Cognition Final
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Recency vs Primacy Effect
Recency: small short term buffer (more recent terms)
Primacy: rehearsal is required (first items said)
Atkinson Shiffron Model (interference)
model has a large duration, going back and forth from STM to LTM
Interference: competition between items preventing consolidation
Reconsolidation massed vs spaced training
Encoding: consolidating a representation of info into memory

Forgetting
Failure to Consolidate: no LTM
Failure to Retrieve: in LTM
Interference among cues
H.M. and types of amnesia
hippocampus removed
unable to form new memories
LTM was unaffected and STM was unaffected
however he couldn’t consolidate (go between) because of lack of hippocampus
Reterograde: LTM damage cant remember past
Anterograde: consolidation damage cant make new memories
Shows Procedural Memory is encoded seperately
HM could do learning task just like everyone else

Types of Memory (Declarative: episodic, semantic, procedural: mental imagery)
Declarative (explicit)
episodic: first person memory of an experience
semantic/propositional: knowledge of facts
Procedural (implicit)
how to do things - motor procedures
mental imagery: knowledge of appearance of things
Verbal Encoding, STM Capacity, Patient SF
Capacity is 7 plus or minus 2
thats why phone numbers have 7 digits!
Verbal Encoding: verbal distraction interferes with encoding while visual doesn’t
Patient SF: taught to chunk rapidly
didn’t have more slots for chunks in memory just could fit more digits in each chunk
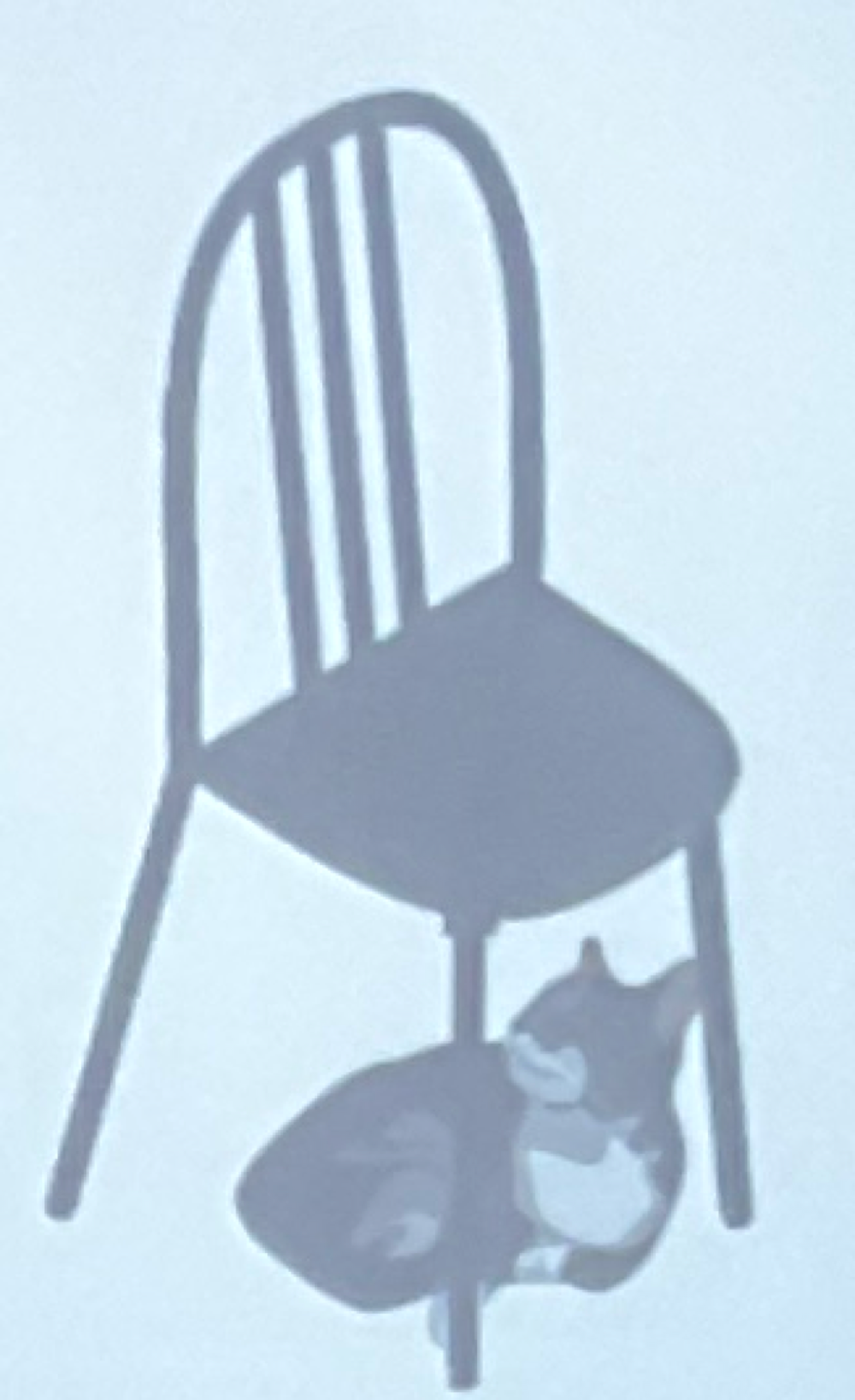
Imagistic vs Propositional Representations
Imagistic: stores the sensory experience
visual representation in your mind: (image)
Propositional: stores the abstract relation
“the cat was under the chair”

Mental Rotation
mental analog of physical rotation
spatially organized analog of a real picture is progressively transformed
Mental Scanning
Mental distance is an analog of real distance
more map distance = longer it takes
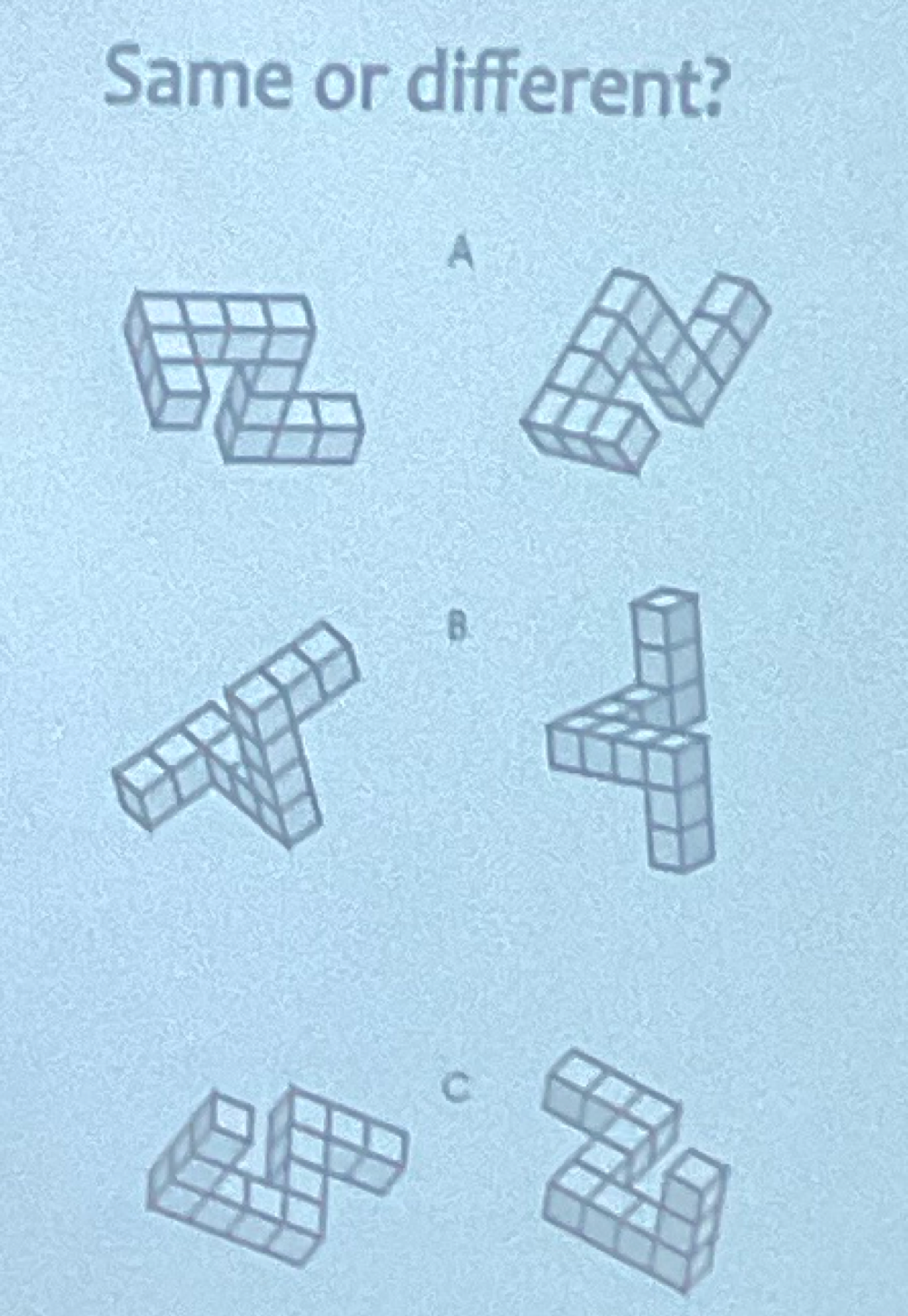
Proof mental imagery exists
Mental Imagery Debate
Kosslyn
pro mental imagery
evaluation → visual system
Pylyshyn (Rutgers)
representations of images are propositional/descriptive
scanning results due to cognitive expectations of subjects
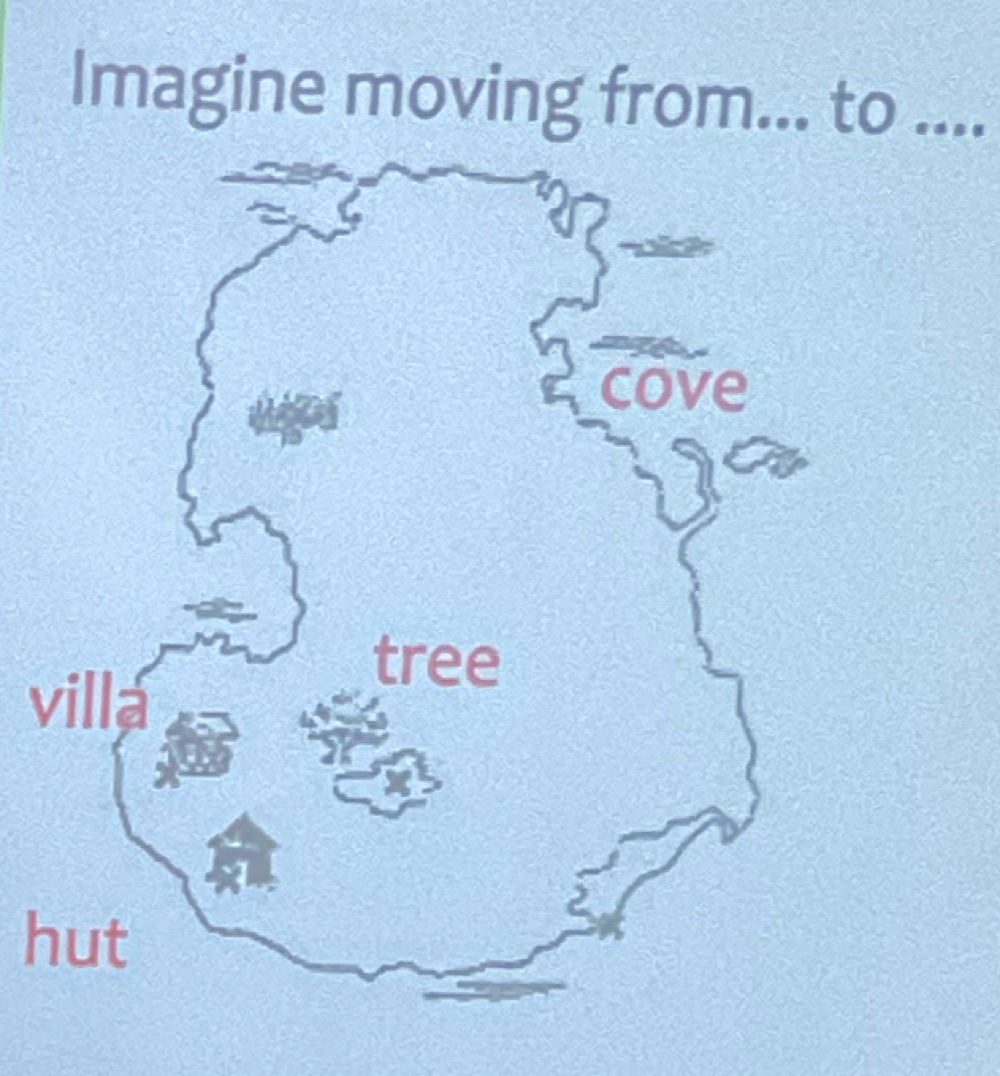
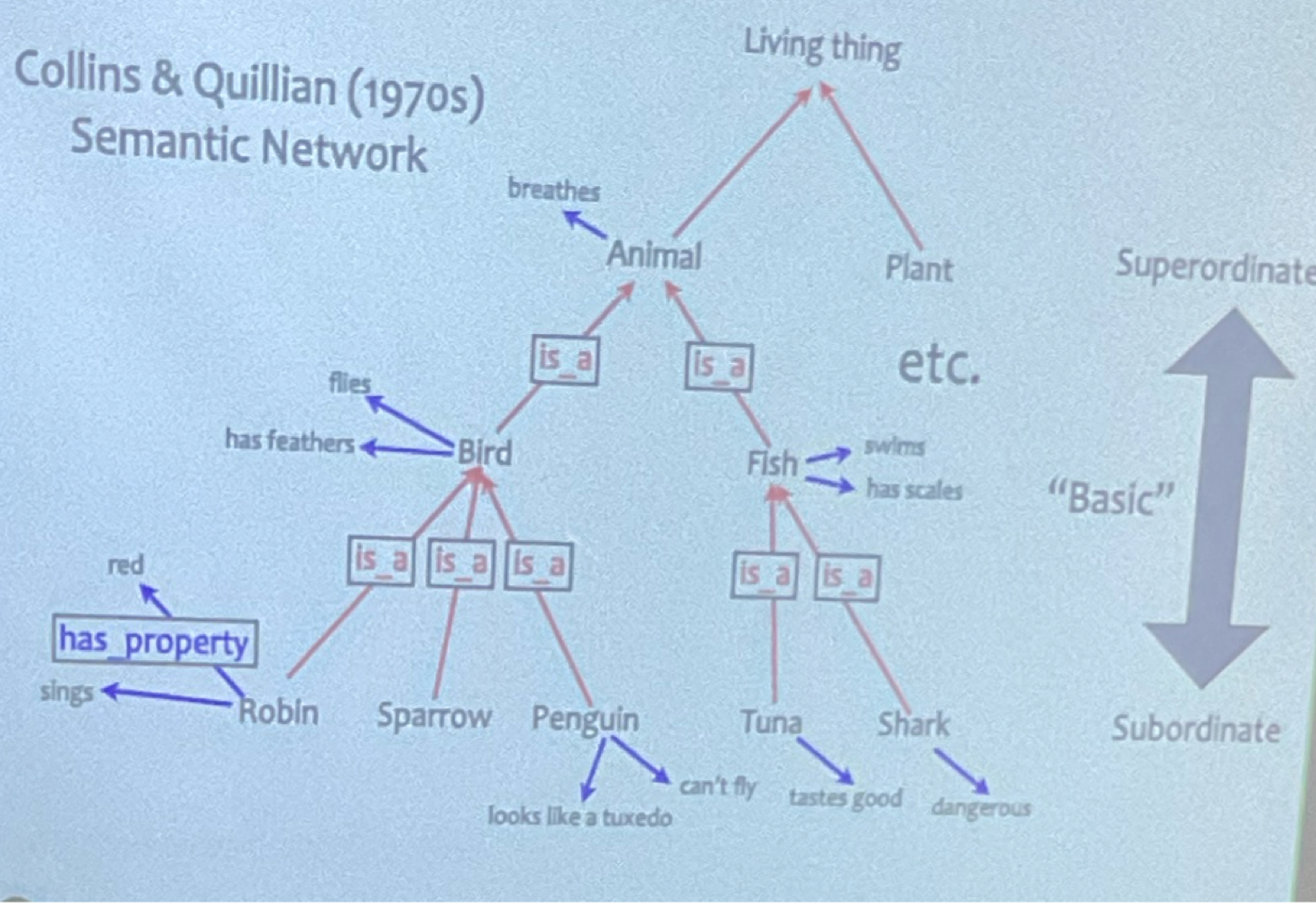
