Crisis and Change in the Ottoman Empire and Qing China
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
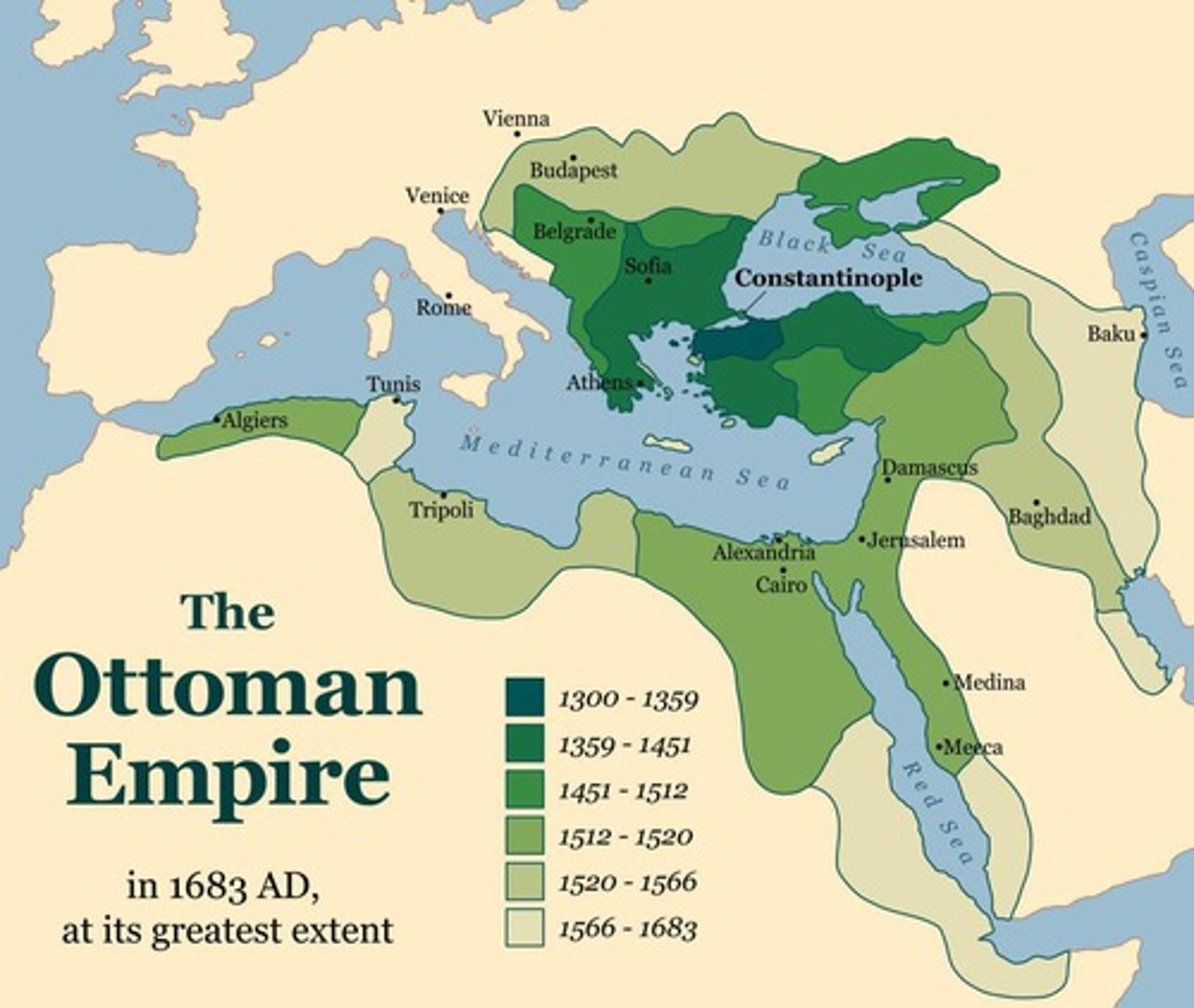
Ottoman Empire
A major Islamic empire facing decline due to internal strife.
Islamic Heartland
Region central to Islamic culture, experiencing political instability.
