Lecture 6: Price Controls, Taxes, and the Wellbeing of Consumers and Producers
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the government policies that change private market outcome?
The government policies tht change the outcome of private markets are:
Price Controls (like Price Ceilings and floors)
Taxes
Price Ceiling
A legal maximum on the price of a good or service
Ex. Rent Control
Price Floor
A legal minimum on the price of a good or a service
Ex. Minimum Wage
Taxes
The government can make buyers or seller pay a specific amount on each unit bought and sold
What is the equilibrium price and quantity of apartments without price controls?
The equlibrium quantity is 300 apartments and the equilibrium price is $800
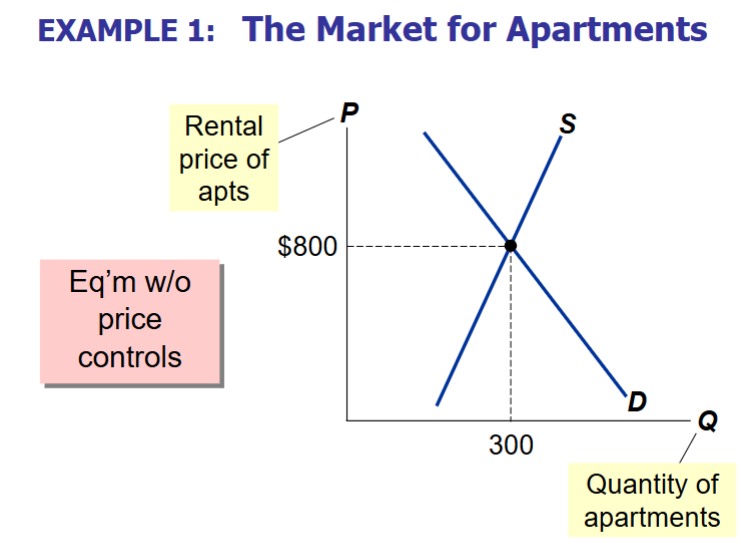
Is a price ceiling above the equilibrium price binding?
Price ceiling= a price maximum
A price ceiling above the equilibrium price has no effect on the market outcome
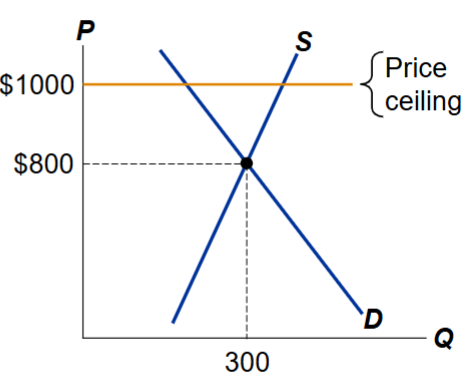
What happens when a price ceiling (maximum price) is below the equilibrium price?
If the equilibrium price is higher than the price ceiling, it is illegal
The ceiling= a binding constraint on the price, causes a shortage
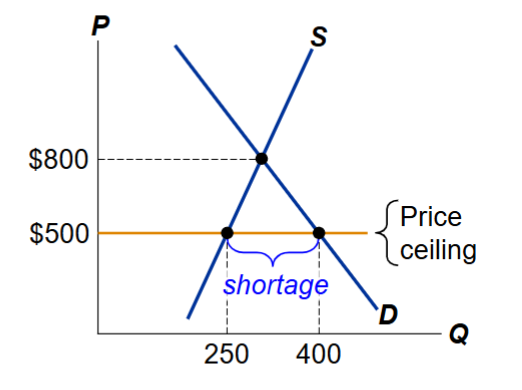
How is a price ceiling below the equilibrium price affected when supply and demand are elastic?
The shortage is larger with elastic supply and demand because both buyers and sellers change their quantities a lot when the price falls, widening the gap between quantity demanded and quantity supplied.
What is the equilibrium quanity of unskilled workers and the wages paid to unskilled workers without price controls?