Property Inheritance
If x is a y and y has property z then x has property z
direct property wins!
inference ability = efficient form of reconstructive memory
Hierarchical Structure (top is superordinate to bottom subordinate)
Induction vs Deduction
Induction: specific to general
if it rains on saturday and it rains on sunday it rains on weekends
a guess/generalization
Deduction: general to specific
all men are mortal, socrates is a man, socrates is mortal
logical conclusion
David Hume
will the sun rise tomorrow? How do you know?
Hume: belief that the sun will rise tomorrow isn’t logically sound and only whats likely
Induction not deduction: not guaranteed to be valid
Classical vs Modern View of Categories
Classical View
categories have logical constructs and definitions
definitions have necessary and jointly sufficient features
clear cut categories but is a hotdog a sandwich?
Fuzziness and Family Resemblance
most mental categories have fuzzy boundaries with family groups
Ex. game, furniture
Exemplar Model
comparing information to stored examples/exemplars in brain
no generalization/abstraction
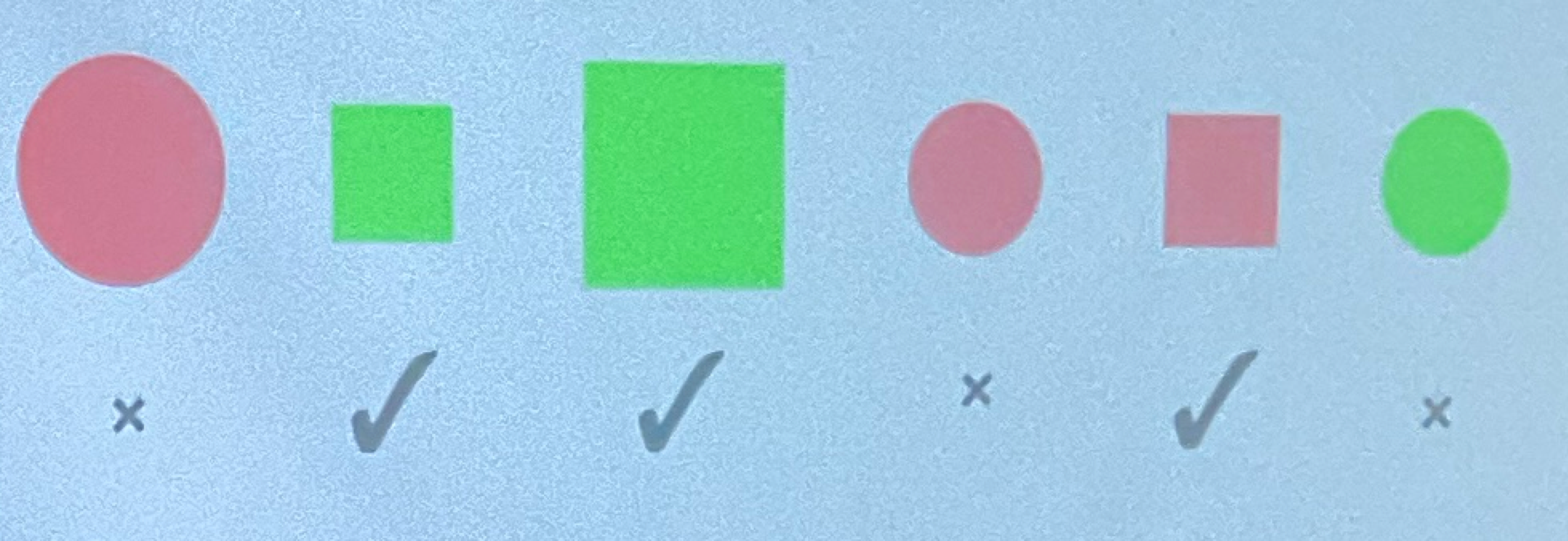
Classical Concept Learning Experiment
Find the rules!
