ASCP BOC Hematology
1/393
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
394 Terms
1. The light-colored zone adjacent to the nucleus in a plasmacyte is the:
A. Ribosome
B. Chromatin
C. Mitochondria
D. Golgi area
Correct Answer: D
2. The following are compounds formed in the synthesis of heme:
1. coproporphyrinogen
2. porphobilinogen
3. uroporphyrinogen
4. protoporphyrinogen
A. 4,3,1,2
B. 2,3,1,4
C. 4,2,3,1
D. 2,1,3,4
Correct Answer: B
3. The majority of the iron in an adult is found as a constituent of:
A. hemoglobin
B. hemosiderin
C. myoglobin
D. transferrin
Correct Answer: A
4. The main function of the hexose monophosphate shunt in the erythrocyte is to:
A. regulate the level of 2,3-DPG
B. provide reduced glutathione to prevent oxidation of hemoglobin
C. prevent the reduction of heme iron
D. provide energy for membrane maintenance
Correct Answer: B
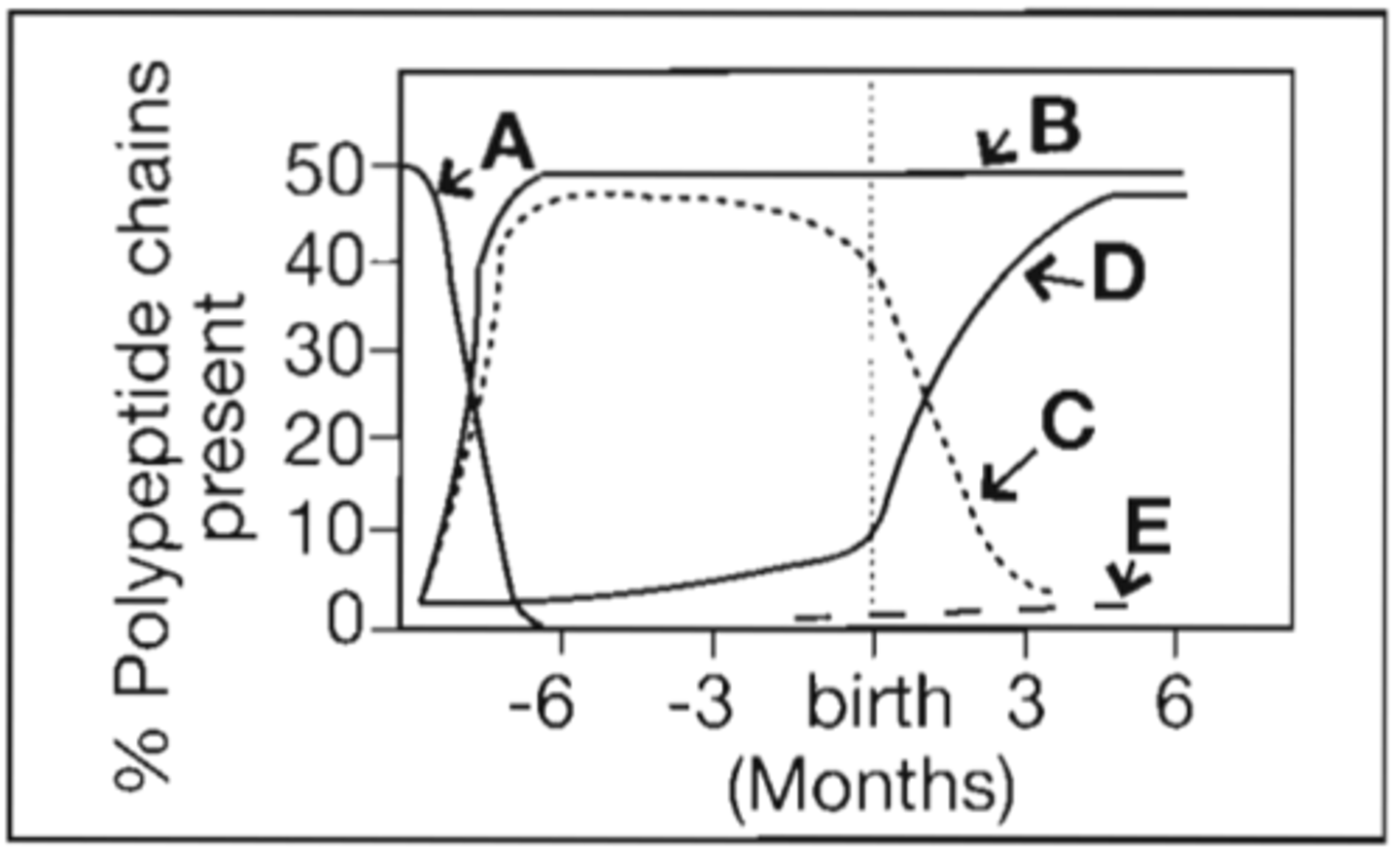
5. Refer to the following illustration:
Which curve represents the production of alpha polypeptide chains of hemoglobin?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
Correct Answer: B
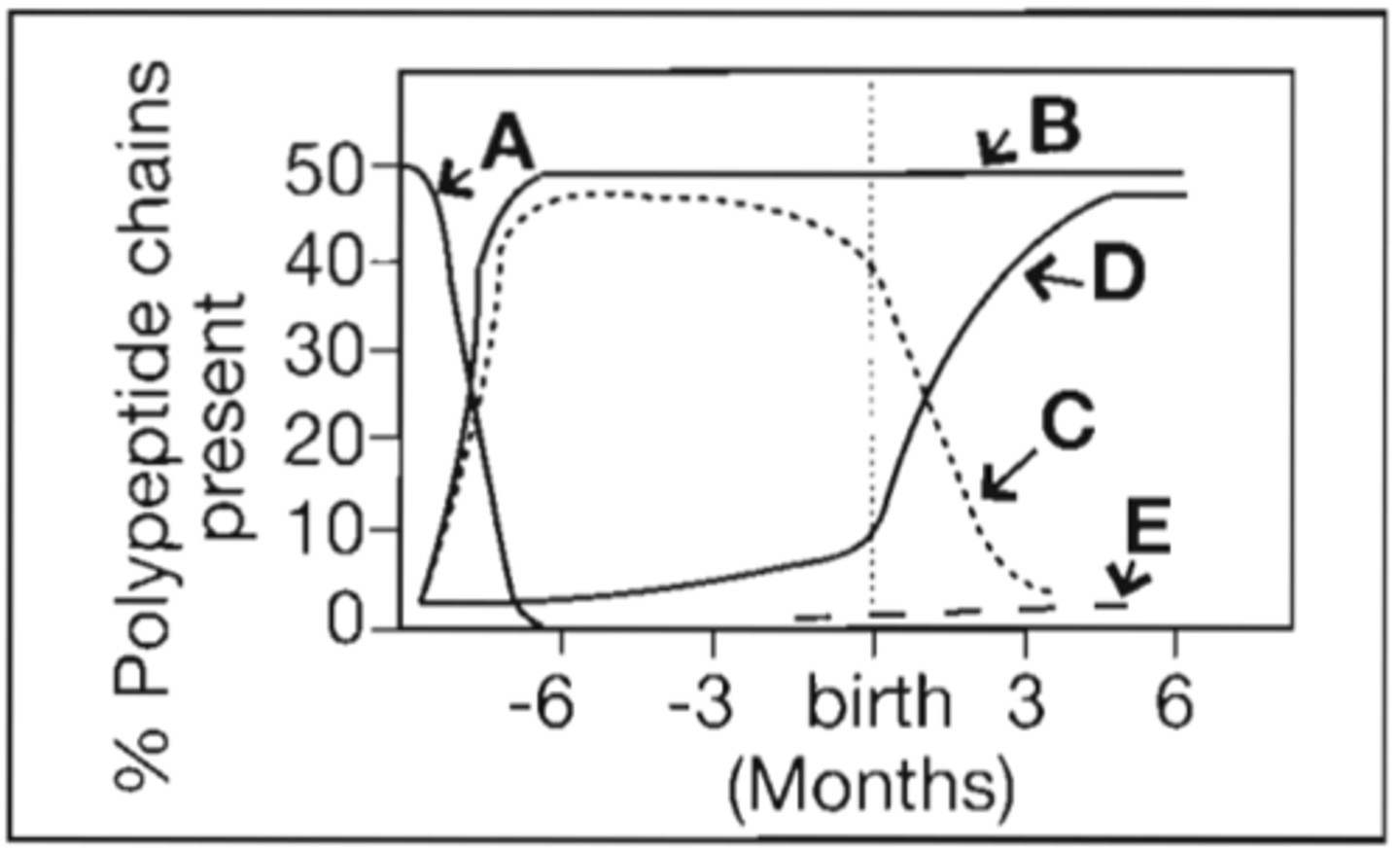
6. Refer to the following illustration:
Which curve represents the production of beta polypeptide chains of hemoglobin?
A. B
B. C
C. E
D. D
Correct Answer: D
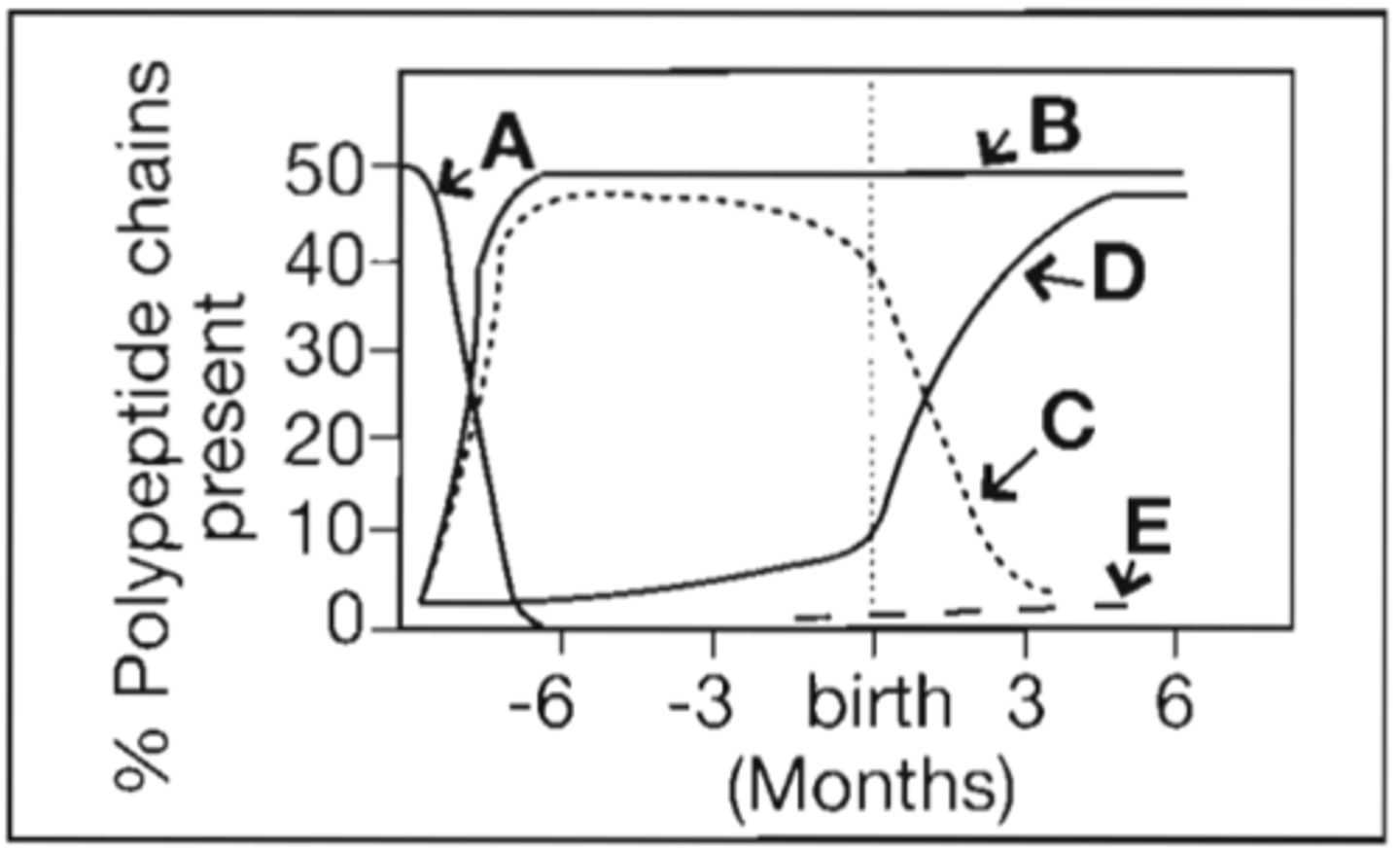
7. Refer to the following illustration:
Which curve represents the production of gamma polypeptide chains of hemoglobin?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
Correct Answer: C
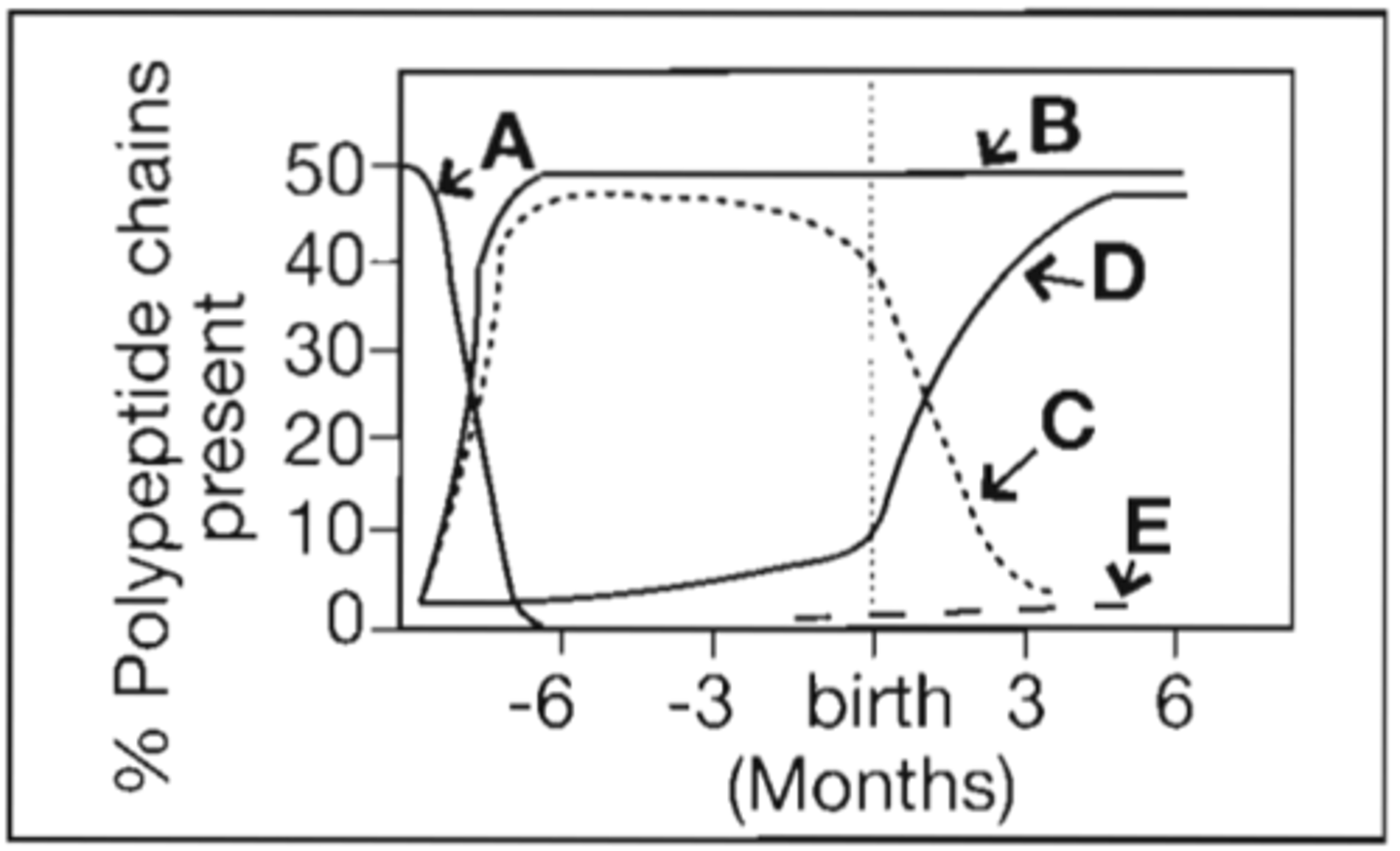
8. Refer to the following illustration:
Which curve represents the production of delta polypeptide chains of hemoglobin?
