lec 7.4 - transcription enhancers, elongation, and termination
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
enhancers
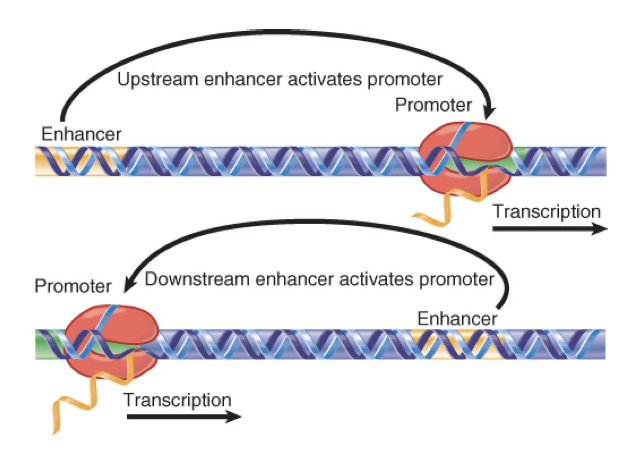
can activate a promoter from upstream or downstream of promoter region of gene (from very far away)
its sequence can be inverted relative to the promoter
only work in cis
regulate gene expression of specific gene on same chromosome where they are located, cannot influence genes on other chromosomes
other initiation sequences/complexes involved in RNA pol II initiation - enhancer sequences and mediator complexes
enhancer sequences - increase freq. of transcription from promoter
mediator complexes - act as communication bridge btwn RNA pol II and other TFs
20 proteins and 3 subdomains
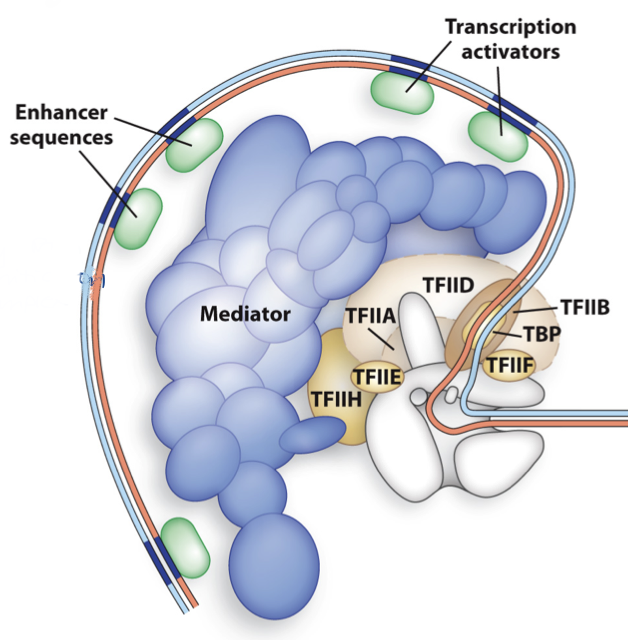
bending DNA in RNA pol II initiation
important factor for expression - transcription machinery can better access promoter region
brings all components together
gene expression is associated with
demethylation of promoter and regulatory regions
determines which genes are on/off - gives an extra regulation mechanism
elongation
continuous process until termination
RNA pol holoenzyme reads the template strand from 3’ to 5’ and makes 5’ to 3’
how does termination vary in eukaryotes
all 3 RNA pols in eukaryotes use different strategies for termination
pol I and pol III in termination
these pols are similar to bacteria
pol I -terminates at termination sequence
pol III -terminates at T-rich sequence
why is a T-rich sequence good for termination?
because it will bind to As and will only have 2 hydrogen bonds
weaker
pol II in termination
terminates several bases to several hundred bases away from 3’ end of mature mRNA
CPSF recognizes AAUAAA and cleaves RNA, then poly-A tail is added at 3’ end (needed to prevent degradation)
exonuclease removes rest of the RNA (gets rid of excess) and RNA pol is released from DNA
why is a poly-A tail added?
to avoid degradation in cytosol
more As in the tail = more stability
fewer As = degraded quickly
longer mRNA lasts = more protein made
poly A tail acts as an extra level of gene regulation/expression