BIO Lab #1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:37 AM on 1/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
Scientific Method
Make Observations, Questioning, Form Hypothesis, Test Hypothesis, Draw Conclusions
2
New cards
Make Observations
Collect info. Data must be verified by another person
3
New cards
Questioning
What is the cause?
Looking at cause and effect
Looking at cause and effect
4
New cards
Form Hypothesis
Tentative explanation, uses inductive reasoning
5
New cards
Test Hypothesis
Conducting the controlled experiment. Uses deductive reasoning. Analyze the data using statistics
6
New cards
Draw Conclusions
Accept or reject hypothesis, revise hypothesis. Hypothesis can't be proven true but can be proven false
7
New cards
Control Group
Controlling the conditions of the experiment
8
New cards
Control Group
Must remain constant throughout the experiment
9
New cards
Experimental Group
Receives the independent variable
10
New cards
Metric System
To convert between units, just move the decimal over the appropriate amount.
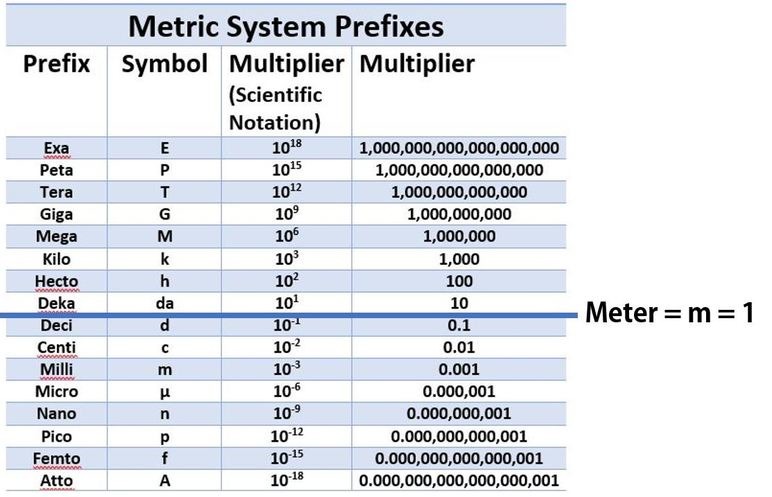
11
New cards
Pipette
Measures Volume
12
New cards
Metric Ruler
Measures Length
13
New cards
Beaker
Measures Volume
14
New cards
Triple beam balance
Measures Mass
15
New cards
Graduated Cylinder
Measures Volume
16
New cards
Erlenmeyer Flask
Measures Volume
17
New cards
What is the meniscus in a graduated cylinder?
The curved surface of the liquid
18
New cards
How to read a metric ruler
pic
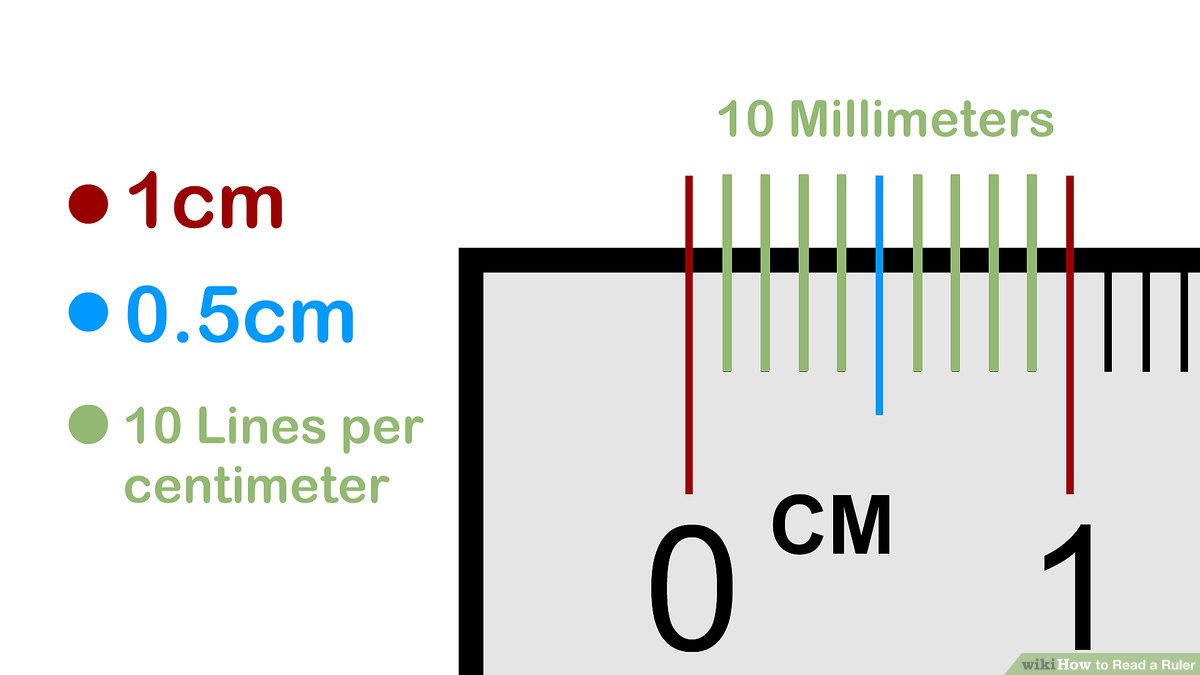
19
New cards
What are the different types of microscopes? Which type do we use in lab?
\-Compound Light Microscope (We use this one in lab)
\-Stereomicroscope
\-Teaching scope (Team scope)
\-Phase contrast microscope
\-Transmission electron microscope
\-Scanning electron microscope
\-Stereomicroscope
\-Teaching scope (Team scope)
\-Phase contrast microscope
\-Transmission electron microscope
\-Scanning electron microscope
20
New cards
Ocular
Lens nearest to eye
21
New cards
Body Tube
Keep ocular and objective lenses at proper distances from each other
22
New cards
Nosepiece
Permits interchange of scanning, low, and high power objectives
23
New cards
Pointer
Found in the ocular, can be moved by turning the black eyepiece
24
New cards
Arm
Supports the body tube and adjustment knobs
25
New cards
Objectives
Contains lenses of various magnifications
26
New cards
Coarse Adjustment
Changes the distance between the slide and objective to focus an image
27
New cards
Fine Adjustment
Permits exact focusing
28