A. B
B. C
C. D
D. E
Correct Answer: D
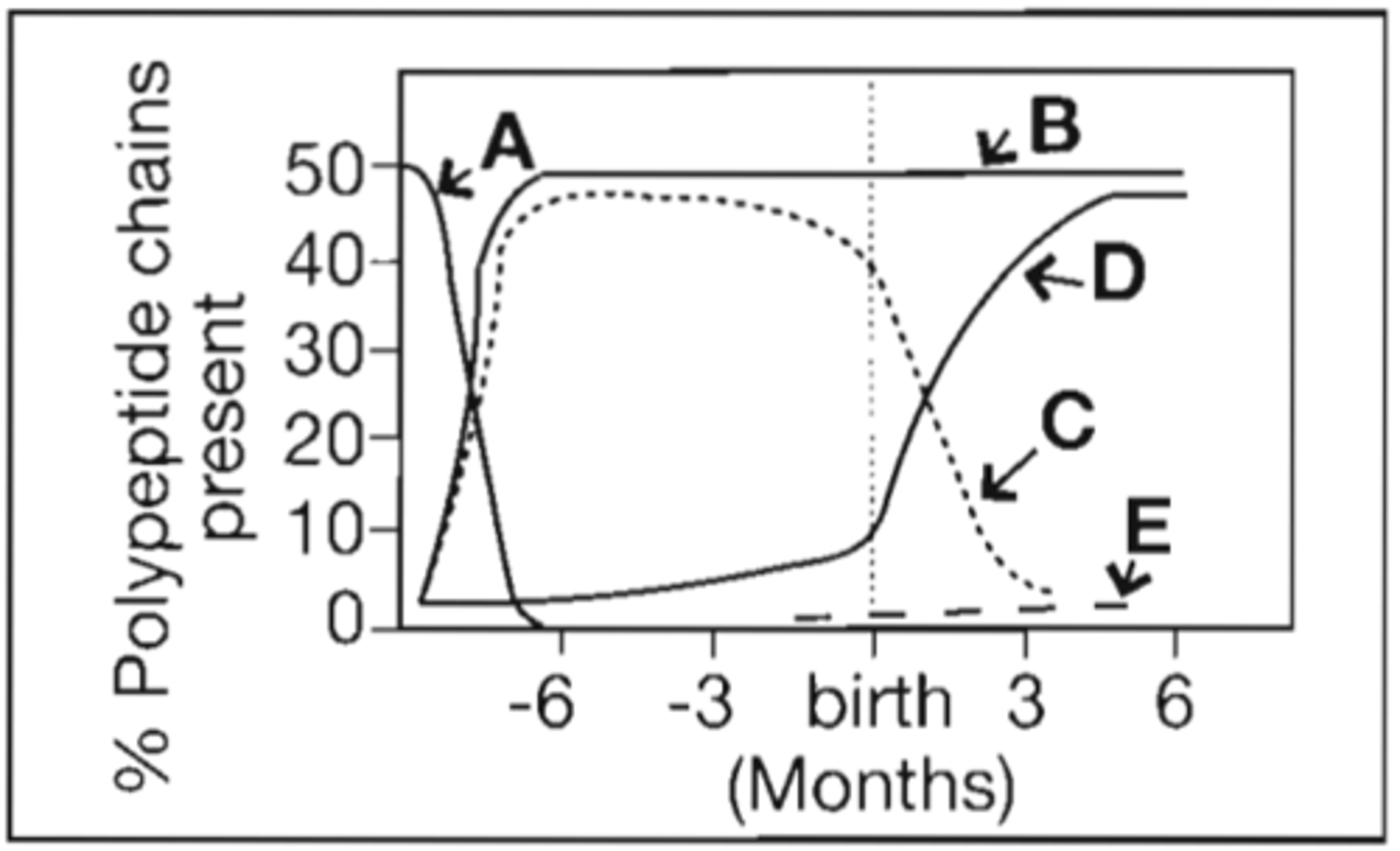
9. Refer to the following illustration:
Which curve represents the production of epsilon polypeptide chains of hemoglobin?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
Correct Answer: A
10. In order for hemoglobin to combine reversibly with oxygen, the iron must be:
A. complexed with haptoglobin
B. freely circulating in the cytoplasm
C. attached to transferrin
D. in the ferrous state
Correct Answer: D
11. In which of the following disease states are teardrop cells and abnormal platelets most characteristically seen?
A. hemolytic anemia
B. multiple myeloma
C. G-6-PD deficiency
D. myeloid metaplasia
Correct Answer: D
12. The characteristic erythrocyte found in pernicious anemia is:
A. microcytic
B. spherocytic
C. hypochromic
D. macrocytic
Correct Answer: D
13. In the normal adult, the spleen acts as a site for:
A. storage of red blood cells
B. production of red blood cells
C. synthesis of erythropoietin
D. removal of imperfect and aging cells
Correct Answer: D
14. After the removal of red blood cells from the circulation hemoglobin is broken down into:
A. iron, porphyrin, and amino acids
B. iron, protoporphyrin, and globin
C. heme, protoporphyrin, and amino acids
D. heme, hemosiderin, and globin
Correct Answer: B
15. Heinz bodies are:
A. readily identified with polychrome stains
B. rarely found in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient erythrocytes
C. closely associated with spherocytes
D. denatured hemoglobin inclusions that are readily removed by the spleen
Correct Answer: D
16. Hemolysis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is:
A. temperature-dependent
B. complement-independent
C. antibody-mediated
D. caused by a red cell membrane defect
Correct Answer: D
17. Cells for the transport of O2 and CO2 are:
A. erythrocytes
B. granulocytes
C. lymphocytes
D. thrombocytes
Correct Answer: A
18. Erythropoietin acts to:
A. shorten the replication time of the granulocytes
B. stimulate RNA synthesis of erythroid cells
C. increase colony-stimulating factors produced by the B-lymphocytes
D. decrease the release of marrow reticulocytes
Correct Answer: B
19. What cell shape is most commonly associated with an increased MCHC?
A. teardrop cells
B. target cells
C. spherocytes
D. sickle cells
Correct Answer: C
20. Which of the following is most closely associated with idiopathic hemochromatosis?
A. iron overload in tissue
B. target cells
C. basophilic stippling
D. ringed sideroblasts
Correct Answer: A
21. A patient with polycythemia vera who is treated by phlebotomy is most likely to develop a deficiency of:
A. iron
B. vitamin B12
C. folic acid
D. erythropoietin
Correct Answer: A
22. The direct antiglobulin test is often positive in:
A. congenital hemolytic spherocytosis
B. march hemoglobinuria
C. acquired hemolytic anemia
D. thalassemia major
Correct Answer: C
23. The anemia of chronic infection is charaterized by:
A. decreased iron stores in the reticuloendothelial system
B. decreased serum iron levels
C. macrocytic erythrocytes
D. increased serum iron binding capacity
Correct Answer: B
24. Factors commonly involved in producing anemia in patients with chronic renal disease include:
A. marrow hypoplasia
B. inadequate erythropoiesis
C. vitam B12 deficiency
D. increased erythropoietin production
Correct Answer: B
25. A 20-year-old woman with sickle cell anemia whose usual hemoglobin concentration is 8 g/dL (80 g/L) develops fever, increased weakness and malaise. The hemoglobin concentration is 4 g/dL (40 g/L) and the reticulocyte count is 0.1%. The most likely explanation for her clinical picture is:
A. increased hemolysis due to hypersplenism
B. aplastic crisis
C. thrombotic crisis
D. occult blood loss
Correct Answer: B
26. The hypoproliferative red cell population in the bone marrow of uremic patients is caused by:
A. infiltration of bone marrow by toxic waste products
B. decreased levels of circulating erythropoietin
C. defective globin synthesis
D. overcrowding of bone marrow space by increased myeloid precursors
Correct Answer: B
27. Which of the following characteristics are common to hereditary spherocytosis, hereditary elliptocytosis, hereditary stomatocytosis, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria?
A.autosomal dominant inheritance
B. red cell membrane defects
C. positive direct antiglobulin test
D. measure platelet count
Correct Answer: B

28. A 89-year-old Caucasian female was transferred to the hospital from a nursing facility for treatment of chronic urinary tract infection with proteinuria. The patient presented with the following laboratory data:
-WBC 10x10^3/uL
-RBC 3.1x10^6/uL
-Hgb 7.2 g/dL (72g/L)
-Hct 24%
-MCV 78um^3 (78fL)
-MCH 23 pg
-MCHC 31%
-Serum iron: 29 ug/dL (5.2 umol/L)
-TIBC: 160 ug/dL (28.6 umol/L)
-serum ferritin: 100ng/mL
These data are most consistent with which of the following conditions?
A. iron deficiency anemia
B. anemia of chronic inflammation
C. hemochromatosis
D. acute blood loss
Correct Answer: B

29. A patient is admitted with a history of chronic bleeding secondary to peptic ulcer. Hematology workup reveals a severe microcytic, hypochromic anemia. Iron studies were requested. Which of the following would be expected in this case?
Serum iron, TIBC, Storage iron
-Result A: dec inc inc
-Result B: inc dec inc
-Result C: dec inc dec
-Result D: inc nL dec
A. result A
B. result B
C. result C
D. result D
Correct Answer: C
30. Which of the following is most closely associated with iron deficiency anemia?
A. iron overload in tissue
B. target cells
C. basophilic stippling
D. chronic blood loss
Correct Answer: D
31. Which one of the following hypochromic anemias is usually associated with a normal free erythrocyte protoporphyrin level?
A. anemia of chronic disease
B. iron deficiency
C. lead poisoning
D. thalassemia minor
Correct Answer: D
32. Evidence indicates that the genetic defect in thalassemia usually results in:
A. the production of abnormal globin chains
B. a quantitative deficiency in RNA resulting in decreased globin chain production
C. a structural change in the heme portion of the hemoglobin
D. an abnormality in the alpha- or beta- chain binding or affinity
Correct Answer: B
33. A 20-year-old African-American man has peripheral blood changes suggesting thalassemia minor. The quantitative hemoglobin A2 level is normal, but the homoglobin F level is 5% (normal <2%). This is most consistent with:
A. alpha thalassemia minor
B. beta thalassemia minor
C. delta-beta thalassemia minor
D. hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin
Correct Answer: C
34. Anemia secondary to uremia characteristically is:
A. microcytic, hypochromic
B. hemolytic
C. normocytic, normochromic
D. macrocytic
Correct Answer: C
35. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings is consistent with hemolytic anemia?
A. normal or slightly increased erythrocyte survival; normal osmotic fragility
B. decreased erythrocyte survival; increased catabolism of heme
C.decreased serum lactate dehydrogenease activity; normal catabolism of heme
D. normal concentration of haptoglobin; marked hemoglobinuria
Correct Answer: B
36. An enzyme deficiency associated with a moderate to severe hemolytic anemia after the patient is exposed to certain drugs and characterized by red cell inclusions formed by denatured hemoglobin is:
A. lactate dehydrogenase deficiency
B. G-6-PD deficiency
C. pyruvate kinase deficiency
D. hexokinase deficiency
Correct Answer: B
37. Patients with A(-) type G-6-PD deficiency are least likely to have hemolytic episodes in which of the following situations?
