Oxygen-Containing Organic Compounds
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Alcohol
hydroxyl group (OH: polar) bonded to carbon chain
How is methanol obtained?
pyrolysis (thermal decomposition of wood at high temperatures in absence of oxygen)
What are the properties of methanol?
colourless, odourless, liquid at rtp
toxic - can cause blindness and death if ingested
What are the uses of methanol
common solvent (e.g. perfumes)
industrial starting material
fuel for car racing
properties of ethanol
colourless, odourless, liquid at rtp
toxicity - can ingest small amount, if blood conc. >1% → coma and death
Uses of ethanol
alcoholic beverages
perfume/lotion solvent
industrial starting material
How is alcohol obtained
Hydration of alkenes
- alkene + H2O(steam) -- alcohol (may have >1 possible structure)
- conditions: 300C, 60-70atm, H3PO4 catalyst
Fermentation (ethanol)
- C6H12O6 -- 2CH3CH2OH + 2CO2
- requires yeast enzymes
- waste product of yeast metabolism (anaerobic respiration)
Alcohol to alkene
alcohol -- alkene + H2O
- dehydration, removes OH group and H from adjacent carbon
- Conditions: 180C, excess conc H2SO4
What is a phenol
Hydroxyl group (OH) bonded to benzene ring
Properties of phenols
colourless solid
weak acid
low melting point
What are the properties of alcohols (boiling point and solubility)
boiling point
increases as chain length increases (LDF)
higher than alkane (HB), difference decreases (LDF)
Solubility
1-4: Highly soluble
5-7: Moderately soluble
>7: Slightly soluble/insoluble
Classifying alcohols
no of alkyl groups attached to C which is bonded to OH (methyl, primary, secondary, tertiary)
Nomenclature of alcohols
Find longest C chain with -OH
replace -e with -ol (keep -e for diol/triol)
number
indicate -OH position on parent chain
name and number substituents
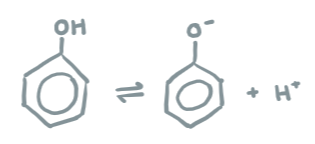
Dissociation of phenols
C6H5-OH <> C6H5O- + H+
resonance makes ring stable
phenoxide allows more resonance - stable
Phenol examples
Cresol - antiseptic
Hexylresorcinol - lozenge
Pentachlorophenol - wood preservative
Salicylic acid - anti-inflammatory
Carboxylic acid formation
alcohol + 2[O] → carboxylic acid + H2O
- oxidation
- conditions: acidified KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7
- color change: purple → colourless or orange → green
![<p>alcohol + 2[O] → carboxylic acid + H<sub>2</sub>O</p><p>- oxidation</p><p>- conditions: acidified KMnO<sub>4</sub> or K<sub>2</sub>Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub></p><p>- color change: purple → colourless or orange → green</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5bf0fde3-4b60-4cb5-ac9c-2fdac4d66af0.png)
Oxidation of secondary alcohols
alcohol + [O] → ketone + water
conditions: acidified KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7
![<p>alcohol + [O] → ketone + water</p><ul><li><p>conditions: acidified KMnO<sub>4</sub> or K<sub>2</sub>Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b39cd168-1be5-453d-9f66-769b2ab2326b.png)
Oxidation of tertiary alcohols
cannot be oxidised
Dissociation of carboxylic acids
RCOOH → RCOO- + H+
Nomenclature of carboxylic acids
Find longest C chain with -OH
replace -e with -oic acid (keep -e for multiple)
Number carboxyl group as 1
name and number substituents
Aliphatic
with carbon chain
aromatic
with benzene
When does carboxylic acid undergo neutralisation
with reactive metals, bases & carbonates
completely neutralised by strong bases/carbonates
qualitative test
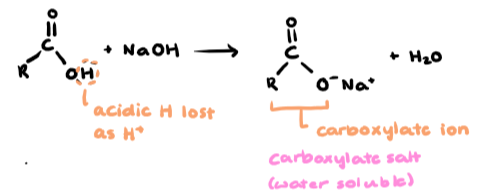
Uses of salts of carboxylic acids (carboxylate salt)
Food preservatives
inhibit bacteria, fungi and microorganism growth to slow food spoilage
calcium propanoate prevents bread mould
MSG - monosodium glutamate
flavour enhancer
Natural sources of carboxylic acids
methanoic acid - ants
ethanoic acid - vinegar
oxalic acid (ethanedioic acid)
Lactic acid - yoghurt
Citric acid - citrusy fruits
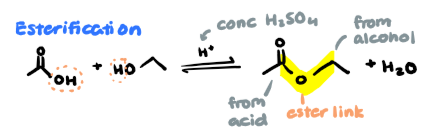
Esterification
carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + water
conditions: conc. H2SO4
done in reflux (force vapour to condense back)
note position of ester link (especially in polyesters)
Uses of esters
Fruity flavours for sweets, drinks, cakes
Solvent for organic compounds (e.g. in glue, varnishes, paints)
Properties of ester
Pleasant odour
Slightly polar; low molecular weight esters are water soluble
Volatile
Nomenclature of esters
Alkyl portion of alcohol in front
Replace -oic acid → -oate
e.g. ethanol + butanoic acid → ethyl butanoate
Application of esterification
Fats and oils - naturally occurring esters
energy storing compound by plants & animals
lipids - insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvent
tri-esters glycerol and fatty acids (condensation)
Polyesters - condensation polymerisation
1 monomer - 1 alcohol, 1 carboxylic acid end
2 monomers - alcohol (2 alcohol ends) and carboxylic acid (2 carboxylic acid ends)
water also formed; if C chain <5C, may form ring
terylene
Polyester, used in clothing, curtains, sleeping bags
Fibres of terylene + cotton → polyester-cotton
Condensation of ethane-1,2-diol and benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid