Chapter 5: Cerebral Cortex
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
neocortex
newest part of the brain; most of the brain is made up of this (language, abstract though, etc.)
paleocortex
old part of the brain
archiocortex
oldest part of the brain
pyramidal cells
predominant output neurons; have very long axon that usually leaves cortex
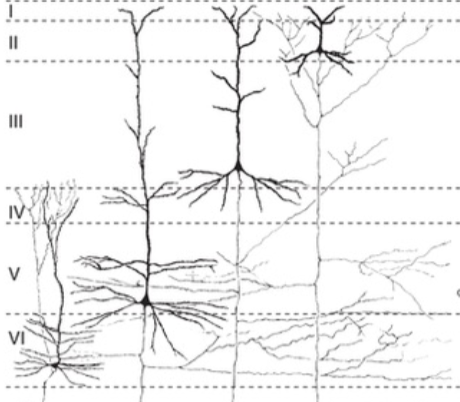
non-pyramidal cells
predominant input neurons; most are short axons or granule (stellate) cells

Betz cell
a very large pyramidal cell
layer I
molecular make-up, relatively cell-free; has intracortical fibers
layer II
made up of external granule cells and has association fibers (same hemisphere)
layer III
made up of external pyramidal cells and has association and commissural fibers (cross hemispheres)
layer IV
made up of internal granule cells and is the primary INPUT layer
layer V