A. following the administration of oxidizing drugs
B. following the ingestion of fava beans
C. during infections
D. spontaneously
Correct Answer: D
38. A patient has a congenital nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia. After exposure to anti-malarial drugs the patient experiences a severe hemolytic episode. This episode is characterized by red cell inclusion caused by hemoglobin denaturation. Which of the following conditions is most consistent with these findings?
A. G-6-PD deficiency
B. thalassemia major
C. pyruvate kinase deficiency
D. paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Correct Answer: A
39. All of the findings listed below may be seen in acquired hemolytic anemias of the autoimmune variety. The one considered to be the most characteristic is:
A. increased osmotic fragility
B. leukopenia and thrombocytopenia
C. peripheral spherocytosis
D. positive direct antiglobulin test
Correct Answer: D
40. Peripheral blood smears from patients with untreated pernicious anemia are characterized by:
A. pancytopenia and macrocytosis
B. leukocytosis and elliptocytosis
C. leukocytosis and ovalocytosis
D. pancytopenia and microcytosis
Correct Answer: A
41. Laboratory tests performed on a patient indicate macrocytosis, anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. Which of the following disorders is the patient most likely to have?
A. anemia of chronic disorder
B. vitamin B12 deficiency
C. iron deficiency
D. acute heorrhage
Correct Answer: B

42. A patient has the following laboratory data:
-WBC 3.0x10^3/uL
-RBC 2.35x10^6/uL
-Plt 95.0 x10^3/uL (95.0 x 10^9/L)
-Hgb 9.5 g/dL (95 g/L)
-Hct 27%
-MCV 115 um^3 (115fL)
-MCH 40 pg
-MCHC 35%
Which of the following tests would contribute toward the diagnosis?
A. reticulocyte count
B. platelet factor 3
C. serum B12 and folate
D. leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
Correct Answer: C
43. The characteristic morphologic feature in folic acid deficiency is:
A. macrocytosis
B. target cells
C. basophilic stippling
D. rouleaux formation
Correct Answer: A
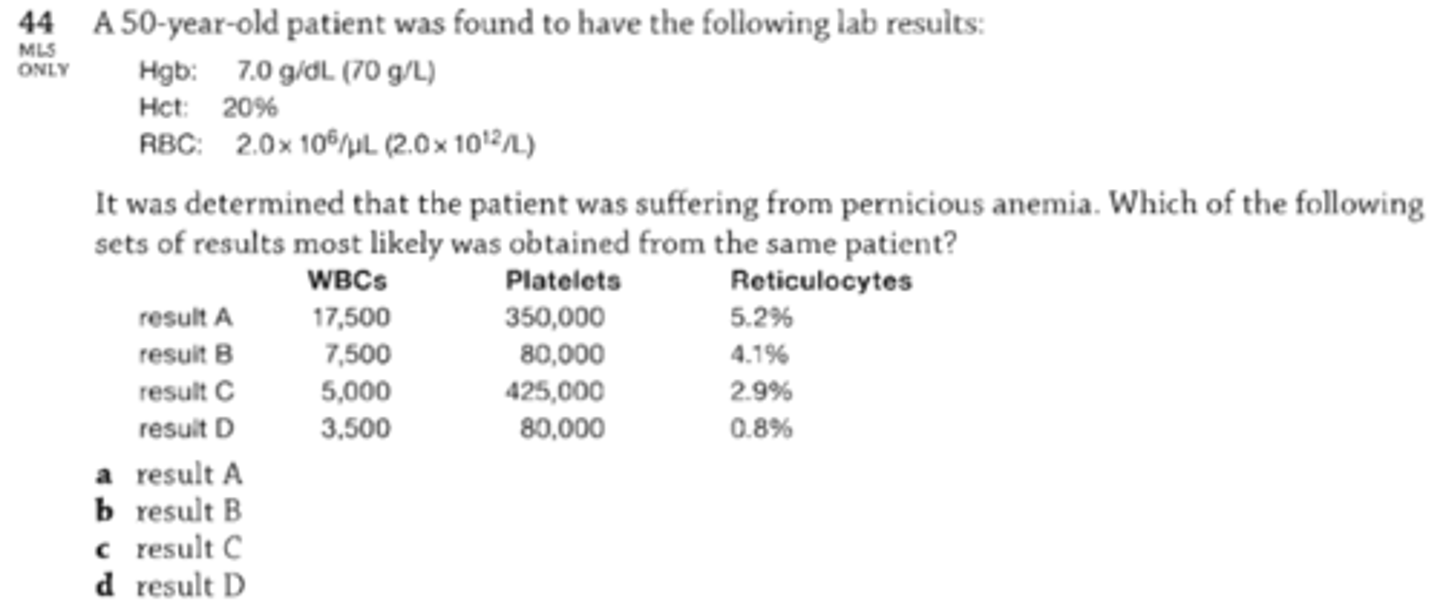
44. A 50-year-old patient was found to have the following lab results:
-Hgb 7.0 g/dL (70 g/L)
-Hct: 20%
-RBC 2.0 x 10^6/uL (2.0 x 10^12/L)
It was determined that the patient was suffering from pernicious anemia. Which of the following sets of results most likely was obtained form the same patient?
WBC Platelets Reticulocytes
-Result A: 17,500; 350,000; 5.2%
-Result B: 7,500; 80,000; 4.1%
-Result C: 5,000; 425,000; 2.9%
-Result D: 3,500; 80,000; 0.8%
A. result A
B. result B
C. result C
D. result D
Correct Answer: D
45. The most likely cause of the macrocytosis that often accompanies anemia of myelofibrosis is:
A. folic acid deficiency
B. increased reticulocyte count
C. inadequate B12 absorption
D. pyridoxine deficiency
Correct Answer: A
46. Megaloblastic asynchronous development in the bone marrow indicates which one of the following?
A. proliferation of erythrocyte precursors
B. impaired synthesis of DNA
C. inadequate production of erythropoietin
D. deficiency of G-6-PD
Correct Answer: B
47. Which of the following are found in association with megaloblastic anemia?
A. neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
B. decreased LD activity
C. increased erythrocyte folate levels
D. decreased plasma bilirubin levels
Correct Answer: A

48. Which of the following represents characteristic features of iron metabolism in patients with anemia of a chronic disorder?
Serum iron, Transferrin saturation, TIBC
-Result A: nL; nL; nL
-Result B: inc; inc; nL or slightly inc
-Result C: nL; markedly inc; nL
-Result D: dec; dec; nL or dec
A. result A
B. result B
C. result C
D. result D
Correct Answer: D
49. A characteristic morphologic feature in hemoglobin C disease is:
A. macrocytosis
B. spherocytosis
C. rouleaux formation
D. target cells
Correct Answer: D
50. Thalassemia are characterized by:
A. structural abnormalities in the hemoglobin molecule
B. absence of iron in hemoglobin
C. decreased rate of heme synthesis
D. decreased rate of globin synthesis
Correct Answer: D

51. A patient has the following blood values:
-RBC 6.5 x10^6/uL (6.5 x 10^12/L)
-Hgb 13.0 g/dL (130 g/L)
-Hct 39%
-MCV 65 μm^3 (65fL)
-MCH 21.5 pg
-MCHC 33%
These results are compatible with:
A. iron deficiency
B. pregnancy
C. thalassemia minor
D. beta thalassemia major
Correct Answer: C
52. Laboratory findings in hereditary spherocytosis do not include:
A. decreased osmotic fragility
B. increased autohemolysis corrected by glucose
C. reticulocytosis
D. shortened erythrocyte survival
Correct Answer: A
53. Which of the following types of polycythemia is a severely burned patient most likely to have?
A. polycythemia vera
B. polycythemia, secondary to hypoxia
C. relative polycythemia associated with dehydration
D. polycythemia associated with renal disease
Correct Answer: C
54. Which of the following is most likelyto be seen in lead poisoning?
A. iron overload in tissue
B. codocytes
C. basophilic stippling
D. ringed sideroblasts
Correct Answer: C
55. Giant, vacuolated, multinucleated erythroid precursors are present in which of the following?
A. chronic myelocytic leukemia
B. myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia
C. erythroleukemia
D. acute myelocytic leukemia
Correct Answer: C
56. Which of the following is a significant feature of erythroleukemia/acute erythroid leukemia (DiGuglielmo syndrome)?
A. persistently increased M:E ratio
B. megaloblastoid erythropoiesis
C. marked thrombocytosis
D. decreased ferritin levels
Correct Answer: B
57. The M:E ratio in erythroleukemia is usually:
A. normal
B. high
C. low
D. variable
Correct Answer: C
58. The characteristic morphologic feature in lead poisoning is:
A. macrocytosis
B. target cells (codocytes)
C. basophilic stippling
D. rouleaux formation
Correct Answer: C
59. Which of the following is increased in erythrocytosis secondary to a congenital heart defect?
A. arterial oxygen saturation
B. serum vitamin B12
C. leukocyte alkaline phosphatase activity
D. erythropoietin
Correct Answer: D
60. A 40-year-old man had an erythrocyte count of 2.5 x 10^6/uL (2.5 x 10^12/L), hematocrit of 22% and a reticulocyte count of 2.0%. Which of the following statements best describes his condition?