The equilibrium quantity of unskilled workers is 500 workers and the wage is $4
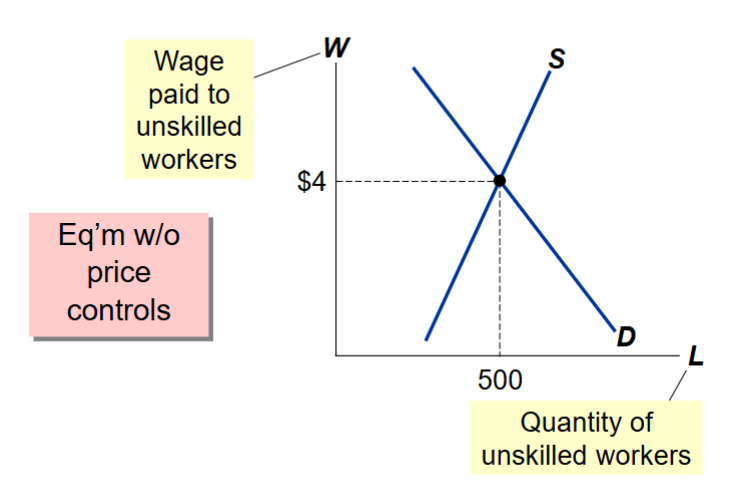
How does a price floor below the equilibrium price affect the market outcome?
A price floor (minimum) below the equilibrium price is not binding and has no effect on the market outcome
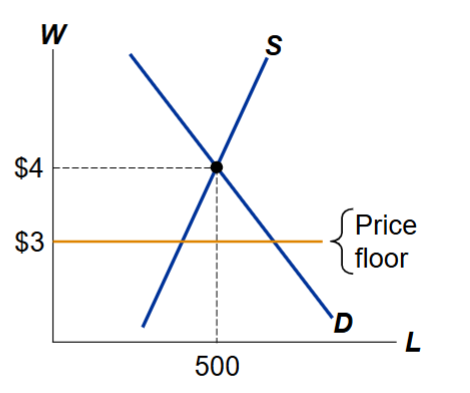
What happens if the price floor (minimum) is above the equilibrium wage?
If the price floor is above the equilibrium, then there is a surplus of labor
More supply of labor than demand for labor
The floor causes a labor surplus (ex. unemployment)
Who pays taxes?
The government makes buyers or sellers pay taxes
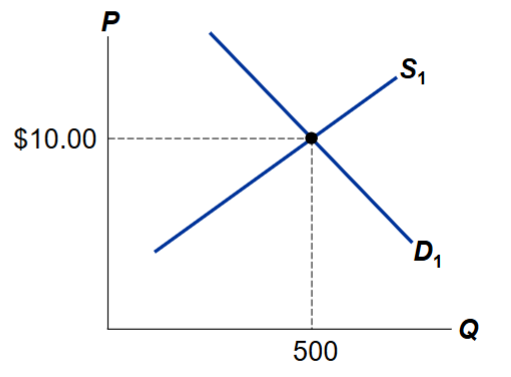
What is the equilibrium for the market for pizza without tax?
The equilibrium quantity for pizza without tax is 500 pizzas, while the equilibrium price is $10
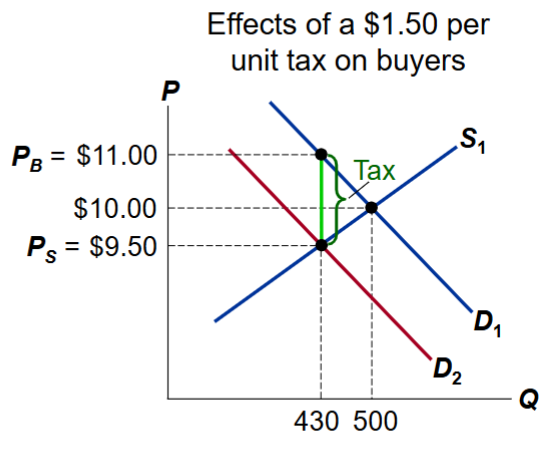
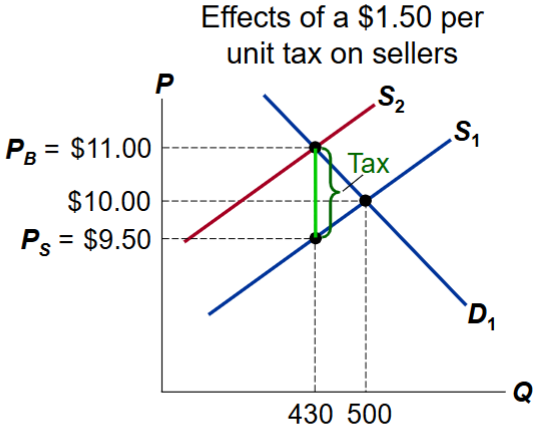
How does a 1.50 per unit tax on buyers affect the market for pizza?
