Poli 210 Midterm 1 Cartes | Quizlet
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Categorical (nominal) data
Categorical variables that cannot be placed in ranked order ( from lowest to highest; agree, neutral, disagree), and no information about the distance between categories ( Colors, Gender, Vote choice, Country of residence, Religious affiliation)
Interval Data
Beyond rank ordering, interval scales indicate the distance of one observation from another (IQ tests)
Ordinal Data
Categorical variables that can be placed in ranked order ( from lowest to highest; agree, nuetral, disagree), but no information about the distance between categories
Likert scales (strongly agree, agree, nuetral, disagree, strongly disagree)
Ratio Data
Interval level but where 0 is conceptually meaningful. i.e. zero means there is none of that variable. Can construct a meaningful fraction or ratio with a ratio variable. Reaction time, height, mass, distance, GDP, number of parties in parliament, voter turn out
Case
single unit of analysis
3 misconceptions
1. No research topic is inherently qualitative or quantitative
2. Specific methodologies do not belong to one or the other
3. Uncommon to refer to researchers as qualitative or quantitative
Qualitative is associated with
positivism
Quantitative is associated with
interpretism
Primary purpose of most quantitative analysis is to
test hypothesis
Triangulation
combination of multiple research strategies in social research
Maximizes the variety of data collected
mixed-methods research approach
Both qualitative and quantitative
Theory
○ integrated set of explanations of the political and social worlds
- Attempt to understand the complex political world by simplifying reality into theories
Hypothesis
statements of the relationships between concepts or more specifically are proposed explanations for an observable phenomenon
Proposition
If-then statement.
Statement of fact that follows from the accuracy of the hypothesis such that is the hypothesis is true the following conditions will prevail
concept
Defined term that enables us to organize and classify phenomena
Enable us to make comparison through categorization
Continuum
Organizing a concepts variables along a dimension
Causality
X changes therefore Y changes
Correlation
X changes when Y changes
positive correlation
Increase in X leads is accompanied by an increase in Y (also works with decreases)
Negative correlation
o relationship between the two variables but that the direction of the change is inverse.
Overall, a hypothesis will state the relationships between the concepts by
providing a statement of the proposed cause of an observable phenomenon and the underlying theory will attempt to explain why these relationships exist.
inference
to acquire knowledge about some facts we don't know yet by studying something we already know
Science requires us to take additional steps
of attempting to
infer beyond the immediate data to something broader that is not directly observe
Causal Relationship
The occurrence of an entity B of a certain class depends on the occurrence of an entity A of another class, where the word entity means any physical objects, Phenomenon, situation, or event. A is called the cause, B the effect
Variables
A characteristic that varies in value or magnitude along which an object, individual or group may be categorized, such as income or age
dependent variable
The measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested. Y
independent variable
a variable (often denoted by x ) whose variation does not depend on that of another.
causal endogeneity
In a statistical model, an endogeneity problem occurs when there is a correlation between the X variable and the unobserved errors
normative research
researches that are prescriptive in nature and address how society and political life should be. It often involves values, judgment, feeling, emotion, things are hard to scientifically measure. And the target of analysis is often an idea, not facts
Interpretivism
(post-modernism)
We can only interpret an event, but
we cannot (or, have to be very careful) to make causal inference and predictions based on that event
Empirical Research
descriptive in nature; the goal is to describe and explain real political phenomena rather than how they should b
Positivism
the application of the scientific approach to the social world. Observer and the observed in social studies can be separated, if we do it properly. And we can make causal inference to predict about future events
Determinism
every event has a cause/explanation
Replication
more than one observation occurs, confirming the findings of others research. the more replication that validates the data, the more valid it is.