A. the absolute reticulocyte count is 50 x 10^3/uL (50 x 10^9/L), indicating that the bone marrow is not adequately compensating for the anemia
B. the reticulocyte count is greatly increased, indicating an adequate bone marrow response for this anemia
C. the absolute reticulocyte count is 500 x 10^3/uL (500 x 10^9/L), indicating that the bone marrow is adequately compensating for the anemia
D. the reticulocyte count is slightly increased, indicating an adequate response to the slight anemia
Correct Answer: A
61. Which of the following is characteristic of polycythemia vera?
A. elevated urine erythropoietin levels
B. increased oxygen affinity of hemoglobin
C. "teardrop" poikilocytosis
D. decreased or absent bone marrow iron stores
Correct Answer: D
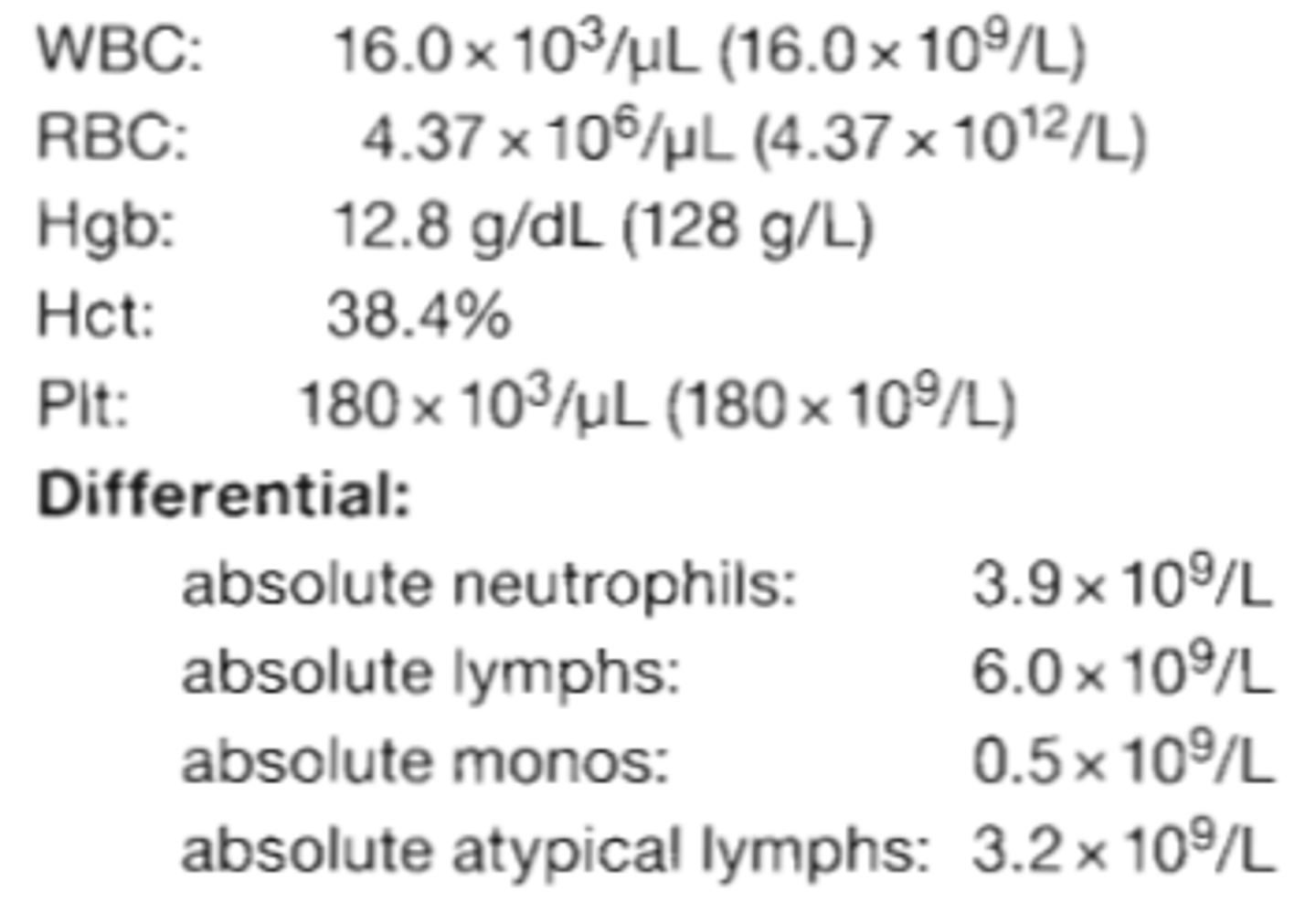
62. A 14-year-old boy is seen in the ER complaining of a sore throat, swollen glands and fatigue. The CBC results are:
- WBC 16.0 x 10^3/uL (16.0 x 10^9/L)
- RBC 4.37 x 10^6/uL (4.37 x 10^12/L)
-Hgb: 12.8 g/dL (128 g/L)
-Hct: 38.4%
-Plt: 180 x 10 ^3/uL (180 x 10^9/L)
Differential:
absolute neutrophils: 3.9 x 10^9/L
absolute lymphs: 6.0x 10^9/L
absolute monos: 0.5 x 10^9/L
absolute atypical lymphs 3.2 x10^9/L
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. acute lymphocytic leukemia
B. chronic lymphocytic leukemia
C. viral hepatitis
D. infectious mononucleosis
Correct Answer: D
63. Which of the following technical factors will cause a decreased erythrocyte sedimentation rate?
A. gross hemolysis
B. small fibrin clots in the sample
C. increased room temperature
D. tilting of the tube
Correct Answer: B
64. Which of the RBC indices is a measure of the amount of hemoglobin in individual red blood cells?
A. MCHC
B. MCV
C. Hct
D.MCH
Correct Answer: D
65. The RDW-CV and RDW-SD performed by automated cells counters are calculations that provide:
A. an index of the distribution of RBC volumes
B. a calculated mean RBC hemoglobin concentration
C. a calculate mean cell hemoglobin
D. the mean RBC volume
Correct Answer: A
66. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) can be falsely elevated by:
A. tilting the tube
B. refrigerated blood
C. air bubbles in the column
D. specimen being too old
Correct Answer: A

67. A Wright-stained peripheral smear reveal the following:
-Erythrocytes enlarged 1.5 x to 2x normal size
-Schuffner dots
-Parasites with irregular "spread-out" trophozoites, golden-brown pigment
-12-24 merozoites
-Wide range of stages
This is consistent with Plasmodium:
A. falciparum
B. malariae
C. ovale
D. vivax
Correct Answer: D
68. Which of the following is the formula for absolute cell count?
A. number of cells counted/ total count
B. total count/ number of cells counted
C. 10 x total count
D. % of cells counted x total count
Correct Answer: D
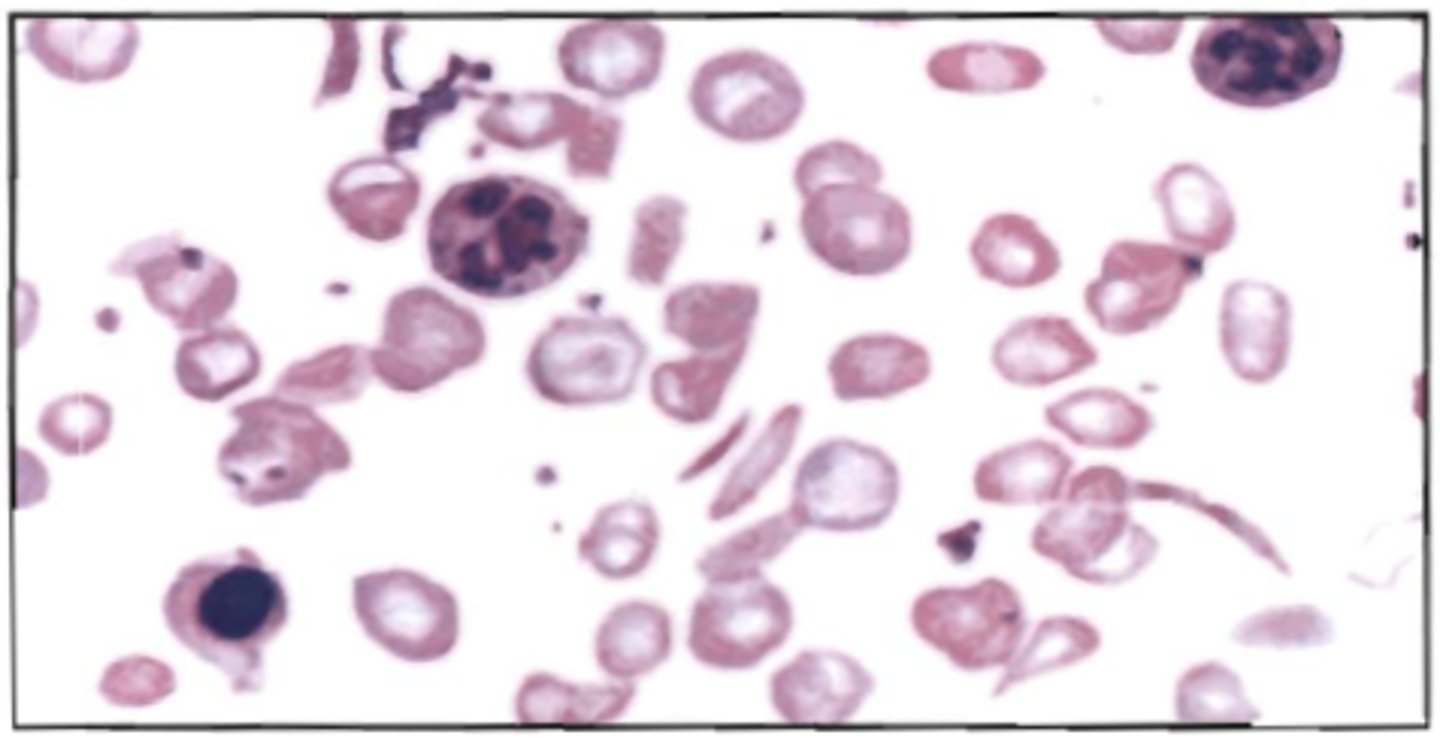
69. Using a supra vital stain, the polychromatic red blood cells below would probably be:
A. rubricytes (polychromatophilic normoblast)
B. retibulocytes
C. sickle cells
D. target cells
Correct Answer: B
70. The laboratory tests performed on a patient indicate macrocytosis, anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. Which of the following disorders is the patient most likely to have?