The buyer’s demand decreases by $1.50
The [price buyers pay rises to $11
The price seller receive falls to $9.50
Equilibrium Q falls
How does a 1.50 tax affect sellers?
A tax on sellers shifts the S curve up by $1.50
The price buyers pay rises, the price that sellers receives falls, equilibrium quantity falls
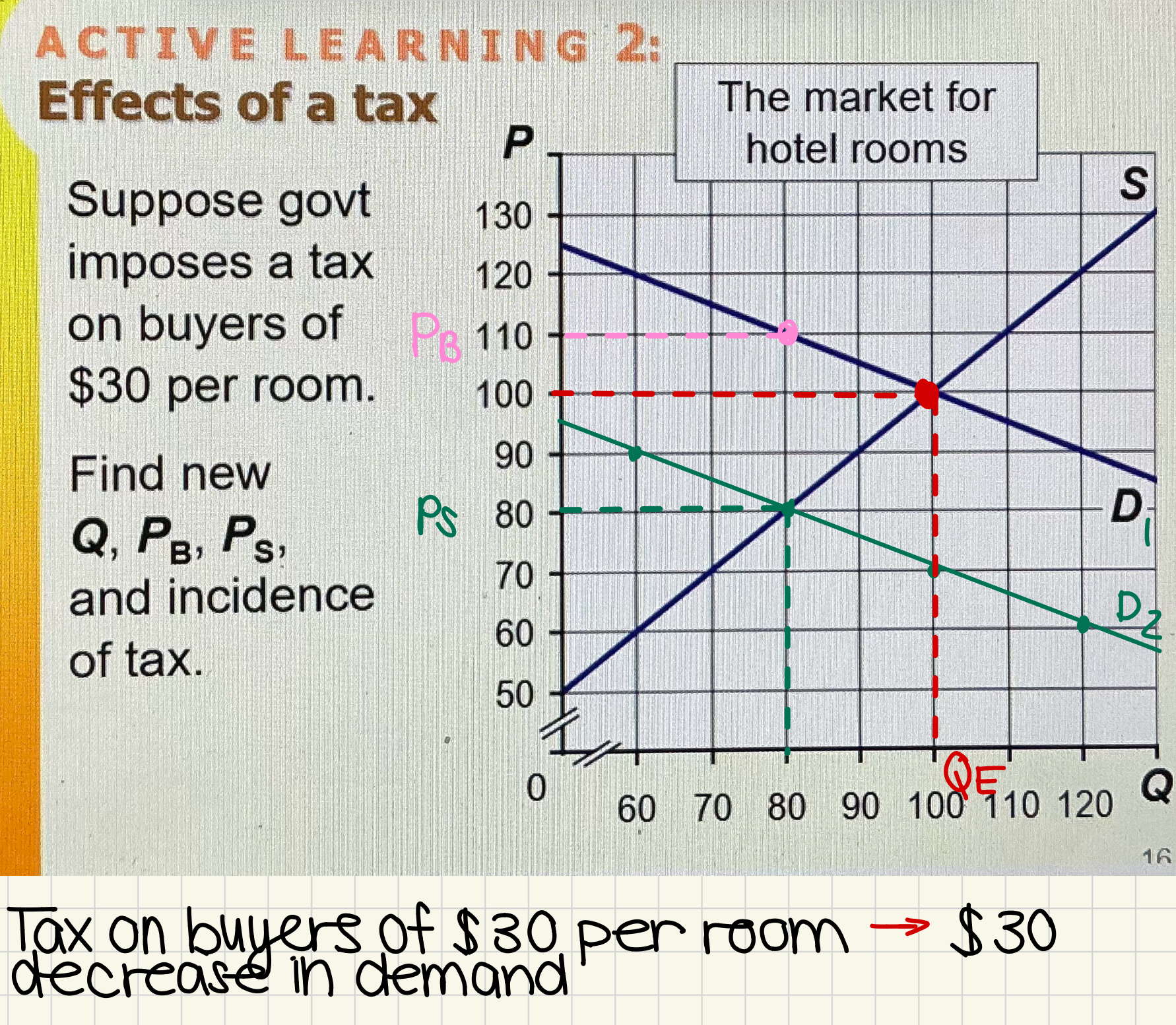
Ex. Effects of tax on a market for hotel rooms
Government imposes a tax on buyers of $30 per room
Demand curve shifts by $30, each point on the curve
Find points where Q and D1 and Q and D2 intersect to get the price that buyers and sellers pay