research question
an interrogatory statement describing the variables and population of the research study
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
literature review
Is an evaluative report of information found in the literature related to your research question. The review should describe, summarize, evaluate and clarify this literature
correlation but not causal relation
A correlation is a measure or degree of to what extent are two variables vary together. A correlation does not automatically mean causality
Operationalization
the process of assigning a precise method for measuring a term being examined for use in a particular study
Conceptualization
Conceptualization is the process of developing and clarifying concepts. Not a measurement. defining so you an go through the process of operationalizing variables
unit of analysis
The major entity that you are analyzing in your study
level of analysis
Unit of analysis has different levels, defined by different forms with which we aggregate units of analysis. The aggregation can be achieved through location, size, organization
micro-level analysis
individual, family
meso-level of analysis
firm, organization, region, state
macro-level analysis
state, international system civilization, empire. big picture stuff
Qualitative Methods
an approach to learn about politics through study of a small number of cases. Depth, detail and quality of the cases are emphasized over the average effects in a large quality
mixed methods research
uses both quantitative and qualitative techniques, in an effort to build convincing claims about the relationships between attributes and outcomes. ADD CLASS DEF
behavioral research
modeling, explaining, and generalizing from the behaviors and actions of individuals
inductive theory building
the practice of reasoning from actual observation to reach a generalizable conclusion
Observations (data) → hypothesis → test hypothesis → generalizable theory
deductive theory building
the process of reasoning from one or more premises (assumption) to reach a logically certain conclusion
generalization → hypothesis → test hypothesis → generalizable theory
quantitative method
a research approach that seeks to understand political life through the study of large quality, or number, of cases
Humean Causality
They think about causality as necessary and sufficient conditions for certain events to happen. A cause must be present to make the effect to occur
counterfactual
Focus on causal effects, rather than the cause itself. The foundation of most quantitative, experimental and comparative qualitative studies
temporal order
the cause must proceed the effect
problem of pre-emption
a cause just happens and preempts another cause
Causal Mechanism
Is a sequence of events, conditions and processes leading from the explanatory variable to the explained outcomes
fundamental problem of causal inferernce
Each part in a causal process still needs to be defined and estimated under counterfactual based causality. The problem of infinite regression.
Spurious causal relation
a relationship wherein two variables that actually have no logical connection are inferred to be related due to an unobserved third variable
autocorrelation/tautology
x and y by definition are the same concepts. So certainly we will observe x and y change together, but it is useless for studying
reversed causality
A situation where what appears to be an effect of an event is actually the cause of the event.
X and Y can vary together, but its Y → X, not X → Y
reinforcing variable
a variable that strengthens or magnifies the relationship between the two other variables
Spuriousness
The independent and dependent variables are both affected by an outside variable (Z)
Equifinality
many explanatory variables and few observations. Same outcomes can be reached with different independent variables
control variables
the variables you keep constant/set in an experiment
confounding variable
Another variable that is not normally considered. Something else could be causing Y. For example, a natural disaster could be a confounding variable
intervening variable
a variable has causal relations with both X and Y, and the causal relations go from intervening variable to X and Y
Measurement
a quantity that has both a number and a unit
reliability of measurement
An operational measure of a concept is reliable when it is repeatable or consistent
ratio/continuous variable
can take on any score or value within a measurement scale. In addition, the difference between each of the values has a real meaning. Familiar types of continuous variables are income, temperature, height, weight, and distance.
the central tendency
a measure that represents the typical response or the behavior of a group as a whole. The mean
Median
the middle score in a distribution; half the scores are above it and half are below it
ordinal variable
A special type of categorical variable that the categories have orders.
dummy variable
type of ordinal/binary variable that has no meaning. a measure in which a quality is dichotomous and is represented by the presence and the absence of the quality, usually using the values of 0 and 1. ( e.g. 0=not female 1=female)
mean
the arithmetic average of a distribution, obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores
concept overstretching
Applying concepts to cases which actually do not fit with the definitional characteristics of the concepts
Denotation (extension)
the class of things to which the concept apply
Ladder of generality
The higher up the more you can include. this includes most regimes and structures. The lower down the more specific types of regimes specifically democracies. Increase differentiation
Connotation (intension)/ definitional attributes
the collection of properties which determines the thing to which the world applies
the tradeoff between connotations and denotations
Connotation: the collection of properties which determines the thing to which the world applies
Denotation: the class of things to which the concept apply
population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
sample
a part of the population. It is the subgroup that is observed in one-round of researcher's observation
random sampling
is about how researchers select cases for inclusion in a study - they are selected at random, which means that every member of the underlying population has an equal probability of being selected.
self selection (sampling)
participants place themselves in a sample rather than being selected for inclusion by a researcher; type of non probability sampling
snowball sampling
gathering further people to sample by asking those whom you have already sampled
non-probalistic sampling
Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population or to inform about processes that are meaningful beyond the particular cases, individuals or sites studied
Variation
A change or slight difference in condition, amount, or level.
