Rural Urban Divide Exam 2
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
How many countries have mandatory voting?
22
What is the UN declaration of rights?
Consists of 30 articles detailing basic human rights and fundamental freedoms
Inspiration for many countries
What is the concept of Legal Social Inclusion and exclusion?
How citizenship is defined, rights for whom?
What is Social inclusion?
Access to the activities and social connections necessary to maintain a meaningful life.
Knowledge and awareness of rights
Ability to participate in society
Income and social class
Social networks
Culture capital.
The prevention of access to resources like
Decent housing
civic activities
local amenities
common consumer goods
cultural activities
social relationships
financial products
Can be defined as ________.
Social exclusion.
What are American Territories, and how many inhabited territories do we have?
Areas that are within the united states, but people inside of them are not full fledged citizens, i.e.Puerto Rico. 5 are inhabited.
What are some characteristics of American territories?
3.62 million people, 90% in Puerto Rico
Self governing
Treated as part of the U.S. but not completely
All are american citizens (EXCEPT Samoa)
U.S. Nationality but not citizenship unless one parent is a U.S. citizen
Non-Voting representative in Congress
Over the past 10 years, from which area did most undocumented immigrants in the U.S. originate?
Central America
What is an Immigrant?
A person who from one country to another with intent to remain there.
What is an Asylum Seeker?
A person who moves to another country in search of protection against being prosecuted for crimes.
What is a Refugee?
A person who moves countries to escape violence.
What is a Temporary proceeded status?
A person who is already within a country that can’t return to their country of origin due to varying circumstances.
What are Push factors?
Cons of staying in a certain country, i.e. war, bad economy, low education
What are Pull factors?
Benefits to moving to a different country, i.e. good economy, benefits, higher education
What is a Stereotype?
Beliefs about individuals based on membership in a social group, broad generalizations.
What is Prejudice?
Attitudes and feeling about an individual or group; resistant to change even with new information.
What is Discrimination?
Positive or negative behavior toward others. (actions.)
What is the Age Discrimination in Employment Act?
Made in 1967, protects individuals who 40 and older?
What is Cultural Capital?
Our tastes, knowledge, attitudes, languages, and ways of thinking that we exchange in interaction with others.
Mobility based inequality, being unable to get where you need to go safely and timely is defined as ________.
Transportation disadvantage and insecurity.
According to the article by Ward and Walsh on transportation disdavantage, what was a primary approach used by people who did not have access to a car?
Staying home.
According to the article on transportation disadvantage by Ward and Walsh, what area of travel research has been neglected?
Impacts on social networks.
Information not written about, disseminated or widely forgotten is defined as _______.
Forgotten history.
What is Redlining?
A discriminatory practice that consists of the systematic denial of services such as mortgages, insurance loans, and other financial services to residents of certain areas based on their race or ethnicity.
What were the Freeway Revolts?
The movement in 1960’s against government efforts to build highways through cities, homes and neighborhoods being torn up.
True or False? Due to Rights of Nature protests in the 1960s, the Olentangy River was not moved as planned during the construction of the Highway 315 freeway north and west of campus.
False
Which of the following is a main concern of California residents living near the wildfire areas?
Proper precautions for hazardous waste removal will not be taken.
What is Zoning?
The division of land by local governments with a set of rules on how the land may be used. Can be used to protect resources, promote economic growth, control traffic, provide living space, and other purposes.
Residential
Commercial
Industrial
Agricultural
What is Exclusionary Zoning?
Laws that place restrictions on the types of homes that can be built in a particular neighborhood. Common examples include minimum lot sizes, minimum square footage requirements, prohibitions on multi family homes, and limits on the height of buildings.
What is Censorship?
Changing or suppression or prohibition of speech or writing that is deemed dangerous or unacceptable.
What is Gerrymandering?
Practice that began in 1789 at the first congressional election in the state of Virginia
Named after Elbridge Gerry
Every 10 years states redraw legislative and congressional district boundaries following the U.S. Census
Drawn to favor political parties
True of False? The practice of gerrymandering, in which Congressional district boundaries are drawn to influence the outcome of elections, started in the 1980's.
False, started late 1700’s
What is Bowling Alone?
Book by Robert D. Putnam, claims…
People not involved like in past
Not good for state of society or health and well being
Name comes from idea that people are not involved in bowling leagues like the past
Defines Social capital.
Blames Television
What are the main critiques of “Bowling Alone?”
1950’s baseline
Shift in form of civic participation
High rates of volunteering, informal helping, and charitable contributions
Grassroots organization by some groups
Attendance at sport events
Decline in crime rates
Ignores role of online communities.
True or False? Robert Putnam, in his book Bowling Alone, indicates that the "vibrancy of civil society" has decreased over the past few decades.
True
What is Social capital?
”Features of social organization such as networks, norms, and trust that facilitate coordination and cooperation for mutual benefit.”
Can be gained in two forms, Bridging and Bonding.
True or False? Different social classes likely have different levels and types of cultural capital.
True.
