1.2.6 Price Determination
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is Equilibrium (Price and Quantity) determined by?
Is determined by the interactions in the demand and supply curve. While it refers to the point were there are no more forces bringing about change.
What is Price Equilibrium?
Is were supply = demand (were the curves cross)
What is the price also known as and why?
The Price is also known as the market clearing price because all products supply to the market and are cleared (bought).
What happens at Equilibrium and the impact it has on buyers?
At equilibrium no buyers are unable to buy the good.
If price was higher or lower what would happen?
If price was higher there would be un-sold goods
If price was lower there would be consumers who are willing to buy the goods but will be unable to do so.
Diagram with Excess Supply and Excess Demand.

When will the Equilibrium Price and Quantity won’t change?
The Equilibrium Price and Quantity will not change unless there was a change in the conditions of supply in the demand.
What is Effective Demand?
For demand to be effective consumers must be both willing and able to buy the good (E.g. I want chocolate and I have the money to afford it.)
How does an Excess Demand diagram look like?
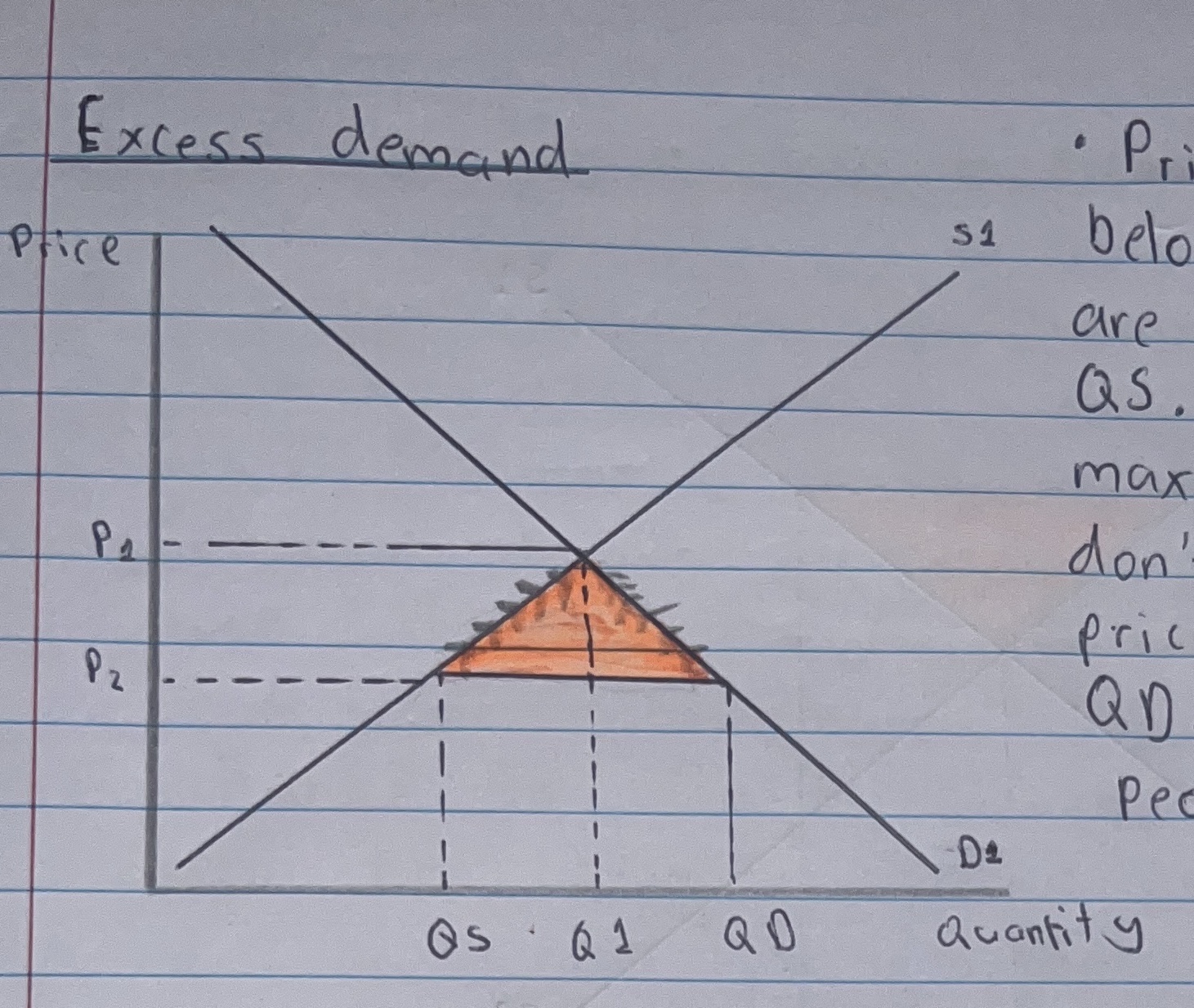
What is excess demand?
Excess demand occurs when price is set below equilibrium (P2).
What is excess demand and how does the market return to equilibrium?
At Lower Price:
Suppliers are only willing to supply QS. (As they want to maximise profit so they don’t want sell at lower prices).
Consumers Demand QD. (As at low prices more people want to buy.
QD > QS therefore there is excess demand of orange demand and creating a shortage.
