UWORLD Pediatrics Step 2 CK
1/291
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
292 Terms
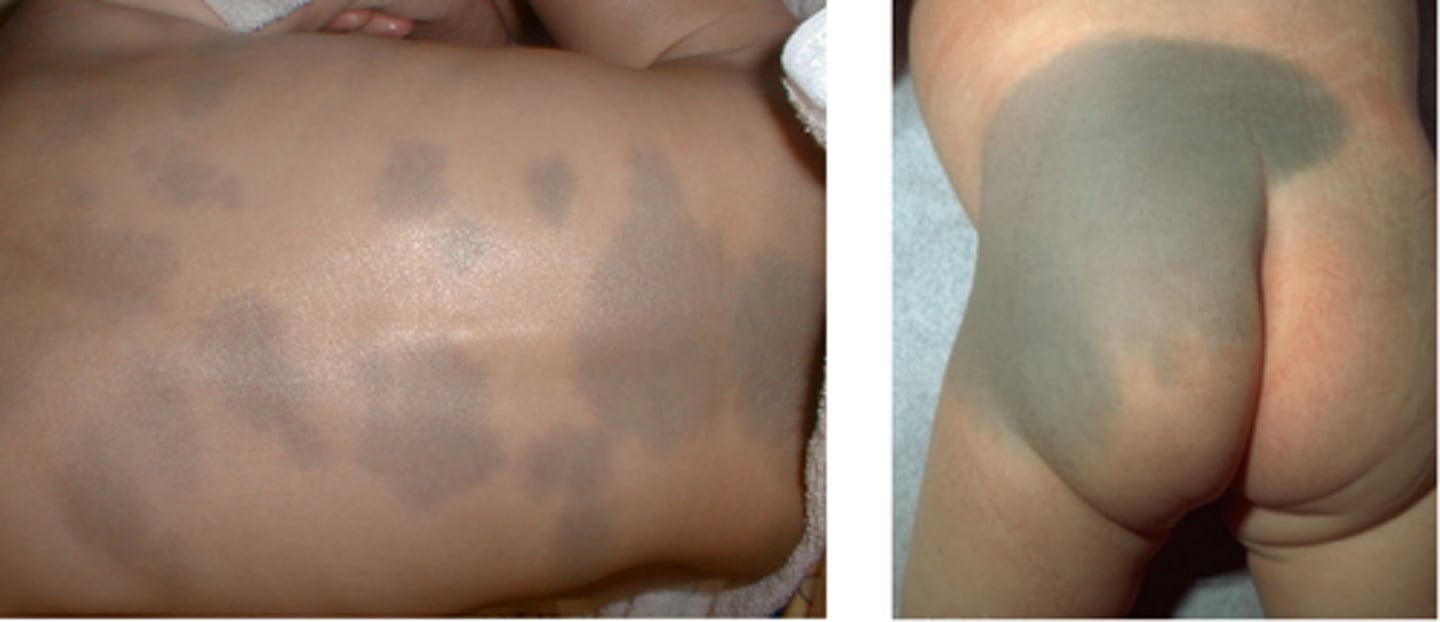
Congenital dermal melocytosis, benign, flat blue-grey patches on the lower back and buttocks that is common in African, Asian, Hispanic, and Native American ethnicity.
Mongolian spots -> usually fade spontaneously
-> document these as they can be mistaken for bruises
What is the most common cause of acute, unilateral lymphadenitis in children?
Staph aureus followed by group A strep
Pts w/ bacterial lymphadenitis usually < 5 y/o and nontoxic, tender lymph node, warm, erythematous, 3-6 cm in size Unilateral acute cervical lymphadenitis
All sexually active women < 24 should undergo which screening?
Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoea
-> recommended for any person with new partner in past 2 mo., multiple partners, history STI, illicit drug use, incarceration, contact with sex workers
-> cervicitis asymptomatic often can lead to PID -> infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain
Best screening test for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae by?
Nucleic acid amplification testing which has high sensitivity and specificity
-> can be done urine, endocervical, vaginal, or urethral specimens
Can sit momentarily on propped hands, transfer objects from hand to hand, and respond to name. Stranger anxiety develops at this age.
healthy 6 mo. old
Pts with Sickle cell anemia suffer from chronic extravascular and intravascular hemolysis. Characteristic lab findings include?
Mild to moderate anemia w/ reticulocytosis + unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, INC lactate dehydrogenase, low to absent serum haptoglobin
-> Acute worsening of anemia can occur from splenic sequestration with manifests as splenomegaly and INC fatigue
___ are the antibiotics of choice for pertussis treatment and post-exposure prophylaxis. All close contacts should be given this antibiotic regardless of age, immunization status or symptoms.
Macrolides
Age < 1 mo. = Azithromycin 5 days
Age > 1 mo. = Azithromycin x 5 days/Clarithromycin x 7 days/ Erythromycin x 14 days
Lethargy, fever, poor oral intake, vomiting presentation, nuchal rigidity of bacterial meningitis in infant what should be performed next?
Lumbar puncture before antibiotics
Infants critically ill (status epilepticus, septic shock) antibiotics before lumbar puncture
Head CT -> comatose infants
Indications for imaging prior to LP for bacterial meningitis suspected in children > 1 mo.
Hx hydrocephalus or neurosurgical procedure
Hx head trauma
Coma or focal neuro findings
Tx Bacterial meningitis in children age > 1 mo.
IV Vanco & Ceftriaxone
OR
Cefotaxime
Dexamethasone for H. influenzae type b meningitis
Fever, toxicity, gray-white pharyngitis, sandpaper-like rash, circumoral pallor.
Scarlet fever -> strawberry tongue
Group A strep erythrogenic exotoxin
tx: Penicillin V
What is herpangina?
Throat infection caused by enteroviruses such as Cox A, high fever, sore throat complete inability to swallow, ulcerative lesions palate, tonsils, pharynx
palms and sole rash, hand-foot-mouth disease
The most important risk factors for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) is?
Prematurity
-> male sex, prenatal asphyxia, maternal diabetes, cesarean section
Maternal diabetes -> INC incidence by delaying maturation of pulmonary surfactant production (high levels insulin in fetus inhibits cortisol and blocks maturation sphingomyelin)
Tx RDS
Antenatal prevention w/ corticosteroids and postnatal tx w/ exogenous surfactant
Space occupying lesion in the parietal lobe in a child what is the most common tumor type?
CNS tumors most common solid tumors => Astrocytoma most common supratentorial and infratentorial groups
In pediatric population, infratentorial tumors are more common than supratentorial tumors, benign astrocytomas are the most common histo type
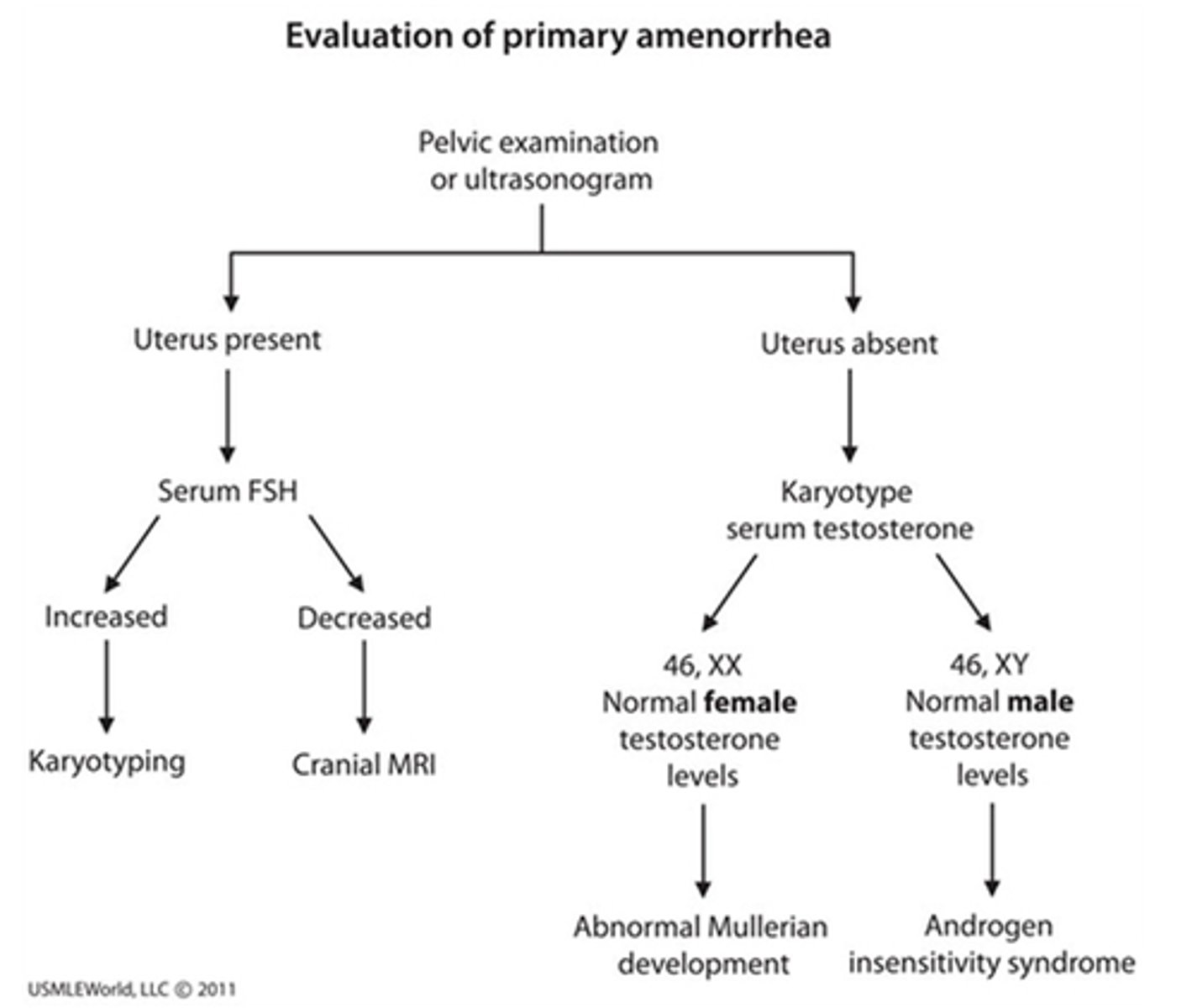
Define primary amenorrhea.
Absence of menarche by age 15
What is the first step in the evaluation of primary amenorrhea?
Pelvic exam determine ovaries, uterus, and vagina are present or absent
US is preferred imaging modality to evaluate anatomy of repro tract
What does US show for Turner syndrome?
One of the most common causes of primary amenorrhea
-> primary ovarian failure gonadal dysgenesis followed by early menopause and infertility -> pelvic US show an infantile uterus and "streak ovaries"
True/False: Human milk protein absorbs better and improves gastric emptying.
TRUE - ideal form of nutrition for term infants until 6 mo. age the major protein source is whey, which is more easily digested than casein and helps to improve gastric empty
Polyhydramnios fetus, excessive drooling as well as chocking, coughing and regurgitation with initial feeding attempts seen immediately after birth. Enteric tube in the proximal esophagus on X-ray. Dx.
Esophageal atresia + tranesophageal fistula
-> gastric fluid can relaxes into the distal esophagus through the fistula and into the trachea and lungs, causing aspiration pneumonia
Obese child 10-16 years common disorder hip overweight adolescents. Urgent surgical fixation is required to prevent avascular necrosis of the hip.
Hip held passive external rotation and DEC internal rotation. Dx AP + flog-leg X-ray.
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis -> displacement of capital femoral epiphysis from femoral neck
Risk: endocrinopathies (hypothyroidism, GH deficiency), renal failure, radiation history
X-linked disorder characterized by the triad of thrombocytopenia, eczema, and recurrent bacterial infections. Thrombocytopenia is caused by DEC platelet production and few platelets that exist are typically quite small.
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS)
- infection due to step. pneumoniae, n. meningitidis, and h. influezae
thrombocytopenia -> minor petechiae or purpura to life-threatening bleeding such intracranial hemorrhage, hematemesis or hematochezia
Fever, exudative pharyngitis, tender anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. Group A streptococcus is suspected. Tonsillar erythema is present, abrupt onset sore throat in child 5-15 with poor oral intake and malaise.
What is the gold standard dx and tx?
Throat culture + empiric Penicillin
Penicillin antibiotic of choice for confirmed or highly suspected step pharyngitis as it hastens recovery, prevents transmission, and reduces risk RF
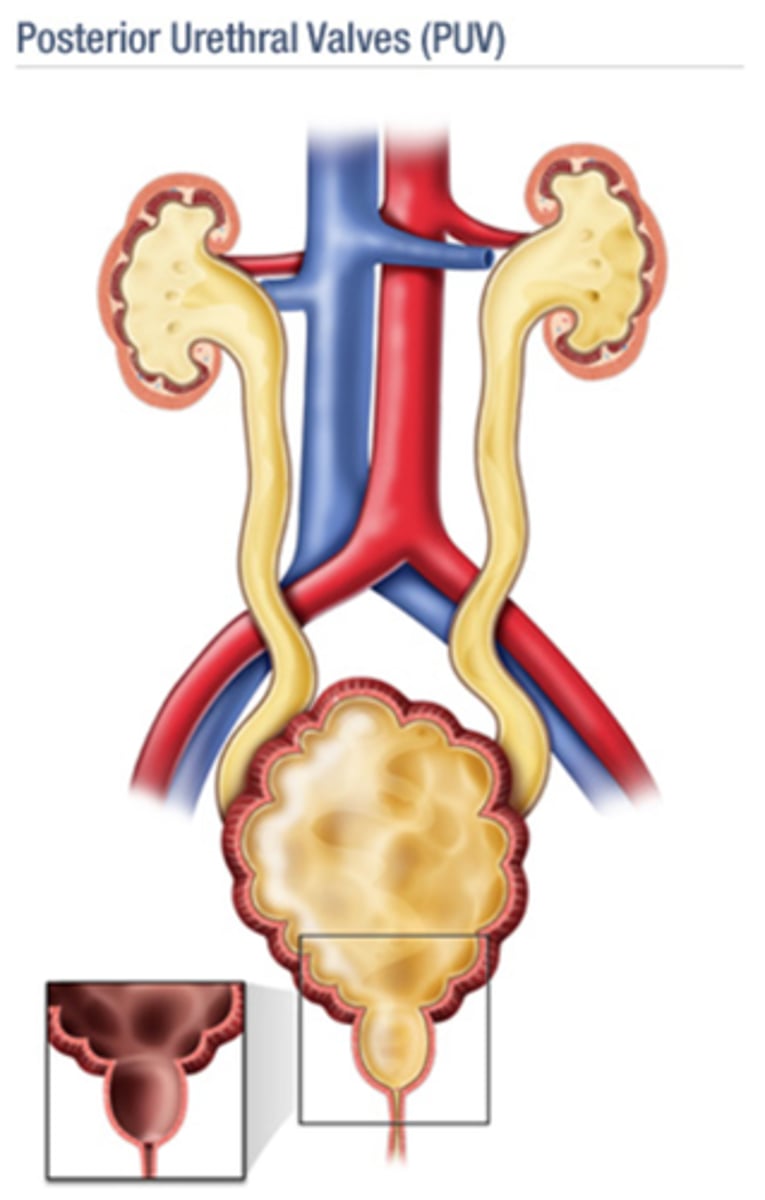
What is the most common cause of urinary tract obstruction in a newborn?