made up of internal pyramidal cells and is the primary OUTPUT layer
layer VI
deepest, polymorphic layer with lots of cell responsible for thalamic projections
intracortical fibers
found in layer I and are horizontal cell projections
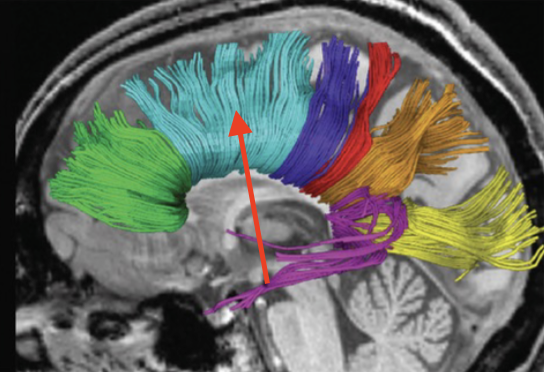
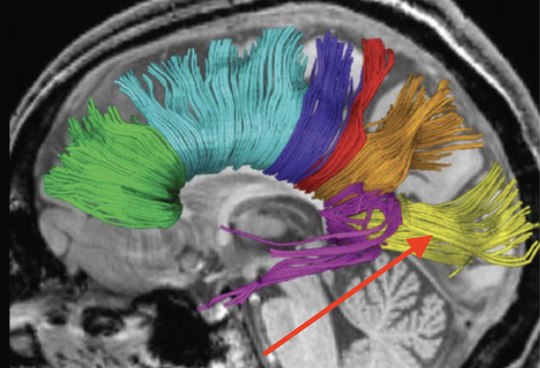
association fibers
found in layers II and III, go from gyrus to gyrus, lobe to lobe, but stay within the same hemisphere
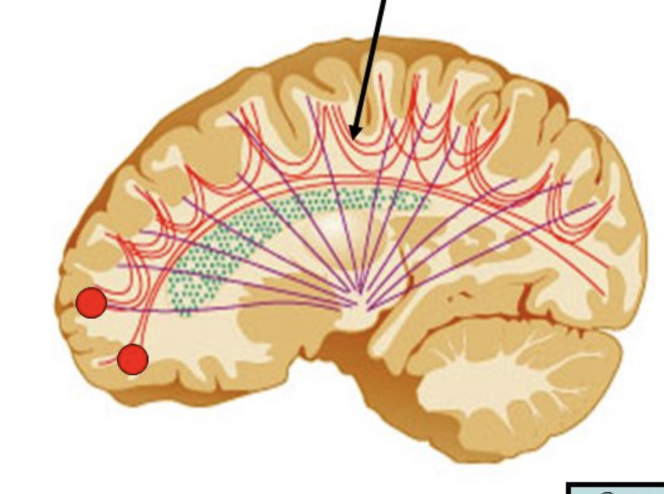
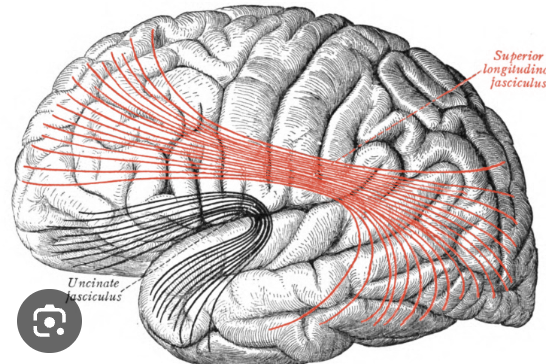
superior longitudinal fasiculus (arcuate)
connects frontal lobe to other 3 lobes
superior occipitofrontal fasiculus
connects the frontal and occipital lobes
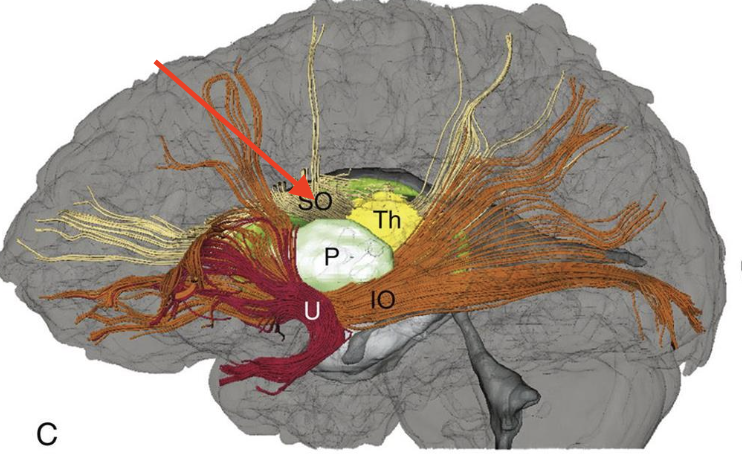
inferior occipitofrontal fasiculus
connects frontal and occipital lobe through temporal lobe
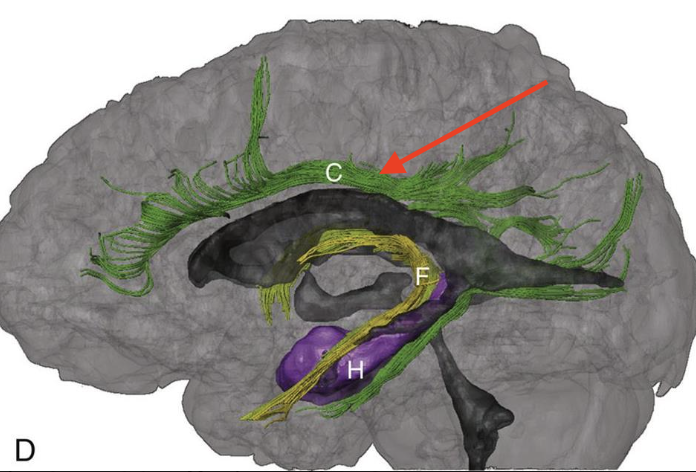
cingulum
course parallels cingulate/parahippocampal gyri
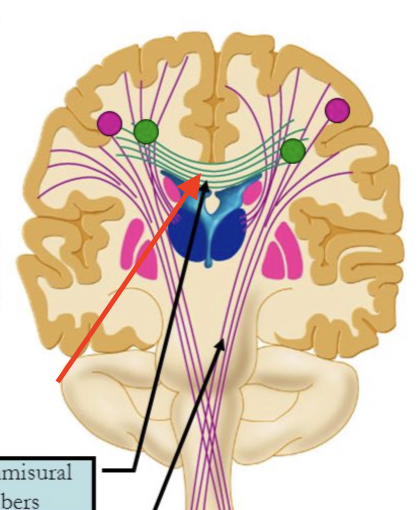
