Anatomy Unit B
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
fuel for cells
Carbs, lipids, proteins
carbohydrates
sugars (saccharine), glycogen, starch, cellulose, provide energy, store energy, spare protein, prevent ketosis
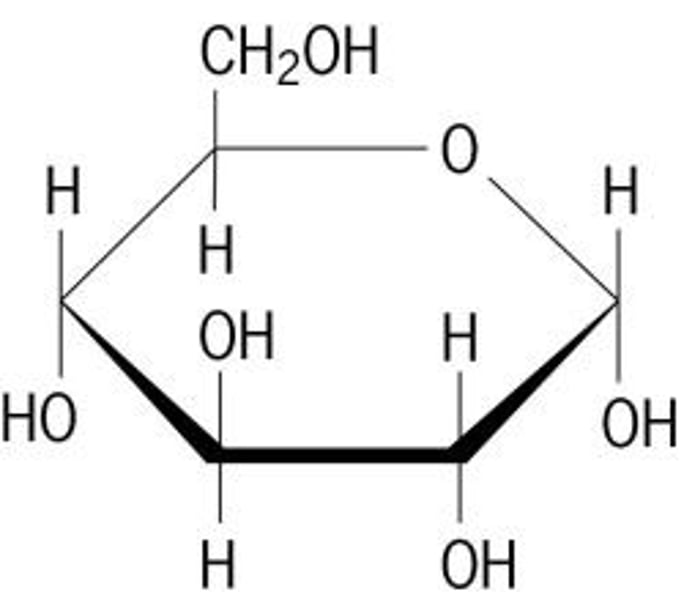
Monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, deoxyribose
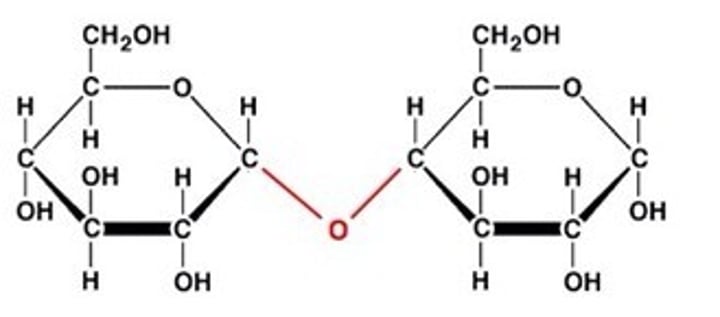
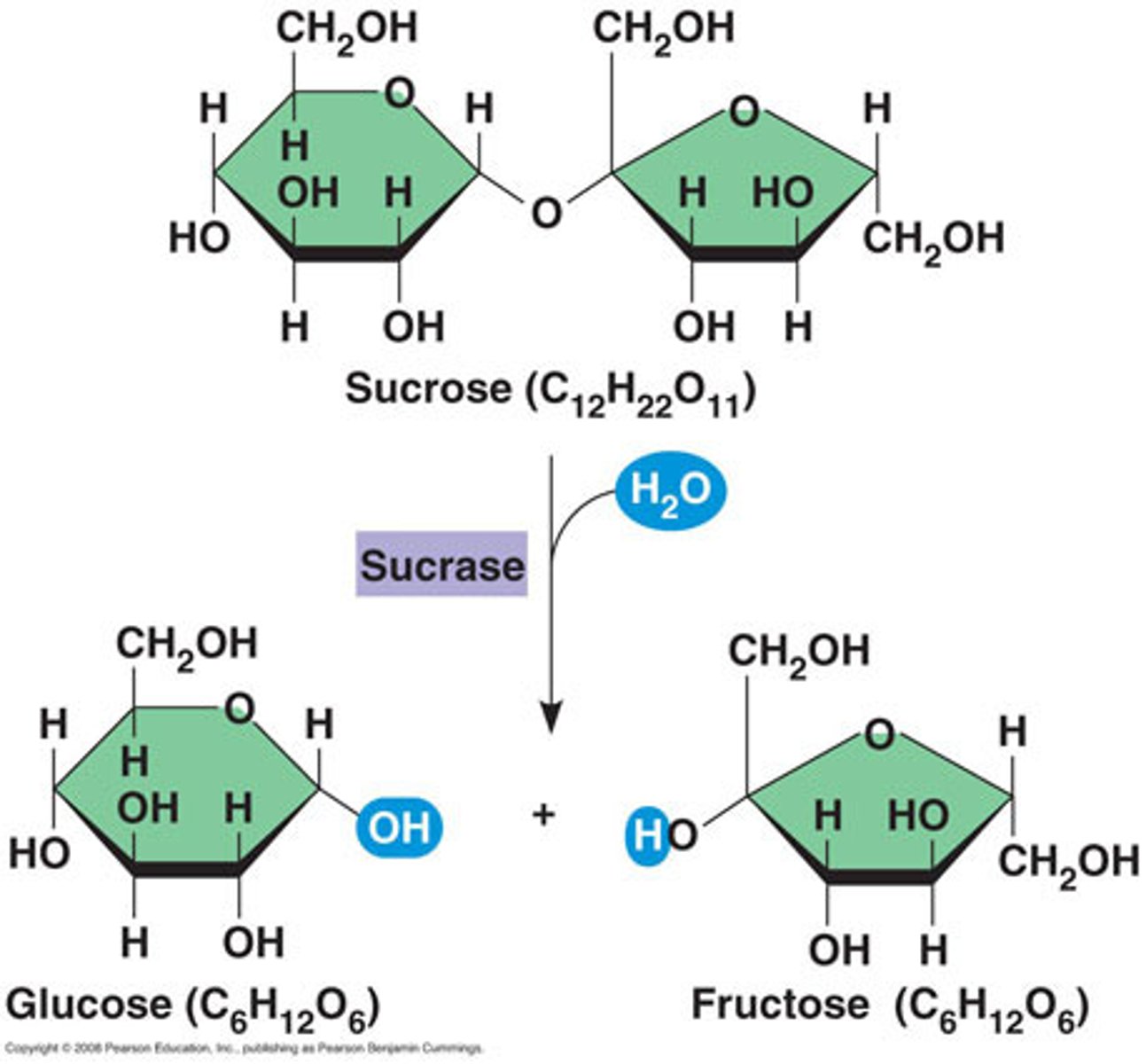
disaccharide
sucrose, lactose, maltose
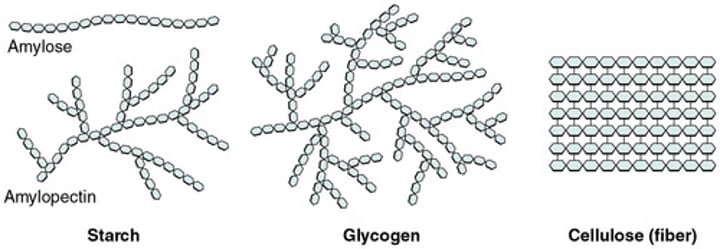
polysaccharides
glycogen, starch, cellulose
dehydration synthesis
removal of water and the bonding of building blocks; pulling out water to build something
A+B -> AB
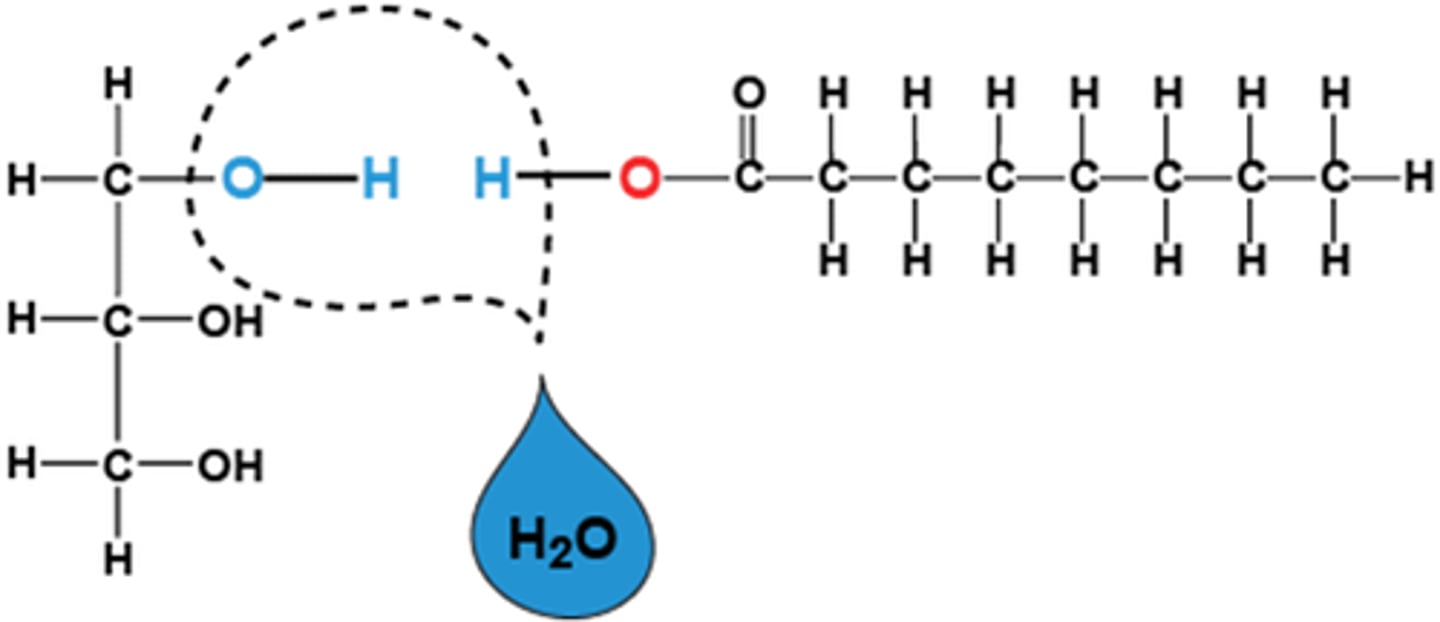
hydrolysis decomposion
adding water to break a bond
AB -> A+B
types of lipids
triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, eicosanoids, lipoprotiens
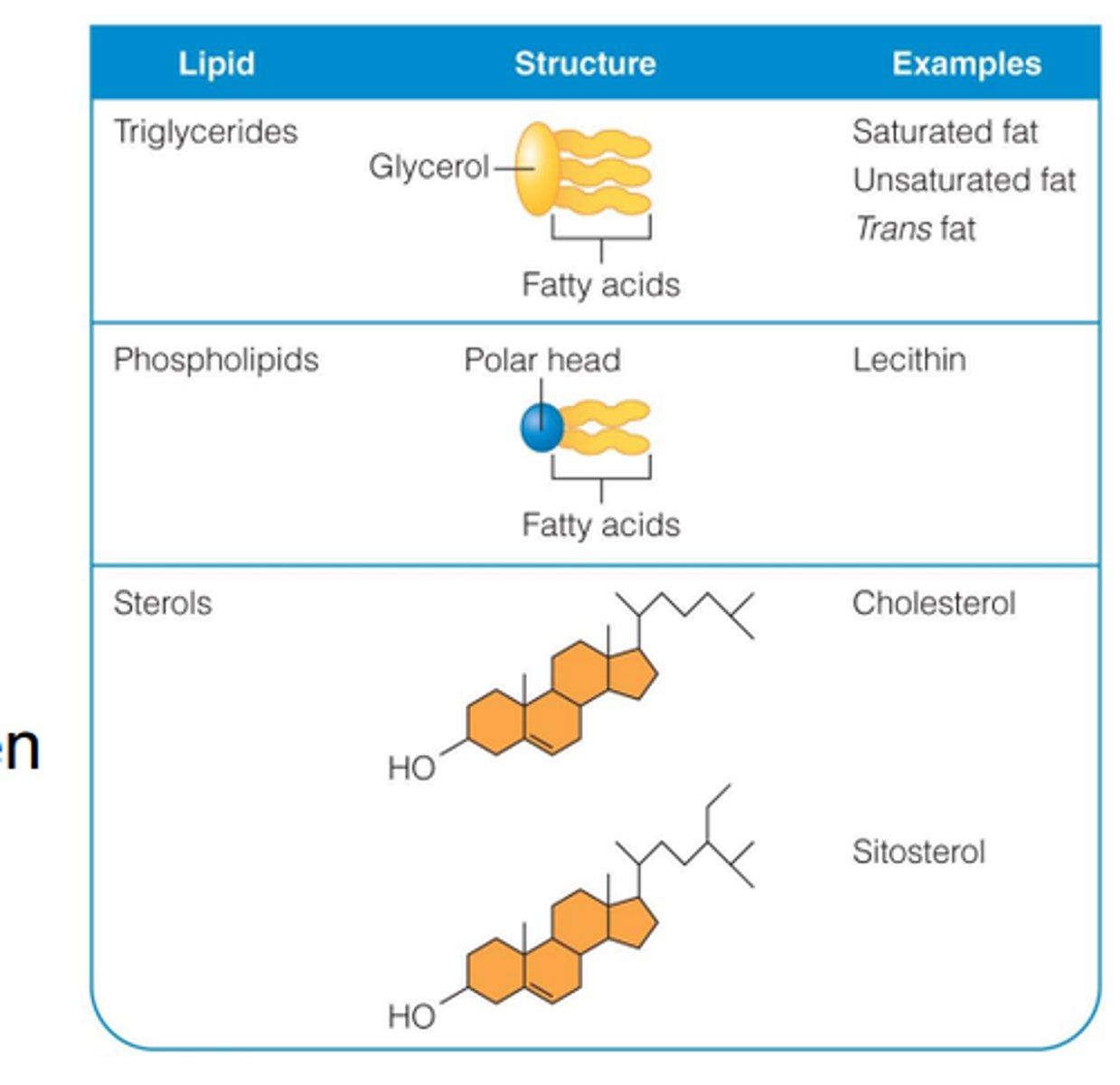
lipids
provide energy, protection, insulation for organs in the body
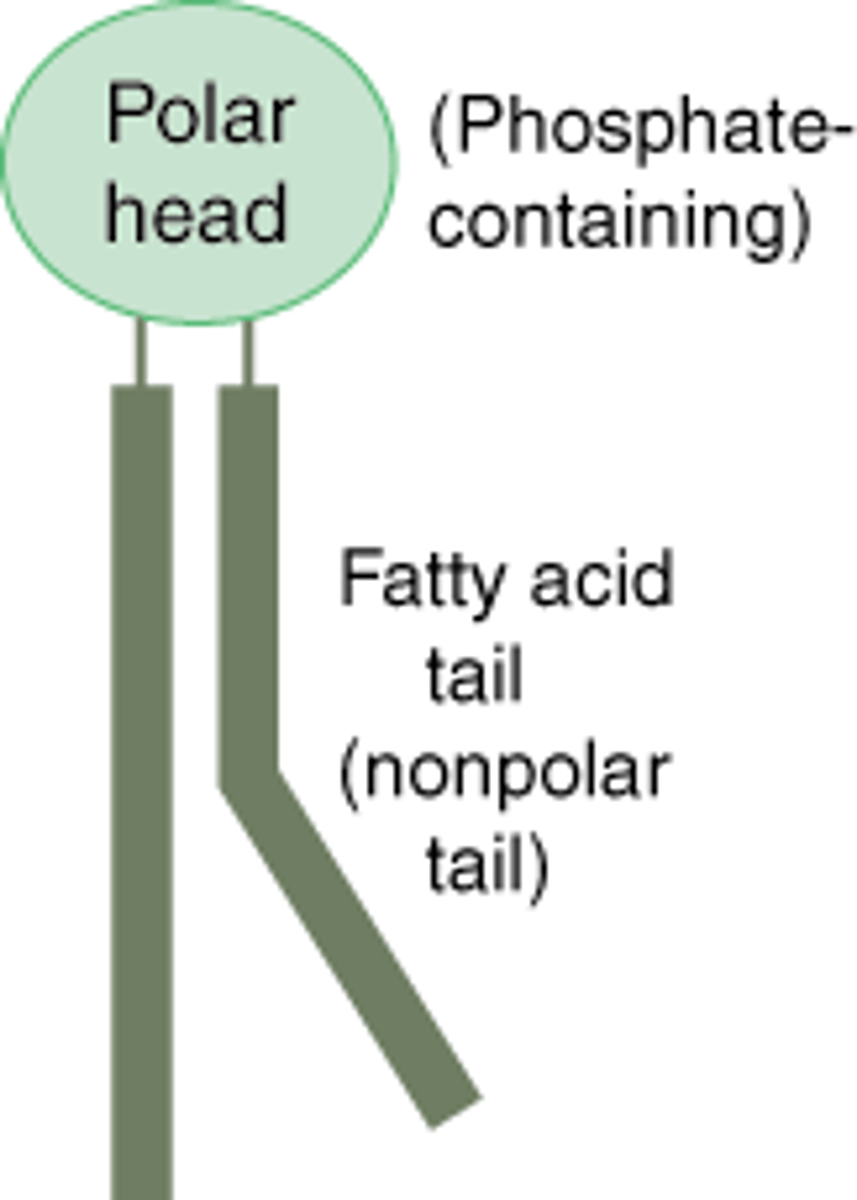
