AP Psychology Unit 2
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Glial Cells (Aka neuroglia)
Help support neurons (structure, nutrition, etc.) ex. Schwann Cells
Neurons
The basic building block of the nervous system
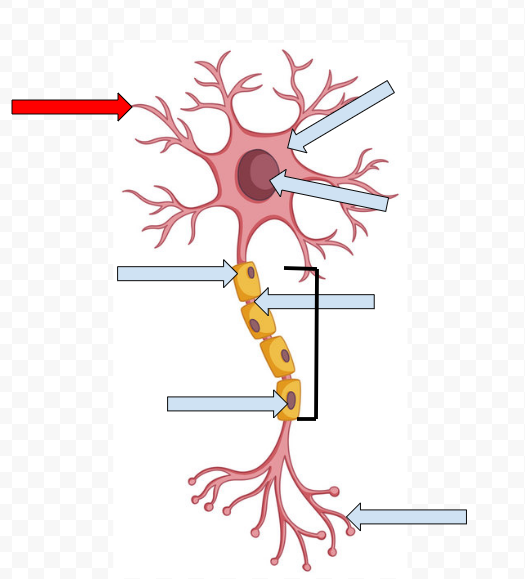
Dendrites - receive incoming messages
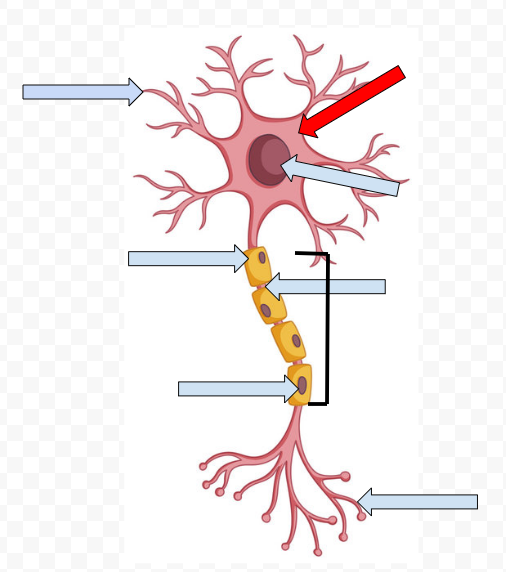
Cell Body (Soma) - Contains the Nucleus
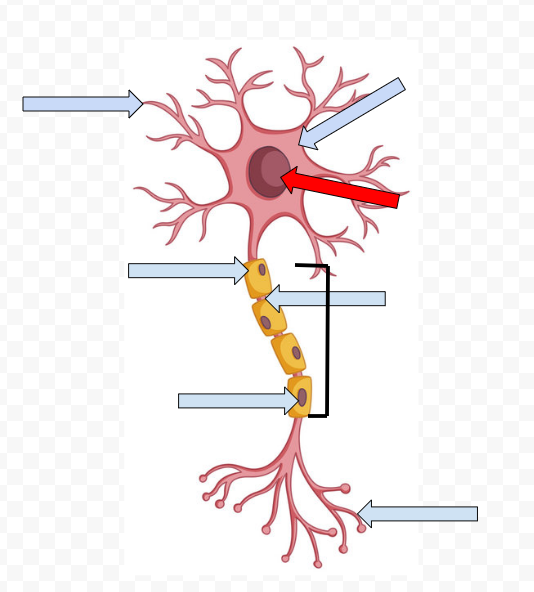
Nucleus - Makes the decision to fire or not fire
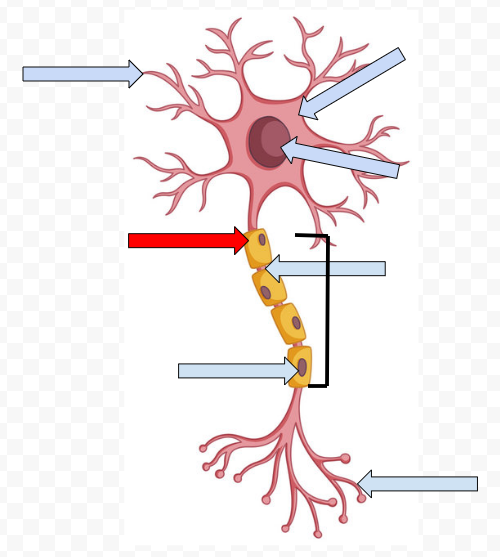
Myelin Sheath - Fatty tissue that insulates axon, speeding up transmission of the passage
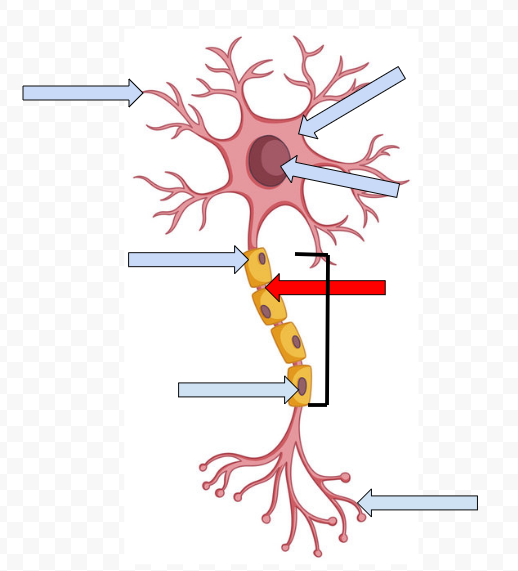
Node of Ranvier - Space between the sheath
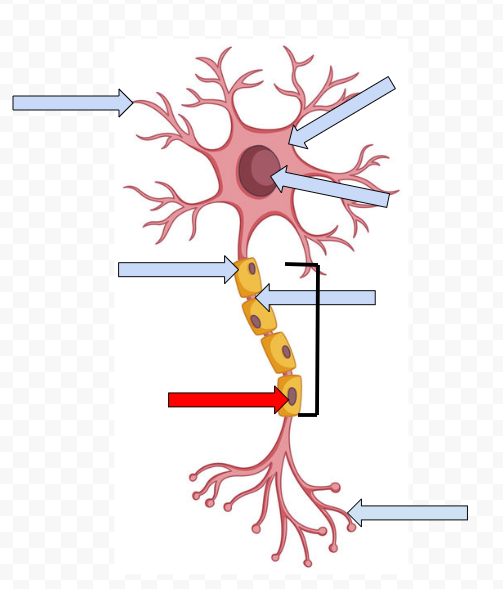