Ex. Squares or small and green shapes
Conjunction was easier than disjunction
assumed concepts are defined with logic

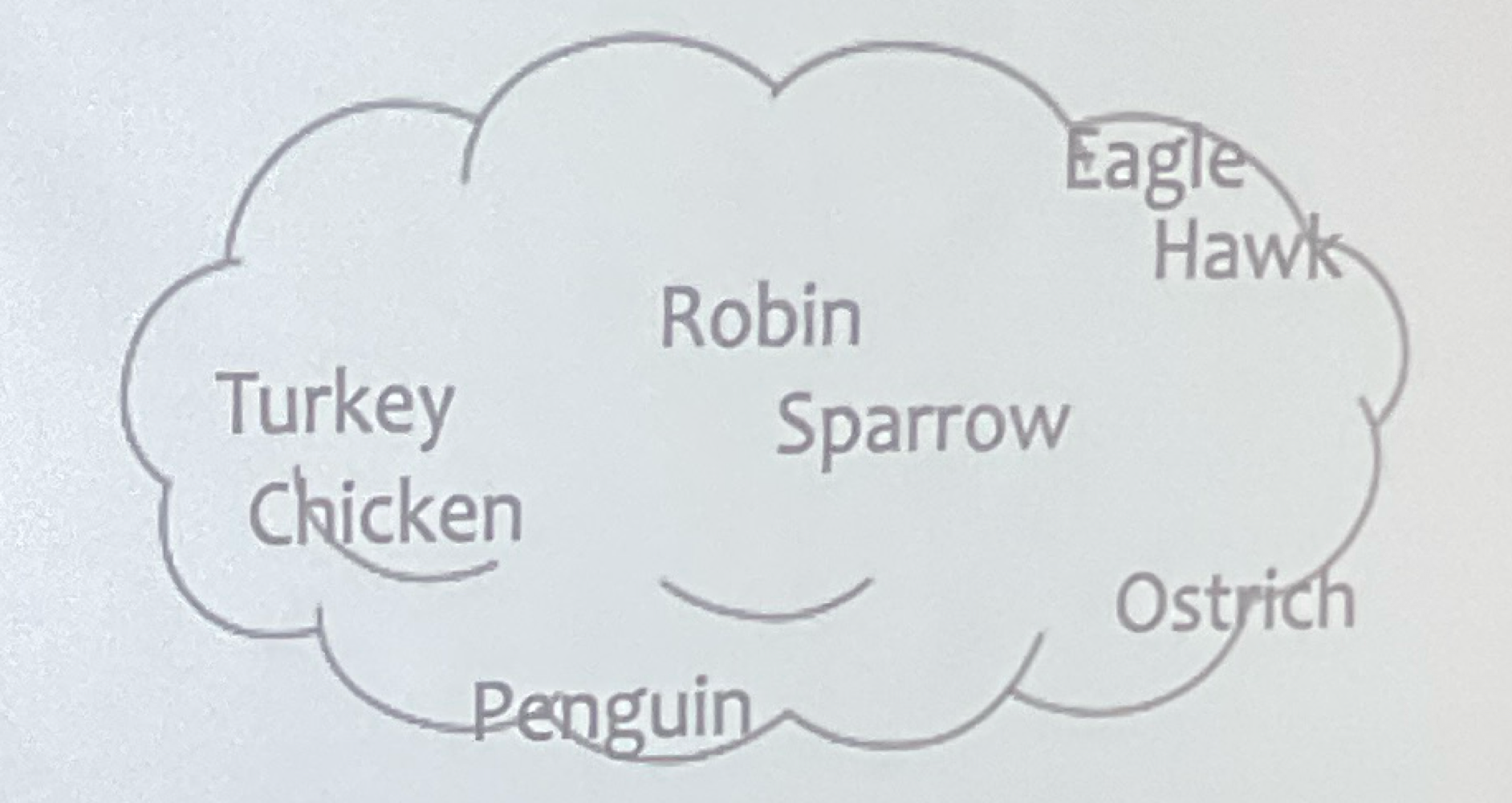
Prototypes
Posner and Keele (1998) - prototypification = “normal form”
Ex. prototype of bird
each feature in proportion to its prevalence; not necessary/sufficient
distinguishing core meaning and identification purposes
Geometric Model + Multidimensional Scaling
Geometric Model
analogous to proximity in some mental space
dissimilarity is more distance, similarity is closeness
Multidimensional Scaling
ranking dissimilarity among set of items finds positions in imaginary space
x axis is money y axis is sporty

Euclidean distance vs city block distance
Euclidean (as the crow flies) - purple
City Block Distance - pink
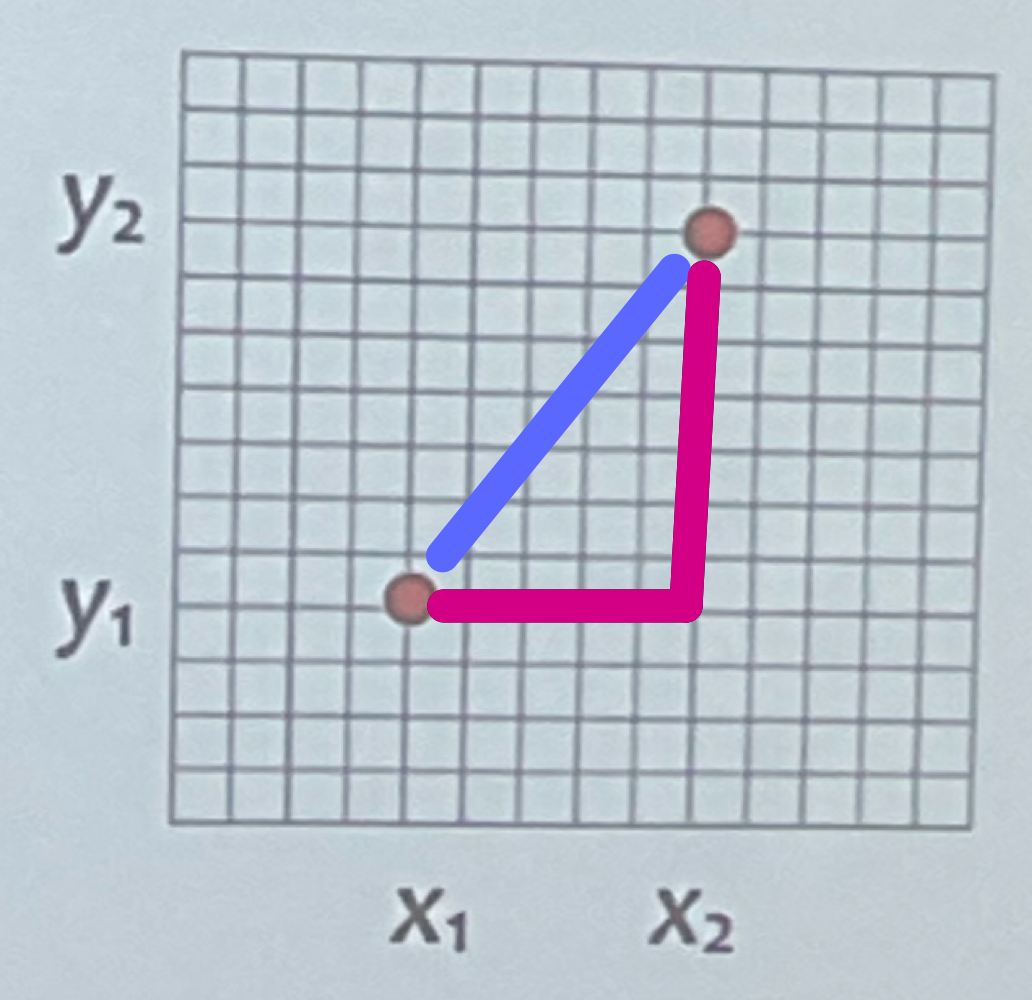
Distance Axioms
Symmetry - distance from A to B = distance from B to A
Triangle Inequality - distance from A to B + distance from B to C has to be greater than the distance from A to C
shortest distance between 2 points is a straight line
Similarity and Distance Axioms
Similarity DOES NOT obey distance axioms
geometric model is wrong
apple compared to pomegranate was more liked compared to pomegranate vs apple
also failed triangle of inequality
Contrast Model
Similarity of A + B = Features shared between A and B - Features of just A - Features of just B
uses featural model to contrast features
can violate triangle of inequality but is still used
Connectionism/Pandemonium
Connectionism
artificial neural network is the alternative approach to cognitive architecture
rooted in empiricism/associationism
ties to neuroscience
Pandemonium
lots of small individual parts and layers make up larger system
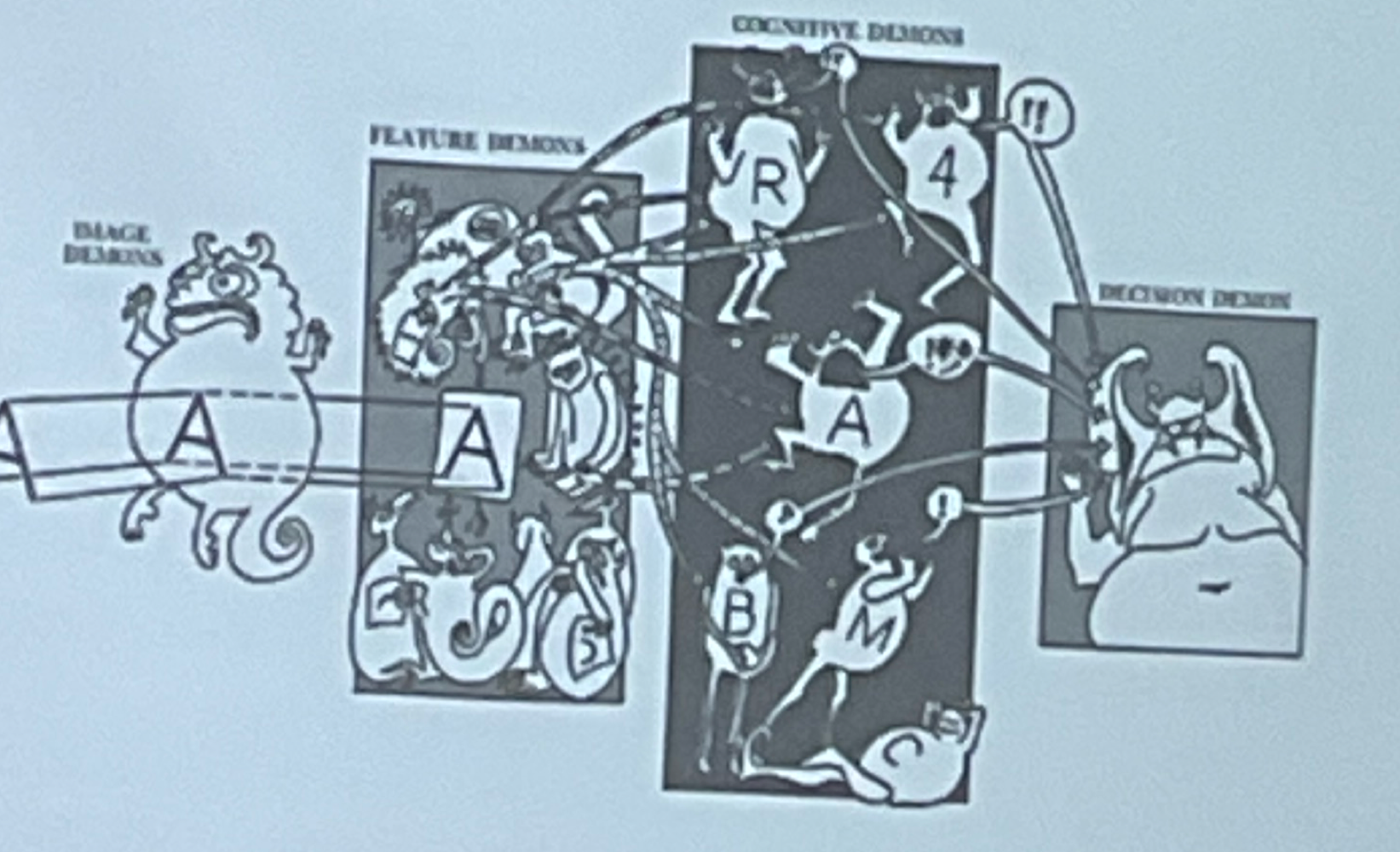
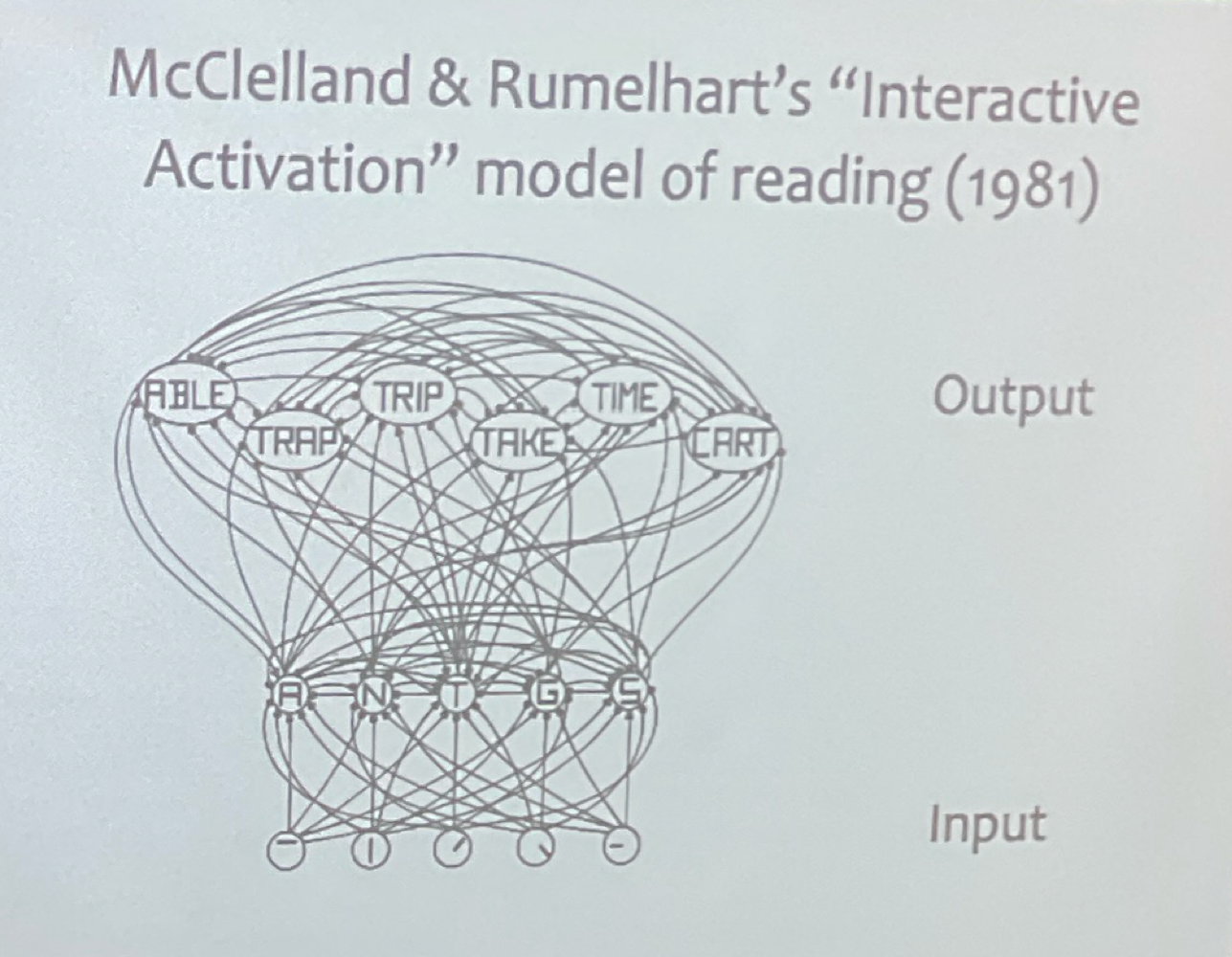