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
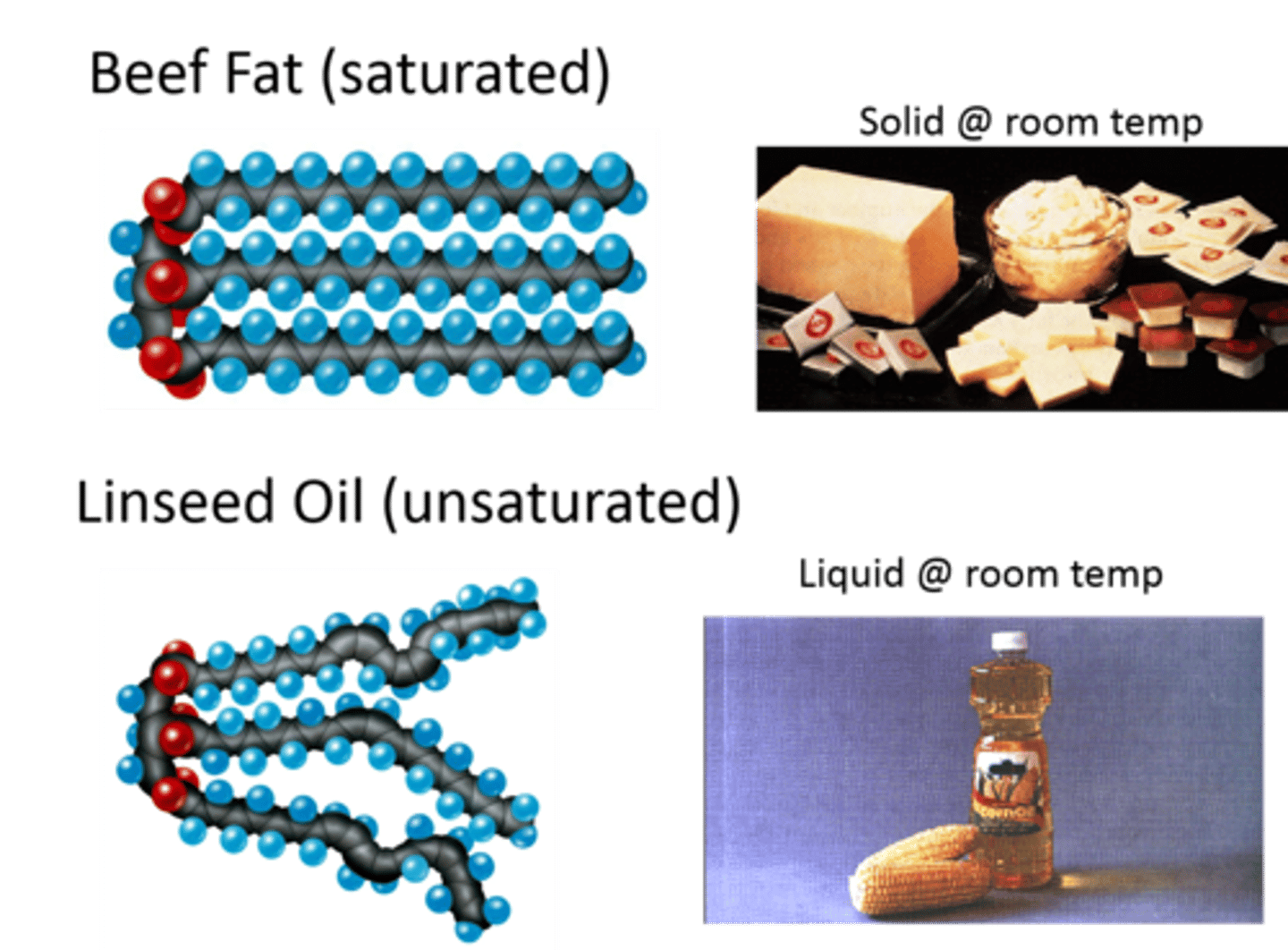
saturated fats
fats that are solid at room temperature; no double bond; packed tightly
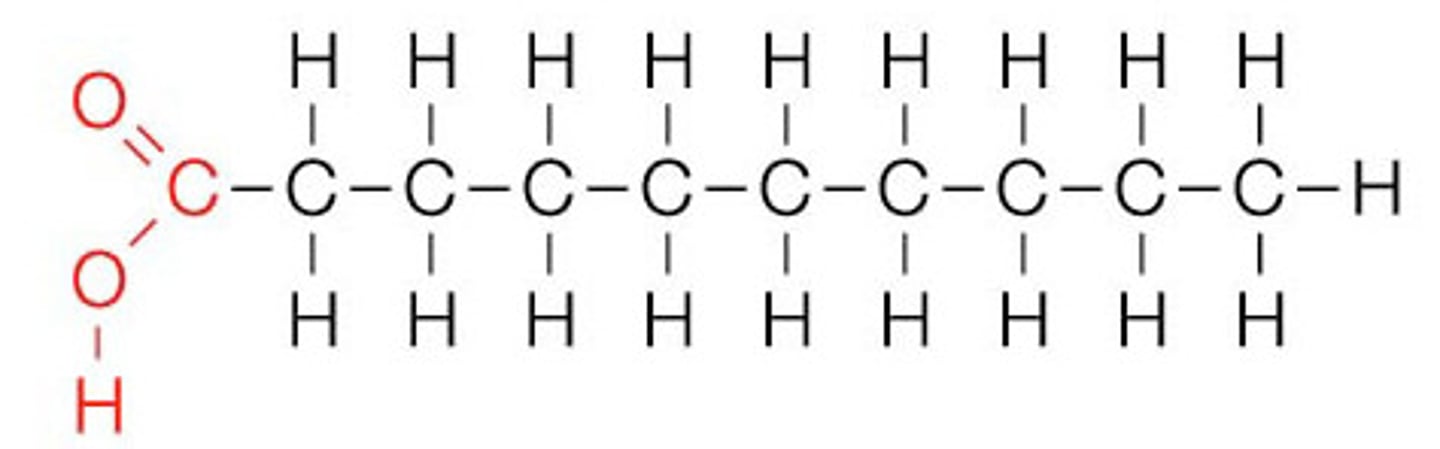
unsaturated fats
A fat that is liquid at room temperature and found in vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds, one double bond, has a kink
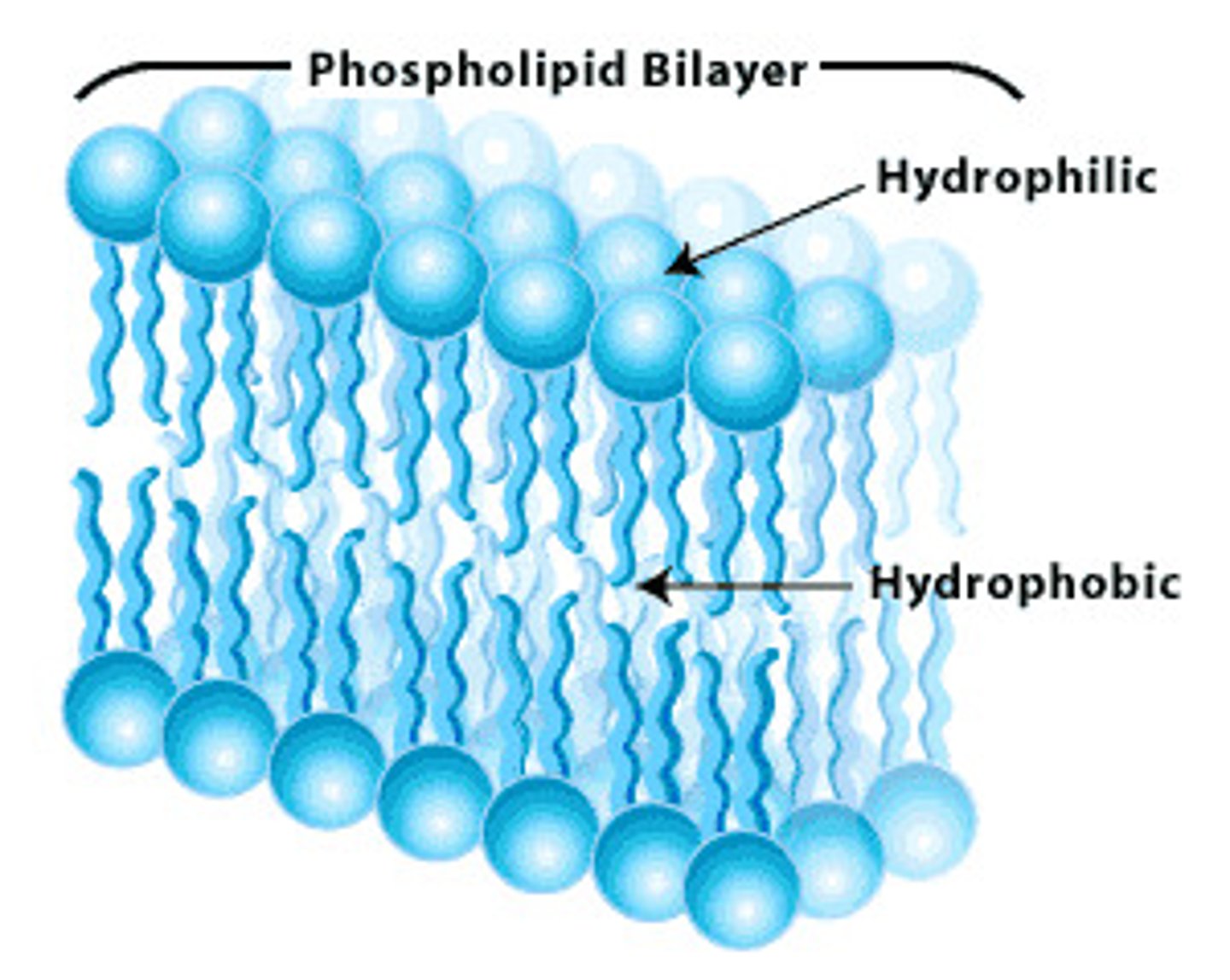
amphipathic
having both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region
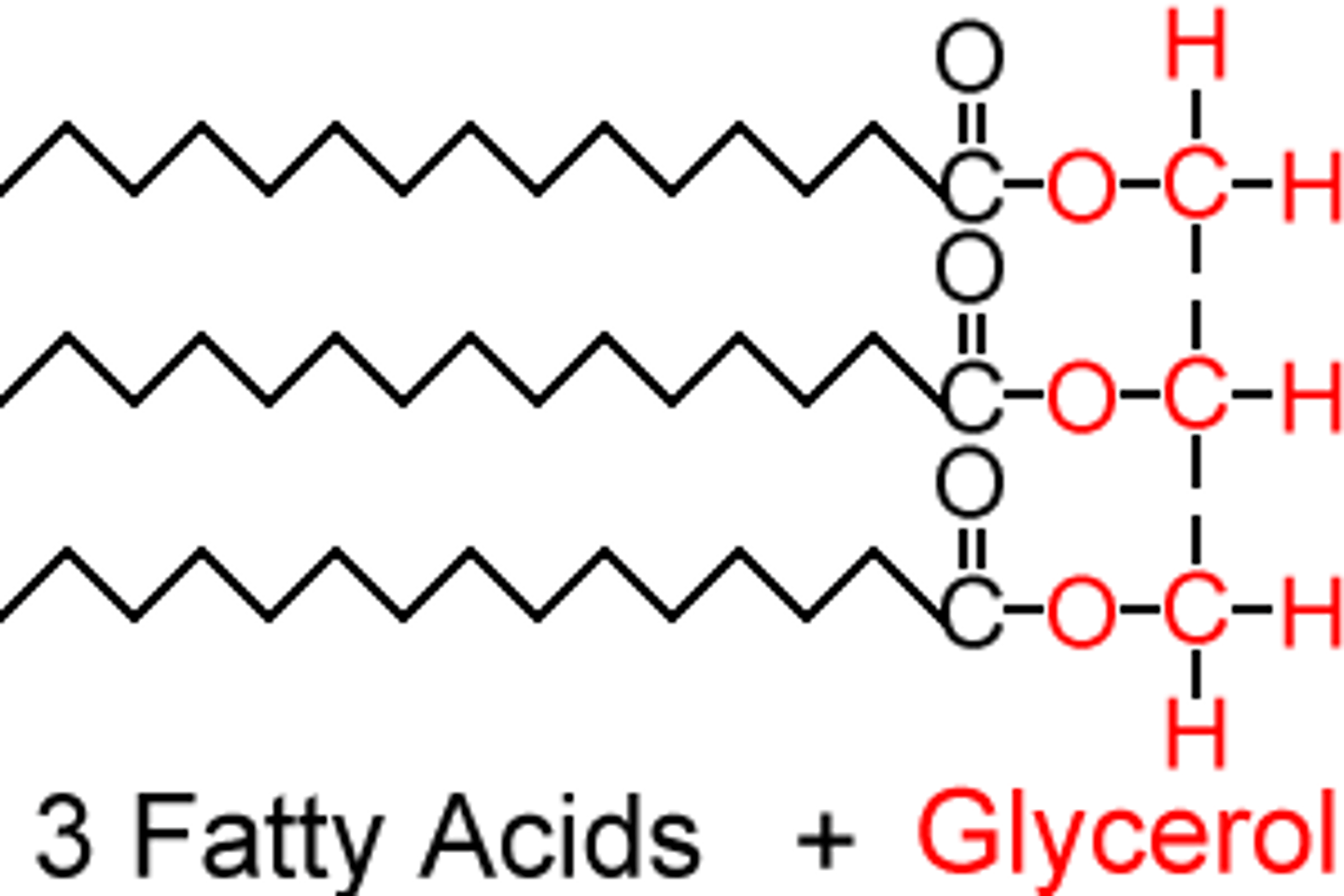
Triglycerides structure
one glycerol + 3 fatty acid tails
Cholesterol
four carbon rings, provides stability in the cell membrane
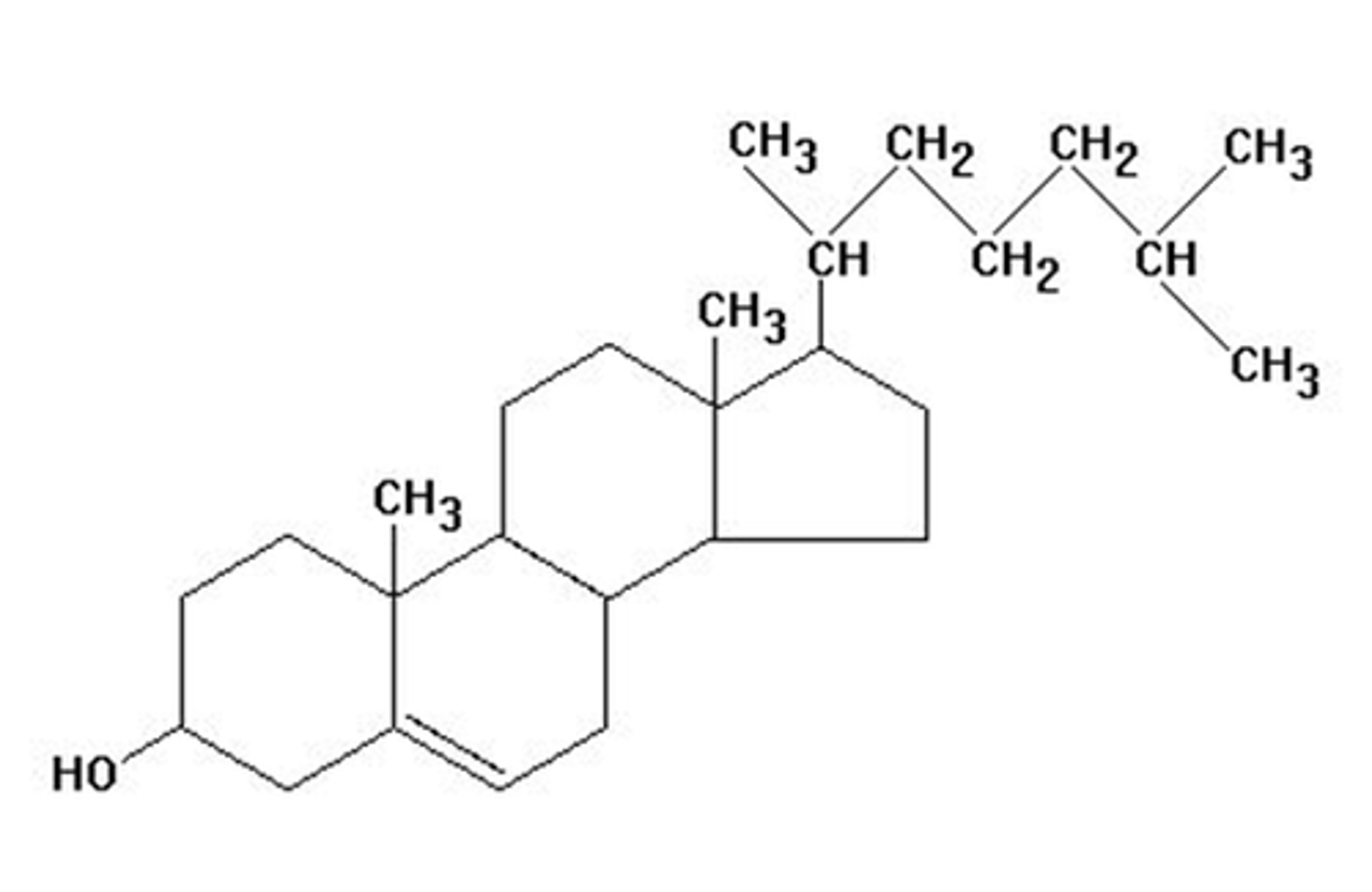
steroids
built from cholesterol, estrogen, testosterone, vitamin D
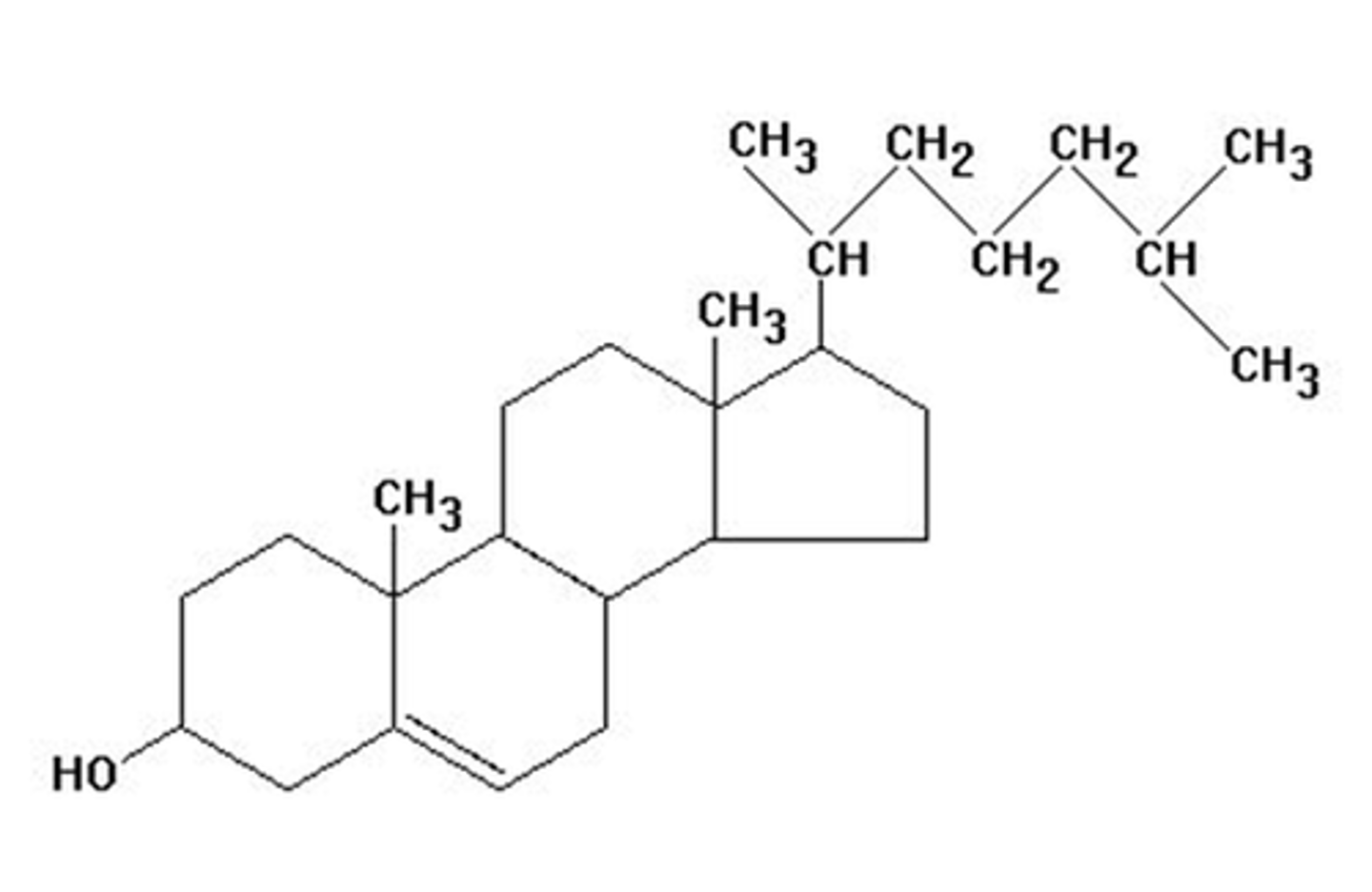
eicosanoids
prostaglandins and leukotrienes - both are involved in inflammatory response, 20C fatty acids
Prostaglandins
regulates body temp
leukotrienes
Chemical substances that contribute to anaphylaxis; released by the immune system in allergic reactions.
protiens
provides building materials, amino acids, for growth, replacement and repair of body tissue
amino acids
The 20 molecules that are held together by peptide bonds to make up proteins. (non-polar, polar, ionizable, aromatic, special fucntion)
- have a special R group
primary organization
the unique sequence of amino acids
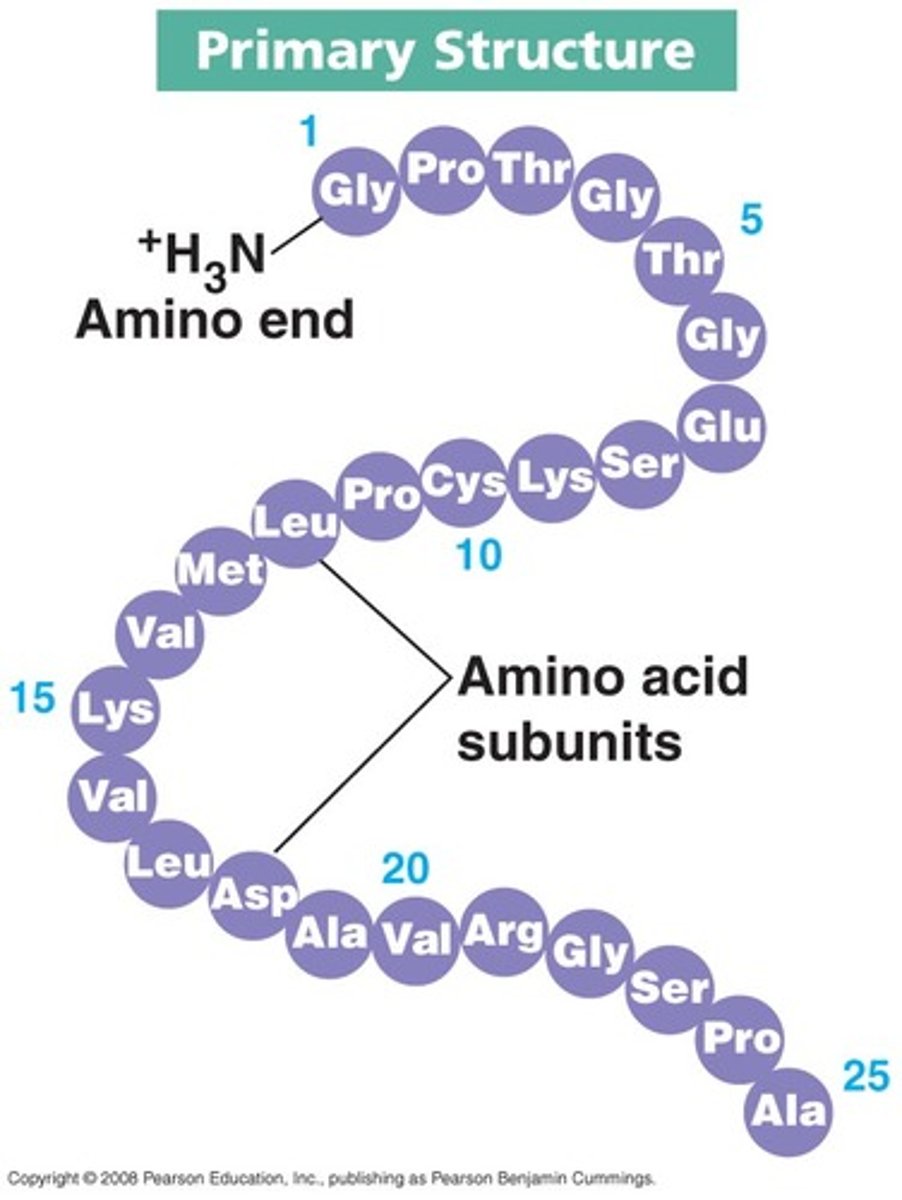
secondary organization
alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
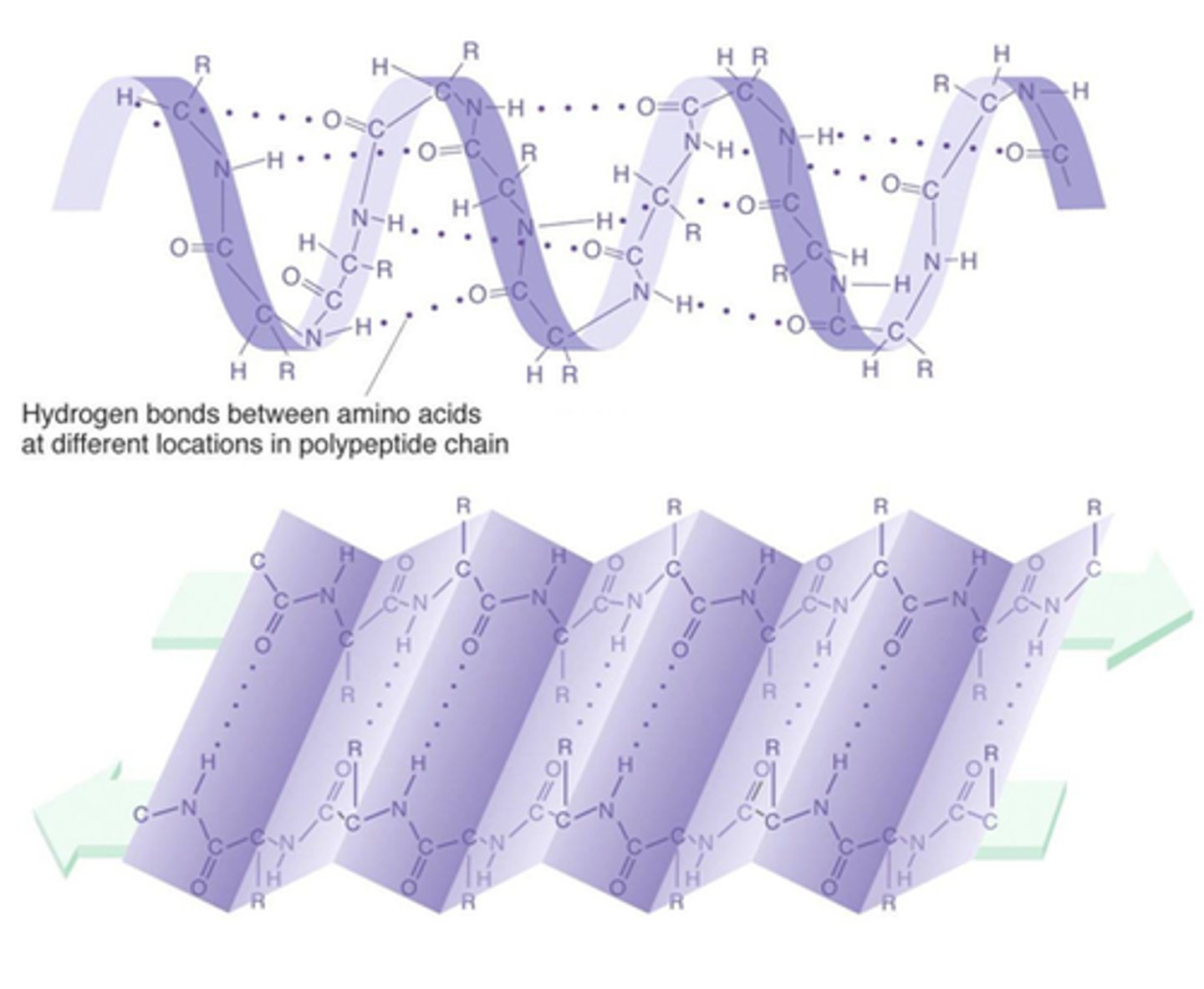
tertiary organization
3D structure
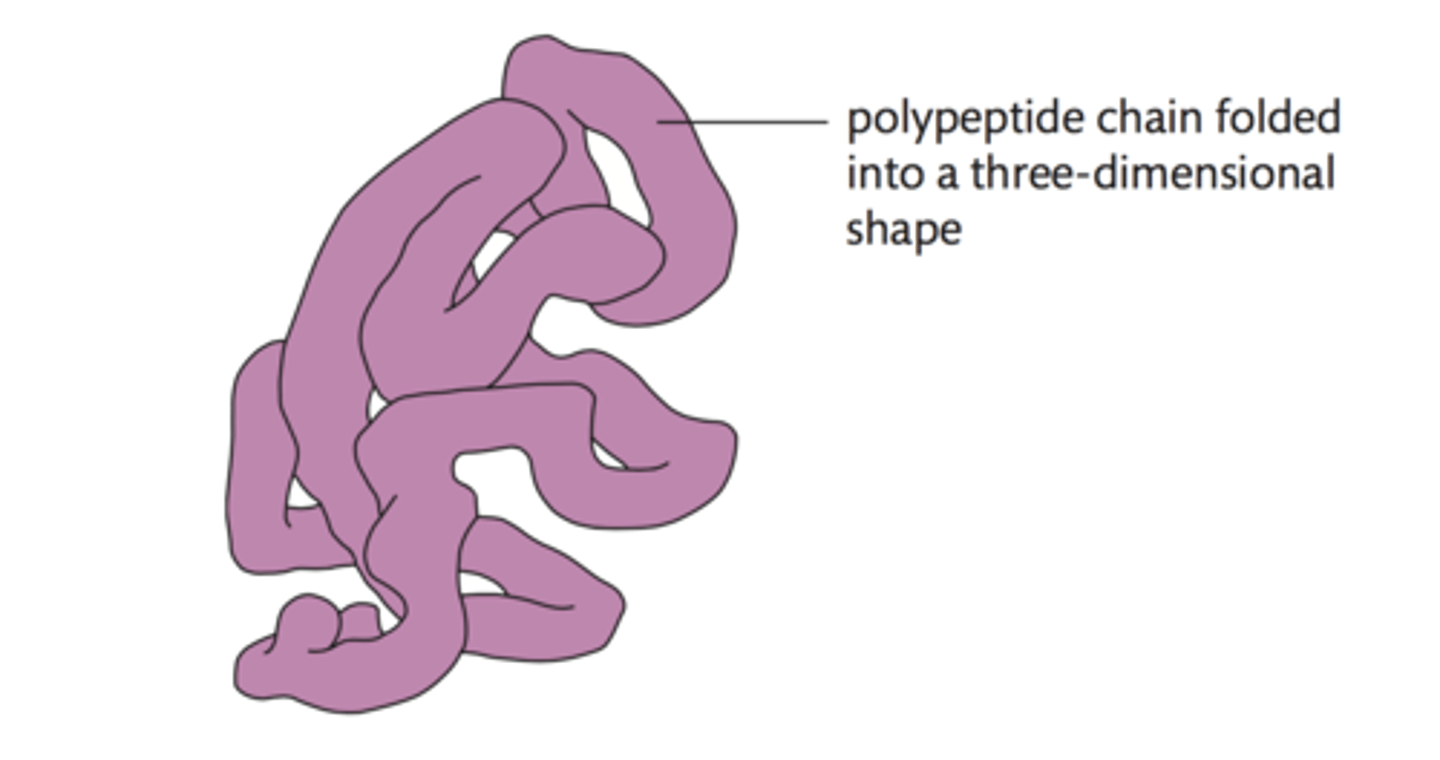
quaternary structure
interaction of multiple polypeptide chains; only in some
Collagen
structural protein found in the skin and connective tissue
insulin
A protein hormone that is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates and the regulation of glucose levels in the blood
actin/myosin
contractile proteins in muscle
amylase and dehydrogenase