At Higher Price:
Since there is a shortage in the market.
Firms know they can charge higher price and still sell their goods, so this causes an extension in supply.
Then they will charge P1 for Q1
At this higher price some consumer will lose effective demand and so are rationed out of the market.
This leads to a contraction in demand and QD becomes Q1.
Eventually P1 and Q1 are reached in equilibrium and excess demand is solved?
How does Excess Supply look like?
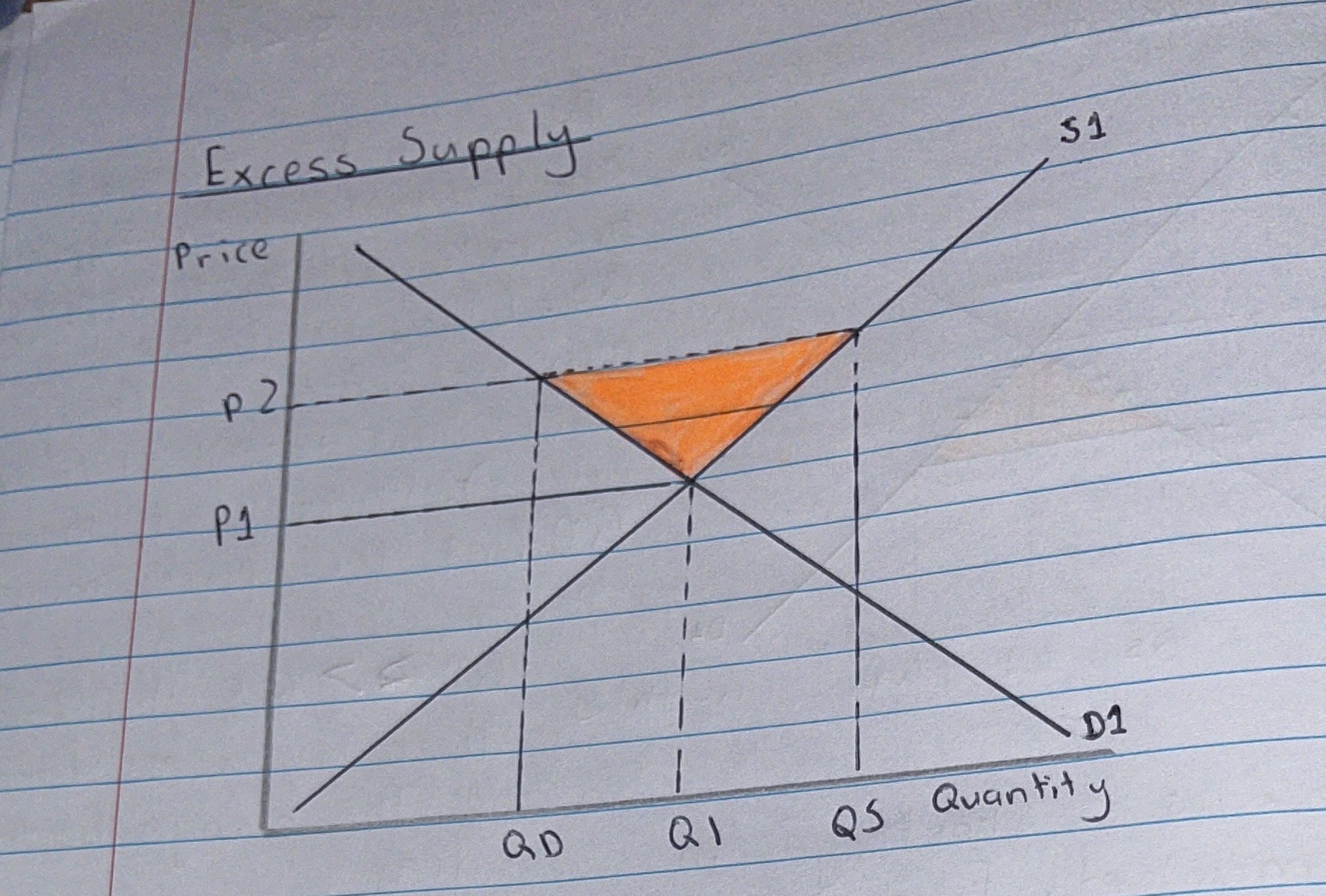
What is Excess Supply?
Excess supply occurs when price is set above Equilibrium (P2)
What is Excess Supply and how does the market return to Equilibrium?
At Higher Price:
At Price P2, suppliers are willing to supply QS but consumers only demand QD meaning there is excess supply in orange shaded area.
QS > QD, creating a surplus.
Therefore Prices have to fall.
At Lower Price:
As a result firms are left with unsold goods.
This then encourages them to put on sales to sell the excess goods, causing prices to fall and supply to contract to P1. (Contraction along the Supply Curve).
As a result demand would extend to P1 because at Lower Prices more consumers would have effective demand and are rationed into the market and causes a extension in demand.
At price P1 & Q1 the market will now be at Equilibrium and excess supply will be solved.
What are the 2 factors that causes a change in Equilibrium Price?
1) A Change in the conditions of the demand which can cause the demand curve to shift.
Or
2) A Change in the conditions of the supply which can cause the supply curve to shift.
