Plateau Iris Syndrome
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Hyperopia
Older age
Female
Asian decent
Short axial length
Thick/anterior positioned lens
Thick/anterior inserted lens
What are the 7 risk factors for Primary Angle Closure (PAC)?
dim; pupil is in mid-dilated to dilated pupil size
To get a good assessment of a narrow angle or angle closure, you want to perform gonio in a (dim/moderate/bright) setting. Why is it important to perform gonio in this setting?
Plateau Iris
Large or anterior placement of ciliary body/processes; pushes peripheral iris forward even though iris is anatomically inserted correctly
True
True/False: Pupillary block can co-exist with plateau iris.
The patient’s plateau iris may co-exist with pupillary block.
If a patient who has plateau iris undergoes an LPI and shows decent improvement, what may this indicate in regards to the patient’s angles?
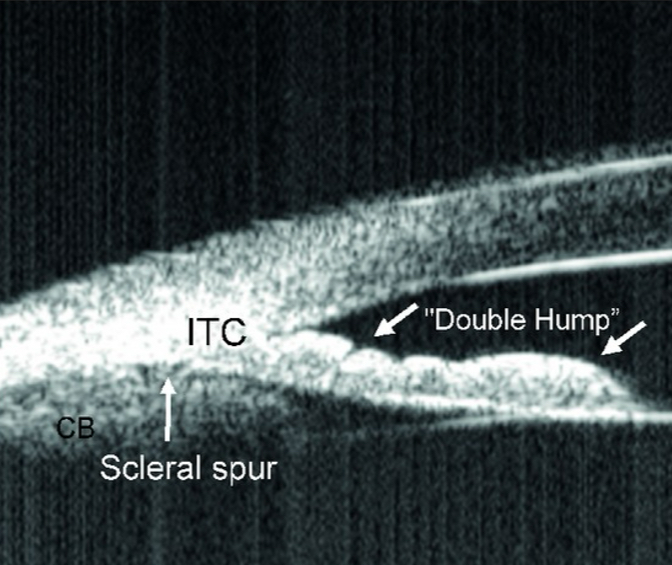
Indentation Gonioscopy; UBM
What is one examination technique that can be used to tell if the iris has a plateau configuration? What form of imaging may be helpful in better analyzing this?
Sine Wave - hump at ciliary body, hump at anterior lens
What do we call the shape of the Plateau Iris?
Using a narrow beam, apply gentle pressure with gonio lens. You will see the iris indents, but near the angle, it is still narrow.
How is indentation gonio performed to prove a patient has plateau iris?
The ciliary body is physically in the way.
When performing indentation gonioscopy, why doesn’t the angle indent and stays narrow in patients with plateau iris?
False - normal anterior chamber depth centrally with crowded angle
True/False: Patients with plateau iris configuration have a narrow anterior chamber.
Plateau Iris Syndrome
Patient with a patent PI but an angle that is still closed or IOP is still elevated
Argon Laser Iridoplasty
Procedure where laser causes contraction of peripheral iris, mainly the pigmented epithelium of anterior iris; can possibly help with PAS
Argon Laser Iridoplasty
What laser procedure is performed to pull iris stroma away from angle structures, deepening the angle recess?
Abraham Iridotomy Lens
What lens is used for Argon Laser Iridoplasty?
500 microns; 0.5 seconds; 240 mW
What spot size is used for an Argon Laser Iridoplasty? Duration? Starting power?
False
True/False: You should be able to see bubbles or pigment release when performing Argon Laser Iridoplasty.
Lighter
(Darker/Lighter) irides need more power for an Argon Laser Iridoplasty to work.
True
True/False: A patient should be able to feel an Argon Laser Iridoplasty.
Alphagan
Pilocarpine
What 2 drops should be used prior to Argon Laser Iridoplasty?
Peripheral iris
For Argon Laser Iridoplasty, what part of the iris should you aim for?
20-25 spots; 2 spot sizes
How many spots are often shot at a patient’s iris during Argon Laser Iridoplasty? How many spot sizes should be between each spot?
iris Cyst
What do we call a “Plateau Iris Imposter"?