What is social capital Bonding?
focuses on connections among individuals and groups with similar backgrounds such as social class, ethnicity, gender
What is social capital Bridging?
connects diverse groups within a community to each other and to groups outside of a community. Fosters identity of ideas and understanding.
What are hypothesized causes of decline in social participation?
Most likely TV, but also women in workforce and in professional occupations, work life balance, commuting time and money.
What are the “Nones”?
A group of people that have no religious affiliation, number is growing rapidly.
True or False? The percentage of eligible voters who voted in all three recent U.S. elections (2018, 2020, and 2022) is 37%.
True
Of all ages, which group has the lowest voter turnout rate?
18-29 year olds
What are Putnam’s suggested solutions?
Educational reform, civics education, service learning, extracurricular activities, smaller schools
Workplace: Family oriented workplaces to build social capital
COmmunities: New urbanism
Religio: More influential and more tolerant
Art and Culture: More interactive
Politics: Campaign reform and decentralization of power.
What is a “Third Place,” and who coined this term?
Based on work of sociologist Roy Oldenburg, “Those homes away from homes where unrelated people relate”
According to Sociologist Roy Oldenburg, what is responsible for the loss of third places?
Suburbanization and development
What makes “Third Places” important?
Essential for a community's social vitality
Foundation of a functioning democracy.
Unify neighborhoods, integrate newcomers, intergenerational, places of political debate, mutual aid.
Name some reasons why the number of “third places” is declining.
Loses due to suburbanization, loss of independent business, chains and generic landscapes, commuting time.
What is a tertiary organization?
Members are free to come and go as they wish, Members give donations to organizations but have little other involvement, Members meet online.
What is/are listed in The Bygone Era Of Marshfield's Rural Taverns as possible reasons for the increased closure of taverns in Wisconsin? (select all that apply)
Ease of purchasing alcohol elsewhere, Decline in the number of farms, Changes to the drinking age, Changes in drunk driving Laws, and Increased operating costs
What is Ferdinand Tönnies known for?
Gemeinschaft vs Gesellschaft concept as a response to industrialization in late 1800’s
What is a Gemeinschaft model of society?
Close knit communities, rural life, people having similar backgrounds, sense of togetherness, little privacy. Social change limited and heavy social control.
What is a Gesellschaft model of society?
Impersonal mass society, modern urban life, people are strangers, relationships related to impersonal social roles, self interest dominates. More formal social control, rapid social change.
What is the U.S Surgeon General's Advisory on the Healing Effects of Social Connection and communities?
Strengthening social infrastructure in local communities (Fairs, taverns, organizations)
Enact Pro - Connection Public Policies (Government Policies)
Mobilize Health Sector - Aid in mental health issues
Reforming Digital Environments.
Deepen our Knowledge
BUild a Culture of Connection.
True or False? The Six Pillars of Social Connection, developed by former U.S. Surgeon General Vivek H. Murthy, has been criticized because it does not include technology and social media.
False
What are the three types of citizen participation?
Electoral, protest/complaint, problem solving.
Describe Electoral citizen participation.
Electoral - Group based campaigning, direct democracy.
Describe Protest/Complaint citizen participation.
Protest/Complaint - Group Based protest, neighborhood organization, lobbying/demand action, attending public hearings, boycotts. Individualistic contacting, voting with your wallet.
Describe Problem Solving citizen Participation.
Problem solving - Group volunteer work, raising awareness. Individual volunteer work, conversations with others, financial donations.
List five Forms of volunteer work.
Episodic - Only once and awhile
Short-term - Help on short term basis
Long-term - Help consistently and long term
Formal - May need to fill out forms
Informal - Just helping someone or something, not part of large organization.
Describe Benjamin Franklin’s role in citizenship.
Known for constitution and electricity
Advocated for better fire protection system
Started volunteering firefighter clubs
True or False? Volunteering in the United States is at a record high.
True
What is JFK’s famous quote about citizenship?
“Ask not what your country can do for you, but what you can do for your country.”
What is Citizen Participation?
Allows citizens to be deliberately included in planning processes. Sharing information, setting goals and policies, allocation of resources, and operating of programs.
What is Civic participation?
How citizens interact with each other
What is Political Participation?
How citizens interact with the government.
In a study of rural students (Martin & Chiodo), being a good citizen was most frequently associated with what?
Helping eachother and volenteering
According to Cao, _____ is central to environmental citizenship.
education
What is the goal of Environmental education, and who is associated with it?
to produce citizenry that is knowledgeable concerning the biospherical environment and its associated problems, aware of how to help solve these problems, and motivated to work toward their solution - William Stapp
Questions - Should it be about or for the environment? Does knowledge lead to action?
What are some examples of environmental education?
Brundtland report
Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit 1992
UN declaration on education for sustainable development
According to Cao, what are the four types of environmental citizens, and what is the description of each?
Personally responsible - Liberal citizenship, assume individual responsibility for the environment. DOMINANT
Participatory - Republican citizenship, participation with others in community-based activities; collective
Justice-oriented - Alternative types of citizenship, emphases on social justice.
