Plantae
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
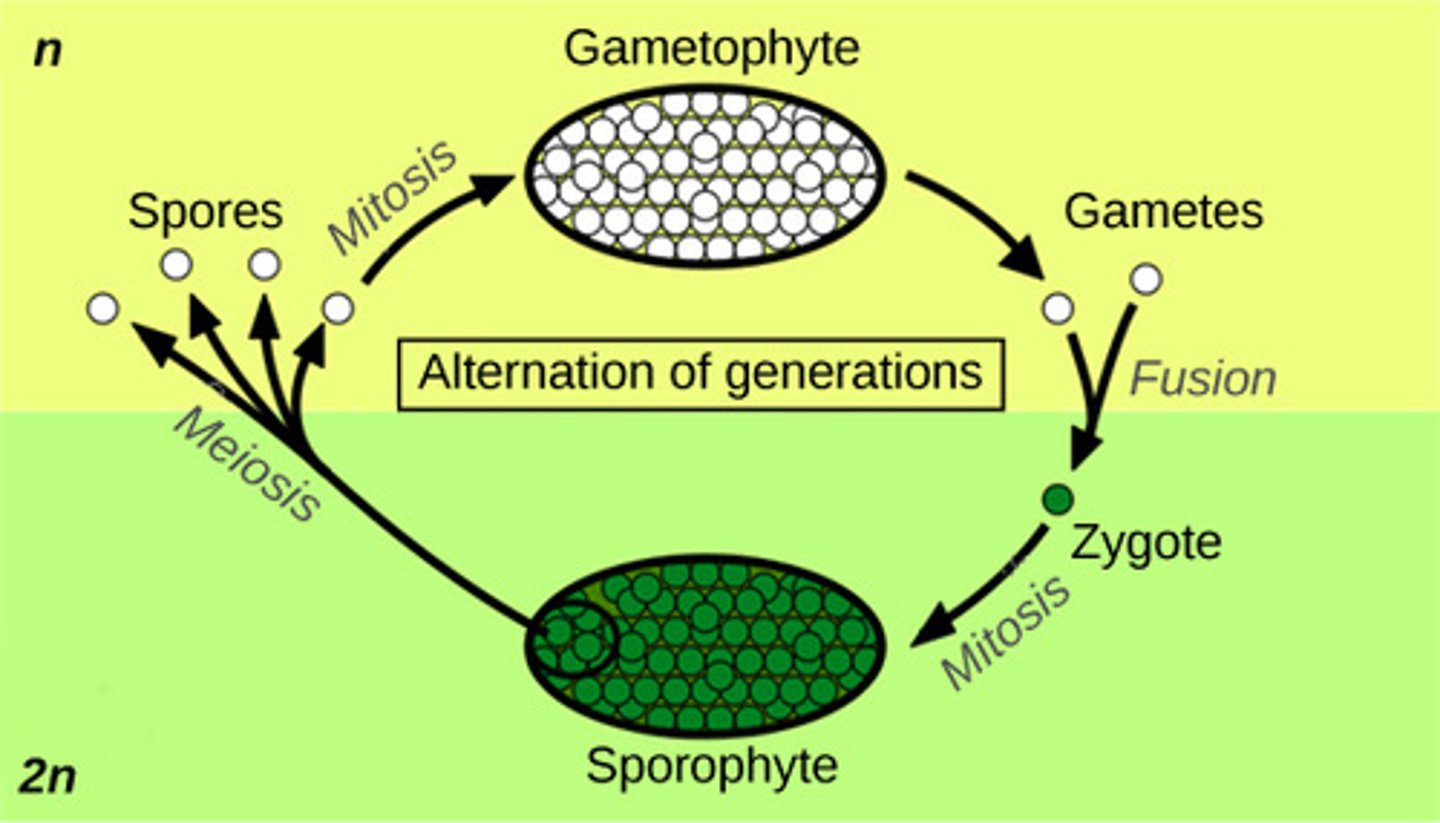
What is the dominant generation in most plants?
diploid sporophyte generation
(Note: exception - bryophytes)
How are plants protected against genetic damage?
have two copies of DNA
in their diploid cells
What is the waxy covering that reduces desiccation (drying up/ water loss) in plants?
cuticle

What system reduces the plant's dependency on water?
vascular system

The development of plants' vascular systems led to the formation of which specialized tissues?
1. true leaves
2. true stems
3. true roots
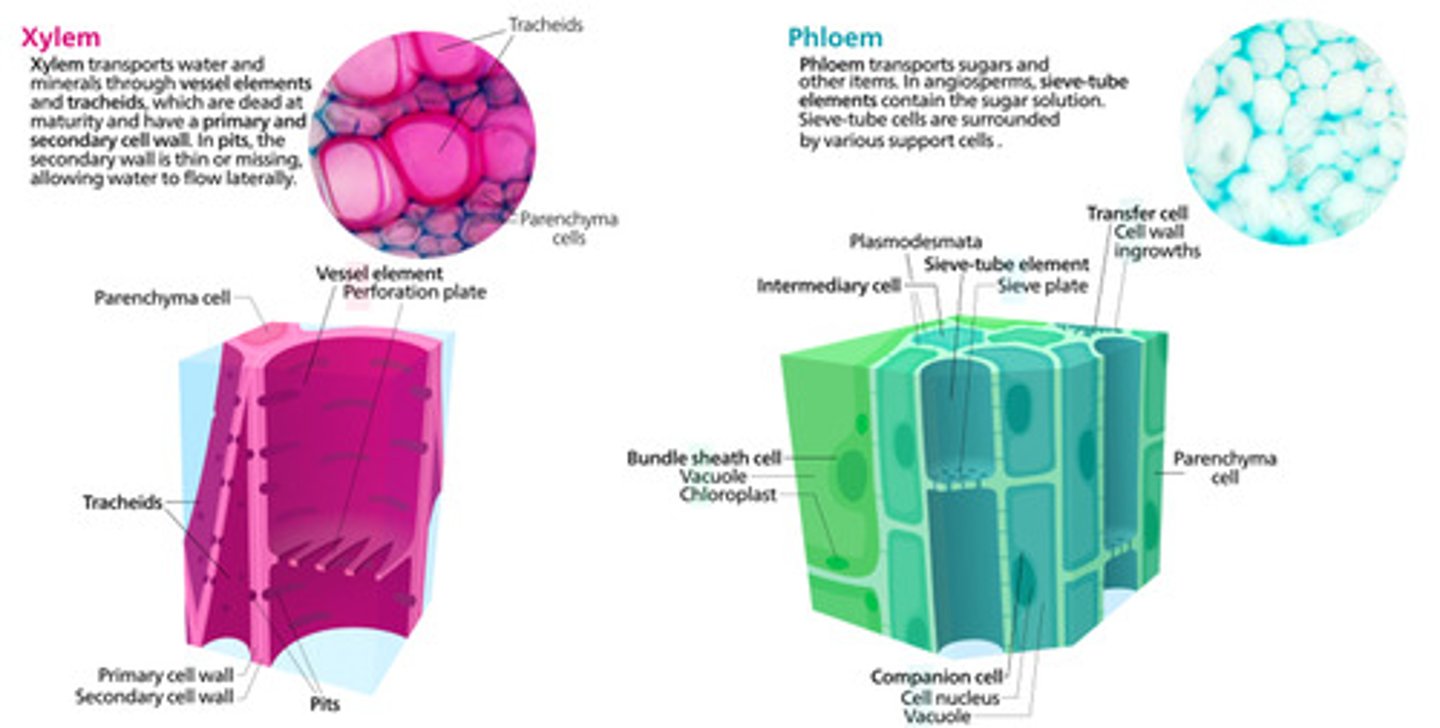
What are the 2 groups of vascular tissues that exist within plants?
1. xylem
2. phloem
In primitive plants, what cells are utilized to fertilize eggs?
flagellated sperm
In advanced plants, what cells are utilized to fertilize eggs?
sperm packaged as pollen
to be dispersed by wind

What is the division of plants otherwise known as angiosperms or flowering plants?
Anthrophyta

plants within Anthrophyta have their gametophytes enclosed and protected within what structure?
ovary
Coniferophyta and Anthophyta express seasonal variations in response to what variables?
availability of water and light
What classification denotes shedding leaves to prevent water loss in slow-growing seasons?
deciduous

what plants will germinate, grow, flower, and produce seeds rapidly in brief periods of rain?
desert plants

What is the only plant division that is avascular?
bryophytes

What is the technical term for vascular plants?
tracheophytes

What are the 3 main characteristics of tracheophytes?
1. true roots
2. leaves
3. stems
What structures in tracheophytes produce diploid zygotes that become a sporophyte?
antheridium and archegonium
(Note: sporophyte is dominant generation)
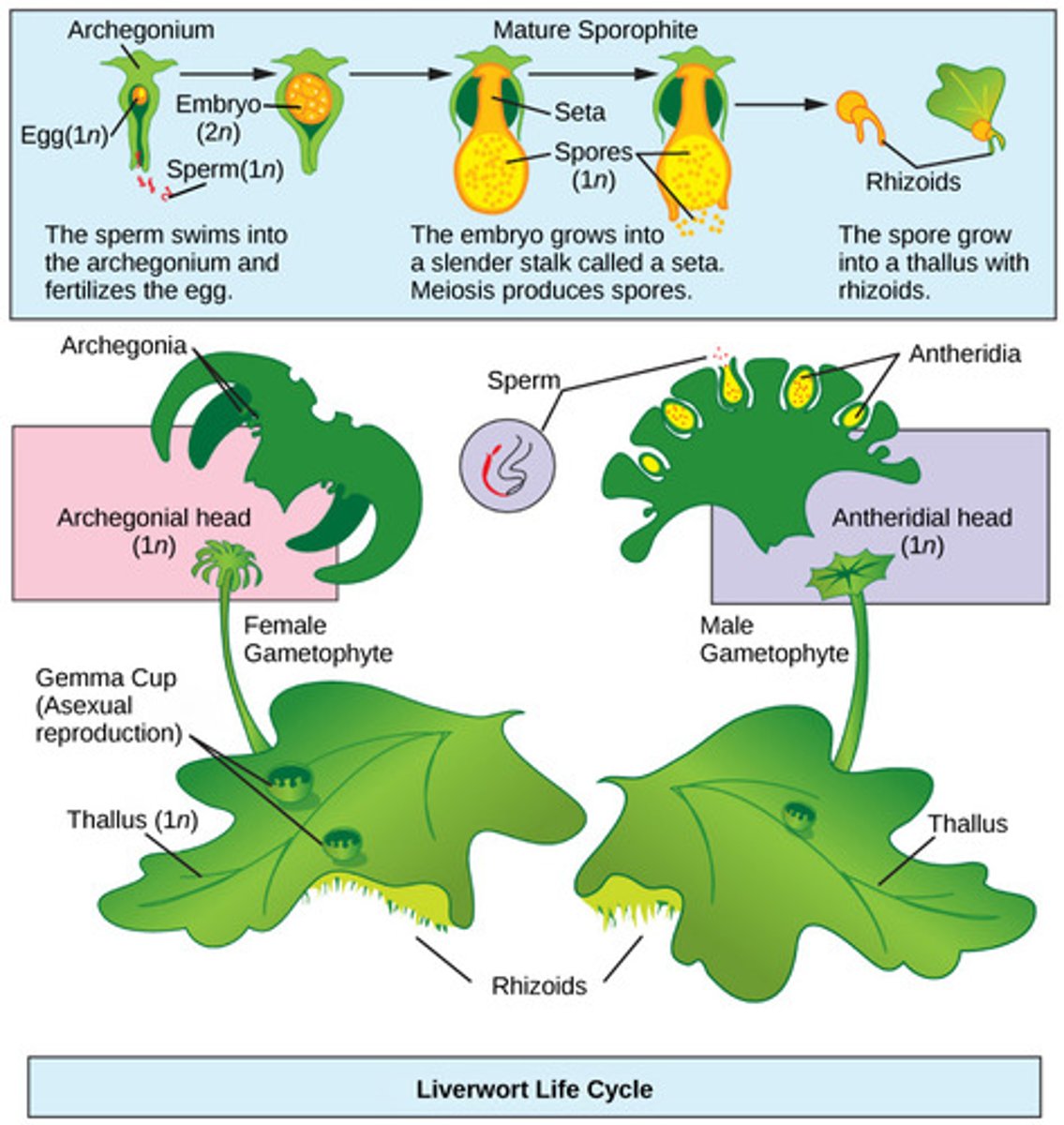
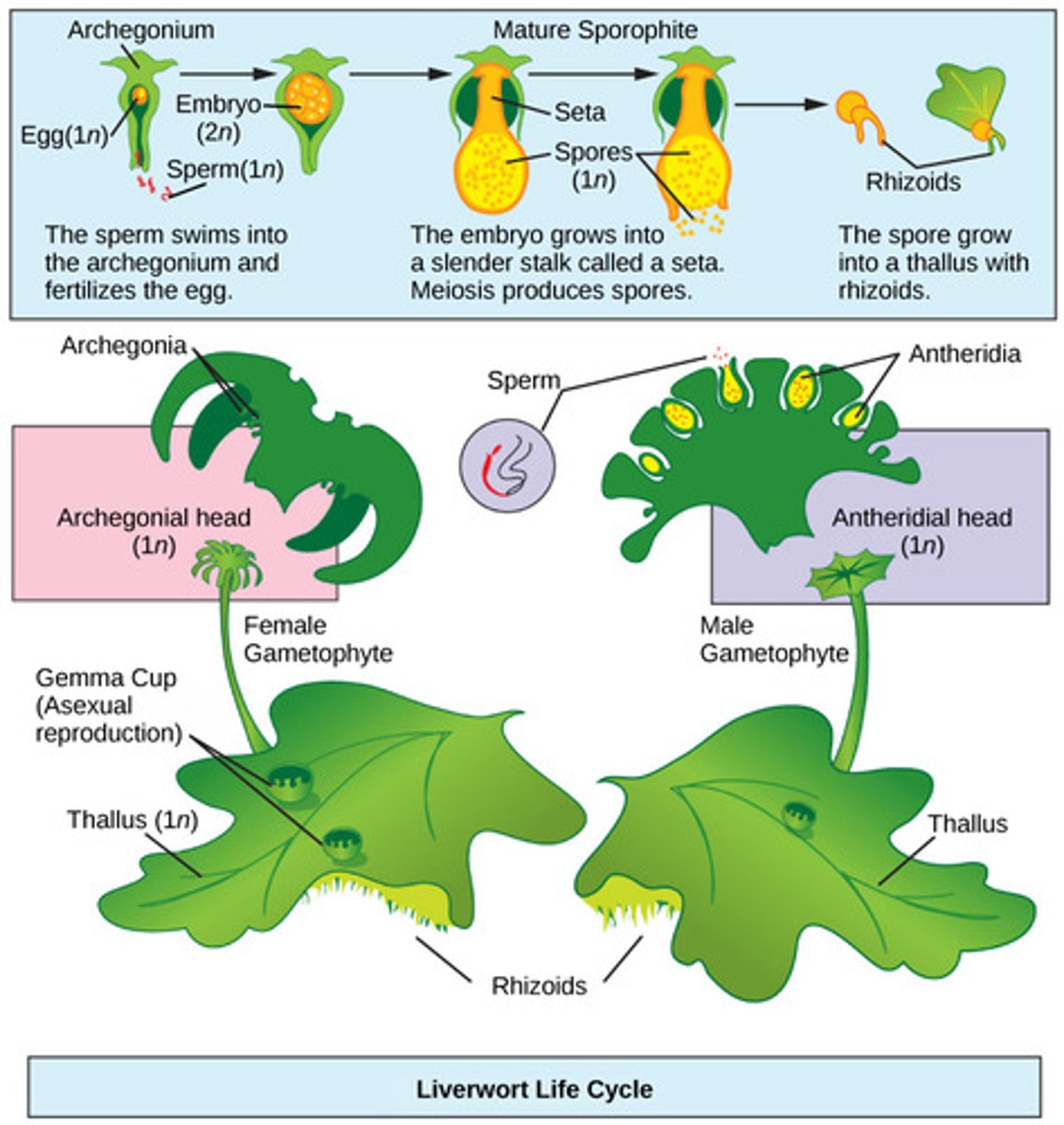
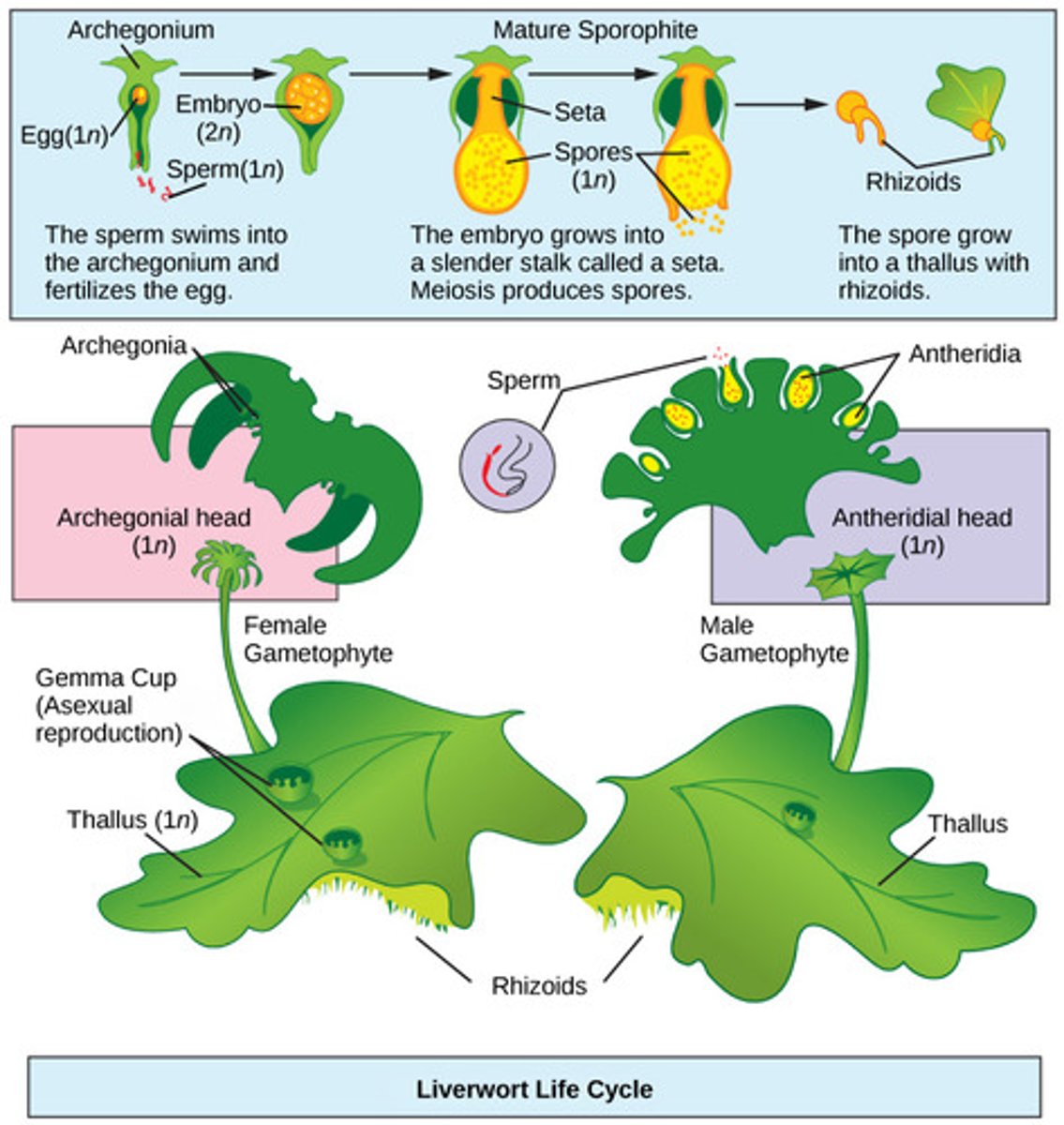
Which seedless plant division includes the mosses, liverworts, and hornworts?
bryophytes