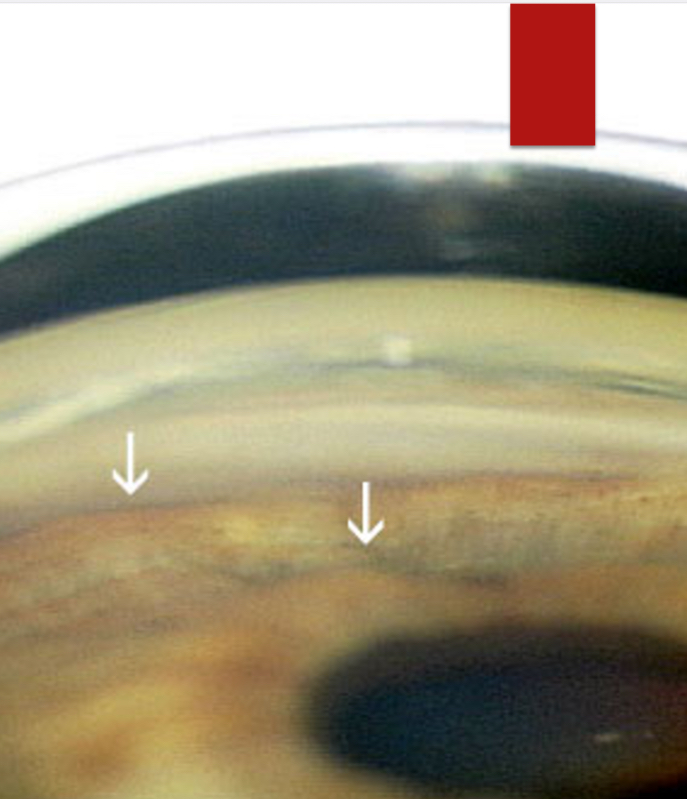
Pupillary Block
The top image is Pre-LPI. The bottom image is post-LPI. With the difference noted between the 2 images, what type of angle configuration do we expect to be the issue in this angle closure patient?
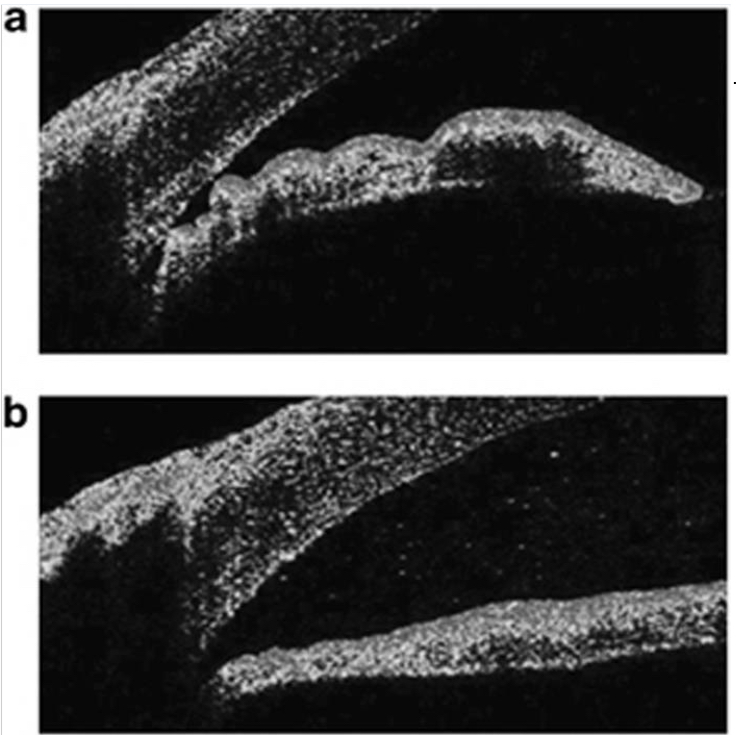
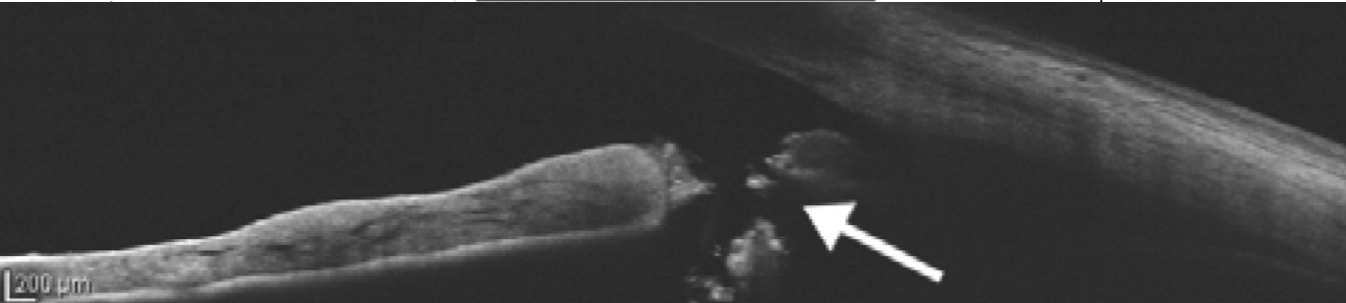
OCT
What form of imaging can be done to check the patency of a PI?