Schwann Cells - Non-neural cells in the CNS that form myelin sheath
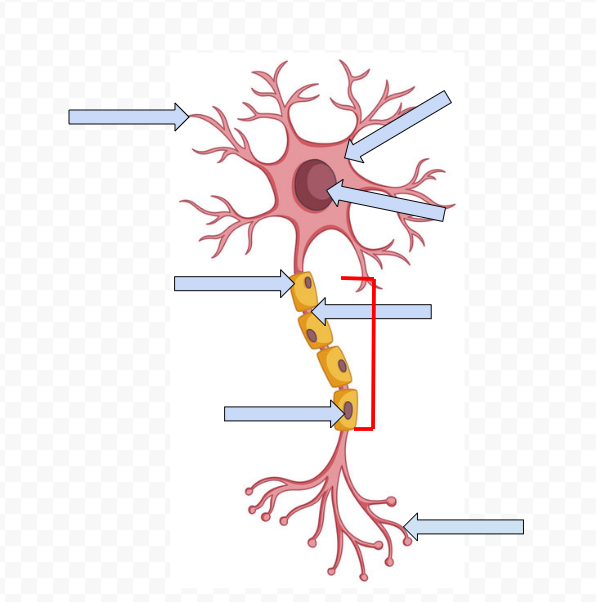
Axon - Longest part of the neuron which the electrical message travels the length of
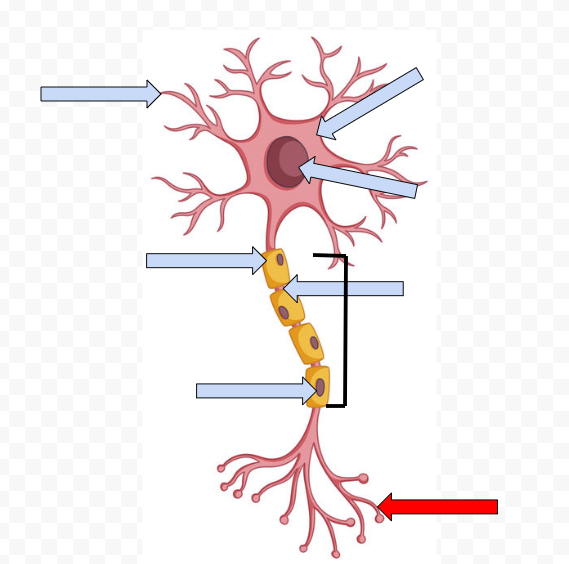
Axon Terminal Buds - The end point of a neuron that releases neurotransmitters into the synapse, hence sending the message on to the next neuron
Resting Potential
When a neuron is NOT firing and has a negative charge with mostly potassium ions inside and mostly sodium ions outside. A neuron in homeostasis
Polarization
At resting potential, when sodium is on the outside, potassium on the inside of a neuron
Action Potential
“nerve impulse” - causes the neuron to fire - the electrical pulse or message that travels the length of an axon.