In bryophytes, where are gametes produced?
in gametangia (protective structures)
on gametophytes
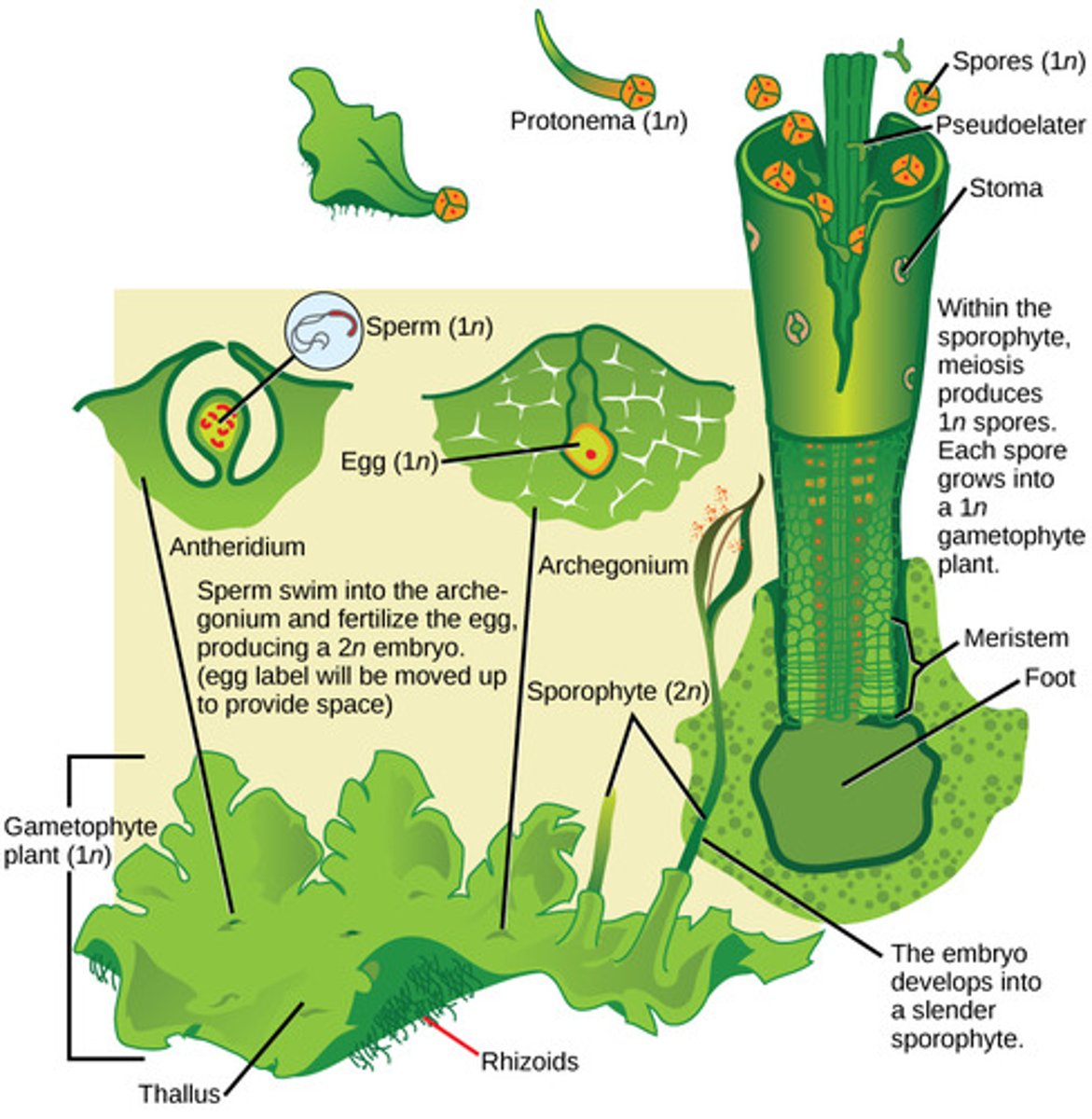
In bryophytes, what is the dominant life cycle stage?
haploid
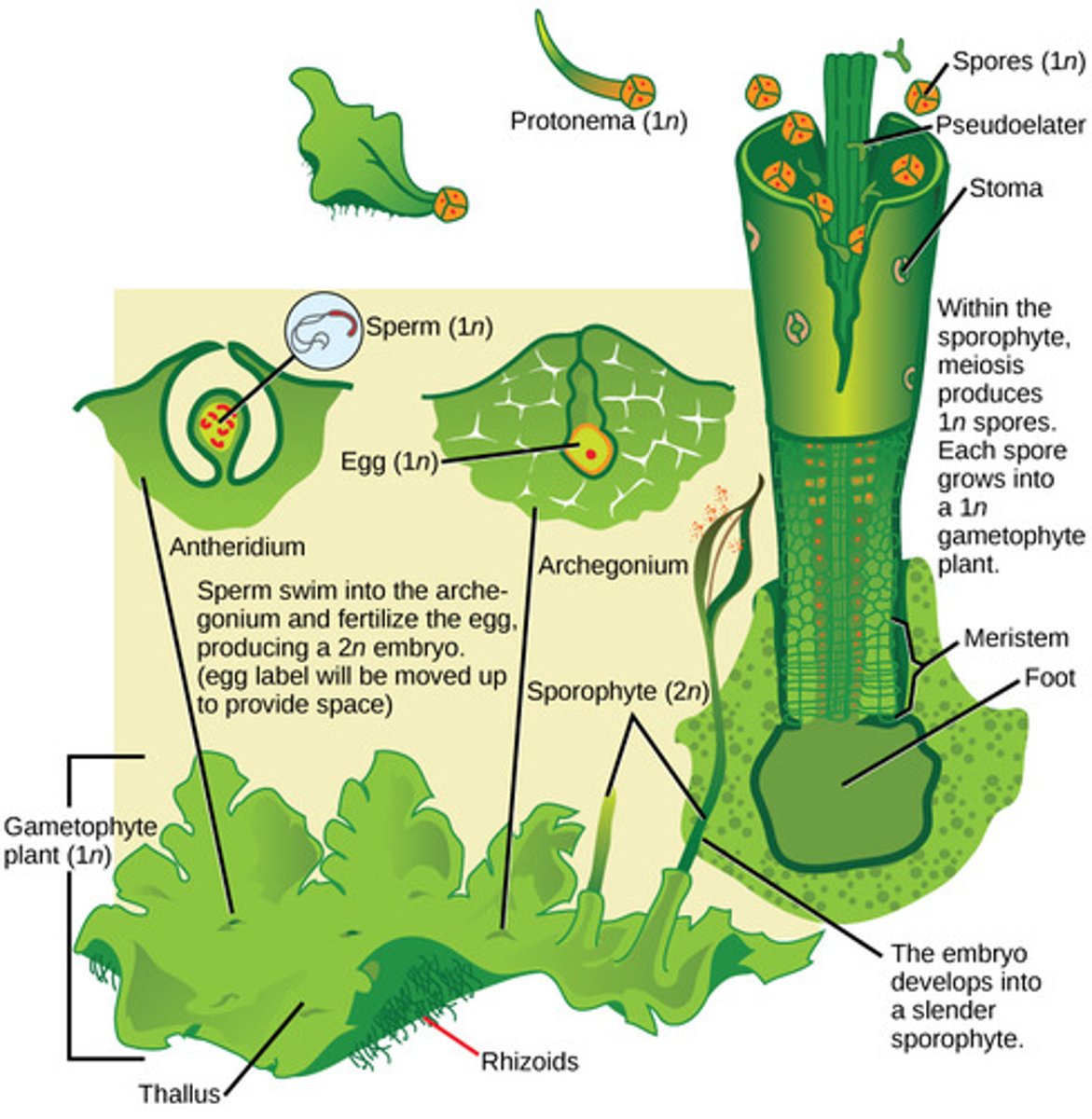
In bryophytes, what is the male gametangium which produces flagellated sperm that swim through water?
antheridium
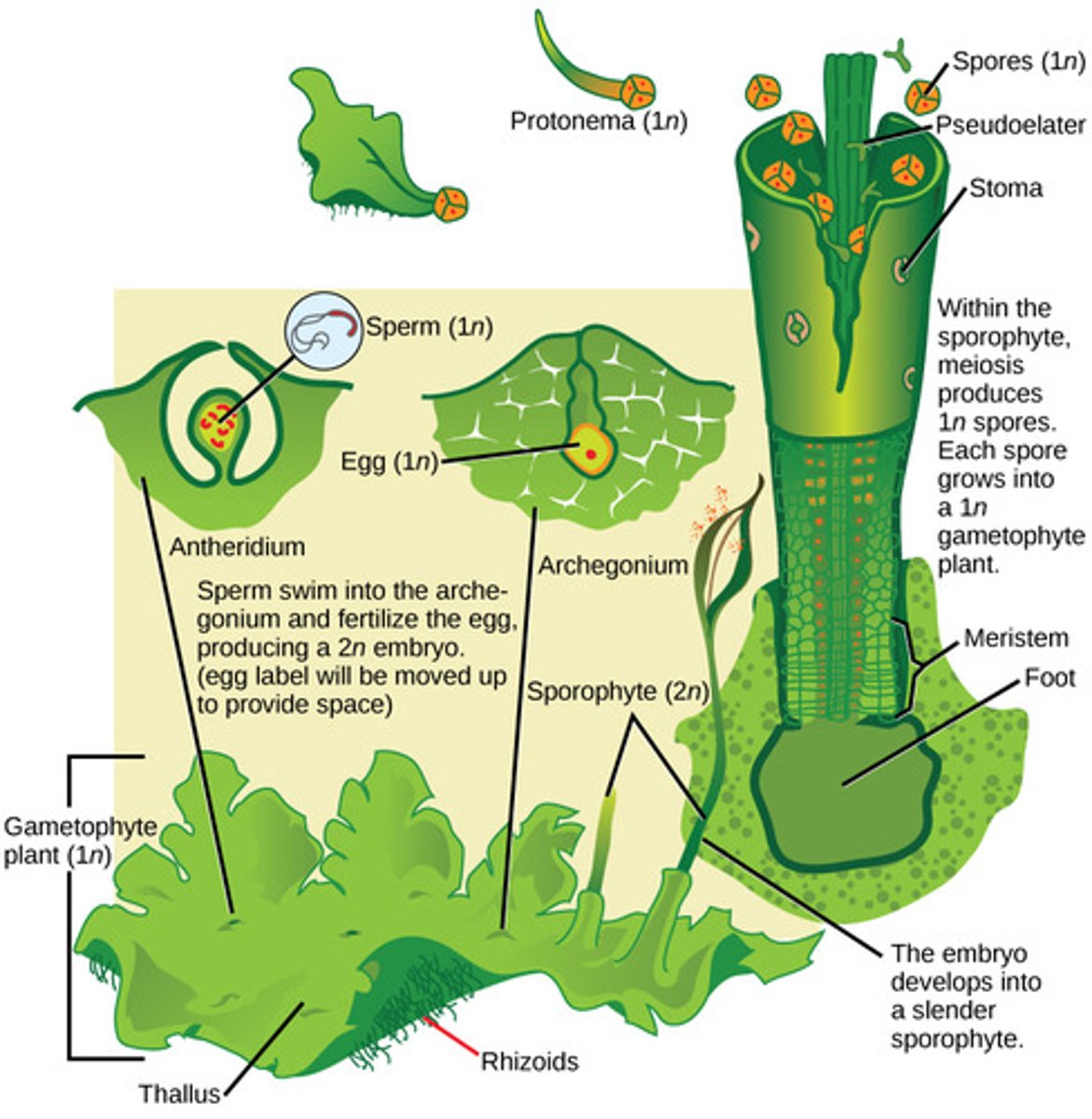
In bryophytes, what is the female gametangium that produces eggs?
archegonium
In bryophytes, the zygote grows into what diploid structure?
sporophyte
(Note: still connected
to the gametophyte)
In mosses, the sporophyte structure is a stalk-bearing capsule that contains haploid spores produced by what process?
meiosis
In bryophytes, spores are dispersed by wind and germinate into what form?
haploid gametophytes
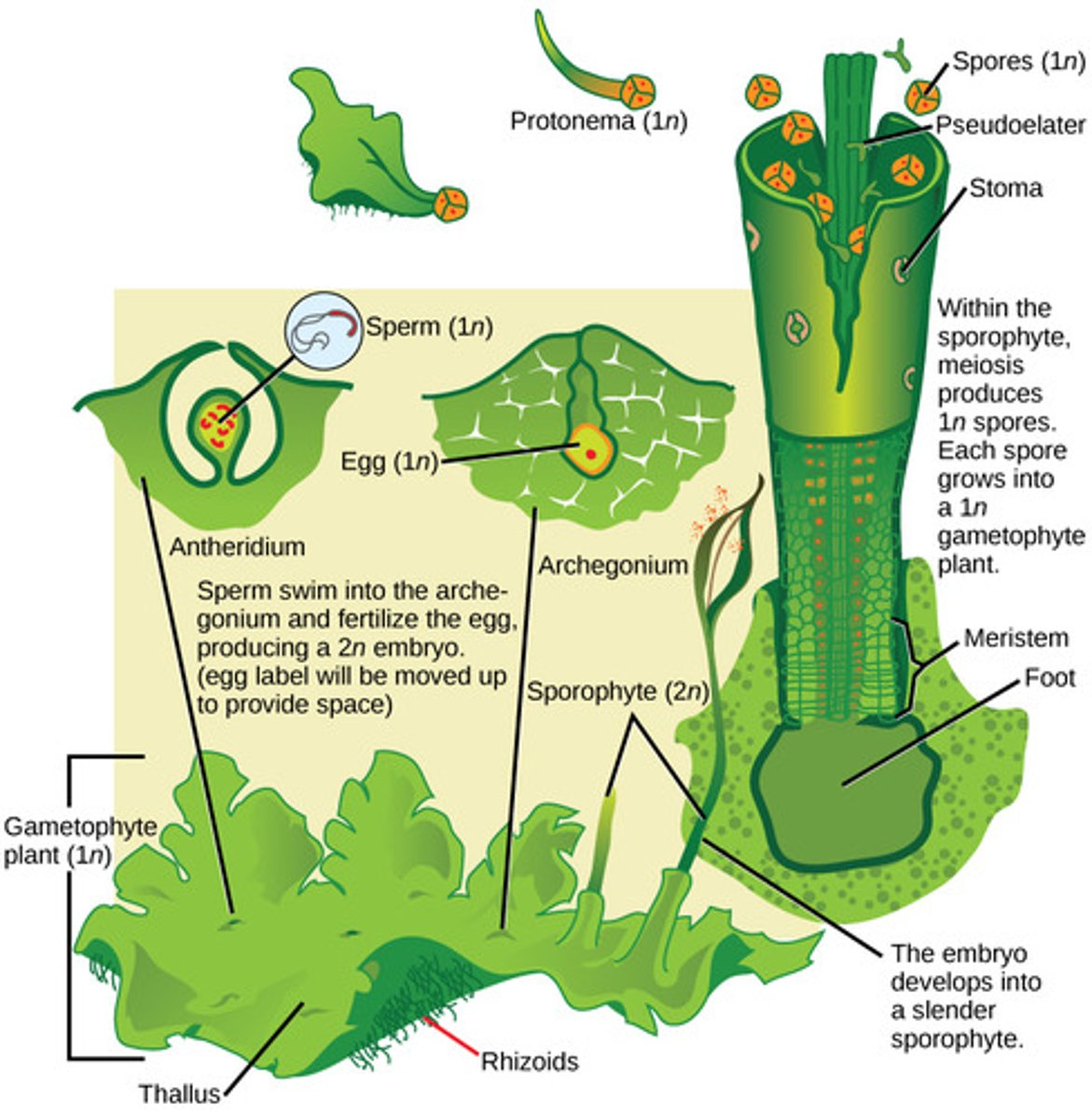
In bryophytes, haploid gametophytes mature and produce what reproductive structures?
antheridium and archegonium
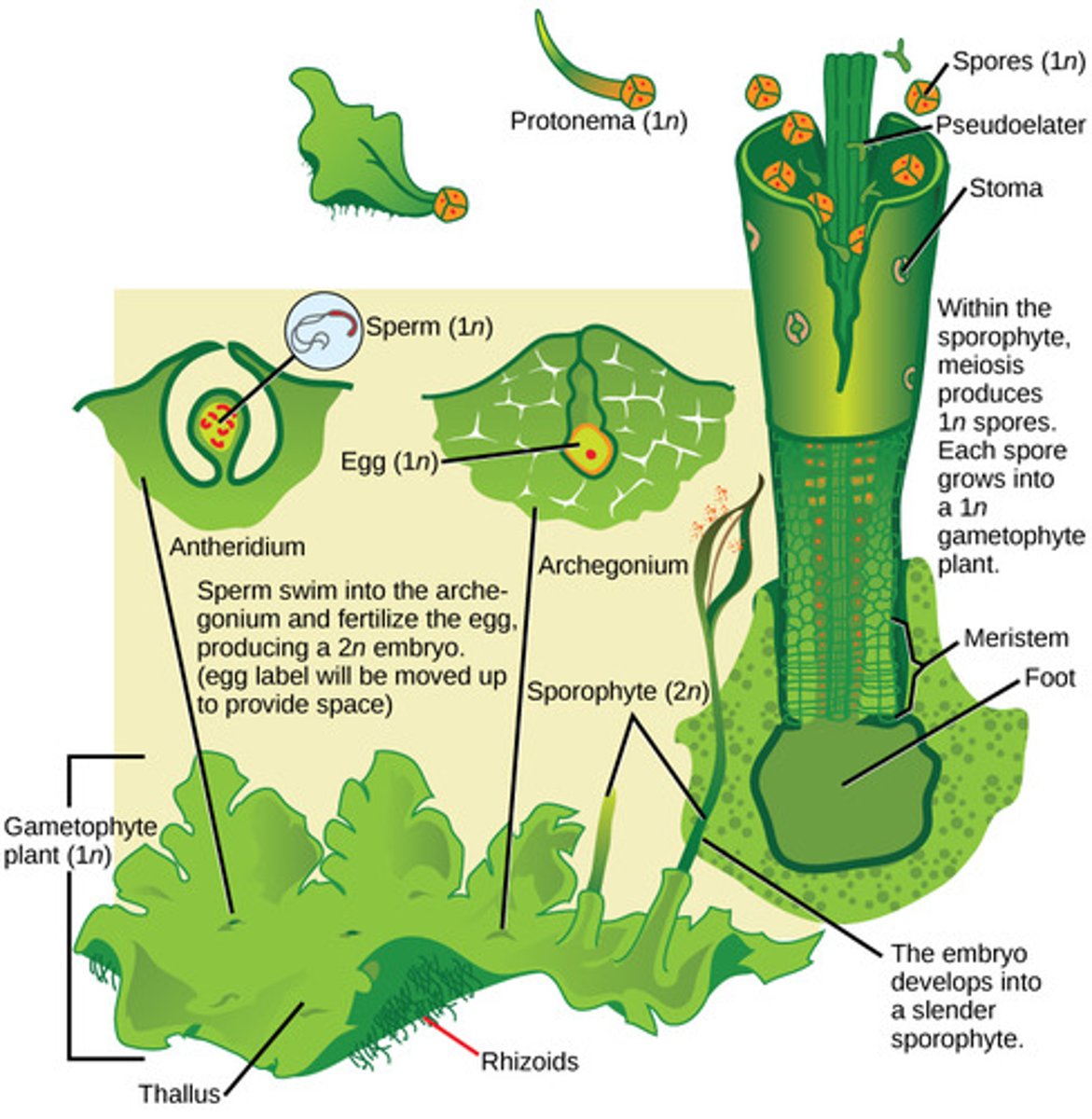
What root-like absorptive structures anchor bryophytes to their substrate?
rhizoids
(Note: instead of roots)

Because bryophytes lack vascular tissue, what resource must they stay near?
water
What organisms can form rhizoids like bryophytes?
algae and some fungi
Which seedless plant division includes club mosses, spike mosses, and quillworts?
Lycophyta
(Note: herbaceous plants)
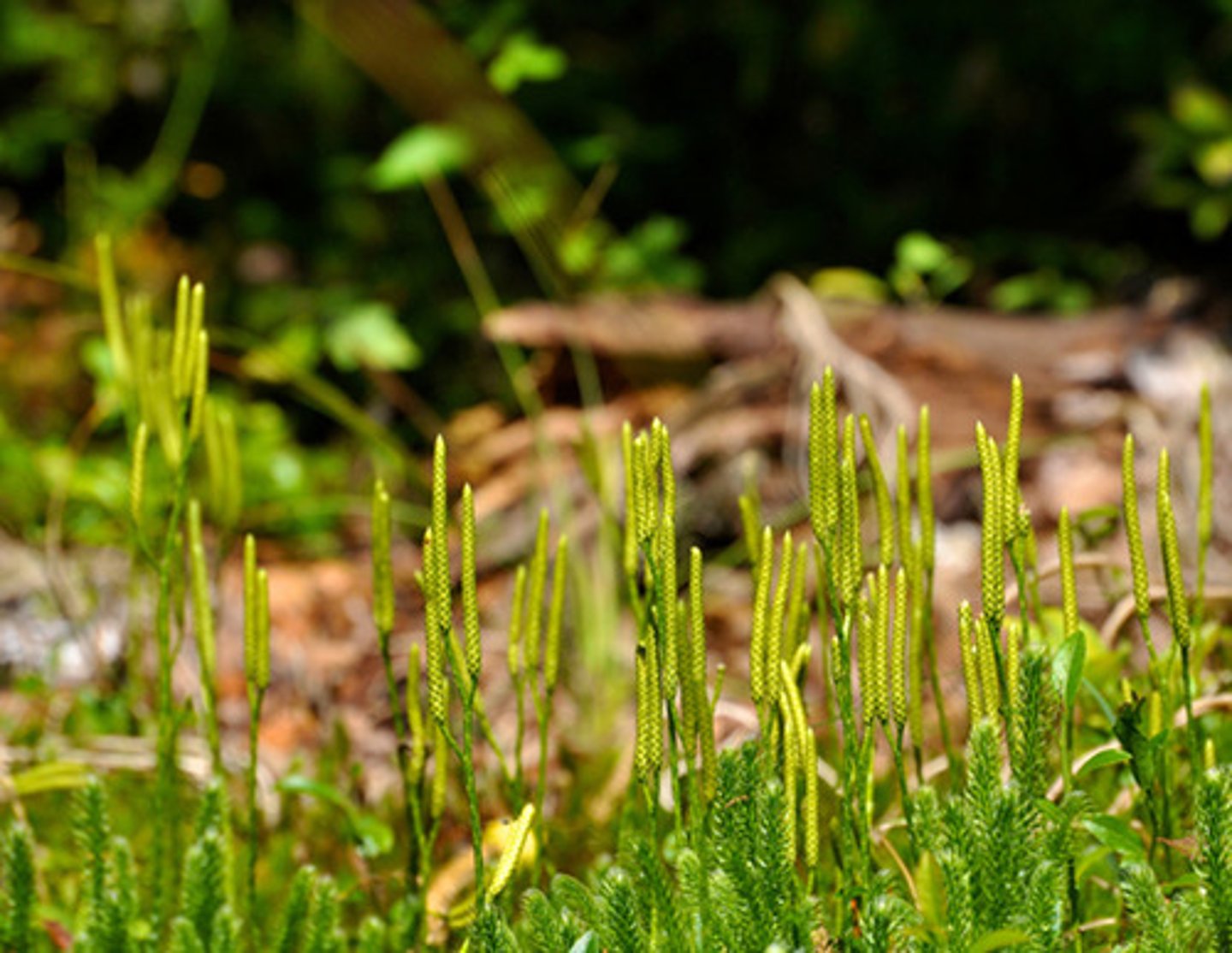

Which lycophytes produce clusters of spore-bearing sporangia in cone-like structures called strobili?
club and spike mosses

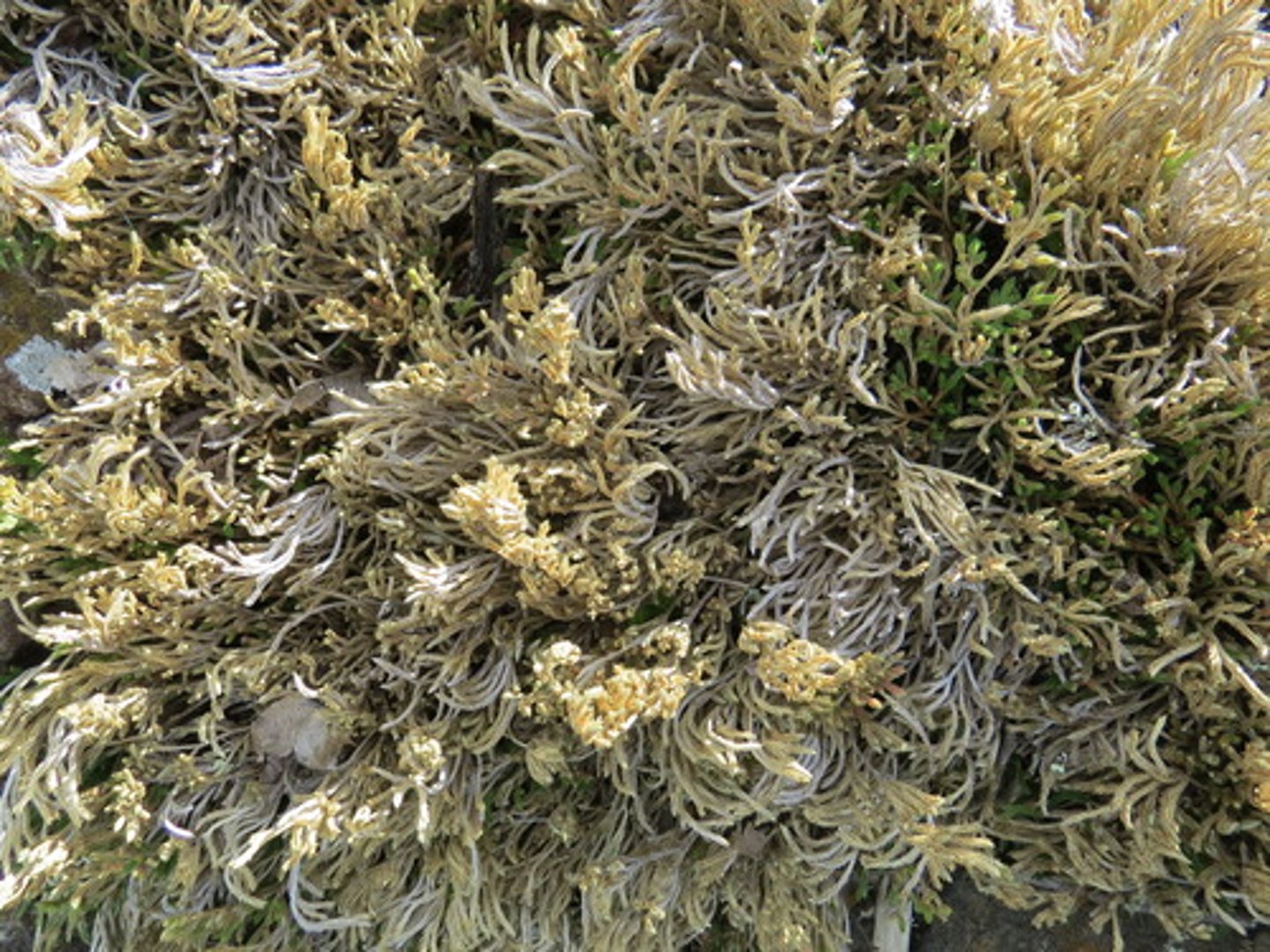
Which lycophyte, a spike moss, can recover from a dead-like appearance after being watered?
resurrection plant

Which seedless plant division contains vascular plants classified as ferns, horsetails, and whisk ferns?
Pterophyta
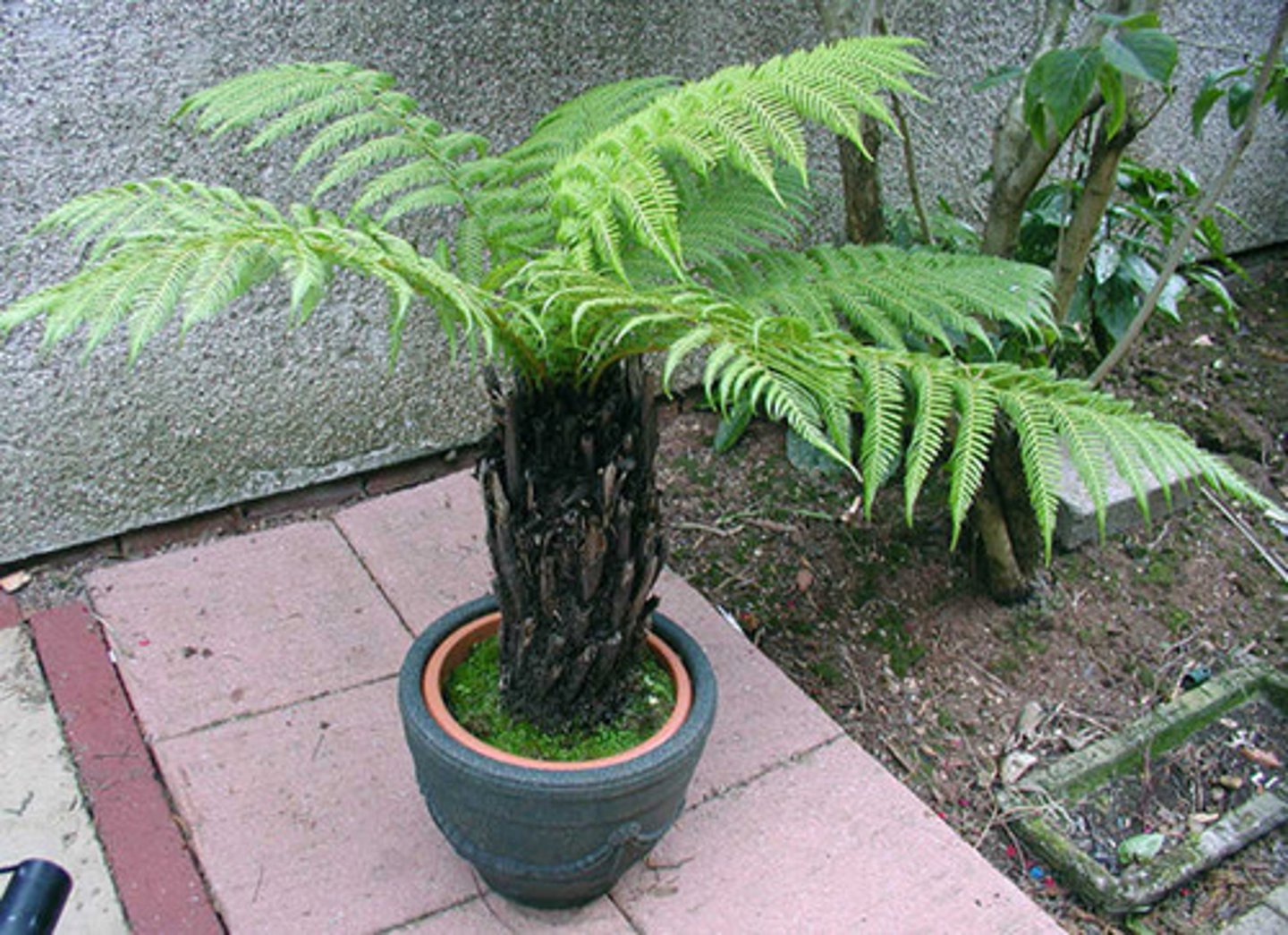

In pterophytes, what are the clusters of sporangia called?
sori
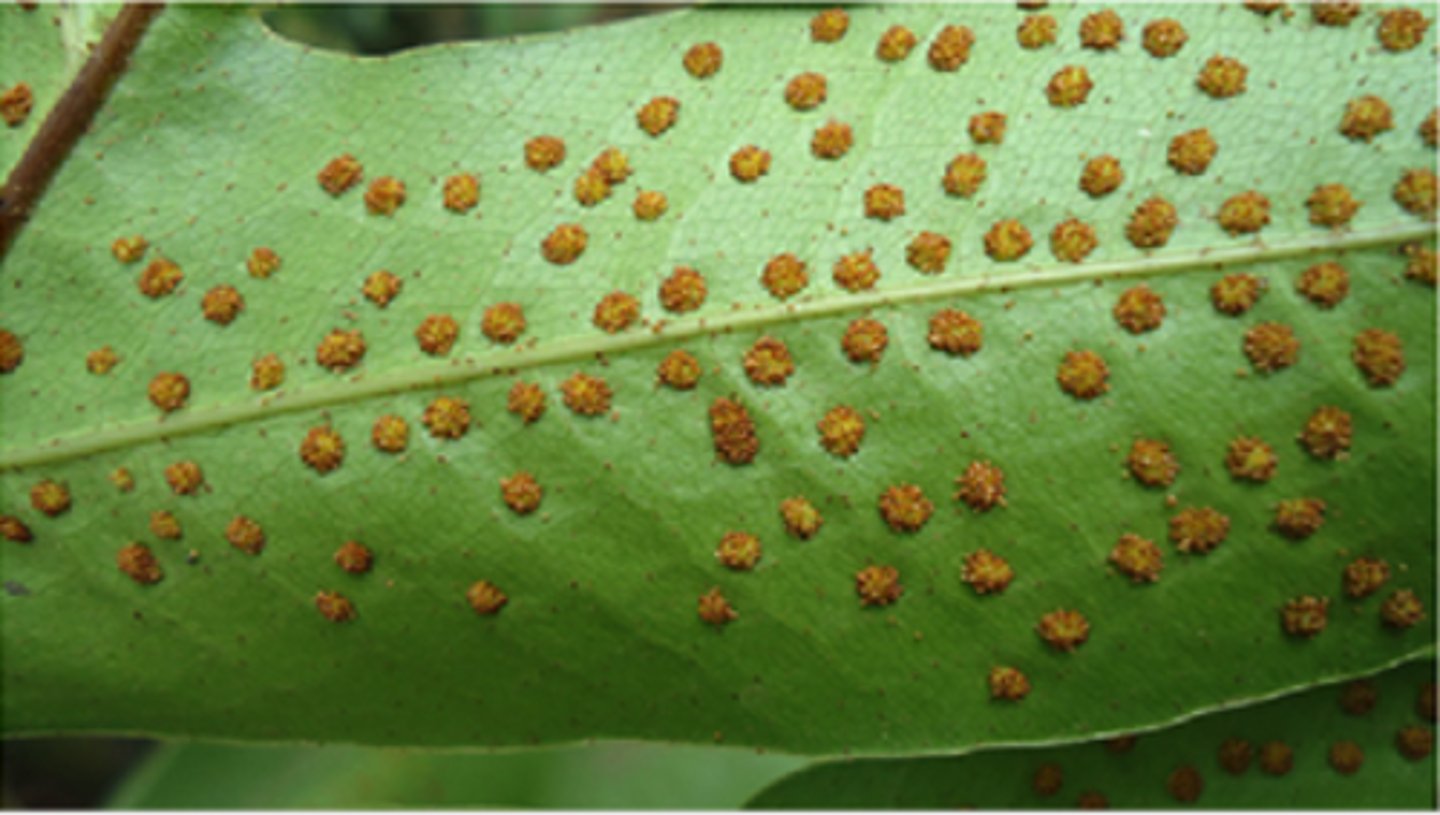

