Clinical induction & maintenance
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the options for induction agents?
Propofol
Alfaxalone
Ketamine
Inhalational agents (sevoflurane & isoflurane)
Thiopental (large animal)
GGE (Guaifenesin)
Etomidate
Potent opioids
What is choice and admin of an induction agent dependent on?
Species
Drugs available & their pharmacology
Personal preferance
Individual animal
Environment
Dogs vs cats when inducing (things to consider)
Dogs —> obesity, brachycephalics, temperament variable, can induce to effect, IV access easy
Cats —> smaller in body mass, can be spicy, IV access more challenging, mask sub-clinical dx well, care with repeated doses of propofol (forming of Heinz bodies in the blood), can induce to effect
What needs to be considered when inducing horses?
Flight reaction to stressful situations
Large body mass
IV access easy
Do not lie down after sedation / do not want to remain recumbent when recover
Cannot easily administer to effect
What needs to be considered when inducing farm animals?
Must follow releavnt food safety legislation —> extremely limiting
What are the licenced UK Induction agents?
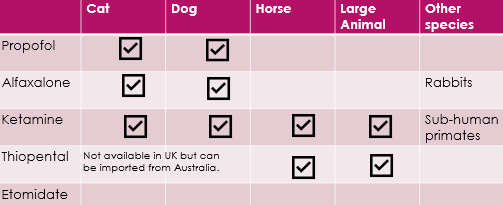
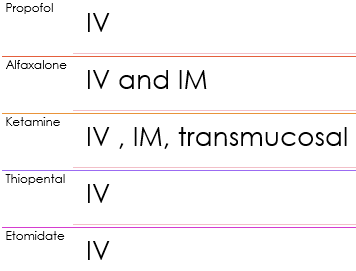
What is the route of administration of the different induction/maintenance agents?
What are some examples of induction co-agents?
Muscle relaxation
Benzodiazepines (not licenced in farm animals)
Midazolam
Diazepam
Guaifenesin (GGE)
Analgesia
Ketamine
Opioids
What does anaesthesia do?
Relaxation of laryngeal & pharyngeal tissues
Abolishes the swallowing reflex
Cause resp depression
Can lead to apnoea
What are the considerations you need to make regarding the pharmacology of the drug when choosing an induction/maintenance agent?
Pharmacokinetics
Route of administration
Onset of action
Pharmacodynamics
Quality of anaesthesia
Cardiovascular and respiratory effects
Other effects
Quality of recovery
Adjunctive drugs
Formulation
Irritancy
Pain on injection
Shelf-life
Combine with other drugs
What are the considerations you need to make regarding the procedure when choosing an induction/maintenance agent?
Procedure
Duration
Complexity
Safety of working personnel
Anaesthetic environment
Hospital vs Field
Quiet and calm vs busy noisy
Facilities and equipment available
What are the different induction techniques in horses?
1 person
2 person
Wall induction
Gate induction
‘Free’ fall
What specific considerations do you need to make with ruminants?
Licencing!!!!
Safety
Handling variable
Most are in sternal recumbency post pre-medication
Risk of aspiration
Quick induction preferable
Position to allow saliva to drain
IV access can be challenging
What are the advantages of intubation?
Protects airway from oesophageal/ gastric content
Allows delivery of oxygen/ medical air +/- maintenance inhalant
What are the different options for airway management?
Face mask
Endotracheal intubation - cuffed and uncuffed
Supraglottic airway devices-LMA/ V-Gel
What are face masks usually used for?
Not commonly used for delivering inhalant agents due to large amount leaking into the working airspace
Commonly used to deliver oxygen
How do you carry out intubation in small animals?
Use laryngoscope to visualise larynx and aid intubation
When would you use a cuffed and uncuffed ET tube in small animals?
Cuffed in dogs
Uncuffed in cats
Can use cuffed in cats but be cautious of laryngeal necrosis
How do you carry out Endotracheal intubation on equines?
Large ETT tube
Placement is blind
Bite block used to keep jaw open to aid placement and prevent biting on the tube
How do you carry out Endotracheal intubation on ruminants?
Cows- same technique as horse
Sheep/ Goats- Like small animal but much longer laryngoscope blade
Often need stylets to aid
What are the uses of Supraglottic airway device?
Bronchoscopy
Cats
Rabbits
How do you deal with laryngeal spasm in cats?
Intubeaze (lidocaine spray)
Apply directly to larynx to prevent laryngeal spasm
1 spray = 0.14ml= 2.8mg lidocaine
What may you need to do when carrying out an emergency intubation?
Horses = urinary catheter, needle into trachea, tracheostomy

What are the different inhalational agents?
Isoflurane
Sevoflurane
What are the different intravenous maintenance agents?
TIVA (total intravenous anaesthesia) or PIVA (partial intravenous anaesthesia)
Propofol
Alfaxalone
Ketamine
What are the inhalational agents administered with?
100% oxygen or medical air
How is TIVA achieved and when would you do this?
Constant rate infusion or intermittent boluses
Field anaesthesia
Upper airway diagnostics or surgery
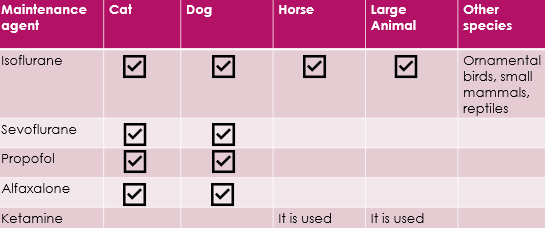
What species are the different maintenance agents licence in?
What are some MAC sparing techniques?
PIVA
Multimodal analgesia
Locoregional techniques
What are the most commonly used induction/maintenance agents in different species?
Cats/ Dogs- Propofol/ Alfaxalone induction with Isoflurane/ Sevoflurane maintenance
Horses- Ketamine (+midazolam) induction with isoflurane inhalant maintenance or Ketamine boluses (TIVA)
Large animal- Ketamine induction with isoflurane inhalant maintenance or Ketamine boluses (TIVA)
Majority of procedures under sedation and local anaesthetic