New cards
Base
Bears the weight of the microscope
29
New cards
Stage
Supports slide
30
New cards
Stage Clips
Holds slide steady
31
New cards
Iris Diaphragm
Regulates the amount of light going through the specimen
32
New cards
Illuminator
\n Provides the light source
33
New cards
What is meant by field of view?
The circular field you see when you look through the ocular
34
New cards
Depth of focus
The thickness of an object that is all in sharp focus at the same time
35
New cards
How do you calculate the total magnification?
Magnification of the objective multiplied by the magnification of the ocular (10) equals total magnification.
36
New cards
What is the proper way to use (focus) the microscope?
1. Use the coarse adjustment knob on scanning power
2. Use the fine adjustment to obtain a sharp focus
3. Turn the nosepiece to low power, use coarse and fine adjustment
4. Repeat the same on high power
37
New cards
How does magnification affect working distance and light intensity?
Increasing the magnification decreases both the working distance and light intensity
38
New cards
wet mount
Slides used to look at tissues or cells of living organisms
39
New cards
Test used for detecting presence of reducing sugars, and color change results from a positive test
Benedict's Reagent + Heat for 2 minutes
Positive test - Yellow
Positive test - Yellow
40
New cards
Starch
Iodine
Positive test - Blue/Black
Positive test - Blue/Black
41
New cards
Lipids
Add vegetable oil to a test tube of water (emulsion)
Add Sudan and mix
Add liquid detergent
Reagent: Sudan
Positive test - Red
Add Sudan and mix
Add liquid detergent
Reagent: Sudan
Positive test - Red
42
New cards
Proteins
Biuret
Positive test - Purple
Positive test - Purple
43
New cards
Name the monomers of starch, lipids, and proteins
Starch - Glucose
Lipids - Fatty Acids and Glycerol
Proteins - Animo Acids
Lipids - Fatty Acids and Glycerol
Proteins - Animo Acids
44
New cards
Monomer
A molecule that can be bonded with an identical molecule to form a polymer
45
New cards
Polymer
\n A chain of monomers
46
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis
\n Bonding of 2 monomers to form a polymer while losing water
47
New cards
Hydrolysis
Splitting of a polymer into 2 monomers while gaining water
48
New cards
reducing sugar
Monosaccharides; has the ability to add electrons to reduce other molecules
49
New cards
function of detergent
Functions as an emulsifier
50
New cards
What is an emulsion? emulsifier
Emulsion - The mixture of two liquids, each insoluble to the other.