Posterior urethral valves
- progressive dilation of bladder, ureters, kidneys
- US shows bladder distention, B/L hydroureters, B/L hydronephrosis
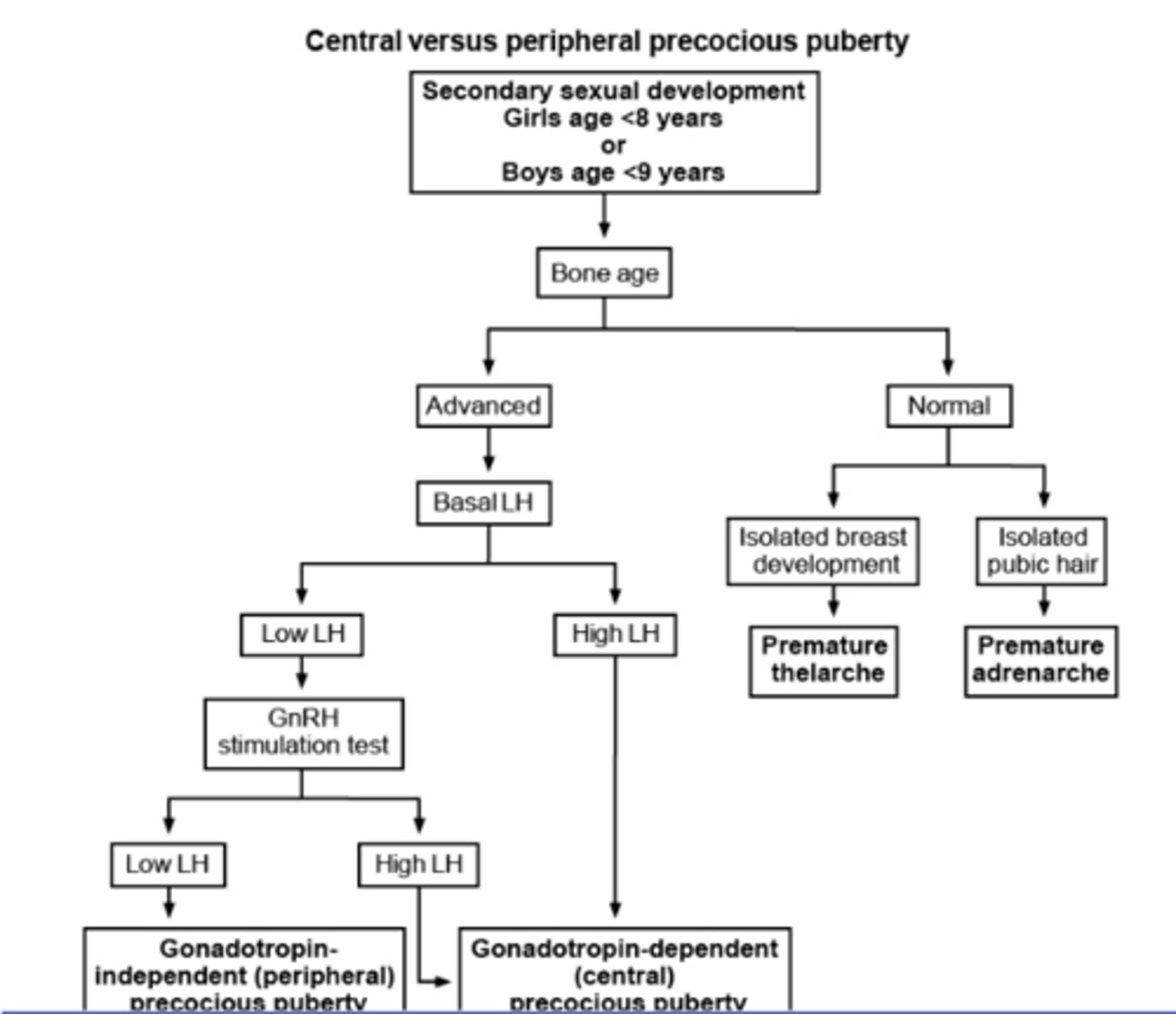
Dx: Premature adrenarche/pubarche, severe cystic acne resistant to tx, accelerate linear growth, advanced bone age, normal electrolytes. Normal testicular volume for age. LH levels low at baseline and do not increase after stimulation w/ GnRH agonist.
Gonadotropin-independent precocious puberty caused by late onset (non classic) congenital adrenal hyperplasia secondary to 21-hydroxylate (CYP21A2) deficiency
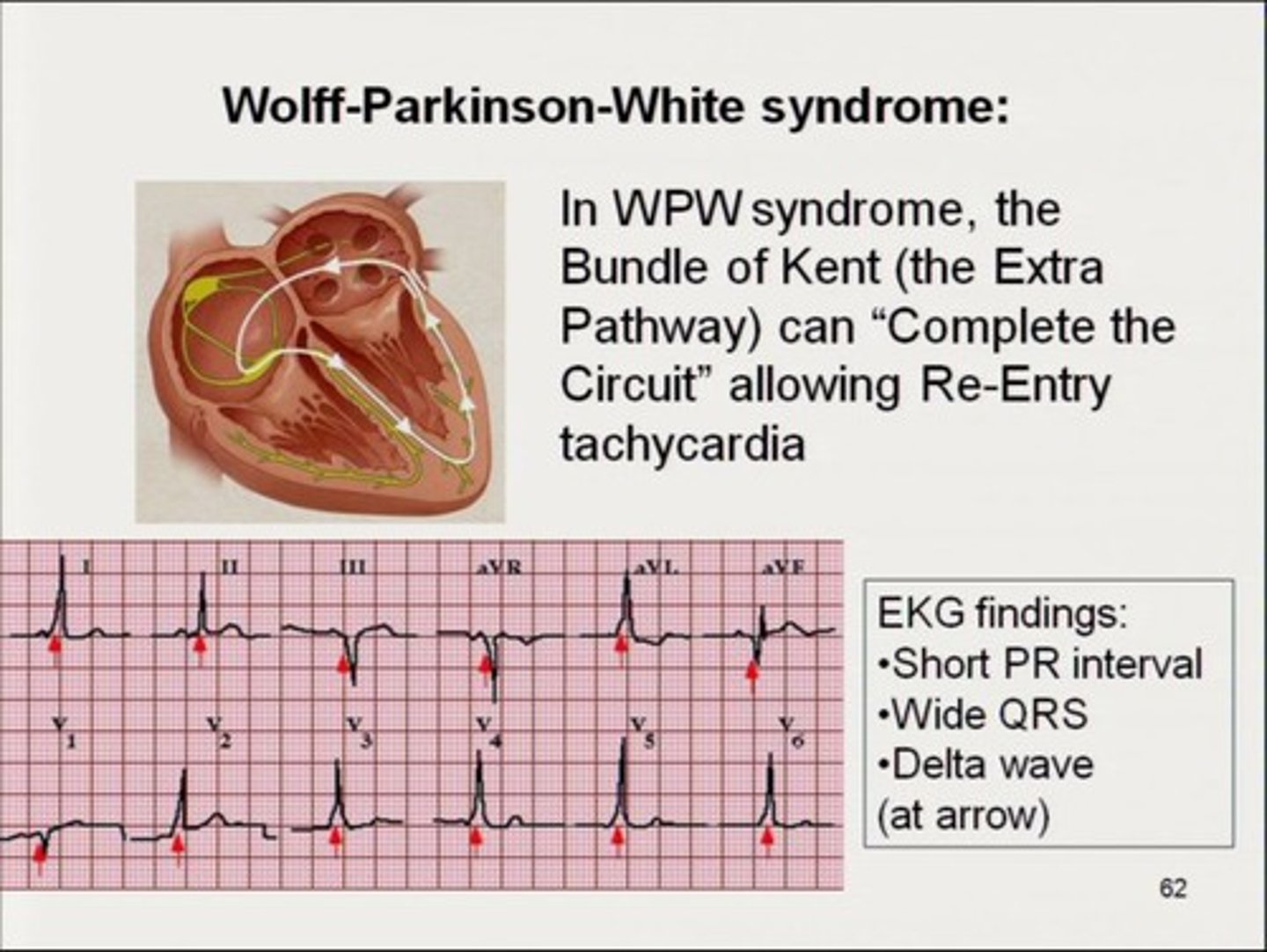
EKG findings WPW syndrome.
Shortened PR interval, delta wave, widening QRS comlex
-> supraventricular tachy can result
-> accessory pathway between atria and ventricle resulting in pre excitation and INC risk tachyarrhythmias
Most common cardiac anomalies Turner's syndrome?
Bicuspid aortic valve
Coarctation of the aorta
Aortic root dilation -> INC risk aortic dissection

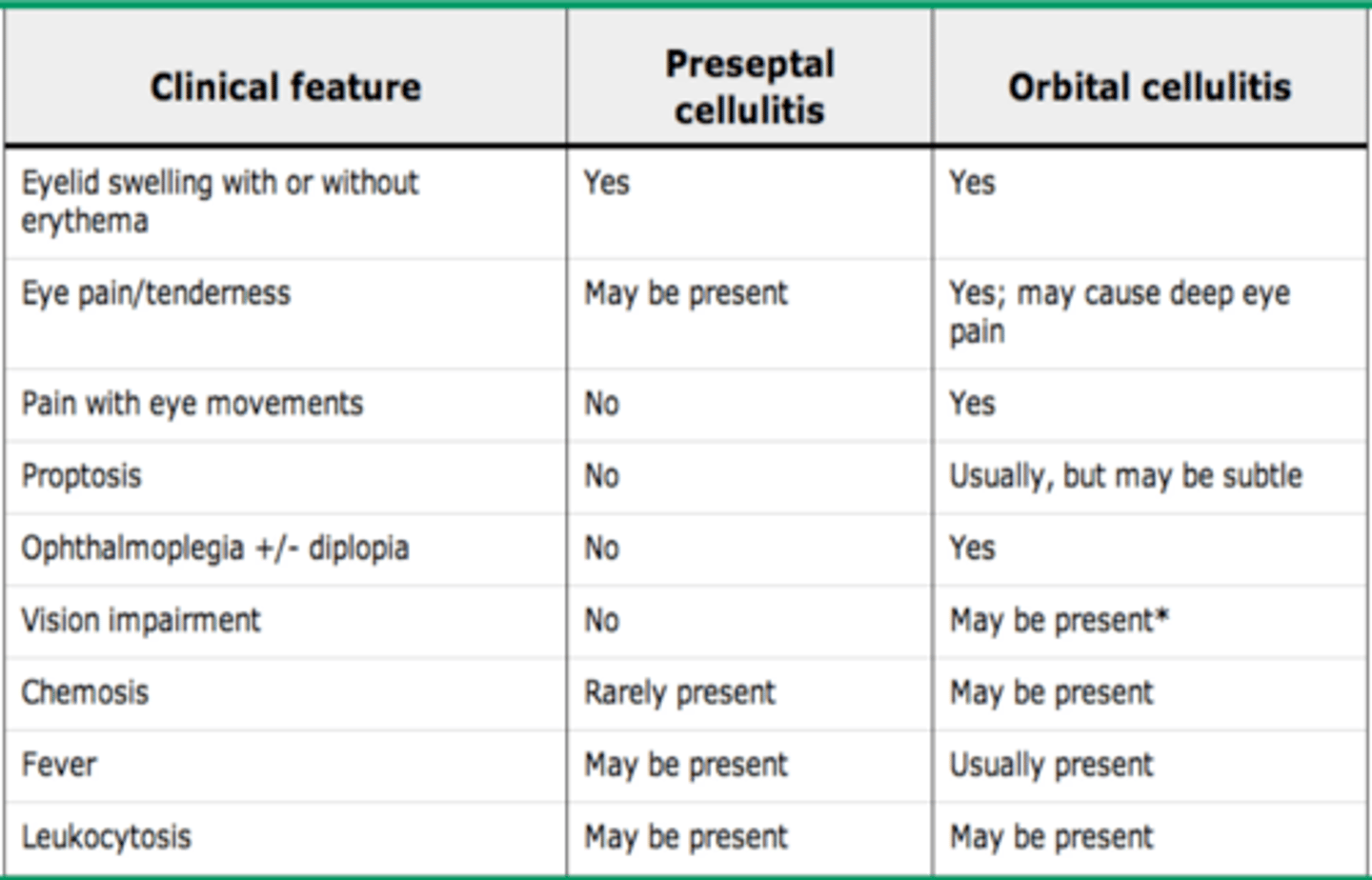
Preseptal vs orbital cellulitis differentiate?