catalytic
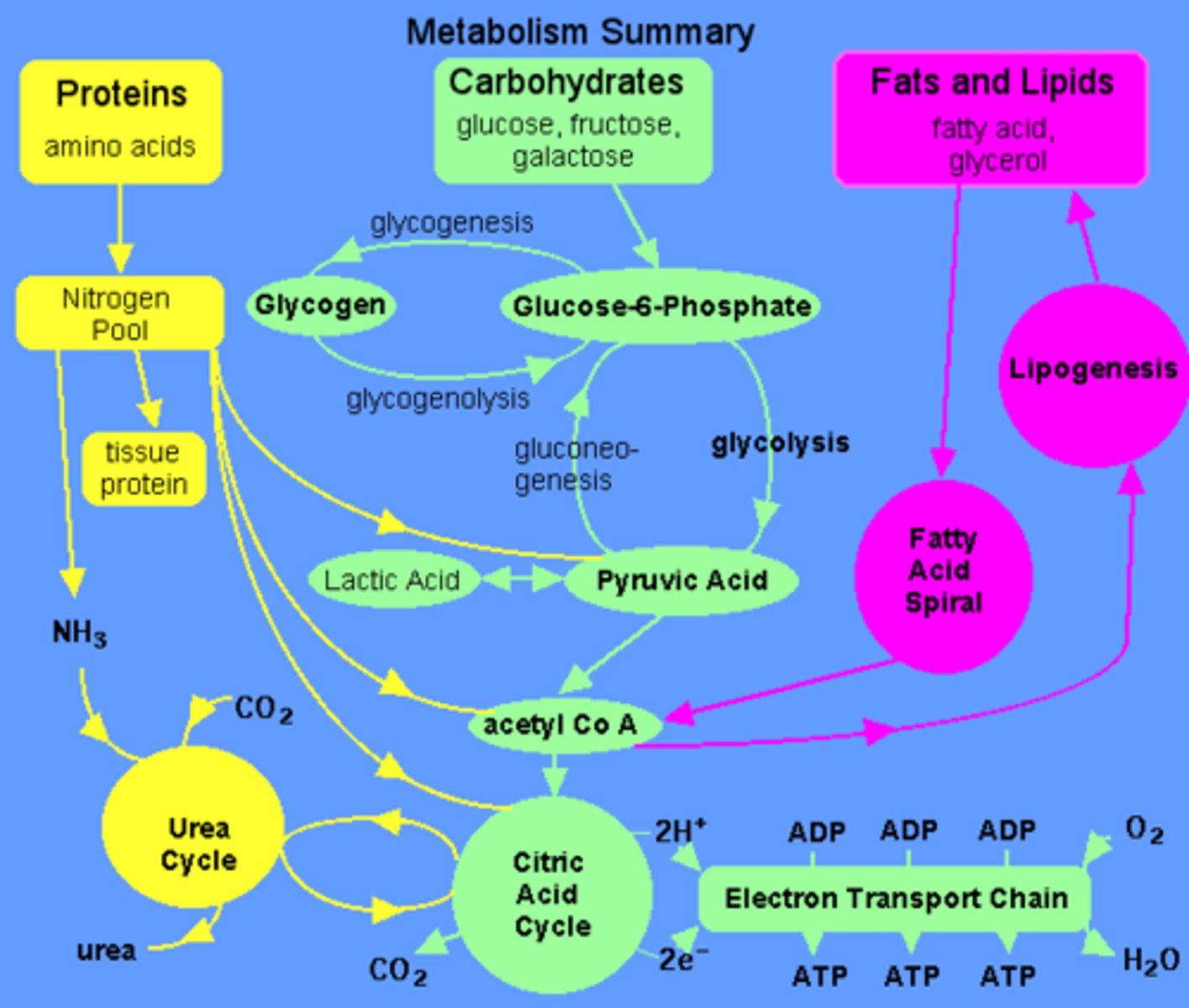
Metabolism
the sum of all biochemical reactions in a cell/body
key chemical reactions in the metabolism
dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis synthesis
Hydrophilic
water loving
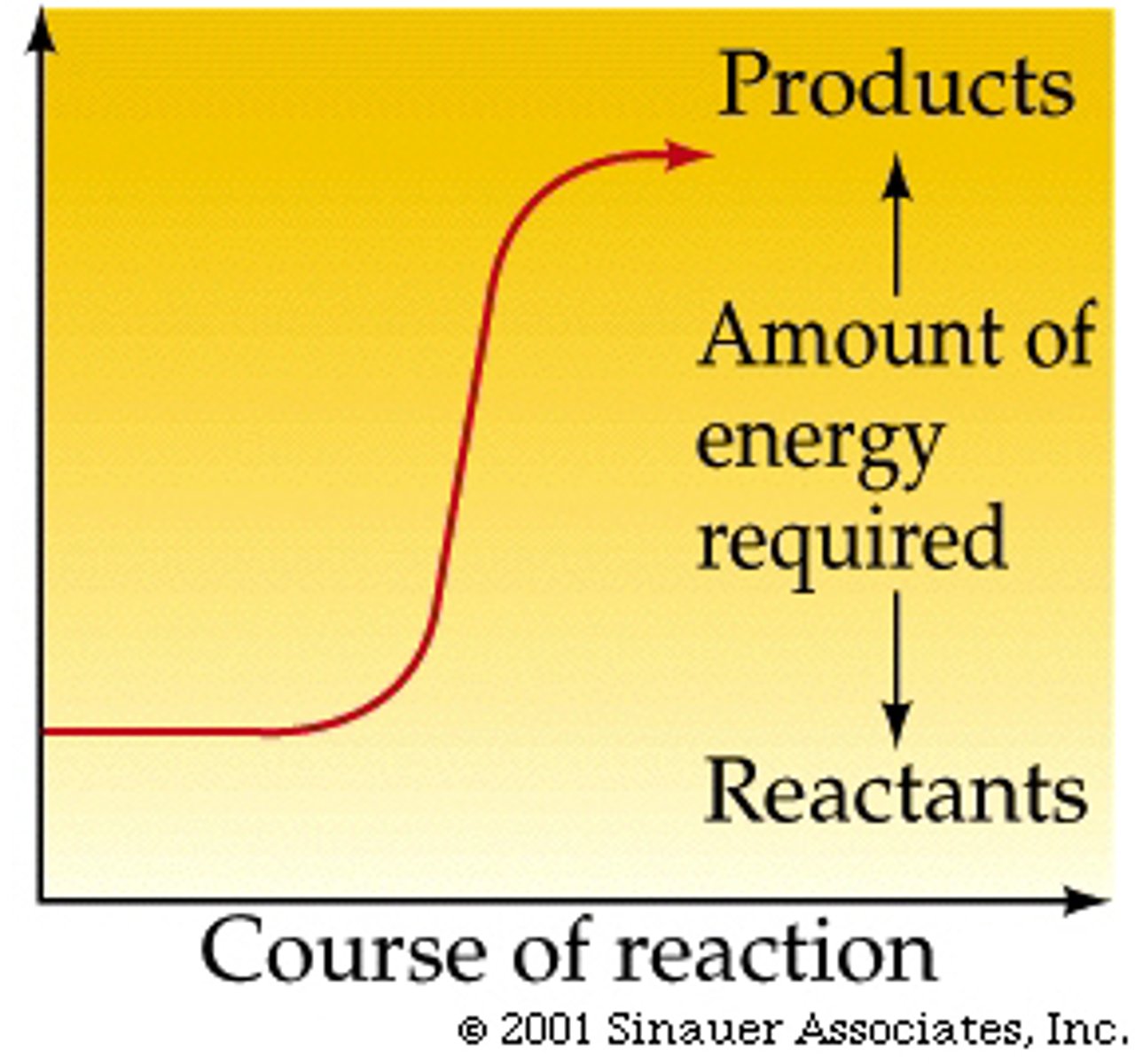
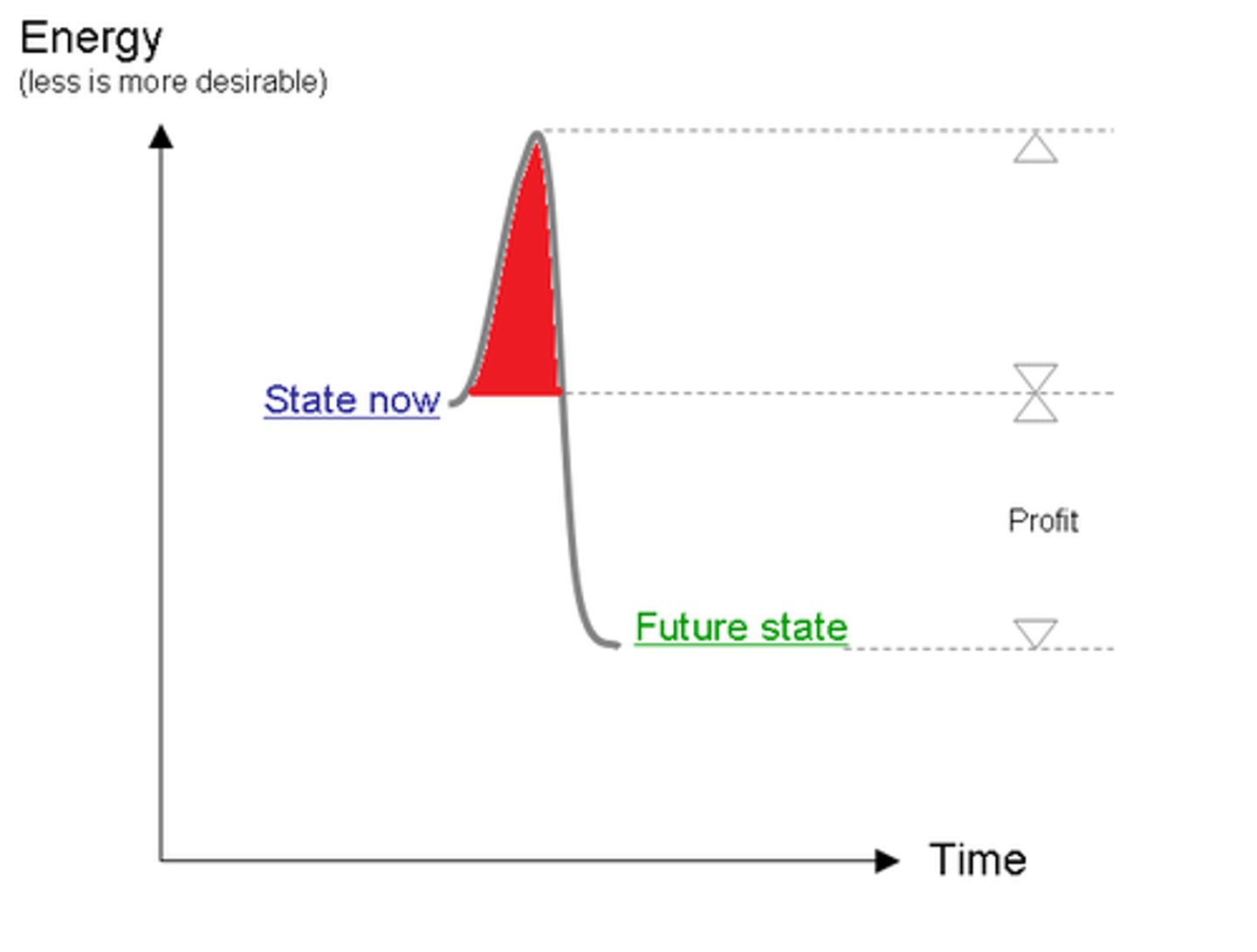
endergonic reaction
uphill, a chemical reaction that absorbs more energy than it is releases, endothermic
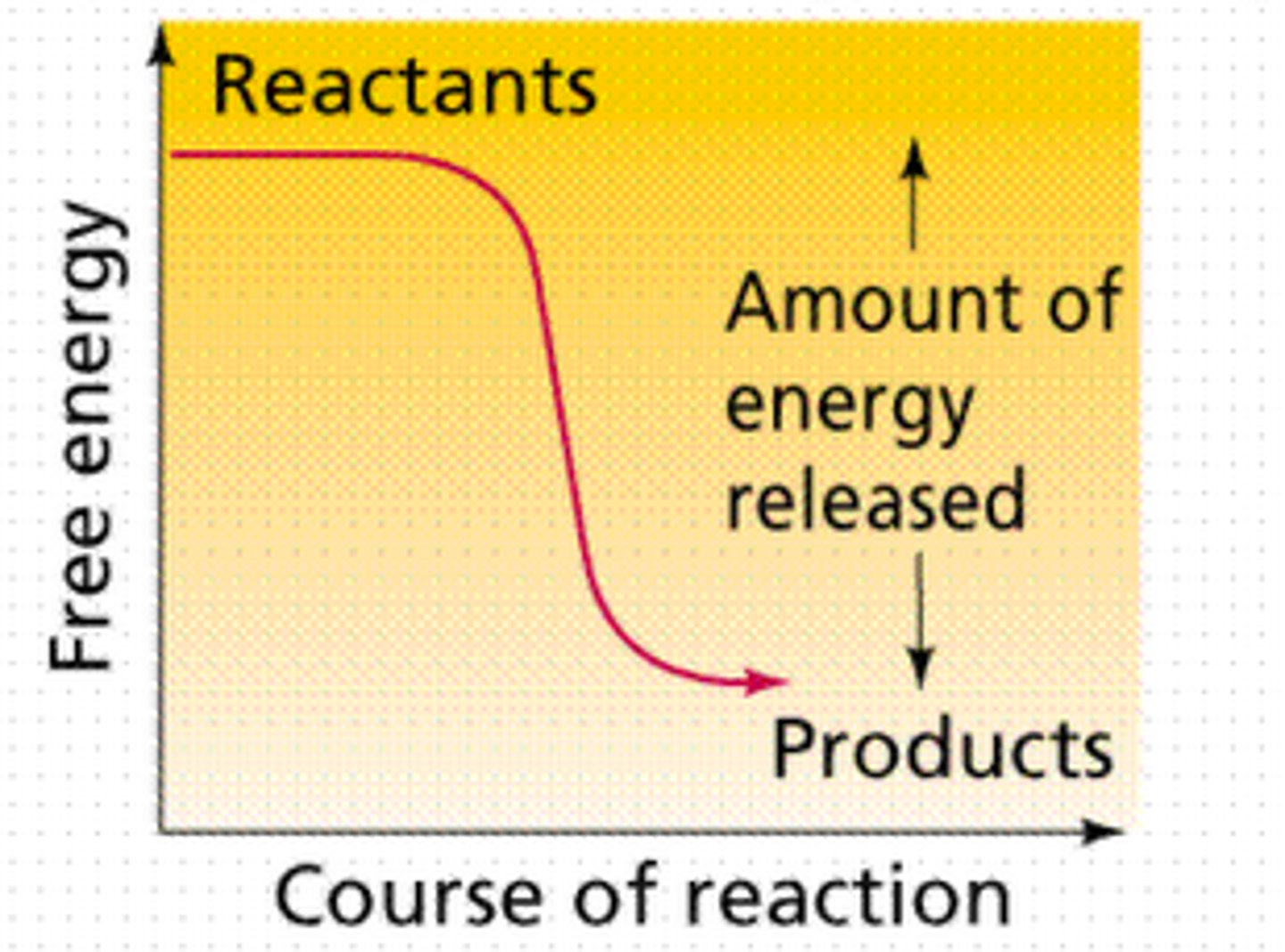
exergonic reaction
downhill, a chemical reaction that releases more energy than it is absorbed, exothermic
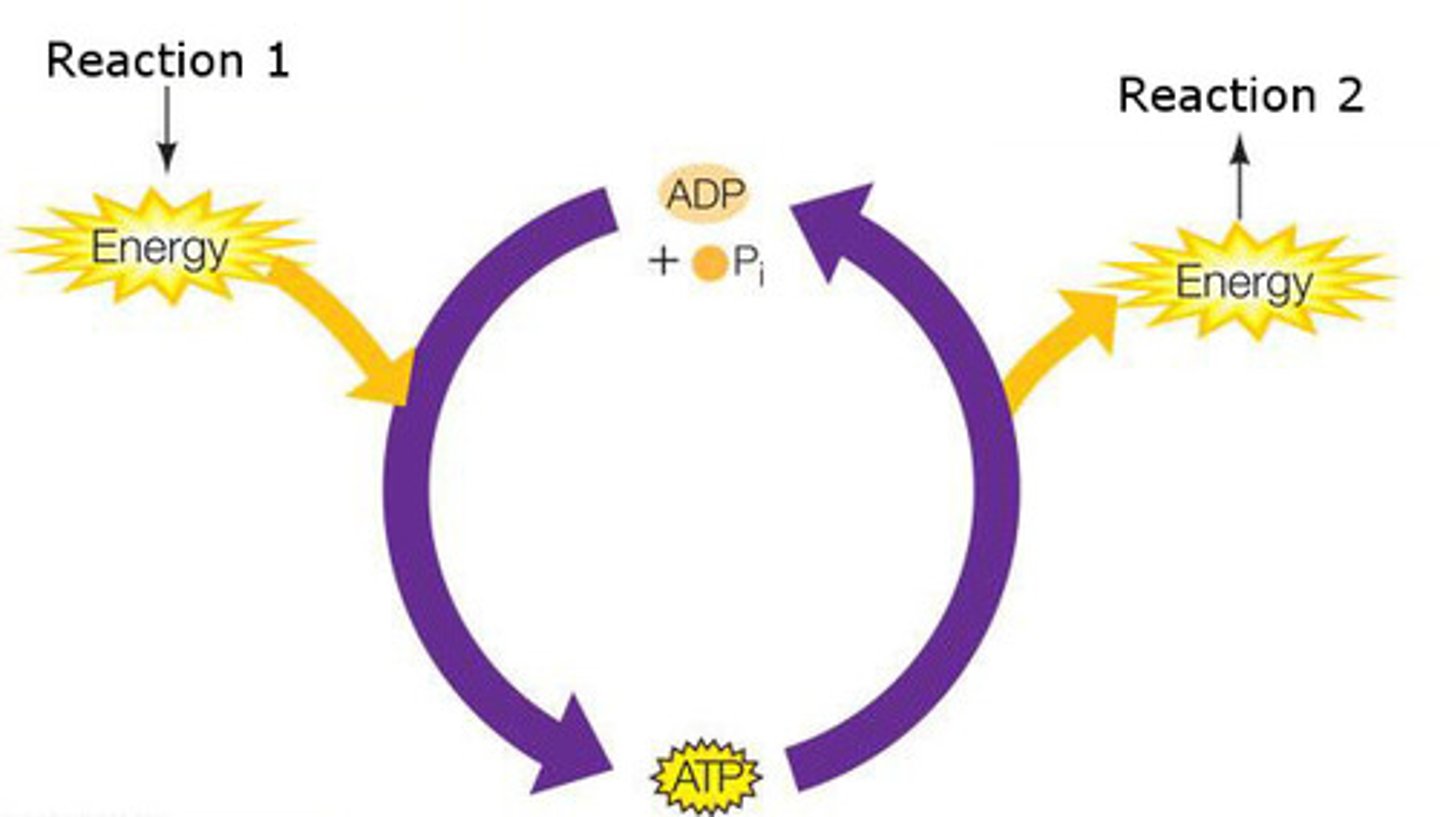
coupled reactions
the energy released by an exergonic reaction is used to drive an endergonic reaction
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction, collision energy needed to break chemical bonds, speeds up reactions
structural pieces of an enzyme
apoenzyme (major part) with coenzyme (carry H ions, vitamins) and cofactor (minerals) as add ons
biological catalyst
