Assessment 2: CH 7-10
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Explain why and how microbes undergo phase variation. Which of these statements is incorrect?
None
Microbes undergo phase variation to change their immunological appearance.
This occurs in the microbe by slipped strand mispairing mutation.
Phase variation gives rise to immuno avoidance.
None
Describe the genome and chromosome structure of prokaryotes. Which of these is incorrect?
Their chromosomes are stored in a membrane-bound nucleous.
All but one
Their chromosomes are organized using histone-like proteins.
The genome structure of prokaryotes have single circular chromosome located in the nucleoid.
All but two
A prokaryote's genome can be composed of multiple chromosomes.
All but two
Define metagenomics and describe its applications. Which of these is incorrect?
Metagenomics can be applied to medicine, agriculture, and ecology.
It studies a collection of microbial genomes.
All but two
Metagenomics is the use of modern genomic techniques to study microbial communities directly in their natural environments.
All but one
It studies the whole genome of a type of microbe.
It studies the whole genome of a type of microbe.
Describe how mutants help researchers answer biological questions.
Mutants help researchers answer biological questions by answering how microbes make antibiotics without killing themselves, what happens when cells divide, and why some species sporulate. Collectively, these studies are called functional genomics.
True/False
True
Outline the steps of PCR.
The steps of PCR require the design of specific oligonucleotide primers that anneal to known DNA sequences flanking the DNA you want to amplify.
These primers are then used to replicate the target DNA.
The PCR reaction mixture then undergoes repeated cycles of heating (denaturing of DNA), cooling (annealing of primer to single-stranded DNA), and heating (extension of new DNA strands) again.
List the functions of quorum sensing systems. Which of these is incorrect?
All but two
They re used for the formation of biofilms.
They are used for bacterial transformation
They are used for expressing the virulence property of a microbe.
None
Quorum sensing systems are used to synthesize, secrete, and respond to extracellular accumulation of small autoinducer signaling molecules.
All but one
None
Outline the mechanism and regulation of bacterial chromosome replication.
The replication begins at the origin.
Replication bubble then forms, and replication fork progresses in opposite directions.
One strand at each fork is then synthesized.
Second strand at each fork is then synthesized.
Replication then ends at terminus.
Distinguish horizontal gene transfer and vertical gene transfer.
[A] is the passage of genes from parent to offspring through reproduction. [B] is the passage of genes from one genome into another, non-progeny genome.
[A] Vertical gene transfer [B] Horizontal gene transfer
Compare the three mechanisms that give rise to horizontal gene transfer. Use one of these keys: Conjugation; transduction; transformation.
[A] is the uptake by living cells of free-floating DNA from dead, lysed cells. [B] is a DNA transfer process mediated by a transferable plasmid that requires cell-cell contact and formation of a protein complex between mating cells. [C] is the process in which bacteriophages transfer fragments of bacterial DNA from one bacterium to another.
[A] Transformation [B] Conjugation [C] Transduction
Summarize the ways plasmids ensure inheritance.
Plasmids ensure inheritance by transduction.
Plasmids ensure inheritance by transduction, transformation, or conjugation.
Plasmids ensure inheritance by transformation.
Plasmids ensure inheritance by making copies of themselves before the bacterial cell divides.
Plasmids ensure inheritance by conjugation.
Plasmids ensure inheritance by making copies of themselves before the bacterial cell divides.
Describe the structure and functions of the RNA polymerase holoenzyme components. Which of these is correct?
It initiates the translation of a RNA template strand.
All but two
RNA polymerase holoenzyme components consist of core RNA polymerase and a sigma factor.
It initiates the transcription of a DNA template strand.
It initiates the transcription of a RNA template strand.
All but two
Define horizontal gene transfer.
Horizontal gene transfer is the natural movement of genes between species or genera.
True/False
True
Propose why some genes have regulated expression but others have constitutive expression. Use one of these keys: constitutive expression; regulated expression.
Some genes have [A] in order to save cellular energy. [B] genes are always being expressed and don’t worry about saving cellular energy.
[A] Regulated expression [B] Constitutive expression
Describe how proteins are purified via affinity chromatography.
Proteins are purified via affinity chromatography by fusing the gene encoding the protein to a DNA sequence encoding a peptide tag that strongly binds a particular small ligand molecule.