Preseptal-> mild infection eyelid anterior to the orbital septum
- outpatient oral antibiotics
Orbital -> serious infection posterior orbital septum, pain extraocular movt, diplopia, opthalmoplegia (dangerous complications: blinds + intracranial infection)
- in patient IV antibiotics
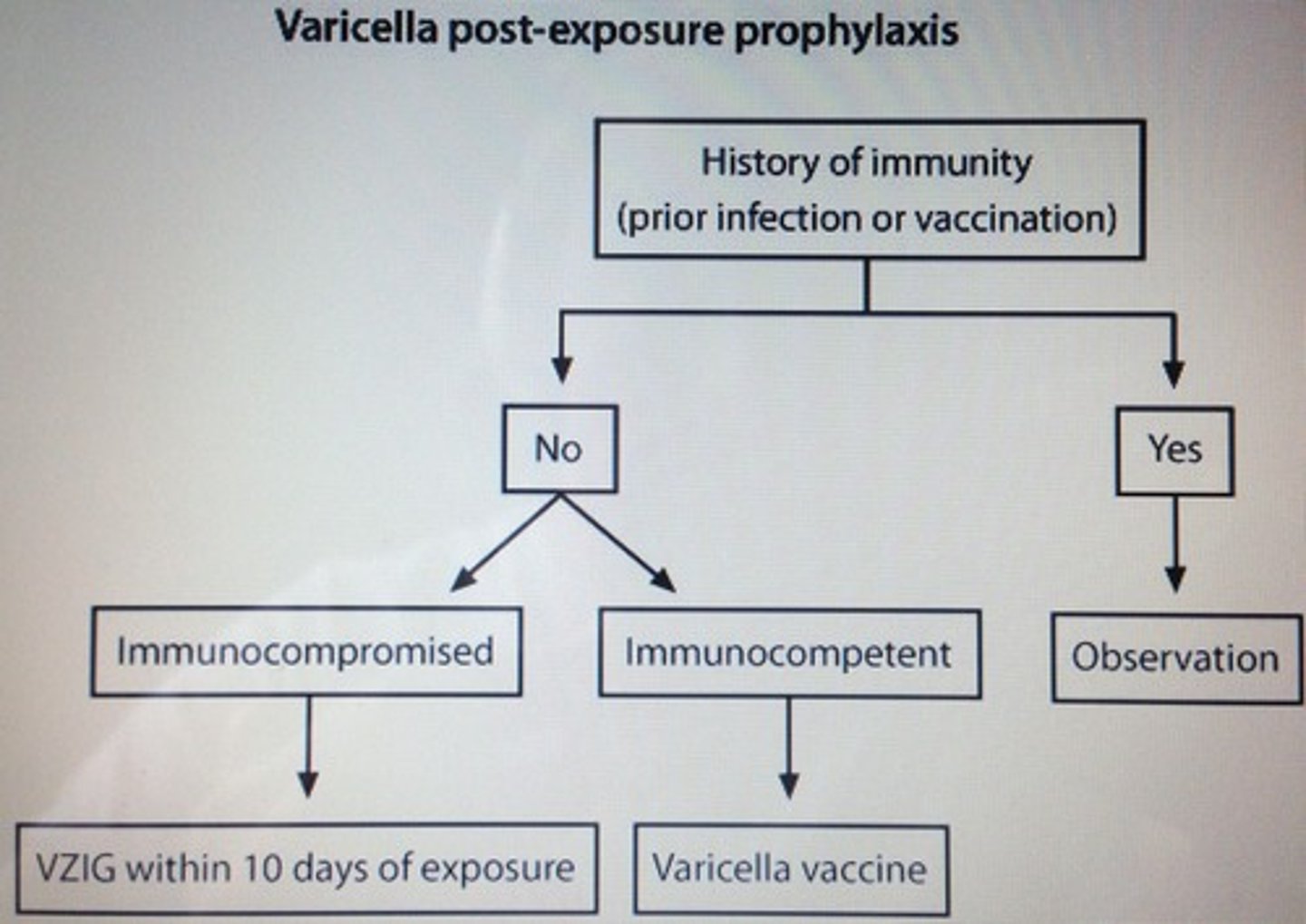
4 y/o boy exposed to chickenpox by his father 4 days ago. Has not had chickenpox vaccine. Next management step?
Varicella vaccine all immunocompetent and asymptomatic nonimmune should have varicella vaccine post-exposure prophylaxis 3-5 days of exposure
- complications varicella infection children bacterial superinfection and pneumonia in adults
Dry cough, yellow-green nasal discharge, mucus thick purulent dripping from nares, nasal turbinates red and swollen > 10 days. Dx. Tx?
Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis
tx: Oral amoxicillin-clavulanic acid
-> viral upper resp infections are the most common predisposing factor for acute bacterial rhinosinuritis

Pediatric abdominal wall defects
1. Umbilical hernia - defect linea alba covered by skin, sometimes contains bowl, umbilical cord insets at apex of defect
- resolve spontaneously over time
2. Gastroschisis - defect right of the cord insertion not covered by membrane or skin, contains bowel, umbilical cord inserts next to defect
- after birth cover sterile saline dressings and plastic wrap
- prompt surgical repair, single-stage closure
3. Omphalocele - midline and wall defect covered by peritoneum, multiple abd organs, umbilical cord apex of defect
- surgical repair
Newborn presents with respiratory distress barrel-shaped chest, absent breath sounds on the left, fair aeration on the right, scaphoid abdomen. Dx. Management.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CHD)
- pulmonary hypoplasia
- pulmonary HTN
- 85% cases on the left abdominal viscera herniate into chest
- concave abdomen + barrel chest
- ER endotracheal intubation + gastric tube decompress stomach and bowel
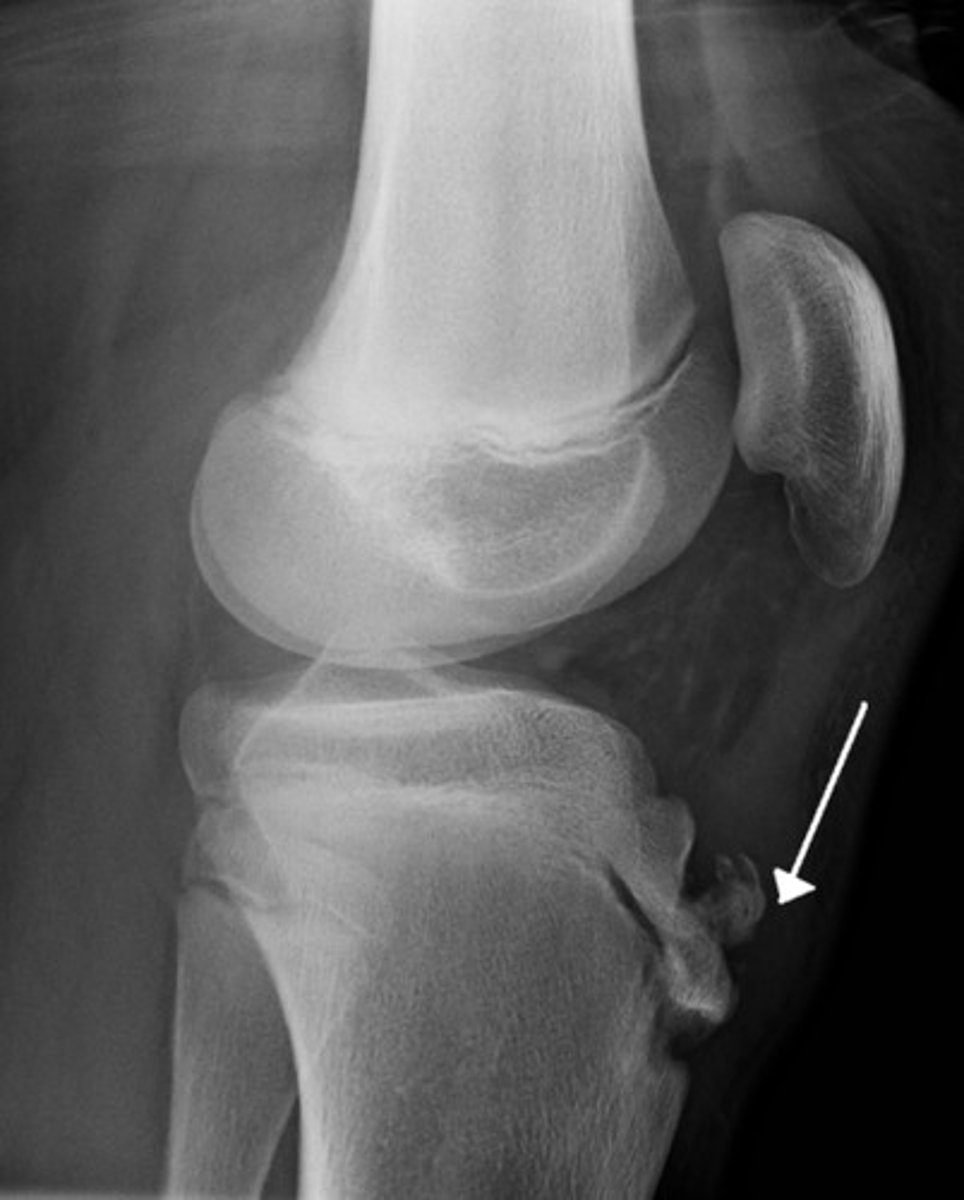
Edema + tenderness over tibial tubercle in athlete 13-14 male, quadriceps tendon puts traction on apophysis of the tibial tubercle where patellar tendon inserts.
Osgood-Schlatter dz common cause knee pain adolescent male athletes
- pain reproduces extending knee against resistant
- tx: activity restriction, stretching, NSAIDs
- X-ray show: soft tissue swelling, lifting tubercle from shaft, irregularity/fragmentation tubercle
What explains irregular periods in initial menstrual cycles pubertal females that are irregular and often anovulatory?
Immature HPA axis -> insufficient gonadotropin secretion -> irregular menstrual cycles women shortly following menarche
Recurrent infections after 6 mo. of age sinopulmonary infections with H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae, lack of IgA predisposes Giardia. Dx.
Genetic B-cell deficiency
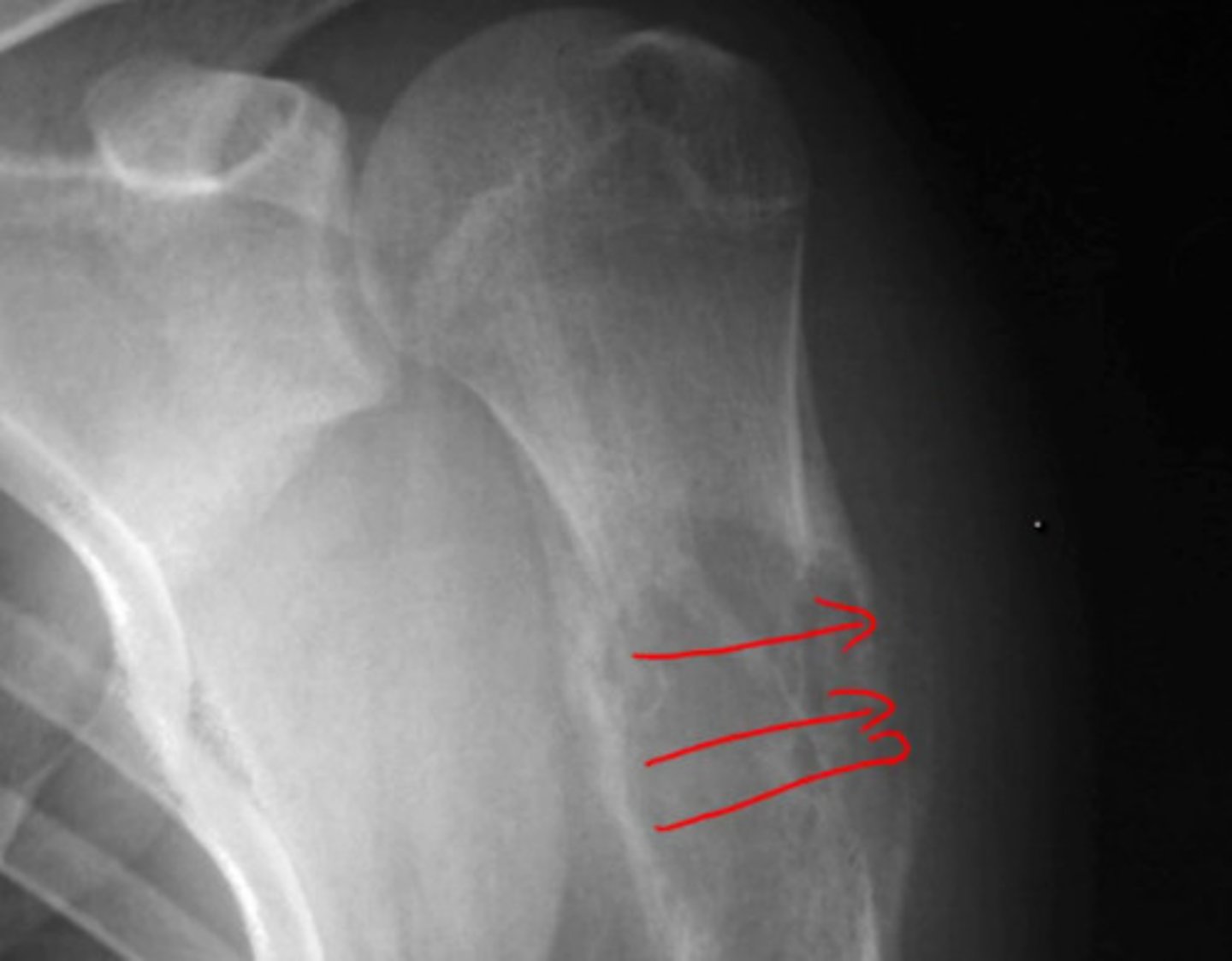
__ is the most common primary bone tumor in children and young adults involves metaphysis of long bones.
Osteosarcoma
- large and tender mass
- sunburts poeriosteal rxn + Codman triangle
___ + ___ prophylaxis can prevent almost all cases of pneumonoccal sepsis in pts with sickle cell anemia.
Pneumococcal vaccine + Penicillin prophylaxis
INC ICP and head circumference in an child should be evaluated via?
