biol 103-001 (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
1
New cards
if a solute moves through the cell membrane with a protein form a n area of low concentration to high concentration
Active transport
2
New cards
all cells share the same key features except
cell wall
3
New cards
what in penicillin breaks down cell walls
peptidoglycan
4
New cards
What is this?
nucleic acid
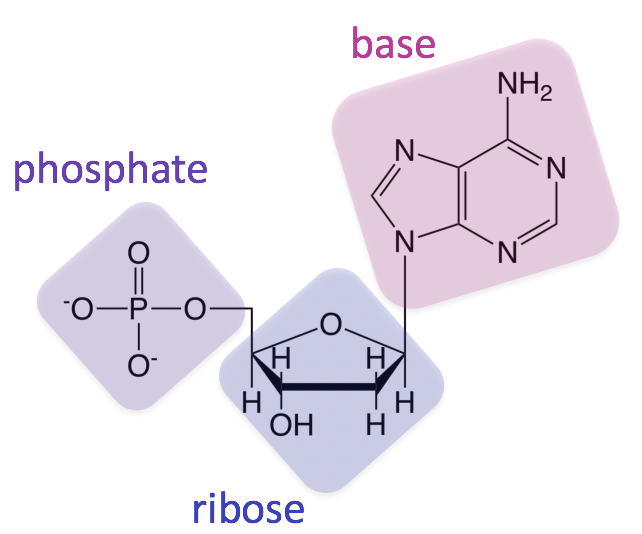
5
New cards
if a cell is 20% salt and it is placed into a solution with 30% salt, where will the water in the cell go
out of the cell
6
New cards
if a cell is 20% salt and it is placed into a solution with 30% salt, what type of solution is it
hypertonic
7
New cards
iof a cell were unable to take up or make sugars, which class of molecules would it be unable to make (2 answers)
carbohydrates and nucleic acids
8
New cards
as an acidic compound dissolves in water, the pH of the water contains more
H+ ions
9
New cards
what part of the cell acts like a post office
golgi apparatus
10
New cards
testosterone is an example of a
lipid
11
New cards
which organelle is responsible for creating phospholipids
smooth er
12
New cards
in a controlled experiment, which group obtains a placebo
control group
13
New cards
the cell membrane is made up of (2 answers)
proteins and phospholipids
14
New cards
what does the enzyme act upon
substrate
15
New cards
breaks down larger structures
anabolic
16
New cards
build smaller structures into larger structures
catabolic
17
New cards
packages and transports proteins
golgi apparatus
18
New cards
A process where experts in the same field as the investigator review scientific studies before it is published in order to ensure that the research is high quality and that the authors have interpreted the study correctly
peer review
19
New cards
A hypothesis that can be supported or rejected by carefully designed experiments or observational studies
testable
20
New cards
A hypothesis that can be ruled out by data that show that the hypothesis does not explain the observation
falsifiable
21
New cards
Observation
Hypothesis
Test
Result
Theory
Hypothesis
Test
Result
Theory
scientific process
22
New cards
Group that experiences the intervention
Experimental group
23
New cards
Group that experiences no intervention
control group
24
New cards
The variable being changed in the experimental group
independent variable
25
New cards
The variable being measured and analyzed from the changes to the experimental group
dependent variable
26
New cards
False treatment given to mimic the experience of the experimental groups
Placebo
27
New cards
What is not a shared feature in all types of cells
Mitochondria
28
New cards
Lacks membrane bound organelles
Bacteria
29
New cards
contain membrane bound organelles and a nucleus
Eukaryotes
30
New cards
bonds between a metal and a nonmetal, electrons are donated from one atom to another
ionic bond
31
New cards
bonds between two nonmetals, two atoms share electrons
covalent bond
32
New cards
if a solution is basic, it contains more...
OH- ions
33
New cards
if a solution is more acidic, it contains more...