Emulsifier - A substance that activates the emulsion (Liquid detergent)
Emulsifier - A substance that activates the emulsion (Liquid detergent)
51
New cards
Plasma Membrane
Structure - Composed of proteins and phospholipids molecules
Function - Provides form to the cell and controls passage of materials in and out of the cell.
Function - Provides form to the cell and controls passage of materials in and out of the cell.
52
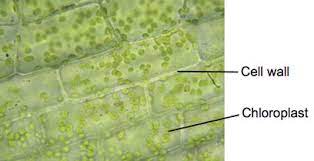
New cards
Cell Wall
Structure - Cellulose fibrils
Function - Provides support and rigidity to the plant cell
Function - Provides support and rigidity to the plant cell
53
New cards
Cytoplasm
Structure - Fluid to jelly like substance
Function - Suspending medium of organelles
Function - Suspending medium of organelles
54
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Structure - Interconnecting hollow channels
Function - Supporting framework of cell; cell transport
Function - Supporting framework of cell; cell transport
55
New cards
Ribosomes
Structure - Granules of nucleic acids
Function - Protein synthesis
Function - Protein synthesis
56
New cards
Mitochondria
Structure - Double-layered sacs with cristae
Function - Production of ATP
Function - Production of ATP
57
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
Structure - Flattened sacs with vacuoles
