Chapter 5: Electron Structure, ionic bonding, and covalent bonding
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
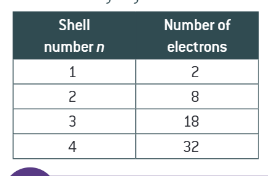
maximum number of electrons in the first four shells:
shells are also known as…
energy levels
formula for working out the maximum number of electrons in a shell:
2n2
what is an orbital?
a region around the nucleus that can hold up to 2 electrons, with opposite spins
how many electrons can an orbital hold?
2
what are the 4 different kinds of orbital?
s-,p-,d-,f-
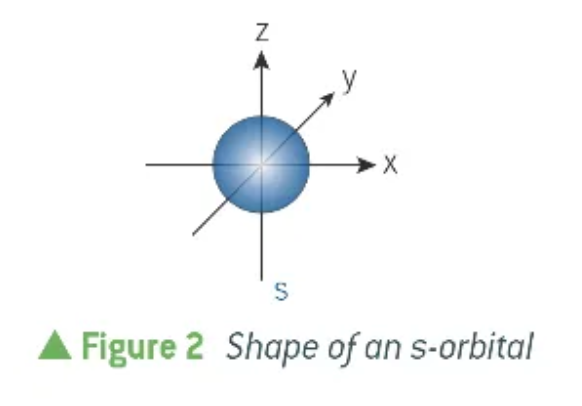
what shape is an s-orbital?
spherical
what shape is a p-orbital?
dumbbell
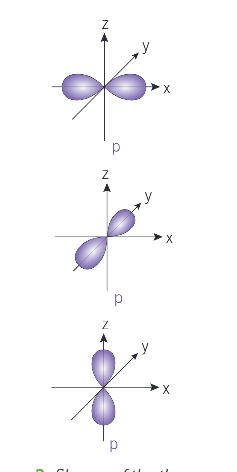
from n = 2, how many separate p-orbitals are there in each shell?
3
each shell from n = 3 contains how many d orbitals?
5
each shell from n = 4 contains how many f orbitals?
7
draw a diagram to show was orbitals, electrons, subshells, and principal quantum numbers are:
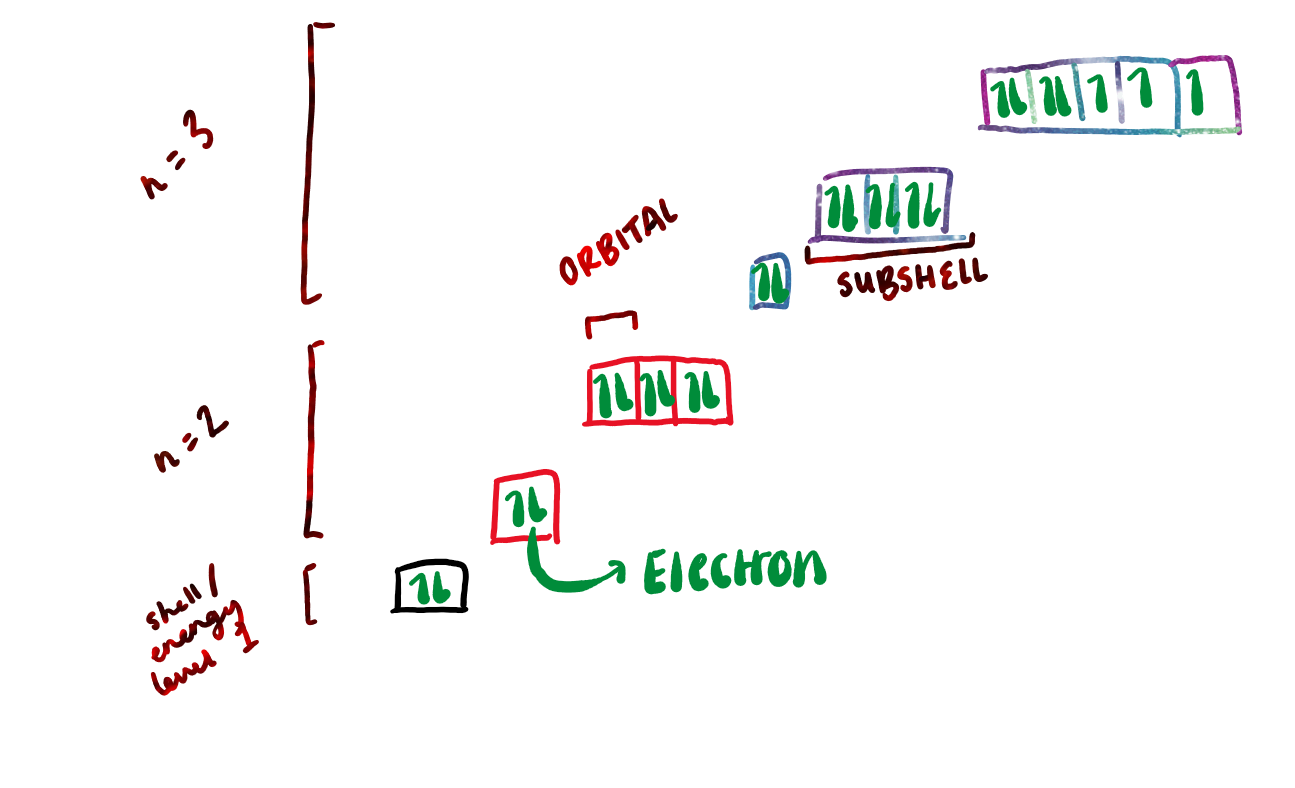
what are subshells?
orbitals of the same type are grouped together as subshells
electrons in the same orbital must have…
opposite spins → helps to counteract the repulsion between the negative charges of the 2 electrons.