CT scan of the brain
- HC > 97%
- poor feeding, irritability, DEC activity, vomiting
- tense + bulging fontanelle, scalp veins, wide spaced cranial sutures, rapidly INC HC
Testicles that have not descended by ___ are unlikely to descend spontaneously and require surgery.
6 mo.
- Orchioplexy performed before age 1
- Prevents testicular torsion, DEC risk testicular malignancy
- Even after surgery still have subfertility
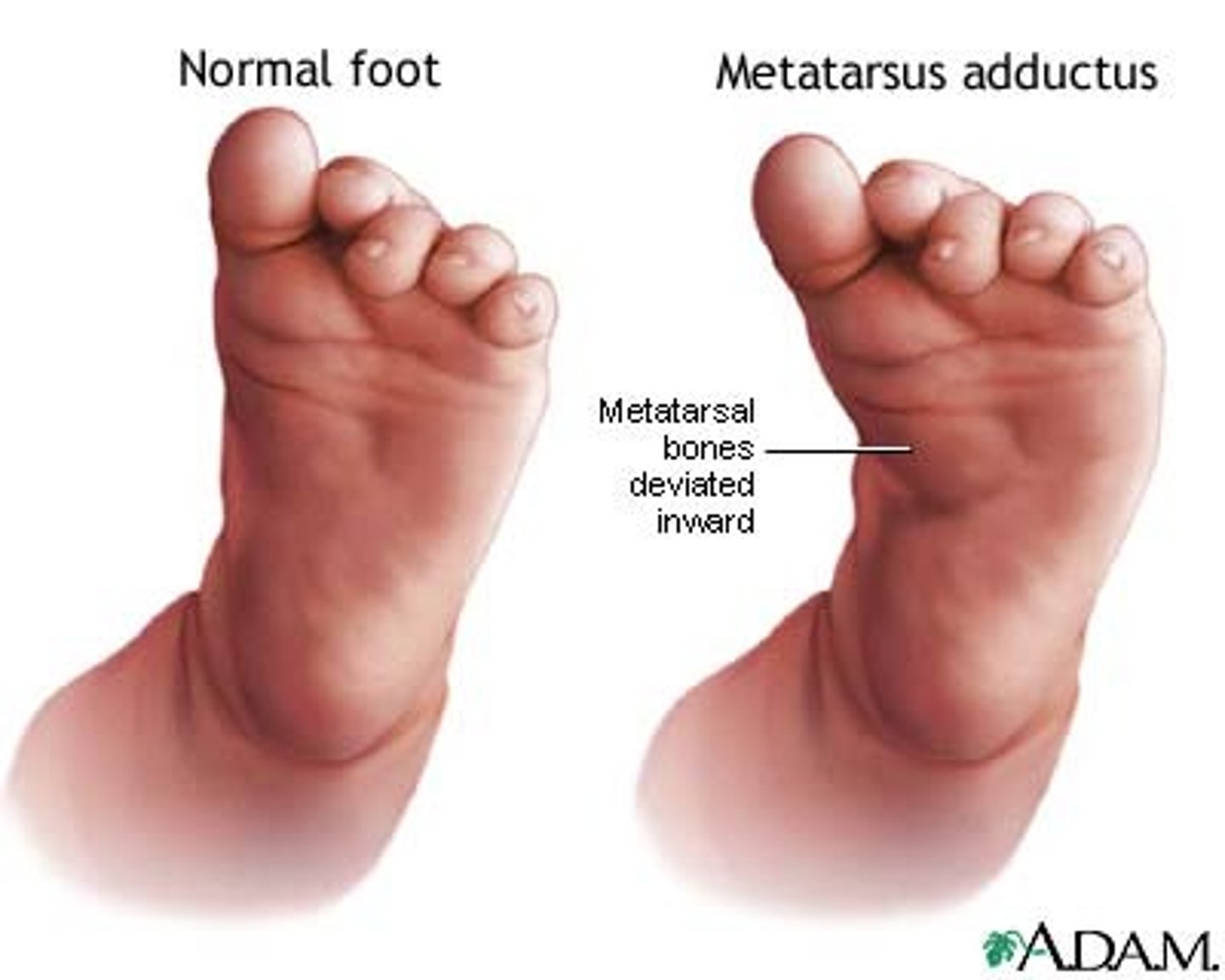
Tx mild metatarsus adductus?
Reassurance, usually correct spontaneously, first-born infants attributed to molding effect primigravid uterus
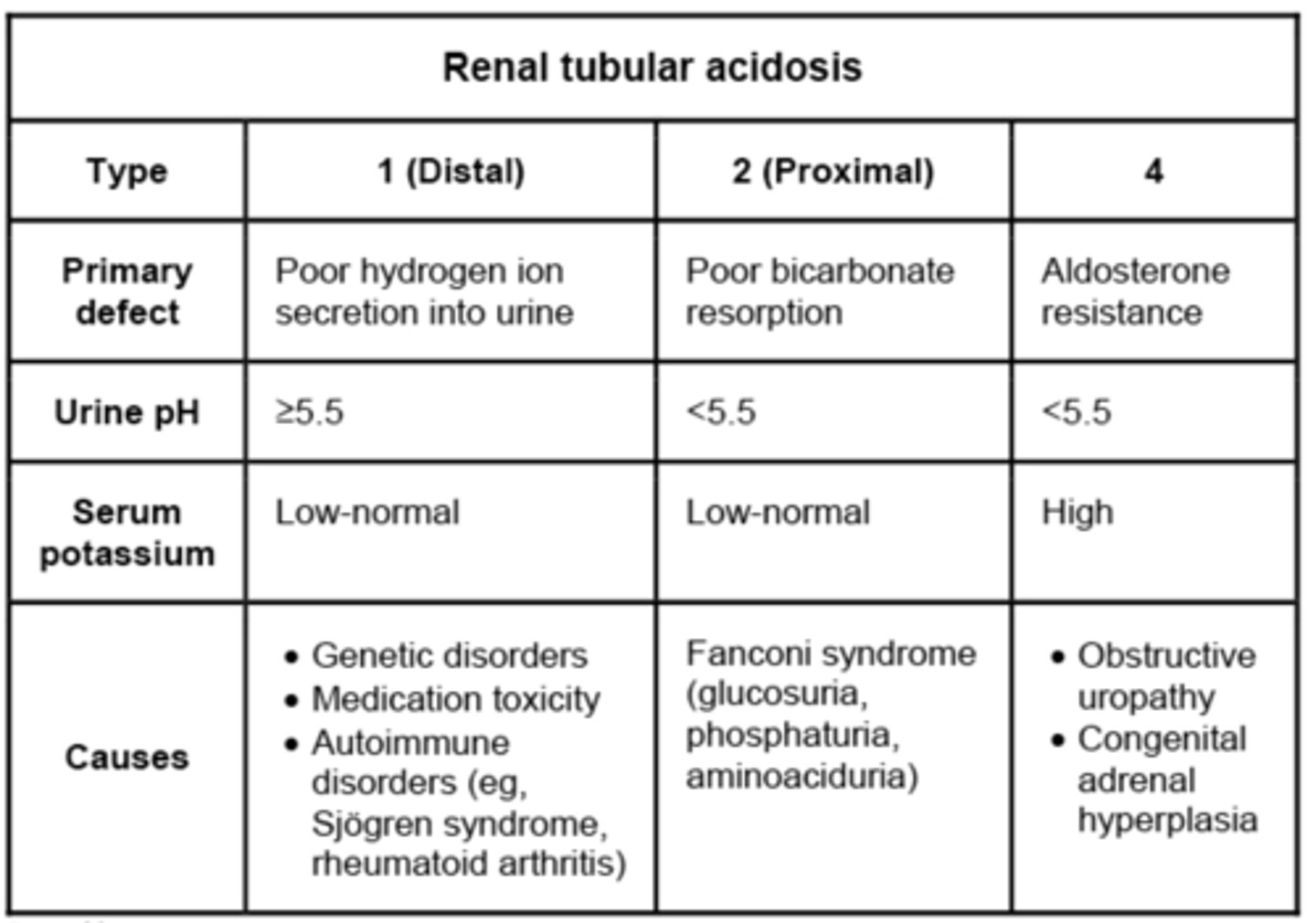
5 mo. old growth failure low serum bicarb, normal anion gap acidosis, failure to thrive, hyperchloremia. Dx.
type 1 Renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
- oral bicarbonate replacement
Child presents with hypovolemic or septic shock and requires emergency fluid resuscitation when intravenous access cannot be obtained, __ access should be attempted immediately.
Intraosseous (IO) access
- proximal tibia
- contraindications: infection (cellulitis), overlying access site, fracture or previous IO attempt, bone fragility (osteogenesis imperfecta)
Post-exposure prophylaxis rabies bite raccoon.
Rabie immune globulin + rabies vaccine
___ is a potential cause of stroke in children that is usually associated with a history of trauma to the soft palate with a foreign body.
Internal carotid artery dissection
- compress internal carotid causing thrombosis that embolus to brain and cause stroke or dissect it leading to ischemic stroke
- MRI/MRA brain confirm
Loss of consciousness is seen which seizure types?
Complex partial - automatisms during their LOC, chewing, picking movt hands, lip smacking
Partial seizures w/ secondary generalization
After diagnosis of Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) most important next step in management is assessing the patient?
Pulmonary function by serial spirometry - measure FVC gold standard assess ventilation
Alpha- and B-thalassemia minor have which lab values?
Low MCV
RDW normal
Total RBC count normal
Mentzer index (MCV/RBC) < 13
Abd pain, N/V, diarrhea, and hematemesis w/in 30 min - 6 hours of ingestion. Hypotensive shock and anion-gap metabolic acidosis. Pt who survive toxicity INC risk gastric scarring and pyloric stenosis.
IRON poisoning
- whole bowel irrigation
- deferoxamine
- supportive care for circulation, airway and breathing
- x-ray (radioopaque can be seen on x-ray)
Stabismus > 4 mo. abnormal and needs tx to prevent amblyopia (vision loss from disuse of deviated eye) asymmetric corneal light reflections + deviation on cover test are concerning. The standard tx?
Occlusion patching or penalizing blurring (cycloplegic drops) of the NORMAL eye
AD disorder characterize by grip myotonia (delayed muscle relaxation), facial weakness, foot drop, dysphagia, cardiac conduction anomalies, cataracts, testicular atrophy/infertility, baldness.
Myotonic muscular dystrophy
___ is a cyanotic congenital heart defect characterize by left axis deviation on electrocardiogram and DEC pulmonary markings on CXR due to hypoplasia of the RV and pulmonary outflow tract.
Tricuspid valve atresia
- left axis deviation
__ is lower abd cramping with menses in absence of other pathology.
Primary dysmenorrhea
- NSAIDs tx
Premature adrenarche, premature thelarche, and advanced bone age. LH is elevated at baseline or after stimulation with GnRH agonist. Which kind of precocious puberty central or peripheral?
Gonadotropin-dependent (central) precocious puberty
- brain MRI w/ contrast
- GnRH agonist tx prevent premature epiphyseal plate fusion and max adult height
Circumstances in which minors do not require consent?
ER case
STIs
Substance abuse (most states)
Prenatal care (most states)
Suspect __ in a patient who presents with equinus and varus of the calcaneum and talus, varus of the midfoot, and adduction of the forefoot.
Clubfoot (talipes equinovarus)
- stretching foot and manipulation
- serial plaster casts
- malleable splints
- taping
Surgical tx indicated if conservative management gives unsatisfactory results, preferably btw 3-6 mo. age
__ should be suspected in any patient with pancytopenia following drug intake, exposure to toxins or viral infections.
Aplastic anemia
HIGH YIELD:___ common complication of sickle cell disease, progressive hip pain restriction adduction + internal rotation of the hip.
Avascular necrosis
- occlusion of end arteries supplying the femoral head, bone necrosis, and eventual collapse of the periarticular bone and cartilage
Tx minor cat bite wounds due to Pasteurella multocida.
Amoxicillin/clavulanate for 5 days
In acute setting, one of the primary tx for stroke in sickle cell patient is ___.