True/False
True
Compare DNA repair mechanisms. Use of these keys: error prone repair; error proof repair
Some repair mechanisms are [A] and do not introduce mutations. Others are [B] and require emergency DNA polymerases expressed under dire circumstances.
[A] Error proof repair [B] Error prone repair
State the enzymatic activity, cellular role, and biotechnology applications of restriction endonucleases. Which of these is correct?
A piece of DNA cut from one organism’s chromosome could be grafted to a plasmid cut with the same restriction endonuclease.
All but one
All but two
All
Proteins rid themselves of foreign DNA through restriction endonucleases.
Restriction endonucleases used for DNA analysis cleave DNA at specific recognition sequences, which are usually 4-6 bp in length and produce either a blunt or a staggered cut.
Type III restriction endonucleases recognize the palindromic sequence of DNA nucleotides.
All but one
Define transcription.
Transcription is the copying of DNA to protein.
True/False
True
List 2 examples of applied biotechnology. Which of these is correct?
One example of applied biotechnology is the directed use of microorganisms for the manufacture of organic products.
Another example is using naturally present bacteria by the mining industry in bioleaching.
The process of making insulin by using microorganisms.
The process of making antibiotics by using genetically engineered strains of microorganisms.
All
All but one
All but two
All
Summarize what occurs in each of the three stages of transcription. List them in the correct sequence.
In initiation, the RNA polymerase binds to the beginning of the gene, melts open the DNA helix, and catalyzes placement of the first RNA nucleotide. In elongation, the sequential addition of ribonucleotides to the 3’ OH end of a growing RNA chain. In termination, sequences at the end of the gene trigger release of the polymerase and the completed RNA molecule.
In initiation, the RNA polymerase binds to the beginning of the gene, melts open the DNA helix, and catalyzes placement of the first RNA nucleotide. In termination, sequences at the end of the gene trigger release of the polymerase and the completed RNA molecule. In elongation, the sequential addition of ribonucleotides to the 3’ OH end of a growing RNA chain.
In initiation, the RNA polymerase binds to the beginning of the gene, melts open the DNA helix, and catalyzes placement of the first RNA nucleotide. In elongation, the sequential addition of ribonucleotides to the 3’ OH end of a growing RNA chain. In termination, sequences at the end of the gene trigger release of the polymerase and the completed RNA molecule.
Compare and contrast insertion sequences and transposons.
[A] are simple transposable elements consisting of a transposase gene flanked by short inverted-repeat sequences that are targets of the transposase. [b] are more complex than simple insertion elements because they carry other genes in addition to those required for transposition.
[A] Insertion sequences [B] Transposons
Describe the mechanisms cells use to sense and respond to conditions within the cell and outside the cell membrane. Which of these is used to sense and respond to conditions within the cell and outside the cell membrane?
repressor and activator proteins
Small regulatory RNAs
regulatory proteins
All but one
integrated control circuits.
gene rearrangement controls
All
All but two
two-component signal transduction systems
All
Compare and contrast the genomes of archaea, bacteria, and eukaryotes.
Both [A] generally only have a single circular chromosome. [B] on the other hand, have multiple, linear chromosomes.
[A] Archeae and bacteria [B] Eukaryotes
State the purpose of PCR.
The purpose of PCR is to amplify one copy of a gene into millions more in a very short amount of time.
True/False
True
Compare and contrast generalized recombination and site-specific recombination.
[A] requires that the two recombining molecules have a considerable stretch of homologous DNA sequence. [B] on the other hand, requires very little sequence homology between the recombining DNA molecules, but it does not require a short sequence recognized by the recombination enzyme.
[A] generalized recombination [B] site-specific recombination
Recall the various ways gene expression can be controlled and assess the advantages and disadvantages of each. Which of these is incorrect?
With transcription, genes in an operon are coordinately regulated by protein repressors, activators, and sigma factors, as well as by small RNAs; thus expressing genes efficiently and quickly.
With mRNA stability, RNase activity can degrade some mRNA molecules as fast as they are transcribed.
With posttranslational control, RNA activity can be controlled.
None
Gene expression can be controlled at several levels and they are at the alteration of DNA sequence, transcription, mRNA stability, translation, and posttranslational control.