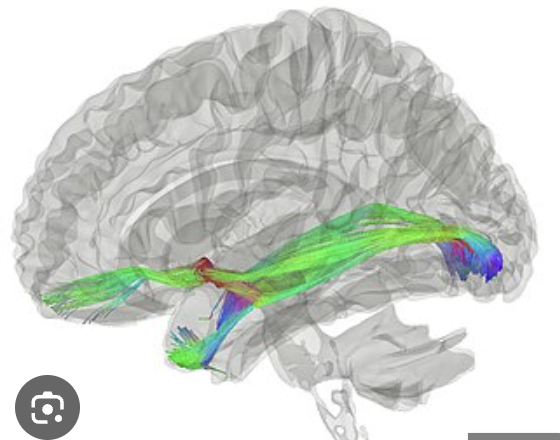
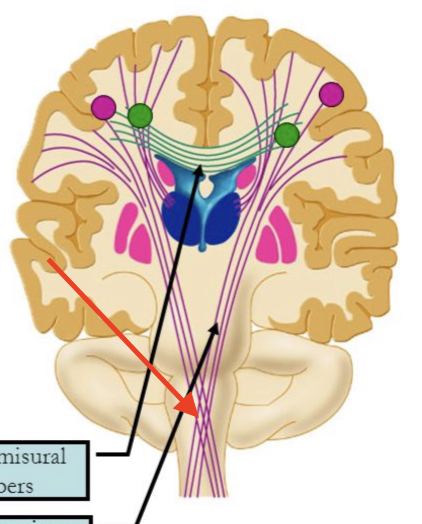
commissural fibers
found in layer III; found in homologous (same) areas of right and left hemisphere and crosses hemispheres
corpus callosum
crucial bridge of nerve fibers that connect right and left hemispheres
rostrum genu
connects anterior right and left frontal lobe
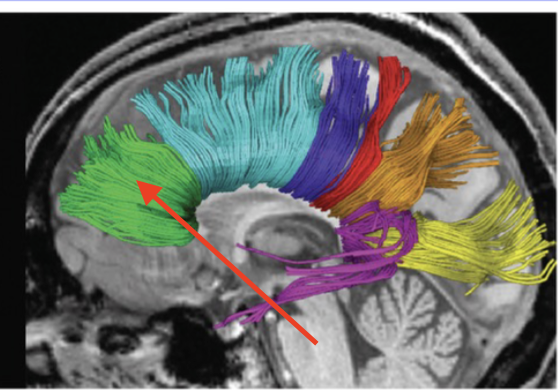
trunk
connects posterior right and left frontal lobes, right and left parietal lobes
splenium
connects right and left occipital lobes
anterior commissure
connects the right and left temporal lobes and right and left olfactory bulbs
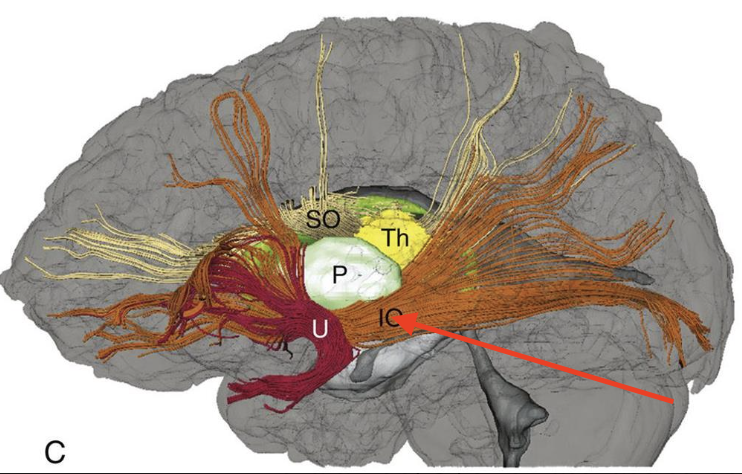
projection fibers
found in layers IV, V, and VI - input and output fibers
corticofugal
efferent (output) fibers to corpus callosum striatum, brainstem, and spinal cord
corticopetal
afferent (input) fibers from thalamus