All-or-nothing principle
When the nucleus decides to fire, it fires down the axon completely (all the way) or not at all. - At the same intensity
Intensity - Strength/power of message
Depolarization
When message begins, Sodium (+Na) ions come in & depolarize (neutralize) section of axon
When “opposites” are no longer away from each other
Refractory Period
Potassium (+K) ions are pushed out and neuron “pauses to reload.” During this time a neuron is unable to fire
Threshold
The minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a neural response or produce a detectable sensation
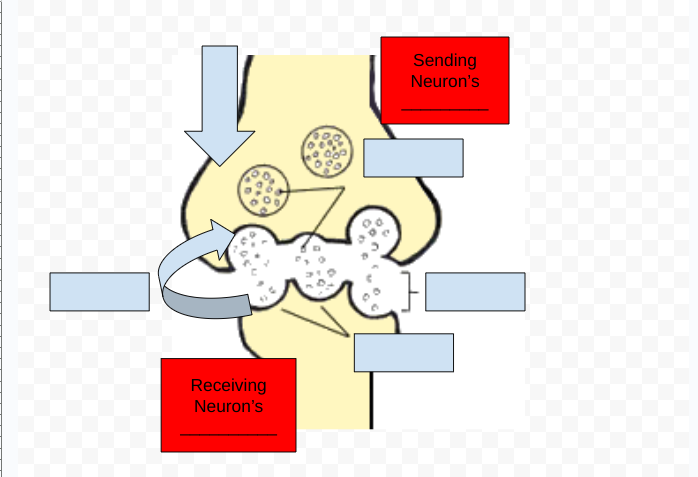
Axon Terminal
Dendrites
Neurotransmitters - chemical substance that crosses the synapse to carry on the message to the next neuron
Synapse - open space between two neurons at which neurotransmitters cross
Receptor sites - specific points on dendrites of neurons that receive specific types of neurotransmitters
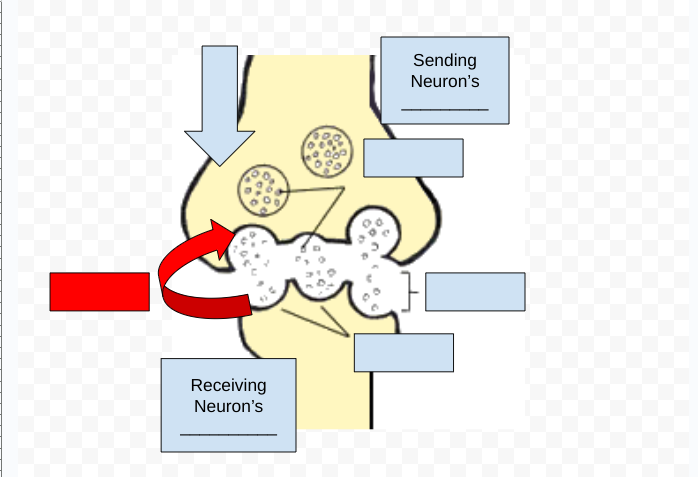
Reuptake - Reabsorption of neurotransmitters by firing neurons
Neurotransmitter - Acetylcholine
Learning. Enables muscle action (spinal cord & skeletal muscles), learning attention, & Memory. Deterioration leads to Alzheimer.
