MCH exam 2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
When were infant mortality rates at their highest? Why?
Early 1900s/ 20th century particularly around 1915
Poor healthcare, inadequate nutrition, and lack of sanitation.
What were some public health strategies used to combat this?
Improved hygiene and sanitation
Milk stations : improved nutrition
Health education
What is Title V? What case led to its origin?
A federal program established in 1935 to improve maternal and child health services, providing funding and support for state health programs.
Shephard Towner Act
First federal legislation to provide funds specifically for maternal and child health services to reduce infant mortality and improve health outcomes.
What is Title X
A federal program established in 1970 to provide access to family planning services and reproductive health care, ensuring that individuals can make informed choices about their reproductive health.
Family planning program
Five factors that led to high infant mortality rates in the early 20th century.
Poor housing conditions, sanitation, and hygiene
Malnutrition
Food fortification to prevent neural disorders
Economic factors
Unsafe home birth
lack of access to healthcare
High rate of premature births
One factor that contributed to better living standards and improved infant health outcomes (not a public health/government program)
Economic growth
Late 19th century _____________ led to significant increases in child labor
Industrialization/urbanization
What is the Children’s Bureau and its mission? What are examples of issues they address?
The Children's Bureau is a federal agency established in 1912
MISSION: address the most pressing social issues related to children and mothers/improving their welfare
It addresses issues such as child abuse, neglect, adoption, and child poverty
In infant mortality studies, what was one of the greatest links they found between which families experienced the greatest rates of low infant health?
Link between father’s income and infant health
Factors associated with declines in maternal mortality
Medical advancements
Antibiotics
Blood transfusions
Public health measures
Pre and post-natal care
Public health campaigns
Social factors
Women's education
Economic growth
Women's suffrage and rights
What is the Sheppard Towner Act?
The Sheppard Towner Act of 1912 was the first legislation providing funds for maternal and infant health programs
Aimed to improve healthcare access through initiatives like health clinics, visiting nurses, and midwife training
Currier stated, “Evolution of ___________ is not completely resolved infant disease but did accelerate the declining rates of milk born infectious disease”
Milk pasteurization
Other factors that contributed to a reduction in infant disease
Education
Basic hygiene
Milk station
Bureau of Child Hygiene (taught older siblings about hygiene)
Three factors that influence infant deaths
Urbanization
Shift to urban lifestyles
Greater reliance on scientific evidence
What is pregnancy-related mortality?
Deaths during pregnancy and up to one year postpartum that are related to pregnancy
Hemorrhage
Eclampsia
What is pregnancy-associated mortality?
Deaths during and up to one year postpartum
Murder
Car Accident
Why is it important to track the rates of maternal mortality?
Important to track to formulate interventions
Tailor issue to a certain community
Inform programs/policies
To make sure we are addressing the right concerns
What group of women are most likely to suffer from high maternal mortality rates?
Women 30-34
Black women are disproportionately at risk of maternal mortality
3 black women die per one white woman giving birth (pregnancy-related)
1.5 Black women die per one white woman (nonpregnancy related)
When do the majority of pregnancy related deaths occur?-
During or within 42 days
Four types of pregnancy-related care
Preconception care
Patient factors
Age
Education
Poverty
Health status
Antenatal care
Delivery and hospital care
Provider factors
Knowledge
Experience
Implicit bias
Cultural competence
Postpartum
An example of a community barrier and a systemic factor
Community: poverty
Systemic: access to quality care
Five sections of support for reducing maternal mortality
Systems
Clinical quality improvement
Social support
Policy
Public health research and communication
Two initiatives set forth by Merk for Mothers
addressing pregnancy-related complications
domestic violence
depression
cardiovascular disease
helping clinicians better manage hypertension, hemorrhage, and other OB emergencies
Two interventions that Dr. Clark implemented to halve his hospital’s rate of MM
triggered automatic and rapid antihypertensive therapy when patients exceeded specific blood pressure thresholds
prompted an emergency chest x-ray to look for pulmonary edema when a woman reported shortness of breath
One material implementation that hospitals can introduce when it comes to maternal hemorrhage
Obstetric hemorrhage bundle
requires hospitals to have emergency carts containing drugs and equipment needed to immediately respond to a mother who is hemorrhaging.
checklist on the cart describes how to recognize and manage hemorrhage
Most difficult factors to address
Suicide, homicide, or drug overdoses
Most of those women hadn’t received mental health care, which can be very difficult for new mothers to access
More than half the deliveries in the US are covered by Medicaid, which stops paying for pregnancy care six weeks postpartum
Problem: Mothers will bring their newborns for a well-baby visit, but many skip their postpartum 6-week visit where depression and other potentially life-threatening problems may be diagnosed
Solution: combining mother and baby visits at 2 weeks postpartum
Community health workers and doulas, also need to be integrated into care systems to support at-risk women when their lives are at stake
Eliminating the racial disparity gap in maternal deaths
Factors that have influenced the evolution of childbrith practices in the USir
Cultural values about childbirth
Fear of childbirth
Trust in science and rationalism
Individualism
Economic pressures to maximize the efficiency of hospitals and reduce spending
Hospitals birth in large maternity wards
Standardization of care
Technological advances
Insurance and Liability
Social and Political Movements
Public health movement
Civil rights movement
Feminist movement
Two types of birth centers
Hospital-based
Free-standing
Some reasons as to why Black women have higher rates of C-sections
Complex interplay of socioeconomic health care system and systemic factors such as
Healthcare system disparities
Socio-economic disparities
Pre-pregnancy disparities
Healthcare providers attitudes and bias
Three indications for C-section
Umbilical cord prolapse
Placenta previa
Fetal misplacement
Give an example for risks associated with C-sections for the mother, baby, and future pregnancies
Mother: infection
Baby: altered immune development
Future: higher rates of pre-term/still-born babies
What impact do doulas have on birth outcomes?