A substance found in living organisms that speeds up reactions (an enzyme).
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
adenosine
adenine + ribose
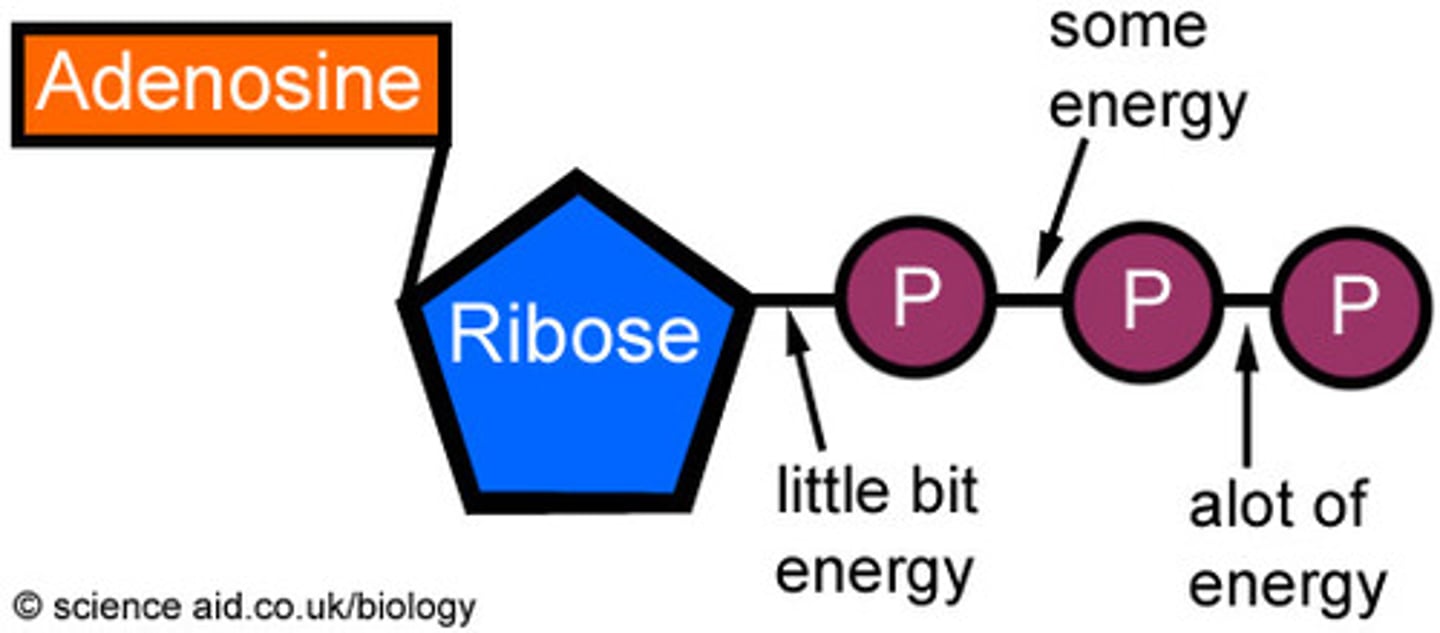
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work, three phosphates, provides readily releasable energy in the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate group
ADP
(Adenosine Diphosphate) The compound that remains when a phosphate group is removed from ATP, releasing energy, two phosphates
AMP
(Adenosine monophosphate) ATP minus 2 phosphate groups
substrate-level phosphorylation
When an enzyme adds to a phosphate to make ATP in the cytosol
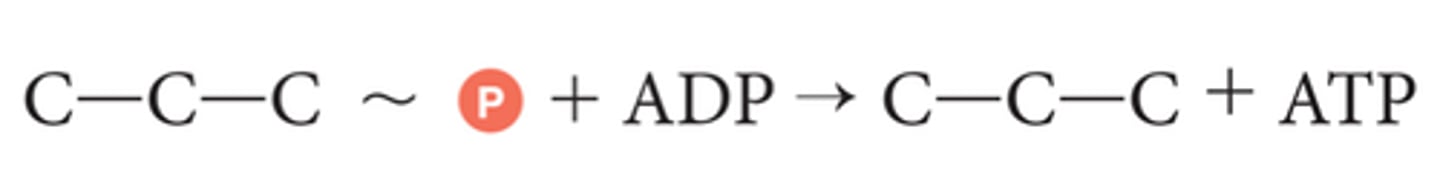
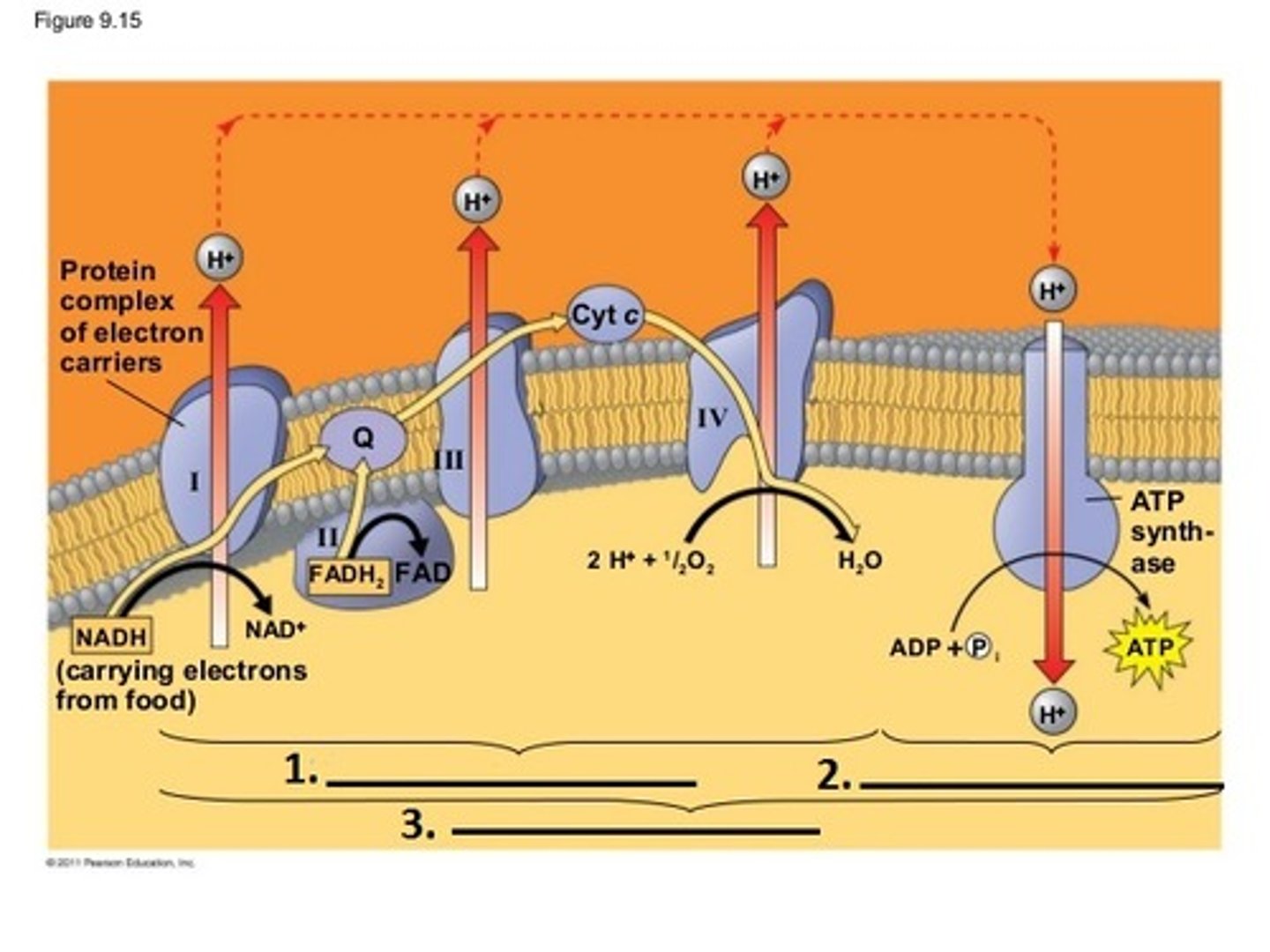
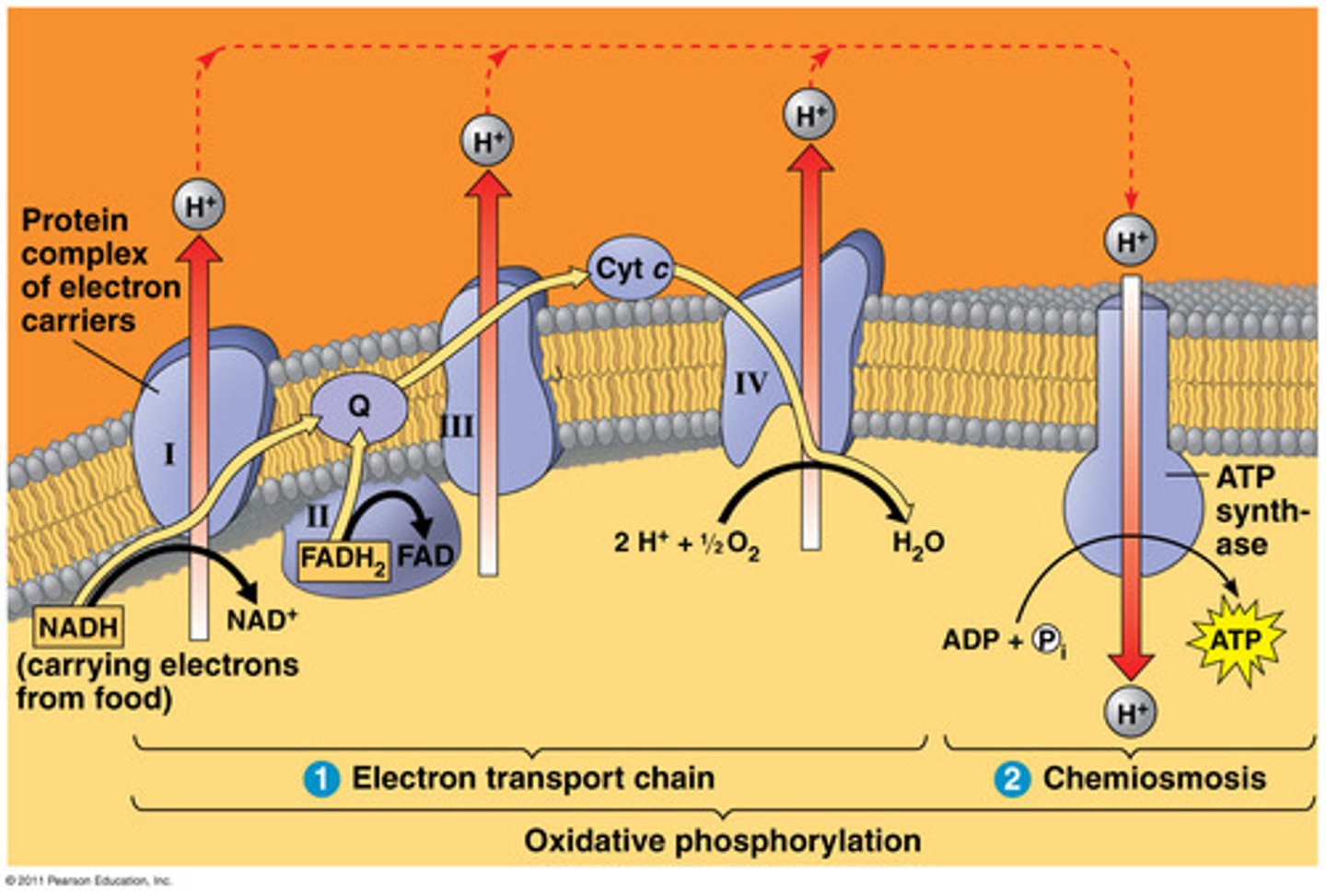
oxidative phosphorylation
Part of the electron transport chain. A process occurring in the mitochondria that results in the formation of ATP from the flow of electrons across the inner membrane to bind with oxygen.