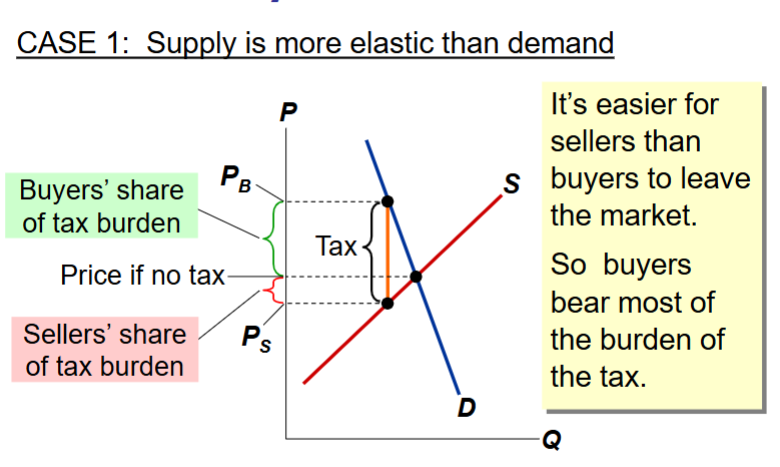
Who bears more of the tax, when supply is more elastic than demand?
When supply is more elastic than demand:
Sellers can easily change quantity, so they avoid the tax burden by reducing supply
Inelastic demand → buyers are not very sensitive to price changes, so they continue buying even when the price rises.
Because buyers don’t cut quantity much, they end up absorbing more of the tax as a higher price.
Easier for sellers to leave the market than buyers
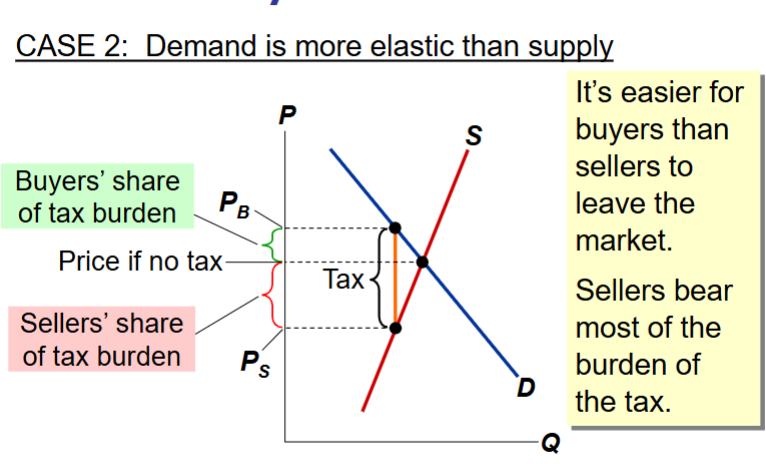
Who bears more of the tax when demand is more elastic than supply?