H+ ions
34
New cards
A phospholipid bilayer with protein that forms the boundary of all cells
cell membrane
35
New cards
A type of lipid that forms the cell membrane
Phospholipid
36
New cards
the head of the phospholipid
hydrophilic
37
New cards
the tail of the phospholipid
hydrophobic
38
New cards
common elements in the body (CaNCHOP)
Calcium Nitrogen Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Phosphorus
39
New cards
Organic molecule made up of one or more sugars, stores short-term energy
Carbohydrate
40
New cards
Glucose, fructose, galactose
monosaccharides/monomers
41
New cards
Starch, cellulose
polysaccharides/polymers
42
New cards
Organic macromolecule made up of amino acid subunits, diverse functions (structural, protective, transport, etc.) includes enzymes
proteins
43
New cards
amino acids
protein monomers
44
New cards
Proteins
protein polymers
45
New cards
Organic molecule that generally repel water, provides the most energy out of the macromolecules, includes cholesterol, hormones, and phospholipids
Lipids
46
New cards
Fatty Acids
lipid monomers
47
New cards
Carbon atoms are single bonded to each other making the hydrocarbons pack more tightly against each other, solid at room temp
Saturated
48
New cards
Some of the carbon atoms are double bonded to each other creating a kink, hydrocarbons do not pack as tightly, liquid at room temp
Unsaturated
49
New cards
Organic molecule made up of linked nucleotide subunits, creates DNA and RNA
Nucleic acids
50
New cards
Nucleotides
nucleic acid monomers
51
New cards
always unicellular
bacteria
52
New cards
has a nucleus
eukaryote
53
New cards
can reproduce or replicate
all cell types
54
New cards
has a cell wall, ribosomes, and cytoplasm
all types of cells
55
New cards
encloses the cell's DNA
nucleus
56
New cards
synthesizes proteins
endoplasmic reticulum
57
New cards
ER that contains ribosome bound organelles
rough ER
58
New cards
ER that produces lipids
smooth ER
59
New cards
Packages and transports proteins made in rough ER
Golgi Apparatus
60
New cards
Convert energy into a useful form
mitochondria
61
New cards
Captures and converts sunlight into energy; only in plants and algae
chloroplast
62
New cards
Break down old cell parts or molecules
Lysosomes
63
New cards
Provides cell support, cell movement, and movement of structures within the cells
cytoskeleton
64
New cards
Diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high to low concentration
osmosis
65
New cards
Solution has lower solute concentration than the cell; Water moves into the cell, cell swells up
Hypotonic solution
66
New cards
Solution has same concentration as the cell; No net movement, cell stays the same
Isotonic solution
67
New cards
Solution has higher solute concentration than cell; Water moves out of the cell, cell shrinks
Hypertonic solution
68
New cards
Macromolecule found in all bacterial cell walls that give it rigidity
Peptidoglycan
69
New cards
Small, uncharged molecules move from high to low concentration without using energy
simple diffusion
70
New cards
Proteins involved in the movement of molecules and ions across a cell membrane
transport proteins
71
New cards
Large or hydrophilic molecules use transport proteins to move molecules from high to low concentration without using energy
facilitated diffusion
72
New cards
Large or hydrophilic molecules move from low to high concentration using transport proteins and energy; requires energy
active transport
73
New cards
weakens cell walls with peptidoglycan which is effective because only bacteria have cells walls containing peptidoglycan. Interferes with cell wall synthesis allowing the cells to fill up with water and burst from osmosis
penicillin
74
New cards
A chemical that can slow or stop the growth of bacteria
antibiotic
75
New cards
Changes in bacteria that cause them to not respond to antibiotics caused by random mutation or gene transfer
antibiotic resistance
76
New cards
An infectious agent that reproduce and pass their genetic information to new viruses but are not made of cells.
viruses
77
New cards
A medical condition resulting from a lack of essential nutrients in the diet
malnutrition
78
New cards
Components in food that the body needs to grow, develop, and repair itself
nutrients
79
New cards
Process of breaking down huge food molecules into smaller pieces so that our body can use them
digestion
80
New cards
Nutrients that can’t be made by the body, so it must be obtained from the diet
essential nutrients
81
New cards
Amino acids that can’t be made by the body, it must be obtained in the pre-assembled form from the diet
essential amino acids
82
New cards
A complex carbohydrate made up of linked glucose molecules, a source of stored energy
starch
83
New cards
All biochemical reactions occurring in an organism
metabolism
84
New cards
Nutrients that organisms must ingest in large amounts to maintain health
macronutrients
85
New cards
Carbohydrates are broken down into
simple sugars
86
New cards
proteins are broken down into...which are used to assemble new proteins
amino acids
87
New cards
Fats are broken down into...and...which are used to build membranes and form cell membranes
fatty acids and glycerol
88
New cards
Nutrients that organisms must ingest in small amounts to maintain health
micronutrients
89
New cards
Inorganic elements (ex. Ca, Fe, K, Zn)
minerals
90
New cards
Organic molecules (A, C, B12)
vitamins
91
New cards
An inorganic substance required to activate an enzyme (mineral)
coenzymes
92
New cards
An organic molecule required to activate an enzyme (vitamin)
cofactor
93
New cards
Protein that speeds up a chemical reaction
enzyme
94
New cards
Molecule where an enzyme binds on and which it acts
substrate
95
New cards
Part of an enzymes that binds to the substrate
active site
96
New cards
Process of speeding up the rate of a chemical reaction
catalysis
97
New cards
Energy required for a chemical reaction to proceed
activation energy