Clin Skills 2 Midterm
1/348
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
349 Terms
Normal Blood Pressure
<120/<80mmHg
Elevated Blood Pressure
Systolic 120-129 mmHg and diastolic less than 80 mmHg
Stage 1 Blood Pressure
Systolic 130-139 or diastolic 80-89mmHg
Stage 2 Blood Pressure
Systolic >140 mmHg or diastolic >90 mmHg
Diagnosis of hypertension
Based on >2 readings obtained on >2 occasions
Urgency HTN
>180/>120 mmHg without evidence of organ damage (normal funduscopic exam and no evidence of headache, dizziness, chest pain, confusion, etc)
Emergency HTN
>180/>120 mmHg with evidence of organ damage (normal funduscopic exam or evidence of headache, dizziness, chest pain, confusion, etc)
Normal temperature
98.6 F
Normal temperature range
97.5 F - 98.9 F
Factors which may influence accuracy of temperature
Eating, drinking, chewing gum, smoking 15 minutes prior, talking &/or breathing through the mouth during a reading
Pyrexia (fever)
infection, heat exhaustion, malignancy, medications
Hyperpyrexia (extreme fever 106.7F+)
Bleeding in brain, infections, sepsis, immune disorders
Hypothermia (low temperature)
exposure to cold, paralysis, excess alcohol, starvation, hypothyroidism, hypoglycemia
Normal range for heart rate
60-100 bpm
Factors which may influence accuracy of pulse
White coat/anxiety, stress, smoking, exercise, caffeine
Tachycardia (>100 bpm)
heart & lung disease, fever, hyperthyroid, electrolyte imbalance
Bradycardia (<60 bpm)
heart disease, medication, inflammatory disease, hypothyroid, electrolyte imbalance
Small/Weak Pulse
diminished pulse pressure; contour: upstroke is slowed and peak prolonged
Large/bounding pulse
increased pulse pressure; contour: rapid rise and fall with brief peak
Bisferiens pulse
increased pulse pressure; contour: double systolic peak
Pulsus alterans pulse
alternating pulse pressure; contour: amplitude varies, rhythm stays the same
Paradoxical pulse
pulse pressure no changes; contour: amplitude decreases on quiet inspiration (10mmHg+)
Normal range for respiratory rate
12-20 rpm
Bradypnea
slow rate, regular depth, regular rhythm
Tachypnea
rapid rate >20 rpm, shallow depth, regular rhythm
Hyperpnea
rapid rate >20 rpm, deep inspiration, regular rhythm
Obstructive respiration
regular rate, shallow depth, prolonged expiration
Sighing respiration
regular rate, frequent increases in depth, regular rhythm
Ataxic (Biot’s)
alternating rate, depth, rhythm
What are the 4 primary vital signs?
Temperature
Pulse rate
Respiratory rate
Blood pressure
5th vital sign
pain
or pulse oximetry (blood oxygen levels)
6th sign
no standard/more informal
based on situation and discipline
arteriosclerosis
hardening and thickening of arterial wall
decrease blood flow
atherosclerosis
type of arteriosclerosis
-build up of waxy plaque which slowly blocks the lumen and decreases blood flow
What side of the stethoscope do you use when auscultating arteries?
bell
bruit
normal: no audible sounds is heard in the arteries from blood flow
abnormally: audible swooshing sound heard over peripheral artery
Coarctation
stricture or narrowing of the wall of the aorta
Methods to take temperature
oral
tympanic
temporal
axillary
rectal
rectal temperature
range: 0.5-1 degrees higher than oral temperature
tympanic temperature
range: 0.5-1 degrees higher than oral temperature
axillary temperature
range: 0.5-1 degrees lower than oral temperature
temporal temperature
range: 0.5-1 degrees lower than oral temperature
what is the “gold standard” of measuring temperature?
