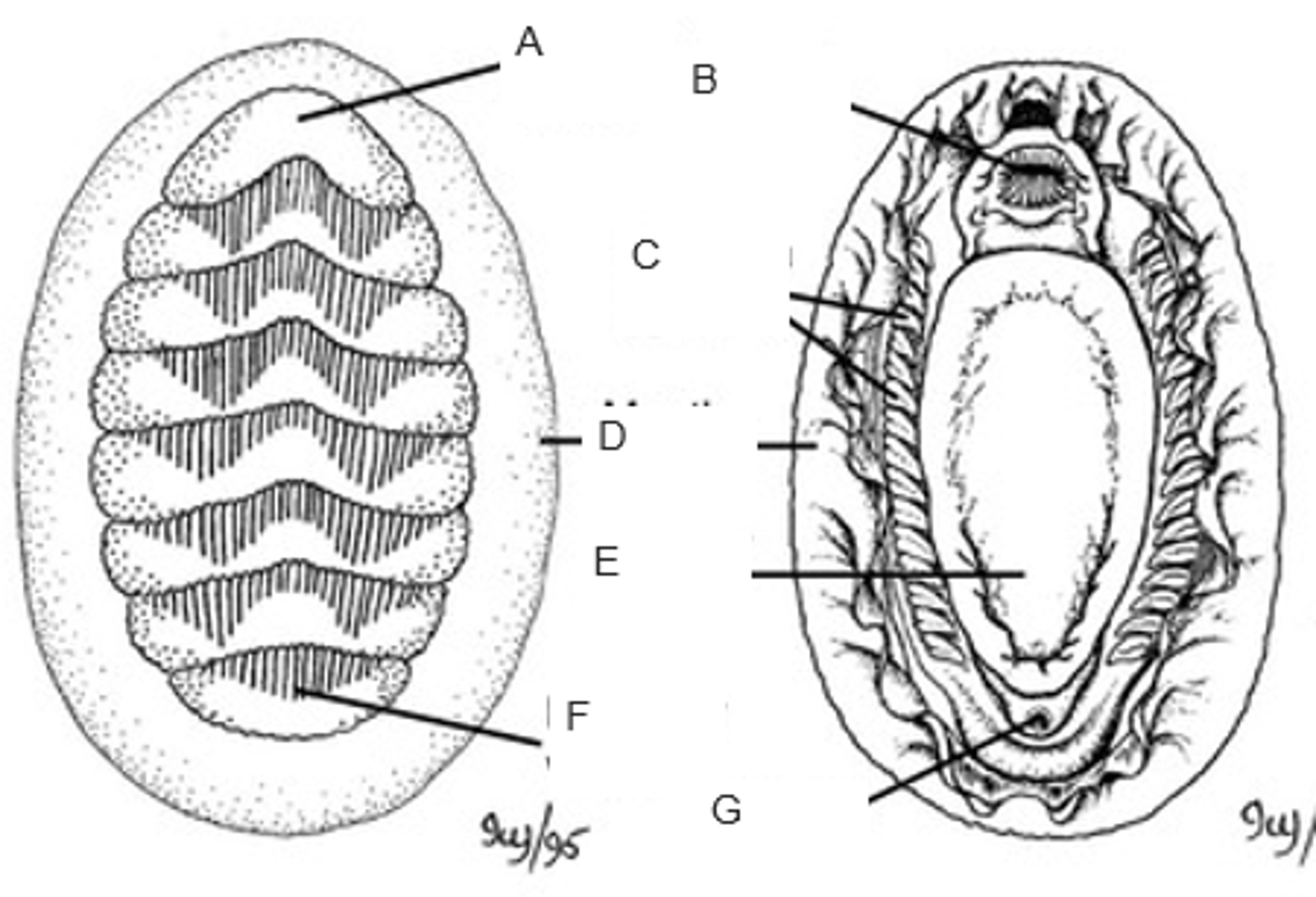
posterior valve
