MODULE 6 - QC 2
1/298
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
299 Terms
Method of analysis: More accurate and precise
Classical/Wet method
Method of analysis: Faster and can analyze trace amounts of analyte
Instrumental
Method of analysis: used for identification and characterization (describing a specific quality or attribute)
Qualitative analyses
Method of analysis: used for measurement and quantification (determining the amount of substance or analyte)
Quantitative analyses
Produces a signal that reflects presence and usually the concentration of the analyte (light source/energy source + sample/chemical system)
Signal generator
The type of signal generated by the interaction of light with sample matter
Analytical signal
Part of the analytical instrument that converts one kind of energy to another. Receives the analytical signal then converts it into an electrical signal that can be processed
Input transducer/detector
Modifies the transduced signal to make it more convenient for the operation of the readout device
Signal processor
Signal is magnified/increased
Amplification
Signal is reduced/decreased
Attenuation
Unwanted noise is removed/reduced from the signal
Filtration
Converts a processed signal to a signal that is understandable by a human operator. Examples: analog meter, digital meter, computer monitor
Readout device
Complete system of energy propagated in a wave form
Electromagnetic spectrum
EM waves: 200-380 nm
UV
EM waves: 380-780 nm
Visible light
EM waves: 200-780 nm
UV-Vis
The electromagnetic spectrum is composed of 2 waves propagated at a ___ angle to each other towards the direction of the light
right angle
Vertical wave in EM spectrum
Electric wave
Horizontal wave in EM spectrum
Magnetic wave
Relationship of frequency and wavelength (direct/indirect)
Indirectly proportional
Velocity of light
3 × 1010cm/sec
1 micrometer = __ cm
10-4 cm
1 nm or millimicron = ___ cm
10-7 cm
1 angstrom = ___ cm
10-8 cm
1 cps/Hz = ___ ergs
107 ergs
1 electron volt (eV) = _____ J
1.6 × 1019 J
Planck’s constant
6.62 × 10-34 Js
Spectroscopic methods: UV-Visible
Absorption
Spectroscopic methods: Fluorometry
Emission
Spectroscopic methods: Turbidimetry
Scattering
Spectroscopic methods: Refractometry
Refraction
Spectroscopic methods: Molecular emission spectroscopy
Emission
Spectroscopic methods: Nephelometry
Scattering
Spectroscopic methods: Atomic absorption spectroscopy
Absorption
Spectroscopic methods: Atomic emission spectroscopy
Emission
Spectroscopic methods: Polarimetry
Rotation
Spectroscopic methods: Nuclear magnetic resonance
Absorption
Spectroscopic methods: X-ray and electron diffraction
Diffraction
Spectroscopic methods: Infrared radiation
Absorption
Chromatographic methods (2)
Gas chromatography, HPLC
Electrochemical methods: Electric potential
Potentiometry
Electrochemical methods: Electric current
Polarography
Electrochemical methods: Electric charge
Coulometry
Miscellaneous methods: Mass-to-charge
Mass spectrometry
Miscellaneous methods: Radioactivity
Radioactive emissions
A general term for the science that deals with the interactions of various types of radiation with matter
Spectroscopy
Refer to the measurement of the intensity of radiation with a photoelectric transducer or other type of electronic device
Spectrometry
A branch of spectrometry which embraces the measurement of the absorption, by chemical species, of radiant energy of definite and narrow wavelength, approximating monochromatic radiation
Spectrophotometry
A branch of spectrometry in which absorption measurement is made in the visible region of the spectrum
Colorimetry
Instruments designed to measure radiant power with the aid of filter, instead of prism or diffraction grating, for the purpose of increasing the sensitivity of the measurement
Colorimeter/Flame photometer
Transition from a lower level to a higher level with transfer of energy from radiation field to an absorber
Absorption
Functional group which absorbs radiant energy in the UV or visible regions of the spectrum
Chromophore

States that the power of transmitted radiant beam increases exponentially as the concentration of the solution containing the absorbing chemical species increases arithmetically
Beer’s law

States that the power of a transmitted radiant beam decreases exponentially as the thickness of the solution containing the absorbing chemical species increases arithmetically
Lambert’s law
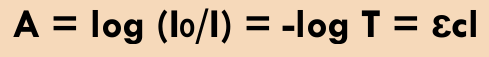
When an EMR with an intensity of Io impinges a solution of concentration c and pathlength l, its intensity is diminished in an exponential fashion (I)
Theory of absorptivity
Principle: The electrons in the bonds within the molecule become excited so that they occupy a higher quantum state and, in the process, absorb some of the energy passing through a solution (range 200-700 or 200-780 nm)