rectal temperature
normal rectal temperature
99.6 F
infrared tympanic thermometers
commonly used in clinics
studies have been shown to have relatively high specificity
0.5-1 degree higher than oral
temporal artery thermometer
least accuracy of the common methods
technology has increased sensitivity
0.5-1 degree lower than oral
diurnal temperature
in most people, there is a diurnal (daily) variation in body temperature of 0.5-2 degrees
lowest ebb: during sleep temperature may fall as low as 95.5 F
basal body temperature
temperature upon waking
normal temperature
98.6 F
normal temperature range
97.5 F-98.9 Fthe typical range of body temperature fluctuations in humans, indicating a healthy state.
elevated temperature reading
results from:
-previous ingestion of warm substances
-recent strenuous activity
-a warm bath/hot tub
-a recently smoked cigarette/other
-inadequate shaking down of the thermometer (older mercury/glass types)
low temperature readings
results from:
-incomplete closure of the mouth
-breathing through the mouth
-recent ingestion of cold substances
-tachypnea (respiraotry rate more than 20/minute)
consider retaking:
-reinstruct
-wait until mouth is warmer
pyrexia: defined as fever
-body temperature is elevated above one’s normal temperature
-one definition- if the oral temperature reaches 99 F in a patient at bedrest
-infection, heat exhaustion, malignancy, medications
hyperpyrexia: extreme fever 106.7 F
-bleeding on the brain, infection, sepsis, immune disorders
fever of undetermined origin: defined as fever of at least 101 F
-lasts for more than 3 weeks
-no explanation despite thorough history and examination
-an occasional phenomenon
-formerly fever of “unknown” origin
hyperthermia: defined as overheated body
-exposure to cold
-drug and alcohol intoxication
-starvation
-hypothyroidism, hypoglycemia
-paralysis
-severe metabolic acidosis (decreased PH and bicarbonate concentration in the body fluids, caused either by the accumulation of acids or by abnormal losses of fixed base from the body, as in diarrhea or renal disease)
chills
-subjective reports of shivering or shaking
-chills often accompany fever
-associated with rapid changes in temperature (results from involuntary muscle contractions that occur in response to a sudden lowering of body temperature below the prevailing set point, shivering causes heat)
night sweats
-subjective reports of nocturnal sweating
-profuse sweating at night
-can be idiopathic or due to menopause
-chronic debilitating affections with low-grade fever (lymphoma, tuberculosis, aids)
pulse locations
-radial
-ulnar
-brachial
-carotid
-femoral
-popliteal
-dorsalis pedis
-posterior tibial
occasionlly radial artery has an anomalous course. Why?
-pulse is impaired or absent
-if this happens, check proximal (brachial/axillary) pulses & the ipsilateral ulnar pulse before concluding that the pulse is absent
-pathological reason: thrombosis involving one subclavian, axillary or brachial artery
pulse rate rate
60-100 bpm
normal pulse rate in children
90-120 bpm
-the younger the higher
Who might have a pulse rate around 50 bpm?
well conditioned athletes
Do men or women generally have slightly higher pulse rates?
women
Pulse rate documentation
Rhythm:
-regular
-irregular
-irregular with respiration
Amplitude/intensity:
-bounding
-amplitude diminished
Contour:
-Smooth
-Irregular
Tachycardia: >100 bpm
-electrolyte imbalance
-emotional stress
-smoking
-exercise
-alcohol/caffeine (large amounts)
-medication side effects
-heart related conditions (hypertension, congenital heart issues, heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias)
-certain lung disease
-fever
-hypertension
-thyroid disease (hyperthyroid)
Bradycardia: <60 bpm
-electrolyte imbalance
-medications
-heart conditions (heart tissue damage related to aging, congenital heart defect, infection of heart tissue)
-inflammatory disease (rheumatic fever/lupus)
-hypothyroidism
-obstructive sleep apnea
Normal pulse
Pressure of the pulse: normal
Contour: smooth and rounded

Small/Weak Pulse
Pressure of the pulse: diminished
Contour: upstroke slow, peak prolong
Causes: decreased stroke volume (heart failure), hypovolemia, aortic stenosis, an increased peripheral resistance (cold exposure and congestive heart failure can cause this)

Large/Bounding Pulse
Pressure of the pulse: increased
contour: rapid rise and fall, peak brief
Causes: increased stroke volume, decreased peripheral resistance (fever, anemia, and hyperthyroidism all potential causes), and decreased compliance (aging and atherosclerosis common offenders)
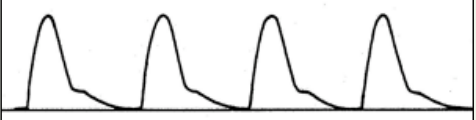
Bisferiens Pulse
Pressure of the pulse: increased
Contour: double systolic peak
Causes: aortic regurgitation, aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Pulsus Alternans
Pressure of the pulse: alternates
Contour: amplitude varies, rhythm same
Cause: left ventricular failure

Paradoxical Pulse
Pressure of the pulse: no change
Contour: amplitude decreased with inspiration (10 mmHg+)
Causes: hypothyroidism, fluid in heart (pericardial tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, obstructive lung disease)
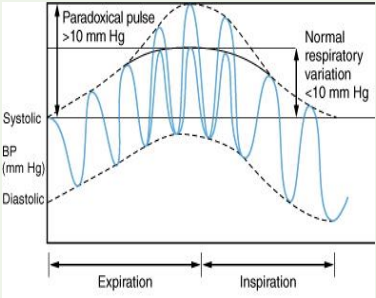
How to palpate a pulse?