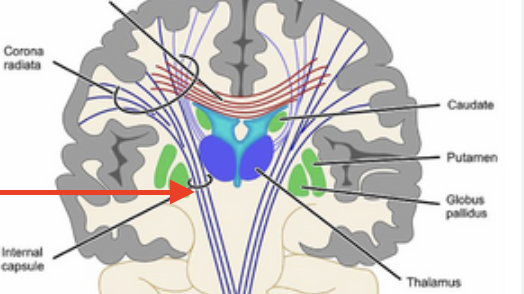
internal capsule
a thick band of white matter located deep within the brain, connecting the cerebral cortex to other parts of the brain and spinal cord
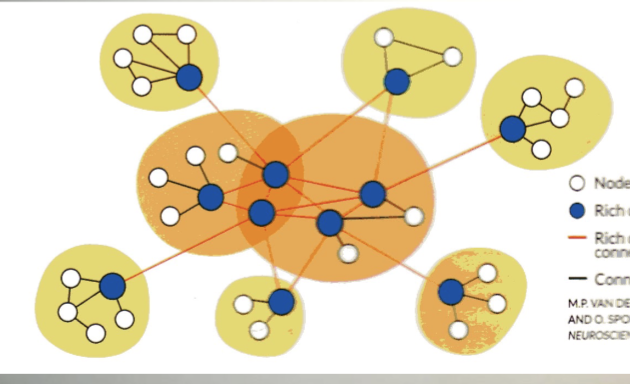
hubs
areas of gray matter (called nodes) highly connected to other areas, forming hubs
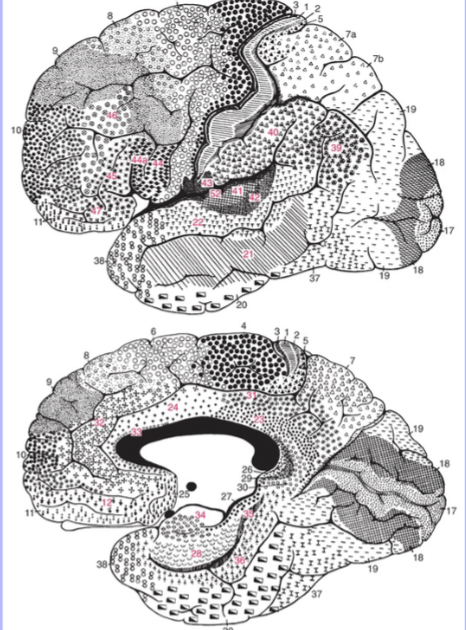
brodmann areas
52 areas originally based on cytoarchitectural features, but now matches functionally as well
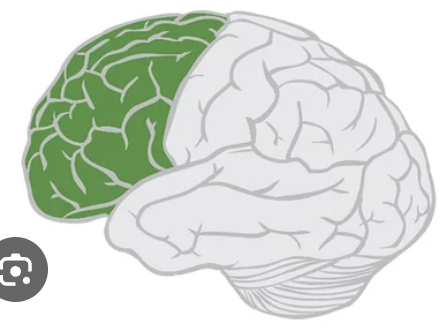
frontal lobe
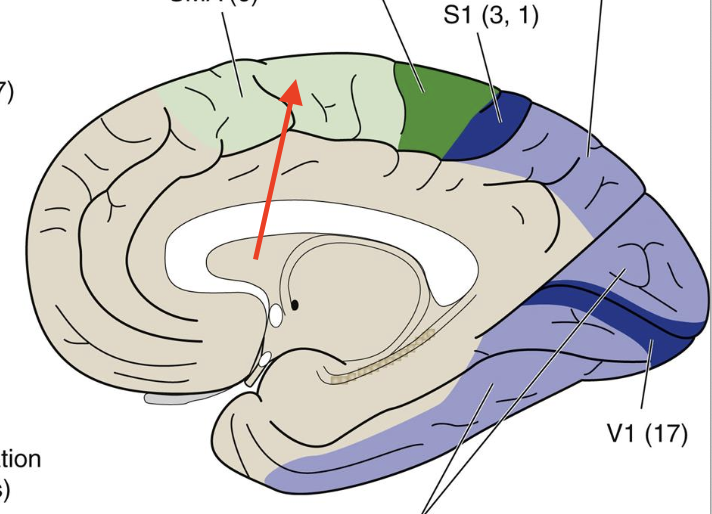
primary motor
Broadmann area 4, controls contralateral body movements
lesion hemiparesis
weakness of planning a movement
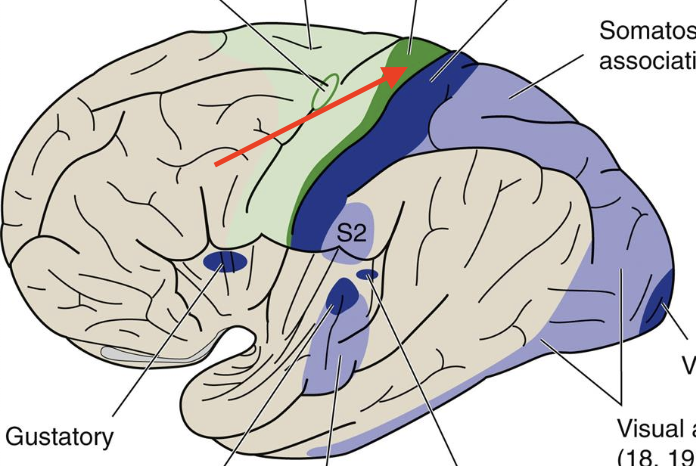
premotor area
Broadmann area 6
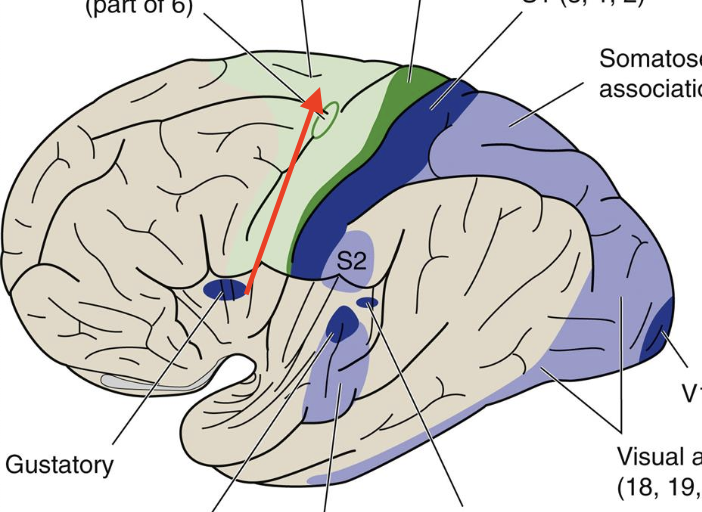
supplementary motor
Broadmann area 6, complex movement programs
lesion apraxia
cannot perform movement on command
prefrontal cortex