Which pterophyte produces sori on the undersurface of fronds?
ferns
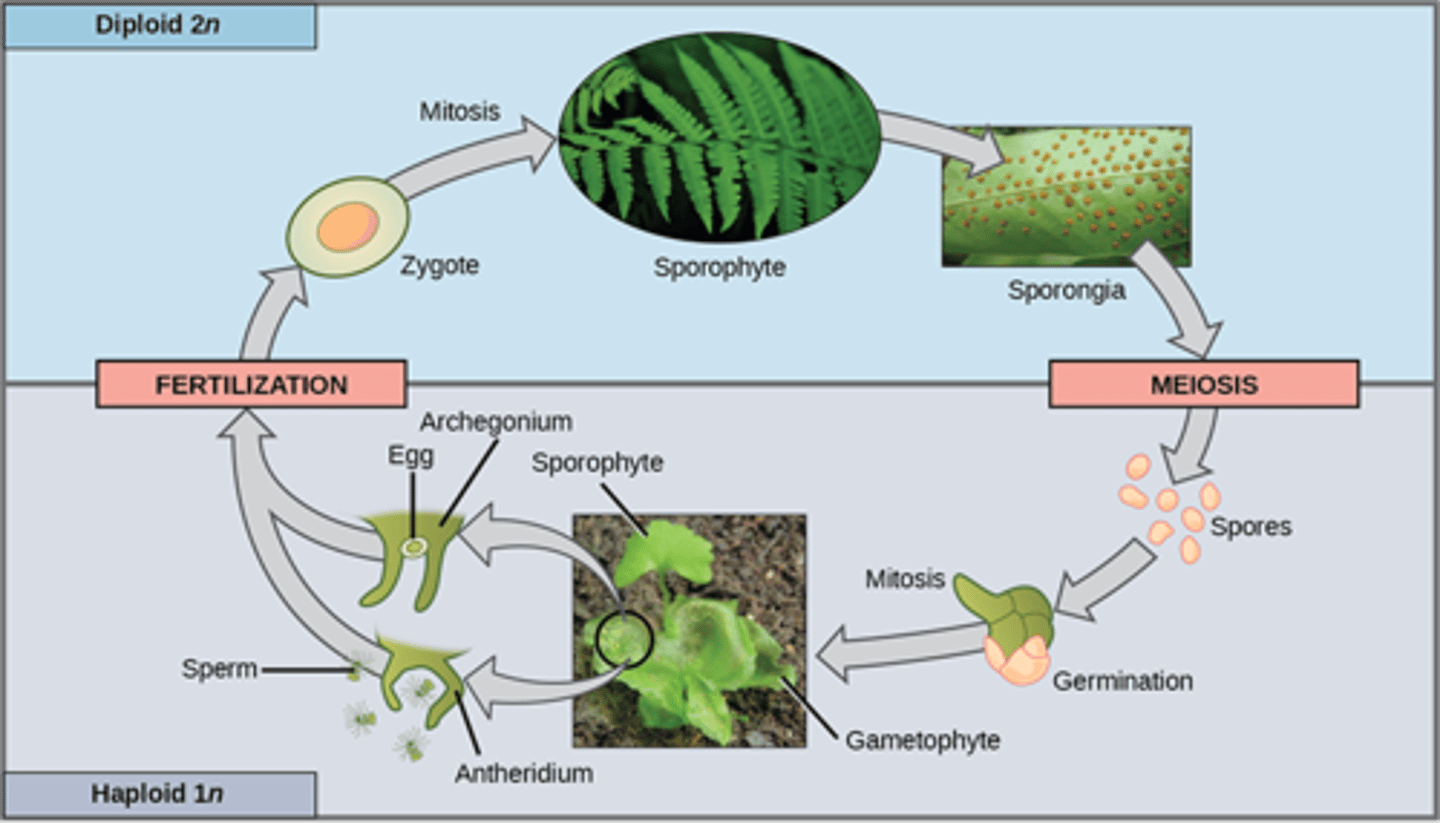
In ferns, what is the dominant life cycle form?
sporophyte
Which pterophyte plants include extinct woody trees?
horsetails
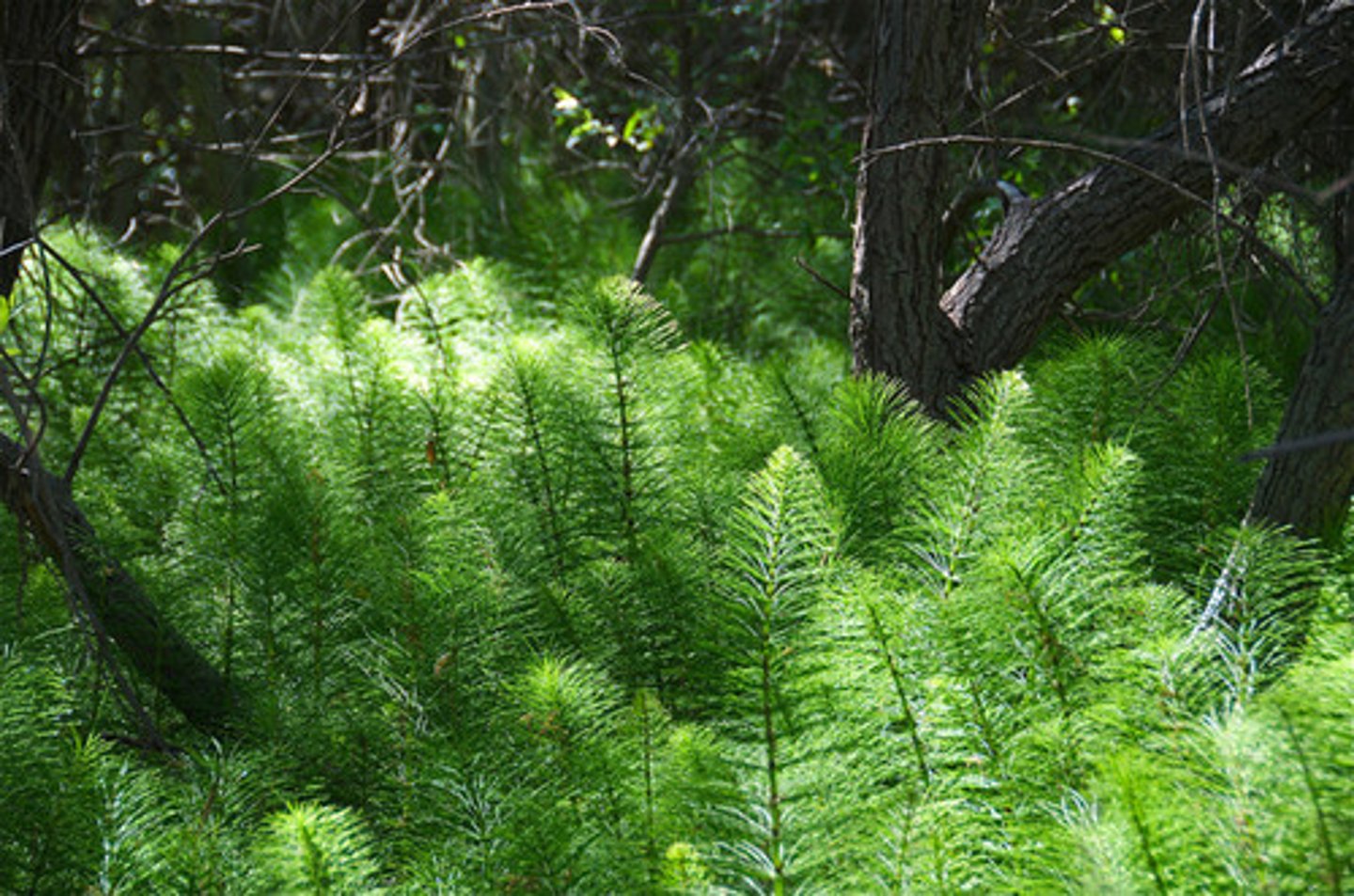

In horsetails, what structures are hollow, ribbed, and joined at nodes?
stems
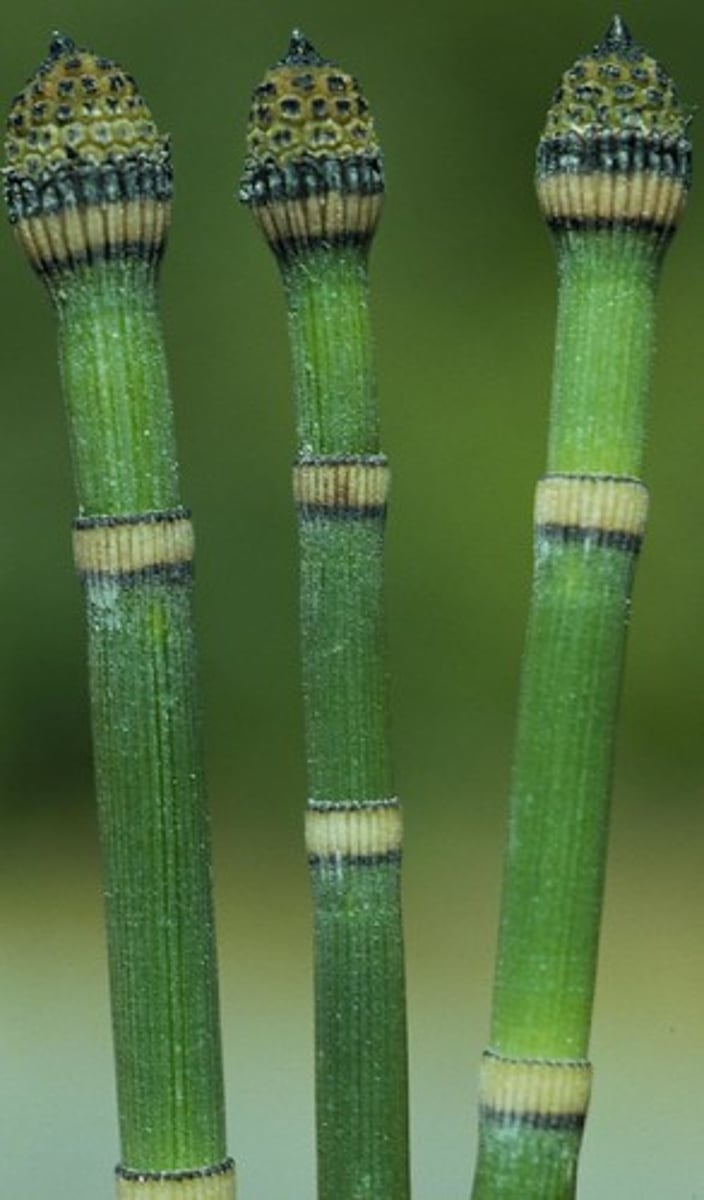

In horsetails, what reproductive structures do their strobili produce?
spores
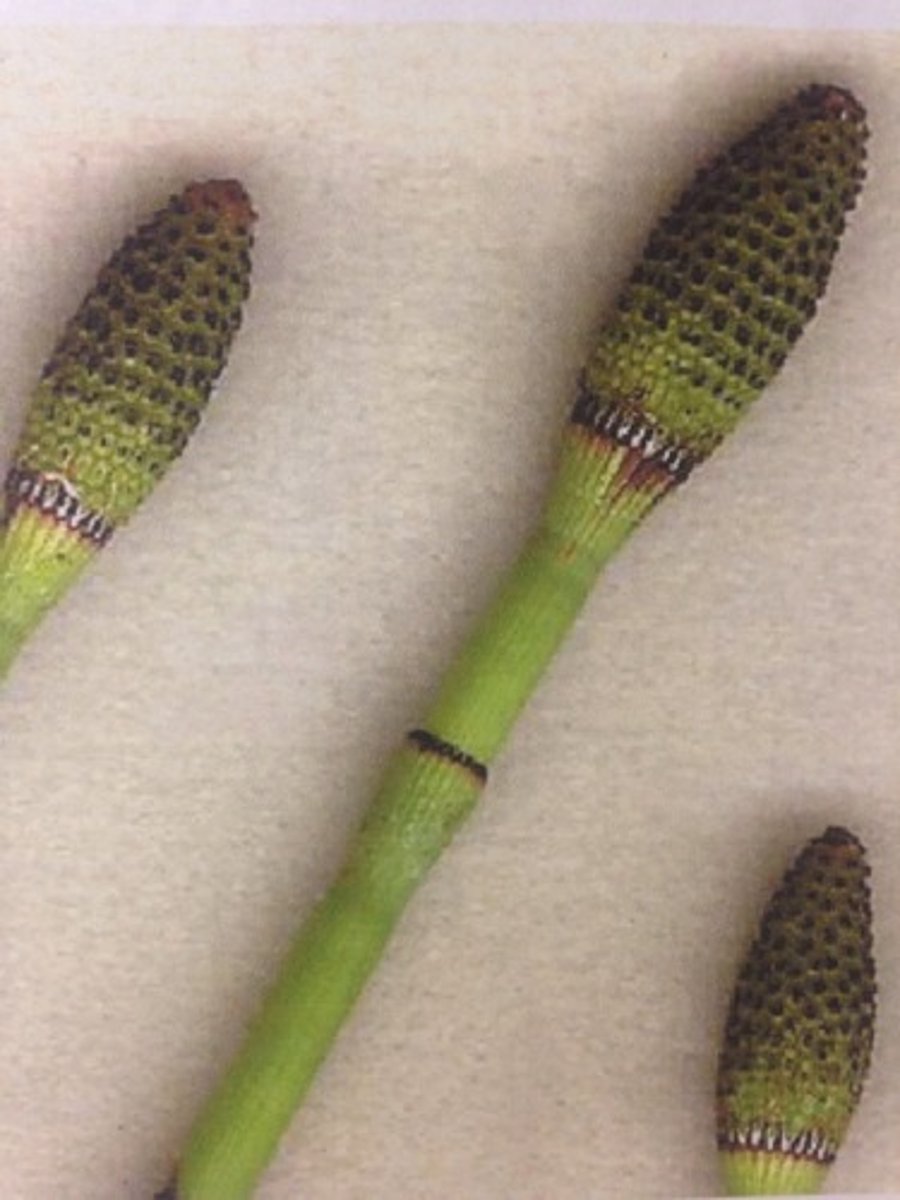

How do horsetails obtain energy?
photosynthesis (autotrophic)
(Note: horsetail structures are green)
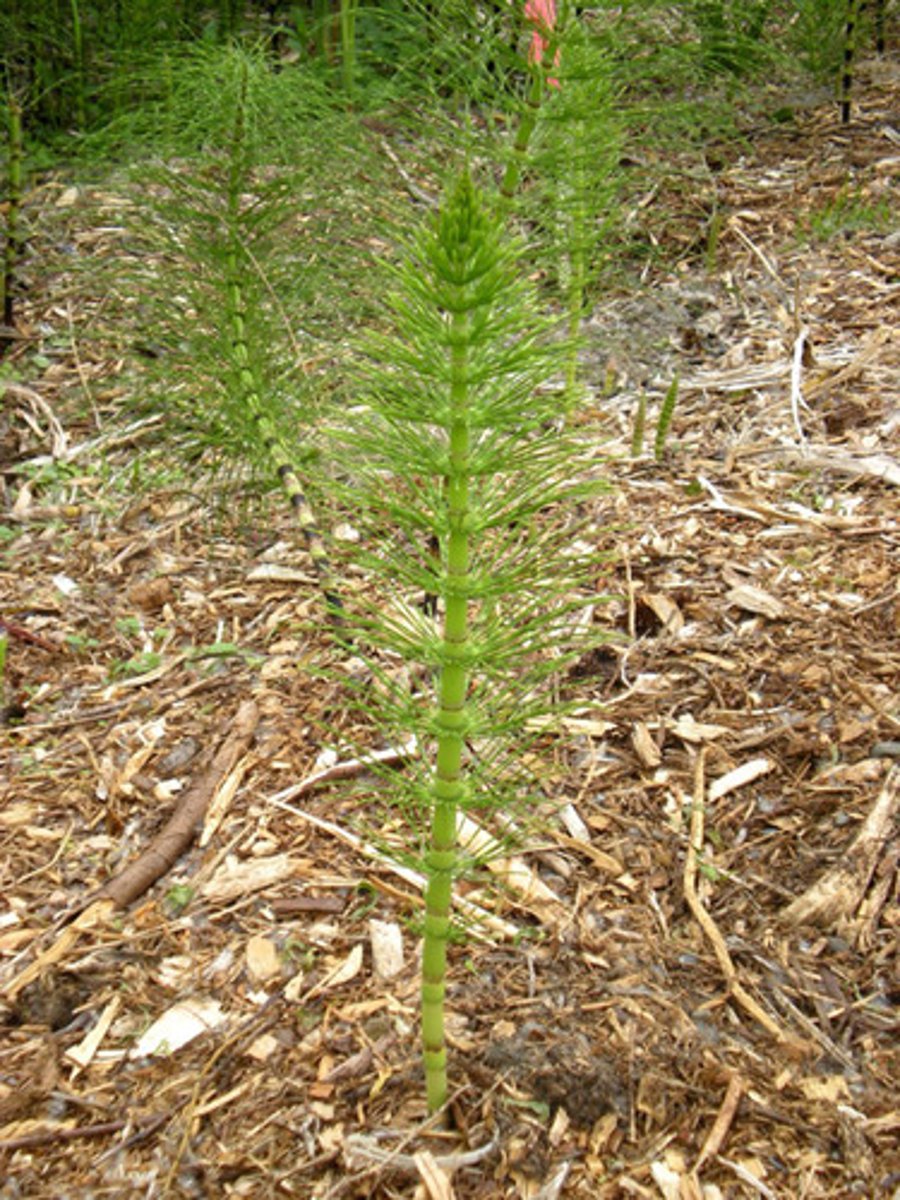

What substance causes horsetails to have a rough texture?
silica
Which pterophyte plants have branching stems without roots?
whisk ferns
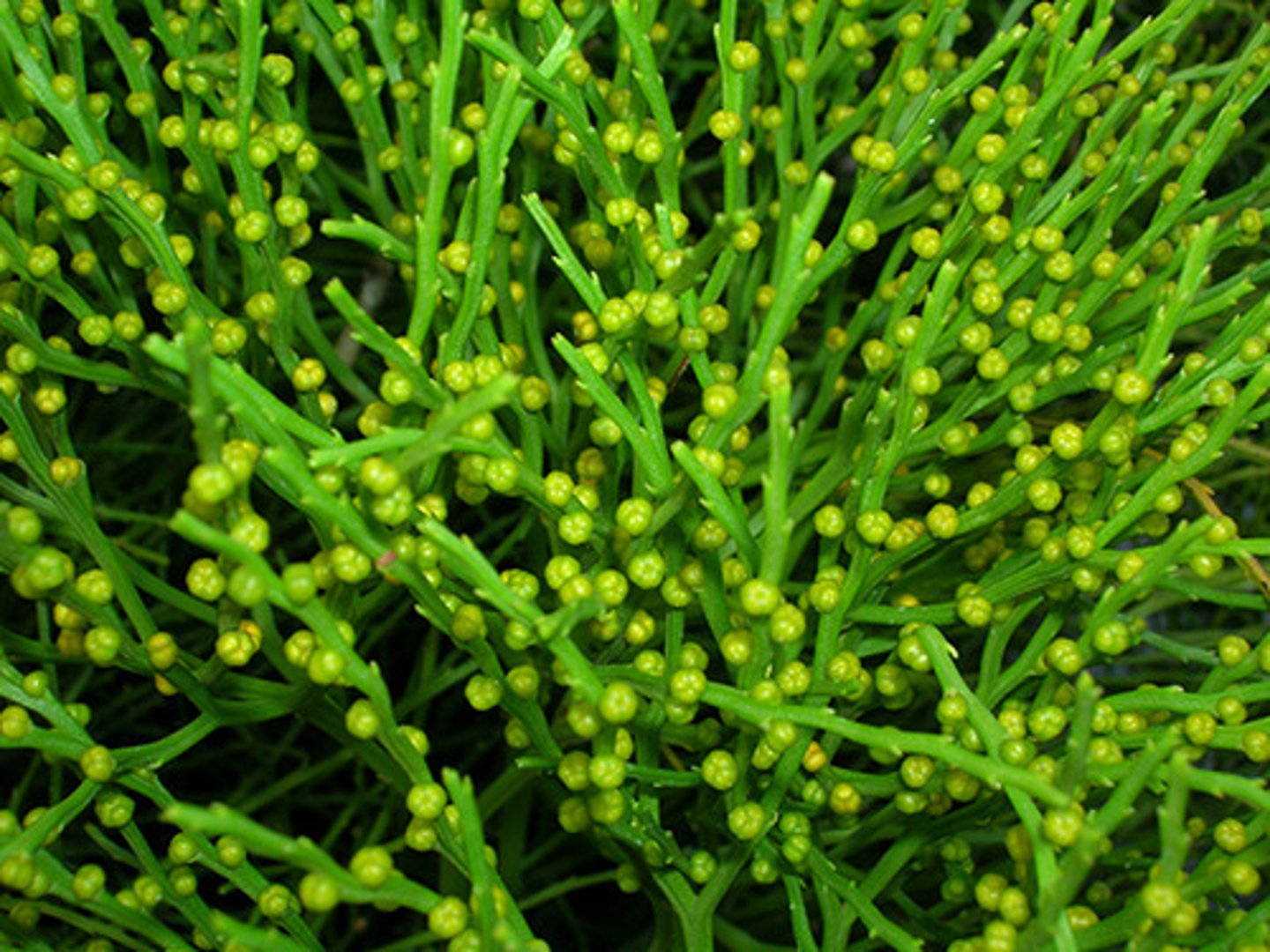