Consumer citizen - Neoliberal citizenship
According to Cao, which is the most dominant type of environmental citizen?
personally responsible
According to Cao, which type of environmental citizen is becoming the most dominant?
Consumer
In the trial, Held v. State of Montana, what was the outcome?
The state lost and the decision was upheld.
Who was the influential person who defined environmental education as "producing a citizenry that is knowledgeable concerning the biospherical environment and its associated problems, aware of how to help solve these problems, and motivated to work towards their solution?"
William Stapp
What is The story of change?
Idea that we need to act as a community to change what the economy prioritized. By Annie Leonard.
Three parts: Big Idea, We, and Action
What are the eight types of change makers?
Investigators - People who study the issue
Communicators - People who raise awareness to the issue
Builders - People who provide support ot the cause and build a network of change makers
Resisters - People willing to quietly or loudly resist the issue
Networkers - Bring people together, facilitator
Nurturers - People who take care of others to make sure needs are meant
Innovator
Advocate
What are Public hearings?
Required by law. Some given rules, like speaking time limit and respectful language
On an array of topics, i.e Ballot issuers
What is Shareholder Activism?
Any effort by shareholders to communicate a need for change in a companies policy or management
What is a B corperation?
Measures a company entire social and environmental impact
What is the Arnstein Ladder of Participation?
Can be used across settings “nobodies” becomeing “somebodies”
Each run correlates to how much power the citizens have.
(From bottom to top)
—Non Participation—
Manipulation
Therapy
—Tokenism—
Informing
Consultation
Placation
—Citizen Power—
Partnership
Delegated Power
Citizen control
What is Harts ladder of children participation?
Coined by Roger A Hart
Ladder mortified and applied to the youth and children participation in different settings like schools, Organizations, Community develop and planning, Addressing climate and societal concernsdressing societal concerns
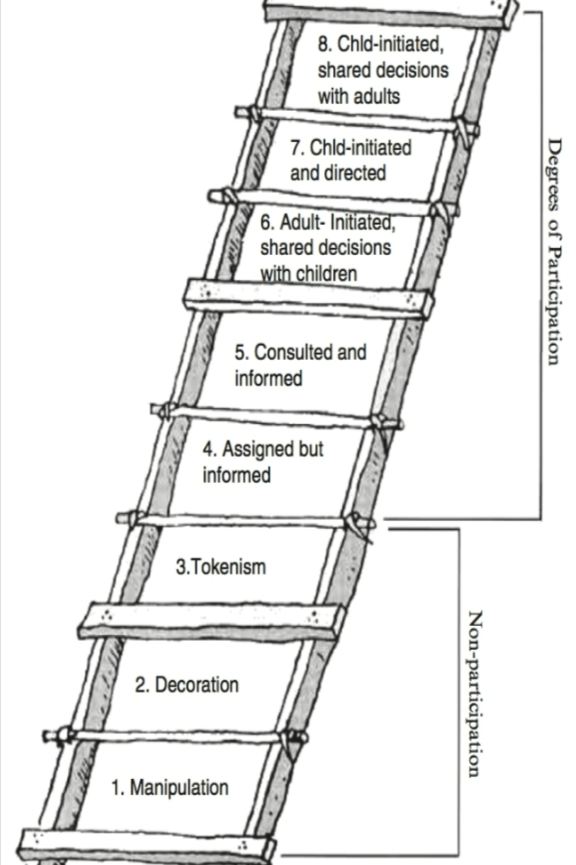
What is Tokenism?
“Those instances in which children are apparently given a voice, but in fact have little to no choice about the subject or the style of communicating it, and little to no opportunity to form their own opinions.” -Roger Hart
What are the benefits of a partnership?
“Partnerships can work most effectively when there is an organized power base in the community to which the citizen leaders are accountable; when the citizens group has the financial resources to pay its leaders reasonable honoraria for their time consuming efforts; and when the group has the resources to hire (and fire) its own technicians, lawyers, and community organizers...” (Arnstein, p. 221)
What is a Co-op?
A group of people who own parts of an organization. Purpose is to serve the community, not make a profit. Credit unions, electric, Green bay packers, etc.
A cooperative or co-op is a business that is owned and democratically controlled by the members who use its services. Cooperatives are found across the U.S. in nearly every sector of the economy.
What is citizen control?
Participants govern a program or institution, are in full charge of policy and managerial aspects, and are able to negotiate changes
• Food and other cooperatives
• Homeowners’ associations
• Lay led groups
• Student, community, and
• professional organizations
• May not always be ideal
What is Capacity building?
Expanding skills such as facilitation, leadership, media and communications, fundraising, organizing, project management, inclusion, outreach, and intercultural dialogue.
-European Youth Parliament
How many physical cooperative locations exist in Ohio?
1,088 mostly credit unions.
What are the green amendments?
the right of citizens to have a safe and healthy environment
Who plays a central role in advocating for rural communities in Other Side of the Hill?
Farmers and ranchers