More likely to attend childbirth preparation classes
Initiate breastfeeding
Less likely to use epidural/pain medication
Less likely to experience postpartum mental health difficulties
What are the five indicators to measure breastfeeding?
Ever breastfed
Breastfeeding at 6 months
Breastfeeding at 12 months
Exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months
Exclusive breastfeeding at 6 months
Two benefits of breastfeeding for children
Immunity boost
Decrease chances of SIDS
Two benefits of breastfeeding for mothers
reduced risk of ovarian cancer
reduced risk of type 2 diabetes
Socioecological model of barriers to breastfeeding
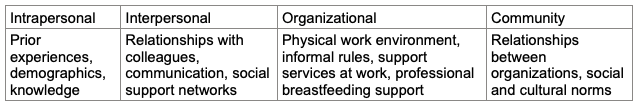 |
Why did people start to use formula instead of breastfeeding? What are some factors associated with exclusive formula feeding?
Why
perception of inadequate milk supply
desire for sleep
plan to breast and bottle feed
Factors
single martial status
birth mother in the US (more widely accepted)
c-sections
Baby Friendly Initiatives
Written breastfeeding policy
Train all medical staff on skills to implement policy
Inform all women of the benefits of breastfeeding
Help mother breastfeed within 30min of birth
Show mothers how to breastfeed
Do not give infants anything other than breast milk unless indicated
Practice rooming in
Encourage on-demand breastfeeding
No artificial treats
Foster establishment of breastfeeding support
Factors that may help mothers breastfeed longer
Baby-friendly hospital initiatives
Home visits
Health care staff education
Peer support with the WIC program
Unique barriers for Black women to meet breastfeeding intentions
Black women are over-represented in the service sector where labor protections are weaker
less access to lactation breaks
less guidance on how to breastfeed
What is the Barrier Analysis Tool used by Tran?
Rapid assessment tool that is used to identify determinants associated with a particular behavior
Strength: provided a framework for a range of questions based on behavior change theories
Limitation: data collected involved individuals who have most likely had some experience or knowledge of breastfeeding
Two key events that marked the history of child maltreatment recognition
"The Battered Child Syndrome" Article
Starting in the 1970 every state required medical professionals to report children who showed possible signs of mistreatment
1974 "Child Abuse Prevention & Treatment Act" was enacted to help individuals identify and report child abuse and to provide shelter and other protective services to victims
Types of child maltreatment
Sexual abuse
Physical abuse
Emotional abuse
Examples of Austin’s risk and protective factors
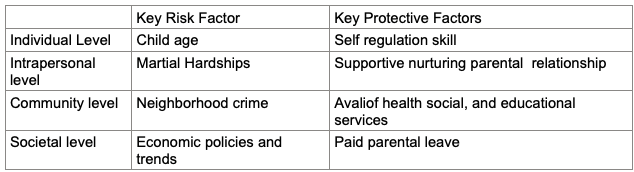 |
What is the Protecting Our Students Act of 2023
Prohibit corporal punishment in schools that receive federal funding
Bill establishes enforcement provisions, including a private right of action for students subjected to corporal punishment
What groups of individuals are most at risk for experiencing abuse?
children 0-3 yrs old
children with disabilities
Spectrum of neglect
Occasional inattention
Chronic under-stimulation
Severe neglect in the family context
Severe neglect in institutional setting
Strategies to prevent child maltreatment (socioecological model)
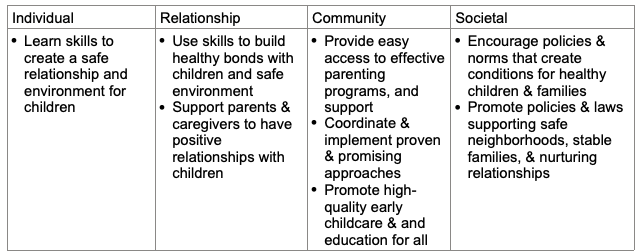
Evidence-based programs for preventing child maltreatment
Nurse family partnership
First-time disadvantaged mothers received home visits from nurses
Early/Head start
Family Services
Education services
Health services
Nutrition Services
Special needs services
Triple P Positive Parenting Program
Multilevel system of family intervention
Aims to prevent severe emotional and behavioral disturbances in children
Abusive head trauma education programs
Enhanced pediatric care