Function - Synthesize carbohydrates and package molecules for secretion
Function - Synthesize carbohydrates and package molecules for secretion
58
New cards
Lysosomes
Structure - Membrane-surrounded sacs of enzymes
Function - Digest foreign molecules and worn cells
Function - Digest foreign molecules and worn cells
59
New cards
Centrosome
Structure - Mass of two rod-like centrioles
Function - Organizes spindle fibers and assist mitosis
Function - Organizes spindle fibers and assist mitosis
60
New cards
Vacuoles
Structure - Membraneous sacs
Function - Stores and excretes substances within the cytoplasm
Function - Stores and excretes substances within the cytoplasm
61
New cards
Fibrils and Microtubules
Structure - Protein strands
Function - Supports cytoplasm and transports materials
Function - Supports cytoplasm and transports materials
62
New cards
Cilia and Flagella
Structure - Cytoplasmic extensions from cell
Function - Movement of particles along cell surface or move cell
Function - Movement of particles along cell surface or move cell
63
New cards
Nucleus
Structure - Nuclear membrane, nucleolus, and chromatin (DNA)
Function - Direct cell activity; forms ribosomes
Function - Direct cell activity; forms ribosomes
64
New cards
Chloroplasts
Structure - Inner (grana) membrane within outer membrane
Function - Photosynthesis