-it is usually better to use light pressure using the fingertips for palpation
-can be palpated against a firmer surface, usually bone
Pulse at the wrist
patient hand: palm upward
doctor: places first 2 or 3 fingers on the radial artery (the radial artery is compressed against the distal radius, use finger tips)
Respiration qualities
normal
-rate: 12-20
-rhythm: regular
-depth: regular
-effort: none (occasional sigh is normal, normally there is no evident use of accessory respiratory muscles)
-variable: with fever, rate increases approximately 4 rpm for each degree F above normal
apnea
no breath
bradypnea
rate is slow
hyperpnea & tachypnea
rapid rate of >20 rpm
tachypnea
rate: rapid rate of >20 rpm
rhythm: regular
depth: shallow
hyperpnea
rate: rapid rate of >20 rpm
rhythm: regular
depth: deep respirations of increased volume per breath
bradypnea
rate: slow
rhythm: regular
depth: regular
Cheyne-Stokes
rate: alternating
rhythm: alternating
depth: alternating
Ataxic/Biot’s
rate: unpredictable
rhythm: variable
depth: variable
Sighing
rate: regular
rhythm: regular
depth: frequent increases in depth
obstructive
rate: regular
rhythm: prolong
depth: shallow
Systole
-period of time within the cardiac cycle when the ventricles are contracting
-the value in mm Hg when the sounds start when taking a blood pressure
Diastole
-period of time within the cardiac cycle in which ventricles are relaxed and filled with blood
-The value in mm Hg when auscultation sounds stop when taking a blood pressure
Pulse Pressure range
30-40 mmHg
What is pulse pressure?
The difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure, indicating the force the heart generates each time it beats.
Korotkoff sounds
Sounds heard through a stethoscope over an artery during blood pressure measurement, indicating the onset and cessation of blood flow.
Auscultatory Gap
A period during blood pressure measurement where sounds are temporarily absent, potentially leading to an underestimation of systolic pressure.
Factors that influence blood pressure
-age
-gender
-technique of examination
-physical exertion
-emotional tension
-pain
what might cause false high readings for blood pressure?
large arms
-pressure applied to cuff must overcome the resistance of the mass before compressing the brachial artery
-an appropriately sized cuff should be used
white coat hypertension
-exhibit elevated blood pressure beyond normal range when in clinical setting
-repeat attempt to take
What can cause high blood pressure?
kidney disease
-chronic glomerulonephritis
-renal artery stenosis
adrenal disease
-pheochromocytoma
-primary aldosteronism
vascular disease
-coarctation of the aorta
What are the signs and symptoms of organ damage?
-abnormal fundoscopic exam
-severe headache
-dizziness
-chest pain
-confusion
hypotension
systolic pressure of 90 to 100 mmHg
orthostatic hypotension
change in position causes lightheadedness or fainting
causes of low blood pressure
-hypertension medication
-blood loss
-dehydration
-cardiac anomalies
-sympathetic failure (parkinson’s disease)
causes of abnormal pulse pressure
-anemia
-hyperthyroidism
-aortic regurgitation
-arteriovenous fistula
-atherosclerosis: aorta and large arteries