McClelland and Rumelhart
parallel distributed processing book
dumb device that recognizes its stroke
Flaw: cant possibly be infinite neurons to make infinite sentences
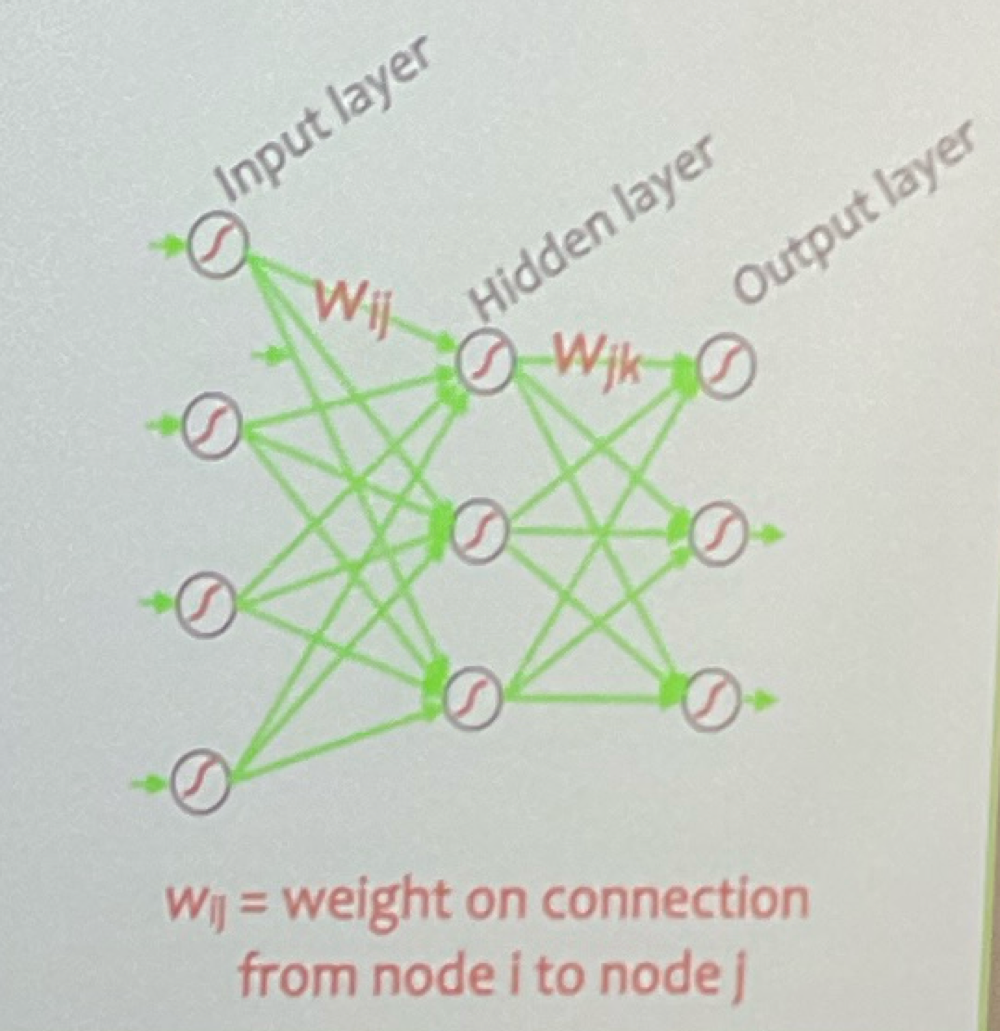
Training a Neural Network
drawing examples from a training set
Supervised: know what the output should be by comparing to an oracle
modify parameters to improve performance by altering connection weights
repeat many times and reevaluate
approximates target function
Backpropagation
feed input and get output
oracle compares actual output to target output
compares discrepancy (error) between target/actual
Reduce error and repeat
Principles of Connectionism
biological plausibility - should be based of the brain
parallel computation - brain = many units working at the same time
distributed knowledge - all info is on the weights (spread)
1 universal learning model - 1 mechanism for all parts
Symbol System vs Connectionism
Symbol System - rationalist/nativist
brain uses rules with symbols
different learning mechanism
some knowledge is innate
Connectionism - empiricist/associationism
rules/symbols = epiphenominon
1 general mechanism
all knowledge is learned
Long Term Potentiation
how one synaptic connection excites another
Excitatory: raising excitatory weight
Inhibitory: raising inhibitory weight
Deep Learning
more layers with a huge database for training
Is it like human learning?
yes - induction/neural network
no - need billions of examples and is bad at generalizing
Reasoning (prescriptive vs descriptive)
going from premises (existing beliefs) to conclusions
Prescriptive - how should reasoning work?
Descriptive - how does reasoning work
Induction
“squirrels like nuts, squirrels are like badgers, badgers like nuts”
plausible not objectively valid
