Phenols
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Phenols are often used as what?
Antiseptics and disinfectants
What is the overall reaction for the bromination of phenol?
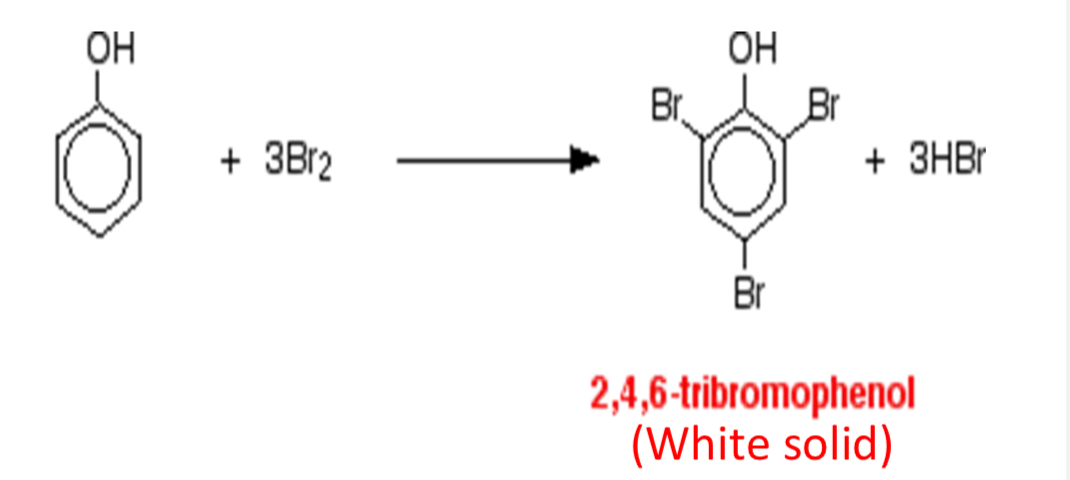
What are the observations for the bromination of phenol? How does this compare to benzene?
Orange solution to a white solid/ precipitate in a colourless solution
Benzene: orange solution to colourless solution
What are the reaction conditions for the bromination of phenol?
Room temperature and pressure
NO halogen carrier
Why is phenol bromination at the 2 and 4 position?
The hydroxyl group is a 2 and 4 directing group
Why is a halogen carrier required for the bromination of benzene but not phenol?
Phenol is more reactive than benzene: has a higher electron density
The lone pair on oxygen from the hydroxyl group in phenol is delocalised into the ring
The hydroxyl group can activate the aromatic ring which increases its electron density
Phenol is able to induce a dipole in bromine:
ELECTROPHILE IS MORE POLARISED
What is the overall reaction for the nitration of phenol?
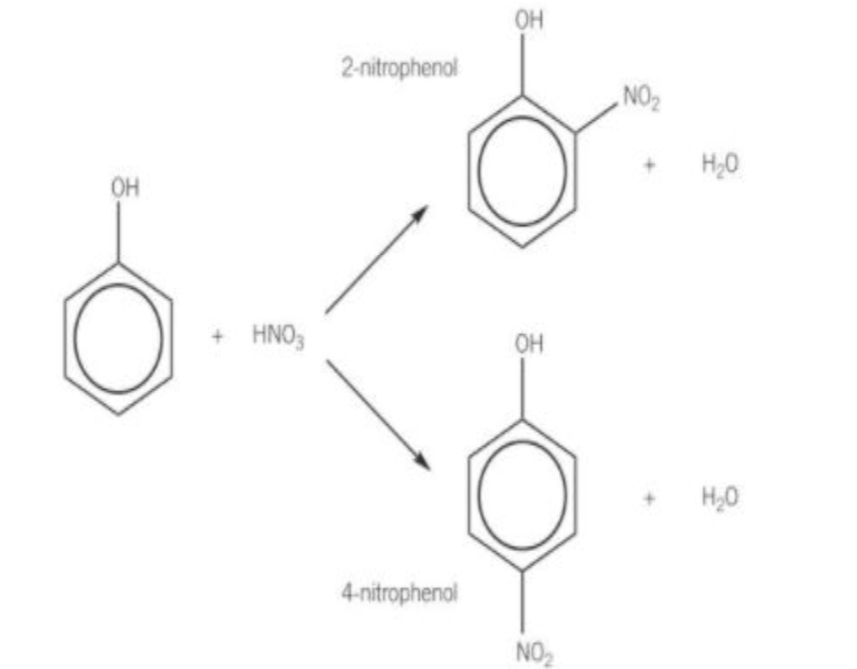
What are the reaction conditions for the nitration of phenol?
Room temperature and pressure
DILUTE nitric acid
No sulfuric acid
Why doesn’t trisbustituion take place when phenol is nitrated?
Nitro group is a deactivating group
Nitro group reduces the electron density of the aromatic ring by drawing π electrons from the aromatic ring towards it
The aromatic ring is less susceptible to electrophilic attack
Why is phenol partially soluble in water?
The hydroxyl group can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
The aromatic ring is non-polar so can’t form hydrogen bonds with water
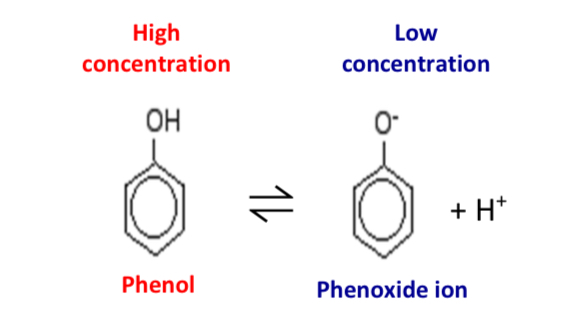
What is the observation when universal indicator is added to phenol? Why?
Orange colour
Phenol is a weak acid
It partially dissociated in aqueous solution: higher concentration of phenol that the phenoxide ion
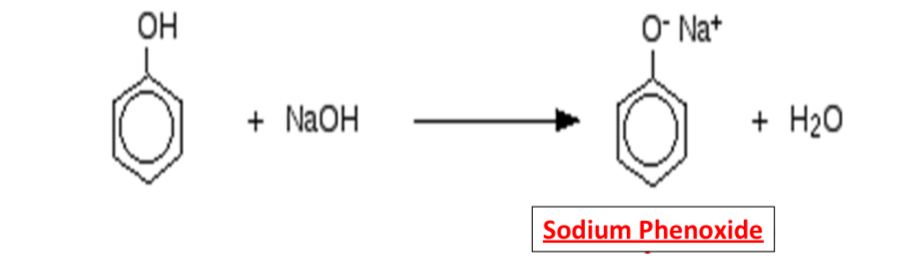
What is the observation when phenol reacts with NaOH? Why?
Phenol completely dissolves
Soluble salt and water is formed
What is the equation for the partial dissociation of phenol?
What is the equation for the reaction between phenol and NaOH?
Why can’t phenol react with weak bases? What are examples of weak bases?
Since it is a very weak acid
E.g sodium carbonate or calcium carbonate
How acidic is phenol compared to alcohols and carboxylic acids?
Phenol is more acidic than alcohols but less acidic than carboxylix acids
How do you test for phenol?
indicator - orange
no reaction with carbonate
OR
bromine water - white precipitate in a colourless solution