anaerobic
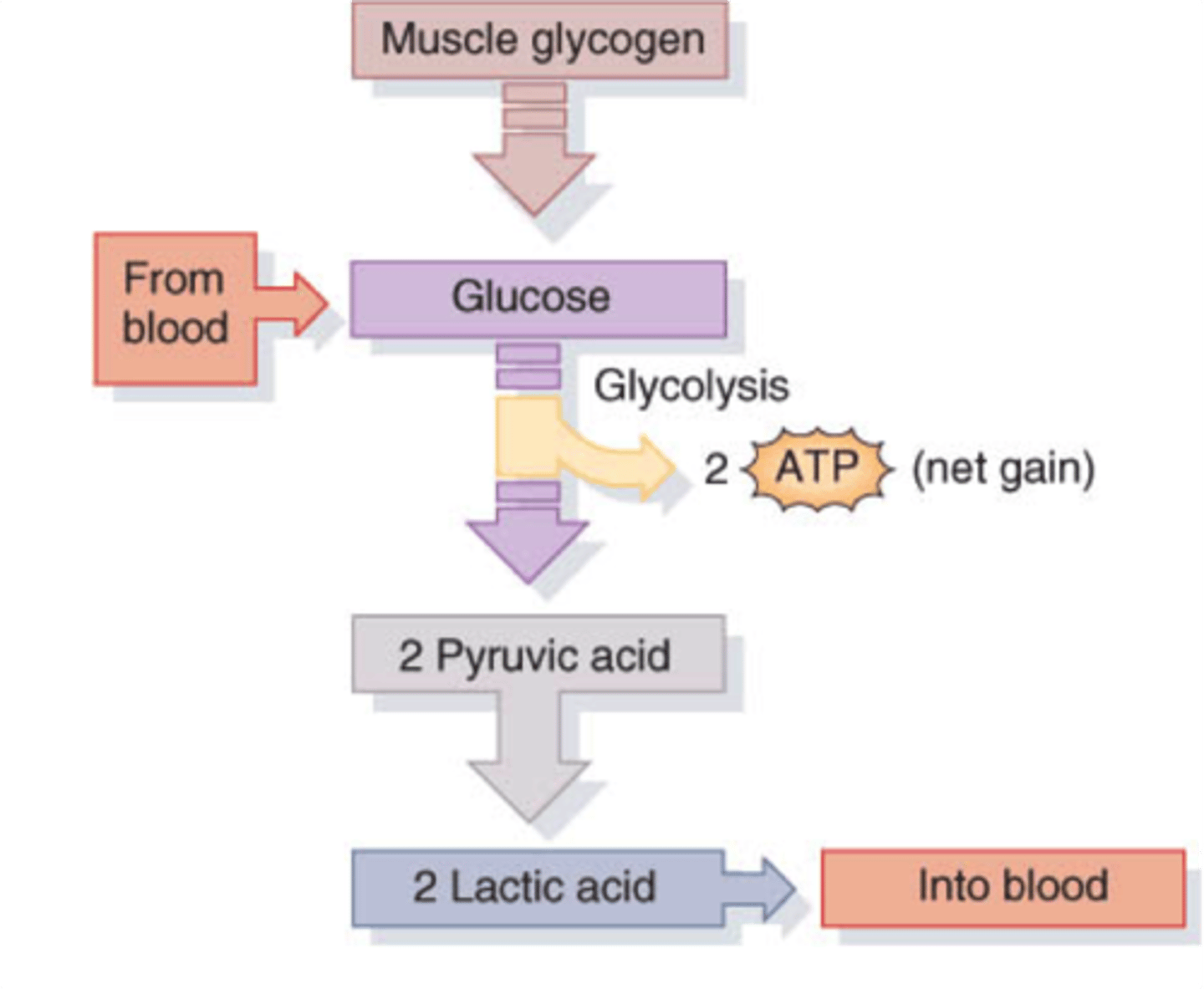
without oxygen, glucose is partially broken down to pyruvate and produces 2 ATP
aerobic
with oxygen, glucose is completely broken down to CO2 and H2O, produces heat and 36-38 ATP

Oxidation reaction
OIL
LOSS of electrons, hydrogen, potential energy,
gains oxygenN
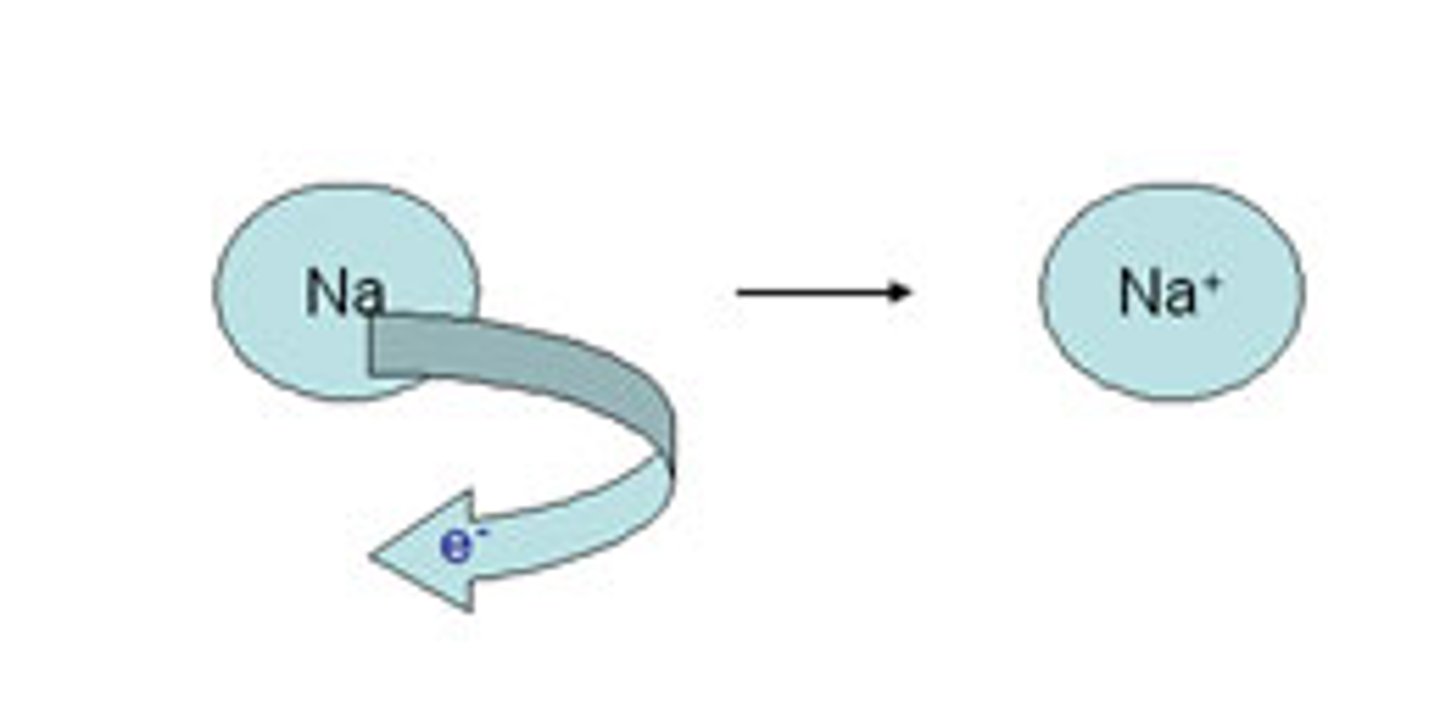
Reduction reaction
RIG
GAIN electrons, hydrogen, potential energy
loss of oxygen
NAD
derivative of niacin; reduces to NADH+ H+ (gains a hydride ion and H+ is released)
FAD
derivative of riboflavin; reduces to FADH2
how does glucose enter the cell?
facilitated transport - glucose gets brought into the cell and has to be carried with a glucose transporter protein (GluT)
what happens to glucose when it enter the cell?
glucose produces ATP, synthesizes amino acids, produces glycogen (glycogenesis), makes triglycerides (lipogenesis)
connection between electron transport, glycolysis, and the Krebs Cycle.