Pigment Dispersion Syndrome
Deposition of pigment on lens, zones, TM, and endothelium; pigment likely released from zonules rubbing on posterior iris
Pigment released from zonules clogs the TM
What is the MOA of Pigment Dispersion Syndrome in causing increased IOP?
Pigment Dispersion Glaucoma (PDG)
If increased IOP from pigment dispersion syndrome starts to cause optic nerve perfusion issues and changes, what does the patient have?
posterior
In pigment dispersion syndrome, the iris may insert more (anterior/posterior).
posterior to anterior
Normal aqueous flow goes from (posterior to anterior/anterior to posterior).
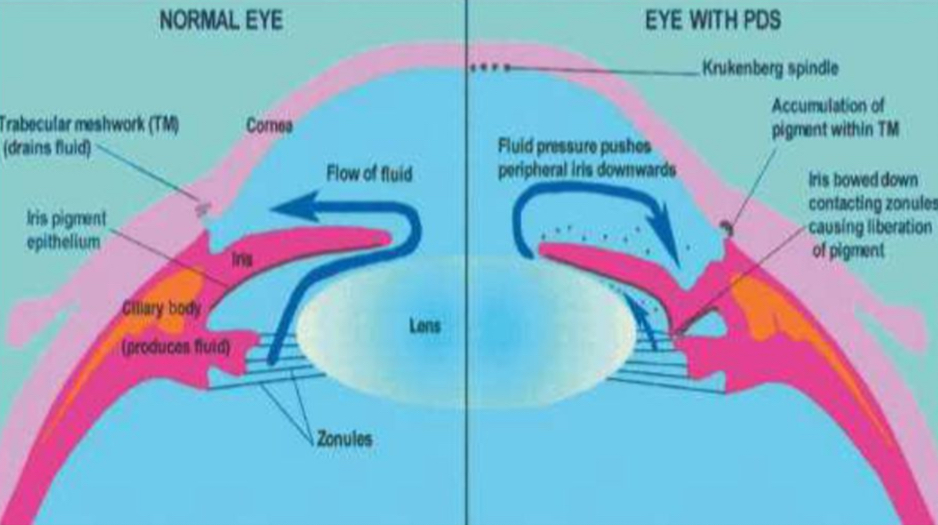
Aqueous moves from posterior to anterior chamber. Pigment blocks the TM, causing pressure to increase anteriorly. This pushes the iris backwards, causing the zonules to against the lens.
Why does Pigment Dispersion Syndrome have the possibility of causing reverse pupillary block?
Equalizes pressure between anterior & posterior chamber
What does an iridotomy do in relation to the pressure within the eye?
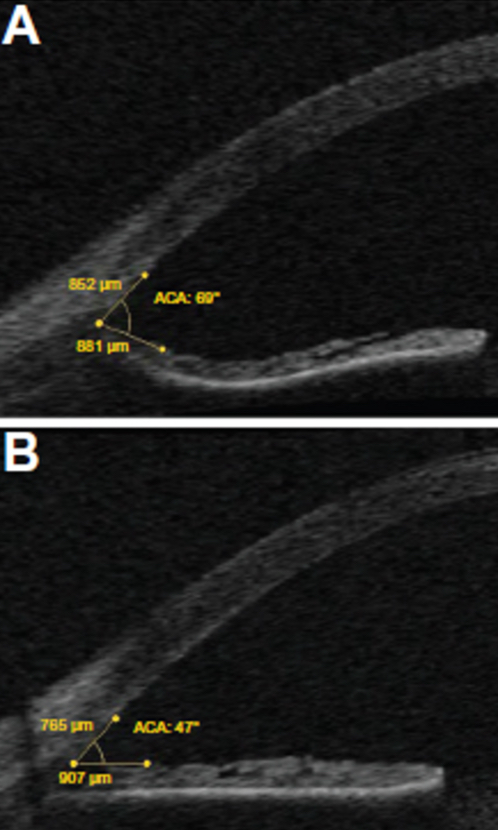
Reduces the concavity of the iris
How does an iridotomy affect the shape of the iris?