A. iron deficiency
B. hereditary spherocytosis
C. vitamin B12 deficiency
D. acute hemorrhage
Correct Answer: C
71. The mean value of a reticulocyte count on specimens of cord blood from healthy, full-term newborns is approximately:
A. 0.5%
B. 2.0%
C. 5.0%
D. 8.0%
Correct Answer: C
72. A red blood cell about 5 um id diameter that stains bright red and shows no central pallor is a:
A. sherocyte
B. leptocyte
C. microcyte
D. macrocyte
Correct Answer: A

73. The following results were obtained on a patient's blood:
-Hgb: 11.5 g/dL (115 g/L)
-Hct: 40%
-MCV: 89 μm^3 (89 fL)
-MCH: 26 pg
-MCHC: 29%
Examination of a Wright-stained smear of the same sample would most likely show:
A. macrocytic, normochromic erythrocytes
B. microcytic, hypochromic erythrocytes
C. normocytic, hypochromic erythrocytes
D. normocytic, normaochromic erythrocytes
Correct Answer: C
74. Evidence of active red cell regeneration may be indicated on a blood smear by:
A. basophilic stippling, nucleated red blood cells and polychromasia
B. hypochromia, microcytes and nucleated red blood cells
C. hypochromia, basophilic stippling and nucleated red blood cells
D. Howell-Jolly bodies, Cabot rings and basophilic stippling
Correct Answer: A
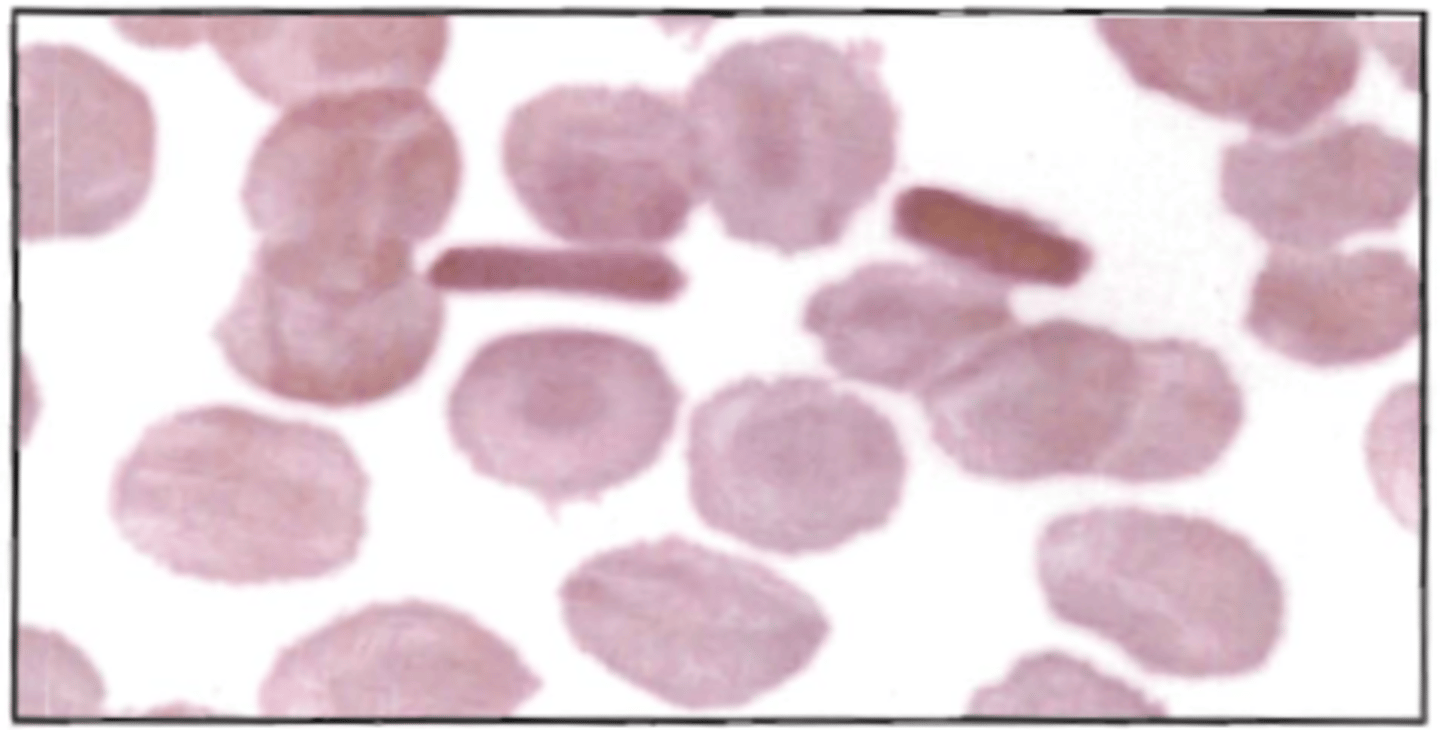
75. The smear represented below displays:
A. congenital ovalocytosis
B. hemoglobin C disease
C. poor RBC fixation
D. delay in smear preparation
Correct Answer: B
76. The presence of excessive rouleaux formation on a blood smear is often accompanied by increased:
A. reticulocyte count
B. sedimentation rate
C. hematocrit
D. erythrocyte count
Correct Answer: B
77. The characteristic peripheral blood morphologic feature in multiple myeloma is:
A. cytotoxic T cells
B. rouleaux formation
C. sherocytosis
D. macrocytosis
Correct Answer: B
78. In polycythemia vera, the hemoglobin, hematocrit, red blood cell count and red cell mass are:
A. elevated
B. normal
C. decreased
Correct Answer: A
79. The M:E ratio in polycythemia vera is usually:
A. normal
B. high
C. low
D. variable
Correct Answer: A
80. Many microsherocytes, schitocytes and budding off of spherocytes can be seen on peripheral blood smears of patients with:
A. hereditary spherocytosis
B. disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
C. acquired autoimmune hemolytic anemia
D. extensive burns
Correct Answer: D
81. Which of the following is most closely associated with erythroleukemia?
A. ringed sideroblasts, nuclear budding and Howell-Jolly bodies
B. disseminated intravascular coagulation
C. micromegakaryocytes
D. lysozymuria
Correct Answer: A
82. The most characteristic peripheral blood smear finding in multiple myeloma is:
A. plasmacytic satellitosis in the bone marrow
B. many plasma cells in the peripheral blood
C. many Mott cells in the peripheral blood
D. rouleaux formation of the red cells
Correct Answer: D
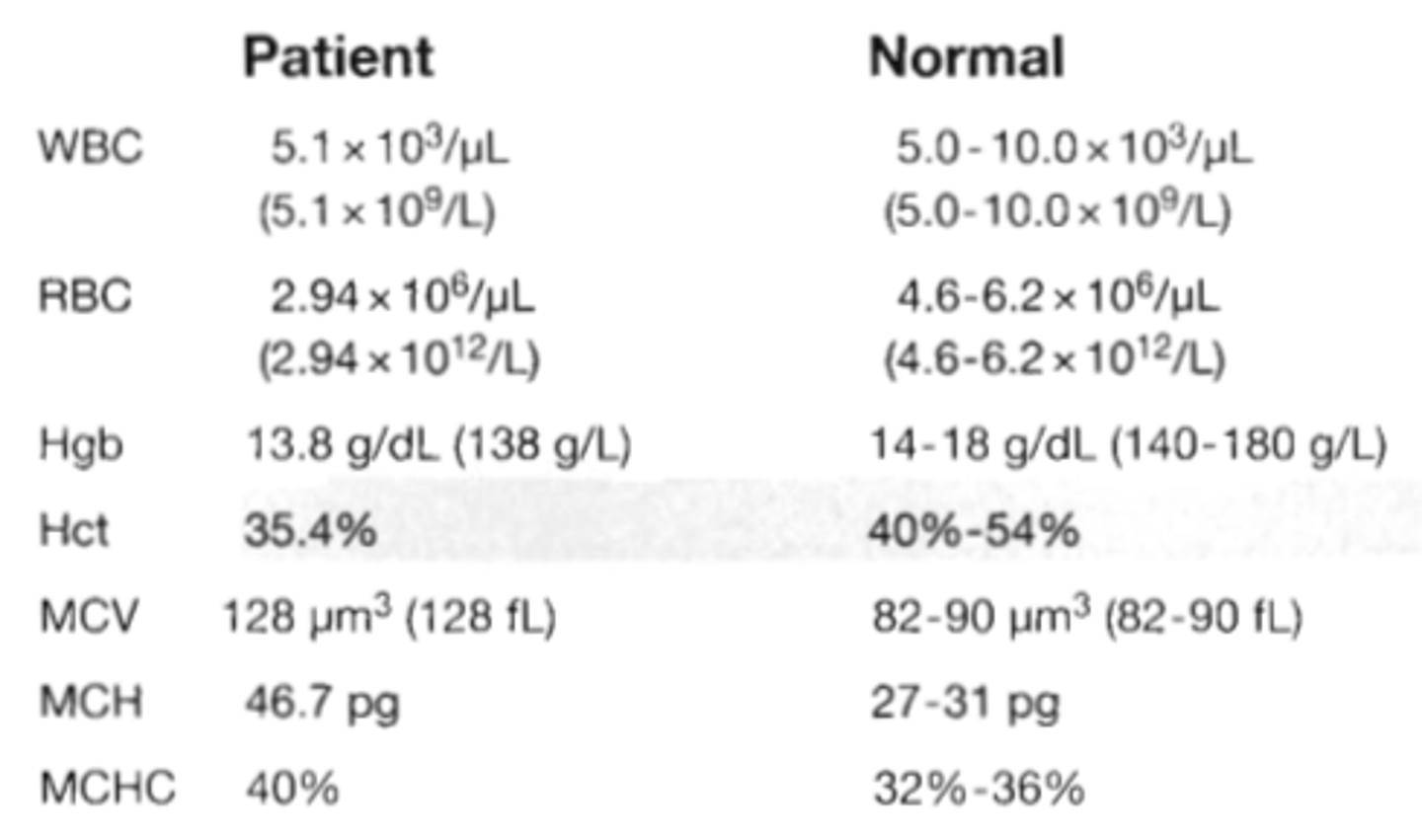
83. The value below were obtained on an automated blood count system performed on a blood sample from a 25-year-old man:
Patient Normal
-WBC: 5.1 x 10^3/uL 5.0-10.0 x 10^3/uL
(5.1 x 10^9/L) (5.0-10.0 x 10^9/L)
-RBC: 2.94 x 10^6/uL 4.6-6.2 x 10^6/ul
(2.94 x 10^12/L) (4.6-6.2 x 10^12/L
-Hgb: 13.8 g/dL(138g/L) 14-18 g/dL(140-180g/L)
-Hct: 35.4% 40%-54%
-MCV: 128 um^3 (128 fL) 82-90 um^3 (82-90 fL)
-MCH: 46.7 pg 27-31 pg
-MCHC: 40% . 32%-36%
These results are most consistent with which of the following?
