ch 2: personality assessment, measurement & research design
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
what is the structured self-report (S-data)?
responses are set…
dichotomos (i.e., forced-choice)
likert-ratings
what is the unstructured self-report (S-data)?
responses are not set…
open-ended questions
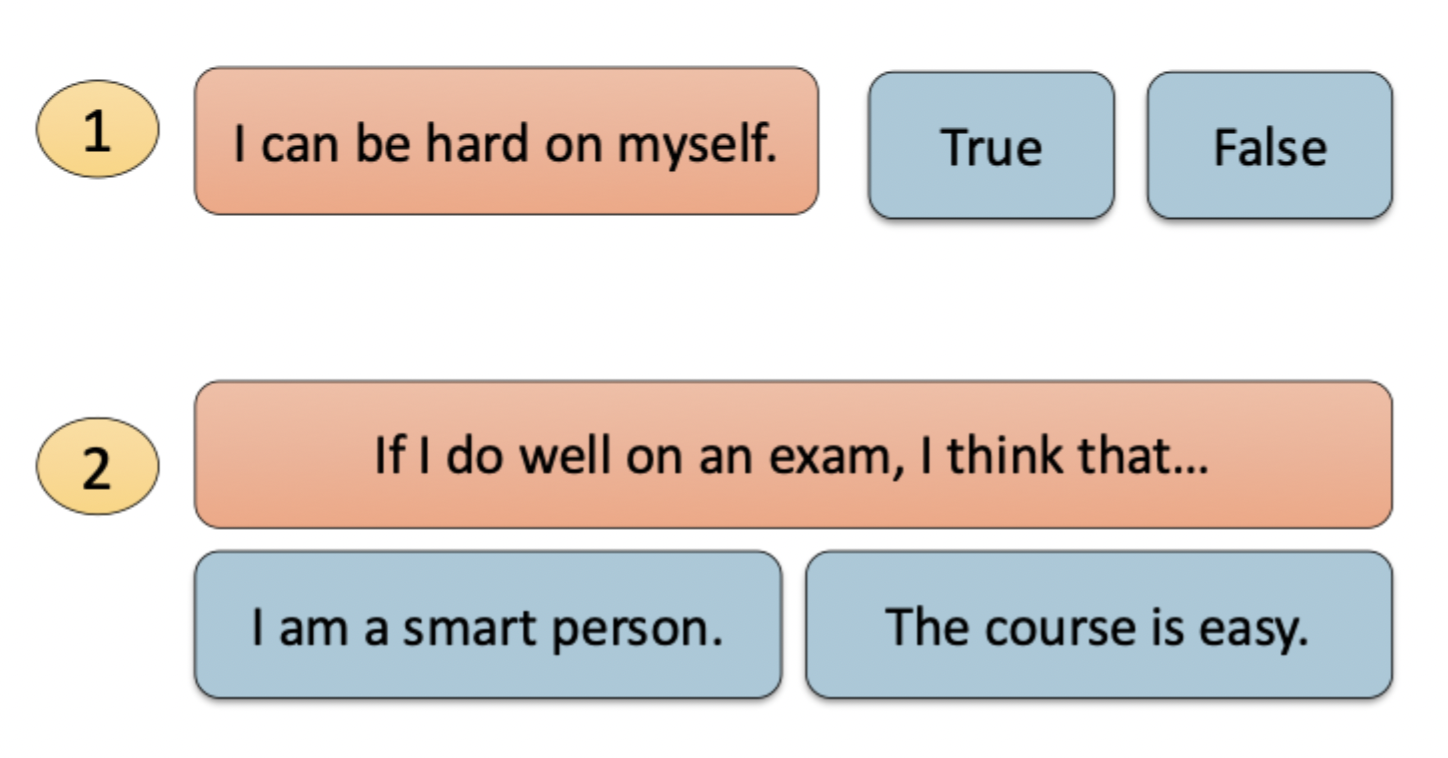
what type of source of data is this?
dichotomous response schemes

what type of source of data is this?
likert rating
what are the pros and cons of structured?
pros
standardization
use of stats
cons
limits in responses
possible limited accuracy
what are the pros and cons of unstructured?
pros
detailed
no limits to responses
cons
may not be standardized
use of statistics may be limited — but research can be qualitative
what are limitations of self-report data?
honesty in responses
not having self-knowledge/objectivity
what are other s-data approaches?
event-sampling → ecological momentary assessment
self-report that occurs over time to assess variables that might change in ‘real-time‘
what was the methods in Kranzler et al., 2017?
mobile tracker app, 2-weeks
intensity of thoughts about self-injury
occurences of self-injury
state-level emotions before and after engaging in self-injury
what were the key findings in Kranzler et al., 2017?
increased negative emotions and decreased positive emotions predicted intensity of self-injury thoughts
increased negative emotions predicted engagment in self-injury
after self-injury, participants reported decreases in intense negative emotion and increases in relief
what were the implications in Kranzler et al., 2017?
self-injury is driven by the need for emotion regulation (coping)
focusing on emotion regulation is likely critical in intervention
what is observer (o-data)?
involved gathering data from other individuals (i.e., not the self)
pros: access to unique data and multiple informants
cons: objectively AND respondents may not be able to infer internal processes (e.g., feelings)
where is o-data collected?
naturalistic setting → observations in a natural, real-life setting
artificial setting → observations that occur in settings created to resemble a real-life setting
what are test (t-data)?
utilizes standardized testing situations to determine aspects of personality
mechanical recording
physiological data
projective tests
what are the limitations to test data?
participants may ‘guess‘ the trait being assessed & create an impression
participants & researchers may view the testing situation differently
the influence of the researcher(s) on the participant(s)
what is reliability?
whether data reflect the true level of what is being measured
consistency of measurement
what are the types of reliability?
test-retest → scores of a measure correlate on repeated measures
internal consistency → items on 1 measure correlate with each other
inter-rater → rating of 1 observer correlates with those of another
what are response sets (impacts reliability…)?
response tendency that is unrelated to item content
acquiescence
extreme responding
social desirability
what is validity?
degree to which a test measures what it claims to measure
what are the types of validity?
face → whether it appears to measure what it should
predictive (criterion) → whether the test predicts criteria it is supposed to
convergent → whether the test correlates with other, similar, tests
discriminant → refers to what the measure should not correlate with
construct → includes all types of validity — broader in scope
what is generalizability?
whether a measure retains validity over different contexts/samples
what are the research designs in personality?
experimental methods
correlational studies
case studies
what are experimental methods
used to determine causality
two main requirements
independent variable is manipulated to affect the dependent variable
participants are equivalent (via random assignment)
what are correlational studies?
used to understand if 2 (or more) variables share a relation
correlation coefficient
indicates direction & degree of relation
range: -1 to +1
limitation
directionality (no causation)
third variable