Neurotransmitter - Glutamine
Memory. Major excitatory (helps neurons fire) involved in memory. Oversupply can overstimulate the brain leading to migraines and seizures.
Neutransmitter - Dopamine
Reward / pleasure. Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion (similar to cocaine). Oversupply = schizophrenia. Undersupply = tremors and Parkinson's. Completing a tasks gets Dopamine.
Neurotransmitter - Serotonin
Mood. Affects hunger, mood arousal, and sleep (similar to LSD & Ecstasy). Undersupply = depression. Antidepressant drugs increase levels.
Neurotransmitter - Norepinephrine
Concentration. Also associated with sympathetic nervous system. Increases alertness, blood pressure, and heart rate. Release glucose to support fight or flight.
Neurotransmitter - GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Calming. Major inhibitory (slows neurons firing) “Get A Break Adjustment.” Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, insomnia, & anxiety.
Neurotransmitter - Endorphins
Pain or pleasure. Linked to europhia, pain control, and pleasure. Associated with OCD & “Runners High.” Opioids can suppress natural supply.
Neurotransmitter - Substance P
Pain & immunity. Found in the brain and spinal cord and is associated with inflammatory processes and pain. Oversupply can lead to chronic pain.
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Increase the likelihood that a neuron will fire an action potential. They essentially stimulate the next neuron.
Glutamate: Learning and Memory
Acetylcholine (in some contexts): excitatory in the muscles
Also plays a role in learning and memory
Norepinephrine (sometimes considered excitatory in CNS): Increases arousal, alertness, and attention.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Decrease the likelihood that a neuron will fire an action potential. They essentially calm or slow down neural activity.
GABA: reduce anxiety and stress
Serotonin: Regulates mood, appetite, and sleep.
Agonist
MIMIC neurotransmitter activity.
Fitting in the receptor site like a master key
It works just like the original key but it is not exactly the same
Example:
Morphine (opiate derivative) mimics endorphins
Antagonist
BLOCK neurotransmitter activity
Fitting in the receptor site like a fake key, preventing the neurotransmitters from getting to its receptor site and doing its job
Example
Botox (form of botulism) blocks Acetylcholine.
Prevents muscles in the face from moving by blocking the neurotransmitter, which ultimately stops wrinkles
Reuptake Inhibitor
A type of agonist that blocks the reuptake process to increase a neurotransmitter
Example
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) like fluoxetine (Prozac), setraline (Zoloft) and citalopram (Celexa), which are widely used to treat depression and other conditions by increasing seretonin levels in the brain
Two parts fo the nervous system
Peripheral: Sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
Includes Autonomic and Somatic
Central (CNS): Contains the spine and brain. In the center of the body
Autonomic vs Somatic
Autonomic: Controls involuntary functions or items that happen automatically within our body - berathing, heartbeat, digestion, etc.
*includes sympathetic and parasympathetic
Somatic: Control voluntary (soma = body) movements and communications to and from the sense organs
You control these items, they don’t “just happen”
Sympathetic Nerves
Physically arouses the body, preparing it to act/react in stressful situations, expending energy. Initiates “fight or flight.”
Dilate pupils
Inhibit Salvation
Increase heartbeat
relax airways
inhibit activity of stomach
inhibit galbladder
inhibit activity of intestines
secrete (produce) epinephrine & norepinephrine
relax bladder
Parasympathetic Nerves
Calms the body, conserving its energy and helping keep a constant internal state (returns the body to homeostasis). Initiates “rest and digest”.