A. megaloblastic anemia
B. hereditary spherocytosis
C. a high titer of cold agglutinins
D. an elevated reticulocyte cout
Correct Answer: C

84. A 56-year-old man was admitted to the hospital for treatment of a bleeding ulcer. The following laboratory data were obtained:
-RBC: 4.2 x 10^6/uL (4.2 x 10^12/L)
-WBC: 5.0 x 10^3/uL (5.0 x 10^6/L)
-Hct: 30%
-Hgb: 8.5 g/dL (85 g/L)
-Serum iron: 40 μg/dL (7.2 μmol/L)
-TIBC: 460 μg/dL (82.3 μmol/L)
-Serum ferritin: 12 ng/mL (12 μg/L)
Examination of the bone marrow revealed the absence of iron stores. This data is most consistent with which of the following conditions?
A. iron deficiency anemia
B. anemia of chronic disease
C. hemochromatosis
D. acute blood loss
Correct Answer: A

85. A 40-year-old Caucasian male was admitted to the hospital for treatment of anemia, lassitude, weight loss, and loss of libido. The patient presented with the following laboratory data:
-WBC: 5.8 x 10^3/μL(5.8 x 10^9/L)
-RBC: 3.7 x 10^6/μL (3.7 x 10^12/L)
-Hgb: 10.0 g/dL (100 g/L)
-Hct: 32%
-MCV: 86 μm^3 (86 fL)
-MCH: 26 pg
-MCHC: 32%
-Serum iron: 200 μg/dL (39.4 μmol/L)
-TIBC: 300 μg/dL (53.7 μmol/L)
-Serum ferritin: 2,800 ng/mL (2,800 μg/L)
Examination of the bone marrow revealed erythroid hyperplasia with a shift to the left of erythroid precursors. Prussian blue staining revealed markedly elevated iron stores noted with occasional sideroblasts seen. This data is most consistent with which of the following conditions?