dorsolateral
part of prefrontal cortex responsible for working memory, planning, solving problems and maintaining attention
ventromedial
part of prefrontal cortex responsible for appropriate responses, emotional reactions, and relating to other people (associated with limbic system)
parietal lobe
biggest sensory area of brain
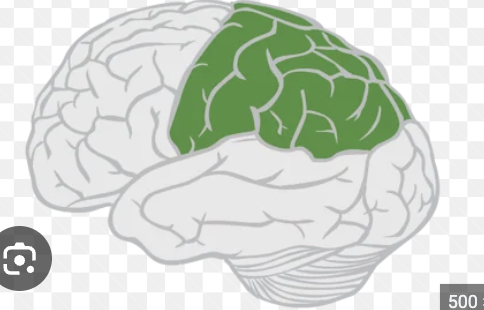
primary somatosensory
Broadmann’s area 3, 1, 2; contralateral body sensation response
lesion hemianesthesia
loss of sensation
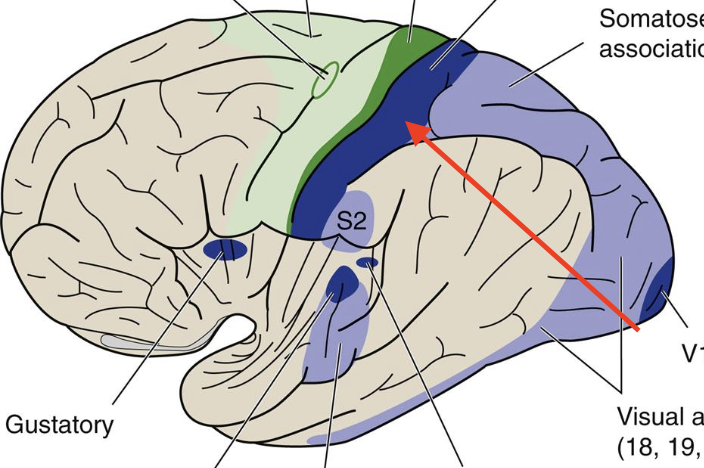
somatosensory association
Broadmann’s area (5,7); posterior parietal cotex/superior parietal lobe
lesion asterogonosis
failure to recognize objects by touch
lesion contralateral neglect
right inferior parietal lobe neglected symptoms vary ignorning the left side
Temporal Lobe
strongly associated with auditory system
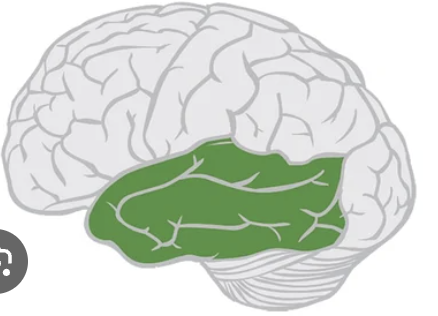
primary auditory