With alteration of DNA sequence, the switch in protein structure helps the microbe evade a host’s immune system.
With translational control, “fine-tuning” of operon control is used.
With posttranslational control, RNA activity can be controlled.
Differentiate gene, operon, and regulon.
A(n) [A] is a distinct series of nucleotides within DNA that has a distinct function or whose product has a distinct function. A(n) [B] is a collection of genes that are in tandem on a chromosome and are transcribed into a single RNA. A(n) [C] is a group of genes and operons located at different positions in a genome that are coordinately regulated and share a common biochemical function.
[A] gene [B] operon [C] regulon
Recall the functions of DNA control elements and structural genes.
[A] work to produce a functional an RNA molecule. [B] work to regulate the expression of a structural gene.
[A] Structural genes [B] DNA control elements
Recall the possible fates of foreign DNA that enters a bacterial cell and factors that favor specific fates. Which of these is incorrect?
The foreign DNA may be degraded by the host nucleases.
None
Factors that favor specific fates are their DNA structure and whether or not the DNA is capable of autonomous replication.
The foreign DNA may be incorporated into the chromosome through recombination.
All but two
Foreign DNA that enters a bacterial cell can coexist in the cell separate from the host chromosome.
All but one
None
Explain how sigma factors help control gene expression. Which of these is incorrectly stated?
Sigma factors help control gene expression by binding to RNA polymerase through the beta and beta-prime subunits.
None
The bound sigma factor helps the core enzyme detect a specific RNA sequence, called a promoter, marking the beginning of a gene.
Sigma factors help control gene expression by binding to RNA polymerase through the beta and beta-prime subunits.
Define mutation and explain how mutations arise. Which of these is correct?
Mutations arise from there being a change in the base sequence and the cell failing to repair the change before the next round of replication.
All but two
All
Mutations could take place artificially.
A mutation is any permanent, heritable, alteration in a DNA sequence, whether harmful, beneficial, or neutral.
All but one
Mutations could take place spontaneously.
All
Describe the structure and function of DNA restriction and modification systems. Which of these statements is correct?
It uses nuclease to degrade foreign DNA.
All but one
It is made of two components, namely, the endonuclease and methylase proteins.
It uses methylase to protect self DNA
All but two
DNA restriction and modification systems protect bacteria from invasion by foreign DNA.
All
All
Recall the functions of the different RNA classes. Use one of these keys: catalytic RNA; messenger RNA; ribosomal RNA; small RNA; transfer mRNA; transfer RNA.
[A] encodes proteins. [B] forms the scaffolding on which ribosomes are built. [C] ferry amino acids to the ribosome. [D] is used to regulate the stability of translation of specific mRNAs into proteins. [E] has properties of both tRNA and mRNA. [F] is usually associated with proteins in which enzymatic activity actually resides in the RNA portion of the complex rather than in the protein.
[A] Messenger RNA [B] Ribosomal RNA [C] Transfer RNA [D] Small RNA [E] Transfer RNA [F] Catalytic RNA
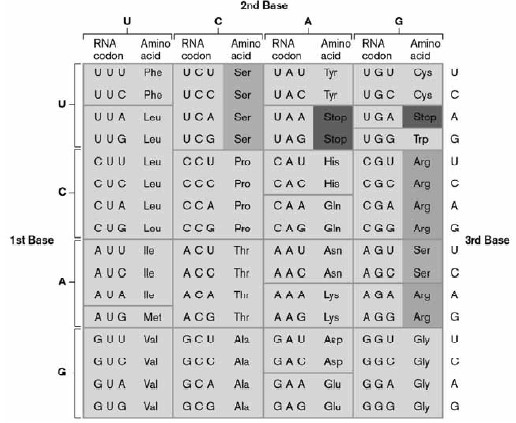
Multiple choice. Using the genetic code shown below, find the correct start and stop codons. Which of the following peptides might this message code for?
5'-GAGUUAUGCACGGGUUCUAUGUGUAG-3'
MET-GLY-SER-MET-CYS
ASP-VAL-TYR-LEU-GLY-TYR-VAL-LEU
MET-HIS-GLY-PHE-TYR-VAL
GLU-LEU-CYS-MET-GLY-SER-MET-CYS
MET-CYS-ILE-LEU-GLY-THR-TYR
MET-HIS-GLY-PHE-TYR-VAL
Summarize how quorum sensing systems produce effects.