A. iron deficiency anemia
B. anemia of chronic disease
C. hemochromatosis
D. acute blood loss
Correct Answer: C
86. A common source of interference in the cyanmethemoglobin method is:
A. hemolysis
B. very high WBC count
C. cold agglutinins
D. clumped platelets
Correct Answer: A
87. A patient with beta-thalassemia characteristically has a(n):
A. elevated A2 hemoglobin
B. low fetal hemoglobin
C. high serum iron
D. normal red cell fragility
Correct Answer: A
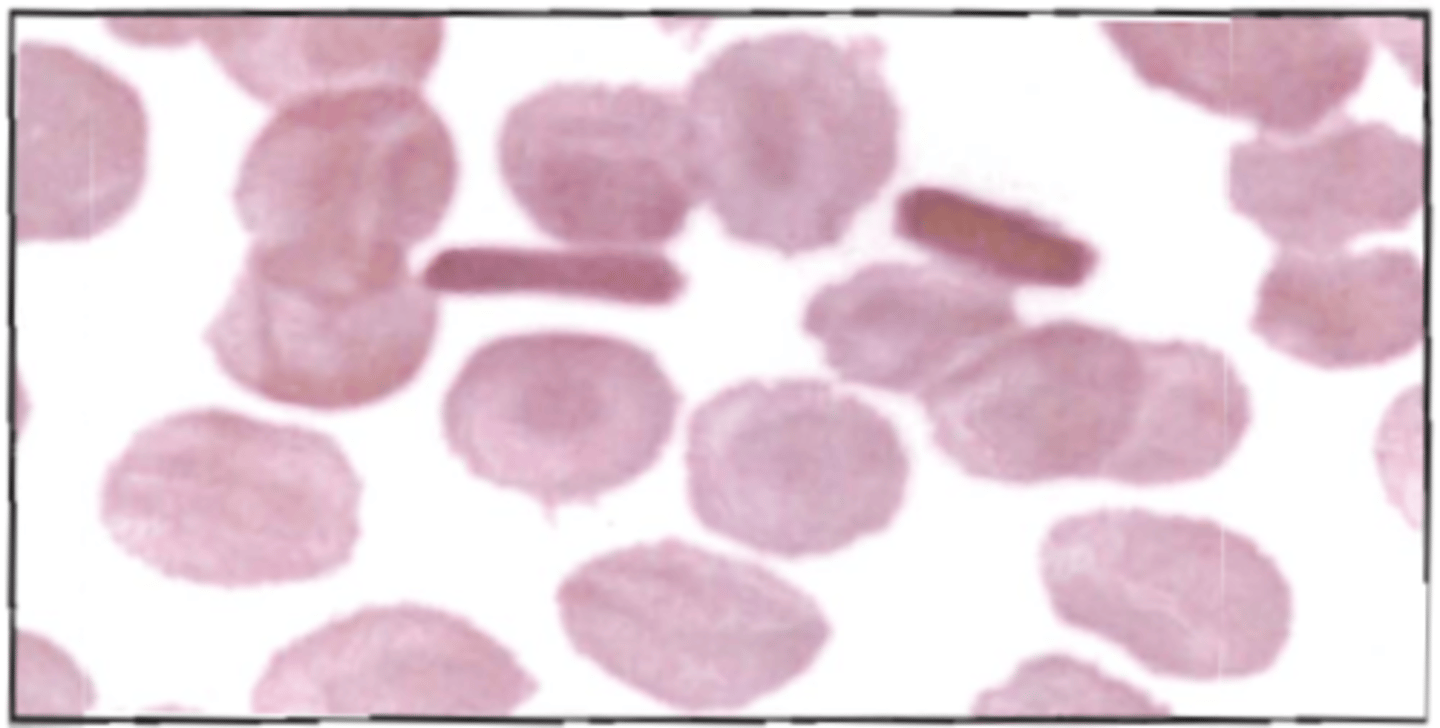
88. With this blood picture, an additional test indicated is:
See BOC pg 159
A. alkali denaturation
B. alkaline phosphatase stain
C. peroxidase stain
D. hemoglobin electrophoresis
Correct Answer: D
89. The most appropriate screening test for detecting hemoglobin F is:
A. osmotic fragility
B. dithionite solubility
C. Kleihauer-Betke
D. heat instability
Correct Answer: C
90. The most appropriate screening test for hemoglobin S is:
A. Kleihauer-Betke
B. dithionite solubility
C. osmotic fragility
D. sucrose hemolysis
Correct Answer: B
91. Hematology standards include:
A. stabilized red blood cell suspension
B. latex particles
C. stabilized avian red blood cells
D. certified cyaanmethemoglobin solution
Correct Answer: D
92. In an adult with rare homozygous delta-beta thalassemia, the hemoglobin produced is:
A. Hgb A
B. Hgb Bart
C. Hgb F
D. Hgb H
Correct Answer: C
93. Which of the following is not a characteristic of hemoglobin H?
A. it is a tetramer of beta chains
B. it is relatively unstable and thermolabile
C. electrophoretically, it represents a "fast" hemoglobin
D. its oxygen affinity is lower than that of hemoglobin A
Correct Answer: D
94. In most cases of hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH)
A. hemoglobin F is unevenly distributed throughout the erythrocytes
B. the black heterozygote has 75% hemoglobin F
C. beta and gamma chain synthesis is decreased
D. gamma chain production equals alpha chain production
Correct Answer: D
95. Hemoglobin H disease results from:
A. absence of 3 of 4 alpha genes
B. absence of 2 of 4 alpha genes
C. absence of 1 of 1 alpha genes
D. absence of all 4 alpha genes
Correct Answer: A
96. When using the turbidity (solubility) method for detecting the presence of hemoglobin S, an incorrect interpretation may be made when there is a(n):
A. concentration of less than 7 g/dL (70 g/L) hemoglobin
B. glucose concentration greater than 150 mg/dL (8.3 mmol/L)
C. blood specimen greater than 2 hours old
D. increased hemoglobin
Correct Answer: D
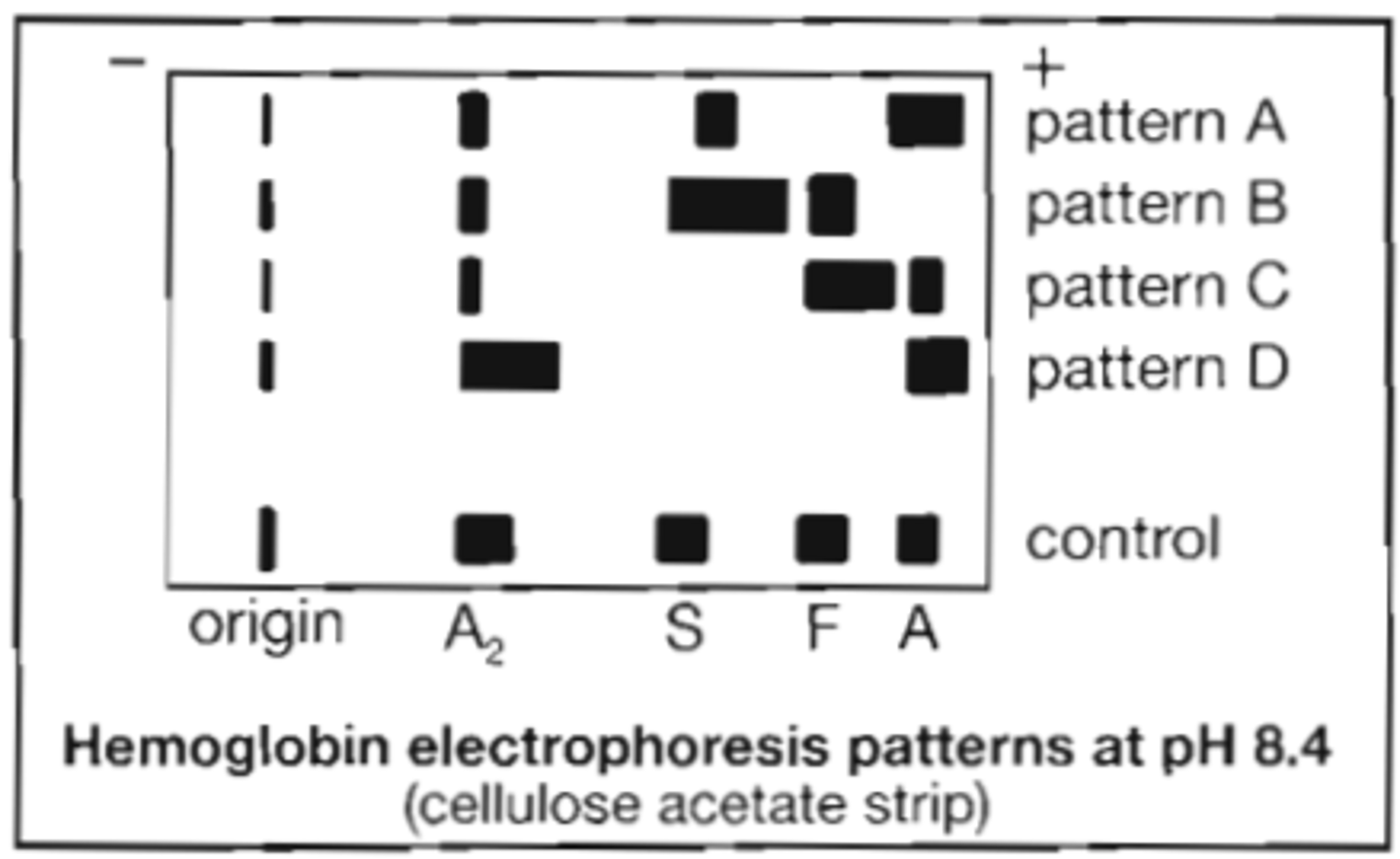
97. Refer to the following pattern:
Which pattern is consistent with beta-thalassemia major?
A. pattern A
B. pattern B
C. pattern C
D. pattern D
Correct Answer: C
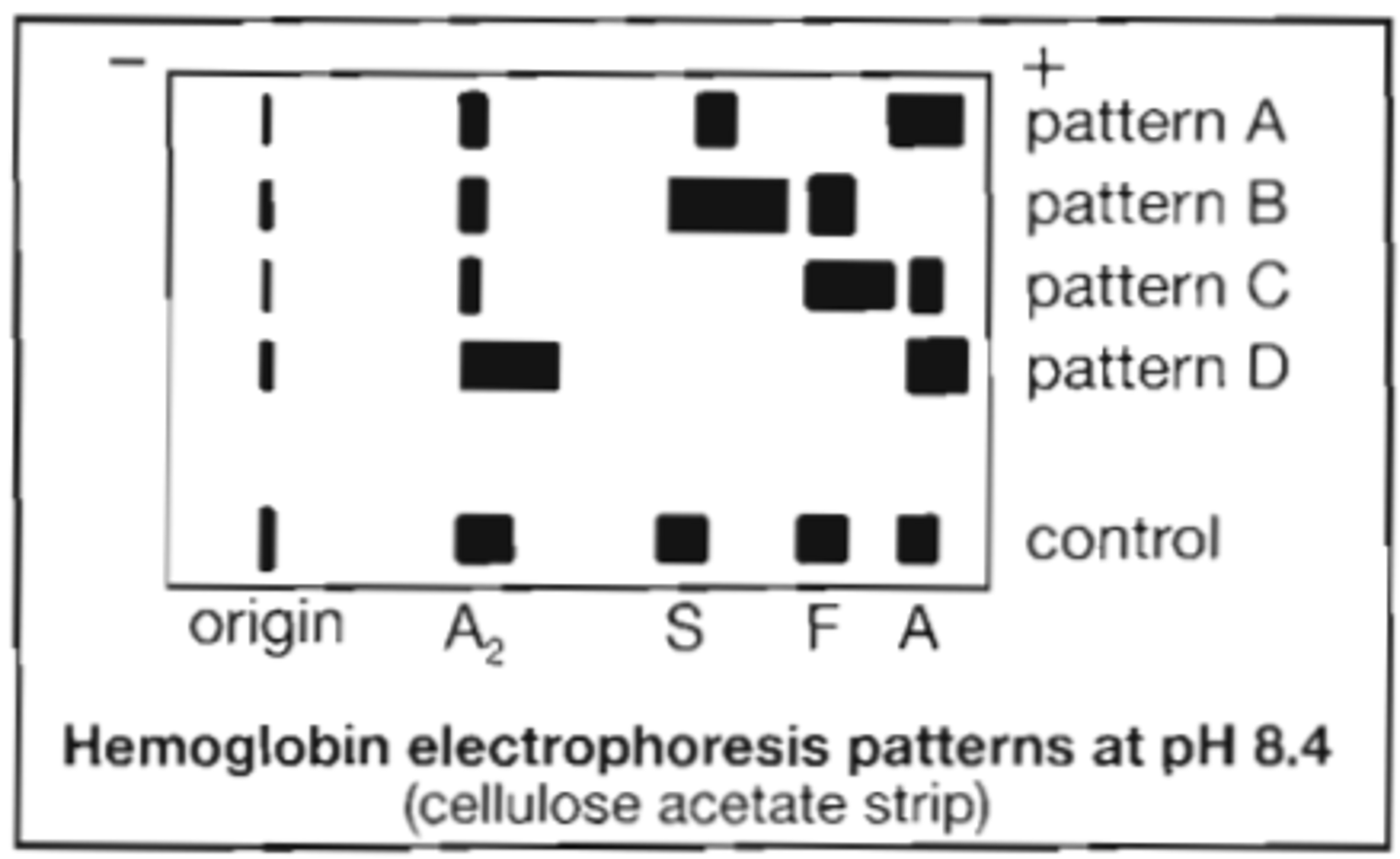
98. Refer to the following illustration:
Which electrophoresis pattern is consistent with sickle cell trait?
A. pattern A
B. pattern B
C. pattern C
D. pattern D
Correct Answer: A
99. A native of Thailand has a normal hemoglobin level. Hemoglobin electrophoresis on cellulose acetate shows 70% hemoglobin A and approximately 30% of a hemoglobin with the mobility of hemoglobin A2. This is most consistent with hemoglobin:
A. C trait
B. E trait
C. O trait
D. D trait
Correct Answer: B
100. The laboratory findings on a patient are as follows:
-MCV: 55 μm^3 (55 fL)
-MCHC: 25%
-MCH: 17 pg
A stained blood film of this patient would most likely reveal a red cell picture that is:
A. microcytic, hypochromic
B. macrocytic, hypochromic
C. normocytic, normochromic
D. microcytic, normochromic
Correct Answer: A