Function - Photosynthesis
65
New cards
Hypotonic
\n Occurs when the osmotic pressure inside the cell is greater than the osmotic pressure outside the cell (Cell Expands)
66
New cards
Isotonic
Occurs when the osmotic pressure inside the cell is identical to the osmotic pressure outside the cell (Normal Cell)
67
New cards
Hypertonic
Occurs when the osmotic pressure inside the cell is less than the osmotic pressure outside the cell (Cell Shrinks)
68
New cards
Crenation
Shrinkage of a cell as a result of losing water
69
New cards
Hemolysis
The bursting of a cell as a result of gaining too much water
70
New cards
Turgor Pressure
The pressure exerted on the cell membrane as a result of water entering the cell
71
New cards
Plasmolysis
Contraction of the protoplast of a plant cell as a result of loss of water from the cell
72
New cards
Flaccid
The cell membrane is not under pressure; is being shrunk
73
New cards
Interphase
the beginning cell
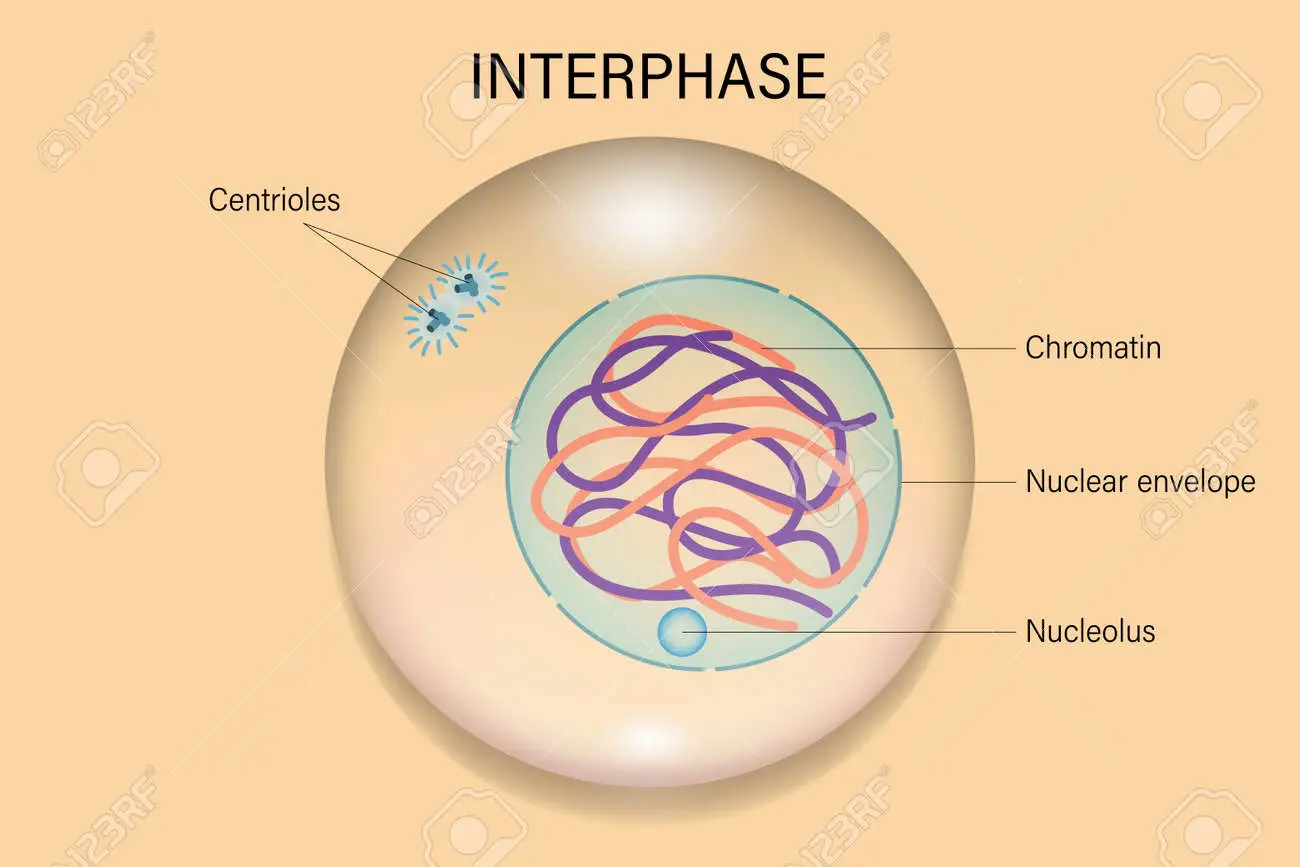
74
New cards
Prophase
the first step to splitting a cell
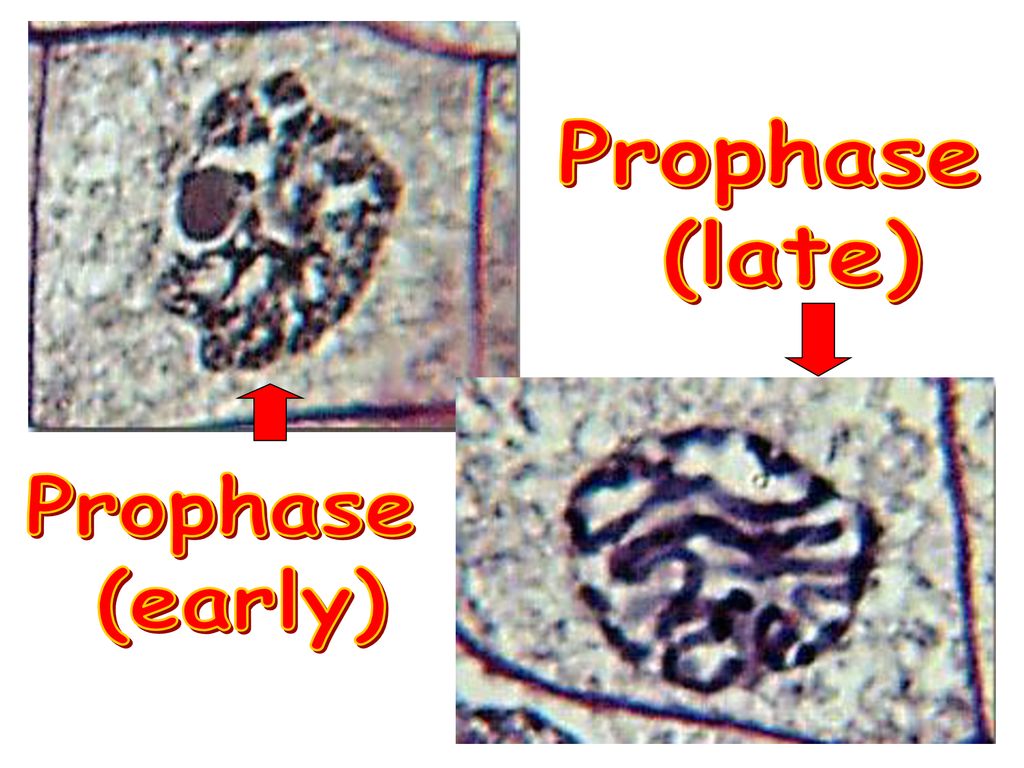
75
New cards
Metaphase
the second step where a wall is visible
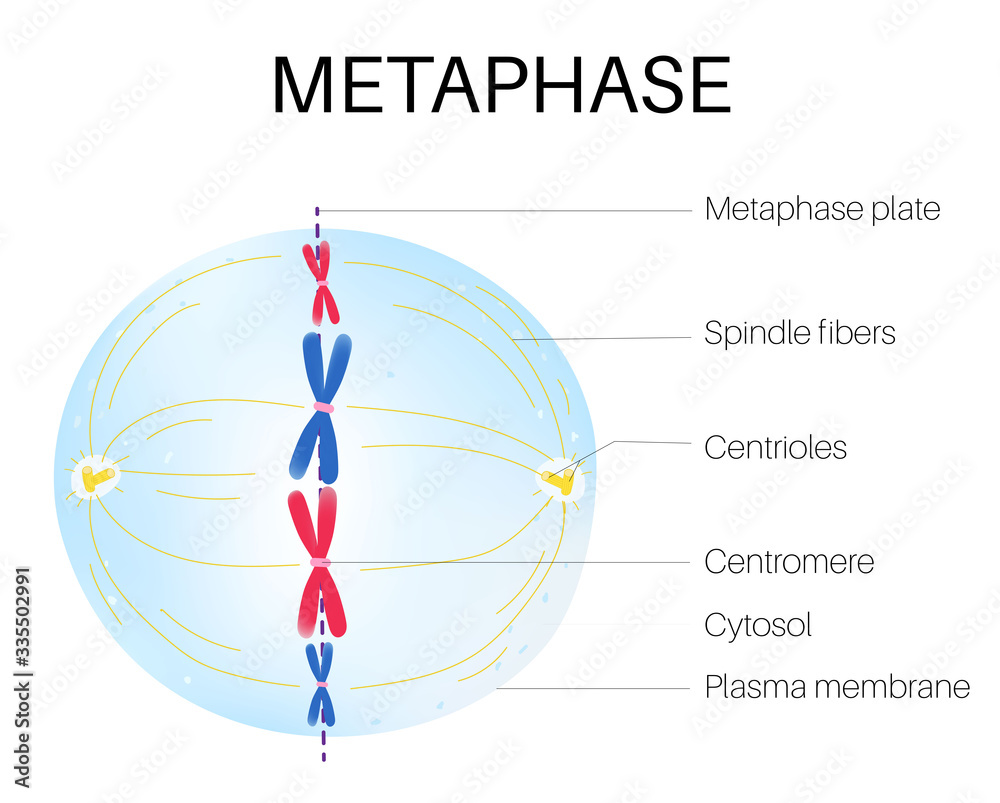
76
New cards
Anaphase
third step where separation can be seen
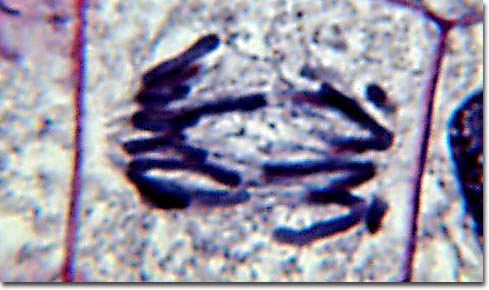
77
New cards
Telophase