UV-Vis spectroscopy
UV-Vis: Source of light for visible light
Tungsten lamp
UV-Vis: Source of light for Ultraviolet
Deuterium, Hydrogen lamp
UV-Vis: Monochromator
Prism/grating
UV-Vis: Cuvette for UV-Vis
Quartz
UV-Vis: Cuvette for visible light only
Optical glass, plastic
Applications of UV-Vis: ____ of drugs in formulations
Quantification
Applications of UV-Vis: Determination of ___ values, ____ and ___ of drugs
pKa, partition coefficient, solubility
Applications of UV-Vis: Part of _____ testing
Dissolution
Applications of UV-Vis: Used in monitoring the reaction kinetics of ____
drug degradation
Applications of UV-Vis: Pharmacopoeial identity checks (___ spectrum)
UV
Summary of UV-Vis applications: IPQD
Identity, pKa-partition coefficient, quantification, dissolution-degradation kinetics
Plot of absorbance readings of the analyte versus the wavelength. Used to determine the wavelength at which maximum absorption occurs (Amax)
Spectral absorbance/Absorbance spectrum
Plot of absorbance values against a series of known solute concentrations. Should yield a straight line. Used to determine the unknown solute concentration
Beer’s plot
Involves measurement of the absorption of EM radiation over the wavenumber range of 4000-400 cm-1 (2.5-25 um, or 2500-25000nm) caused by promotion of molecules from the ground state of their vibrational modes to an excited vibrational state.
IR-Spectrophotometry
IR: Sample is contained within discs or cells made of alkali metal halides: _____ or _____
KCl or NaCl
IR: 50-1000 um
Far IR
IR: 2.5-50 um
Middle IR
IR: 0.8-2.5 um
Near IR
IR: Makes use of monochromator to select each wavenumber in turn in order to monitor its intensity after the radiation has passed through the sample
Dispersive
IR: Makes use of an interferometer that generates a radiation source in which individual wave numbers can be monitored within 1s pulse radiation without dispersion being required
Fourier transform
IR: Solid sample is prepared by grinding with a mulling agent (mineral oil/Nujol) in a mortar or pestle to a fine paste. The paste is placed on a plate and covered with another.
Mull technique
IR: Solid sample preparation by suspending in KBr pellet and prepared under high pressure
Pellet technique
IR: Solid sample is prepared by cutting into sheets of suitable thickness with a microtome or melted at low heat and allowed to dry as a film.
Film technique
IR: Solid sample is prepared by dissolving in a suitable solvent and used as a liquif sample
Solution technique
IR Applications: Qualitative ___ check for the identity of raw materials and for identifying drugs
Fingerprint
IR Applications: ___ of samples in the solid and semi-solid dosage forms
Characterization
IR Applications: Detection of ___ of drugs
Polymorphs
IR Applications: ____ for films, coatings, and packaging plastics
Fingerprint test
IR Applications Summary: PFC
Polymorphs, fingerprinting, characterization
IR: Region for identification
3-15 um
IR: Group frequency region (4000 to 1500cm-1)
3-8 um
IR: Fingerprint region (1500 to 500 cm-1)
8-15 um
Principle: Metal atoms are volatilized in a flame and their absorption of a narrow bond of radiation produced by a hollow cathode lamp, coated with the particular metal being determined is measured
Atomic absorption spectrophotometer
AAS: Instrument/energy source unique to the AAS for the analysis of metals
Hollow cathode lamp
AAS Applications: Determination of ____ in drugs remaining from the manufacturing process
Metal residues
AAS Applications: Analysis of trace ___ in multivitamin preparations
Minerals
Principle: Radiation in the radiofrequency region is used to excite atoms, usually protons or carbon-13 atoms, so that their spins switch from being aligned with to being aligned against an applied magnetic field.
Nuclear magnetic resonance
NMR Principle summary: NMR
Nuclei 13C and 1H, Magnetic field, Radiofrequency region
NMR Applications: Powerful technique for the characterization of the ___ of raw materials and finished products
Exact molecular structure
NMR Applications: Can determine impurities, including __, without separation down to approximately 10% level
Enantiomeric impurities
Transition from a higher level to a lower level, and the radiation is transferred to the radiation field
Emission
Emission if no radiation is emitted
Nonradioactive decay
Principle Certain molecules, particularly those with a chromophore and a rigid structure, can be excited by a UV/Visible radiation, and will then emit the radiation absorbed at a longer wavelength. The radiation emitted can then be measured. Requires chromophore AND rigid structure.
Molecular emission spectroscopy