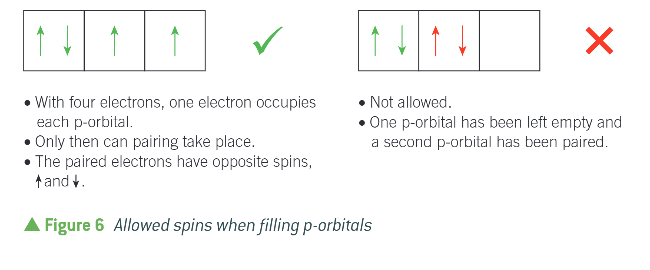
how do electrons fill up orbitals in sub shells?
by having one in each orbital before putting them in the same orbital
(bus analogy)
which is the higher energy level? 3d or 4s??
3d !! 4s fills up before → when written out, it is fine to put 3d before it though.
shorthand electron configuration:
[previous noble gas in square brackets] continued notation
![<ul><li><p>[previous noble gas in square brackets] continued notation </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5bab1879-f4bd-4920-8b08-a3bfd1152bce.png)
with the 4s and 3d sub-shells, it is a case of…
first in, first out:
the 4s electrons are first in
the 4s electrons are first out
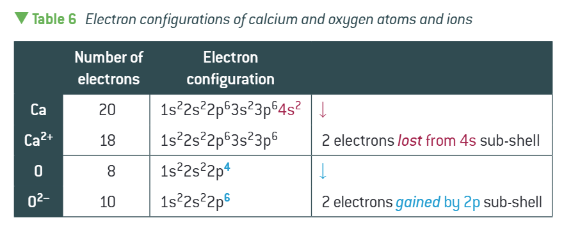
an ionised element will have the same electron configuration as…
a different element
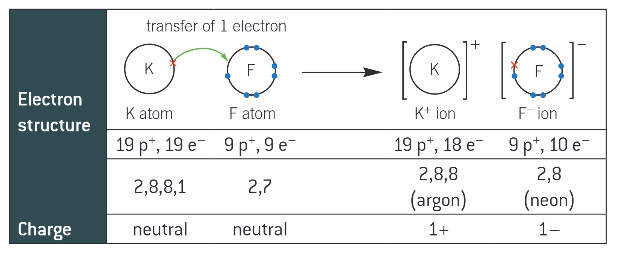
def. ionic bonding:
the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions
draw the ionic bonding for KF
what is a giant lattice structure??
a huge structure, where the atoms are innumerable:
each ion is surrounded by oppositely charged ions, forming a giant ionic lattice
ionic compounds solubility:
dissolve in polar solvents
water molecules attract + surround ions
ionic lattice is broken down
compounds with large charges may not break down → attraction too strong in lattice
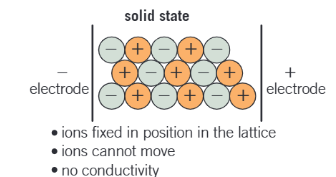
why can’t ionic compounds conduct electricity in solid states?
ions are fixed in a position in the giant ionic lattice
there are no mobile charge carriers
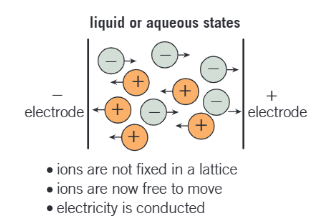
why are ionic compounds able to conduct electricity in liquid/dissolved in water?
solid ionic lattice breaks down
the ions are now free to move as mobile charge carriers
covalent bond def.
the overlap of atomic orbitals, each containing one electron, to give a shared pair of electrons.
what is a lone pair:
a pair of electrons that are not in a covalent bond
how many covalent bonds do carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen form?
carbon forms 4 bonds
nitrogen forms 3 bonds
oxygen forms 2 bonds
hydrogen forms 1 bond
what is the expansion of the octet?
available from the n = 3 shell, there can be more than 8 electrons in the outer shell:
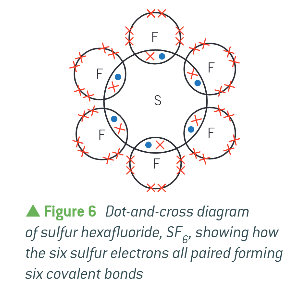
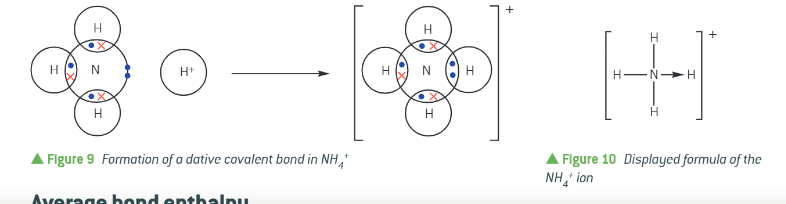
what is a dative covalent bond?
originally a lone pair
both electrons are supplied by the same atom