final step where cell is still connected but with a cell wall between
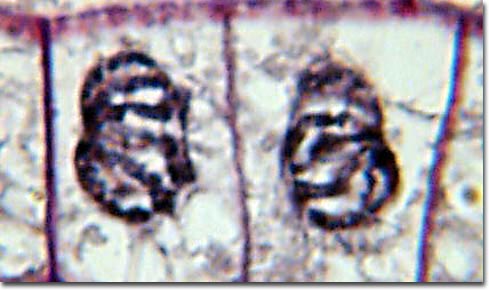
78
New cards
Identify chromosomes
pic
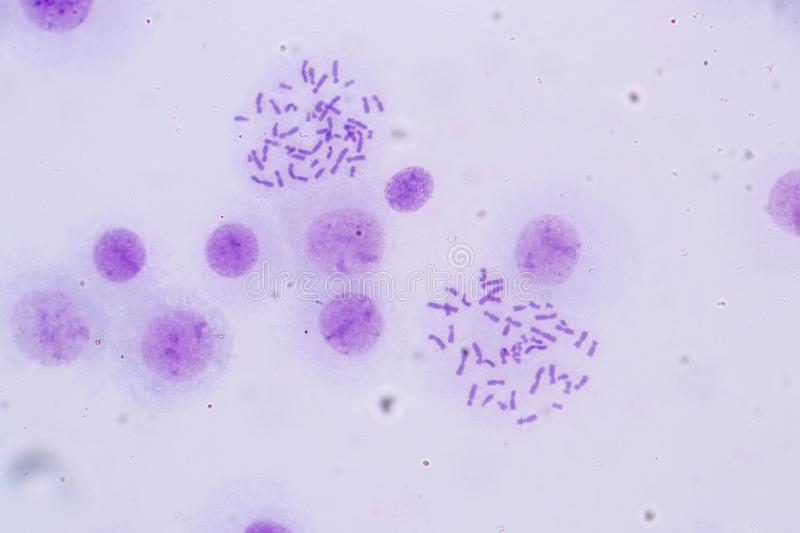
79
New cards
Identify the cytoplasm
pic
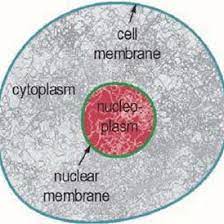
80
New cards
Identify the nucleus
pic
81
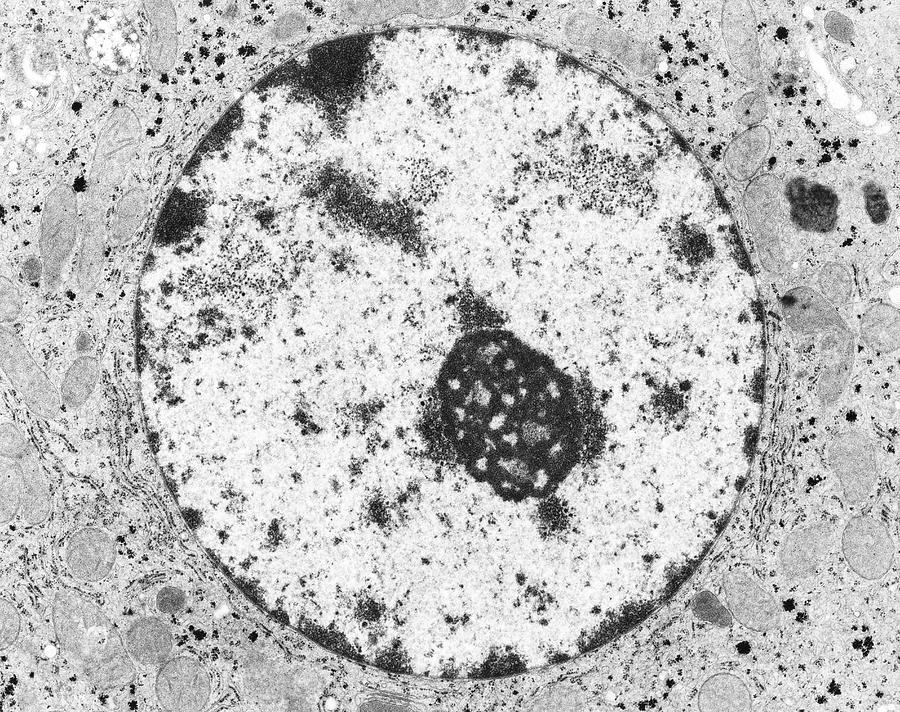
New cards
Identify the nucleolus
pic
82
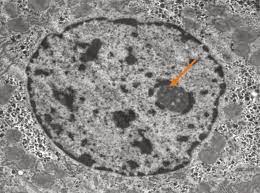
New cards
Identify the cell wall
pic
83
New cards
Mitosis
a process where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells
84
New cards
Meiosis
a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information.
85
New cards
Enzymes & how they work
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions; lower the activation energy and bind to a specific molecule
86
New cards
Denature
take away or alter the natural qualities of
87
New cards
What effect do temperature and pH have on the rate of reaction?
Raising temperature generally speeds up a reaction, and lowering temperature slows down a reaction; Changing the pH outside of the optimal range will slow enzyme activity
88
New cards
What did the experiment involving a mixture of milk and rennin incubated at different temperatures illustrate?
how temperature effects enzymes: the rate of reaction and color
89
New cards
Rennin
an enzyme secreted into the stomach of unweaned mammals, and in some lower animals and plants, causing the curdling of milk
90
New cards
What’s the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide involving catalase? What were the bubbles?
A catalase detoxifies hydrogen peroxide by breaking it down into water and oxygen gas; the bubbles resulting from production of oxygen gas clearly indicate a catalase positive result
91
New cards
What effect did macerating (mashing) the potatoes have on the rate of reaction? Why?
It sped the process up because the cells were already destroyed
92
New cards
Gene
Structural and functional subunits that contain coded information for making a specific protein
93
New cards
Trait
individual’s observable physical characteristics
94
New cards
Allele
different forms of a gene that occupy the same position on homologous chromosomes
95
New cards
Heterozygous
an individual has two different alleles for a given trait
96
New cards
Homozygous
an individual has two alike alleles for a given trait
97
New cards
Genotype
the genetic makeup of an individual
98
New cards
Phenotype
a specific trait (i.e. brown eyes for eye color)
99
New cards
Dominant
the stronger allele when one allele may completely mask the presence of the other one
100
New cards
Recessive
the weaker allele when one allele may completely mask the presence of the other one