Exchange transfusion
- DEC % of sickle cells in bloodstream
- continue hydroxyurea
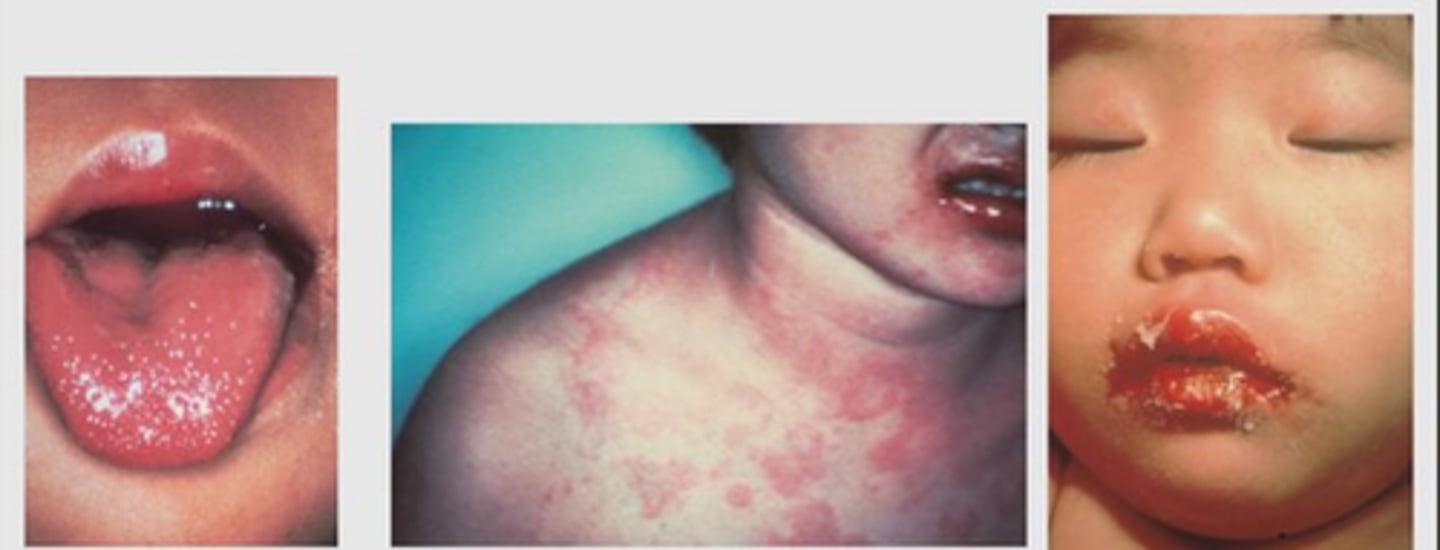
Kawasaki disease diagnosis
Fever > 5 days
AND
4 out of 5 findings:
- Nonexudative conjunctivitis
- Extremity changes
- Cervical lymphadenopathy
- Oral mucosa changes
- Polymorphous rash
___ and __ are the most common cause of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis.
Strep. pneumoniae
Nontypable H. influenzae
- > Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid
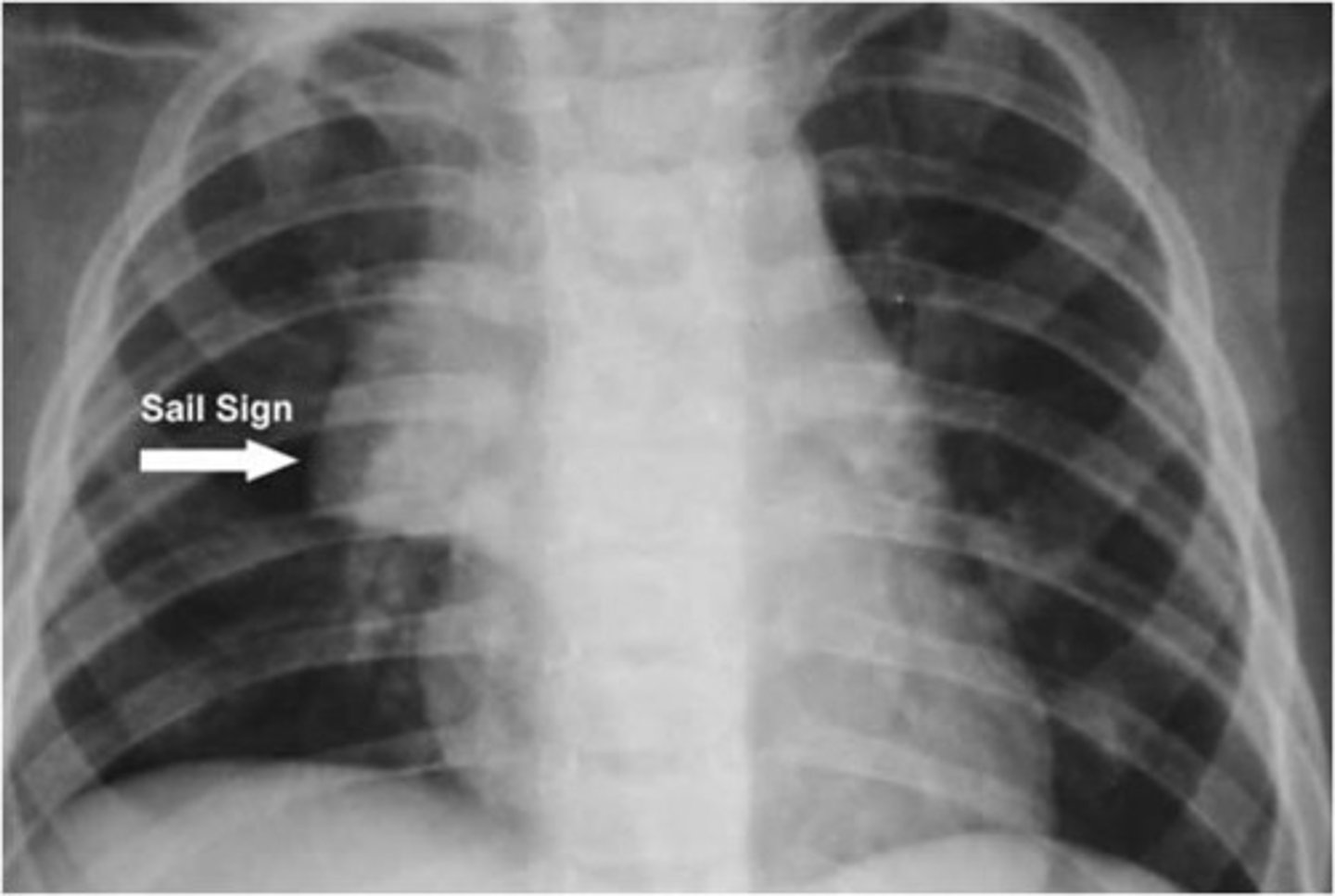
"sail sign" noted child x-ray < 3 years. What can this be?
Thymus
- triangular shape, scalloped border, uniform density
- anterior mediastinum behind sternum + front of the heart, aortic arch, trachea
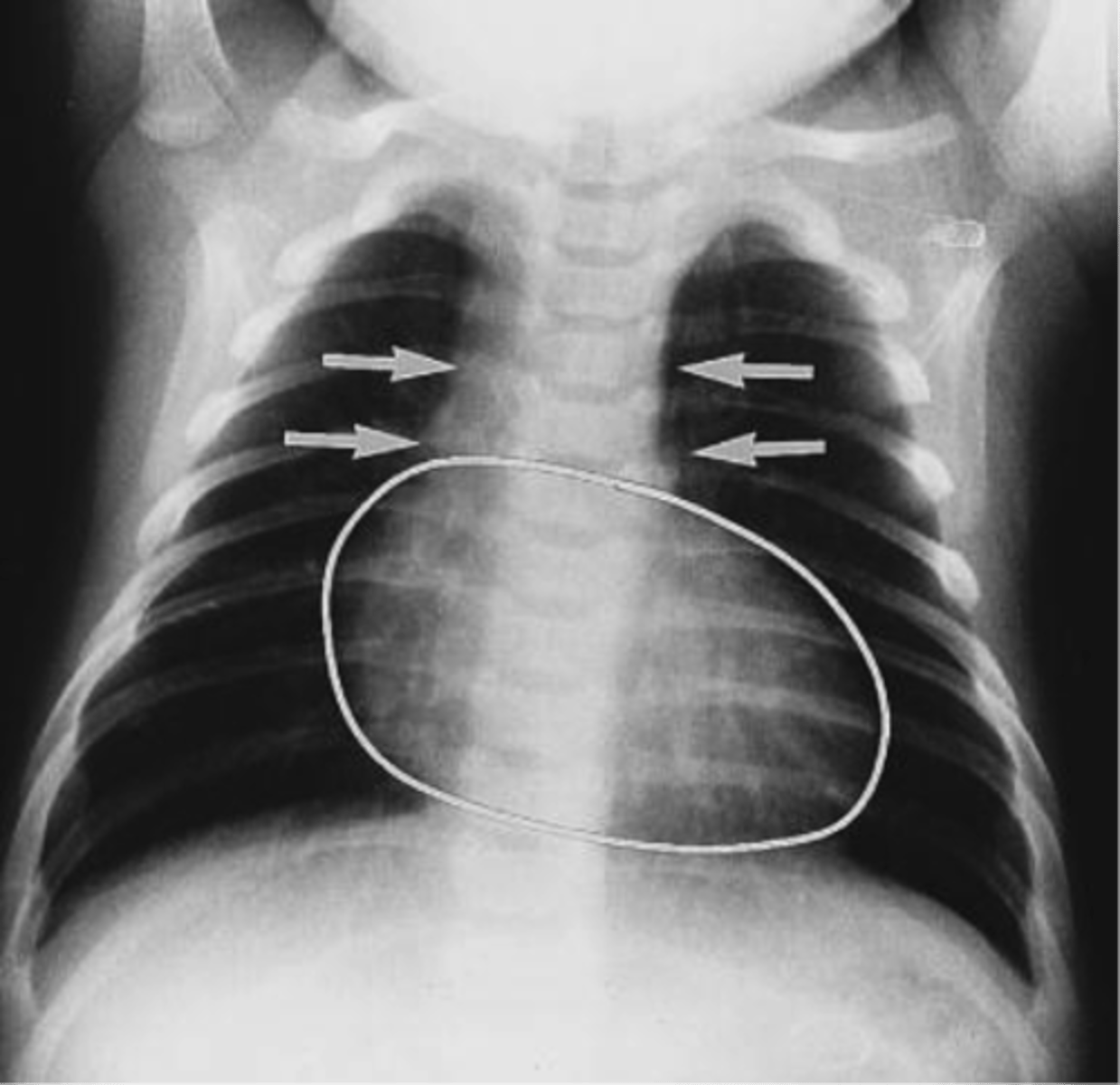
Cyanosis w/in 24 hrs of life, a single S2 on auscultation and narrow mediastinum which heart anomalie?
Transposition of the great vessels
- egg-on-a-string heart
- Prostaglandins initiated to keep ductus arteriosus patent, ECHO obtained
___ is the most common congenital cyanotic heart disease in the neonatal period.
D-transposition of the great vessels (TGV)
___ and __ are the most common causes of osteomyelitis in pts with sickle cell disease.
Salmonella
Staph aureus
Contraindications to rotavirus vaccine?
- Anaphylaxis to vaccine ingredients
- Hx intussusception
- Hx uncorrected congenital malformation of GI (Meckel's diverticulum)
- SCID
Evaluation of primary amenorrhea uterus is present 15 y/o underdevelopment of secondary sexual characteristics what is the next step?
Serum FSH
- secondary sexual characteristics are absent work-up should not be delayed beyond 14
- isolated amenorrhea w/ secondary sexual characteristics normal up to age 16
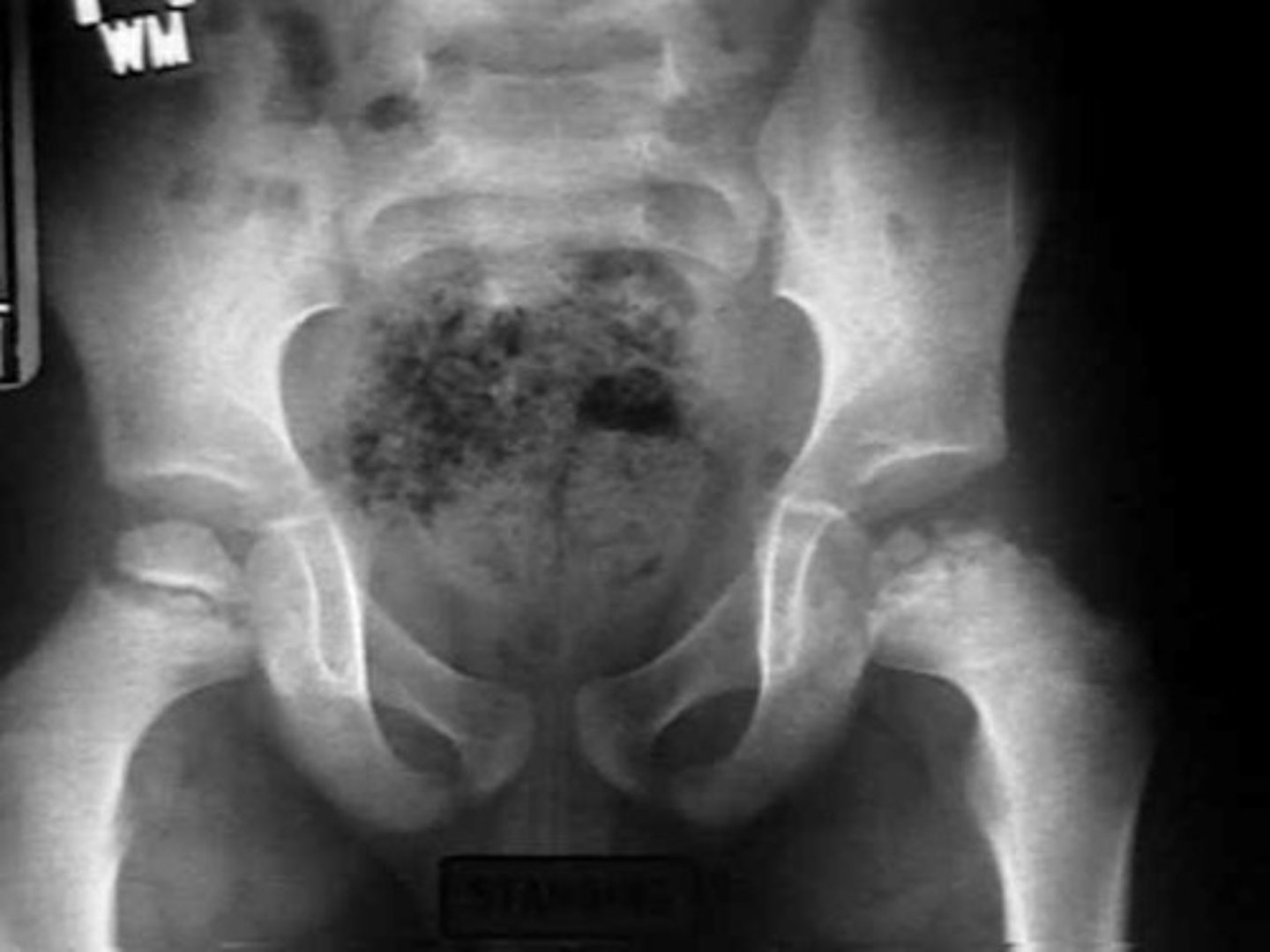
___ is characterized by osteonecrosis of the femoral head presents in boys 4-10 y/o with insidious-onset hip or knee pain and an antalgic gait.
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
- underlying throbophilia may be predisposing factor
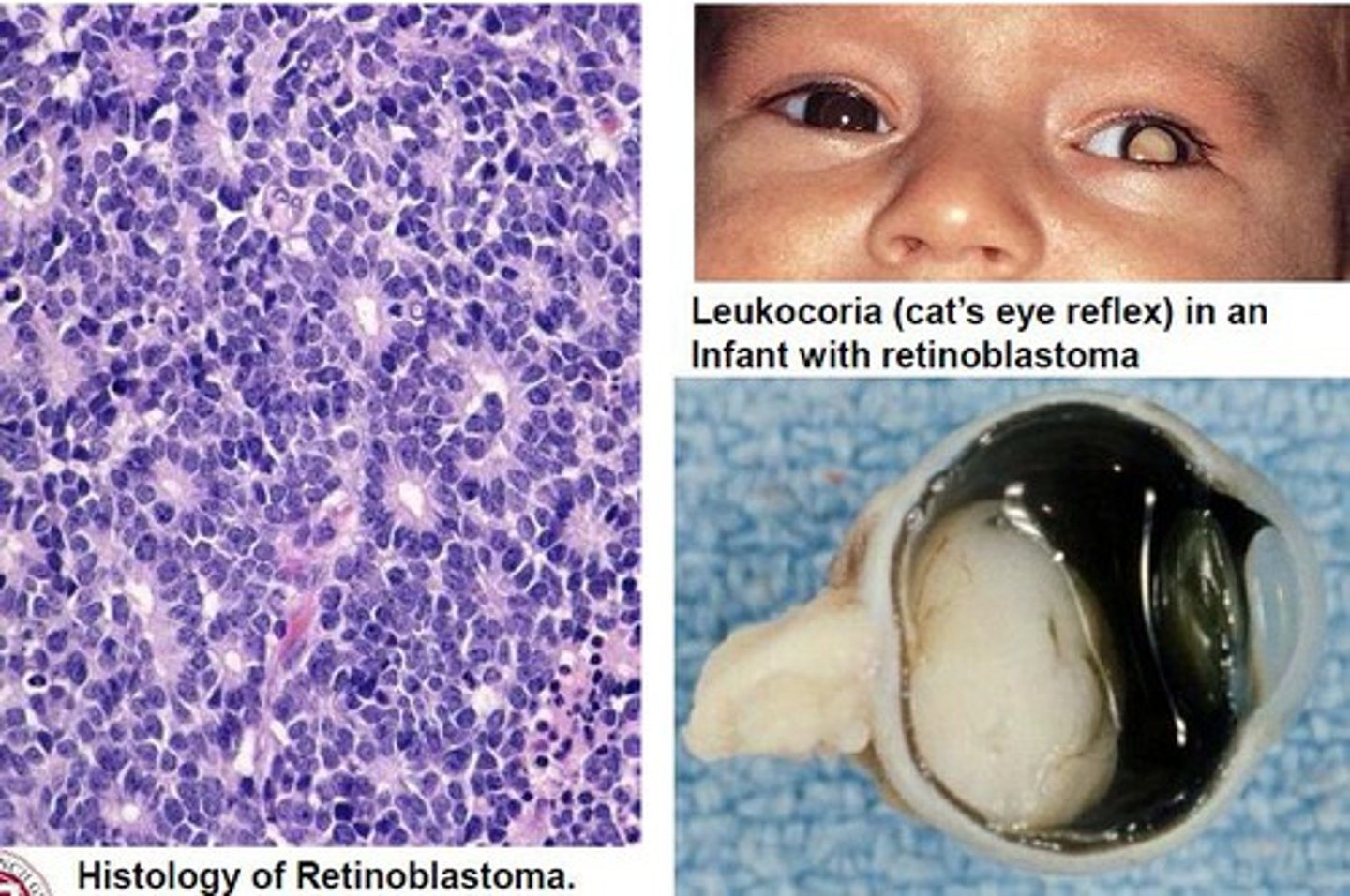
HIGH YIELD: Every case of leukocoria is considered a ___ until proven otherwise, child needs prompt referral to the ___.
Retinoblastoma
Ophthalmologist
- failure to diagnose lead to liver and brain metastases
- Dx highly suspected with US or CT scan finding of a mass w/ calcifications
Ataxia, dysarthria, scoliosis, feet deformities, concentric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. What are the most common cause of death from this?
Friedrich ataxia - most common type of spincerebellar ataxias
Cardiomyopathy 90% patients develop this
Respiratory complications
Pt w/ Hx rheumatic fever have INC risk recurrent episodes and progression of rheumatic heart disease w/ repeated infection Group A step. All pts should receive ___ to prevent recurrent GAS and limit progression of Rheumatic HD.
Continuous antibiotic prophylaxis (IM benzathine penicillin G every 4 weeks)
Pansystolic murmur loudest left lower sternal border and diastolic rumble at the apex due to INC flow across mitral valve. Dx.
VSD
- failure to thrive
- easy fatiguability
- heart failure
ECHO should be performed
Children with bacterial sinusitis present with persistent symptoms of nasal discharge, congestion, and cough, symptoms last 10-30 days w/o improvement. Pt ill high fever and purulent discharge for at least 3 days. The most common predisposing factor?
Viral upper respiratory infection
- contaminated bacteria cannot be cleared by mucociliary clearance due to mucosal inflammation from viral infection
tx: Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid
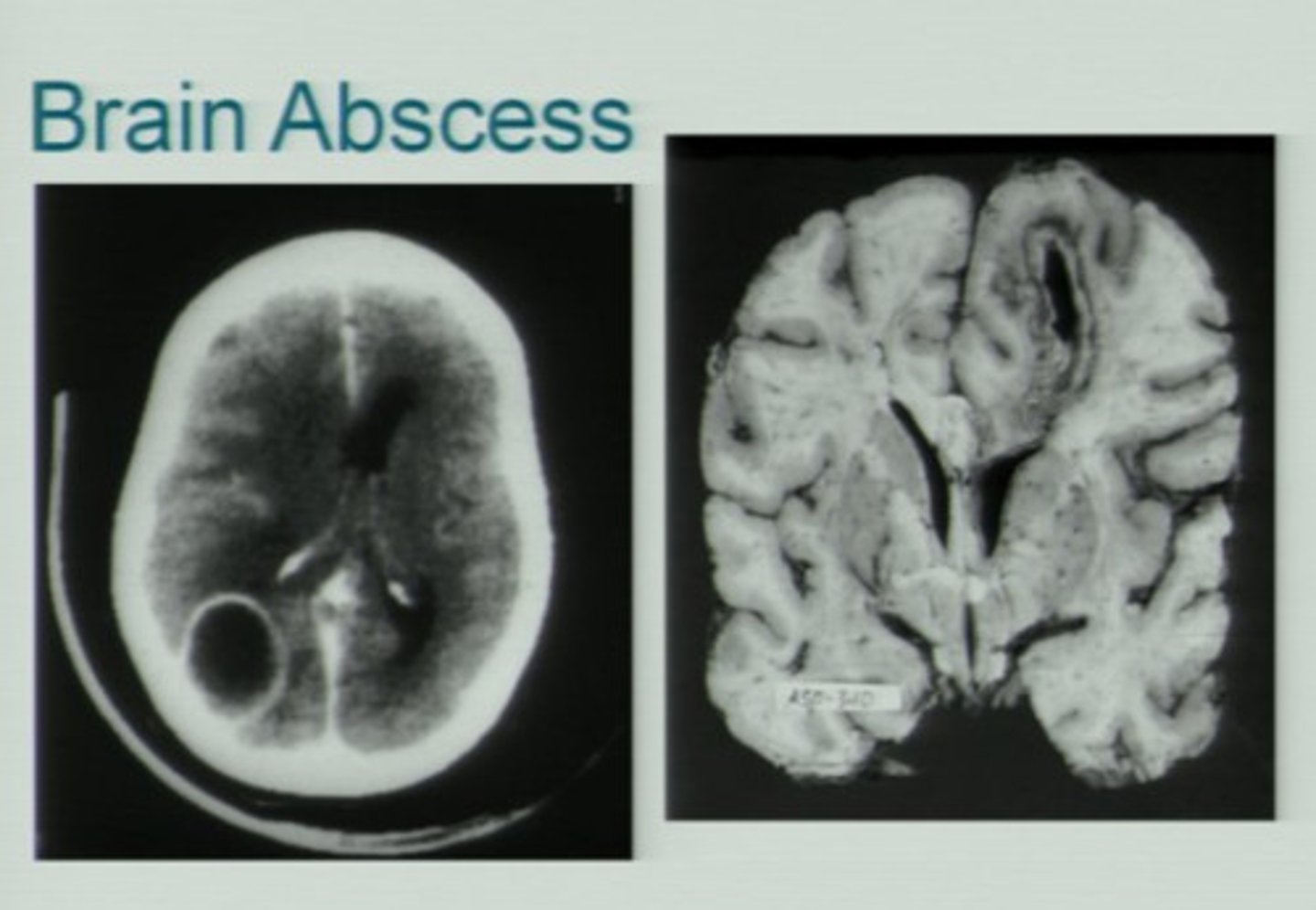
Nocturnal HA + morning vomiting are red flags for intracranial path. Continuous spread of bacteria from otitis or mastoiditis can result in life-threatening ___. Dx is confirmed via?
Brain abscess formation
- Ring-enhancing lesion on CT or MRI
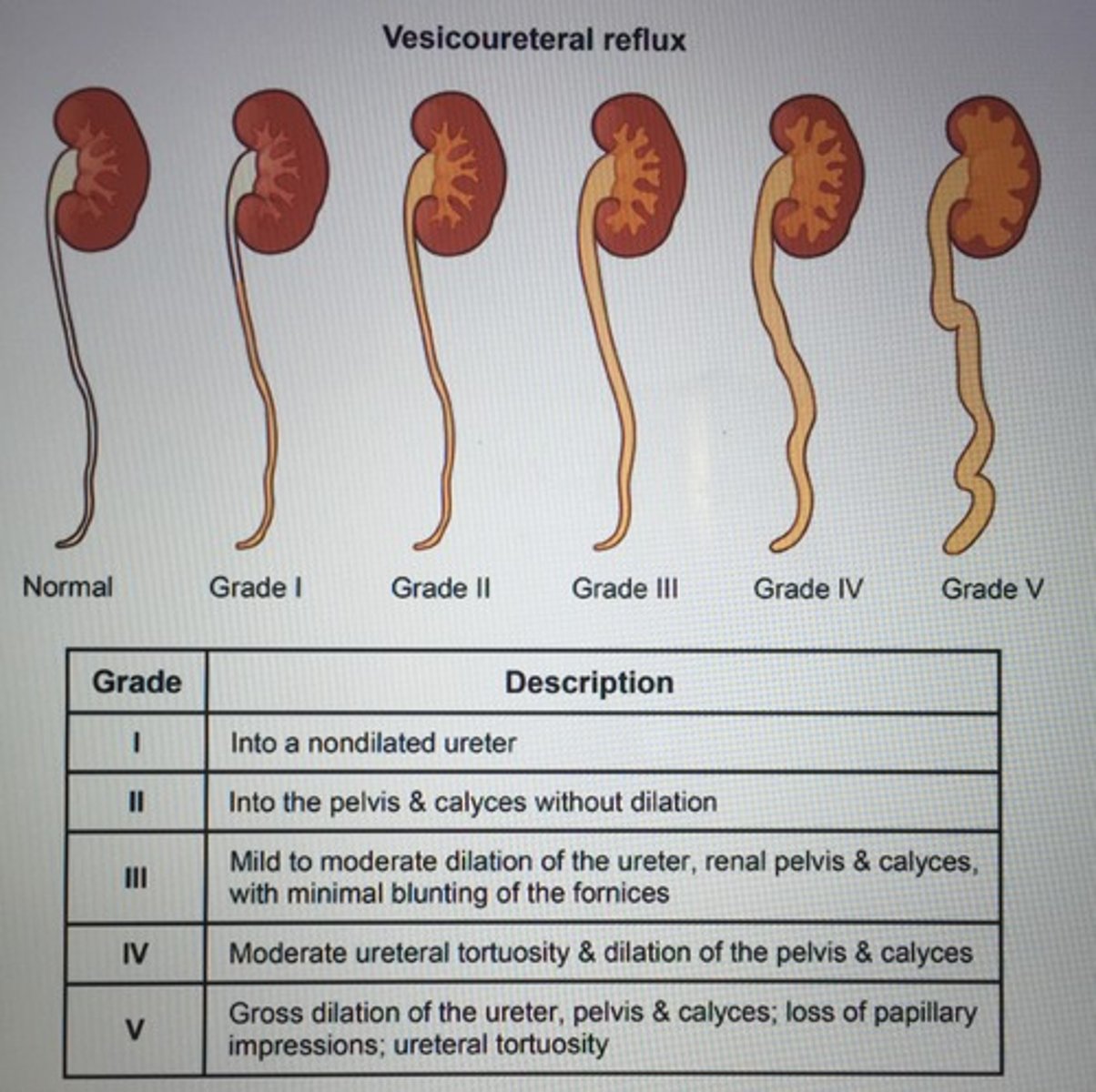
Recurrent UTIs in infants and children and one of the most common abnormalities is primary ___. Definitive diagnosis made via?
Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
- Contrast voiding cytourethrogram
- Renal US to screen hydronephrosis
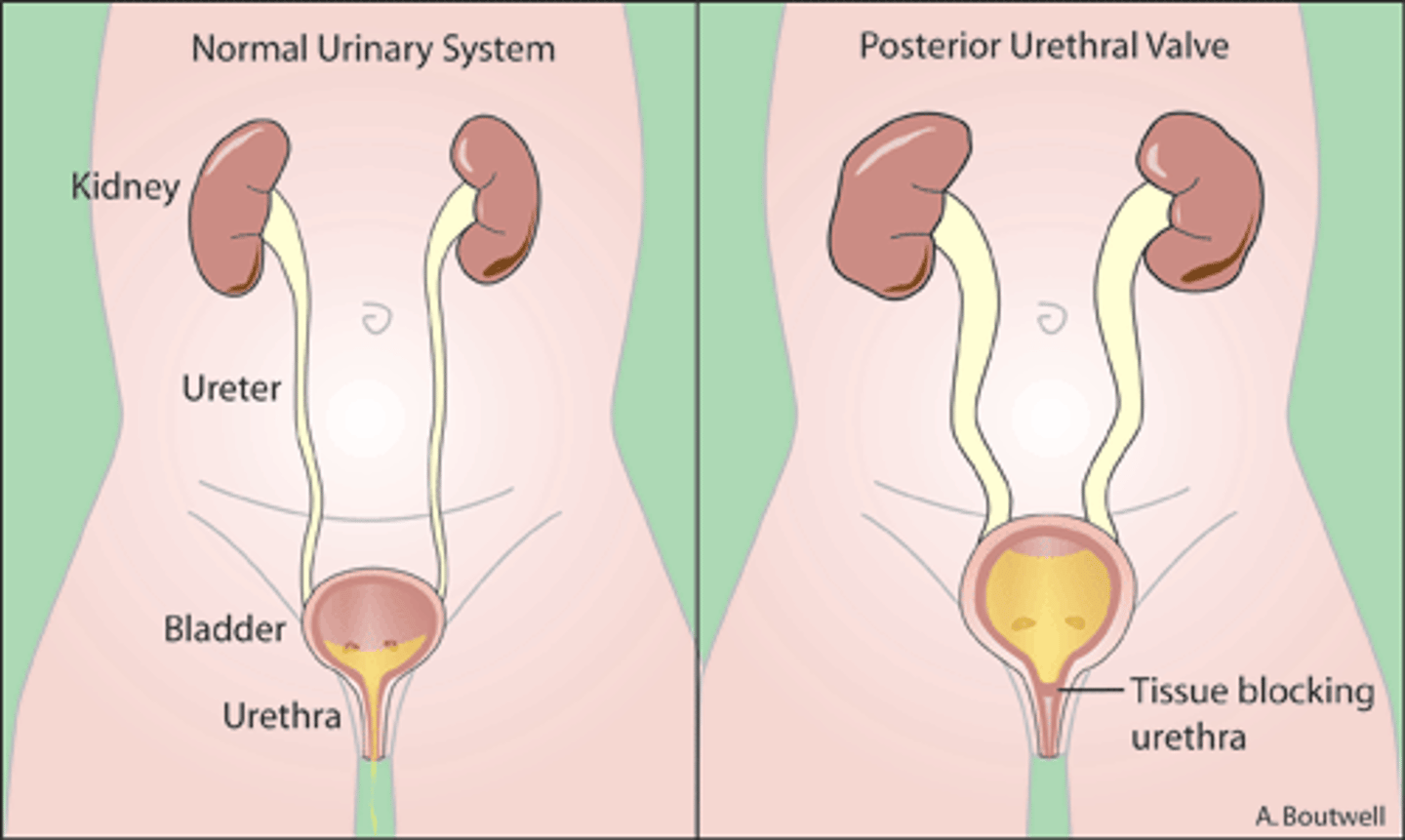
___ are the most common cause of renal insufficiency/failure in children.
Posterior urethral valves
Tx constipation in children
INC dietary fiber
Limit cows milk < 24 oz
Laxatives (polyethylene glycol, mineral oil)
+/- Suppositories, enema
An infant have failure to thrive, diarrhea, diffuse lymphadenopathy, and thrush in the setting of maternal IV drug abuse. What test is the gold standard for HIV infant?
HIV infection
- PCR gold standard from birth until 18 mo.
- Pregnant pts w/ risky behavior should undergo HIV antibody testing in 1st and 3rd trimester as it can take up to 3 mo. to develop detectable antibody
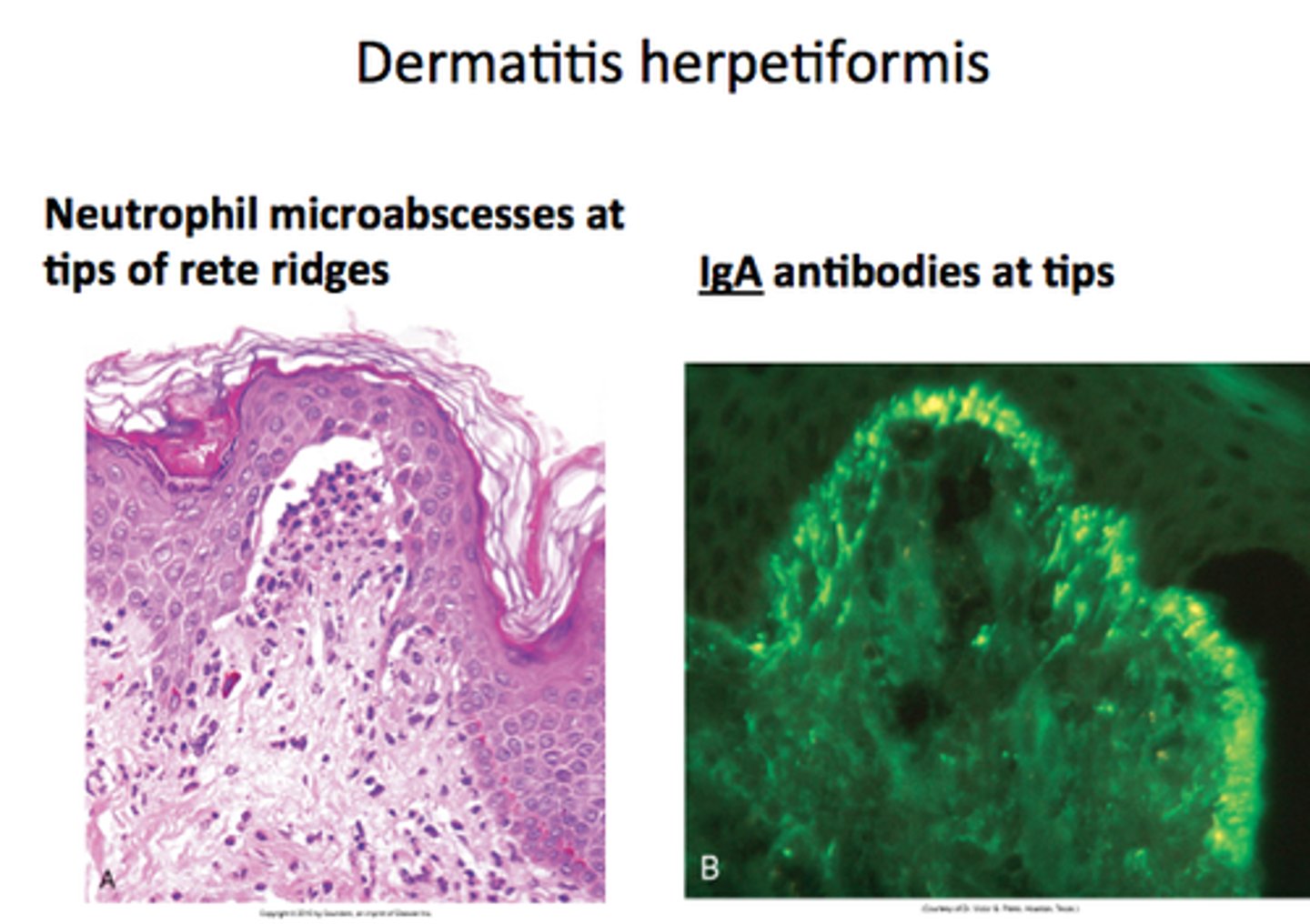
Celiac dz is a frequent cause of malabsorption and can lead to iron deficiency anemia. Common association with celiac dz include __ and ___.
DM 1
Dermatitis herpetiformis
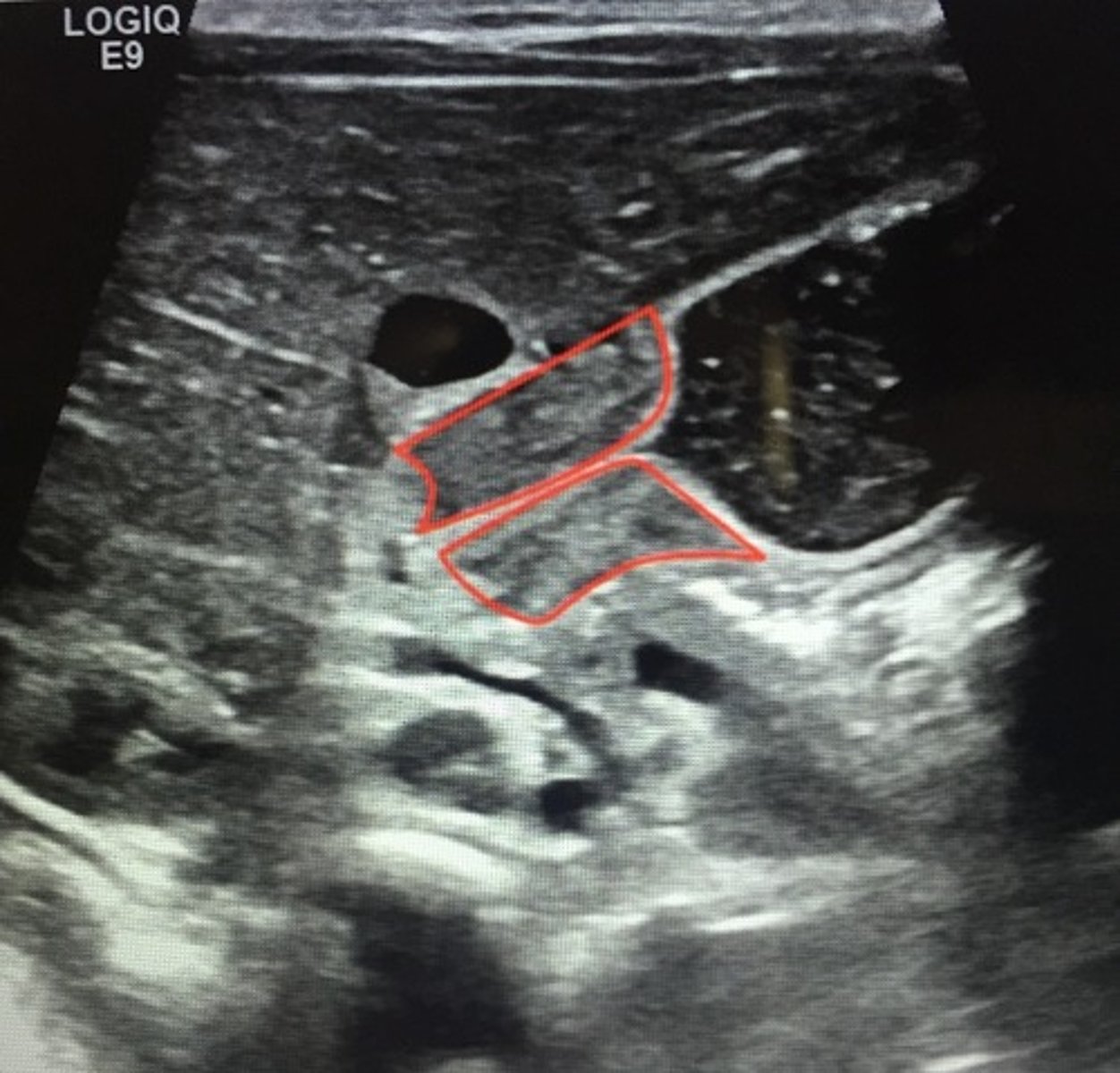
Definitive tx pyloric stenosis?
Pyloromyotomy
- boys age 3-5 weeks
- projectile, non-bilious vomit, hypochloremic metabolic alkalsosis
- "olive-shaped abd mass"
- dehydration (sunken fontanel, dec skin turgor, delayed cap refill)
Abdominal US confirms diagnosis
Gold standard diagnostic test CF?
Sweat testing by quantitative pilocarpine iontophoresis
- cholinergic drug includes sweating
- chloride > 60 mmol/L on 2 sep occasions confirms diagnosis
Exhaled nasal NO is a screening test for ___.
Primary ciliary dyskinesia
Infant has failure to thrive, B/L cataracts, jaundice, and hypoglycemia. Dx.
Galactosemia -> galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase deficiency
-> eliminate galactose from diet
-> pts INC risk E.coli neonatal sepsis
The clinical presentation with patient with Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) depends on the degrees of ___.
Right ventricular outflow obstruction (RVOT)
- murmur harsh, systolic ejection murmur
- squatting INC peripheral systemic vascular resistance (afterload) DEC R-> L shunt, improves cynosis INC intensity of murmur due to INC flow across RVOT
___ are the fluid of choice for initial resuscitation in severe hypovolemic hypernatremia.
Isotonic solution such as normal saline 0.9% or lactated Ringer's
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is connective tissue disorder most commonly inherited from an ___ mutation of COL1A1.