Thomas Bayes: we can quantify degree of belief as probability “common sense calculations
Deduction (Modes of Deduction)
Modus Ponens: If A then B, if A is true, B is true
Modus Tollens: If A then B, B is false, A is false
A → B (A is antecedent and B is consequent)
Probable Modus Ponens: P(AIB) is high = P(B) is high
Probable Modus Tollens: P(AIB) is low = P(B) is low
Wason Selection Task
Vowel on one side # on the other
Cards say: U K 4 7
most people want to flip U and 4
Logically you should flip U and 7
If under 18 you have to drink coke
most people want to check under 18 and wine drinkers
logically you should flip under 18 and wine drinkers
Conclusion: humans are not very good at reasoning, deductions aren’t always useful, many inferences we make are not deduction
Probabilities
P(A) = probability that A is true (true is 1, false is 0, P(A) = between 0-1)
P(-A) = 1 - P(A) probability of not A is the probability of 1-P(A)
P(A and B) - probability that A and B are true
Conjunction Rule: probability of A and B has to be greater than 0 and less that P(A)
P(A V B) - probability of A or B
Disjunction Rule: probability of A or B is greater than the P(A) but less than 1
Conditional Probability / Reasoning
P(AIB) = probability of A given B is true
P(AIB) = probability of A and B / Probability of B
P(AIB) x P(B) = P(A and B)
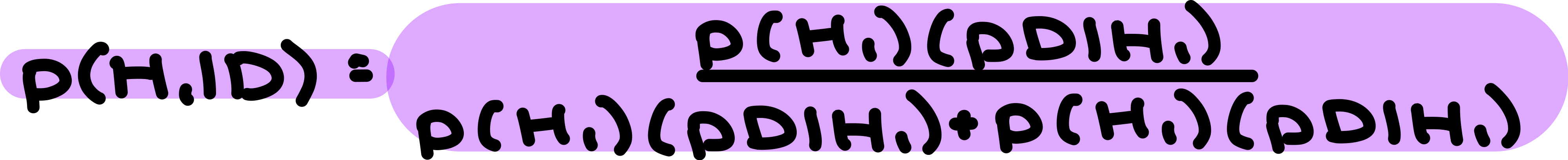
Bayesian Inference
allows you to compute how strongly to believe H as a function
form beliefs in an optimal way, normative reasoning, objectively correct
Likelihood - degree which H fits evidence
Prior Probability - how likely H before evidence
Posterior Probability - probability of H given D

Are People Bayesian? (Conjunction Fallacy)
Economics - people make optimal use of information acting in own rational self interest → Bayesian!