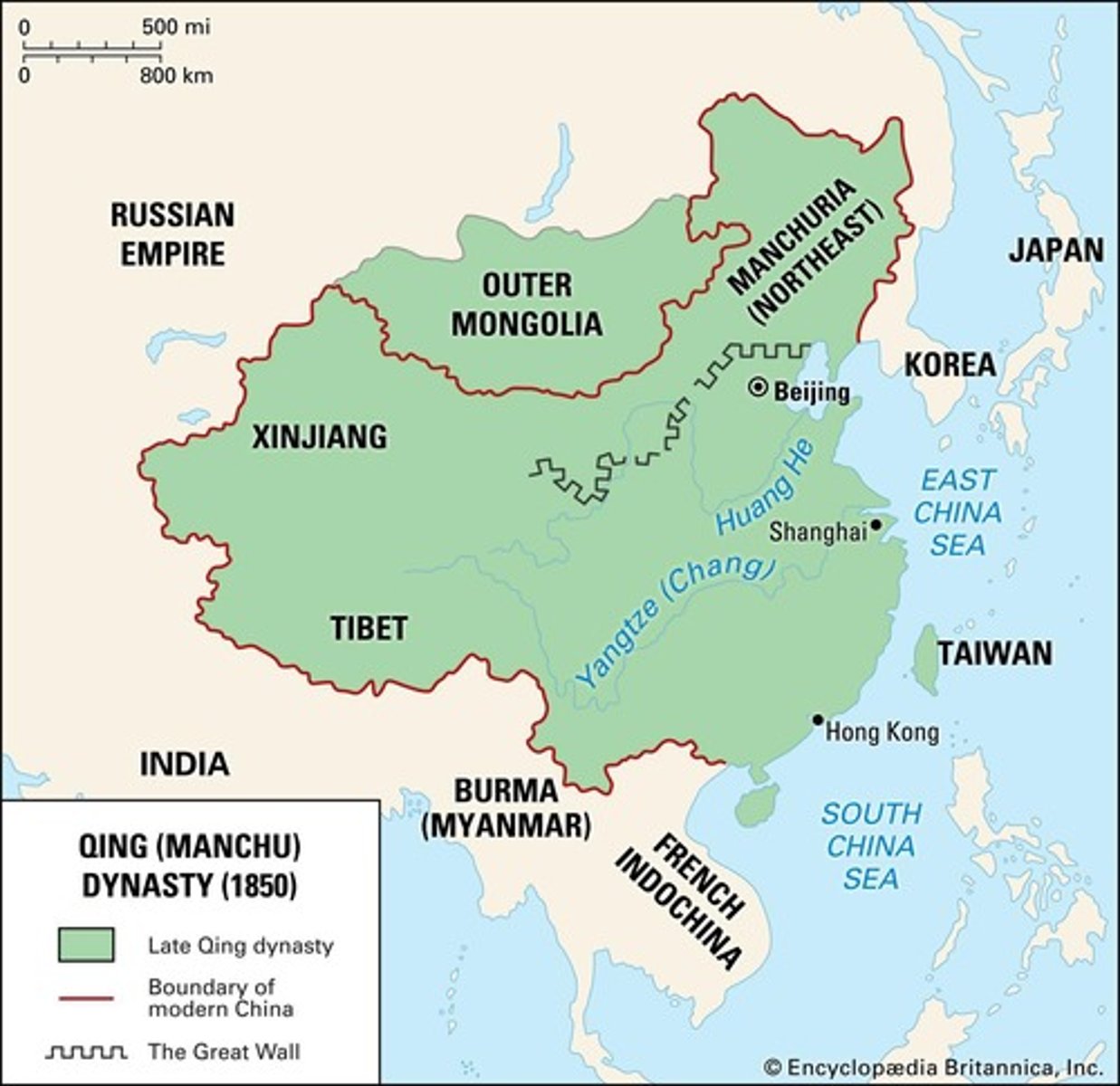
Qing China
Last imperial dynasty of China, weakened by foreign pressures.
European interference
External influence disrupting stability and sovereignty of empires.
Qing China
Experienced growth and prosperity before late 19th century.
Ottoman Empire
Faced territorial losses and internal challenges post-1750.
Janissaries
Elite military corps that resisted reforms in the empire.
Auspicious Incident
Mahmud II's successful elimination of Janissary power.
Tanzimat Reforms
Westernization efforts in the Ottoman Empire from 1839-1876.
Sultan Abd al-Hamid II
Shifted to despotic rule, abolished constitution (1876-1909).
Young Turks
Reformist group that overthrew Abd al-Hamid II.
Selim III
Initiated modest reforms but faced Janissary rebellion.
Mahmud II
Implemented successful military and bureaucratic reforms.
Ottoman Retreat
Period of decline marked by weak leadership and territorial loss.
Western Imperialism
External influence contributing to internal challenges in Asia.
Balkans Independence
Greece (1830) and Serbia (1867) gained independence from Ottomans.

European Competition
Ruined local industries in the Ottoman Empire.
Economic Decline
Ottomans struggled economically against advanced Western industries.
Reforms Impact
Did little to improve the economy or women's rights.
Naval Presence
Britain's strategy to support the Ottoman Empire in 19th century.

Despotism
Abd al-Hamid II's response to threats against his power.
Constitution Restoration
Young Turks restored civil liberties after 1908 coup.

Power Struggles
Regional governors and leaders vied for control in the empire.
Religious Leaders
Influential figures involved in Ottoman power dynamics.
Ottoman Bureaucracy
Western-style administration established by Mahmud II.
Industrial Capability
Lack thereof weakened Asian states against Western powers.
Political Decline
Resistance to European intrusion led to internal challenges.