In whisk ferns what structures are reduced to small appendages or are absent?
leaves
Why is the absence of roots and leaves in whisk ferns considered secondary loss?
they were lost as whisk ferns diverged from their ancestors
In seeded vascular plants, what structures produce microspores (male spores)?
microsporangia
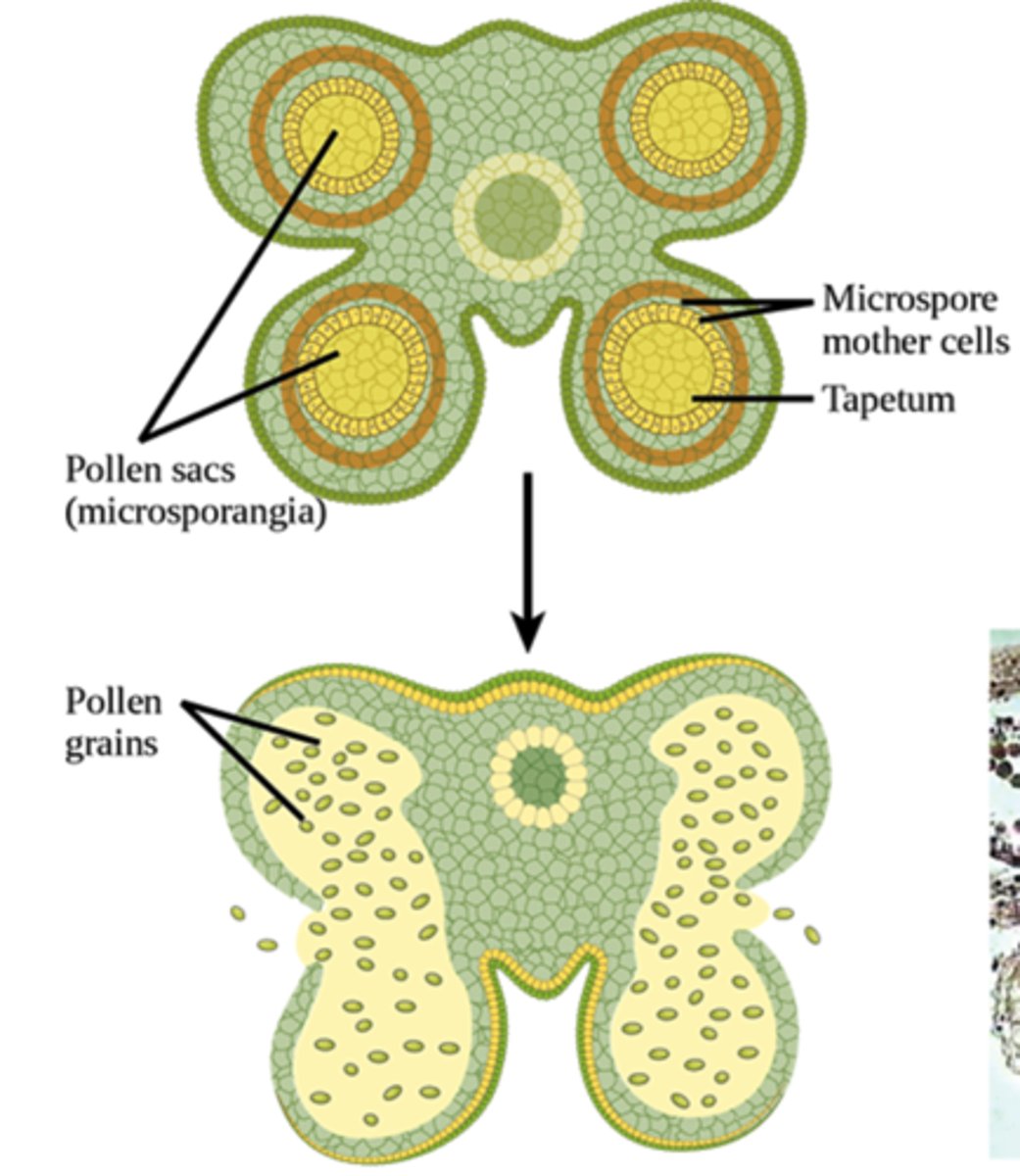
In seeded vascular plants, what structures produce megaspores (female spores)?
megasporangia
In microsporangia, microspore mother cells divide by meiosis to produce which cells?
4 haploid microspores
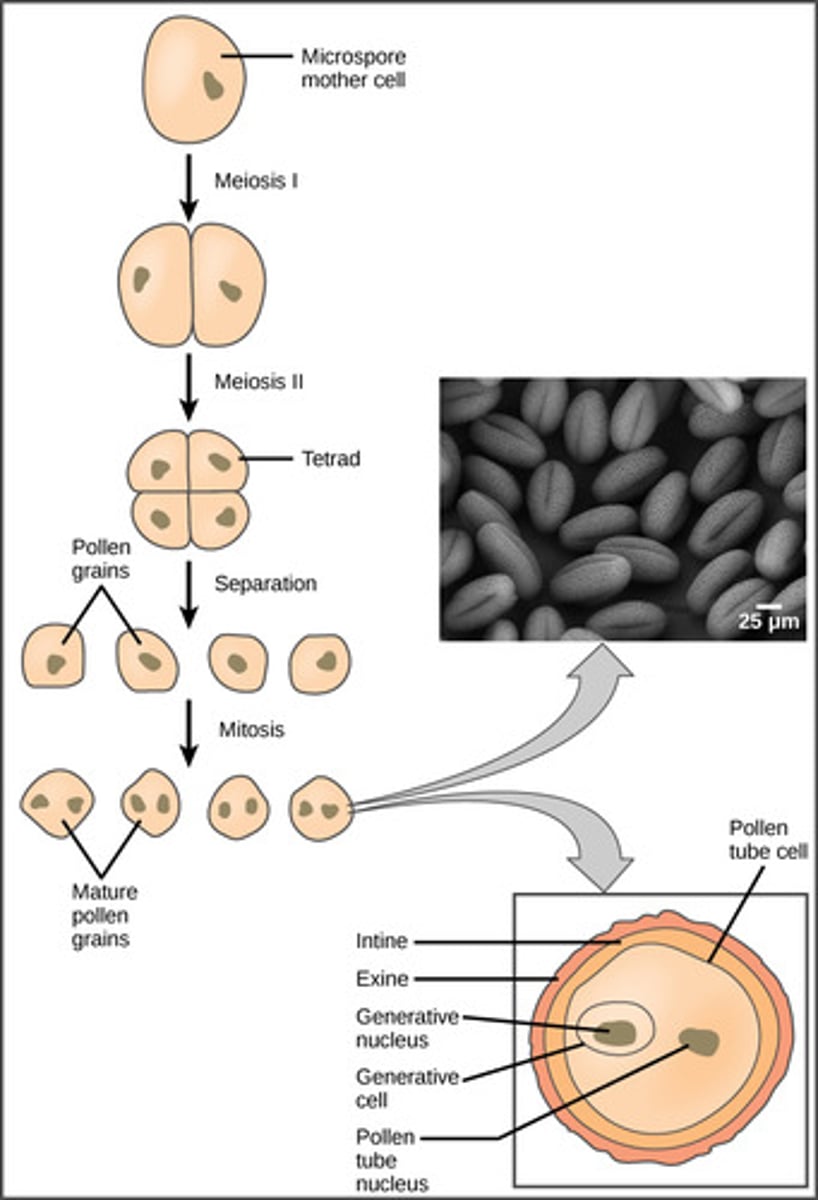
In microsporangia, microspores mature into which structures?
pollen grains
(Note: immature male
gametophyte with hard
covering)
In which plants do pollen grains divide into 3 cells?
flowering plants
The pollen grains represent what generation?
gametophyte generation
In which plants do pollen grains divide into 4 cells?
conifers
What are the functions of the pollen grain cells when they divide?
1. one vegetative/tube
cell that controls the
growth of the pollen tube
2. other cells are sperm cells
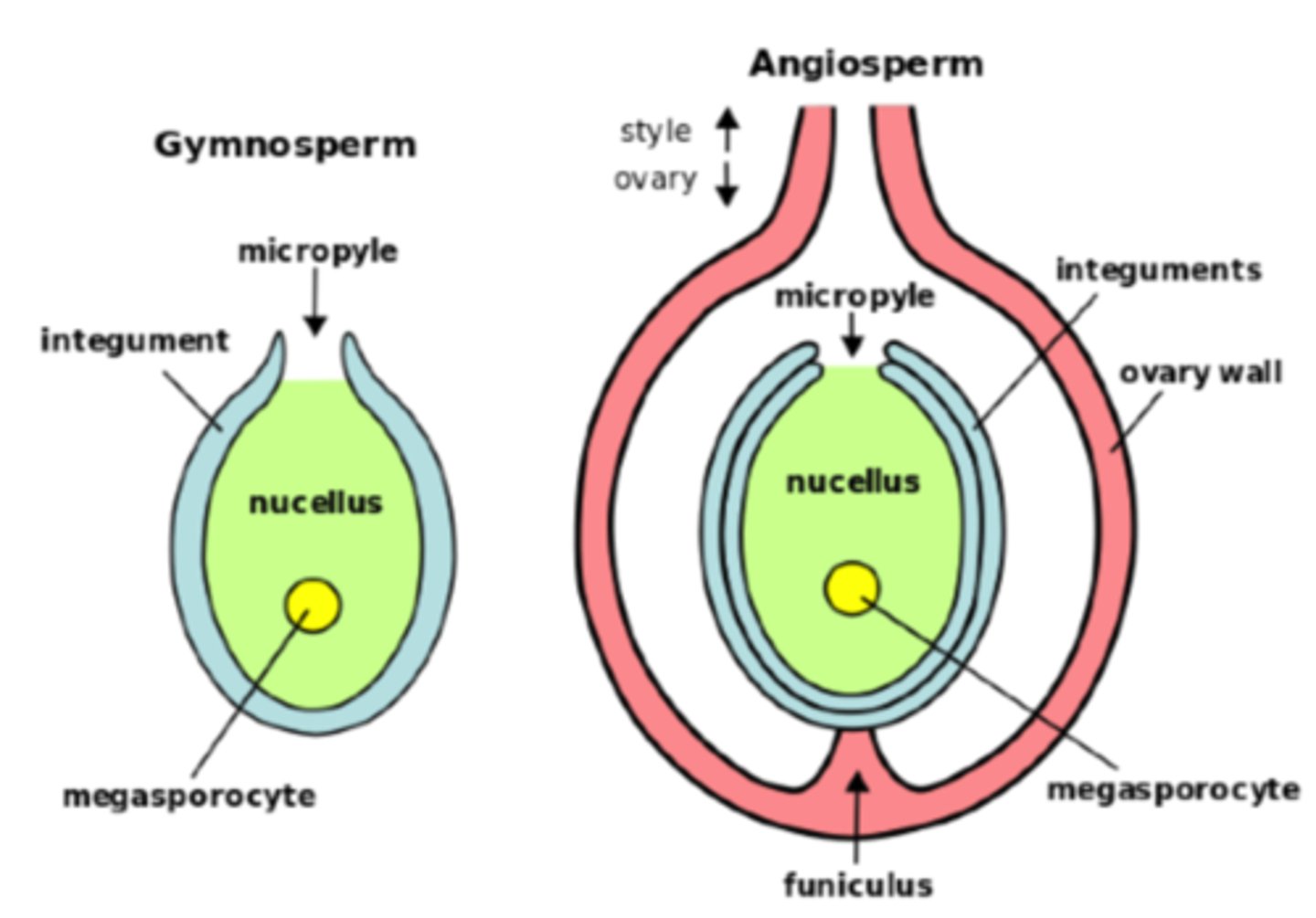
In megasporangia, what structure produces the megaspore mother cell?
nucellus
In megasporangia, the megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce which cells?
4 haploid cells
(Note: only one survives!)
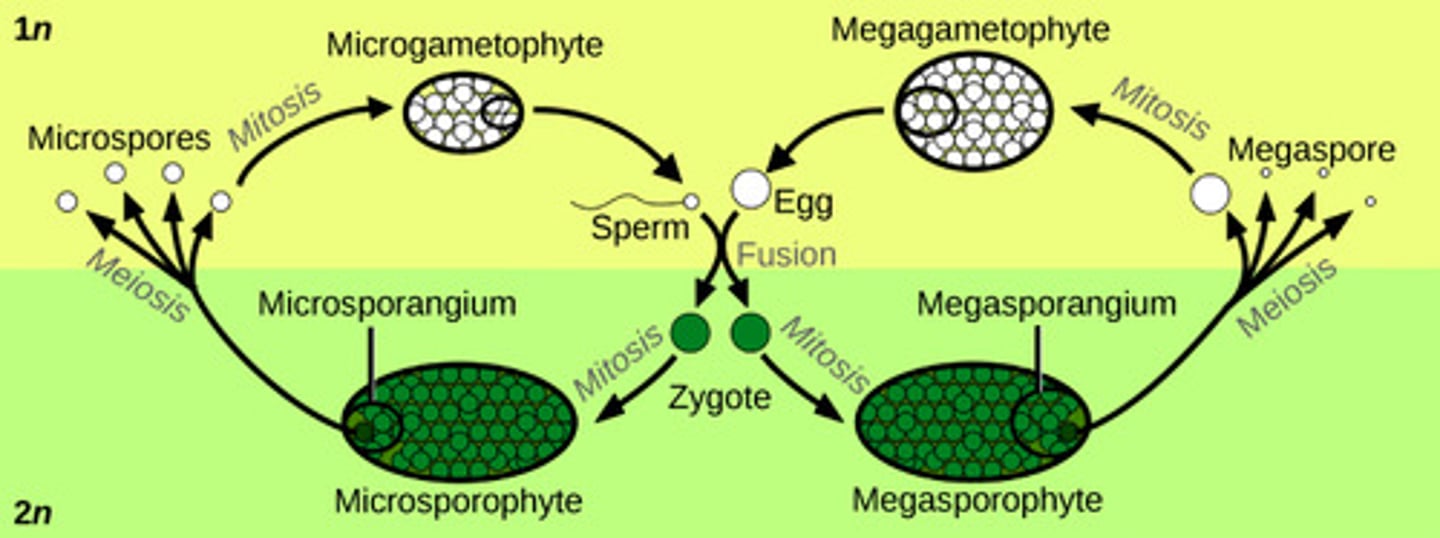
In megasporangia, what is the 1 surviving haploid cell called?
megaspore
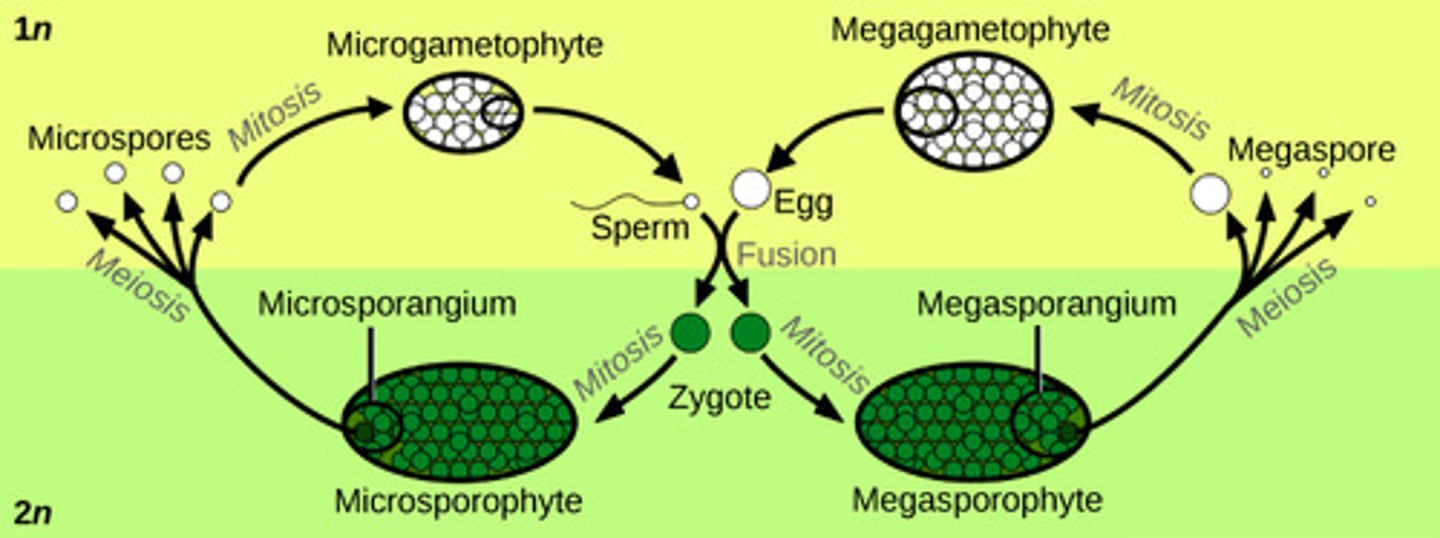
In megasporangia, the megaspore represents what generation?
female gametophyte generation
In megasporangia, the megaspore undergoes mitosis to produce which structure?
embryo sac
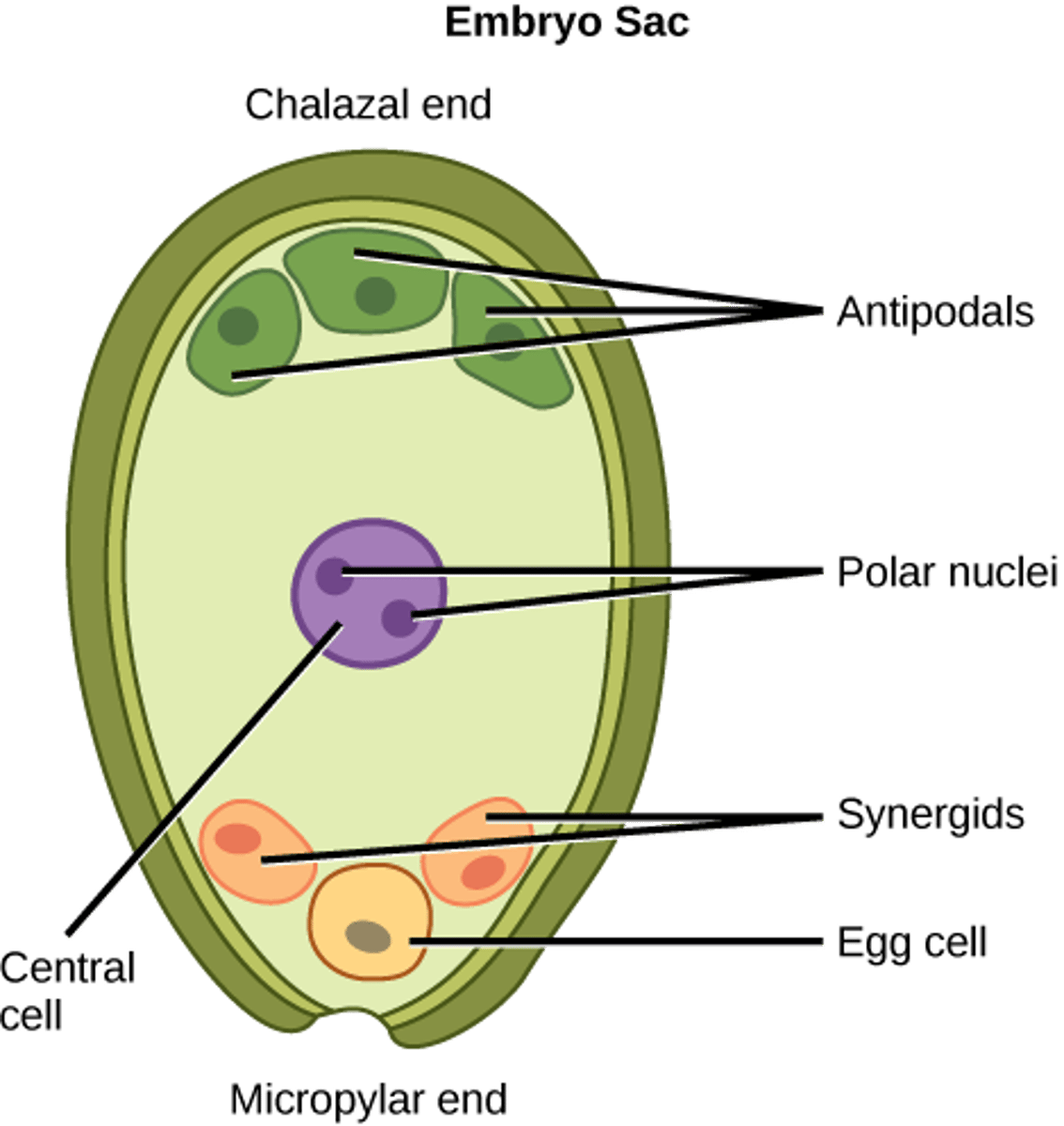
In which plants are 1 egg present in the embryo sac of the megasporangium?
flowering plants

In which plants are 2 eggs present in the embryo sac of the megasporangium?
conifers