Conjunction Fallacy: more people are likely to say Linda is a feminist and bank teller rather than just a bank teller
subset should be smaller than the whole thought
Perhaps perception is but cognition isn’t but its still highly debated

Representativeness Heuristic
Heuristic: approximate strategy for problem solving thats easier than optimal strategy
In this scenario subjects typically say 80% because people ignore the prior
people dont use bayes rule but instead use heuristics and biases
Prescriptivists: this kind of reasoning is genuinely defective
Adaptive Strategies: heuristics work well in real ilfe

Fallacies
Law of small numbers - people use small representations to draw conclusions
Hot Hand fallacy - one side of the coin is hot so p(H) is more than 50%
Gamblers Fallacy - HHHHHTHHHH tails is due so P(T) is more than 50%
Expected Value
long run average value (EV=sum of xp(x))
50% chance of one inch of rain
0.5×1+0.5×0 =0.5 inches
The rational price of a bet is its expected value
Subjective Utility
how desirable something is to someone
Maximizing expected utility is how people make decisions

Risks and Risk Aversion
Do you pick 100% chance of $10 or 50% chance of $20
expected values are the same
Risk Aversion: preference for certain gain over chance of loss
50% chance of $20 or 99% chance of $12
EV 1 = $10 EV 2 = $10.88
Temporal Discounting
Do you want 90% chance of $11 now or 90% chance of $15 in a year?
Most people choose the first option because subjective devaluation of future value
Preference Reversals
if you prefer A to B it shouldn’t matter the other choices
You have a choice between chocolate, german chocolate, and vanilla, you prefer chocolate but you are scared because of similar option so you go with vanilla
Allais Paradox - offered 50% of $100 or 100% of $50 people choose 2 even though both EVs are $50;
however they want 5% of $100 instead of 10% of $50 even though they are the same too
Framing Effects
changing the wording of a question to alter decisions
You have 600 people on a sinking ship do you
save 200 or kill 400? Same thing hahaha
Sunk Cost Fallacy
continuing to invest in something due to the resources you have previously spent on it
past should not impact your choice but the framing of the past does
Bounded Rationality
humans are rational but limited in terms of info, time, comp resources
Satisficing: choosing the first acceptable pick or deciding based on one issue only
Chomsky vs Skinner
Skinner
humans learn language via reinforcement
Chomsky
infinite compositionality and productivity proves that Skinner was wrong
not all sentences have been said… so how could they be reinforced?
“colorless green ideas sleep furiously” makes no sense but is still valid
all leads to an abstract rule system which makes up grammar
Ape Language
Skinner - if correct apes should be able to learn ASL
Chomsky - if right they shouldn’t be able to because they need innate structures
Result: apes can learn vocab but they learned little syntax
Competence vs Performance
Competence: abstract knowledge held by a competent speaker, what you implicitly know about distinguishing between languages
Performance: how this works in practice, actual mechanisms for carrying out speech/hearing
Prescriptivist vs Descriptivist
Prescriptivist: rules tell you how to do language correctly “don’t split infinitive”
Descriptivist: rules tell you how its actually done
Universal Grammar
all natural languages have common structures which are innate (Chomsky)
all have words and sentences
all have nouns, verbs, and other parts of speech
systematic variations of each other (SVO, SOV, OSV)
how to form a question (insert SV, Auxiliary verbs)
which words modify the others (the boy with the dog was happy)
Is Language Innate?
humans have unique ability to learn language without overt instructions
