Metallic bonding
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
What is a metallic bond?
The electrostatic force of attraction between positive metal ions & a sea of negative electrons
Describe the structure of a metallic bond
A giant 3 dimensional lattice of positive metal ions surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons
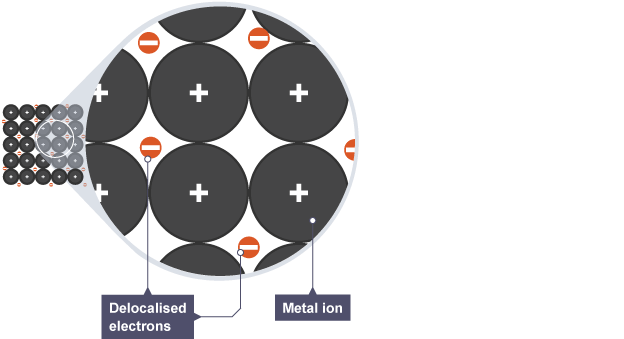
How are the positive metal ions kept close together?
By the sea of delocalised electrons
More delocalised electrons means a stronger metallic bond
Why do metallic bonds have high melting & boiling points?
Because the bonds between the positive metal ions & the negative delocalised electrons are very strong, allowing the metal to maintain a giant regular structure
This requires a lot of energy to overcome, therefore high temperatures are needed to break the bonds, giving metallic bonds high melting & boiling points
Why are metallic bonds good conductors of heat & electricity?
Because they have a sea of delocalised electrons, meaning that they have charged particles that are free to move
What are the properties of metals?
- Ductile (can be drawn / pulled into a wire)
- Malleable (can be bent & shaped without breaking)
- Conductors of heat & electricity
- High melting & boiling points
- Shiny
- Sonorous (clangs when hit)
Why are metals malleable?
Because their layers can slide over each due the sea of delocalised electrons