Constrict Pupils
Stimulate saliva
Slow heartbeat
Constrict airways
Stimulate activity of stomach
Stimulate galbladder
Stimulate activity of intestines
Contract bladder
Brain vs Spinal Cord
Brain: The neural center of the body; the body’s control center
Spinal Cord: Super Highway of nerves - the body’s means of transmitting messages to and from the brain
Reflex Arcs
The neural pathway for a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus bypassing the brain and acting through the spinal cord
Ex. Withdrawal reflex: When you touch a hot stove
Interneurons vs Sensory Neurons vs Motor Neurons
Interneurons: The only neurons in the CNS, acting as messengers between sensory and motor neurons
Sensory (afferent) neurons: Carries incoming mesages/information from the sense receptors to the CNS
Motor (efferent) neurons: Carries outgoing information from the CNS to the peripheral nervous system and muscles.
Endocrine system
Communicates with the brain using chemical messages called hormones
Hormones are released into and circulate through the bloodstream - recieved only at a specific site
Under “normal” circumstances works in parallel with the parasympathetic NS to sustain our basic processes. (HOMEOSTASIS)
In a crisis, the sympathetic nervous system actitvates, and the endocrine system (adrenal gland) releases adrenaline/epinephrine
The Pituitary Gland
The “Master Gland
Directed by the hypothalamus
It releases several important hormones and controls the function of many other endocrine system glands.
Adrenaline
Secreted by the adrenal glands; responsible for arousal and the "fight or flight" response. Plays a role in emotional memory formation. Same chemical as Epinephrine.
Leptin
Involved in turning off hunger (keeps you LEAN). Produced by fat cells it sends signals to your hypothalamus.
Ghrelin
Involved in turning on hunger (tummy goes grrrr) comes from the stomach and activates the pituitary gland
Melatonin
Secreted by the pineal gland; signals the relaxation and lower body temperature that help with a restful sleep.
Oxytocin
Produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary gland. When it affects the brain, it acts as a neurotransmitter. Plays a role in mother-child attachment; believed to play a role in social bonding and is the “Us vs them” hormone (social trust / bonding).
Hormones vs Neurotransmitters
Hormones | Neurotransmitters | |
|---|---|---|
Speed | Minutes or longer | Milliseconds |
Length | Hours, days, or weeks | Short-term |
Method | Travel through the blood | Neuron-to-neuron signaling |
Cerebral Cortex
Outer portion of brain, higher order thought processes, perception, and voluntary movement (& 4 lobes)
💀 If damaged: Varied effects including memory, personality, decision making, motor control.
Corpus Callosum
Bundle of nerve fibers that connect hemispheres, enabling communication
💀 If damaged: “Split-Brain
Hippocampus
Processes conscious memories (explicit memories)
Converts short-term to long-term memory
Involced in processing and retrieving declarative (facts and events) memory
Spacial Relationship memories
💀 If damaged: Inability to remember, getting lost, difficulty following directions.
Thalamus
Brain’s relay center for all but smell
Directs messages to sensory receptors
Transmits replies to cerebellum & medulla
💀 If damaged: sensory issues (blind, aphasia), numbness, coma.
Hypothalamus
Directions maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temp)
Helps govern endocrine system
Fight or Flight
Linked to emotion & reward/pleasure.
Homeostasis
💀 If damaged: Weight change, fatigue, insomnia, thirst, dehydration, high or low blood pressure, frequent urination, infertility
Amygdala
Plays a role in emotion, (fear, anger, aggression, anxiety)
💀 If damaged: high emotional responses, no emotional responses
Cerebellum
Processes sensory input, coordinates movement output and balance
Enables nonverbal learning and implicit memory. (long-term memory that involves unconscious recall of skills, tasks, and knowledge without conscious effort)
Known as the “little brain”
Pons
Connects upper and lower brain
Sleeping
waking
dreaming
Bladder Control
💀 If damaged: Coma, sleep issues
Medulla
Controls autonomic functions heartbeat and breathing, blood pressure, reflexes.
💀 If damaged: respiratory failure, paralysis, or loss of sensation.
Reticular formation
Controls arousal, alertness, attention, regulating sleep cycle
💀 If damaged: Coma, difficulty staying awake or paying attention.