Glucose -> Glycolysis -> pyruvate -> acetyl CoA -> krebs cycle -> NADH and FADH2 -> electron transport -> ATP
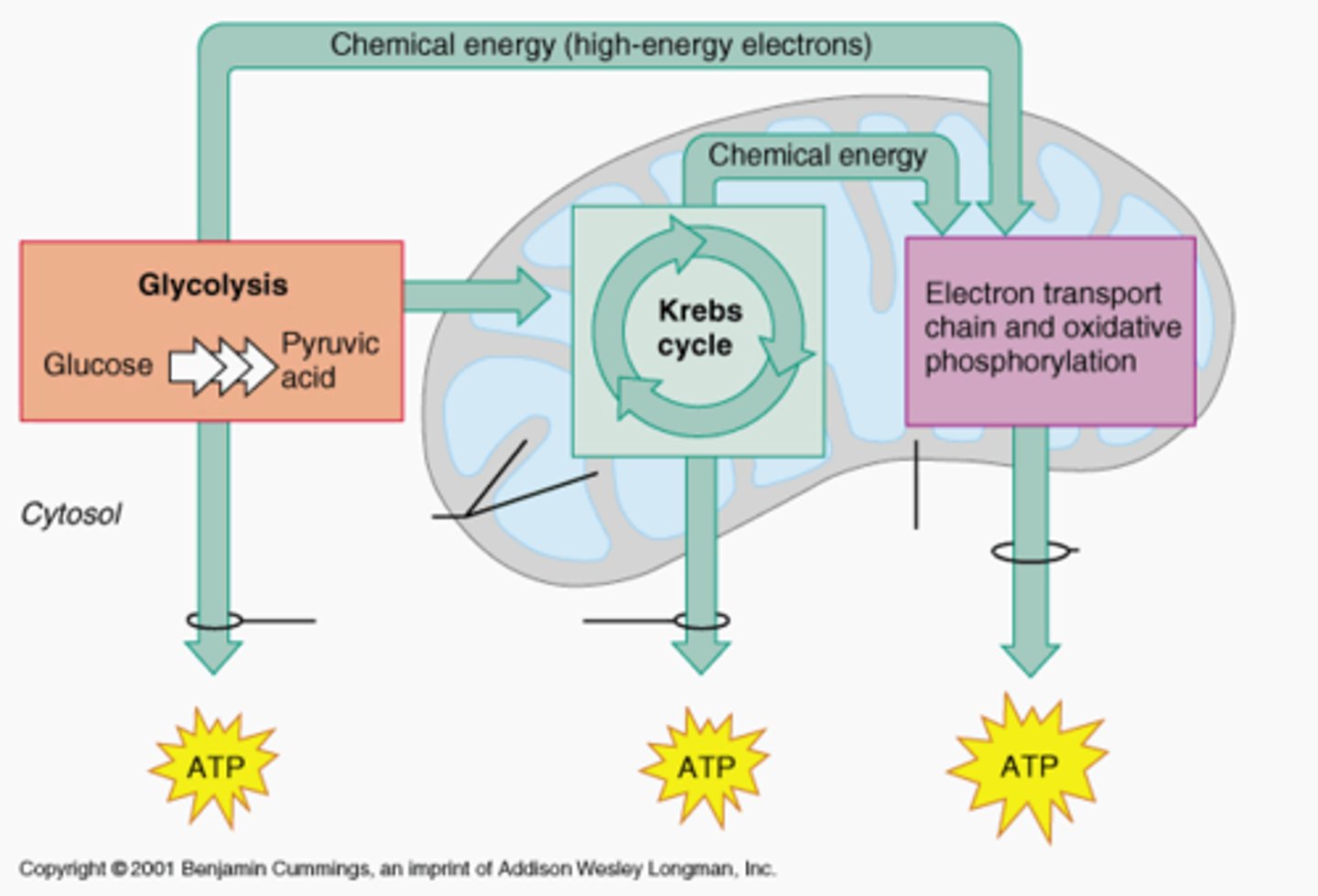
glycolysis
a set of reactions occur that oxides one glucose molecule into 2 pyruvic acids; 2 ATP is produced, 2 NADH + H+ are produced
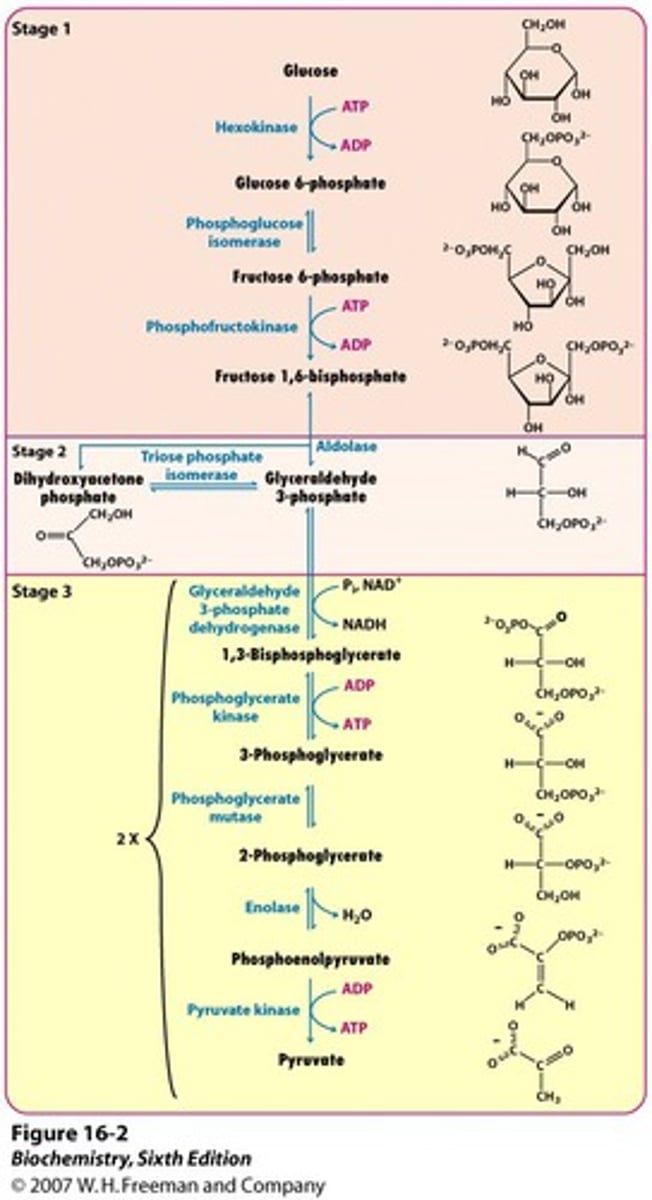
1st step of glycolysis
Phosphorylation of glucose->glucose-6-p catalyzed by hexokinase; uses ATP to make ADP
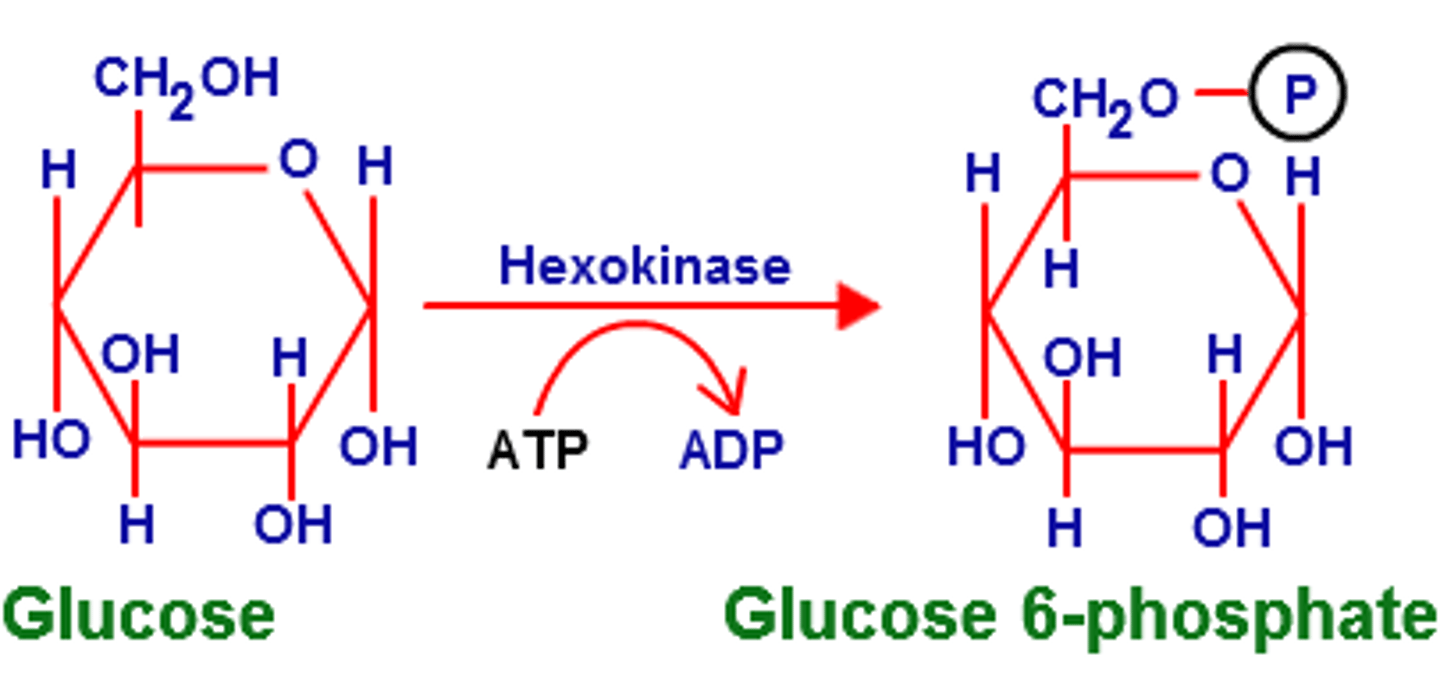
Hexokinase
enzyme that converts glucose to glucose 6-phosphate in peripheral tissues
2nd step of glycolysis
glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate using isomerase
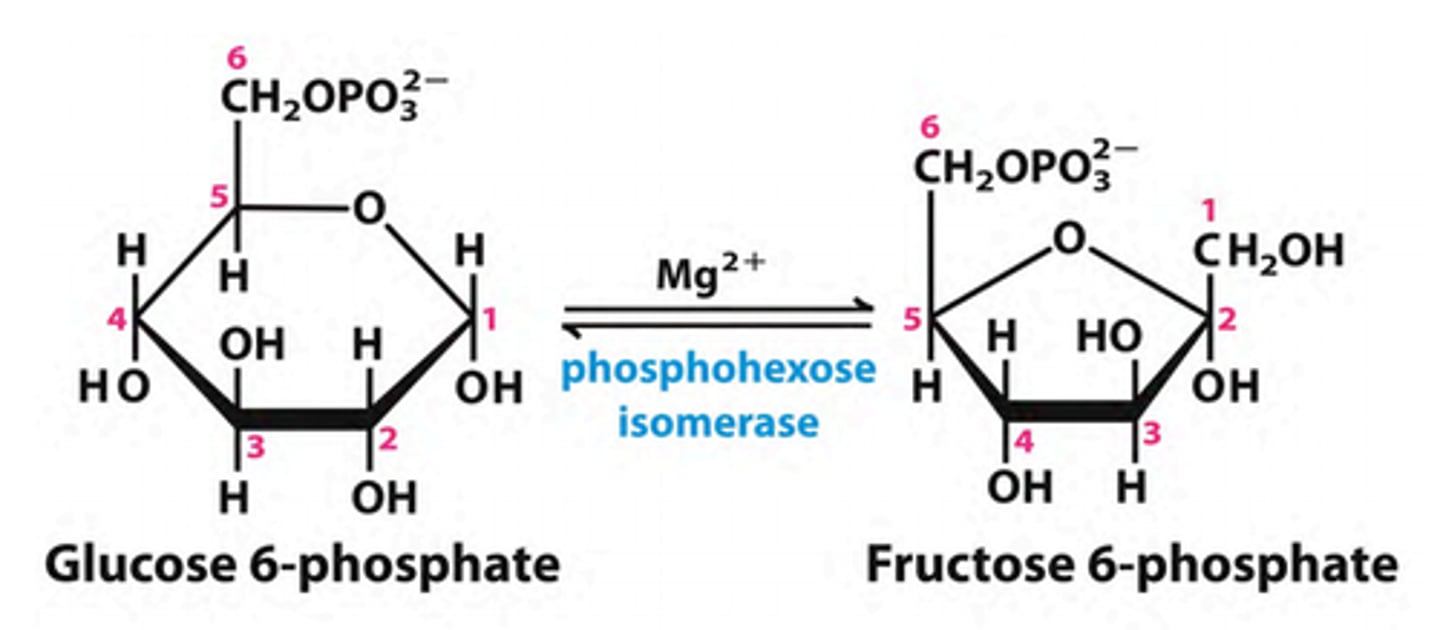
isomerase
rearrangement of atoms
3rd step of glycolysis
Fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate using phosphofructokinase; uses ATP to make ADP
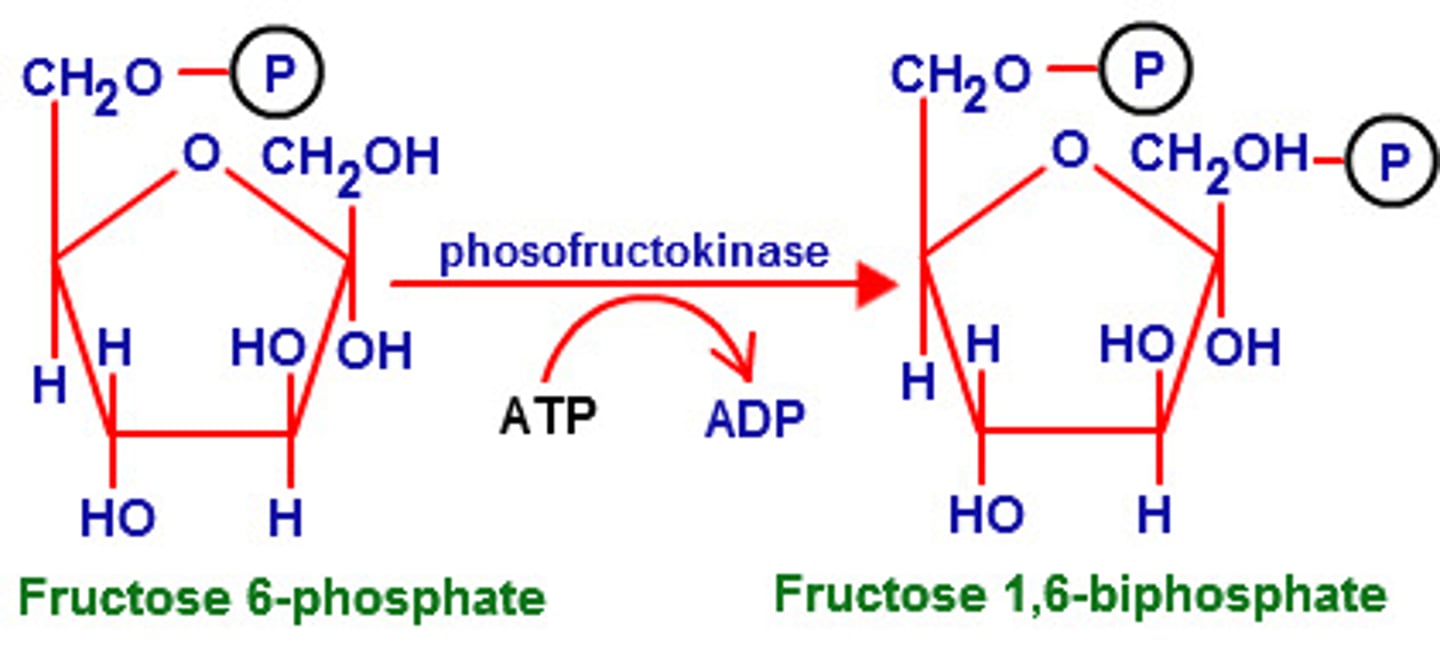
Phosphofructokinase
enzyme that is feedback-inhibited by ATP; check point; regulates glycolysis rate (high ADP = low ATP, speed up glycolysis)