When demand is more elastic than supply:
Elastic demand → buyers reduce quantity a lot if the price rises, so they avoid most of the tax burden.
Inelastic supply → sellers cannot easily reduce quantity, so they end up absorbing the tax through a lower price they receive.
Sellers bear most of the tax burden, since it is easier for buyers than sellers to leave the market
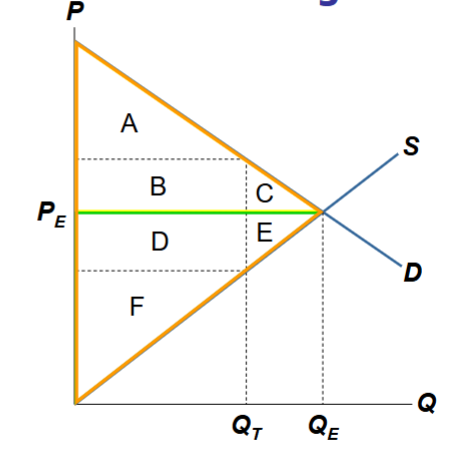
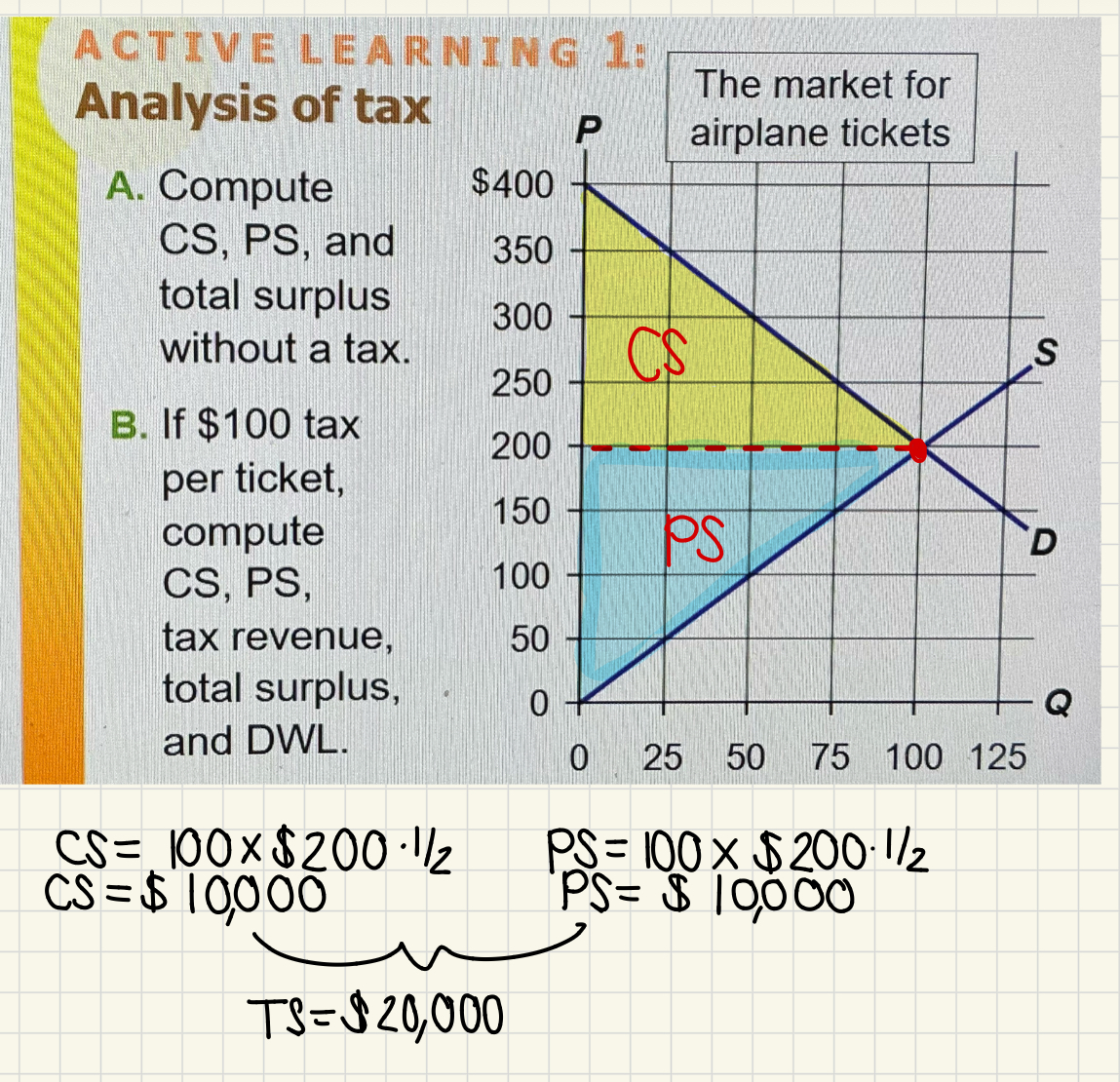
What is the total surplus and tax revenue in this supply and demand diagram without taxes?