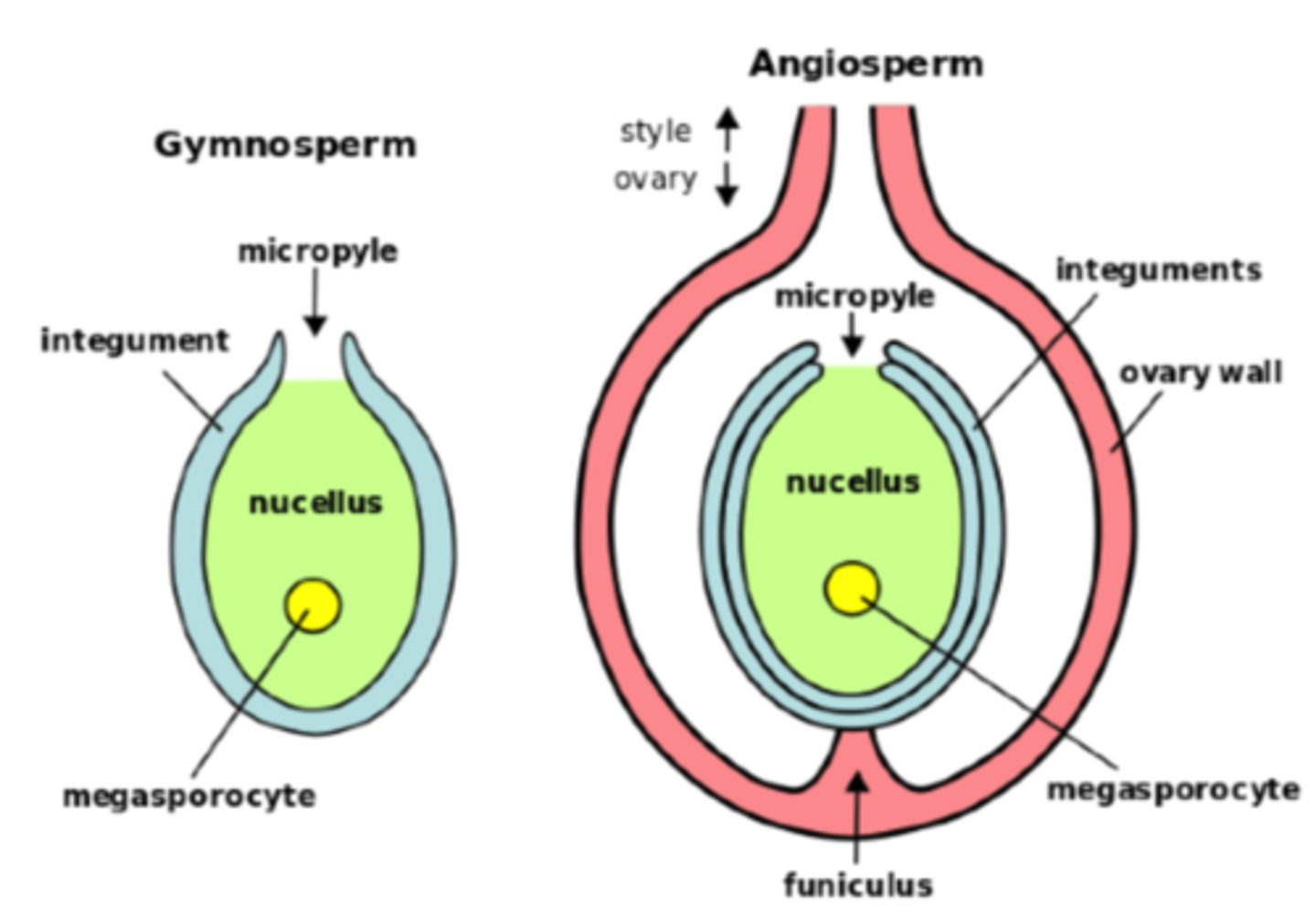
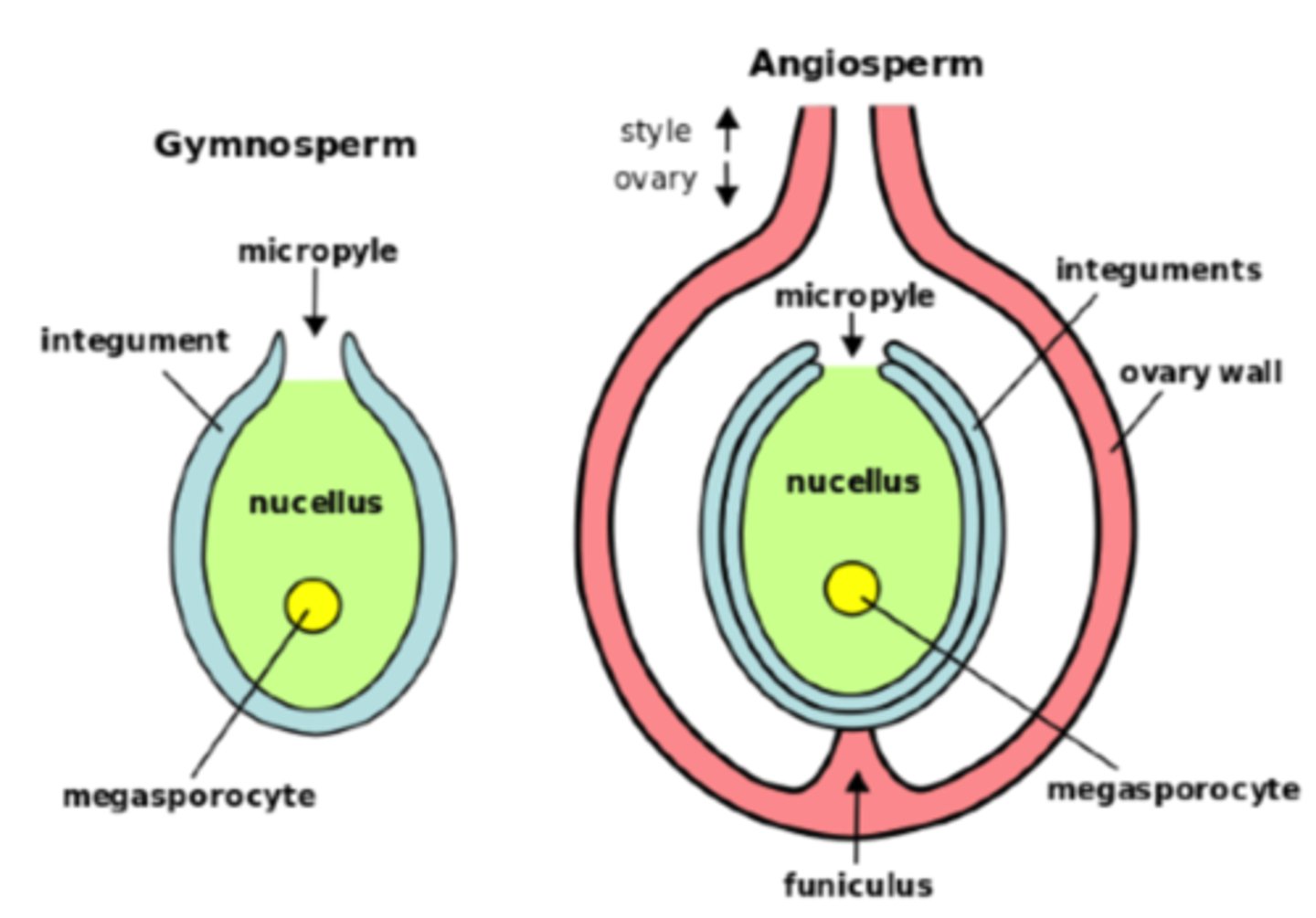
In megasporangia, what are the 1 or 2 tissue layers that surround the megasporangium?
integuments
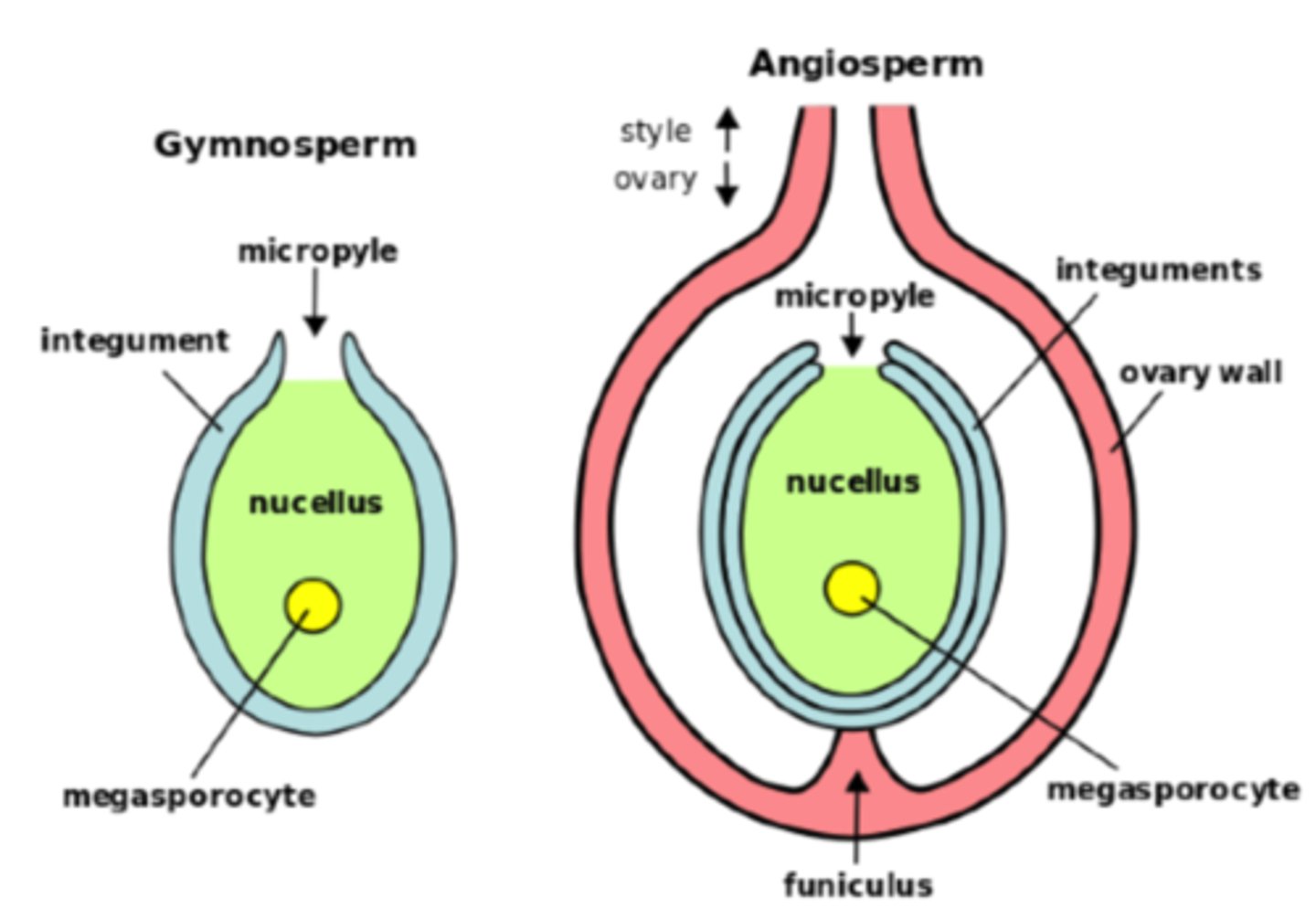
In megasporangia, what structures compose the ovule?
1. integument
2. nucellus
3. megaspore daughter cells
In megasporangia, what is the opening within the integuments for pollen to access the egg?
micropyle
In seeded vascular plants, what are the dispersal units?
seeds
(Note: note the spores directly)
In seeded vascular plants, what cell directs the growth of the pollen tube through the micropyle toward the egg?
tube cell of the sperm
(Note: occurs once
the pollen grain
contacts the
megasporangium)
In seeded vascular plants, what process occurs when the pollen tube contacts the egg?
fertilization and the creation of a zygote
In seeded vascular plants, what is the zygote created by fertilization is called?
embryo
(Note: beginning of the sporophyte generation)
In seeded vascular plants, what structures become the seed coat for the embryo?
integuments
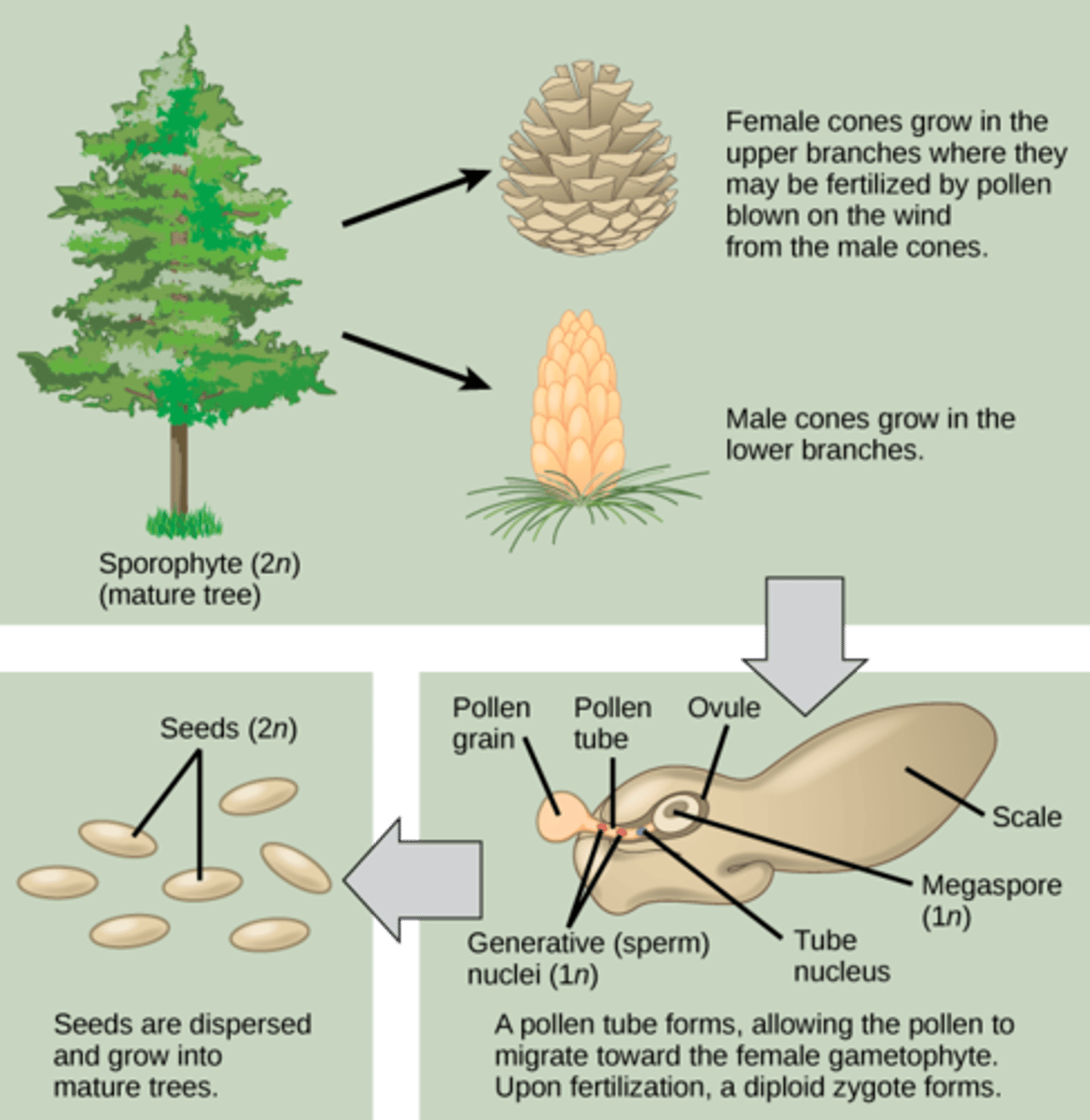
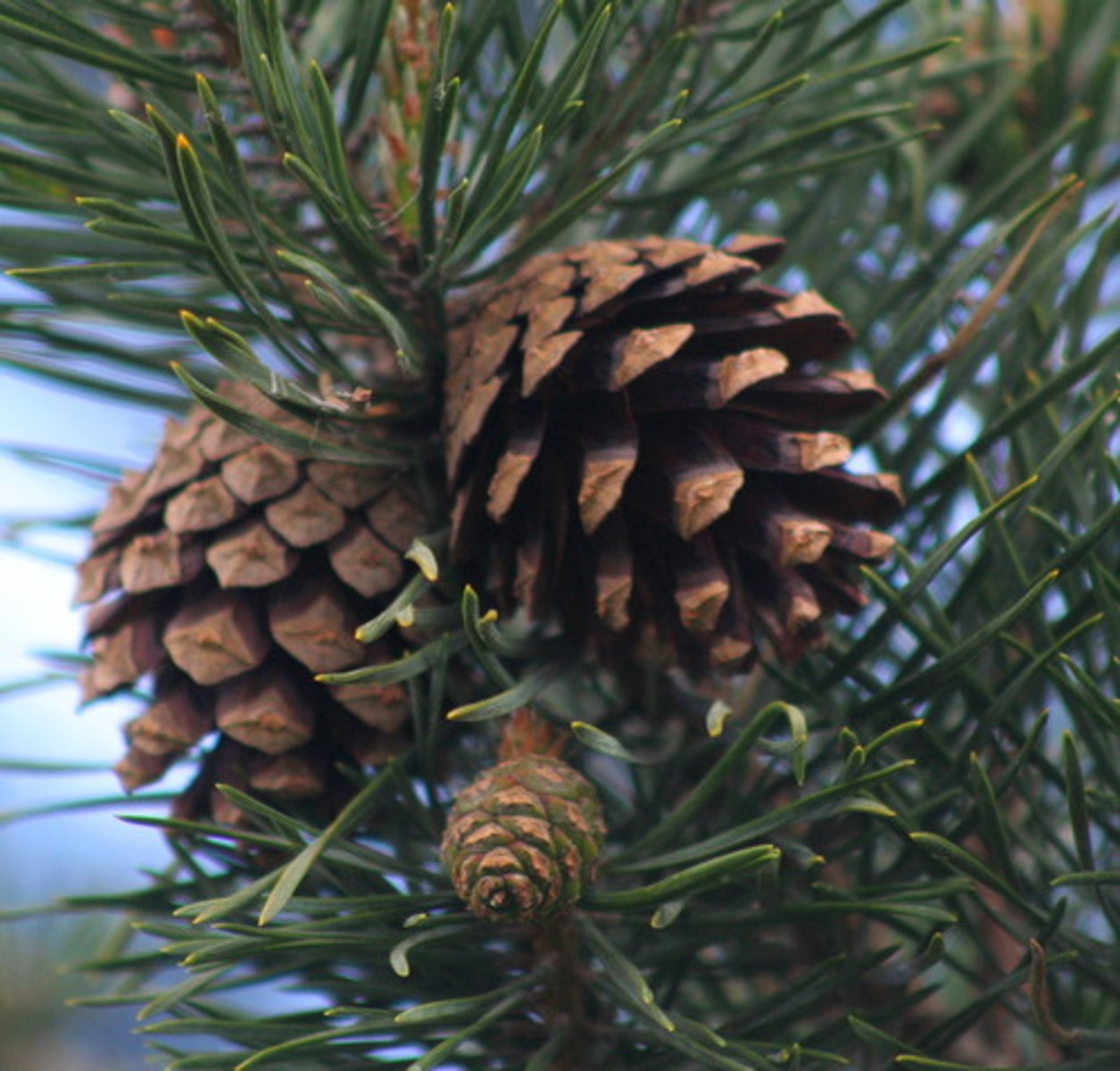
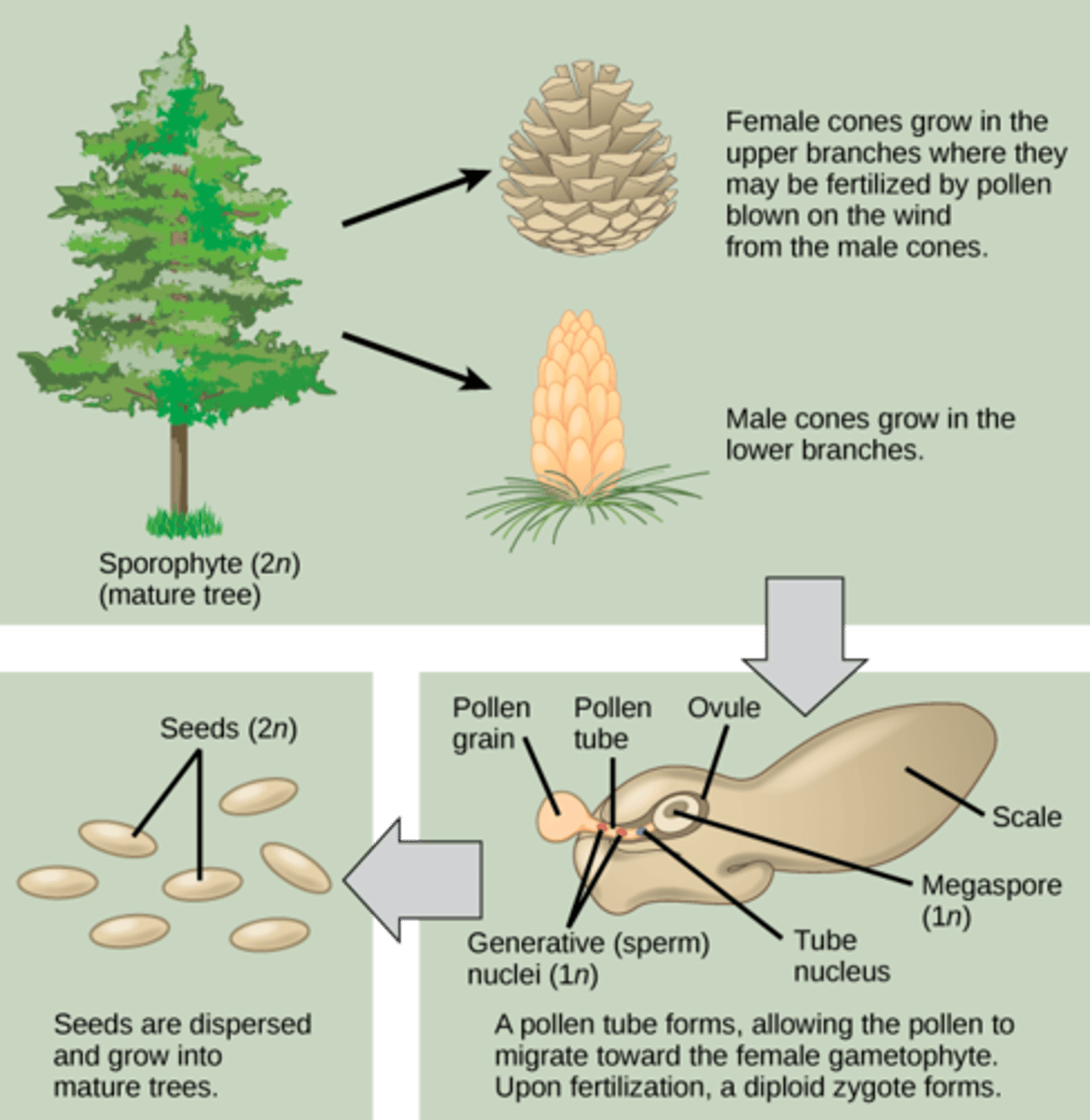
Which seeded vascular plants division includes pines, firs, spruces, junipers, redwoods, and cedars?
Coniferophyta
(Note: all bear cones)

What is the other name for Conferophyta?
the gymnosperms
(Note: meaning naked seeds)

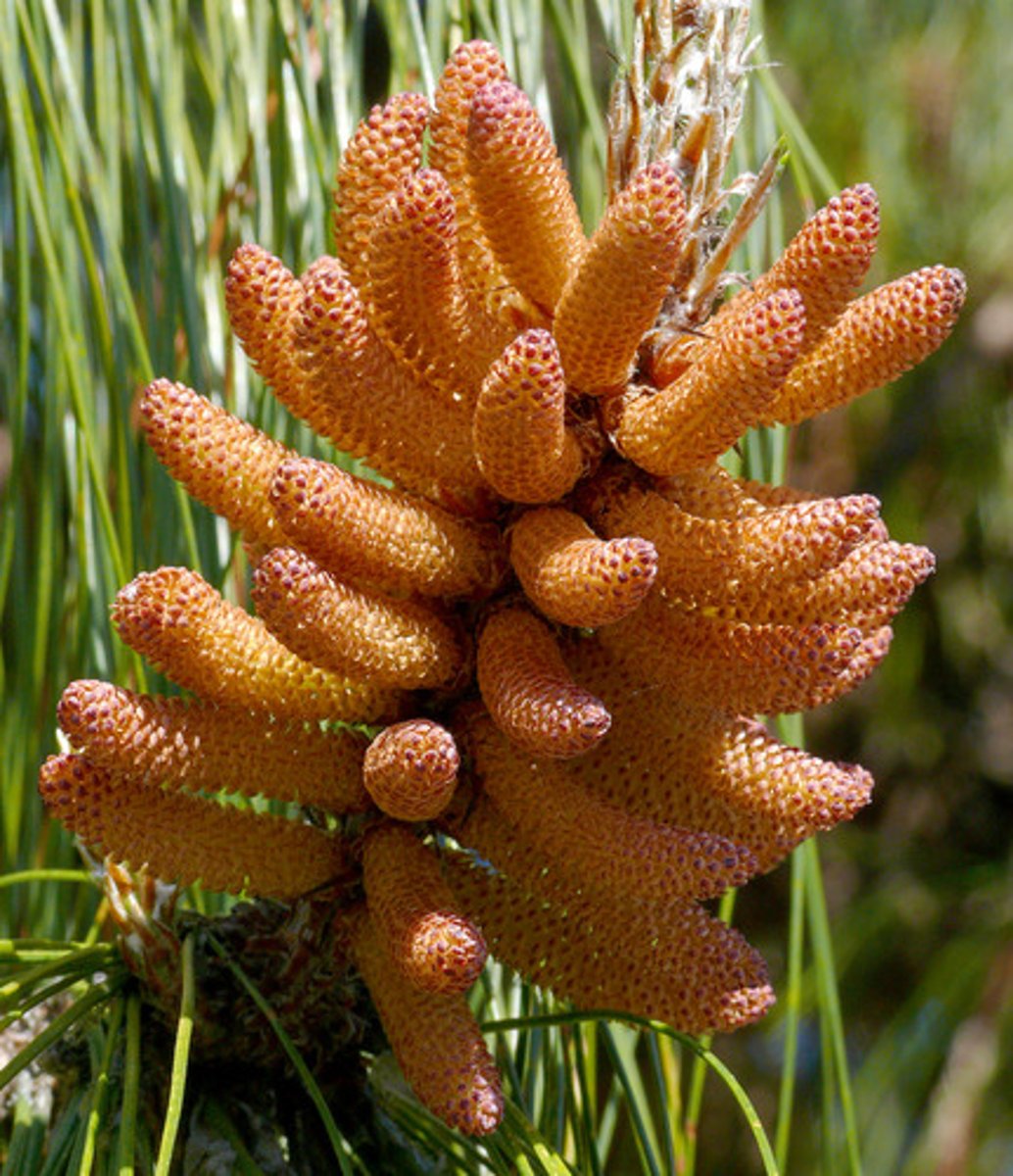
In conifers, what do male cones produce?
pollen

In conifers, what do female cones produce?
ovules
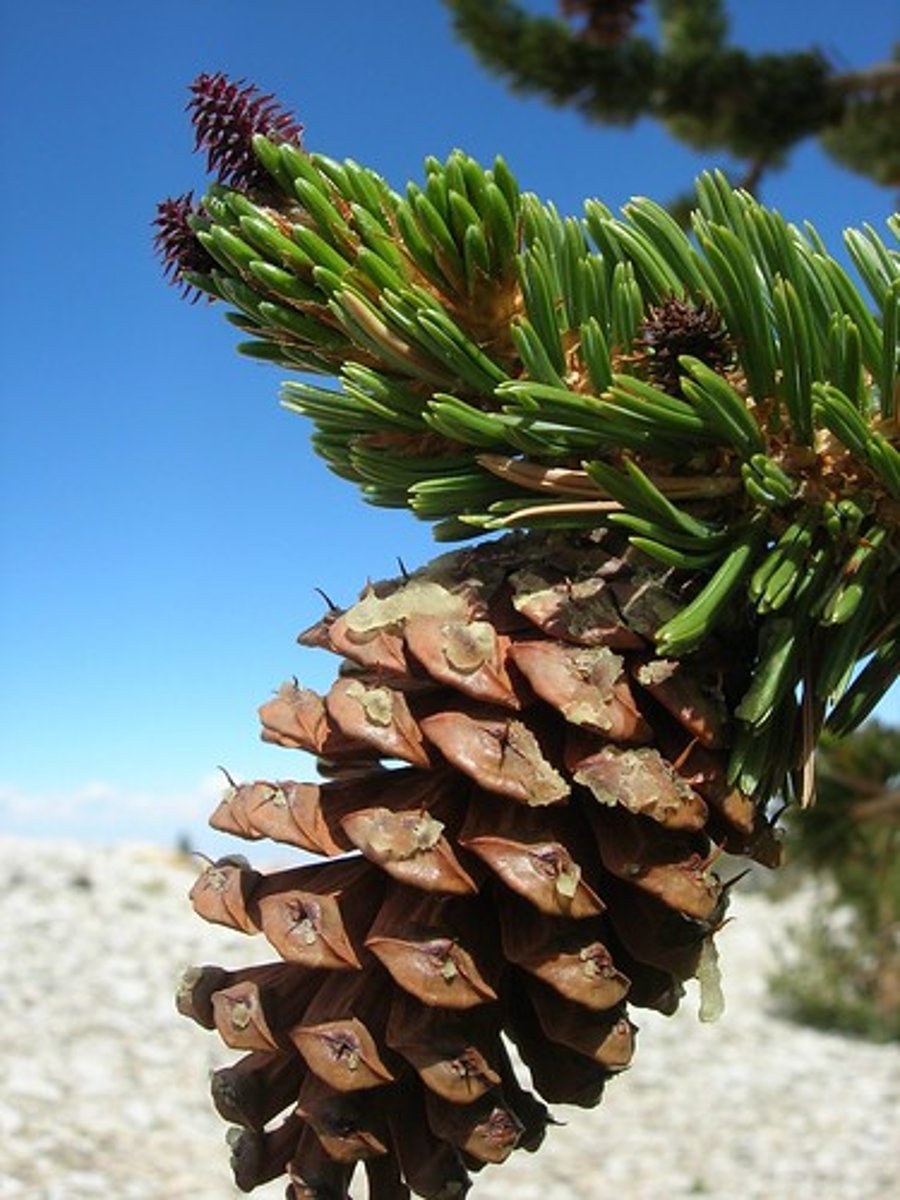

In conifers, where are seeds produced in unprotected megaspores located?
near the surface of the reproductive structure

In conifers, how long is the fertilization and seed development process?
1-3 years
(Note: lengthy)
Which seeded vascular plant division includes the flowering plants like fruits, maple, oaks, and grass?
Anthophyta
(Note: dominant land plant form)