Ventricles
Fluid filled with cavities in the brain which serve as reservoirs of cerebrospinal fluid
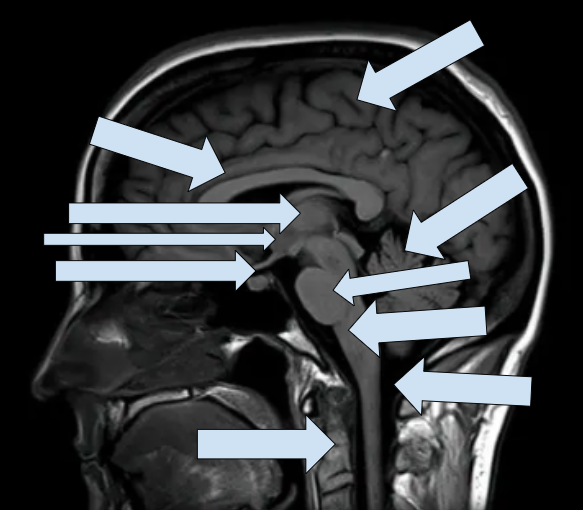
Left to right
Corpus Callosum
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Spinal Cord
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebellum
Pons
Medulla
Reticular Activating System (RAS) *Back of brain stem (activiating system)
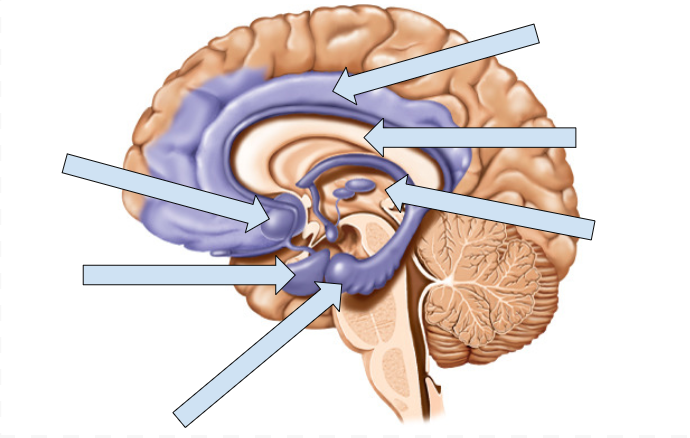
Left to Right
Hypothalamic Nuclei
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Cingulate Gyrus
Corpus Callosum
Thamalus
Cingulate Gyrus
Involved in processing emotions, regulating behavior, as well as autonomic motor function
The Lymbic System’s functions include…
controlling emotion, behavior, motivation, learning & memory
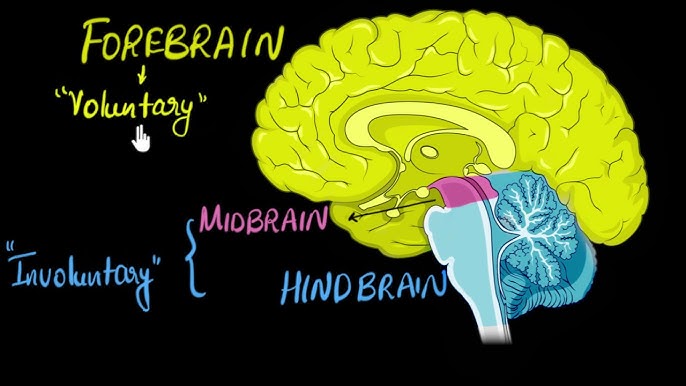
Hindbrain
Lizard Brain -brainstem, cerebellum, and hypothalamus
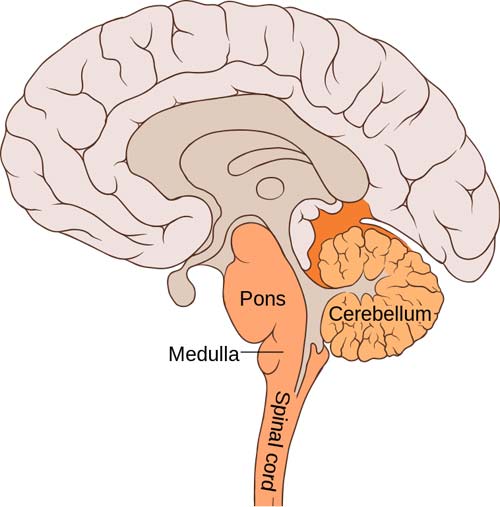
Midbrain
Mammal Brain - limbic system and hippocampus
Forebrain
Human Brain - cerebral cortex
Brain Lesions
Portions of the brain are cut / removed.