F
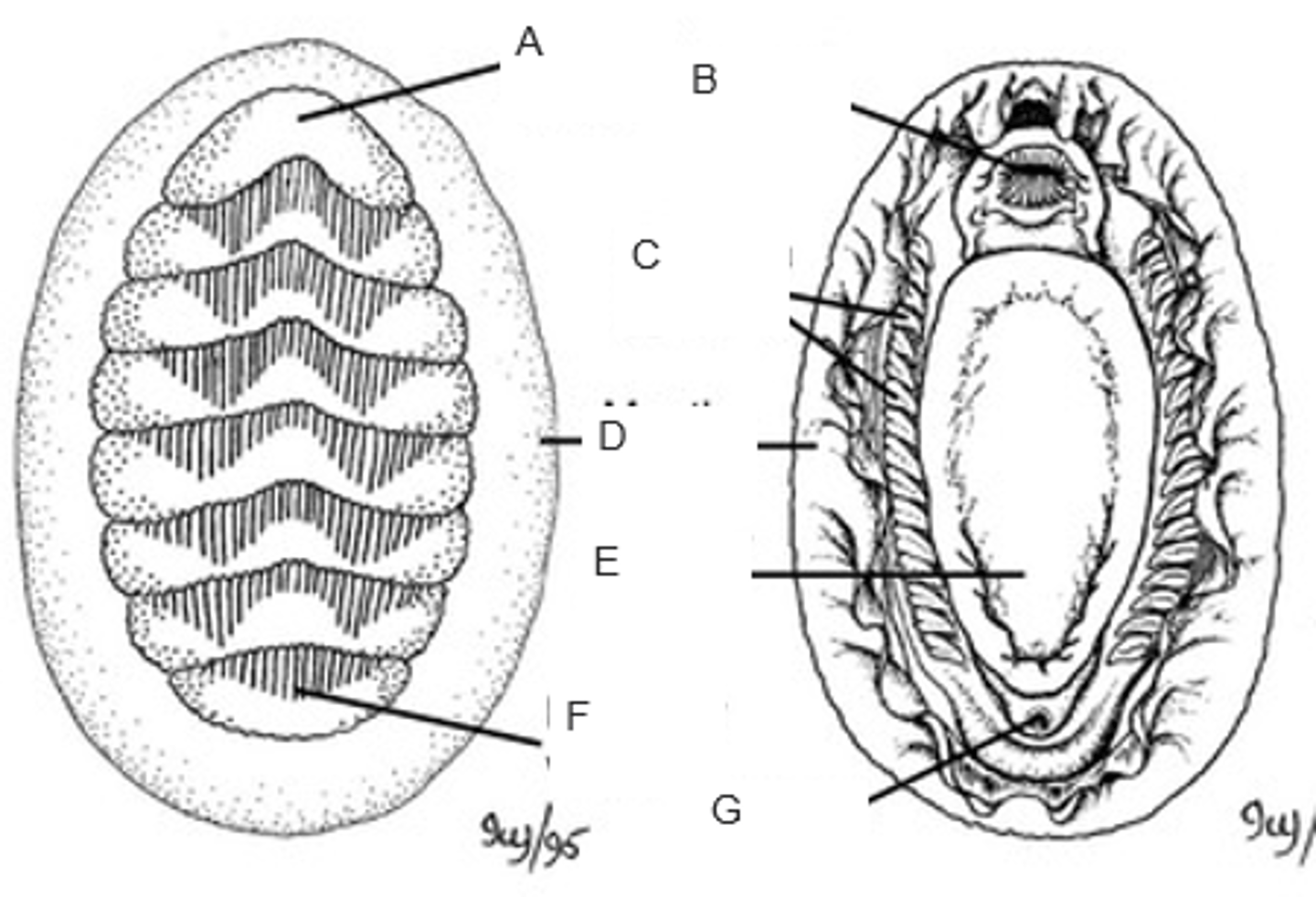
anus
G