2A - Periodicity
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
How is the period table arranged?
By atomic (proton) number
What do all elements in a period have in common?
Same number of electron shells
What do all elements in a group have in common?
They have the same number of electrons in their outer shell
How is the periodic table split up?
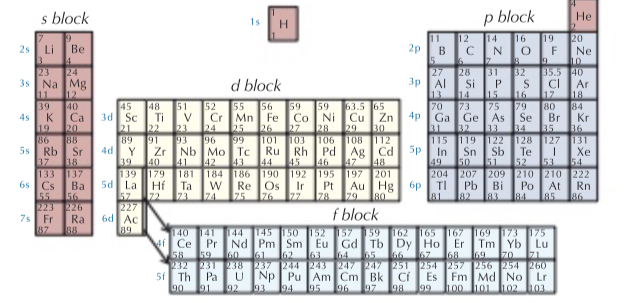
What happens to atomic radius across a period?
Decrease as the number of protons increases, the nuclear charge increases, the electrons on the outer shell are pulled closer to the nucleus (extra electrons don’t really effect)
What happens to melting points as you go across period 3? (Broad)
Increasing reaching peak at Si and then decreases
Why does sodium, magnesium and aluminium have a high melting point?
Metallic bonding which gets stronger as the metal ion has increasing positive charge so an increased number of delocalised electrons and stronger attraction
Why does silicon have the highest melting point?
Macromolecular with strong covalent bonds that a lot of energy is needed to overcome
What is the formula of phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine and argon?
P4
S8
Cl2
Ar
Why do phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine and argon have the lowest m.p.?
Molecular substances held together by van der waals (sulfur is the largest so has the highest)
What is the first ionisation energy?
The energy needed to remove 1 electron from each atom in 1 mol of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions
What happens to the first ionisation energy as you go across the period 3?
Increase because of increase in attraction between the outer shell electrons and the nucleus due to the increase in protons