Broadmann’s area 41; senses sound distancce and direction recognition
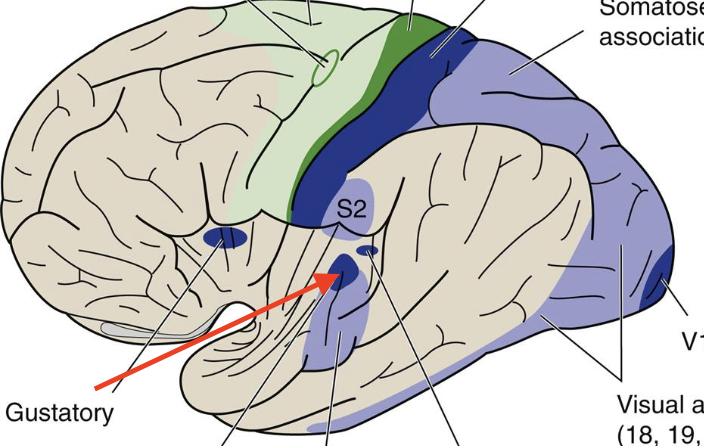
Auditory association cortex
Broadmann’s area 42, 22
Posterior temporal cortex
visually-based information, face recognition, face recognition
lesion prospagnosia
failure to recognize someone’s face
Occipital lobe
visual lobe
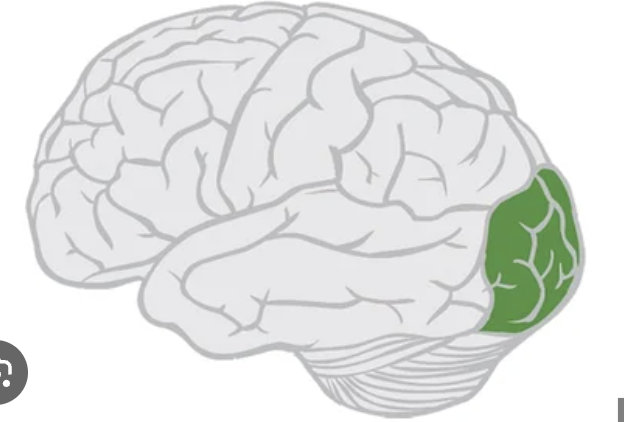
primary visual
Broadmann’s area 17, focuses on visual fields
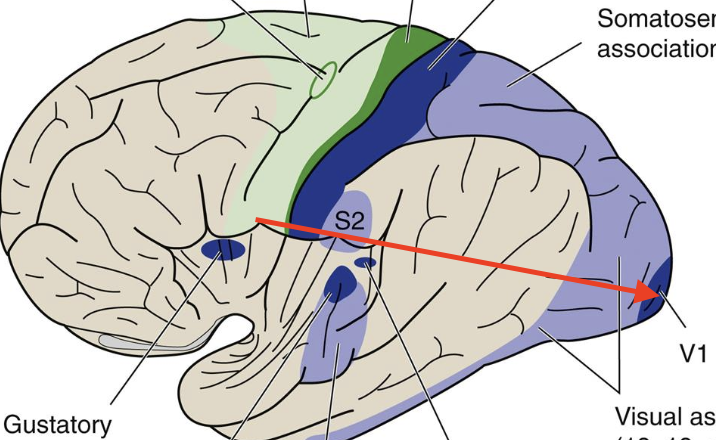
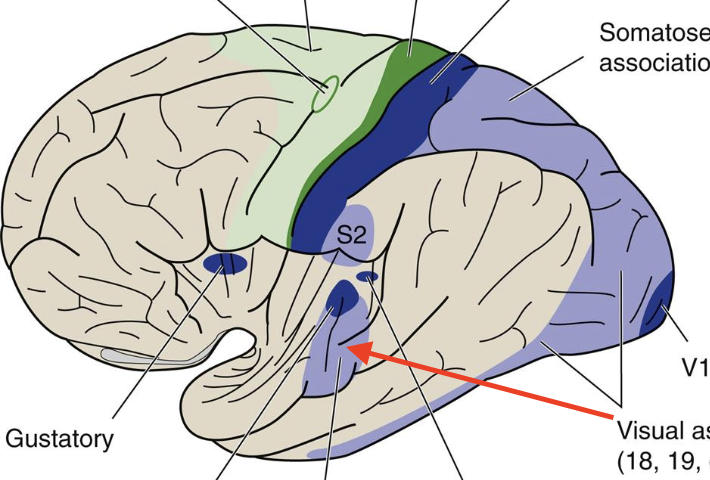
Visual association
Broadmann’s area 18,19; visual perception, color, and movement
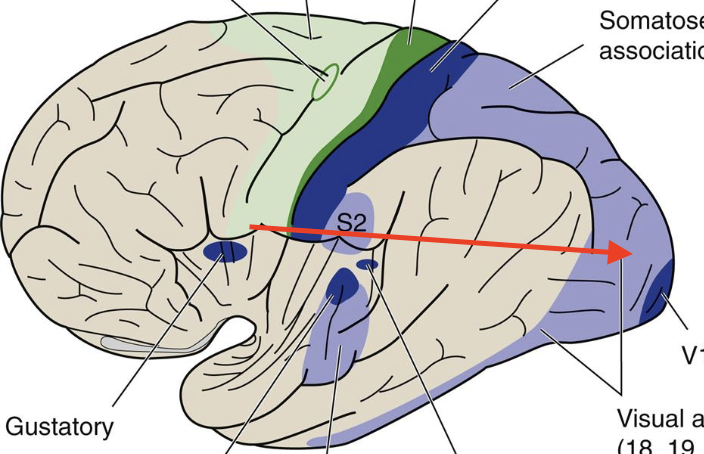
lesion visual agnosia
failure to recognize objects by sight
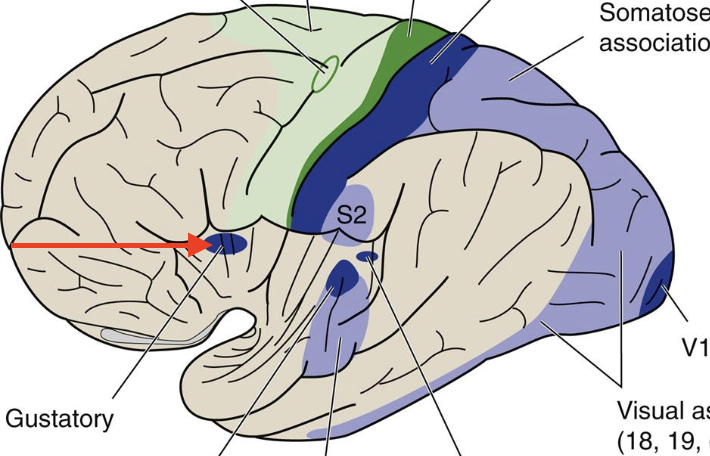
insula
“hidden” area by temporal lobe
primary gustory
part of insula; Broadmann’s area 43; sense of taste
dominant hemisphere