Quorum sensing systems produce effects by accumulating a secreted small molecule called an autoinducer.
True/False
True
State the tasks performed by the CRISPR-Cas9 system
The CRISPR-Cas9 system programs a synthetic csRNA to direct Cas9 endonuclease to a specific eukaryotic gene and manipulates microbial gene expression in the intestine. In other words, it is used to introduce mutations.
True/False
True
Summarize what occurs during each of the three stages of translation. List the stages in the correct order.
During initiation, the small ribosomal subunit binds to the start of the mRNA sequence. In termination, the ribosome reaches a stop codon. During elongation, the ribosome continues to translate each codon in turn.
During initiation, the small ribosomal subunit binds to the start of the mRNA sequence. During elongation, the ribosome continues to translate each codon in turn. In termination, the ribosome reaches a stop codon.
During initiation, the small ribosomal subunit binds to the start of the mRNA sequence. During elongation, the ribosome continues to translate each codon in turn. In termination, the ribosome reaches a stop codon.
Differentiate northern blot, real-time PCR, and southern blot.
[A] is used to analyze the presence, size, and processing of a specific RNA molecule in a cell extract. [B] is used to detect specific DNA instead. [C] uses fluorescence to monitor the progress of PCR as it occurs.
[A] Northern blot [B] Southern blot [C] Real-time PCR
List possible protein delivery locations in a bacterial cell. Which of these is correct?
the extracellular surroundings
the periplasm
the outer membrane
All
the inner membrane
All
Explain why bioinformatics is a key tool for microbiologists. Which of these is incorrect?
It helps with the determination of an unknown protein.
It is an interdisciplinary field that combines computer science, mathematics, and statistics.
It helps with the determination of a microbial strain (virulence vs avirulence strain).
It helps with the determination of an unknown microbe.
It helps with the determination of an microbial genus and species.
All but one
None
All but two
None
Define an operon and explain why it assists gene regulation. Which statements is correct?
It assists gene regulation because they allow the cell to efficiently express sets of genes whose products are needed at the same time.
It requires multiple sigma factors
All
It requires multiple promoter regions.
All but two
All but one
An operon is a group of genes co-transcribed from a common promoter.
All but two
Define synthetic biology and state some applications.
Synthetic biology applies engineering principles to design and construct new biological parts for a desired purpose. Some applications of that are using engineered strains of microbes for antibiotic and insulin manufacturing.
True/False
True
Recall the purpose of a western blot.
It is used to examine gene regulation by detecting the protein products.
True/False
True
Compare and contrast the DNA protection assay and the electrophoretic mobility shift assay.
[A] examines protein interactions with DNA. [B] reveal the bases in a DNA sequence protected by a DNA-binding protein.
[A] Electrophoretic mobility shift assay [B] DNA protection assay
Describe the two ways plasmids can replicate. Which of these is correct?
Plasmids can replicate by rolling-circle or bidirectional mechanisms.
Plasmids can replicate by transduction and heat-shock transformation.
Plasmids can replicate by conjugation and transformation.
Plasmids can replicate by rolling-circle or bidirectional mechanisms.
Categorize different types of mutations. Use one of these keys: insertions; inversion; point mutation; reversion.
A(n) [A] is a change in a single nucleotide. [B] involve the addition and subtraction of one or more nucleotides. A(n) [C] results when a fragment of DNA is flipped in orientation relative to DNA on either side. A(n) [D] restores a sequence altered by mutation to its original sequence.
[A] Point mutation [B] Insertions [C] Inversion [D] Reversion
Describe the mechanisms that deliver proteins to the correct locations in a bacterial cell. Which of these is correct?
N-terminal amino acid signal sequences
secB protein
All
All but 3
the general secretory system
All but two
the signal recognition particle
the twin arginine translocase
Type I secretion systems.
All
Describe different types of horizontal gene transfer. Which of these is correct?
All but two
Transformation can be done naturally or artificially.
All
Conjugation is performed via cell-to-cell interaction.
Transduction is performed using viral particles.
Heat shock transformation is an example of artificial transformation.
Streptococcus pneumonia can be transformed naturally using the self-produced competence factor.
All