standard deviation
The square root of variance sometimes expressed as sd(y) or sY. measure of spreadoutness
normal dsitribution
an arrangement of data in which most values cluster around the mean value and the rest taper off symmetrically toward either end
bell curve
distribution of scores in which the bulk of the scores fall toward the middle, with progressively fewer scores toward the "tails" or extremes
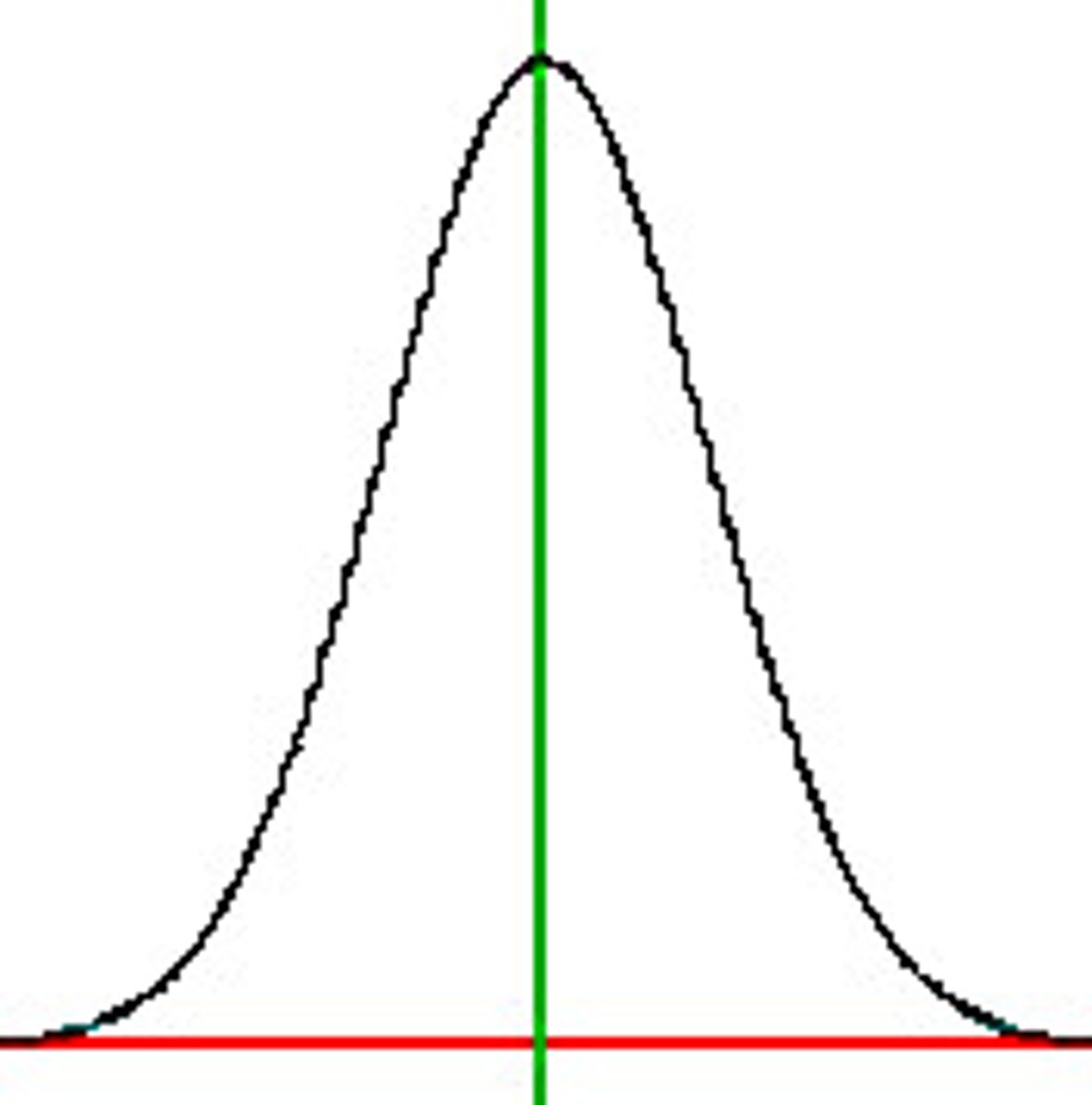
68-95-99 rule for normal distribution
If the values of a variable X follows normal distribution, then we are sure 68% of all possible values of X fall in a range of one standard deviation away from the central mean, 95% of all possible values of X fall in the range of two standard deviations away from the central mean, and 99.7% of all possible values of X fall in the range of three standard deviations away from the central mean.
Small N study
Explore the complex interaction of many variables in a small number of cases.
large N study
focus on the causal effects of a small number of variables in a large numbers of cases
Successful least-likely case
A case that is expected to refute the operating assumptions of a particular theory but in practice confirms them
Barrington Morre
wrote The Social Origin of Dictatorship and Democracy
Galton's problem
when all existing possible Xs are not properly controlled in case comparison, you will encounter the too many variable, not enough cases problem aka Galton's Problem
most different systems design
A research design in which we compare cases that differ with respect to multiple factors but in which the outcome is the same
most similar systems design
a common approach of the comparative method that selects cases that are alike in a number of ways but differ on a key question under examination
the social origin of dictatorship and democracy
The only well-elaborated Marxist work of the politics of modernization. Written by Moore.
descriptive case study
a type of single case study aiming to describe the phenomena as the basis of contributing to an emerging future research agenda
random error
the non-systemic fluctuation in the measured data due to the precision limitation of the measurement method