the hemisphere in a person that contains centers for language (in 95% of people it’s left)
Wernicke’s area
posterior part of superior temporal gyrus/inferior parietal lobe; receptive speech/work comprehension or formulation
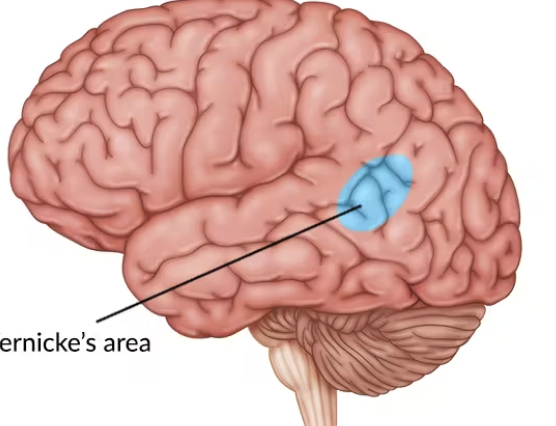
lesion fluent aphasia
normal word production, but inappropriate usage; poor comprehension
Broca’s area
inferior frontal gyrus; contributes to motor speech and word production
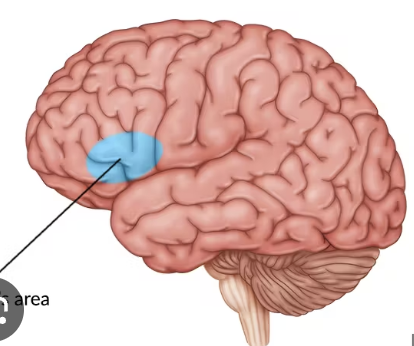
lesion non-fluent aphasia
slow speech, poor articulation, but intact comprehension
reading pathway step 1
visual input areas to 17-19
reading pathway step 2
left angular gyrus (object recognition)
reading pathway part 3
Wernicke’s area (word formulation)
reading pathway step 4
Broca’s area (word production)
reading pathway step 5
motor cortex
reading pathway step 6
brainstem/cranial nerves (vocalization)
conduction aphasia
sounds like fluent aphasia, but intact comprehension
word blindness
alexia without agraphia; no way to get visual input to language part of brain
prosody
rhythmic, emotional content of language; usually on right hemisphere; interprets tone
lesions motor aprosodia
lack of ability to put emotion into voice
lesions sensory aprosodia
inability to comprehend emotion in voice
left hemisphere dominance
dominance in mathmatics, logic, sequential problem-solving; tends to think linearly
right hemisphere dominance
dominance in musical skills, facial recognition, and spacial relationships; tends to thing relationally
Alzheimer’s disease
accumulation of amyloid B-peptides forming diffuse and neuritic plaques; interferes with normal axonal transport and leads to formation of neurofibrillary tangles and memory problems
frontotemporal dementia (FTD) “Pick’s disease”
causes behavioral, speech, and motor problems because of inclusions or “pick bodies”