Directional Terms and Histology
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biol 251 Quiz 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
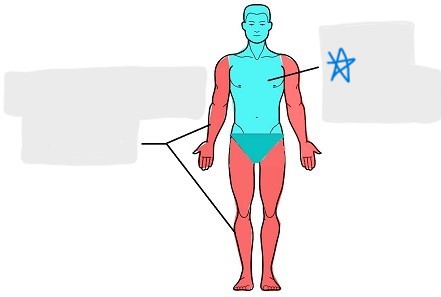
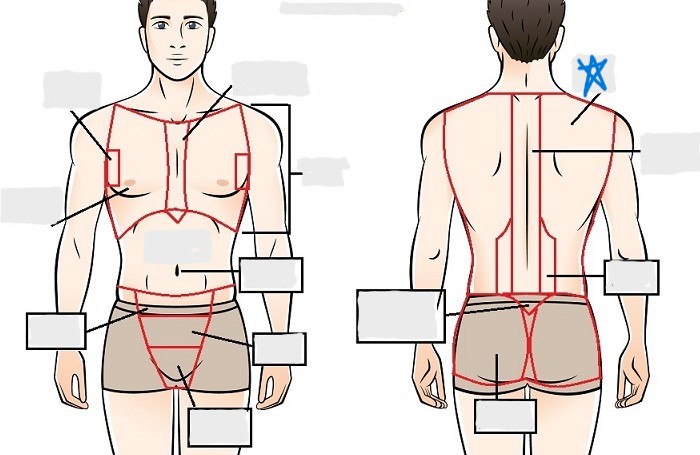
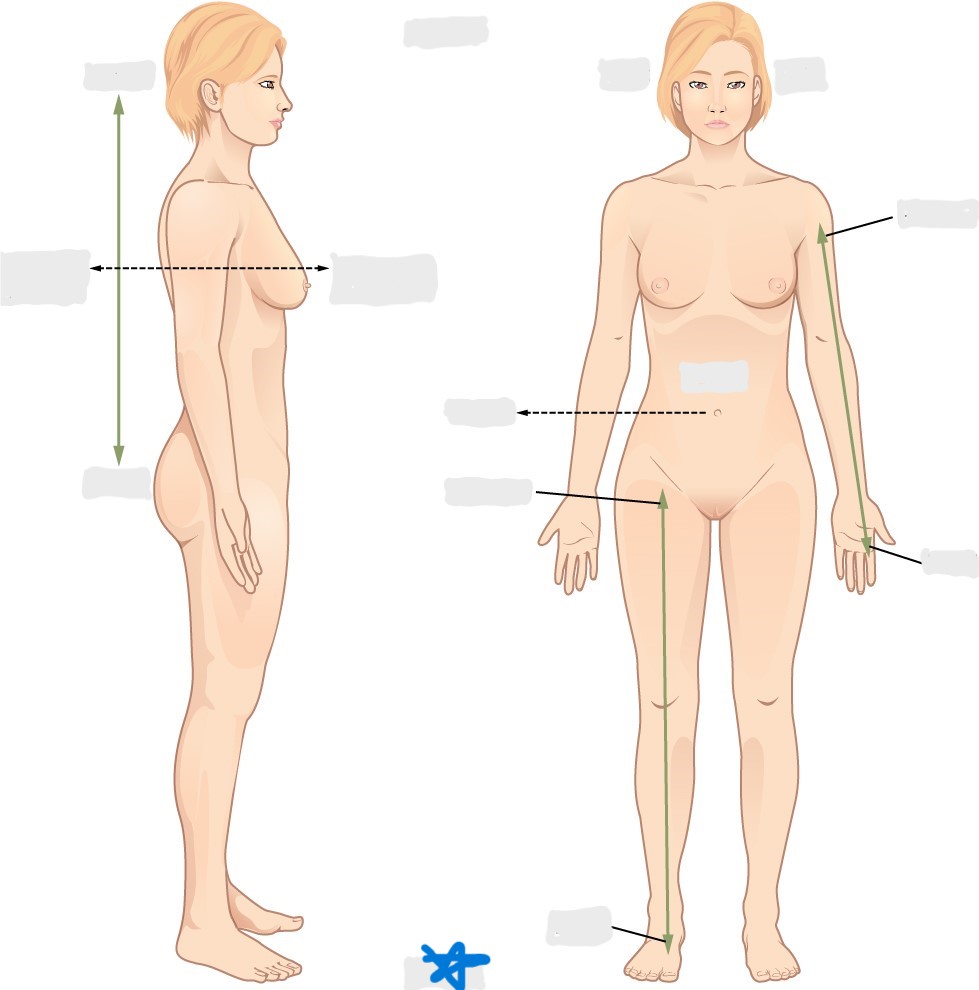
axial
cephalic
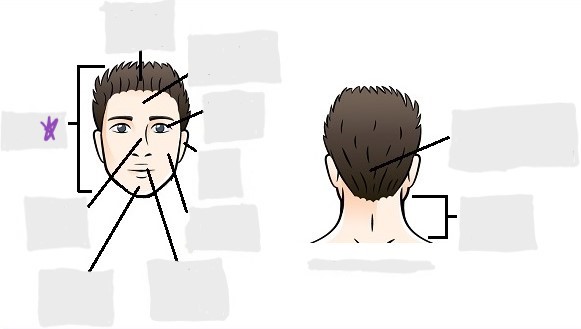
occipital
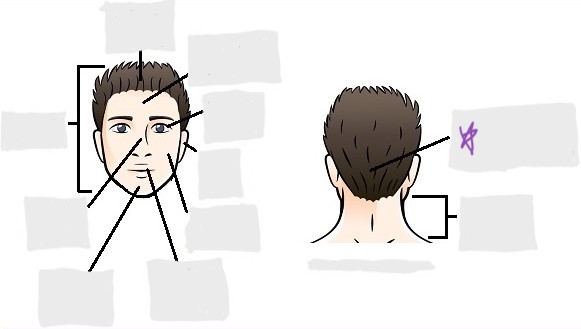
frontal
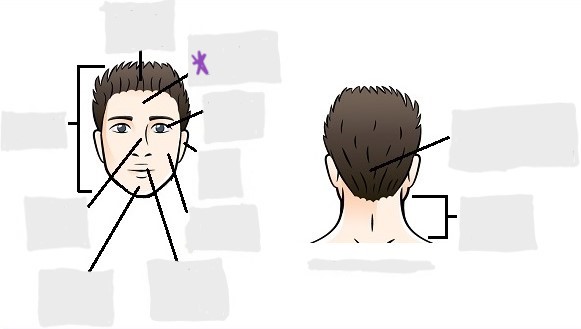
otic
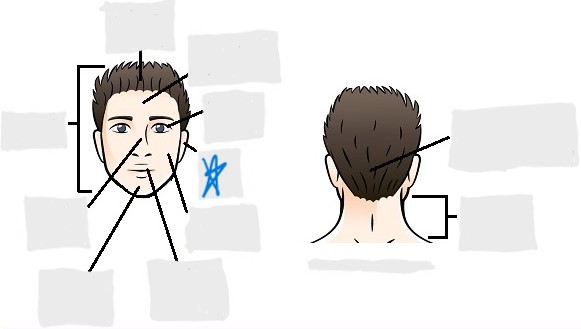
orbital
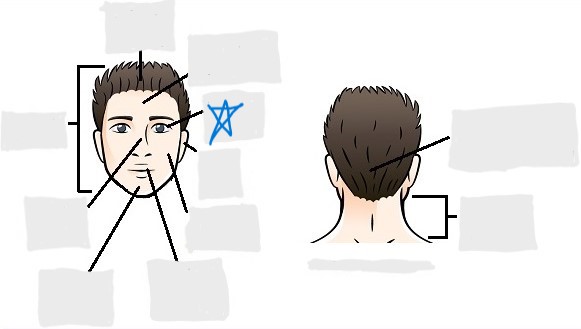
nasal
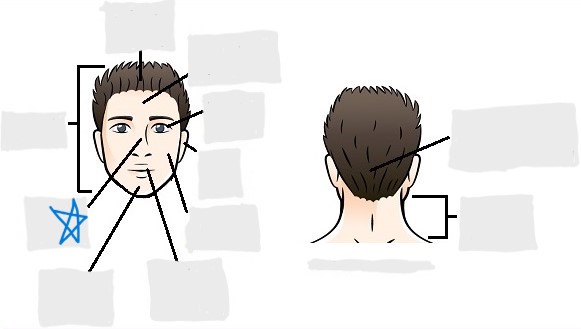
oral
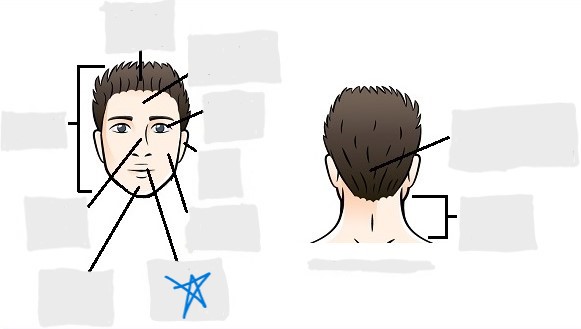
mental
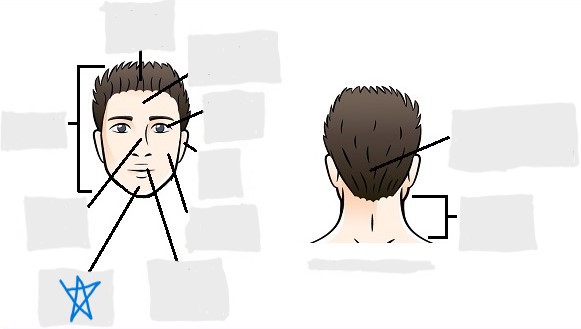
cervical
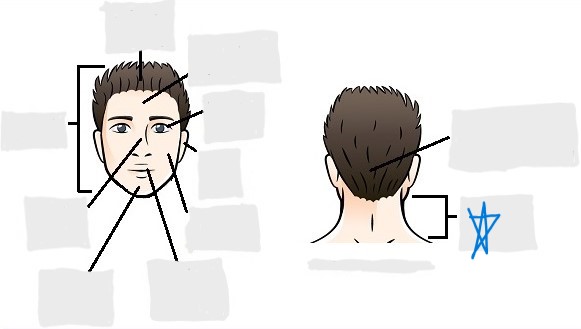
dorsal
scapular
vertebral
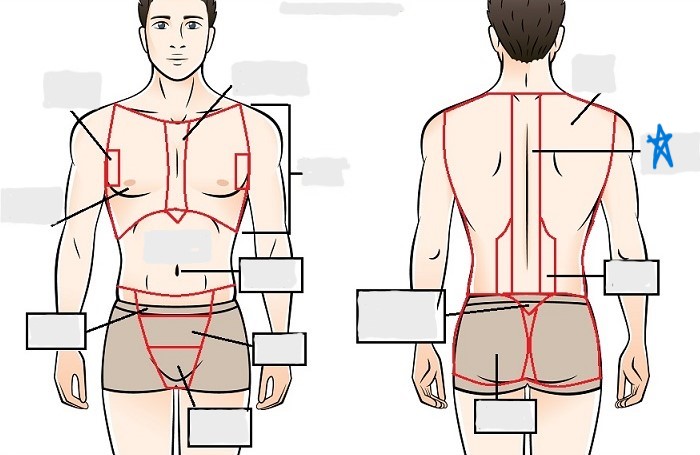
lumbar
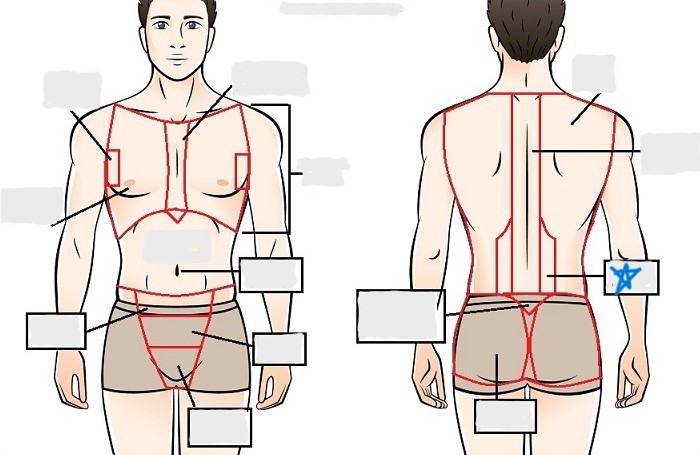