Changes as a result of the lesions (what is different?).
Shows Structure.
EEG (electroencephalogram)
Electrodes placed on the scalp.
Measures electrical activity of neurons in the brain.
Often used to study sleep, seizures, and brain activity over time.
Shows Function; brain activity – not specific
PET scan (Positron emission tomography)
Brain activity detected by a radioactive form of glucose.
Active regions “light up” as they consume more energy.
Used to observe metabolic processes in the body and brain.
Shows function; “hot spots” where brain areas are active as a person does various activities
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of brain structure
Provides detailed pictures of soft tissues, including the structure of the brain
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
Comparing successive MRI scans by looking at blood flow.
Shows which areas are active during specific tasks.
Reveals brain functioning as well as structure
Computed tomography Scan (CT / CAT)
X-Rays taken from multiple angles and combined into a composite.
Reveals brain structure, including brain damage
Cerebral Cortex & Cerebrum
As mass of deeply folded tisue that accounts for 80% of the brain’s total mass
It is responsible for most of the sophisticated information processing in the brain
It makes up Four major sections of lobes
Frontal Lobe
Involved with personality, decision-making, and movement.
Found at the front of the head.
Planning, speech, sounds, emotions, temperment.
Frontal lobe sensors your amygdila
Includes Motor Cortex (voluntary movements) and Borca’s Area (speech, production, left hemisphere
Parietal Lobe
Processes body’s senses (touch, temperature, pain).
Found on top of the head and includes the somasensory cortex (body position, spacial reasoning)
Temporal Lobe
Language, Hearing, Facial recognition.
Found near the temples of the head. Long term memories, speech, and understanding.
Auditory Cortex (hearing).
Wernicke’s Area (language comprehension, left hemisphere)
Occipital Lobe
Vision. Found at the back of the head, allows us to interpret visual data like location, space, motion, and colors recieived from our retinas. Visual Cortex (visual info)
Association areas
Over ½ of cerebral cortex is uncommitted to sensory or muscular acivity… these “areas” are involved in higher mental functioning
Wernike’s area
Broca’s area
Wernicke’s area
Area in left temporal lobe that is involved in language, comprehension, and expression
Wernicke’s Aphasia = Damage where person speaks fluently but nonsensically and has trouble understanding language
Broca’s area
Area in the left frontal lobe that directs muscle movement involved in speech
Broca’s Aphasia = Damage here, person struggles to produce speech (slow, halting, but meaning intact)
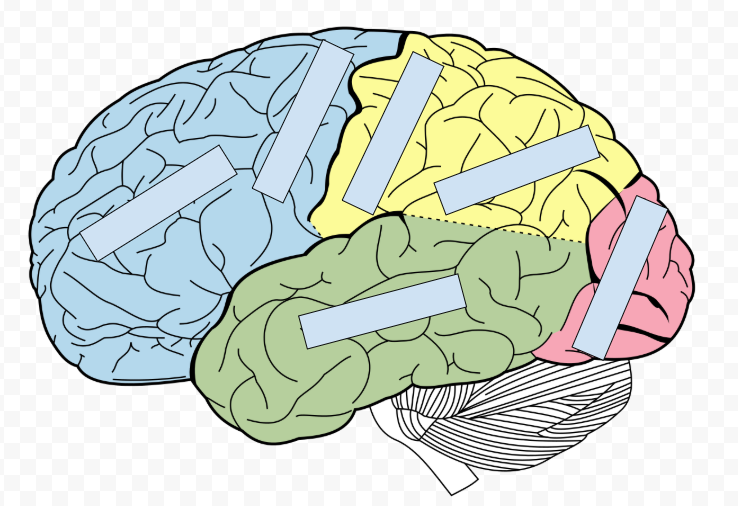
Left to Right then down
Frontal Lobe, Motor Cortex, Somasensory Cortex, Pariental Lobe, Occipital Lobe, Temporal Lobe
Psychoactive Drugs
A chemical substance that alters perceptions and mood (affects consciousness)
Blood-brain barrier - protective filter that blocks out substances from entering the brain, but psychoactive drugs can cross it to alter neurotransmitters activity and change behavior
Additiction
Tolerance:
Dependence:
Withdrawal:
Tolerance: Continued use of psychoactive drug produces tolerance . With repeated exposure to a drugm the drug effect lessens. Thus it takes bigger doses to get the desired effect.