AD
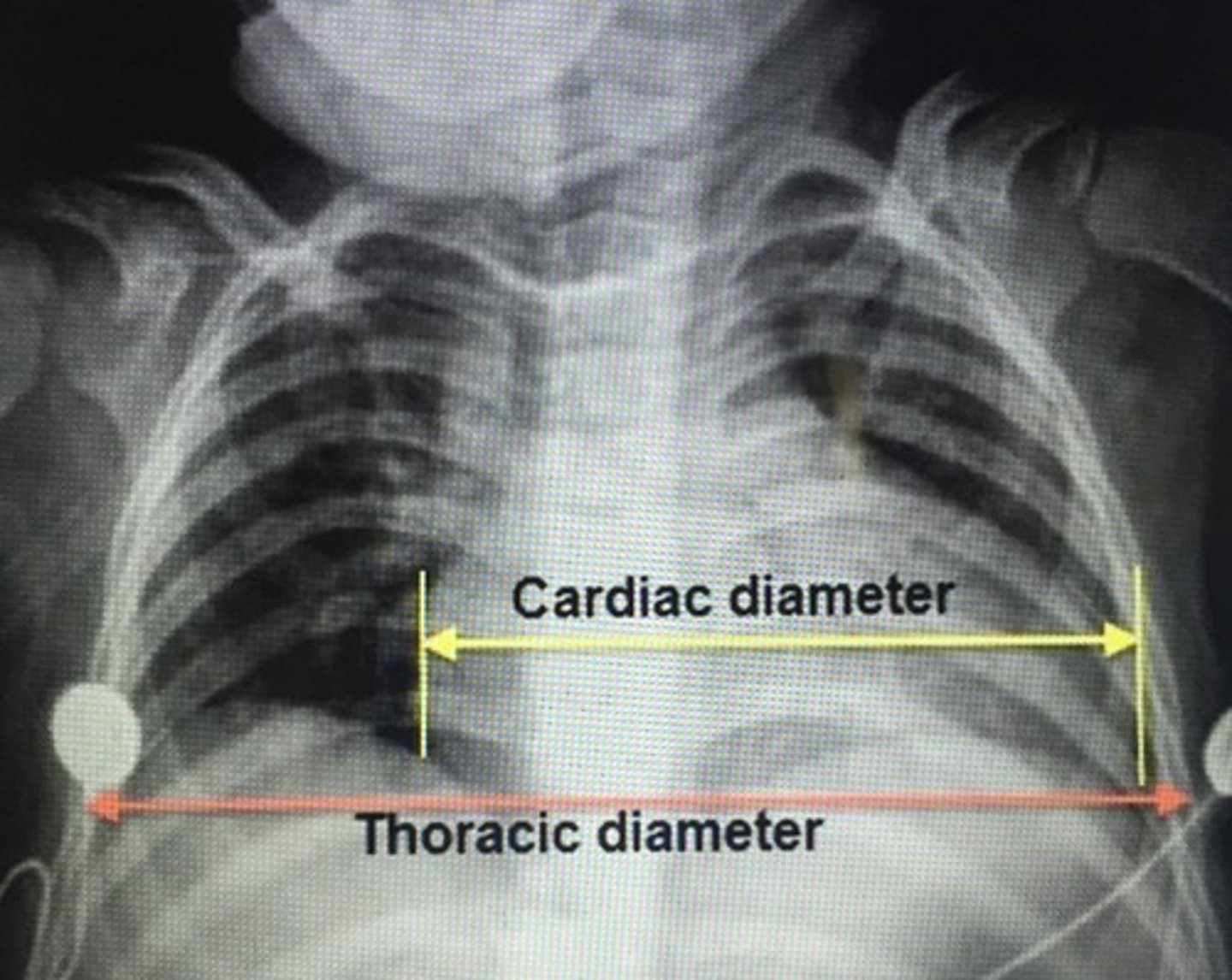
Viral prodrome (upper resp infection precedes worsening resp distress), heart failure signs dyspnea, syncope, tachy, hepatomegaly, cardiomegaly, pulmonary edema on x-ray. Dx.
Pediatric viral myocarditis
- Coxsackie B virus
- Adenovirus
Endomyocardial biopsy (gold standard): inflammatory infiltrate of myocardium w/ myocyte necrosis
Tx: Diuretics + inotropes, affected children monitor ICU due to risk of shock and fatal arrhythmias
___ is a malformation in 10-15% of pts with Down syndrome most commonly due to excessive laxity in the posterior transverse ligament.
Atlantoaxial instability -> INC mobility btw C1 and C2
- urinary incontinence, dizziness, vertigo, + Babinski, UMN findings
Tx: surgical fusion of C1 to C2
Deficiency in newborn in vitamin K due to?
Poor placental transfer
Absent gut flora
Immature liver fxn
Inadequate levels in breast milk
- Vitamin K deficiency presents first week of life, risk of intracranial hemorrhage
Pregnant women on phenytoin during their last trimester often receive prophylactic ___ to prevent neonatal bleeding.
Vitamin K -> phenytoin may INC the rate of fetal vitamin K degradation
Gold standard diagnosing Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
Genetic testing, show deletion of the dystrophin gene Xp21
__ most common type of intracranial lesion in NF1.
Optic pathway glioma
- order MRI of the brain + orbits
__ should be suspected in an inadequately vaccinated patient w/ severe, paroxysmal cough, posttussive emesis. During first mo. illness dx by cultures and/or PCR of nasopharyngeal secretions.
Pertussis
- inspiratory whoop
- Macrolide antibiotics
Retinal hemorrhage in an infant virtually pathognomonic finding for?
Abusive head trauma
- vitreoretinal traction
- subdural bleed manifest seizures, INC head circumference, bulging/tense anterior fontanelle, alt mental status
- non-contrast head CT scan
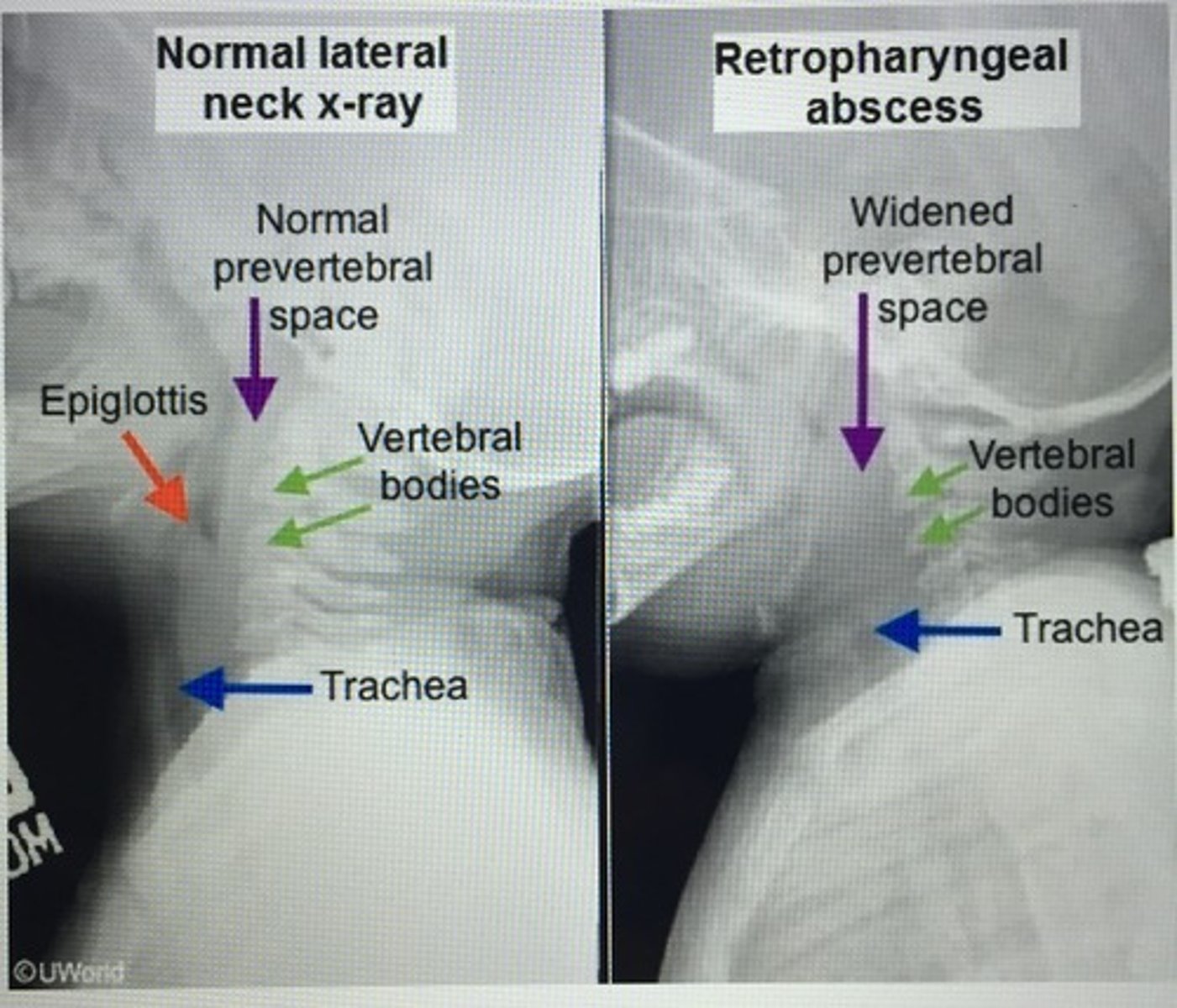
Inability to extend the neck and widened prevertebral space suggests a diagnosis of ____. Fever, dysphagia, muffled voice.
Retropharyngeal abscess (RPA)
= CT scan w/ contrast
- > polymicrobial
Baby initially well-appearing, followed by development of the following over 1-8 weeks: jaundice, acholic (pale) stools or dark urine, hepatomegaly, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, mild elevation in transaminases.
Biliary atresia
- US: absent or abnormal gallbladder then hepatobiliary scintigraphy: failure tracer excretion
- tx: hepatoportoenterostomy (Kasai procedure), Liver transplant
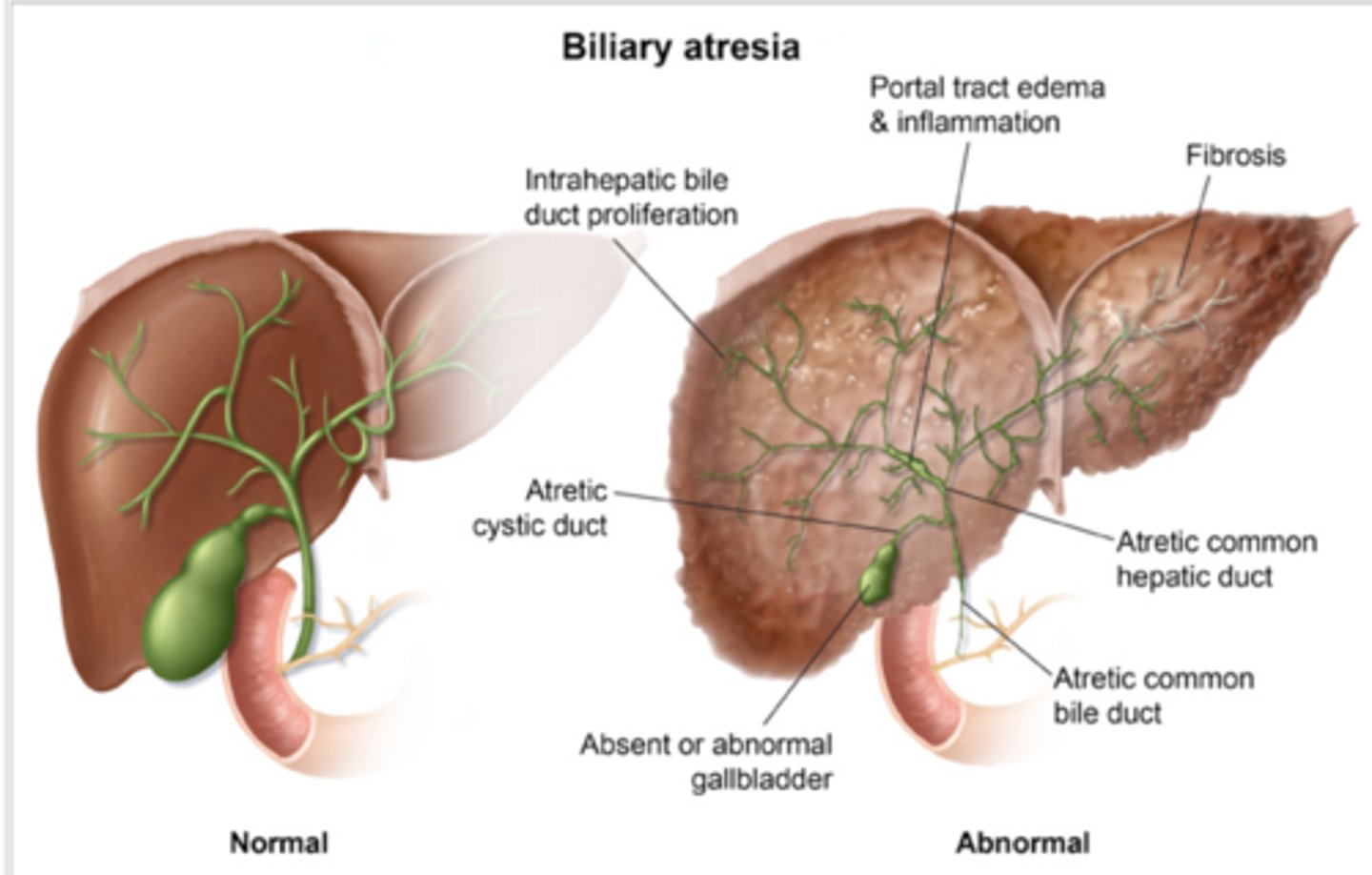
Gold standard diagnosis biliary atresia?
Cholangiogram
Copious purulent ocular discharge and eyelid swelling in 2 to 5 day old newborn are most consistent with ___ conjunctivitis.
Gonococcal
-> topical erythromycin ointment 1 hour of birth
5-14 days after birth chemosis; moderate eyelid swelling, water, mucoid discharge which neonatal conjunctivitis?
C. trachomatis
- cause neonatal conjunctivitis + pneumonia
Androgen insensitivity syndrome is characterized by phenotypic female w/ 46, XY karyotype. When is B/L gonadectomy recommended?
After completion of puberty (attainment of adult height) to DEC risk of gonadal malignancy