Without a tax:
CS = A + B + C
PS= D + E +F
Tax Revenue is 0
Total Surplus= CS + PS = A + B + C + D + E + F
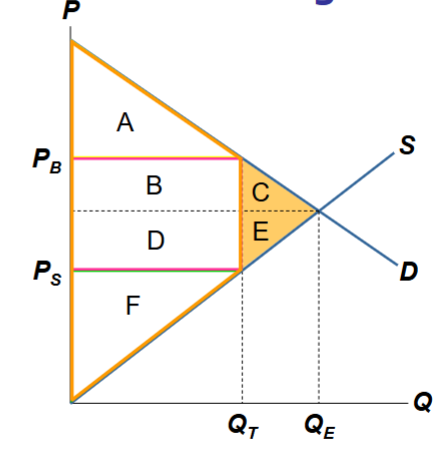
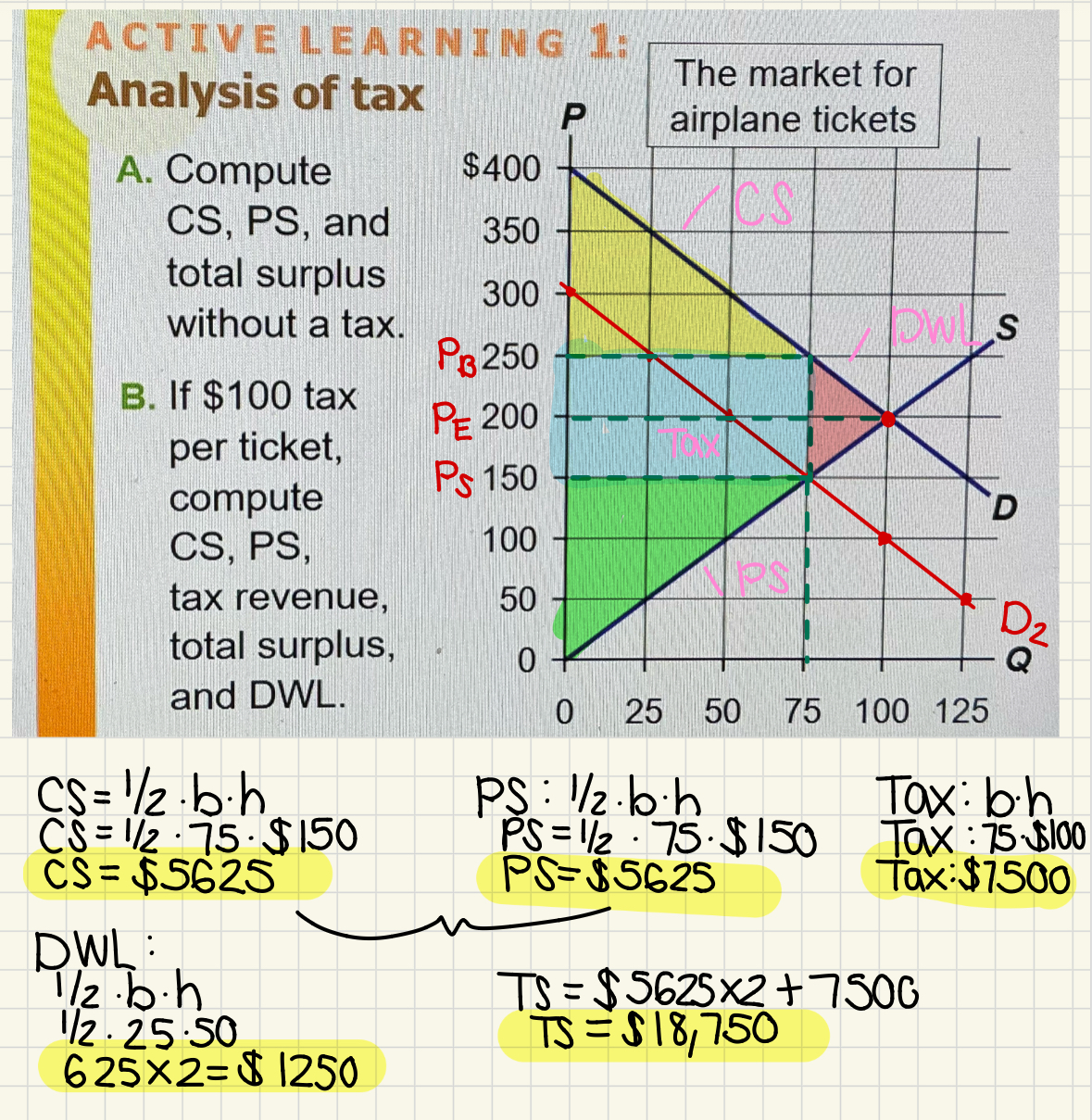
What is the tax revenue and total surplus with a tax
With a tax:
CS= A
PS= F
Tax Revenue: B + D
Total Surplus: A + B + D +F
Tax reduces the total surplus by C+ E
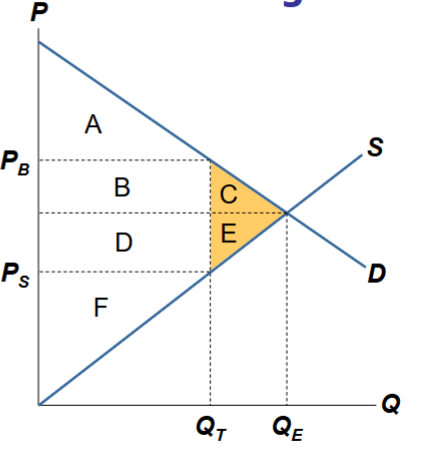
Deadweight Loss
The fall in total surplus that results from a market change, such as a tax
Ex. C + E
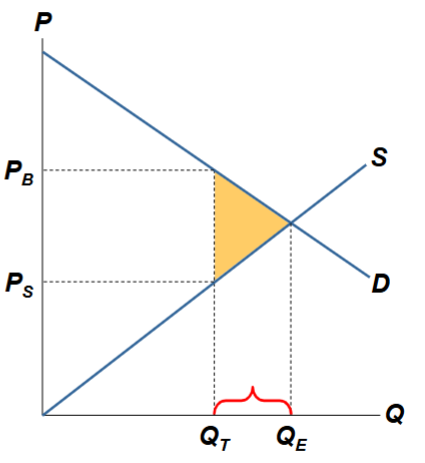
Because of the tax, what quantity isn’t sold in this market?
Because of the tax, the units between QT and QE aren’t sold
Value of the units to the buyers is greater than the cost of producing them
Tax prevents some mutually beneficial trades
Tax Analysis Example (Pre and after tax)
Why is the DWL small when supply or demand are inelastic?
DWL is small when demand or supply are inelastic:
Buyers or sellers don’t change quantity very much when the price changes.
The tax reduces quantity only a little.
Only a tiny triangle of lost trades appears → small DWL
How does a tax distort the market outcomne?
