Air Pollution and Ecosystems Review
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards covering key terms and concepts related to air pollution, ecosystems, and their impacts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
A gas mostly produced from the combustion of gasoline.
Ozone (O3)
A secondary air pollutant formed from reactions between NO2 and VOCs in the presence of sunlight.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
A gas primarily resulting from burning coal and diesel fuel.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
A gas mainly produced from combustion of gasoline and natural gas.
Lead (Pb)
A toxic metal historically found in gasoline, emitted from metal refineries.
Particulate Matter (PM)
A mixture of tiny solid particles and liquid droplets in the air; includes PM2.5 and PM10.
PM2.5
Fine particulate matter that can penetrate deeply into the respiratory system, often from fossil fuel combustion.
PM10
Coarse particulate matter including pollen, dust, and bacteria, usually trapped in the upper respiratory tract.
Primary Air Pollutants
Pollutants emitted directly into the atmosphere, such as NOx and SOx.
Secondary Air Pollutants
Pollutants formed through reactions between primary pollutants and other substances.
Photochemical Smog
Air pollution causing a brown haze, primarily produced by sunlight interacting with NOx and VOCs.
Catalytic Converters
Devices in vehicles that reduce NOx and CO emissions by converting them to less harmful gases.
Thermal Inversion
A condition where warm air traps cooler air and pollutants near the ground.
Coral Bleaching
A phenomenon where stressed corals expel their algae, turning white due to warmer temperatures, pollution, or disease.
Eutrophication
The process where excess nutrients lead to algal blooms, depleting oxygen and harming aquatic life.
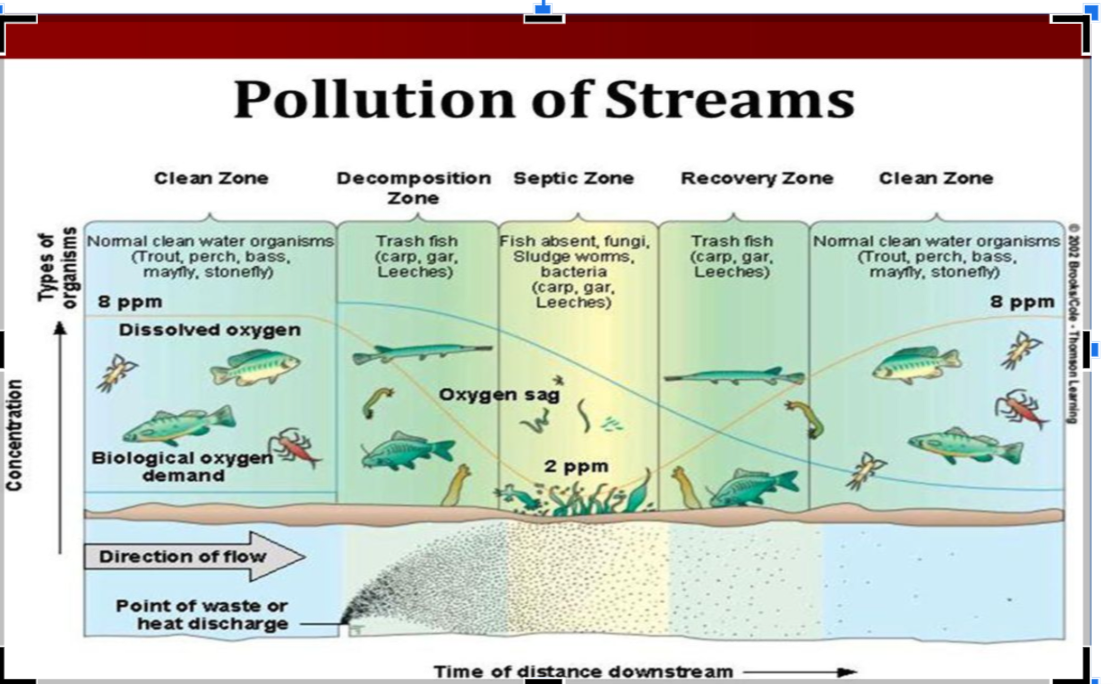
Oxygen Sag Curve
A graphical representation showing dissolved oxygen levels decreasing downstream from a pollution source.
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD)
A measure of the amount of oxygen used by aerobic bacteria to decompose organic matter.
Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
The amount of oxygen available in water; essential for aquatic life.
Endocrine Disruptors
Chemicals that interfere with hormone function in animals, impacting their reproduction and development.