Dependence: Upon stop taking a drug (after addiction) users may experience undersirable effects of withdrawal.
Withdrawal: Absence of drub may lead to feelings of…
Physiologically: Physical Pain, Intense Cravings
Psychologically: Negative Emotions
Depressants
“downers” - drugs that reduce neural activity and low body functions
Alcohol
Barbiturates
Opiates
Alcohol
Depressant
In low doses - relaxes the drinker by slowing down sympathetic nervous system (lowering inhibitions and judgement)
In high doses - reactions slow, speech slurs, and skilled performance
Also affects memory by - disrupting the processing of recent events into long-term memory, reduces self-awareness, and focuses one’s attention on immediate situation rather
Barbiturates
Depressant
Mimics the effects of alcohol - depresses CNS activity and in larger doses, can lead to impared memory and judgement (Nembutal, Seconal, Amytal)
In large doses - unconsciousness, supressed breathing, coma, or even death
Opiates (Narcotics)
Depressant
Opium and derivatives (morphine, heroin) depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety. They are highly addictive
Heroin - Causes short-lived feeling of blissful pleasure (3-5 hours), then craving for another, in larger doses, and physical withdrawal symptoms
Methadone used to combat this addiction
Stimulants
“Uppers: drugs that exite neural activity and speed up body function.
Ex. Caffine, Nicotine, Cocane, Ecstasy, Amphetamines, Methamphentamines
Caffine
Stimulant
Effects: Increase heart and breathing rates, and other autonomic functions to provide energy. Increases attentiveness
Improves modd by mimicking adenosine (a neurotransmitter). Physically addictive
Amphetamines
Stimulant
“speed” or “uppers”
Effects: Suppress appetite and were onece prescribed as diet pills (No longer because its addicting)
Increases concentration and reduces fatigue… can increase anxiety and irritability as well
Cocaine
Stimulant
Illegal - derived from coca trees. Derivatives (nonvacaine) are used today as anesthetics
When inhaled/”snorted” - reaches brain in minutes - producing intense euphoria, mental alertness and self-confidence which lasts for several minutes (10-30 fir binge users)
Blocks the reuptake of dopamine causing the brain to be flooded with dopamine
Hallucinogens (aka psychedelics)
(mind-manifesting) drugs that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absense of sensory input
Ex. LSD (Lysergic Acid Diethylamide), Marijuana
LSD (Lysergic Acid Diethylamide) “Acid”
Hallicinogen
one of the most powerful drugs - only takes one-millionth of an ounce to produce altering effects
Trip lasts 6-14 hours - effects vary greatly (visual distortions and hallucinations)
“Bad Trips” - Terrifying and users are in a state of panic, feek as they will go mad and never come out
Flashbacks - have sudden without warning brief recurrences of trip weeks/months after use
Marijuana
Hallucinogen
Produces feeling of elation, promotes relaxation, relieves inhibitions
THC - the ingredient that produces the high, remains in the body long after use (10% after 7 weeks)
Effects - Impairs attention/coordination, slows reaction time, intenferes with concerntation, logical thinking, ability to form new memories and ability to hold in mind what is said
Chronic use associated with - loss of motivation and general apathy also causes respiratory damage faster than cigarettes, smoking and heavy use/abuse affects the reproductive system
Role of expectations in drug use
Expectation (placebo effect) plays a rule because a persons beliefs about a drug’s effect can influence how strongly they actually experience those effects, sometimes even mimicking or amplifying the drugs impact.
Multiple Sclerosis
Autoimmune attack on the myelin sheath surrounding axons, slowing neural communication.
Myasthenia Gravis
Disruption of communication between neurons and muscles due to antibodies interfering with neurotransmitter receptors.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Degeneration of neurons and loss of acetylcholine, leading to impaired memory and cognitive function. Associated with acytlcholine