Cyclophotocoagulation
Laser ablation of the ciliary body; can be done with endoscope or transscleral
During cataract surgery
When is a cyclophotocoagulation often performed?
Endoscopic Cyclophotocoagulation
What procedure is shown in the image (be specfic)?
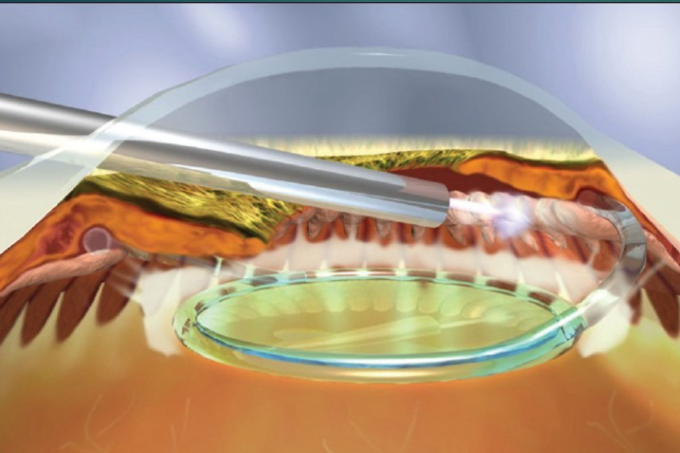
Transscleral Cyclophotocoagulation
What procedure is shown in the image?
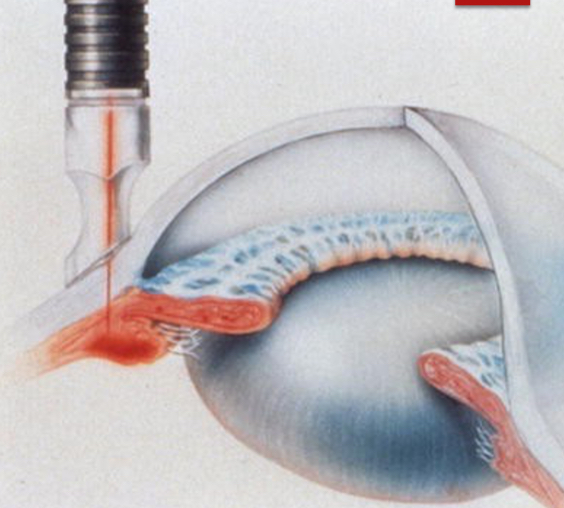
True
True/False: Transscleral Cyclophotocoagulation uses multi-pulse or continuous wave lasers.
Severe Glaucoma
What is cyclophotocoagulation performed for?
Hyphema
CME
Hypotony/phthisis
Sympathetic Ophthalmia
What are the 4 main complications of cyclophotocoagulation?
Vitreolysis
Using a YAG laser to break up vitreous floaters
YAG laser
What type of laser is being used for vitreolysis?
3 mm
How many mm are you supposed to stay away from the retina and lens during a vitreolysis procedure?
Paracentesis
Quickly lowering IOP when highly elevated via needle or incision
paracentesis
What quick procedure can help clear the cornea in angle closure situations?
Proparacaine
Betadine
What 2 medications should be used prior to paracentesis via incision or needle aspiration?
26-30 gauge needle (no plunger)
What gauge needle is used for paracentesis?
parallel; temporal
For paracentesis, you should insert the needle (perpendicular/parallel) to the iris near the (nasal/temporal) limbus.
0.5 mL
How much aqueous should you remove during a paracentesis?
True
True/False: It is normal to see the iris move or the pupil constrict during a paracentesis.
Hemorrhage
Iris or lens damage
Decompression retinopathy
Choroidal Effusion
Endophthalmitis
What are the 5 main concerns of paracentesis?