sacral
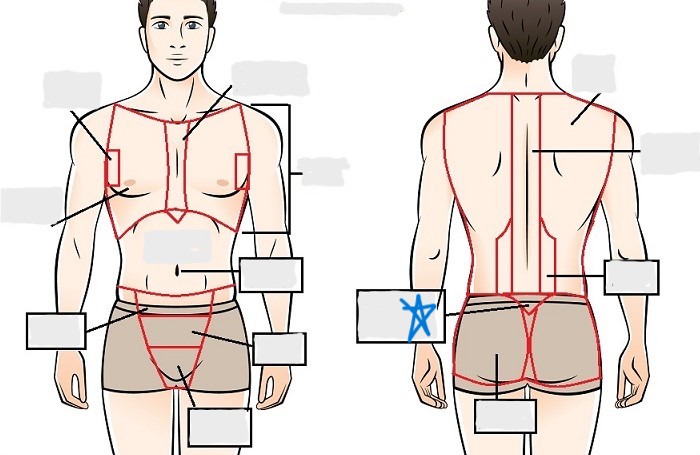
gluteal
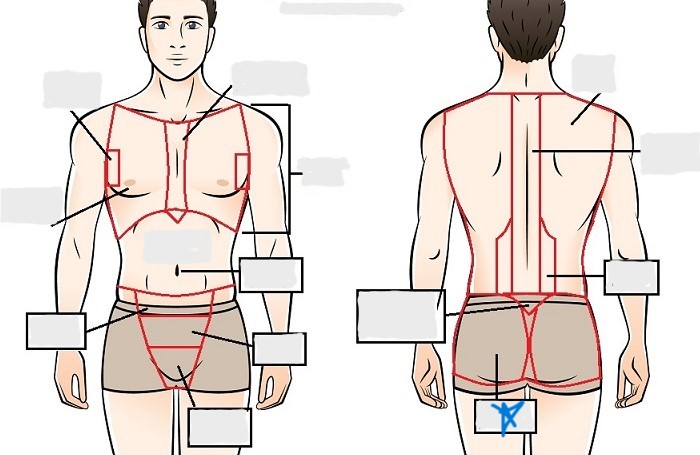
thoracic
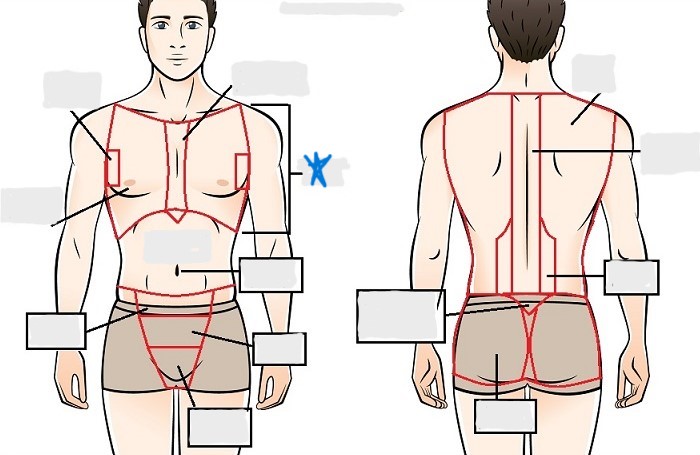
sternal
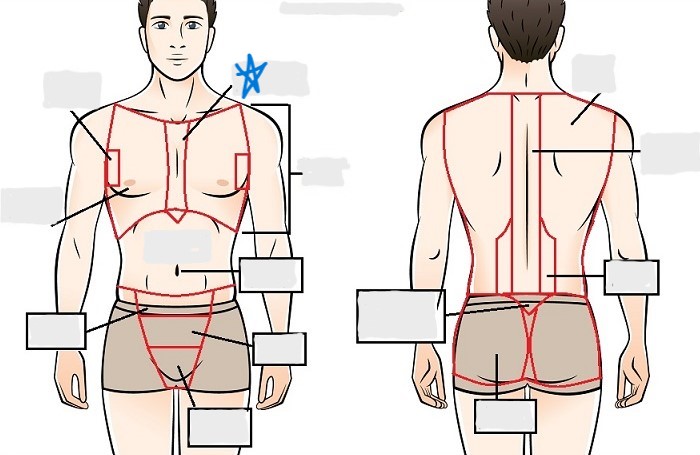
mammary
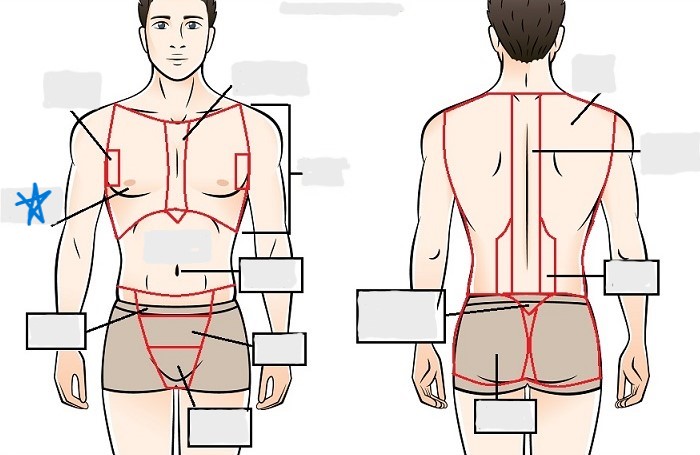
axillary
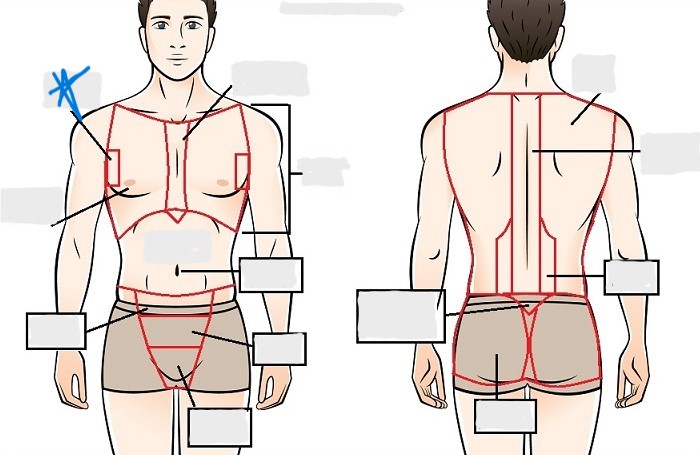
abdominal
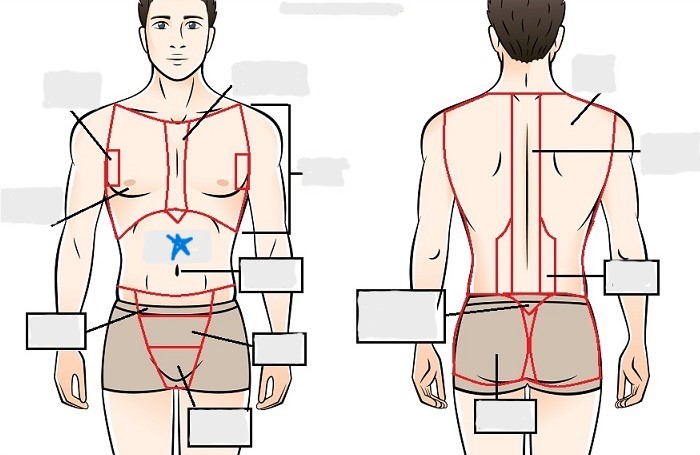
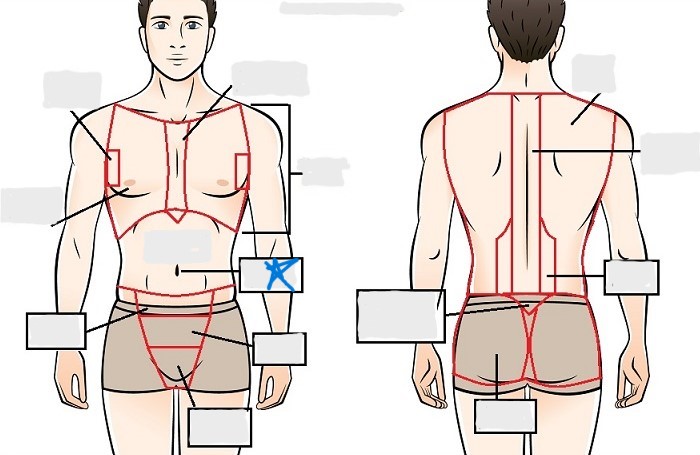
umbilical
pelvic
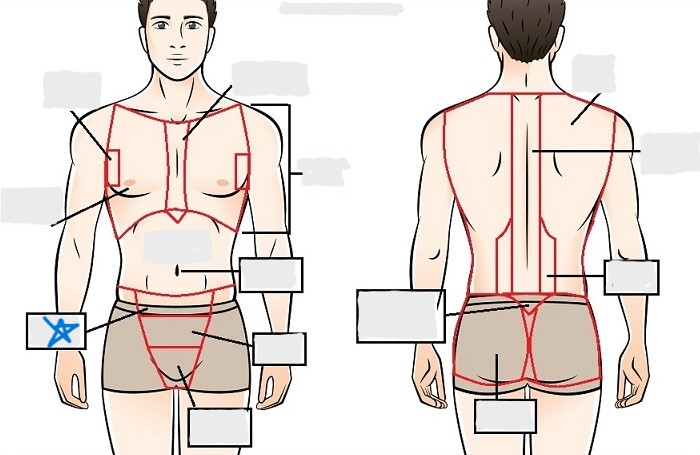
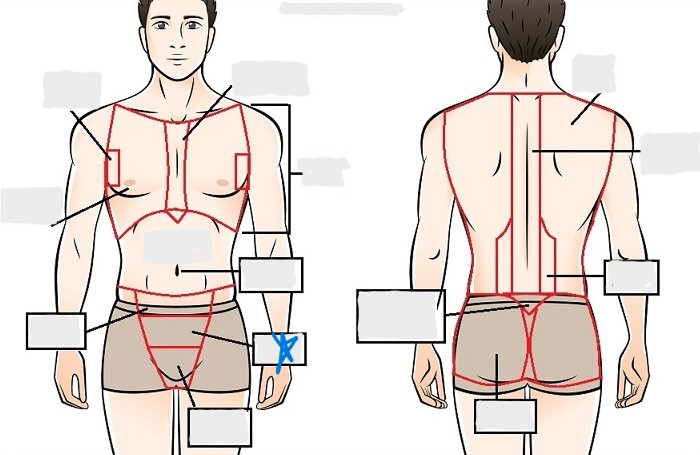
inguinal
pubic
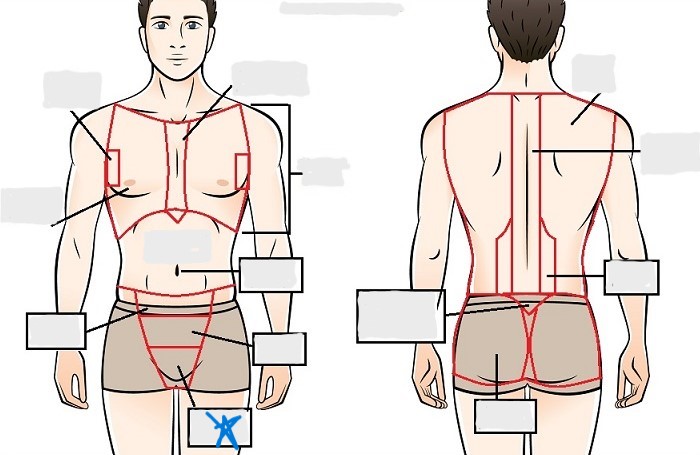
perineal
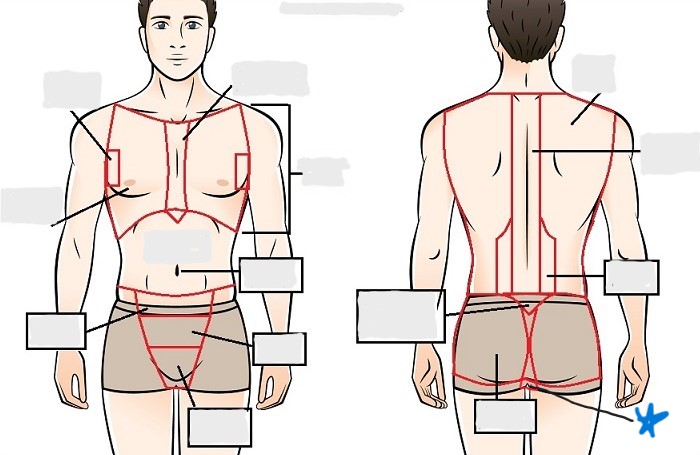
appendicular
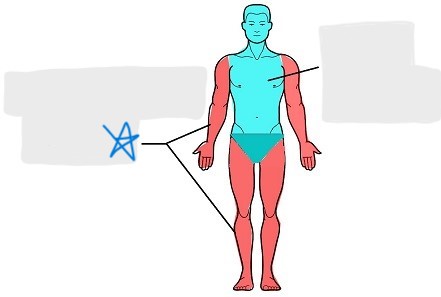
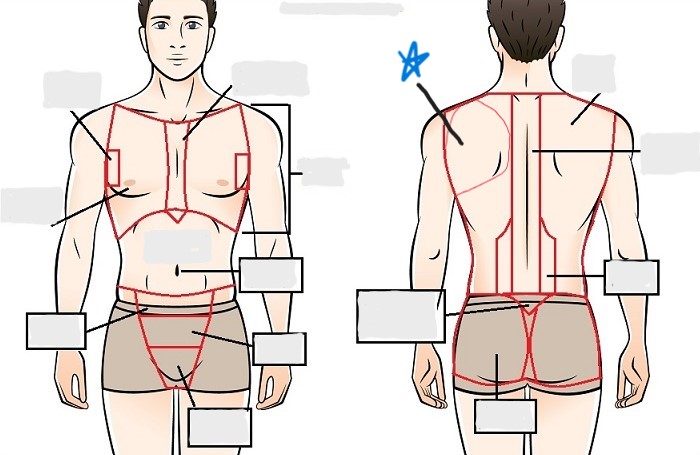
acromial
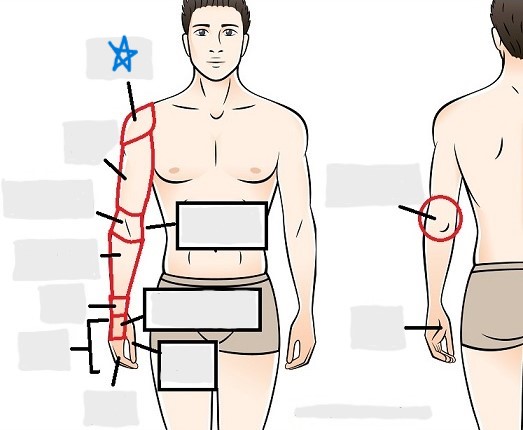
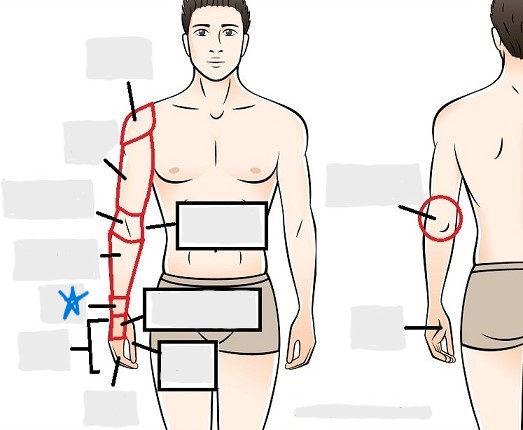
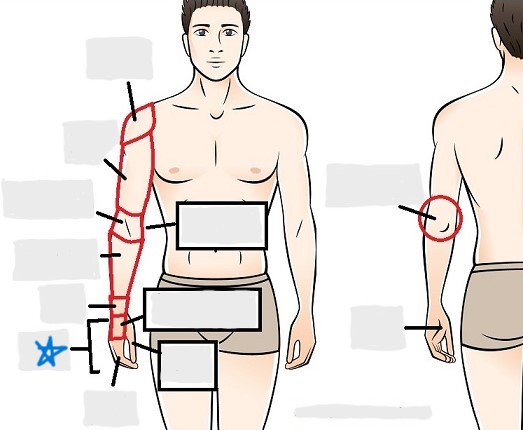
brachial
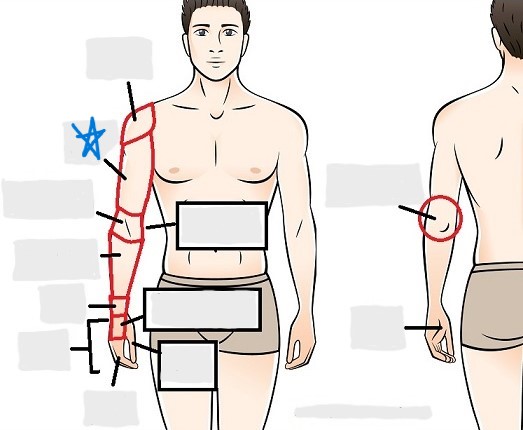
antecubital
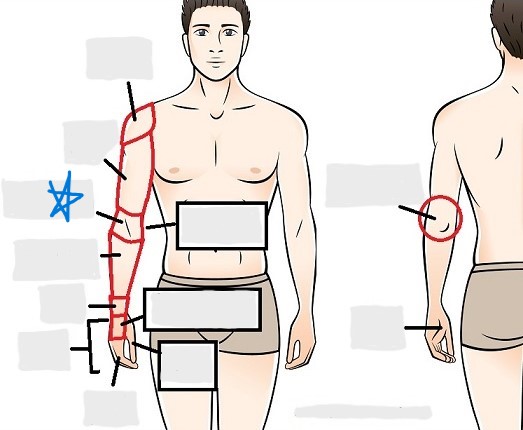
olecranal
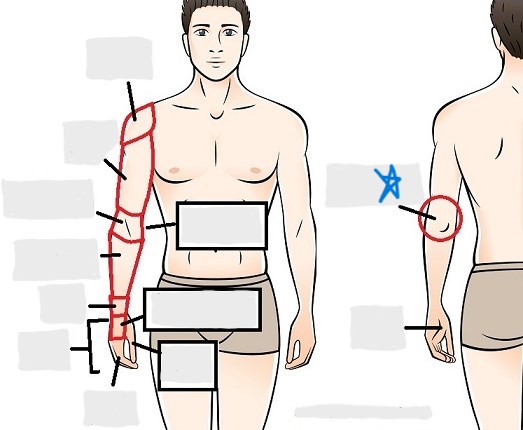
antebrachial
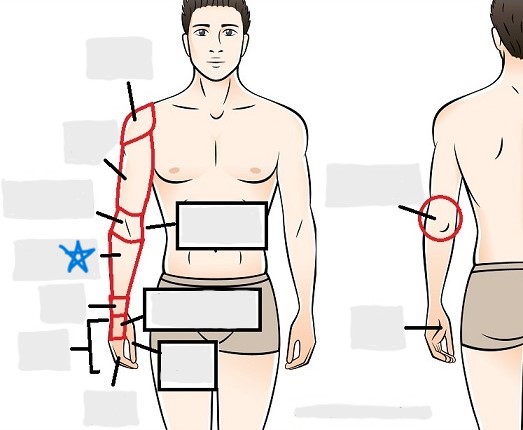
carpal
manus
coxal
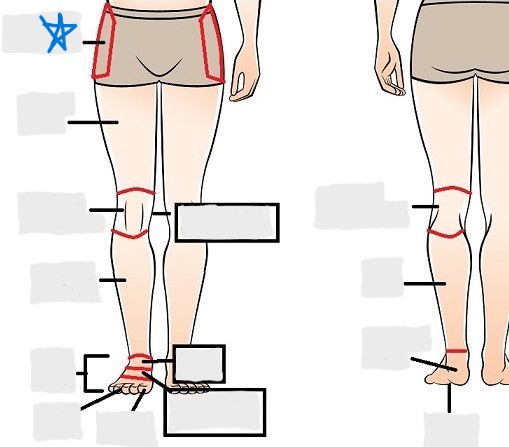
femoral
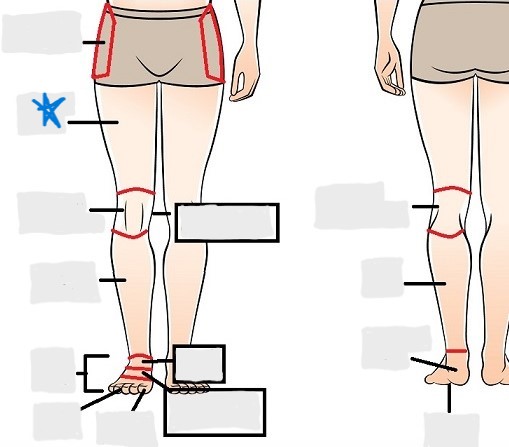
patellar
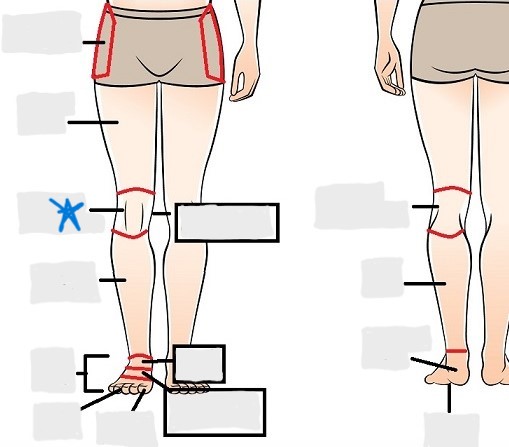
popliteal
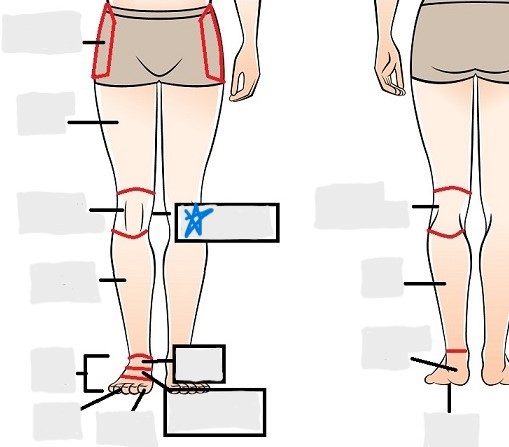
crural
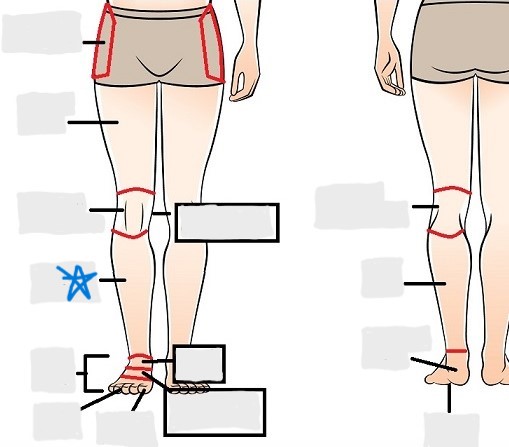
sural
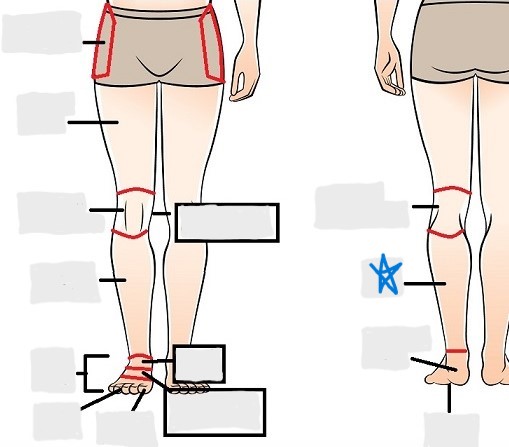
peroneal
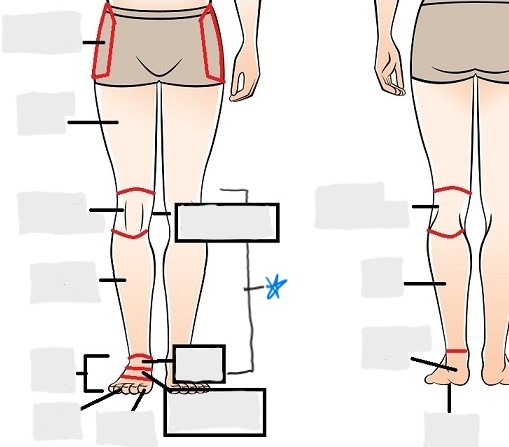
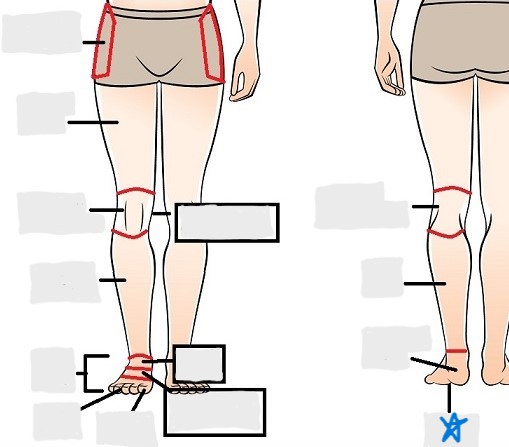
calcaneal
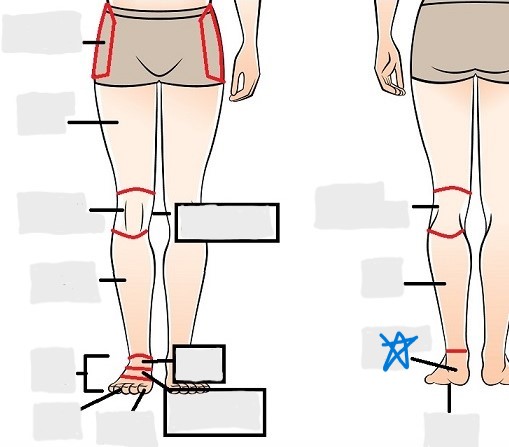
plantar
mucous membrane
soft tissue that lines the body's canals and organs that are open to the outside
location: digestive, respiratory, and reproductive systems
serous membrane
a smooth tissue membrane of mesothelium lining the contents and inner walls of body cavities, which secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding movements between opposing surfaces
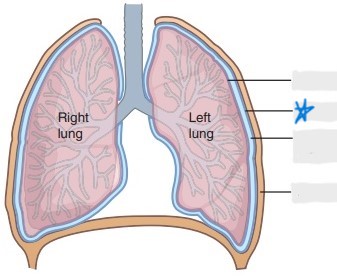
visceral pleura
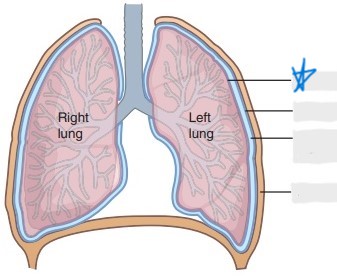
parietal pleura
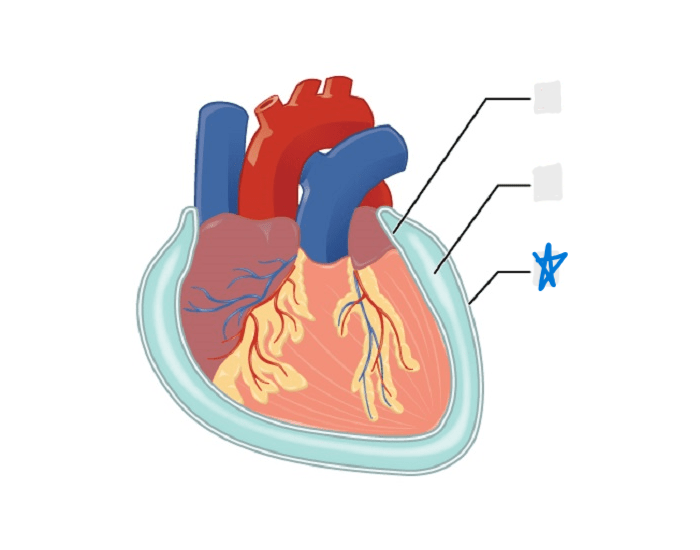
visceral pericardium
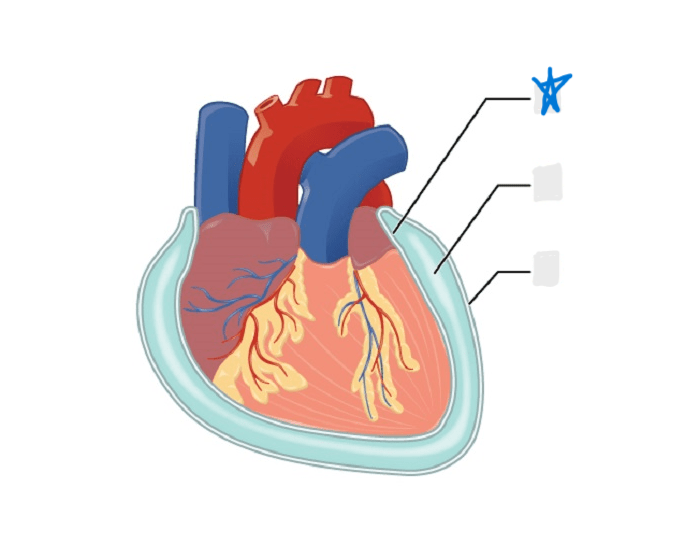
parietal pericardium
visceral peritoneum
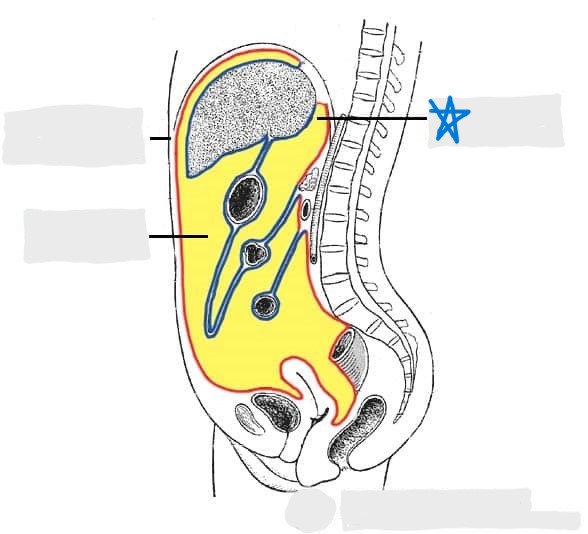
parietal peritoneum
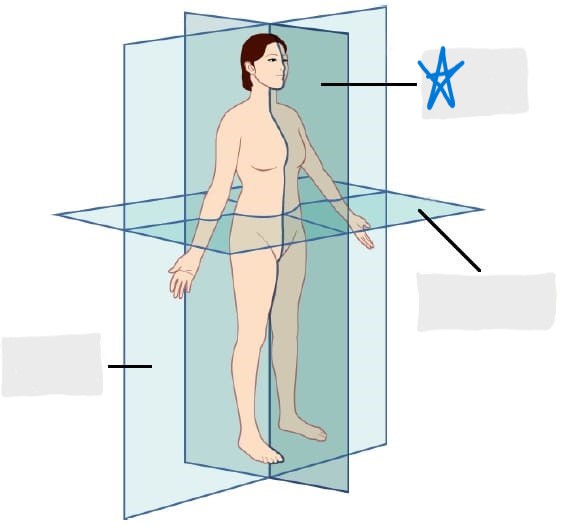
sagittal plane
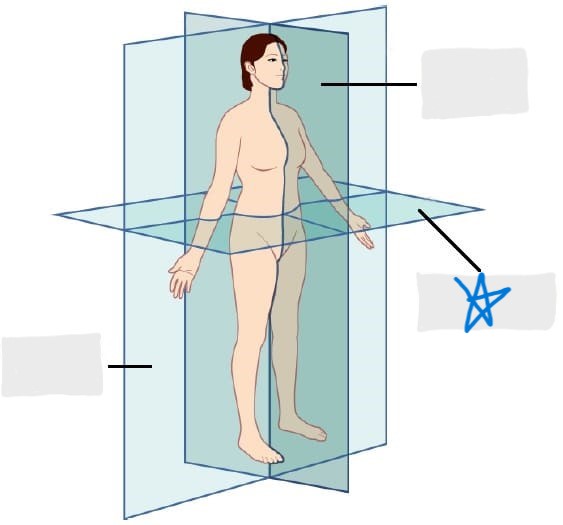
frontal/coronal plane
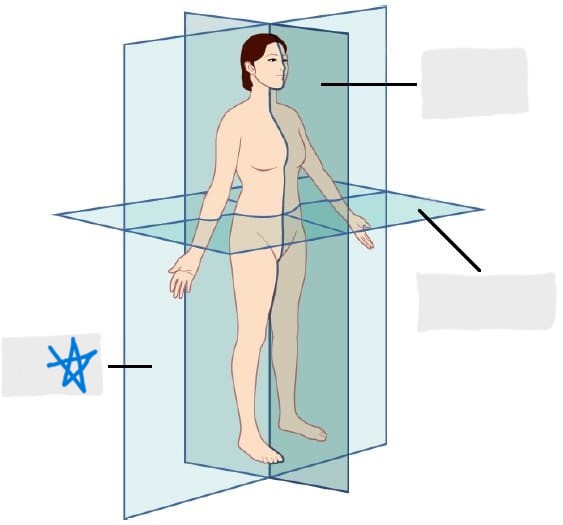
transverse plane
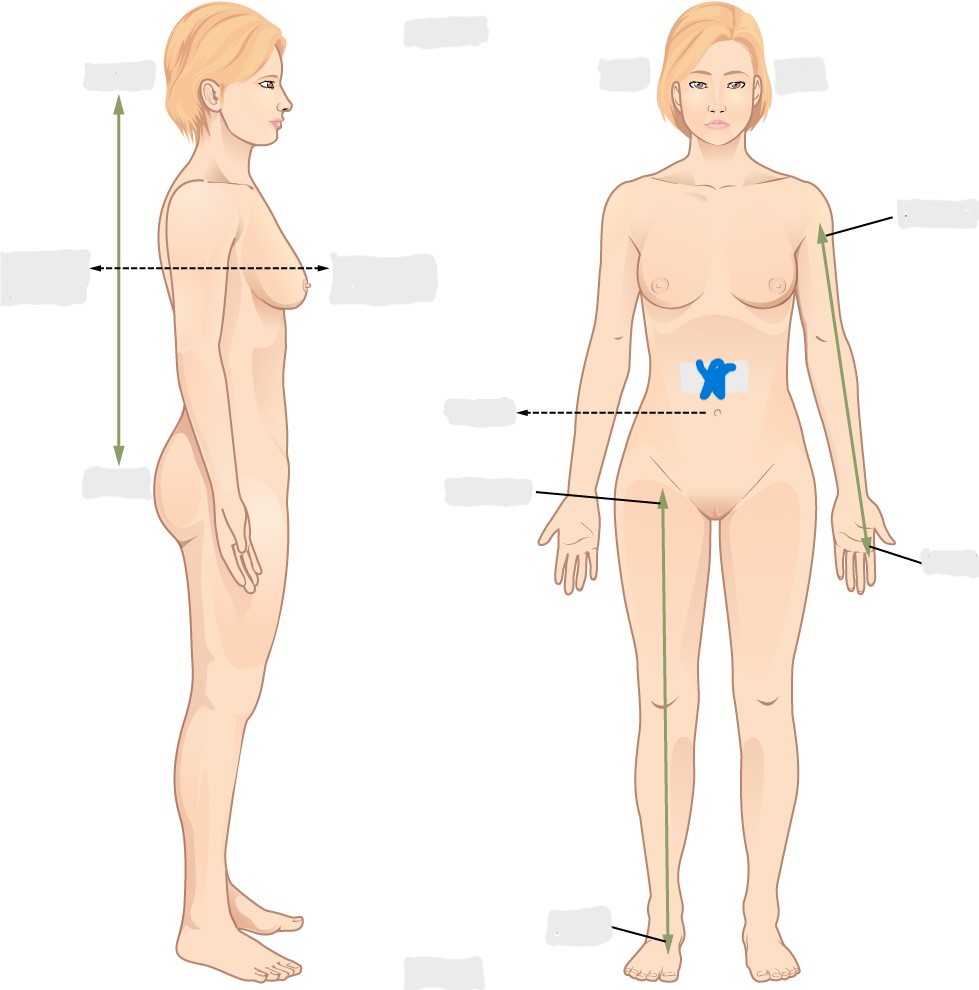
dorsal/posterior
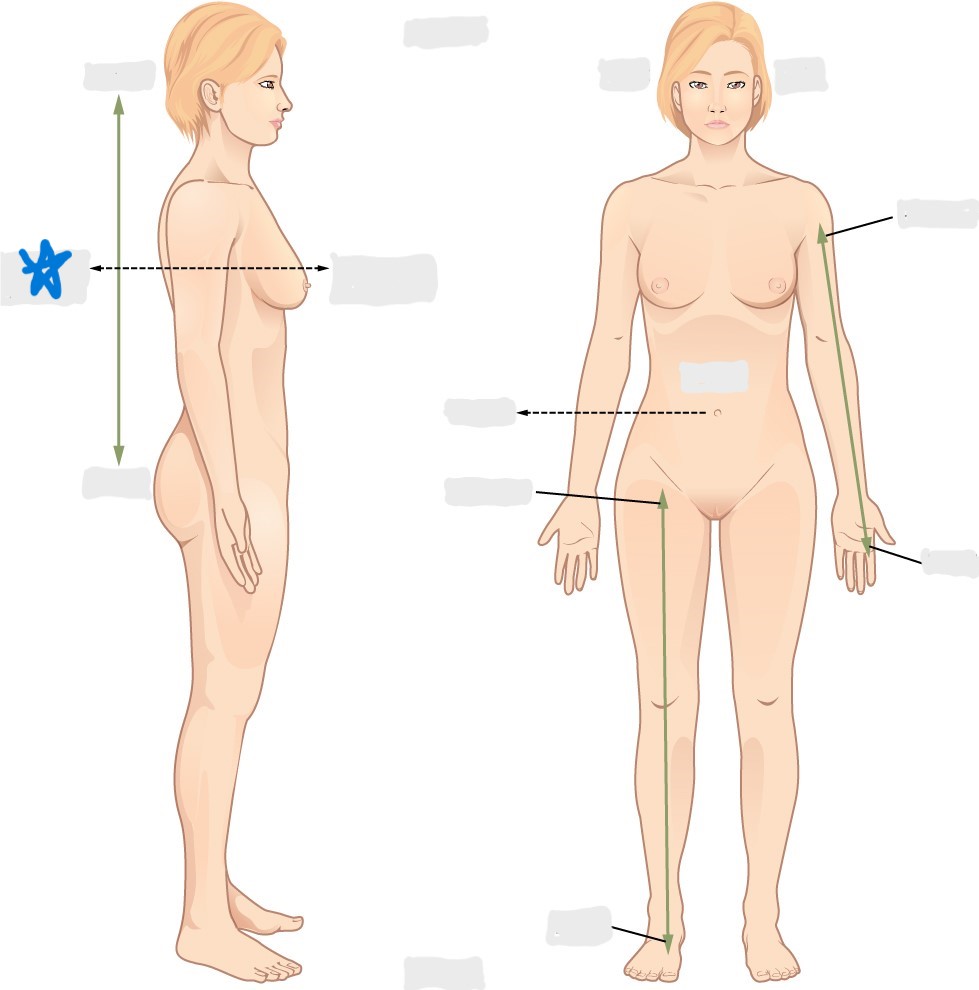
ventral/anterior
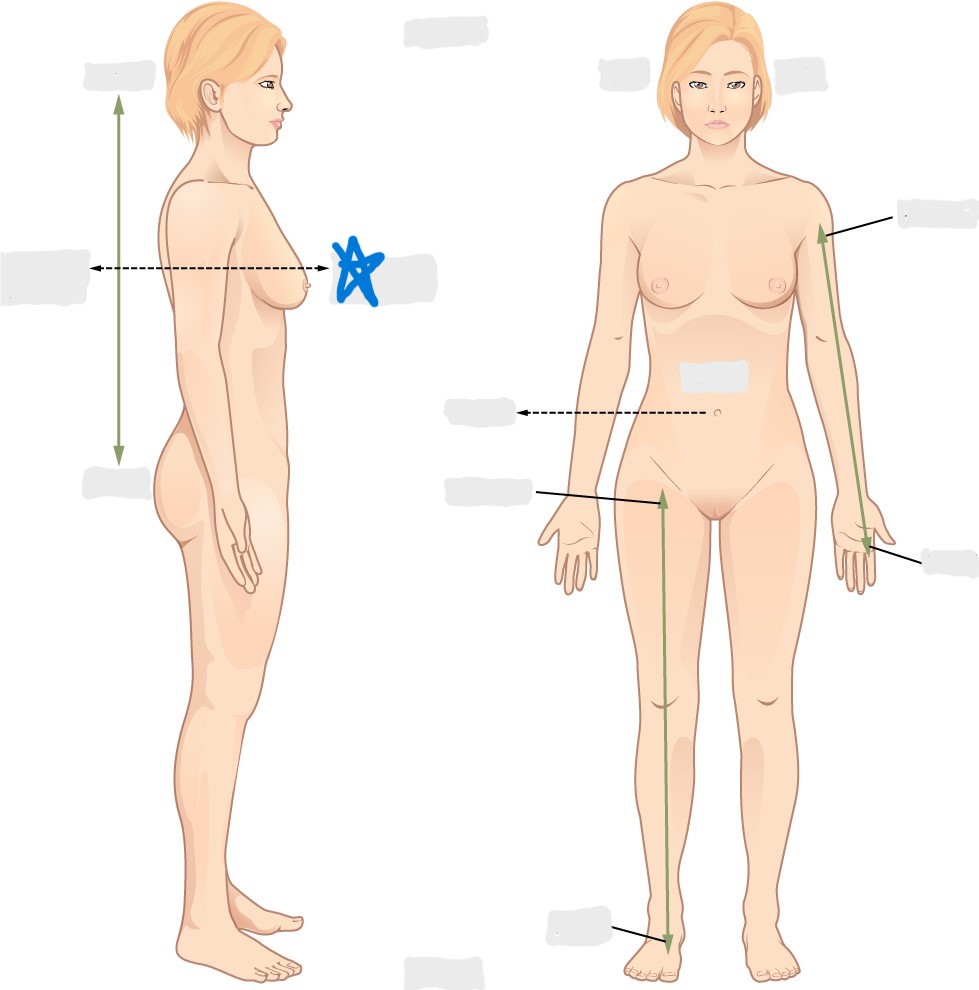
lateral

medial
distal
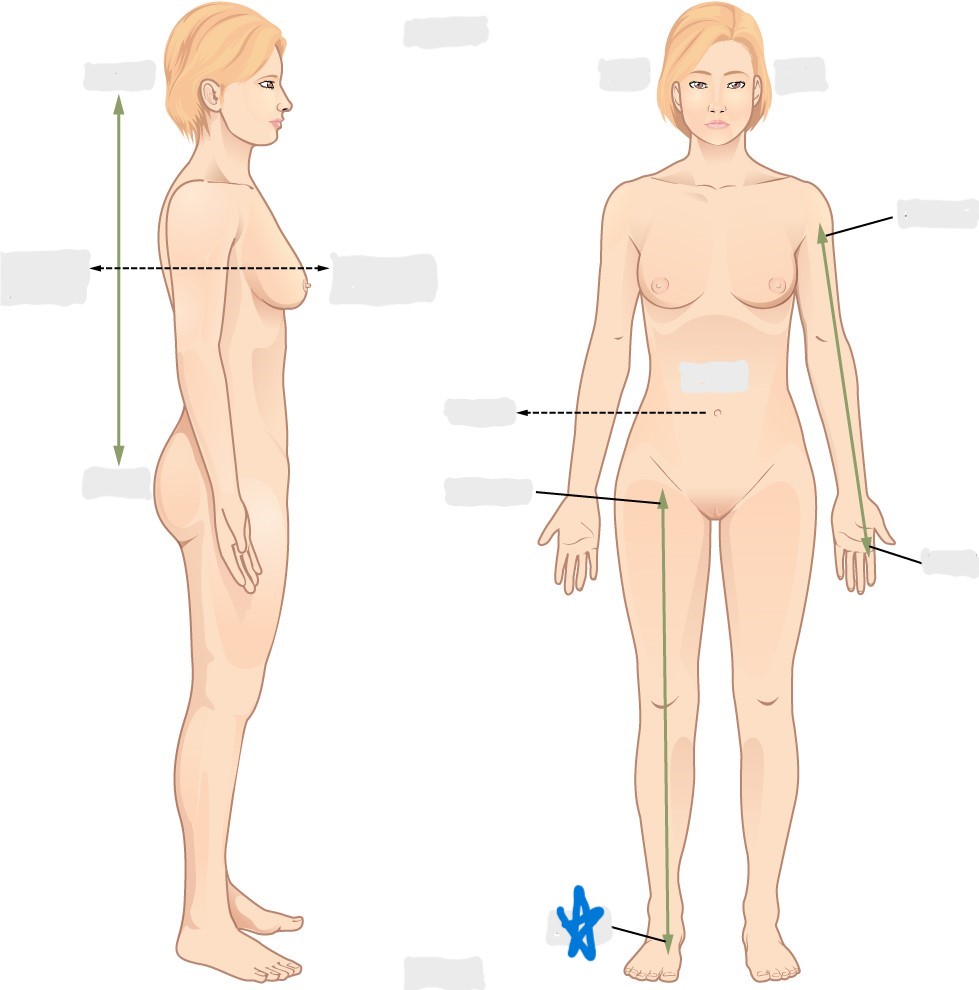
proximal
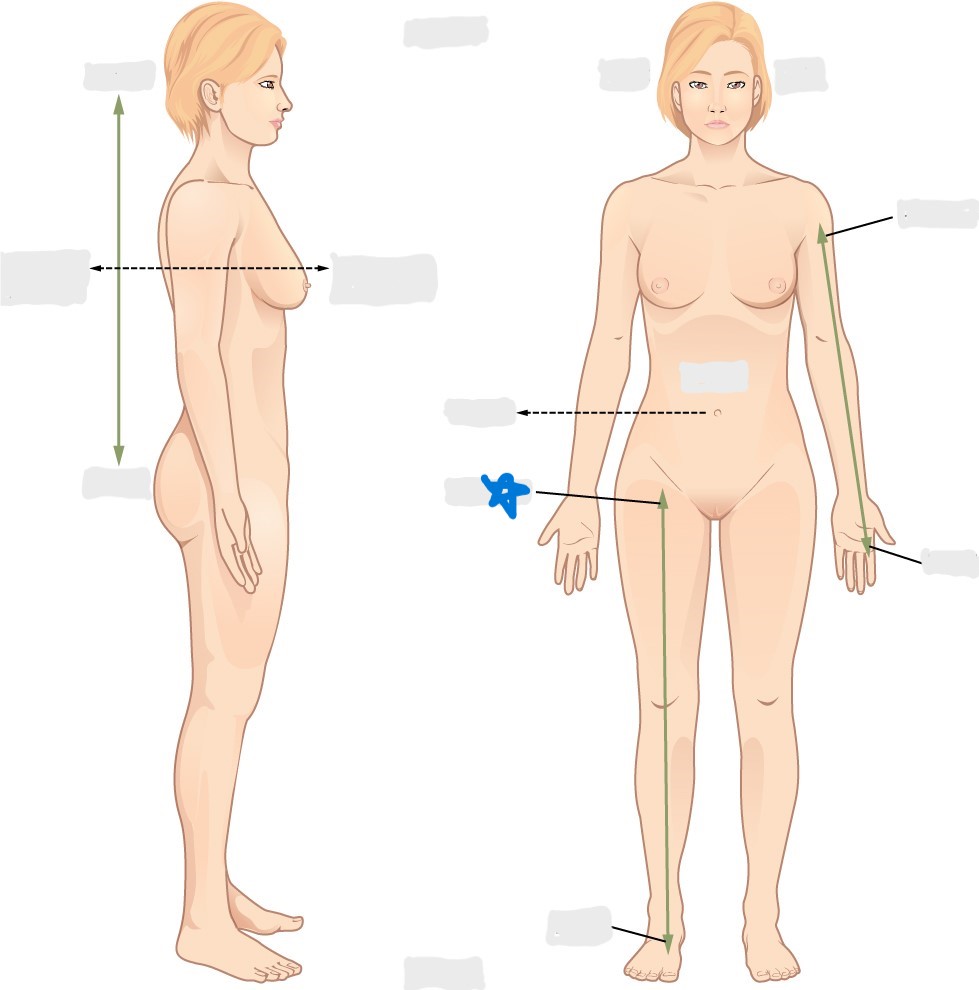
superficial
deep
superior
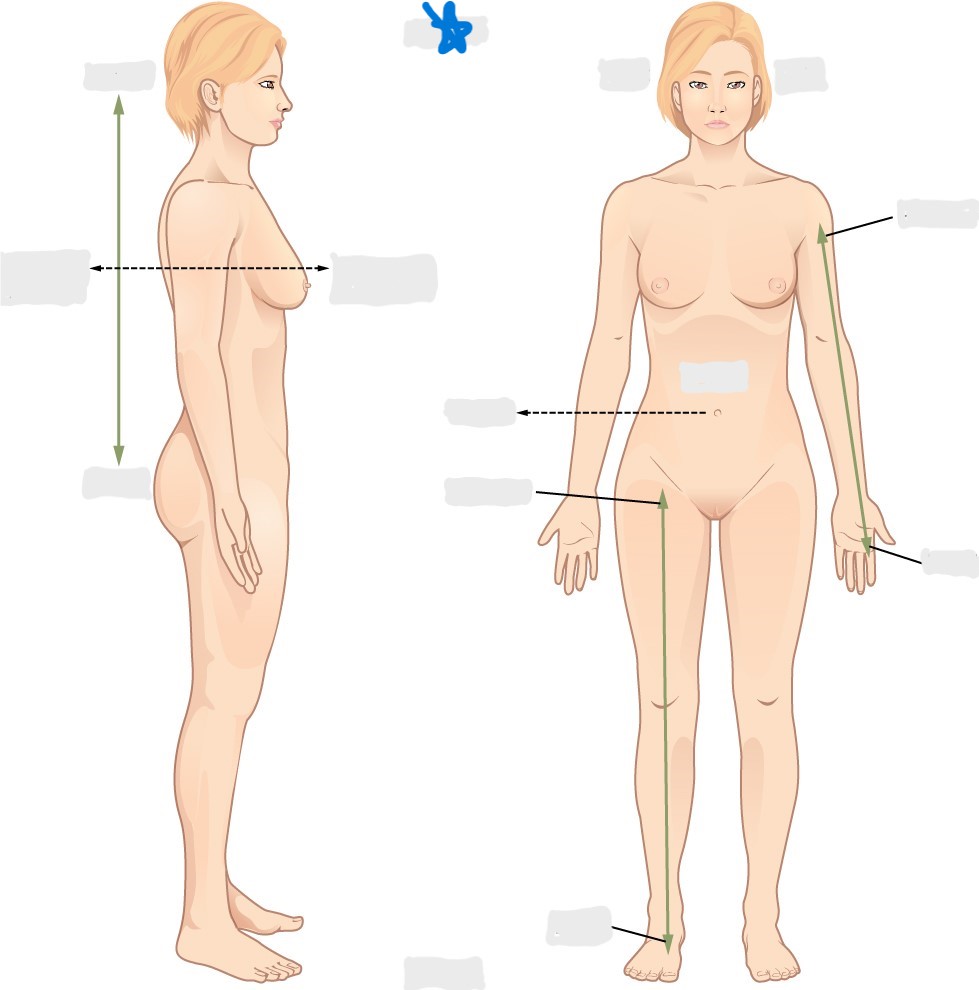
inferior
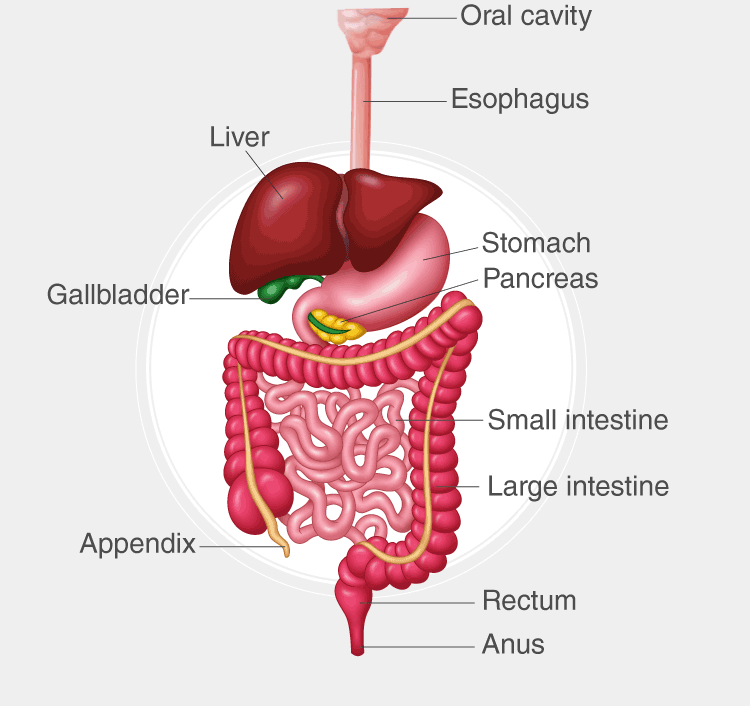
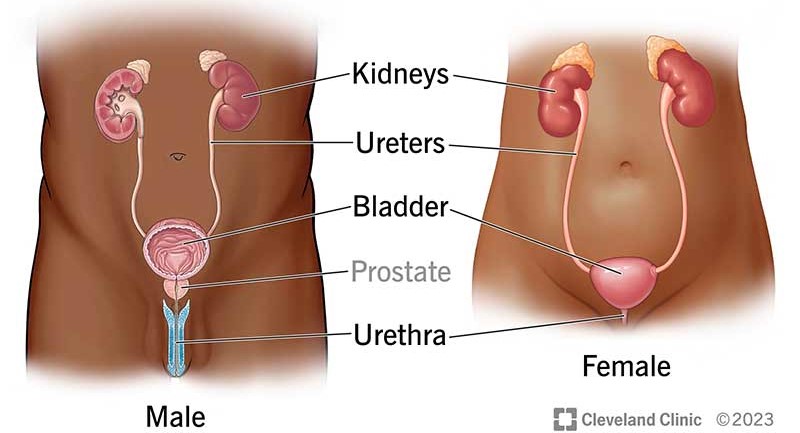
digestive/gastrointestinal cavity
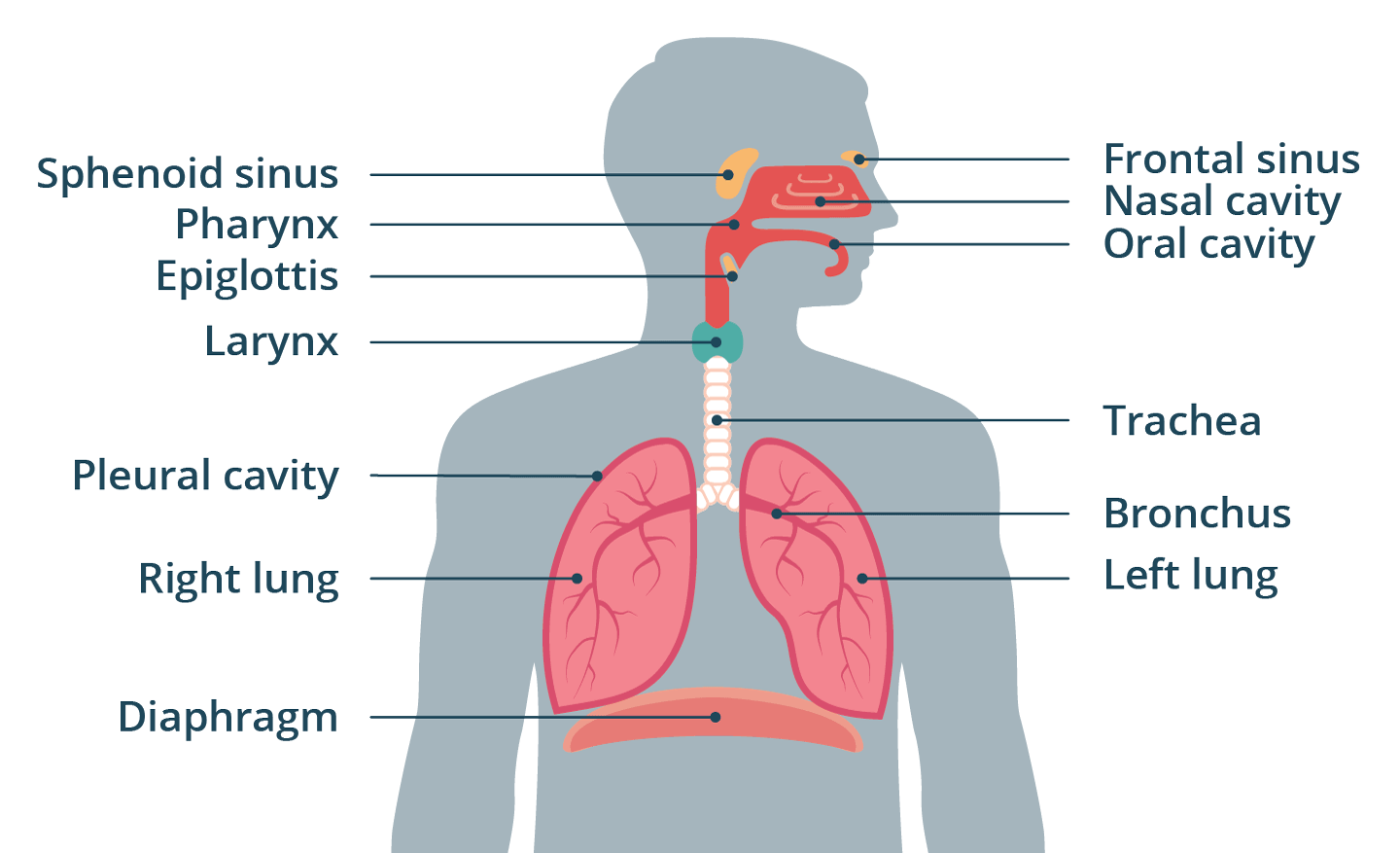
respiratory tract
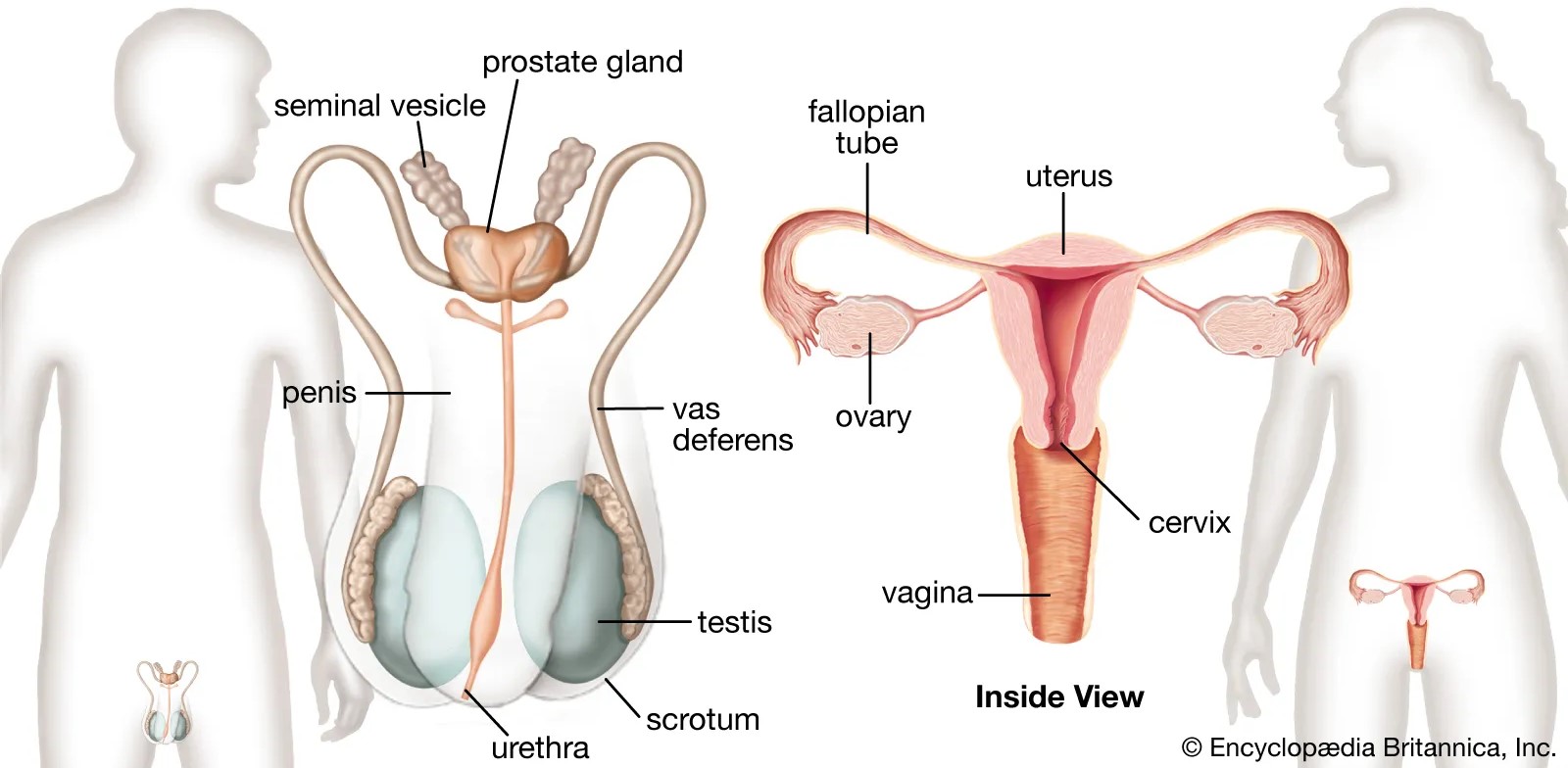
reproductive tract
urinary tract
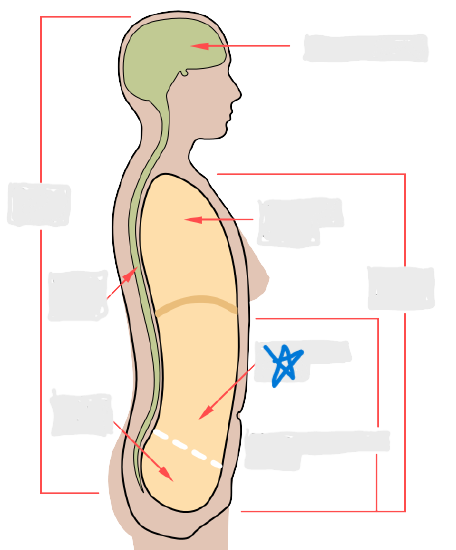
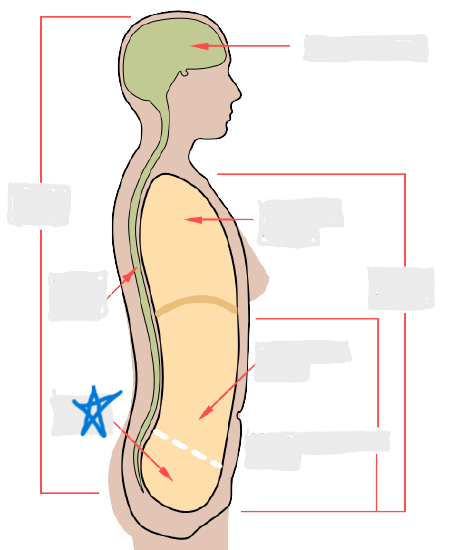
cranial cavity
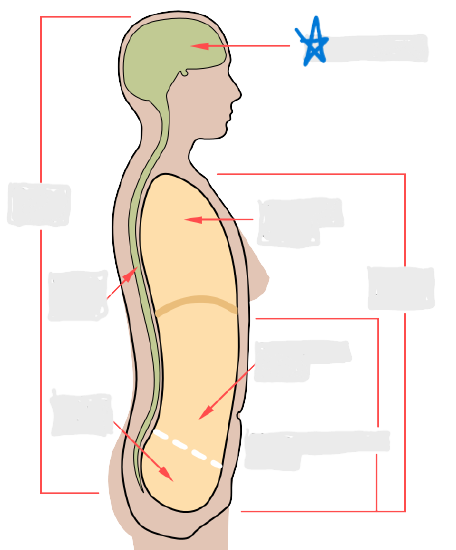
vertebral cavity
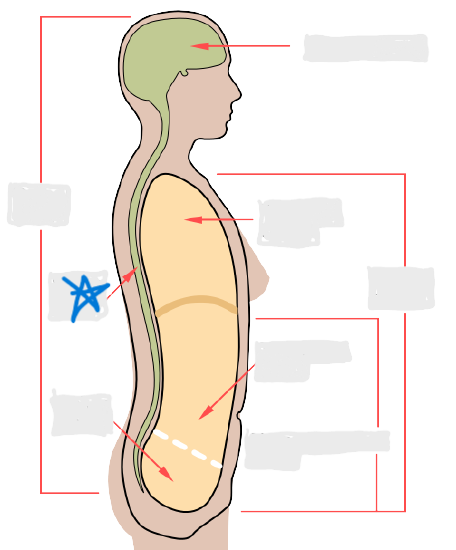
pleural cavity
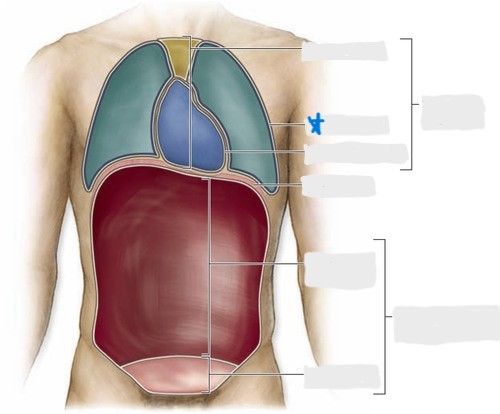
pericardial cavity
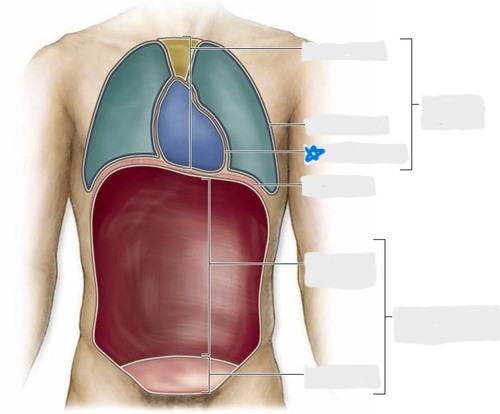
mediastinum
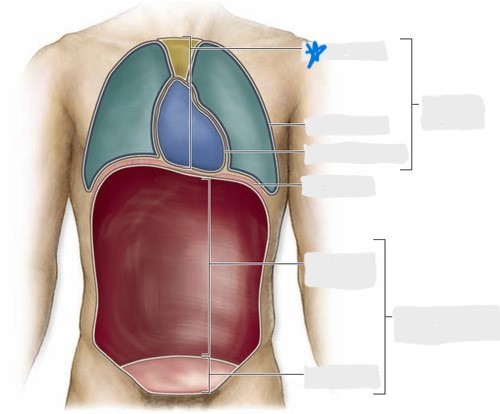
abdominal cavity
pelvic cavity
tissue
any grouping of cells in the body that are similar in structure and carry out a similar function
epithelial tissue
a covering tissue that is often found as the innermost lining of hollow organs and body cavities, along with organs that lead immediately outside the body
simple epithelium
epithelial tissue with one layer
stratified epithelium
epithelial tissue with two or more layers
squamous epithelium
epithelia made of flattened cells
cuboidal epithelium
epithelia made of cube-like cells
columnar epithelium
epithelia made of rectangular cells
simple squamous epithelia
epithelia composed of a single layer of flattened cells
function: allows substances to cross quickly and easily
location: alveoli in lungs
stratified squamous epithelia
epithelia composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that provide a protective quality without being excessively thick
function: reduces friction
location: mouth lining
simple cuboidal epithelia
epithelia composed of cube-shaped cells that are usually found in a circular pattern
function: absorption or secretion
location: kidney tubes
simple columnar epithelia
epithelia composed of cube-shaped cells that frequently have microvilli or cilia
function: absorption or secretion
location: GI tract lining
pseudostratified columnar epithelia
epithelia composed of cube-shaped cells with cilia that appears to contain multiple layers
function: produce and secrete mucous to prevent infection
location: lungs
transitional epithelia
epithelia composed of stratified cells in which the cell shape varies from layer to layer, starting out as cuboidal/columnar cells and transitioning into more variety in higher layers
function: shape variation, stretching
location: urinary bladder
skin
stratified squamous epithelium that contains keratin
keratin
a fibrous protein seen most heavily in the outermost skin layers and provides skin with protective qualities
connective tissue
tissue functioning as support, protection, insulation, storage, and transport
loose areolar connective tissue
widespread connective tissue that holds organs, tissues, and anatomical structures in place
adipose tissue (fat)
connective tissue found under the skin and various organs that are used as a cushion to absorb shock and store energy reserves; characterized by empty-looking cells
dense connective tissue
connective tissue that is tightly packed, and is therefore very resistant to tension and found in areas that are frequently pushed and pulled, such as tendons and ligaments