What is the other name for Anthophyta?
angiosperms

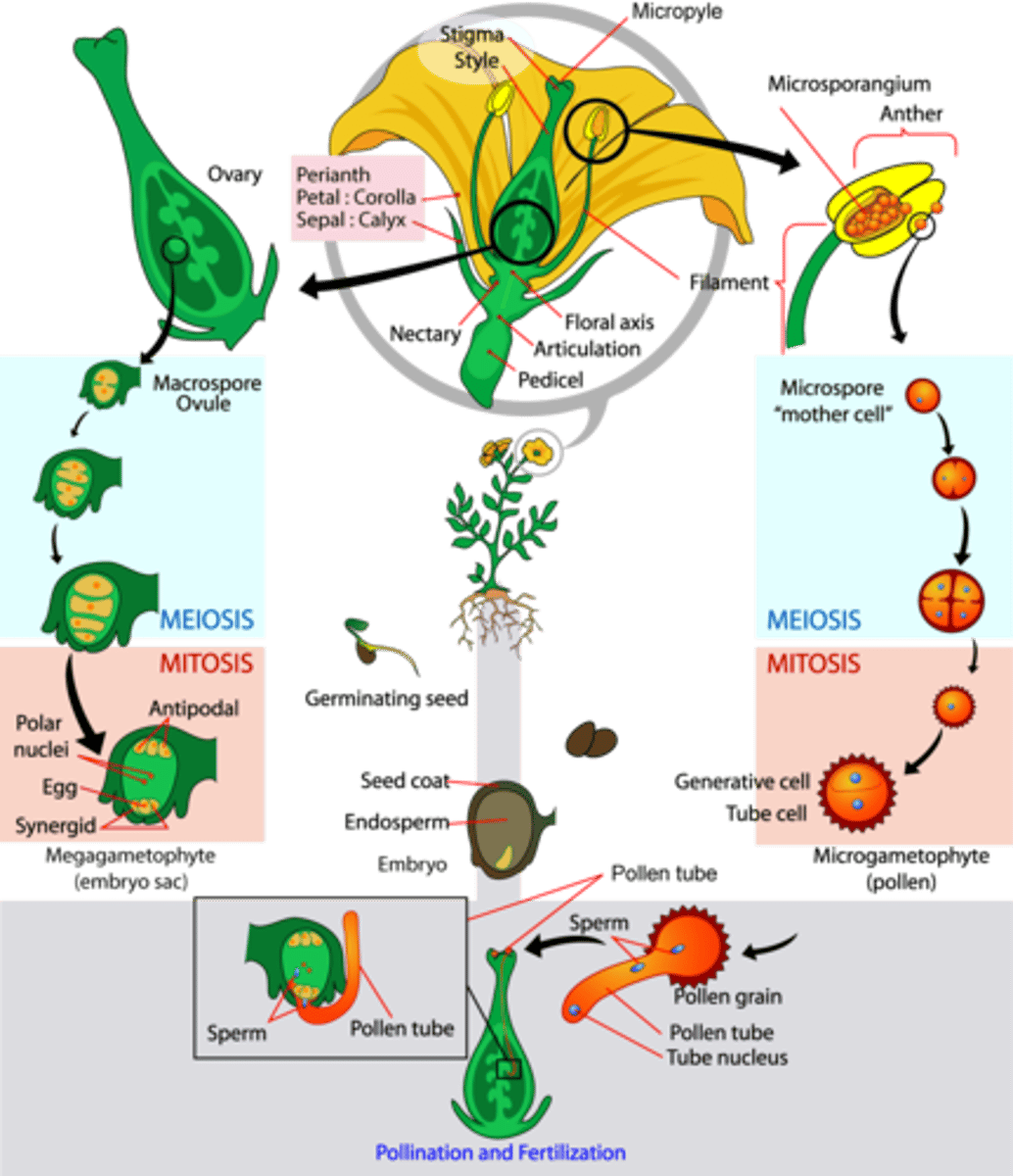
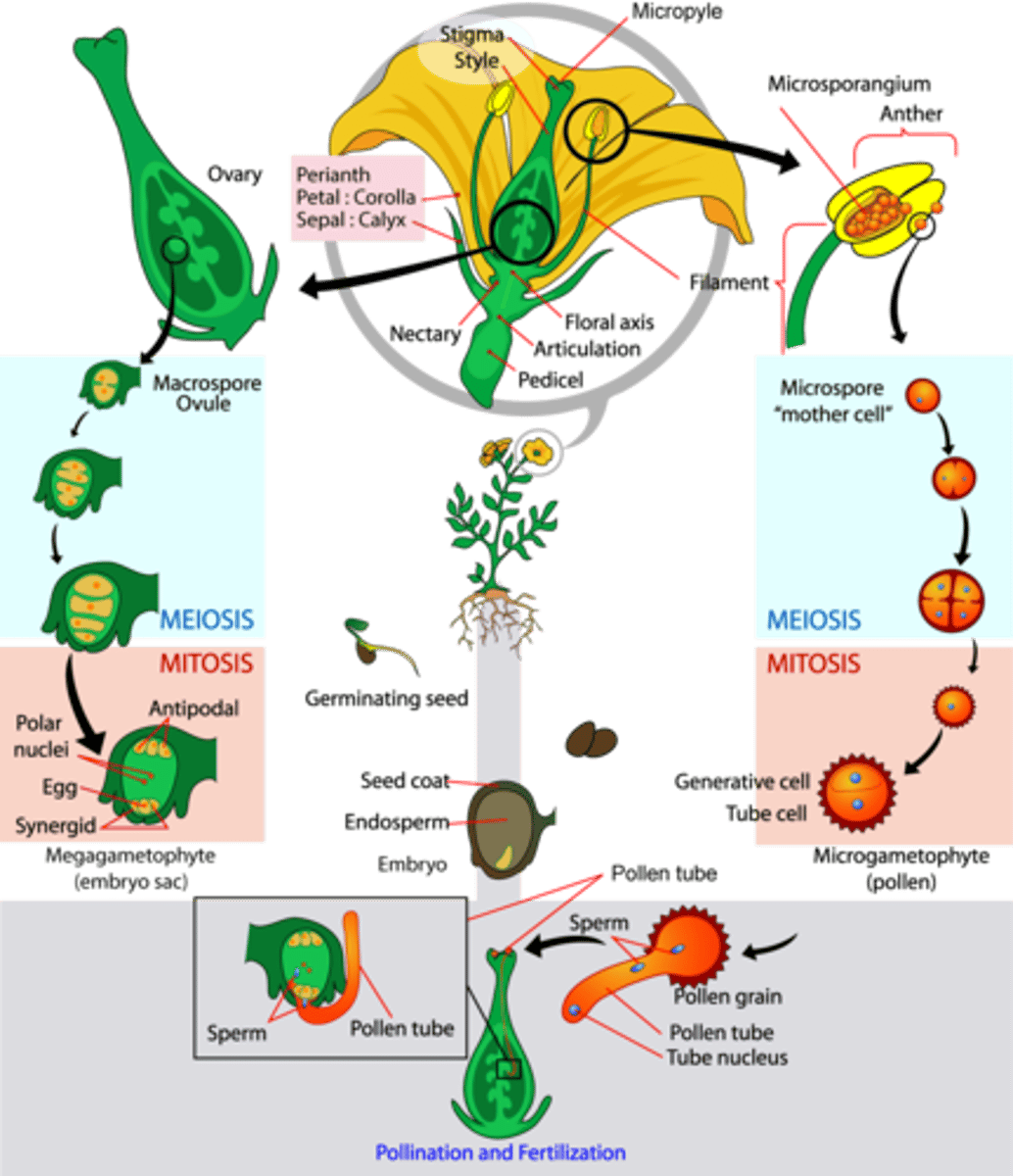
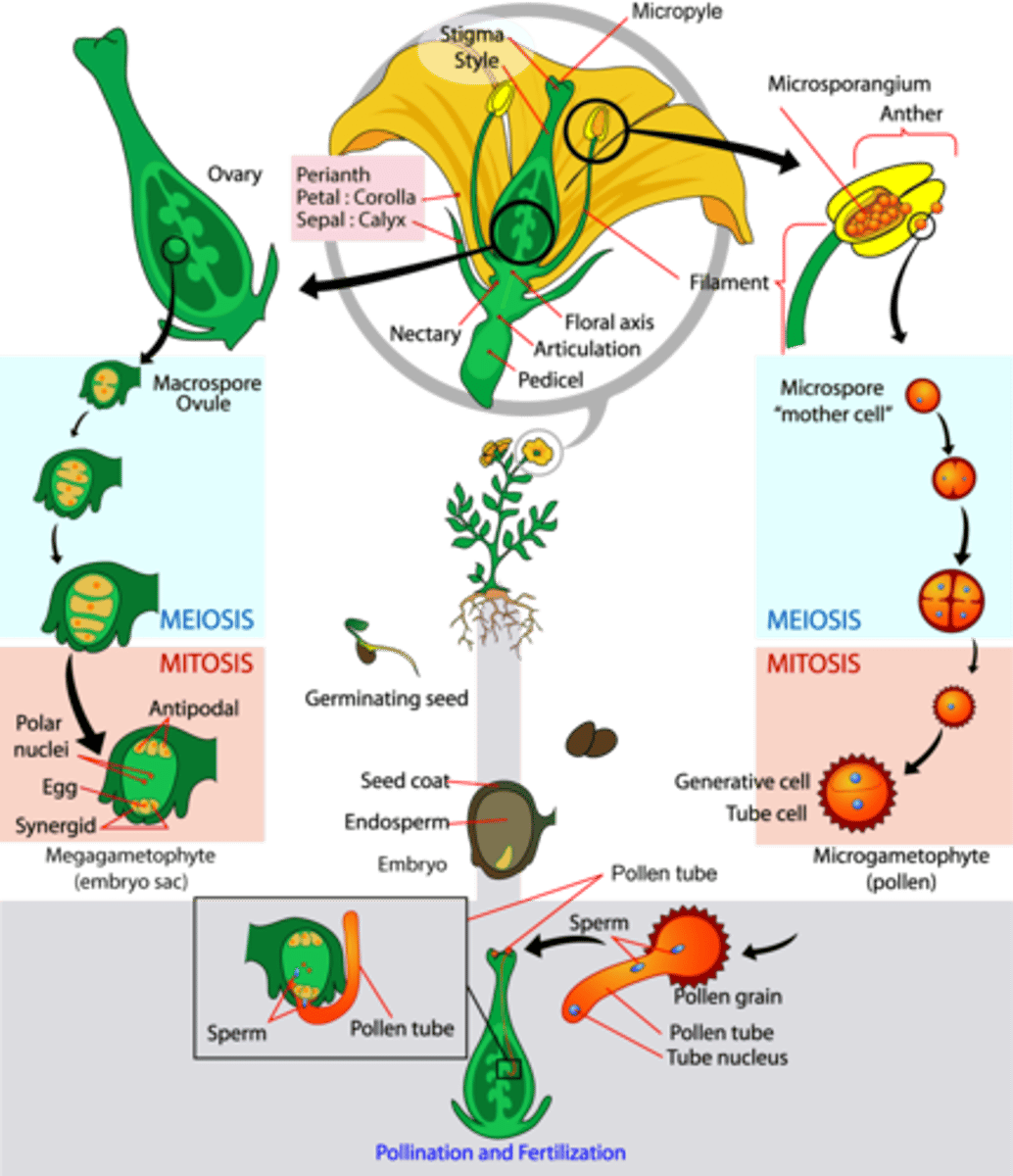
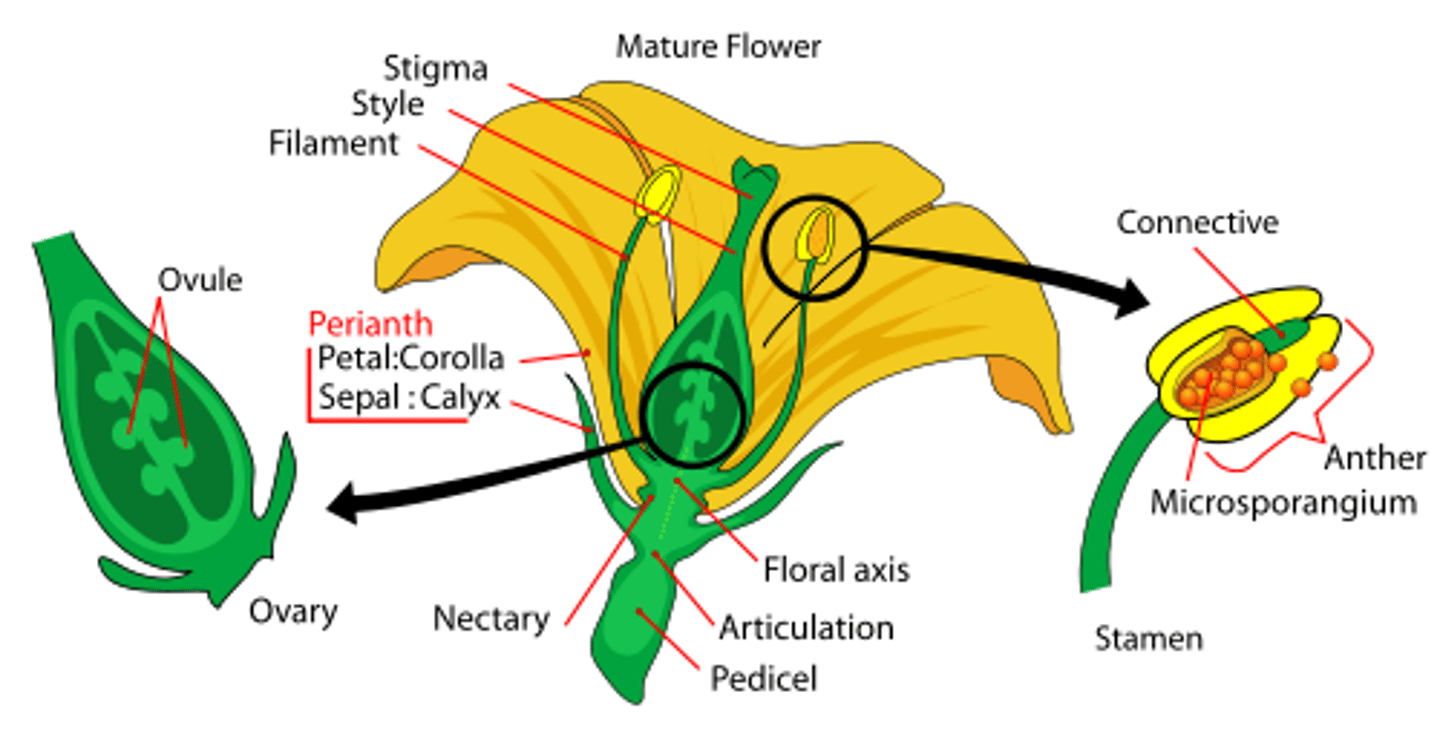
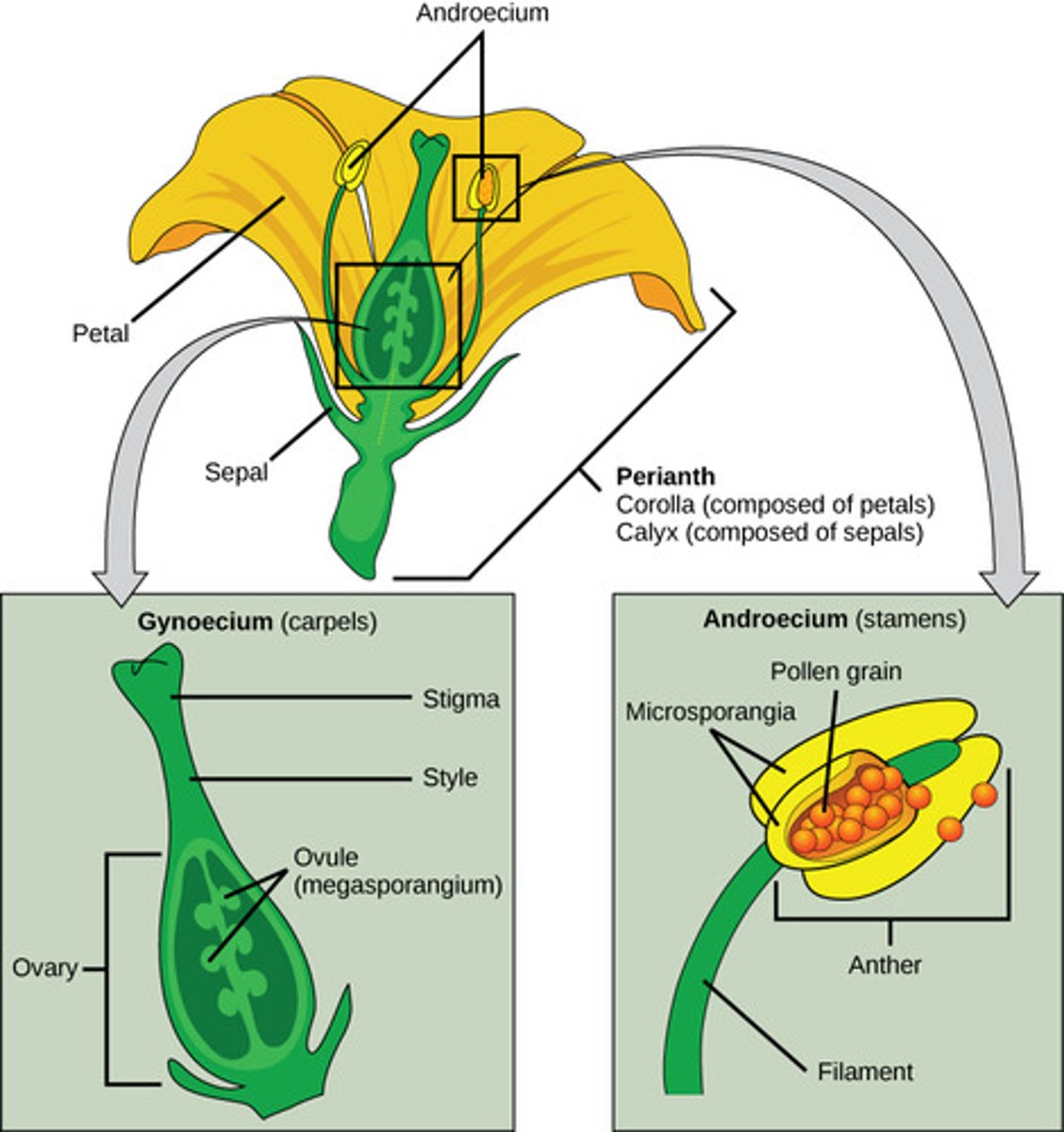
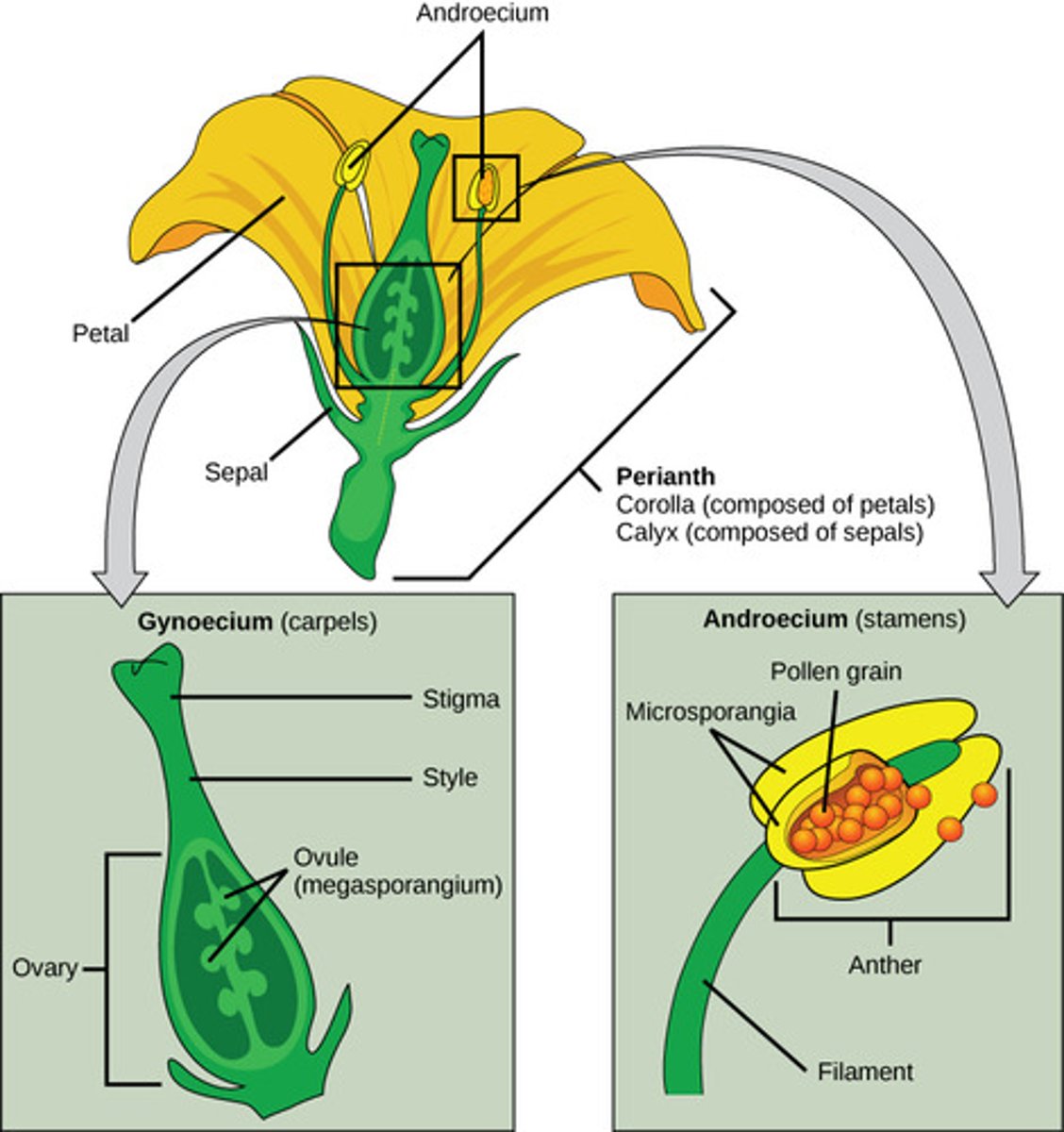
What is the reproductive structure of angiosperms?
flower
Which part of the flower is the female reproductive structure?
pistil
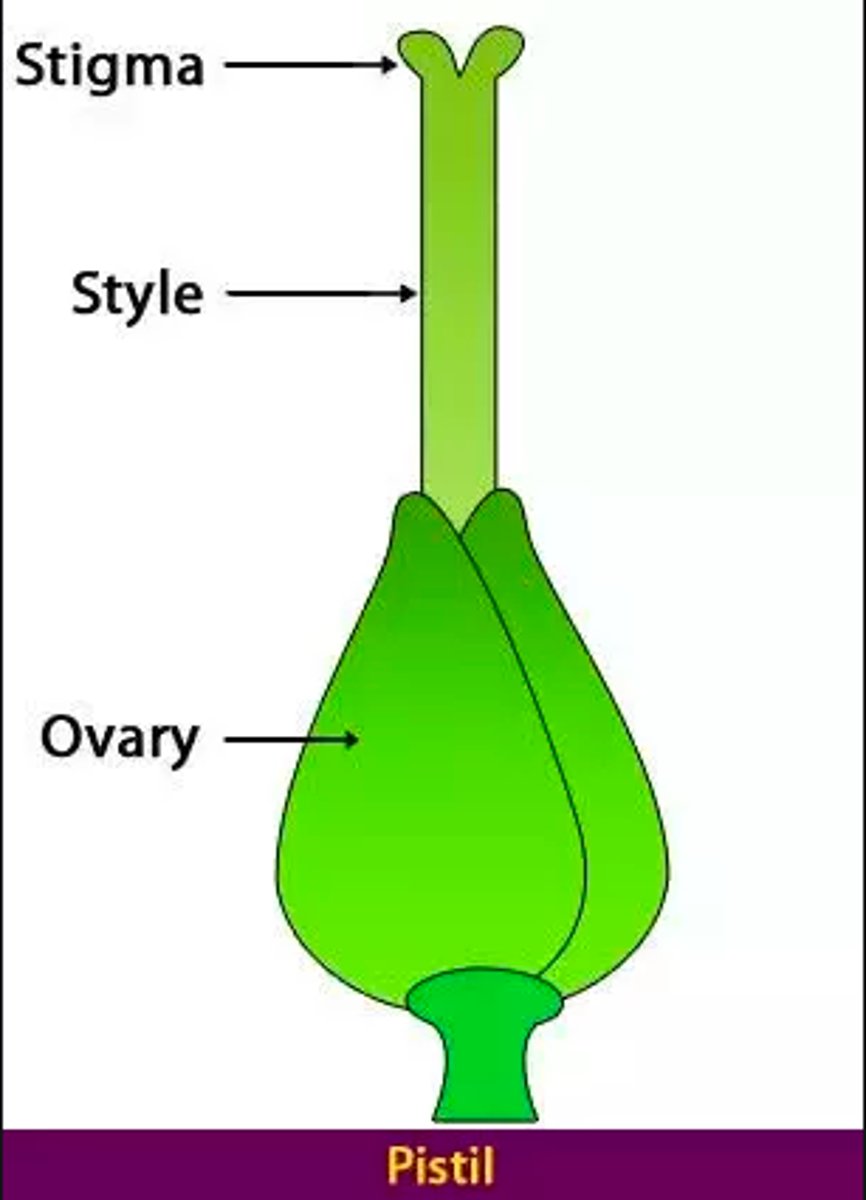
What are the 3 parts of the pistil?
1. ovary (egg bearing)
2. style
3. stigma
The ovary encloses 1 or more ovules with what covering?
monoploid egg nucleus
Which part of the flower is the male reproductive structure?
stamen
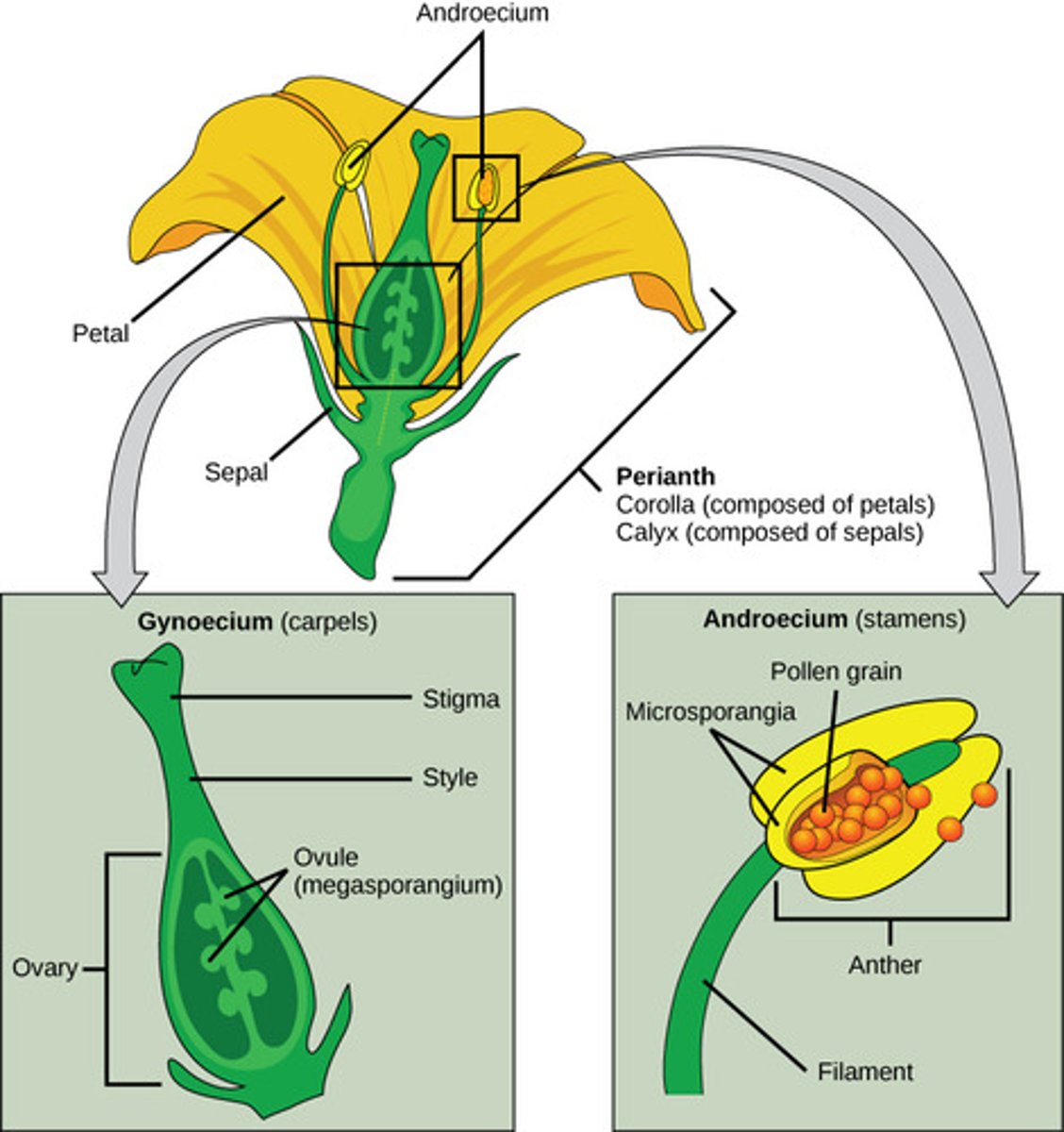
What are the 3 parts of the stamen's pollen bearing structure?
1. anther
2. stalk
3. filament
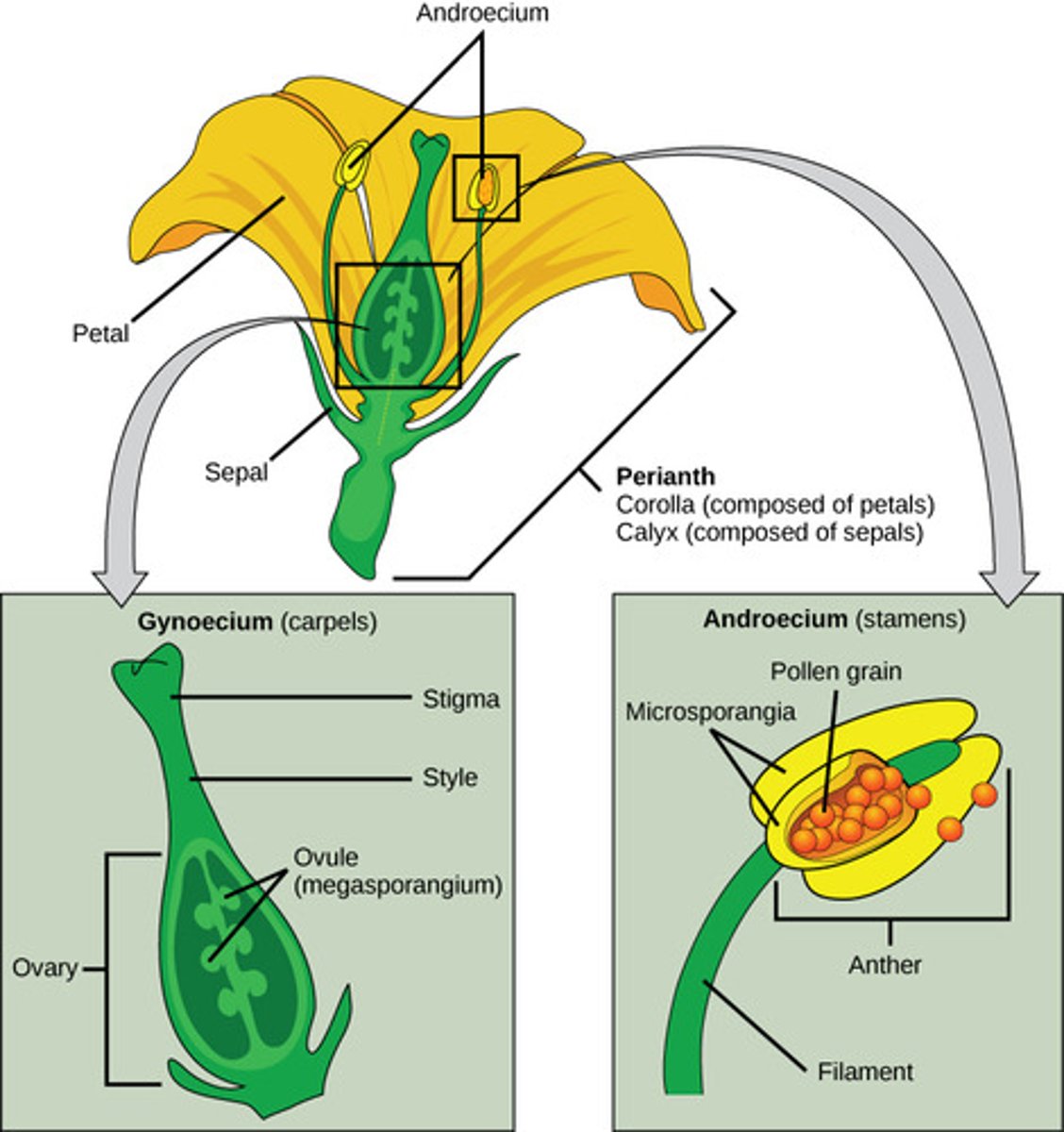
What is the chamber where the pollen develops within a stamen?
anther
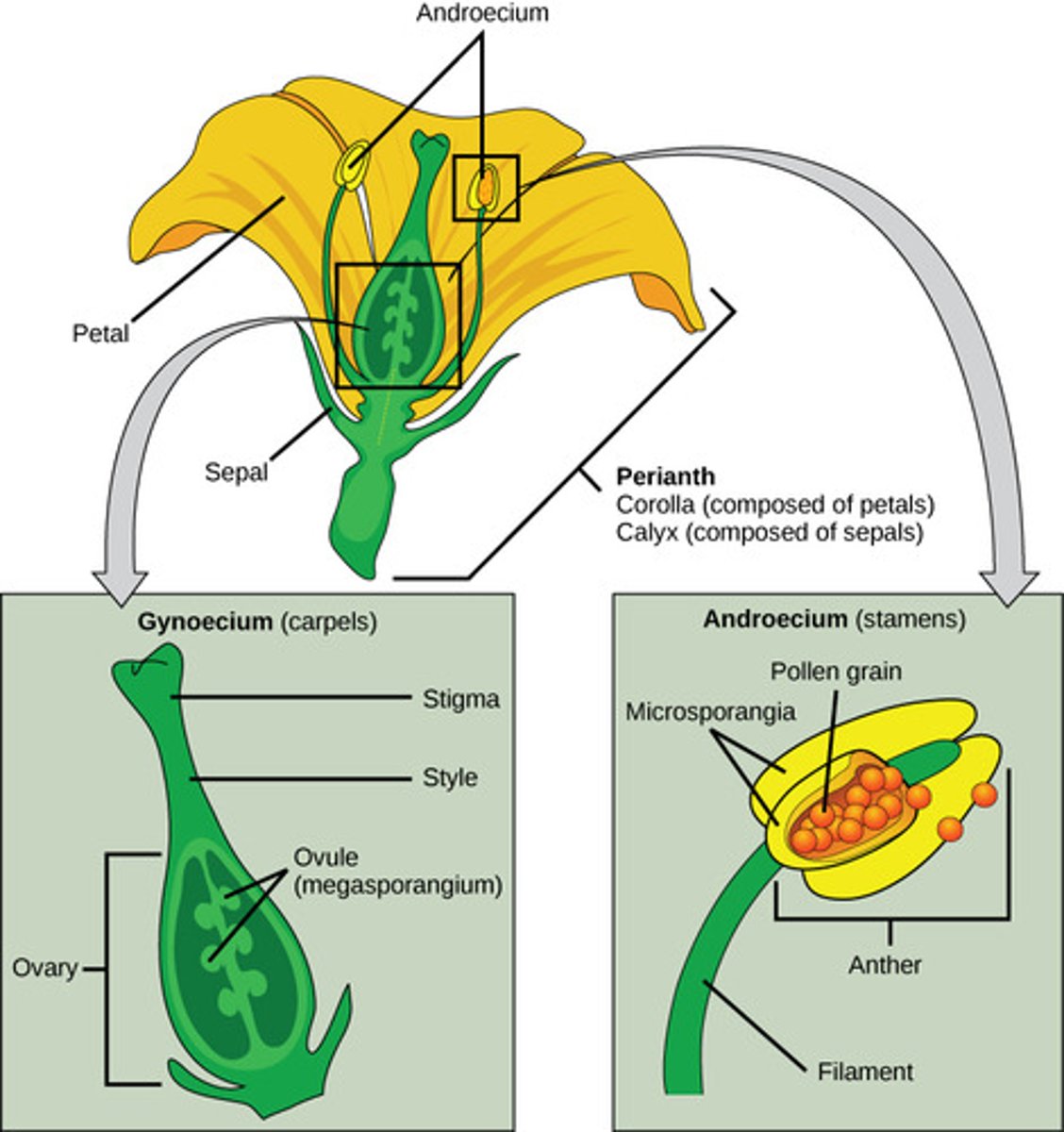
Which part of the flower functions to attract pollinators?
petals