some aspects of language have a critical period
Poverty of the Stimulus - linguistic input isnt enough for a child to learn rules of a language
Im going to eat lunch → im gonna eat lunch
Im going to New York → Im gonna New York
Only universal grammar is innate while specific details have to be learned
Subjects in Linguistics
Phonology - study of sounds (consonants, vowels, variations)
Morphology - construction of words out of units that carry meaning (morphemes)
Syntax - ordering words to form sentences (grammar)
Semantics - meaning and logical form
Pragmatics - practical aspects of conversation (what did someone mean? what do i say next?)
Syntax
abstract rules for legal sentences that sound normal and make sense to a native speaker
generative grammar - produces all and only the legal structures in the given language
ex. rewrite rules: The dog chased the cat. The tree chased the cat. The noun chased the cat
Recursion adds an extra adjective every time you do it
Tone localization experiments confirm “psychological realities” of boundaries
Syntactic Ambiguity/Garden Path Sentences
sentences can be parsed i 2 or more ways
ex. “the girl hit the dog with the stick”
Garden Path Sentence - principle of minimal attachment
ex. “the cotton shirts are made from comes from Alabama.”
Phonology
Sounds of a language; individual sounds = phonemes
“Tooth” = /t/oo/th
English has 44 phonemes
Phonological Parameters
Manner of Articulation - stop (p,b,t,d) or fricative (f,s,th)
Place of Articulation - bilabial (p,b) or labiodental (f,v)
Voicing characteristics - voiced/voiceless (f/v, s/z, th/th)
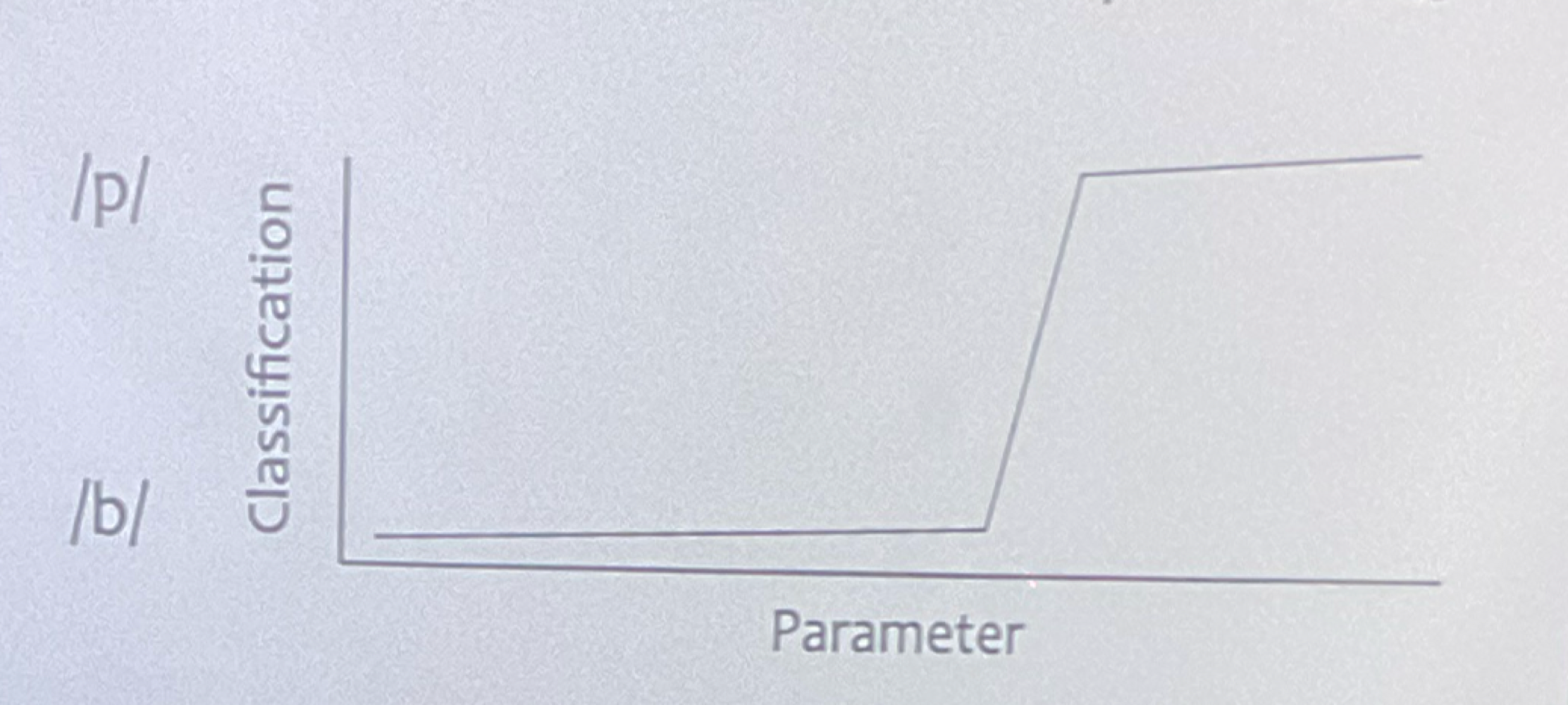
Categorical Perception
elevated sensitivity to sensory differences across categorical boundaries
In continuous categories (color spectrum) people see categories instead of one fluid scale
after critical period - can hear distinction between categories but not within
Semantics
lexical semantics - accessing mental lexicons
ex. man gave woman a hand → knowing meaning
Reference
the man ate the sandwich he made (he and the man corefer)
the man looked at him in the mirror (the man does not refer to him)
Locigcal Form
the boss takes her coffee with sugar
she usually takes it with sugar OR she is currently drinking coffee with sugar
Everyone has a cell phone
all people share 1 phone OR all people have their own phone
Phrase Semantics
brick house/rabbit house
house made of bricks vs a house where rabbits live
Implicature: inferred propositions that are understood as premises
Where in England did he visit implied that he visited England
Do you beat your wife on Sundays implied that you beat your wife other days
Morphology
pieces of words that carry meaning (tense, gender, number)
roots, prefixed, suffixes
Cat+s = 2 morphemes
Potato = one morpheme
re+paint+s = 3 morphemes
Past Tense War
Morphological Rule - add -ed
talk → talked (+1 sound)
aid → aided (+1 syllable)
bug → bugged (d sound)
Lots of exceptions: is/was go/went read/read but not need/needed
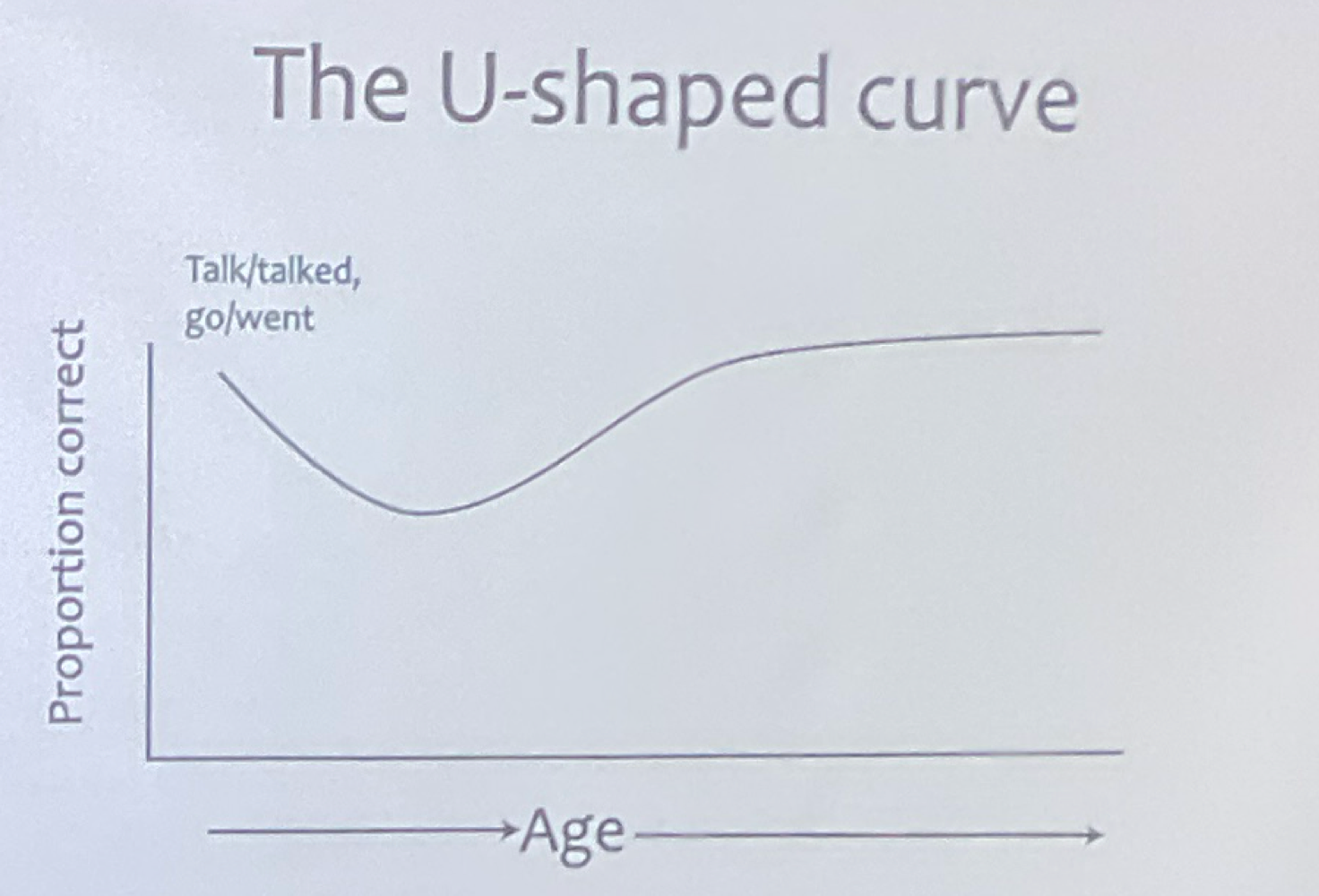
U shaped Curve and Over-regularization
Overregularization: child learns the rules and over-applies it as the learn the exceptions
this is why there seems to be a dip in childs progress of language learning
Wug Test: today I wug, yesterday I _____
any common speaker can pass this test
Pinker + Price’s Rebuttal
Network generalizes incorrectly
some make mistakes no kid does (squat → squakt; mail → membled)
cant handle homophonous verbs (fly/flew; but flied out)
Mis ordering issue and rigged U shape curve (regulars first - irregulars later when its actually a mix of both)
Past Tense Neural Network
input/output by backpropagation on surface forms
no rules, no morphemes, no distinction (1 mechanism)
application of a general mechanism
replicated U shaped learning curve