A tax changes the market outcome, since:
Consumers buy less, producers sell less, and the market Q is below the surplus maximizing Q
What does elasticity do in terms of taxes?
Elasticity measures how much buyers and sellers respond to a change in price
Determines how much the tax affects the market
Would the DWL of a tax be larger if the tax were on
Rice Krispies or sunscreen?
DWL would be larger on Rice Krispies than sunscreen, which have a very elastic demand, meaning that the demand is sensitive to a change in price
As a result, the tax will reduce the quantity signficiantly, leading to more DWL
Would the DWL of a tax be larger on
Hotel rooms in the short run or hotel rooms in the long run?
Hotel rooms in the long run are more elastic than the short run, since the supply can change more easily with time, so suppliers are more responsive to a change in price and can change the quantity of hotel rooms
As a result, a tax would decrease the quantity of hotel rooms in the long run, leading to more DWL
Would the DWL of a tax be larger?
On groceries or meals at fancy restaurants
Meals at fancy resturants have an elastic demand, since they are not necssities. As a result of this, consumers are very responsive to a change in price
When a tax is implemented, the quantity of meals at fancy restaurants drops significantly, leading to more DWL than a tax on groceries
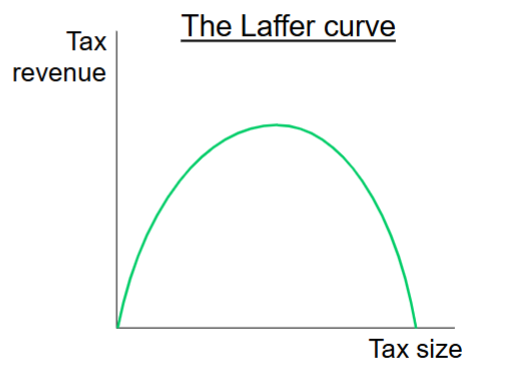
What happens when a tax is small and you increase it?
When a tax is small and it’s increased, tax revenue rises
The tax per unit is larger
Quantity traded in the market only falls a little (demand and supply haven’t reacted much yet)
This corresponds to the rising part of the Laffer curve.
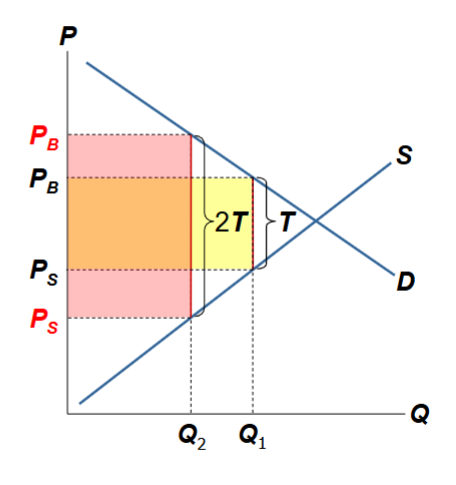
What happens when tax is large and increased?
When the tax is larger, increasing it causes the tax revenue to fall
Discourages trade
The tax creates a large difference between what buyers pay and what sellers receive.
This makes the good much more expensive for buyers and less profitable for sellers.
Quantity traded falls
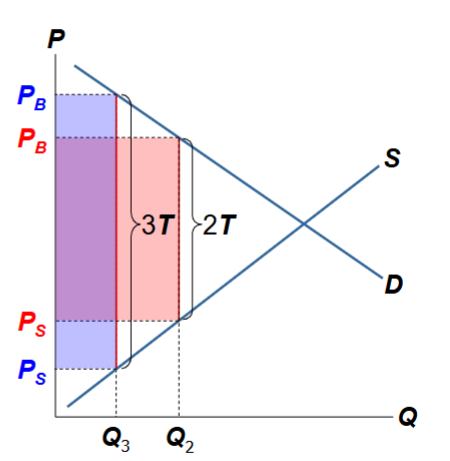
Laffer Curve
Curve that shows the relationship between the size of the tax and tax revenue
As tax rates rise, government revenue first increases, then decreases after a certain point because high taxes discourage work and trade