In angiosperms, what structure encloses and protects the flower bud?
sepal
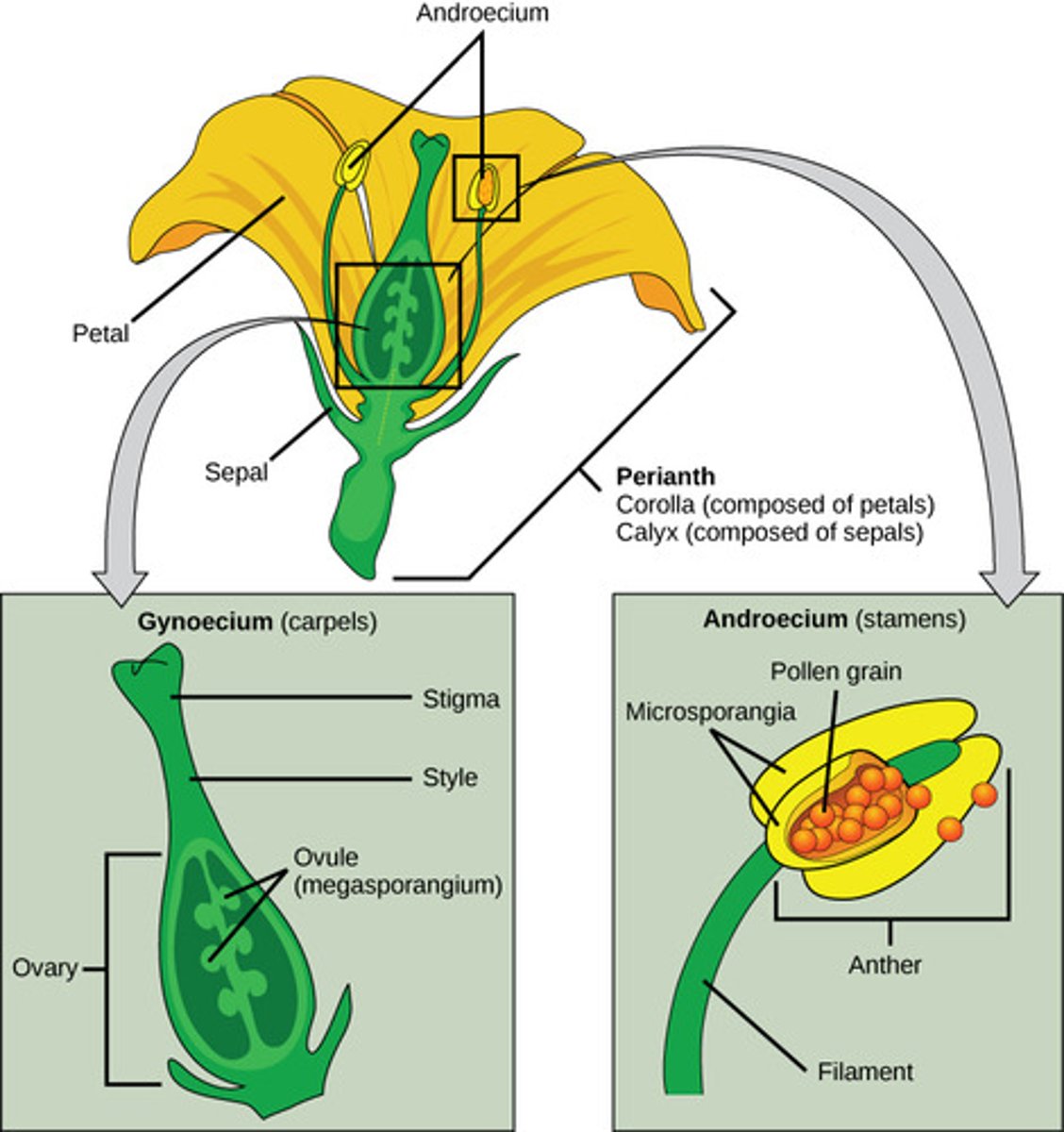
In angiosperms, what reproductive structure develops into fruit following fertilization?
ovary
(Note: ovule is protected
within the ovary)
In angiosperms, how are seeds dispersed?
wind or animals
In angiosperm fertilization, where does pollen land?
stigma
(Note: it's sticky)
In angiosperm fertilization, the pollen tube grows down the style toward what reproductive structure?
ovule
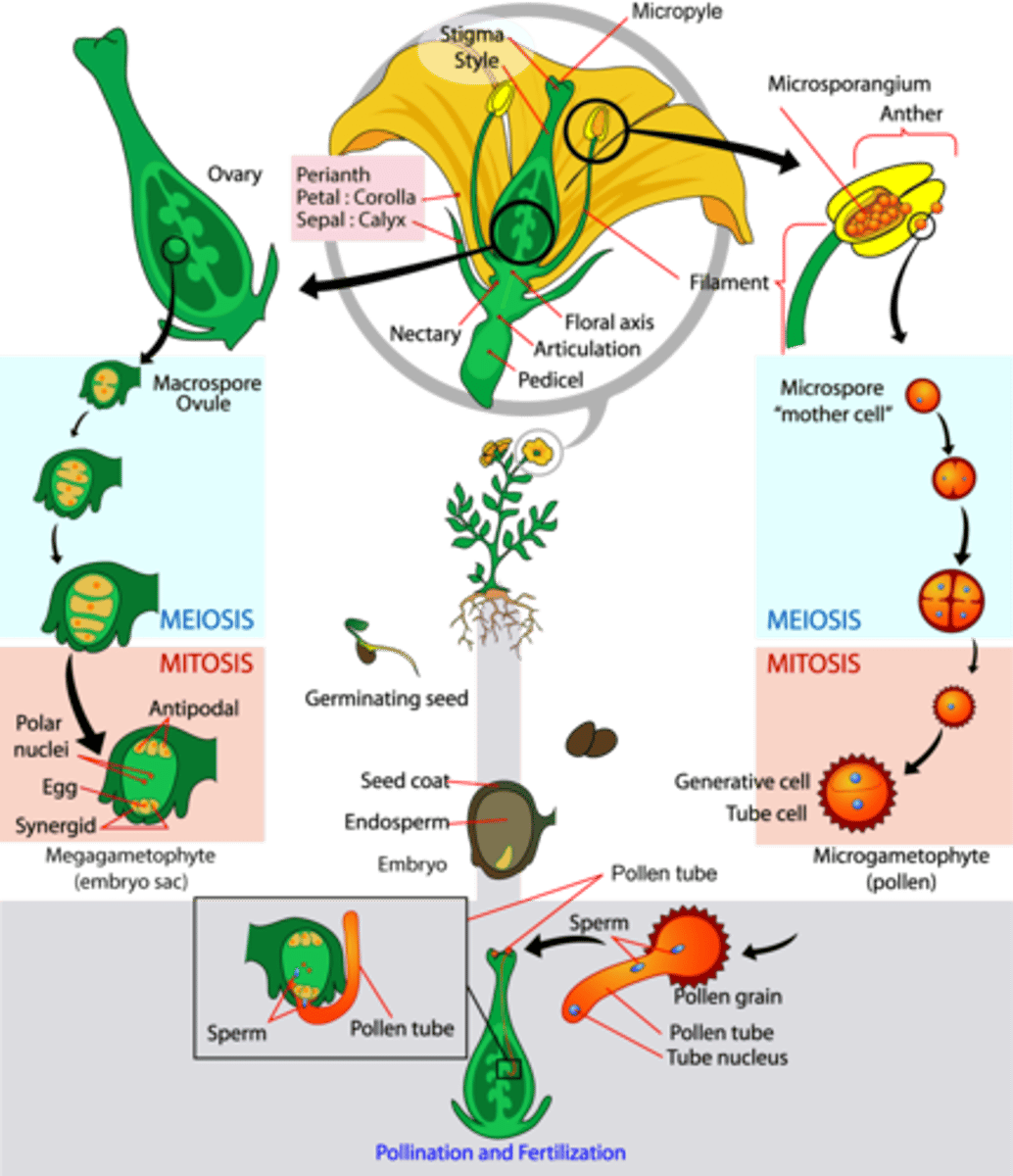
In angiosperm fertilization, how many sperm cells are present in the pollen tube?
2 sperm cells
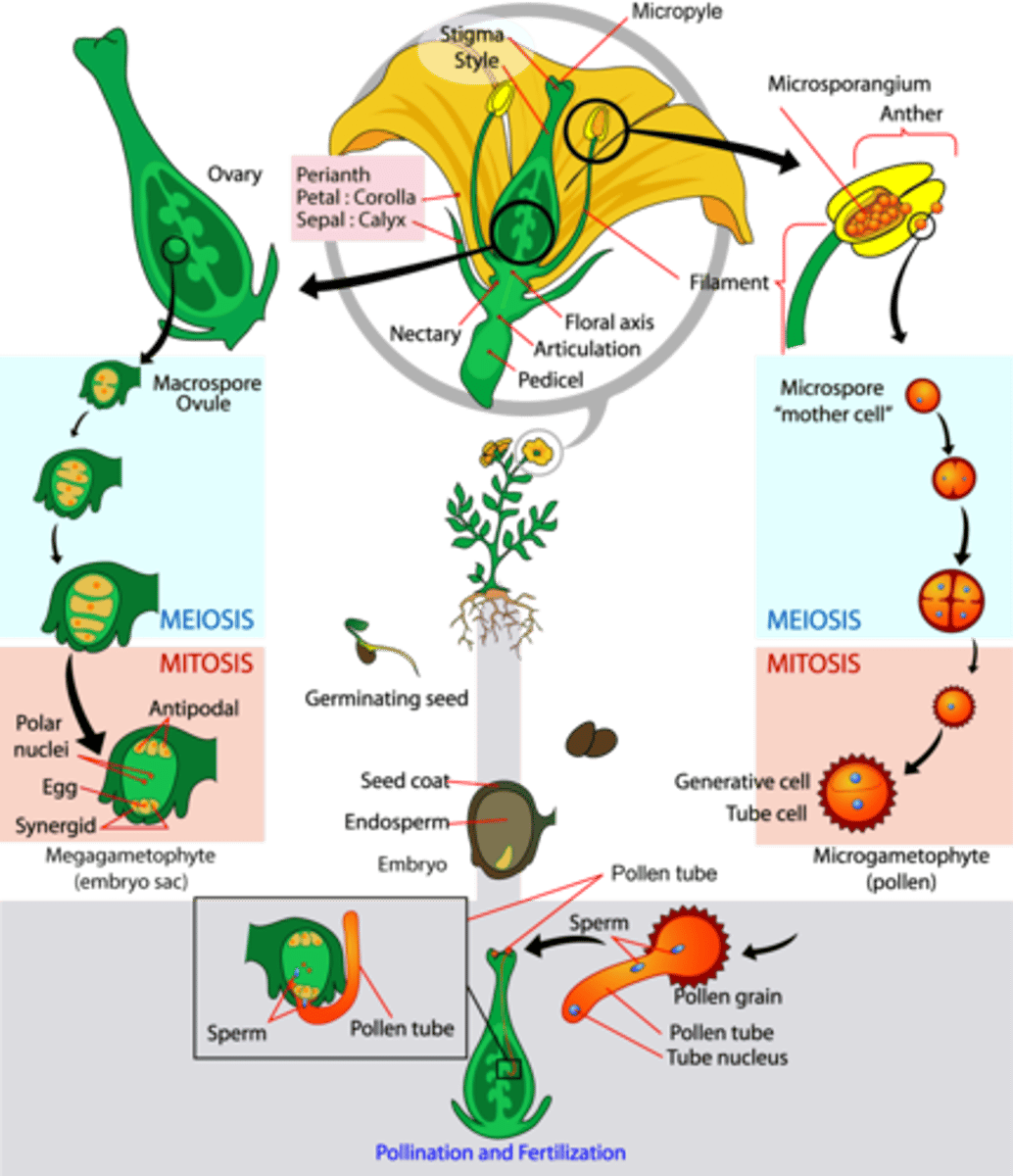
In angiosperm fertilization, the surviving megaspore undergoes mitosis 3 times to create how many nuclei?
8 nuclei
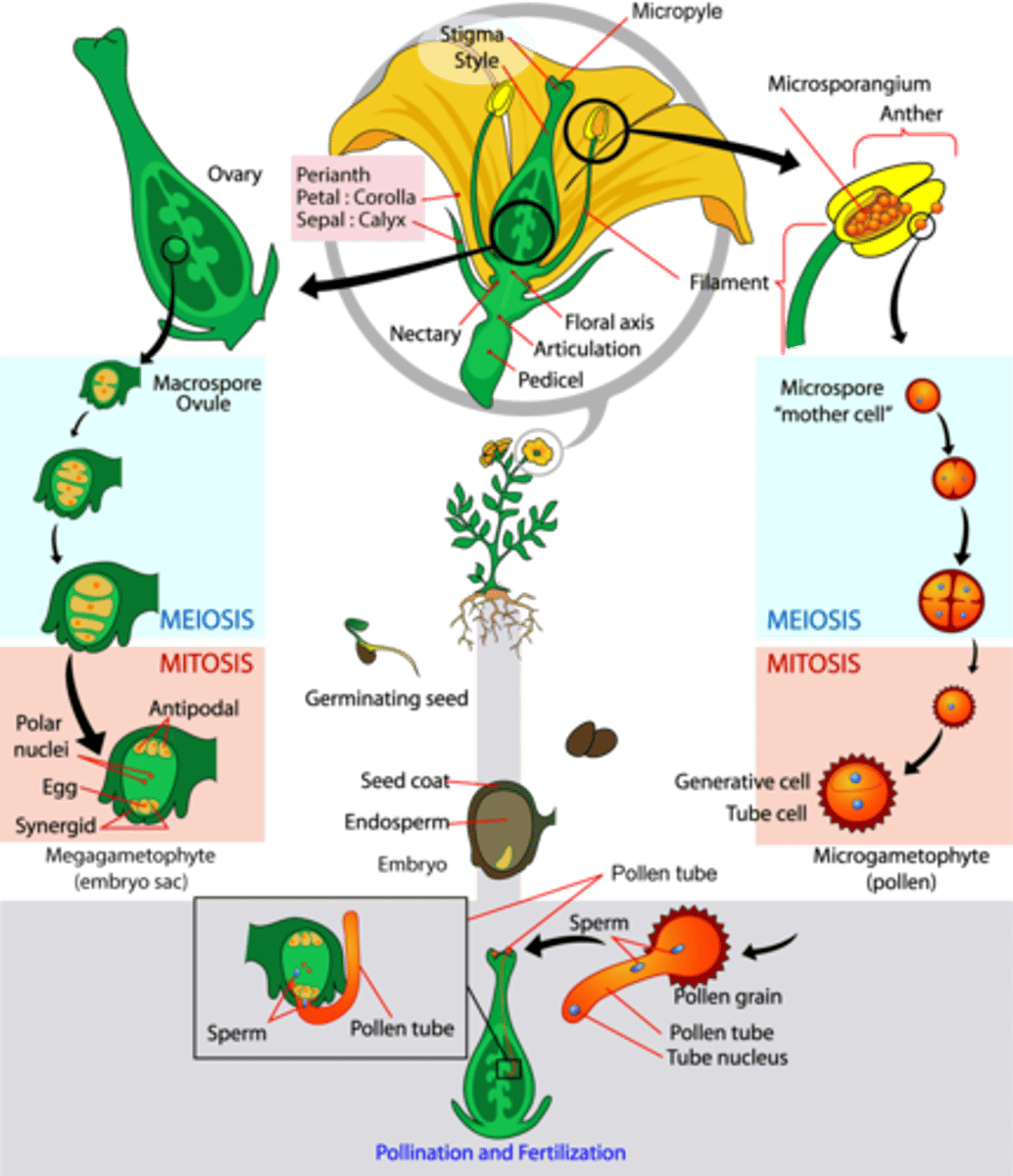
In angiosperm fertilization, how many of the 8 nuclei undergo cytokinesis to form plasma membranes (embryo sac)?
6 nuclei
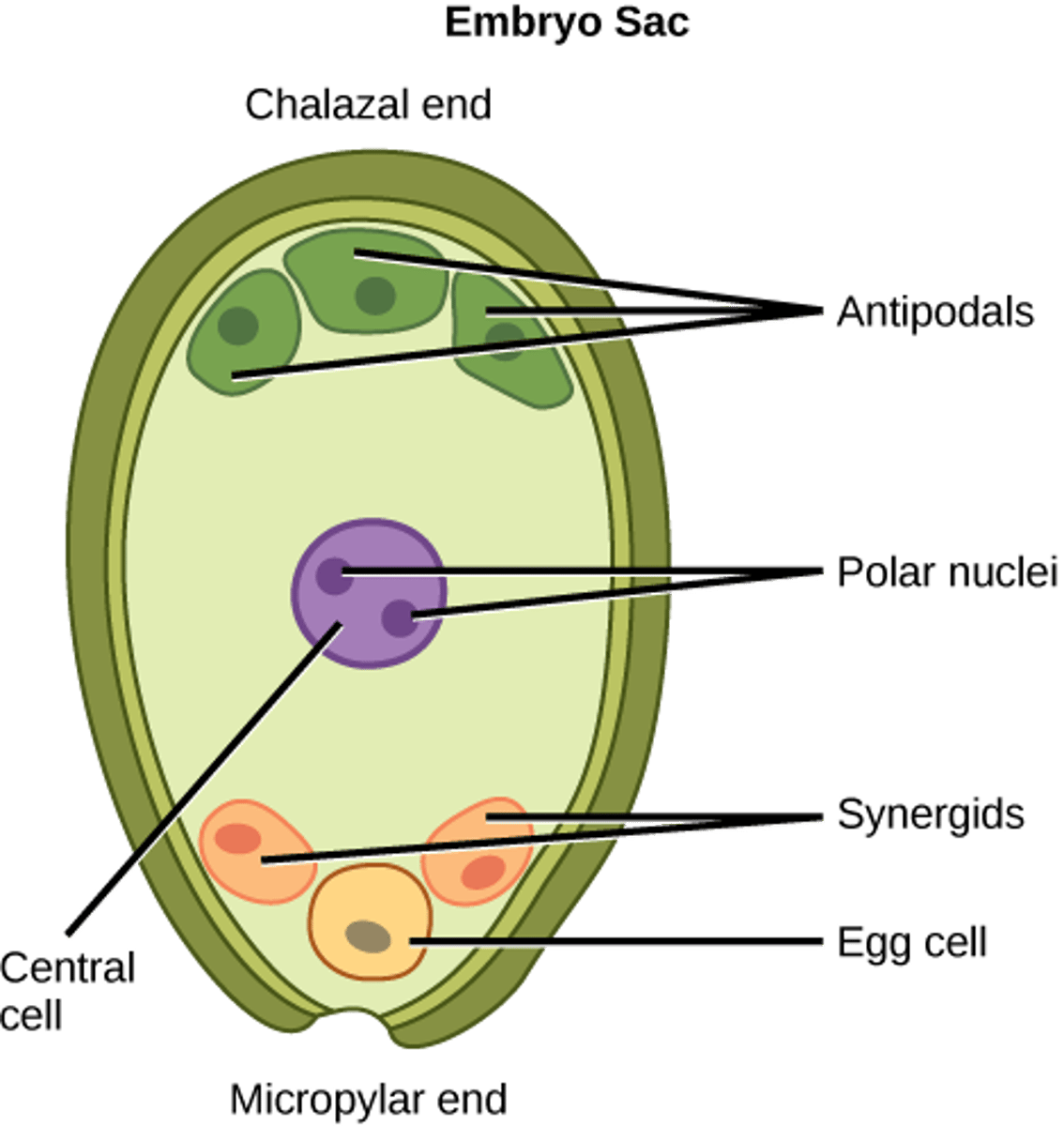
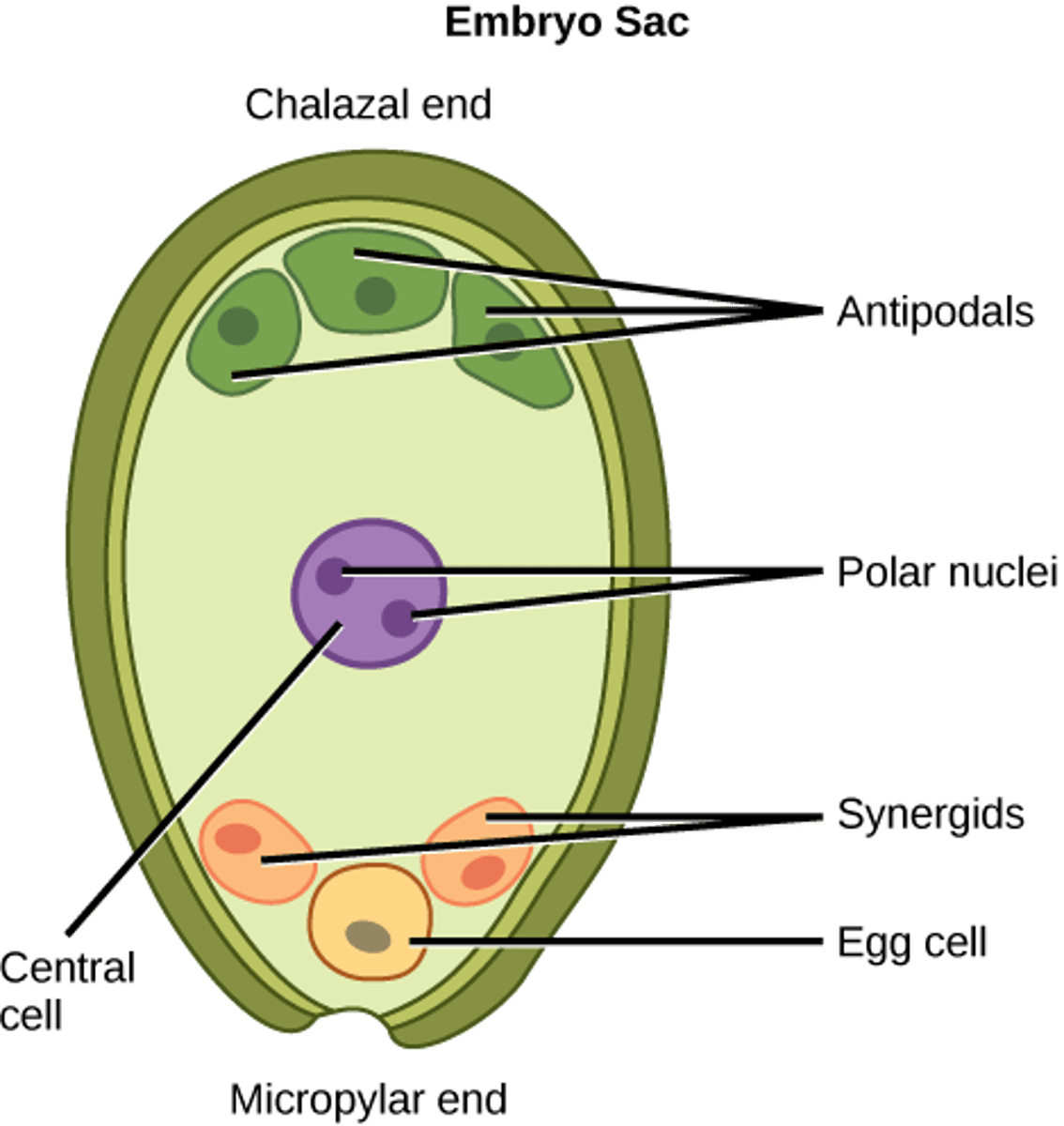
In angiosperm fertilization, what cells are located at the micropyle end of the embryo sac?