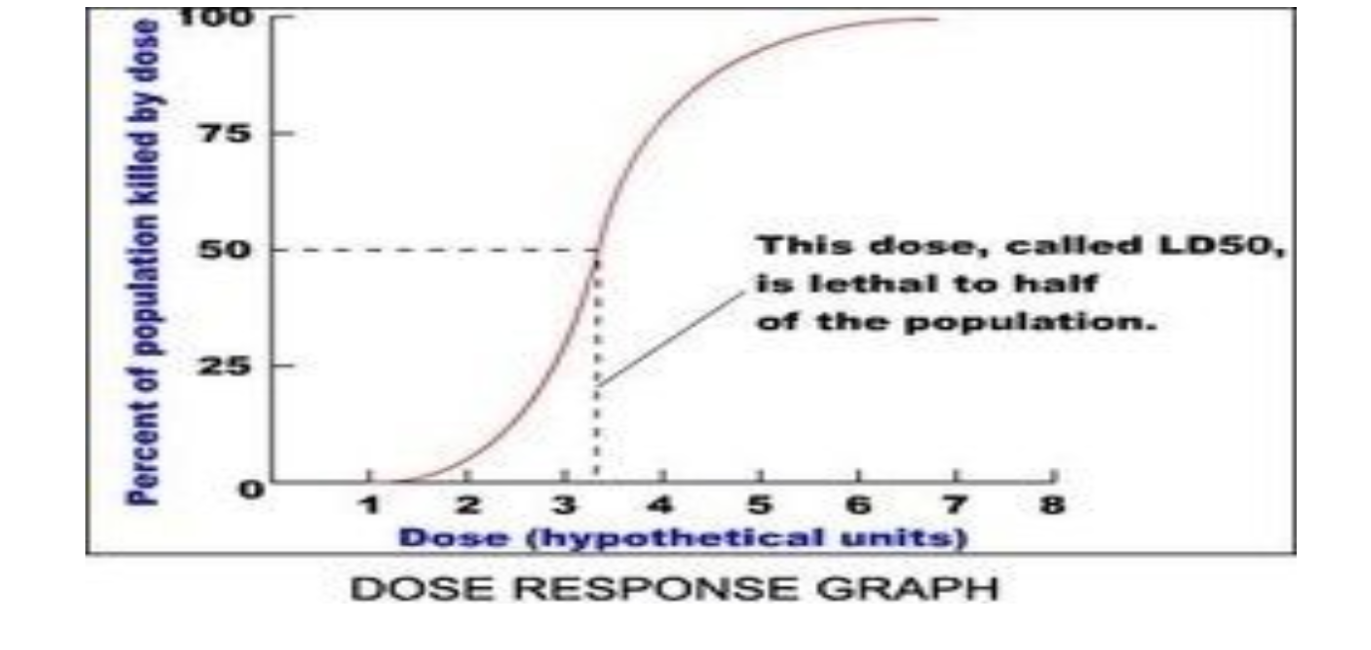
Lethal Dose 50% (LD50)
The amount of a substance that will kill 50% of a tested population, often used to measure toxicity.
Dose-Response Curve
A graph showing the relationship between the dose of a substance and its observed effects.
Stratospheric Ozone
Ozone found in the stratosphere that protects Earth from harmful UV radiation.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Synthetic compounds that lead to ozone depletion when they break down in the stratosphere.
Montreal Protocol
An international treaty aimed at phasing out substances that deplete the ozone layer.
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
Chemicals used as substitutes for CFCs; although they are greenhouse gases, they don't deplete ozone.
Greenhouse Gases
Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to climate change.
Ocean Acidification
The process of decreasing pH levels in oceans due to increased CO2 absorption.
Positive Feedback Loop
A process in which a change causes further changes in the same direction, such as melting ice leading to increased heating.
Dead Zones
Areas in bodies of water with low oxygen levels that cannot support marine life.
Septic Zone
The stage in a water body where DO is critically low and BOD is high, indicating pollution.
Recovery Zone (in sewage treatment)
The area where DO levels increase again after wastewater treatment.
Clean Zone (in aquatic systems)
A state where water is non-polluted, with high dissolved oxygen and low biological oxygen demand.
Tropospheric Ozone
The harmful ozone formed near the Earth's surface, created from chemical reactions involving sunlight.
UV Radiation
A type of radiation from the sun that can cause skin cancer and cataracts.
Acid Rain
Precipitation with high levels of nitric and sulfuric acids, formed from reactions with atmospheric pollutants.
Nitric Acid (HNO3)
A secondary pollutant produced when NO2 reacts with water vapor.
Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4)
A strong acid formed from the oxidation of sulfur dioxide in the presence of water vapor.
Greenhouse Effect
The warming of the Earth due to the trapping of heat by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Albedo
The reflectivity of a surface; lighter surfaces reflect more sunlight.
Acidification
The decrease in pH levels in a solution, affecting carbonate levels necessary for marine organisms.
Thermal Expansion
The increase in water volume as temperatures rise, contributing to sea-level rise.
Methane (CH4)
A potent greenhouse gas produced by the digestion processes of animals and organic waste decomposition.
Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
A greenhouse gas emitted from agricultural practices, particularly from nitrogen-rich fertilizers.
Denitrification
The microbial process converting nitrates into nitrogen gases, reducing nitrogen levels in soils.
Carbonic Acid (H2CO3)
An acid formed when carbon dioxide dissolves in water; contributes to ocean acidification.
Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
The ability of soil to hold and exchange cations, important for plant nutrient availability.
Flow of oxygen in water bodies
The movement and availability of dissolved oxygen, critical for aquatic life.
Hydrological Cycle
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll.
Aquatic Ecosystems
Water-based environments that host diverse biological communities.
Wetlands
Ecological areas that are saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally, providing habitat for wildlife.
Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Fossil Fuels
Natural fuels formed from the remains of living organisms, including coal, oil, and natural gas.
Carbon Footprint
The amount of carbon dioxide emissions for which an individual or organization is responsible.
Pollutants
Substances that contaminate the environment or alter the natural balance.
Air Quality Index (AQI)
A measure used to communicate how polluted the air currently is or how polluted it is forecast to become.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature, contributing to smog formation.
Biodiversity Loss
The reduction in the variety and variability of life forms within a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Nutrient Limitation
A condition where the growth of organisms is restricted due to a lack of essential nutrients.
Trophic Cascade
When the addition or removal of a top predator alters the structure and species composition of a community.
Restoration Ecology
The scientific study of renewing and restoring degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystems.
Carbon Sequestration
The process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide to mitigate climate change.
Environmental Health
The branch of public health that is concerned with all aspects of the natural and built environment affecting human health.
Sustainable Development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Renewable Resources
Resources that can be replenished naturally over short periods of time.
Non-renewable Resources
Resources that do not renew at a sustainable rate relative to their consumption.