Naval Strategy
Britain's military presence aimed to deter Russian expansion.
Reformers' Threat
Sultans felt endangered by calls for political change.
Civil Liberties
Limited freedoms under Abd al-Hamid II's rule.
Puppet Sultan
Installed by Young Turks after Abd al-Hamid II's removal.
Ottoman Empire
A historical empire that declined over time.
World War I
Conflict Ottoman Empire hoped to regain territory.
Muhammad Ali
Albanian Ottoman who reformed Egypt's government.
Mamluk Vassals
Ottoman allies defeated by Napoleon in Egypt.
Nile Valley
Region taken by Napoleon during his campaign.
Cotton Textile Industry
Economic reform attempted by Ali in Egypt.
Suez Canal
Completed in 1869, financed by foreign investment.

Khedive
Ruler of Egypt under Ottoman control.
Puppet Khedives
Leaders controlled by British consuls in Egypt.
Jihad
Call for struggle against foreign influences.
Al-Azhar
Meeting ground for Muslim intellectuals in Egypt.
European Intrusion
Interference in Egypt's affairs by European powers.
Ahmad Orabi
Led a failed revolt against the khedive.
Debt to Europeans
Egypt's financial obligation due to foreign investments.
Single Crop Producer
Egypt focused primarily on cotton production.
Landlords
Local elites who profited from peasant exploitation.
Peasant Resistance
Failure of Ali's reforms led to peasant unrest.
Extravagant Events
Government spending on lavish activities and military.
British Protectorate
Status imposed on Egypt after Orabi's revolt.
Sudanic Nomads
Local peoples opposing Egyptian exploitation in Sudan.
Limited Success
Ali's reforms did not fully achieve intended goals.
Crisis in Arab Lands
Territories faced European intrusion post-Ottoman decline.
Military Campaigns
Egypt's government engaged in conflicts in Sudan.
European Control
Foreign powers exerted influence over Egyptian governance.
Mahdi
Religious leader who initiated Sudanese Jihad.
Jihad
Struggle or fight against enemies of Islam.
Khalifa Abdallahi
Successor of Mahdi, established strong Islamic state.
Battle of Omdurman
1898 conflict where British defeated Sudanese forces.
British Empire
Colonial power that controlled Egypt and Sudan.
Qing Dynasty
Last imperial dynasty of China, ruled by Manchu.
Manchu
Ethnic group that seized power in China, 1644.
Ming Dynasty
Preceding dynasty, overthrown by Manchu in 1644.
Examination System
Merit-based system for selecting government officials.
Non-Manchu Bureaucracy
Majority of officials were not of Manchu descent.
Patriarchal Society
Social structure emphasizing male authority and lineage.
Female Infanticide
Cultural practice of killing female infants.
Agricultural Infrastructure
Systems supporting farming and crop production.
Population Growth
Increase in population that strained resources.
Socio-Economic Gap
Disparity between rich landlords and poor peasants.
Commercialism
Economic system focused on trade and commerce.
Silver Profits
Wealth gained from trade, especially in silver.
Compradors
Chinese merchants facilitating foreign trade.
Trade Entrepots
Ports for international trade, like Canton and Macao.
Internal Decay
Decline of Qing authority and effectiveness.
Nepotism
Favoritism shown to relatives in bureaucratic positions.
Military Weakness
Decline in military power due to financial issues.
Yellow River Dikes
Flood control structures left in disrepair.
Peasant Migration
Movement of peasants seeking better living conditions.
Corrupt Officials
Government representatives failing to address public issues.
Food Scarcity
Insufficient food supply due to population pressures.
Guerrilla Tactics
Irregular warfare methods used by Mahdists.
Islamic Right
Conservative Islamic governance under Khalifa Abdallahi.
British Demands
Economic pressures imposed on Sudan by British rule.
Opium Wars
Conflicts over opium trade between Britain and China.
Manchu
Chinese dynasty that viewed Europeans as barbarians.
Lin Zexu
Official who blockaded Canton to stop opium trade.
Treaty of Nanjing
1842 agreement granting Britain control of Hong Kong.
Taiping Rebellion
1850-1864 revolt led by Hong Xiuquan against Manchu rule.
Hong Xiuquan
Leader of the Taiping Rebellion advocating social reforms.
Sino-Japanese War
1894-1895 conflict causing loss of Korean control.
Boxer Rebellion
1899 uprising against foreign influence in China.
Empress Dowager Cixi
Last powerful ruler of the Manchu dynasty.
Order of Harmonious Righteous Fists
Group known as Boxers opposing foreign devils.
Chinese Exclusion Act
1882 US law banning Chinese immigration.
Chinese Migration
Movement of Chinese workers to various global regions.
Ethnic Enclaves
Communities preserving culture, e.g., Chinatown in SF.
Silver Revenues
Decline due to increased opium trade in China.
Opium Addiction
Widespread addiction in China from opium trade.
Military Force
Britain threatened China with military action over trade.