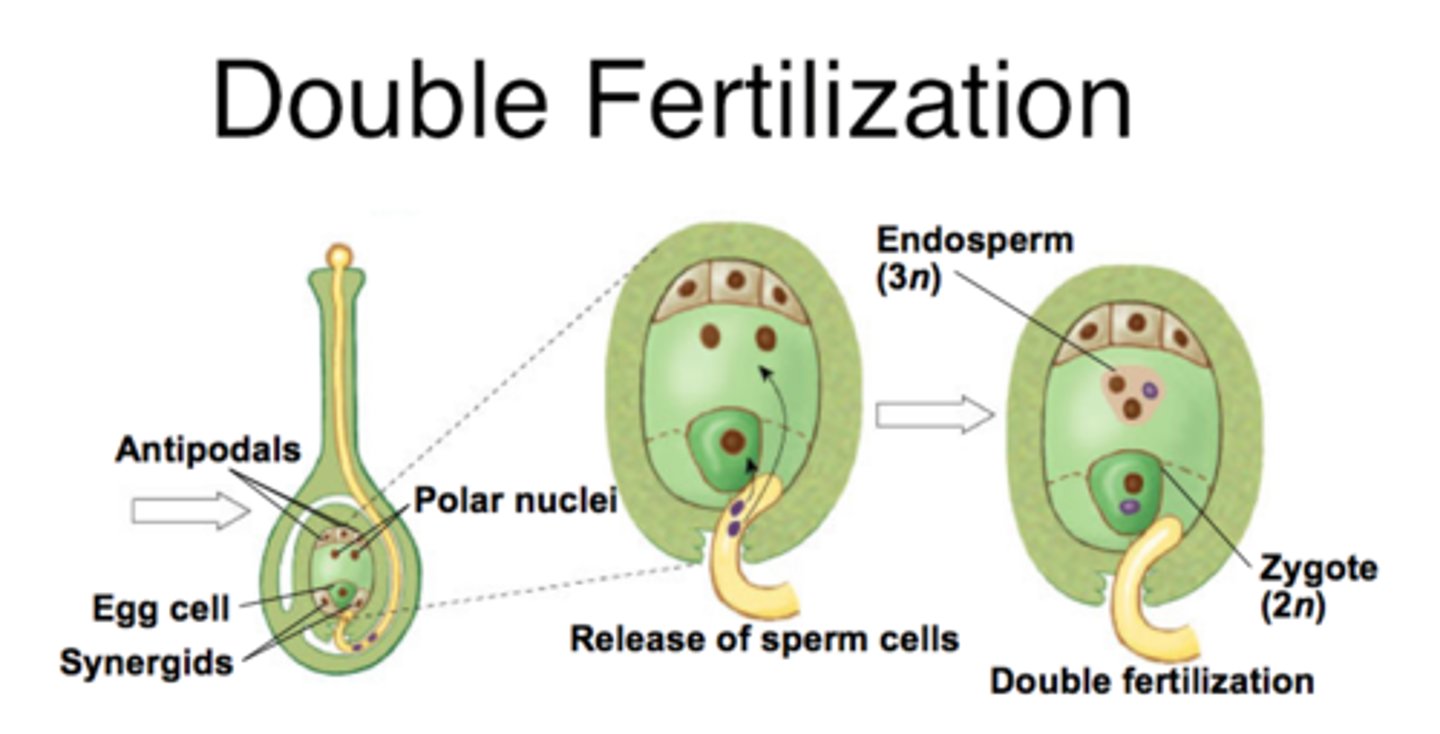
1 egg and 2 synergids
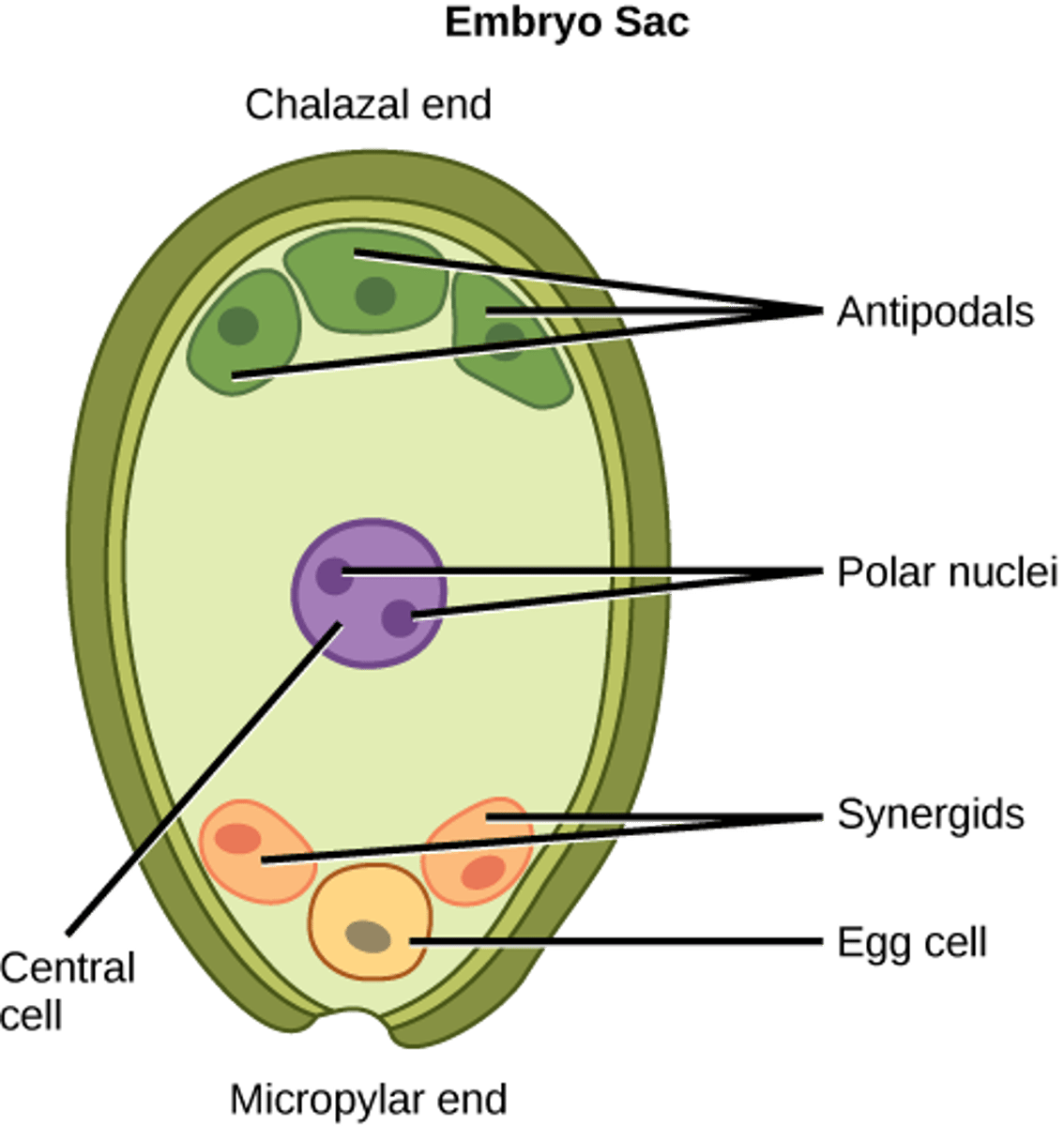
In angiosperm fertilization, what cells are located at the non-micropyle end of the embryo sac?
3 antipodal cells
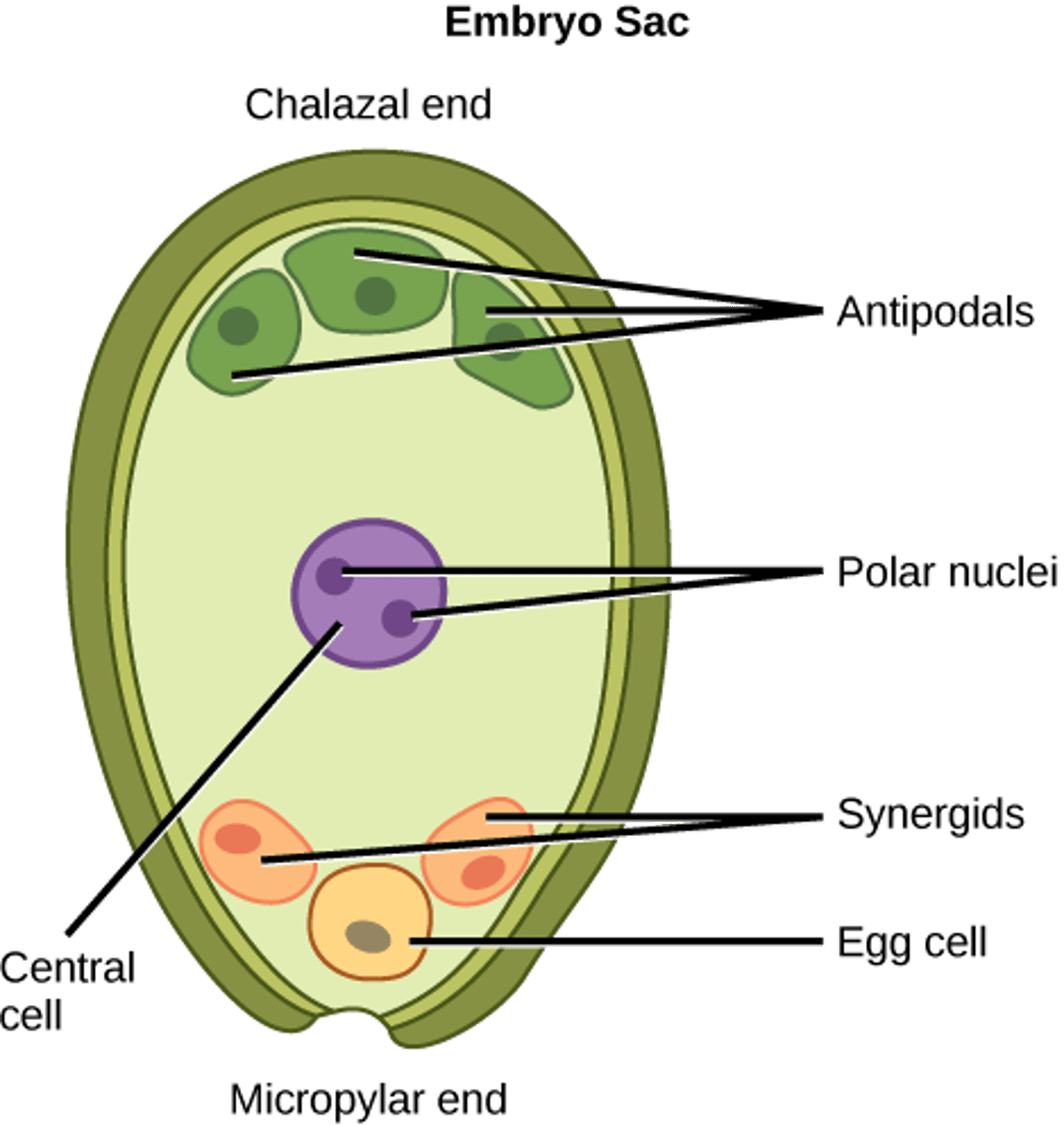
In angiosperm fertilization, what cells are in the middle of the embryo sac?
2 polar nuclei
(Note: 2 haploid cells)
In angiosperm fertilization, what reproductive unit is formed when one sperm fertilizes the egg?
diploid zygote
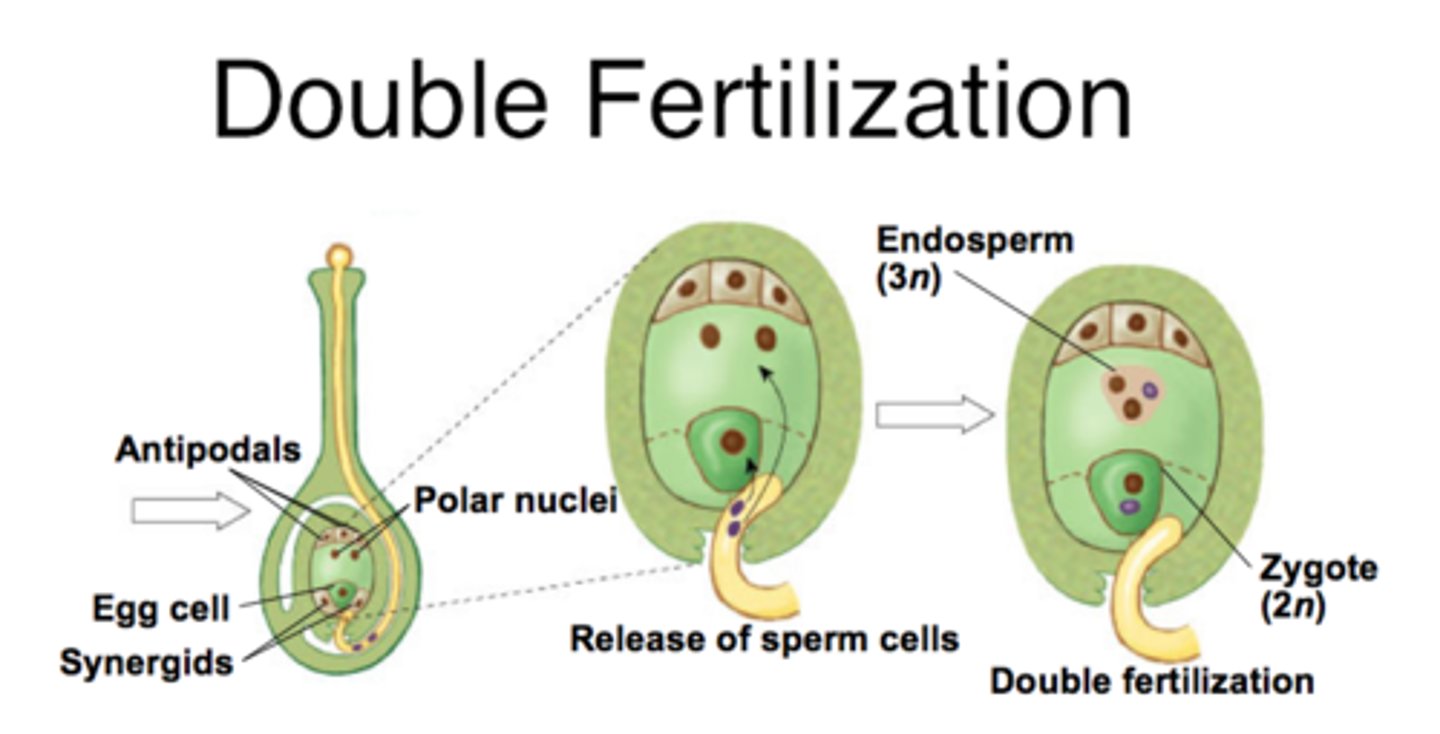
In angiosperm fertilization, the nucleus of the second sperm cell fuses with both polar nuclei to create what structure?
triploid nucleus and endosperm
(Note: triploid = 3n)
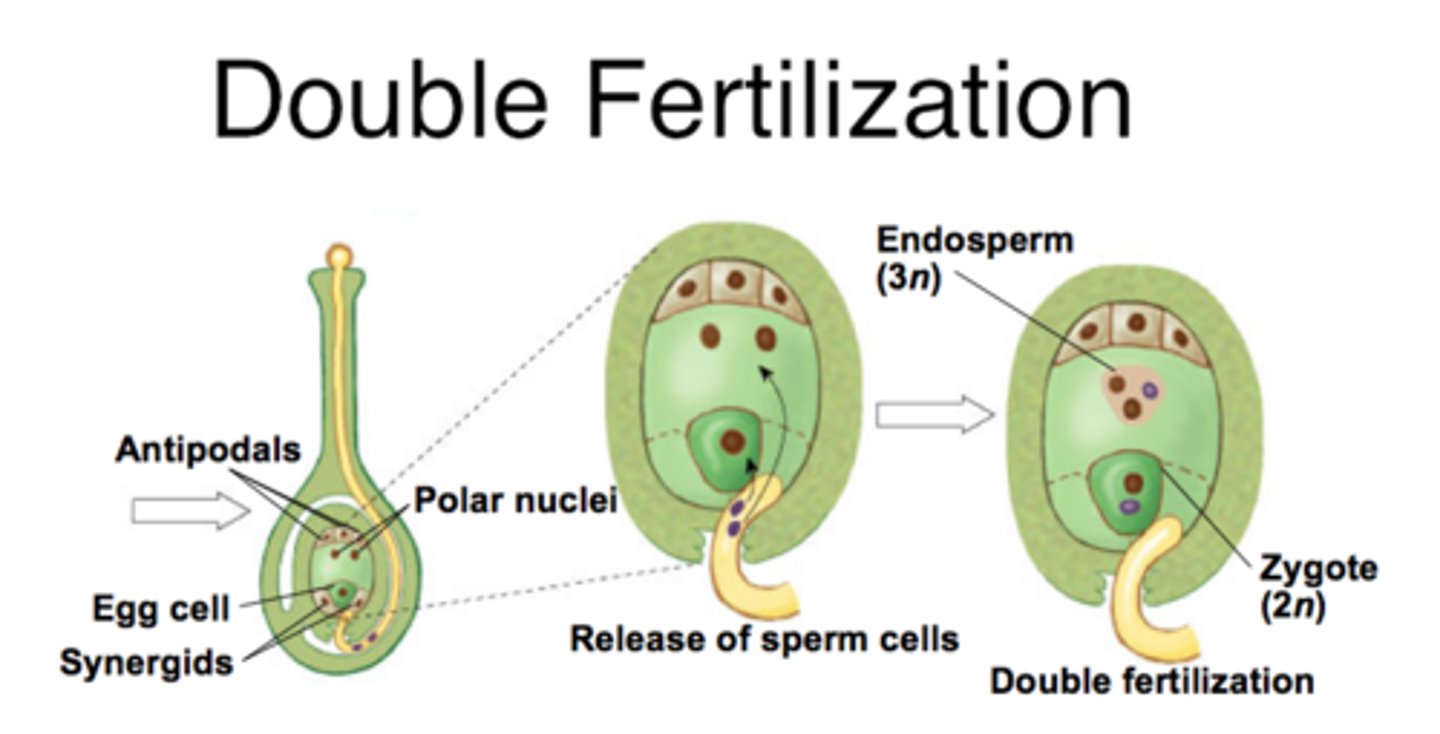
In angiosperm fertilization, what is the function of the triploid nucleus and endosperm?
provide nutrients
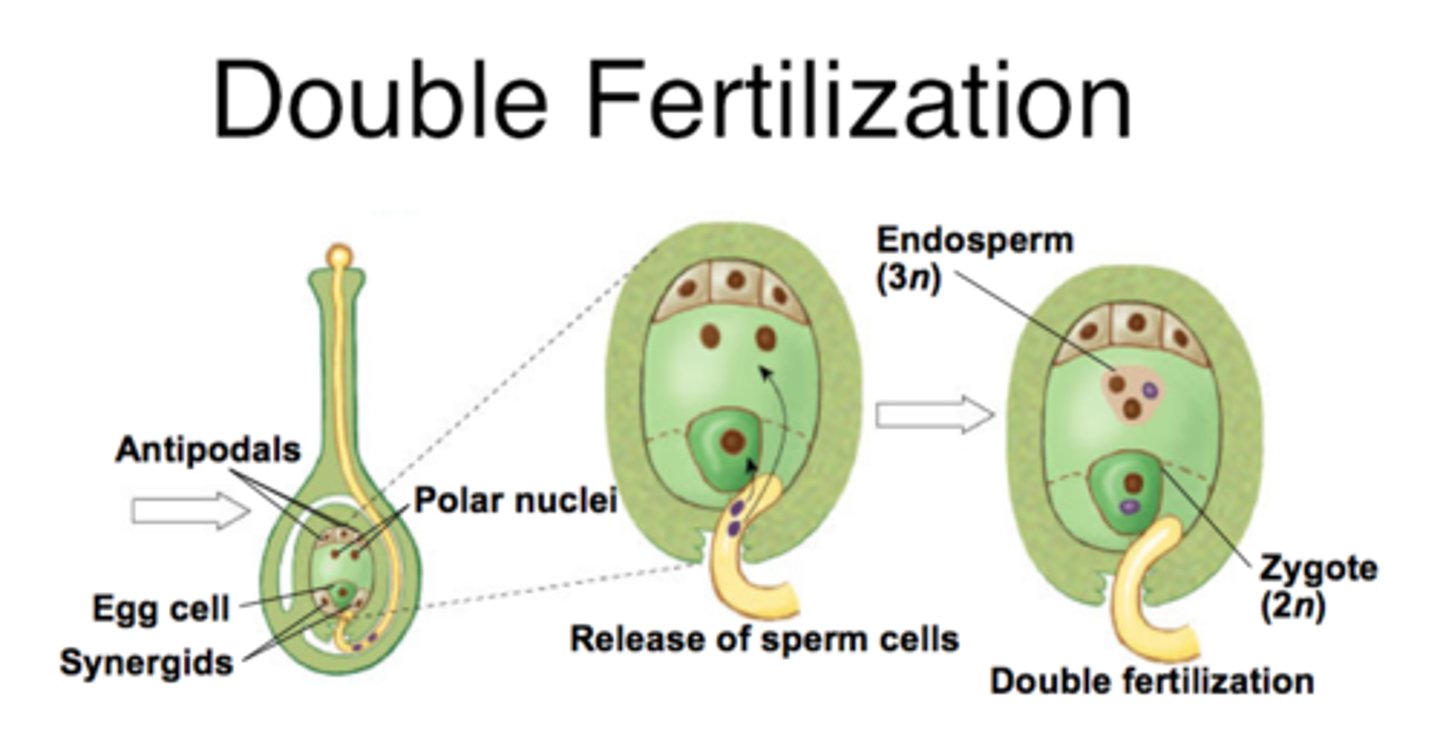
What is the term for the fertilization of the egg and polar nuclei each by a separate sperm cell?
double fertilization
(Note: unique to angiosperms)
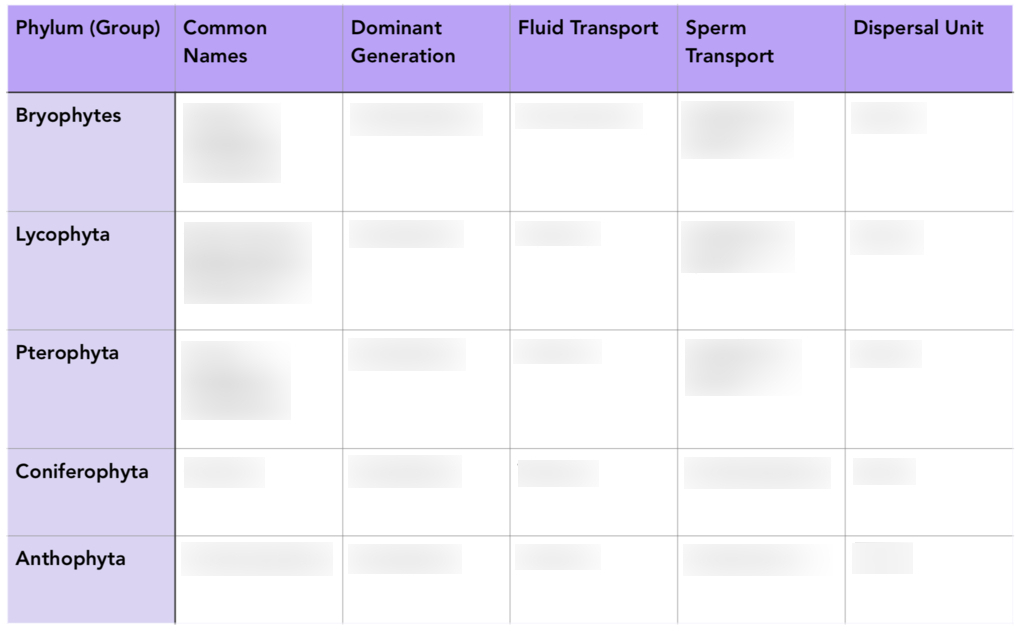
mosses, liverworts, hornworts
club mosses, spike mosses, quilworts