4th step of glycolysis
fructose 1,6-biphosphate converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (DHAP is converted to G3P); makes 2 of everything now
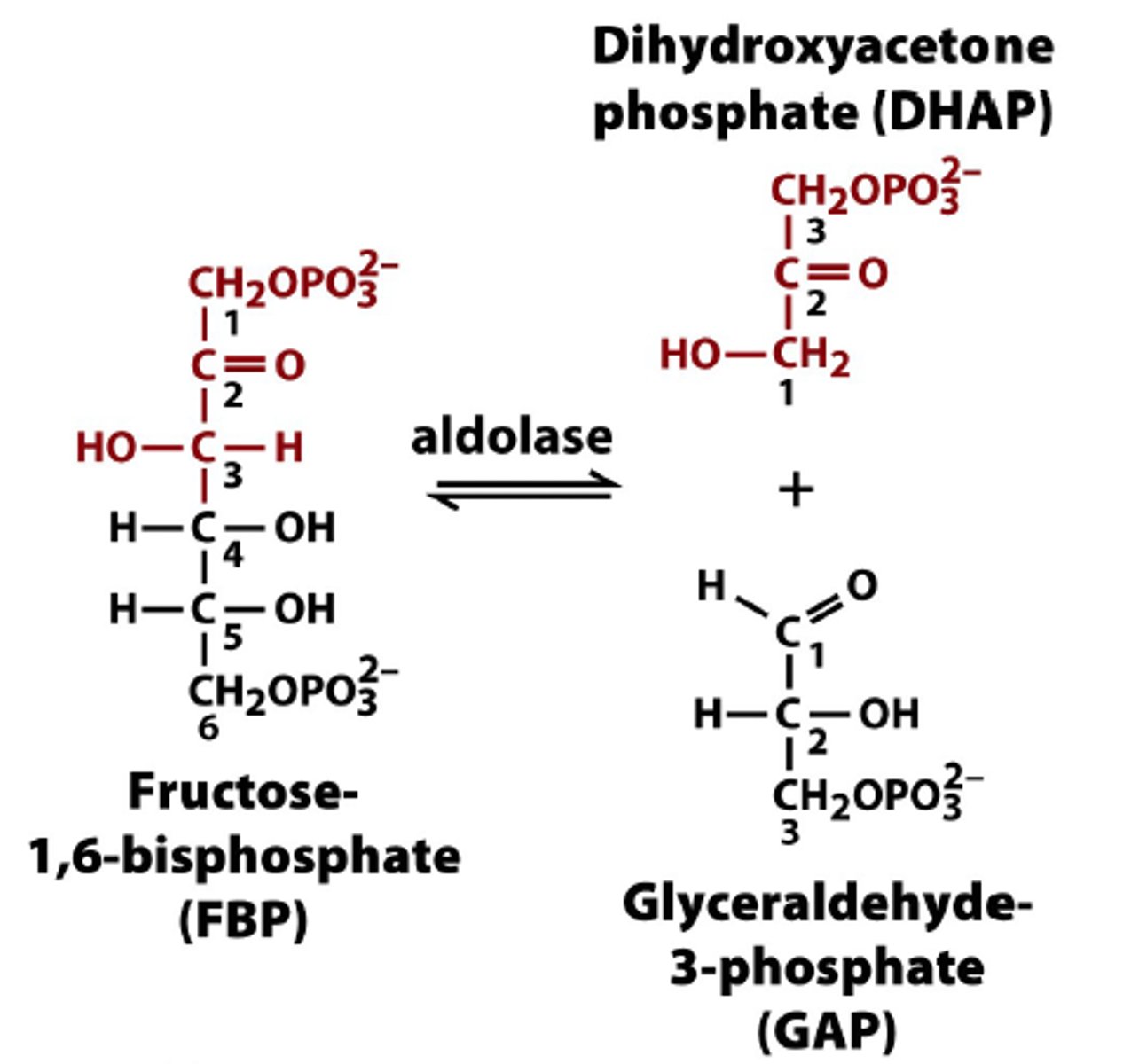
5th step of glycolysis
the two G3P converts 2 NAD+ to 2NADH + 2H+ which creates 1,3 bisphosphoglyceric acid
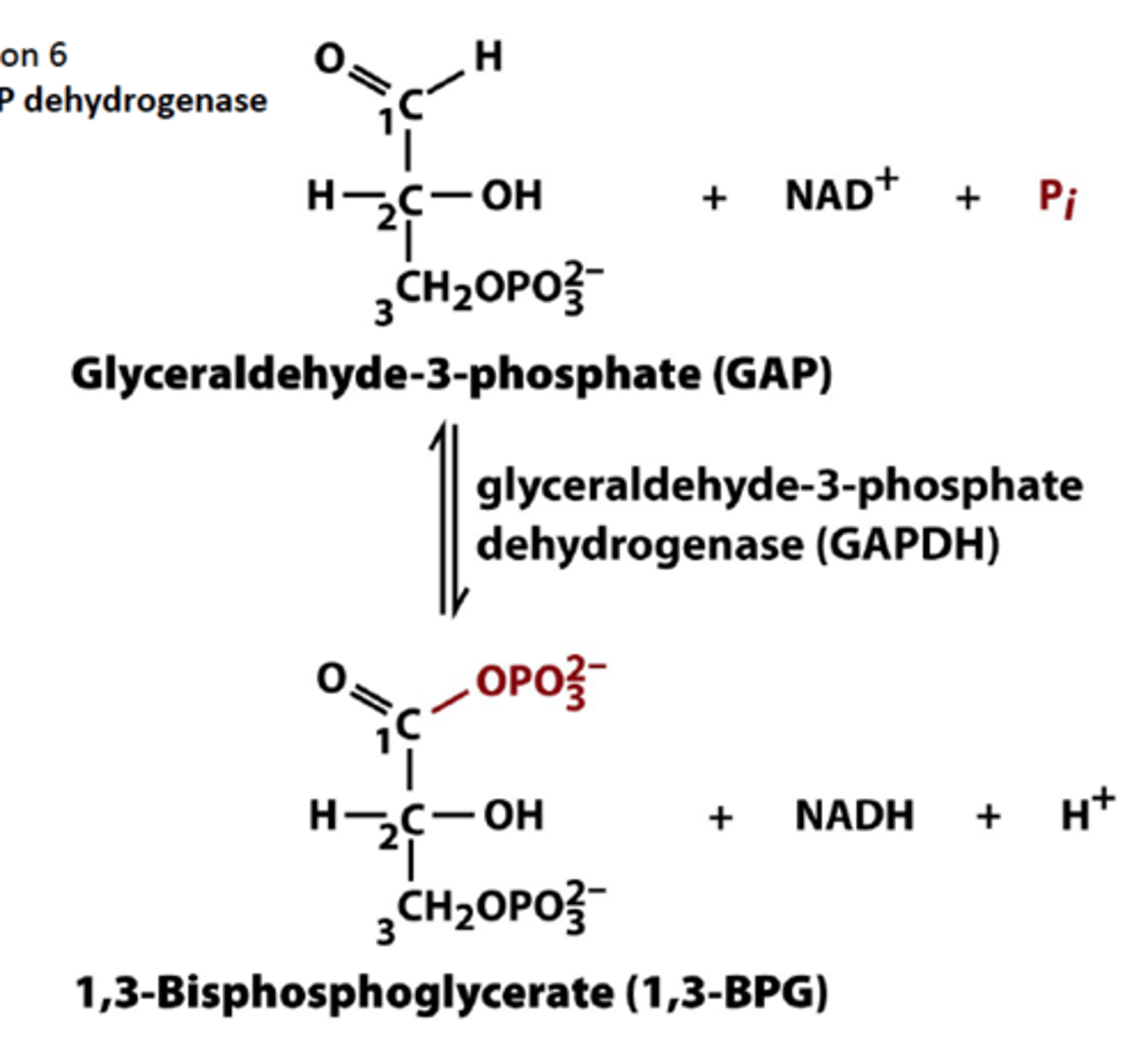
6th step of glycolysis
1,3 bisphosphoglyceric acid is converted to 3-phosphoglyceric acid; makes 2 ATP
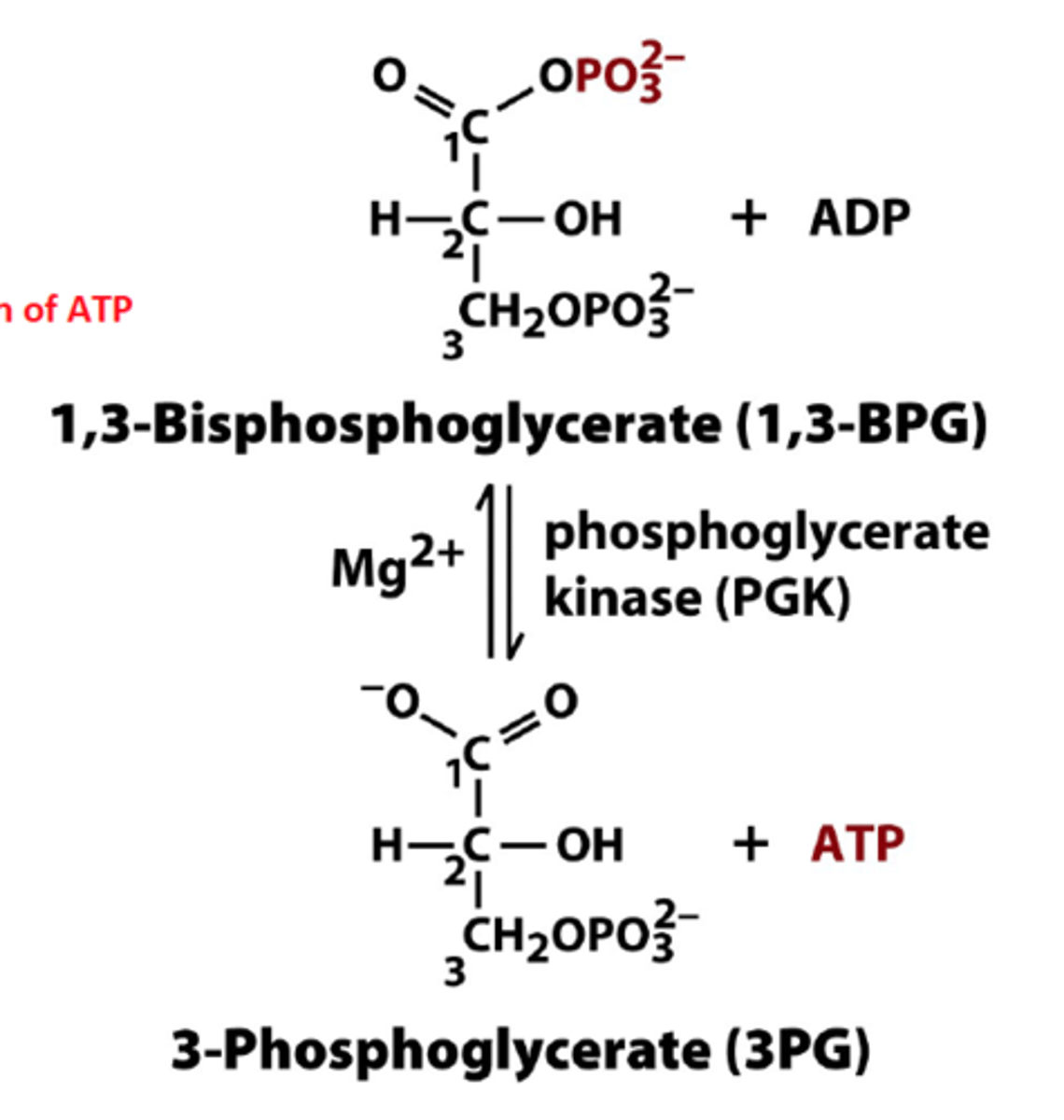
7th step of glycolysis
3-phospholygeric acid turns into 2-phospholygeric acid
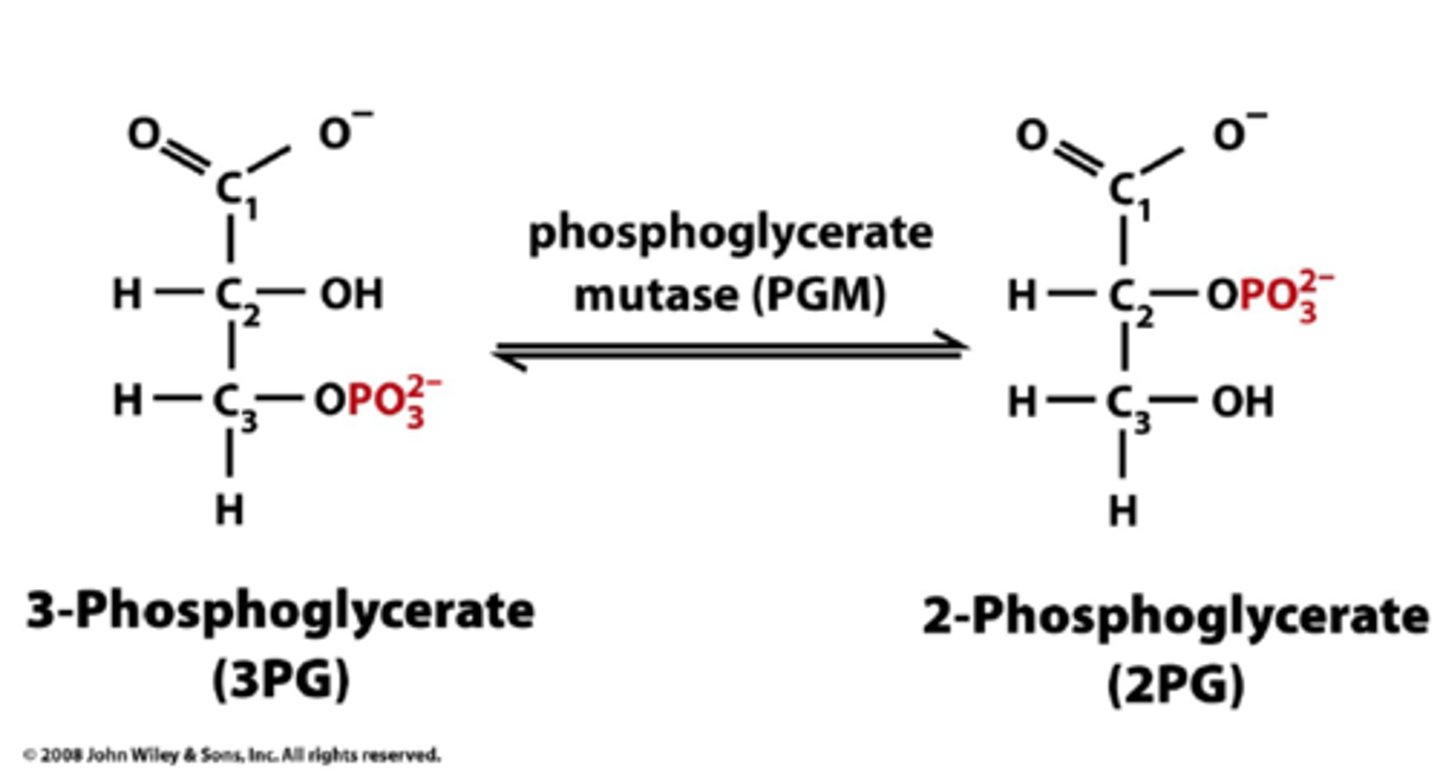
8th step of glycolysis
2-phospholygeric acid turns into phosphoglyceric acid
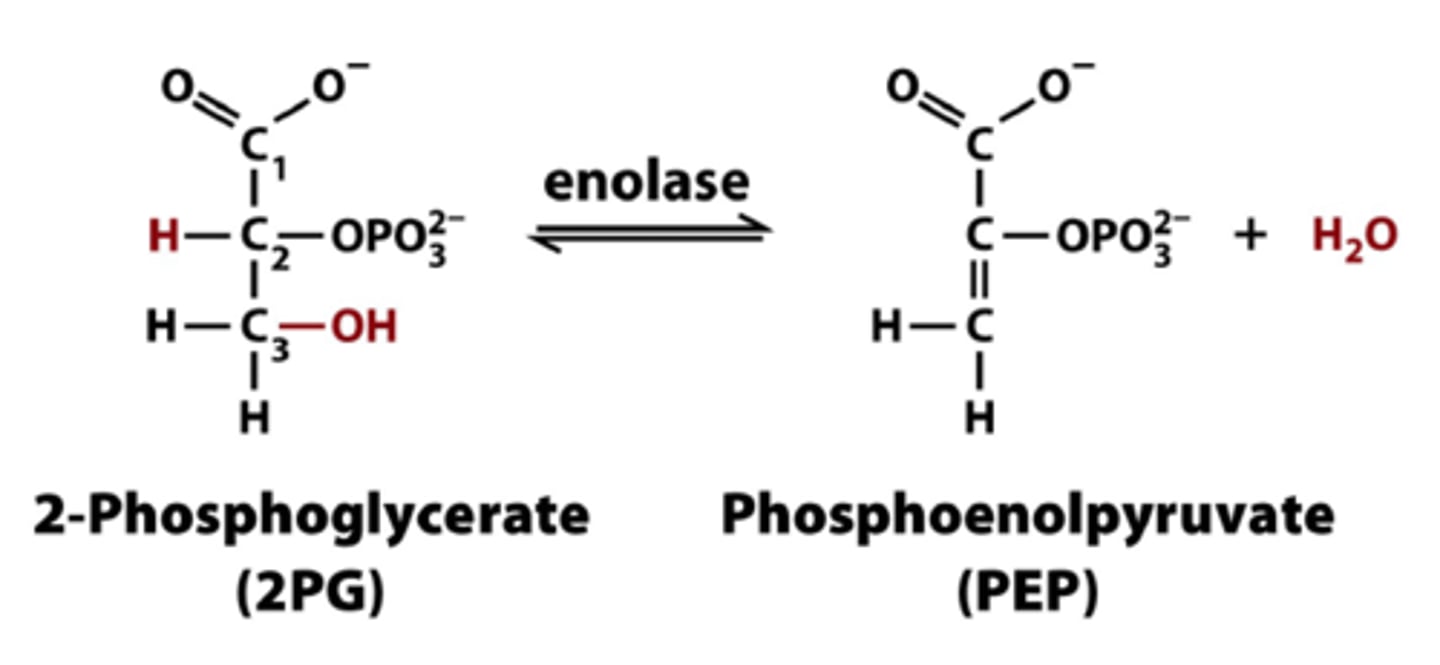
9th step of glycolysis
pyruvate kinase transfers a P from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to ADP to form Pyruvate and ATP

phosphorylase
Adds inorganic phosphate onto substrate without using ATP (e.g., glycogen phosphorylase).
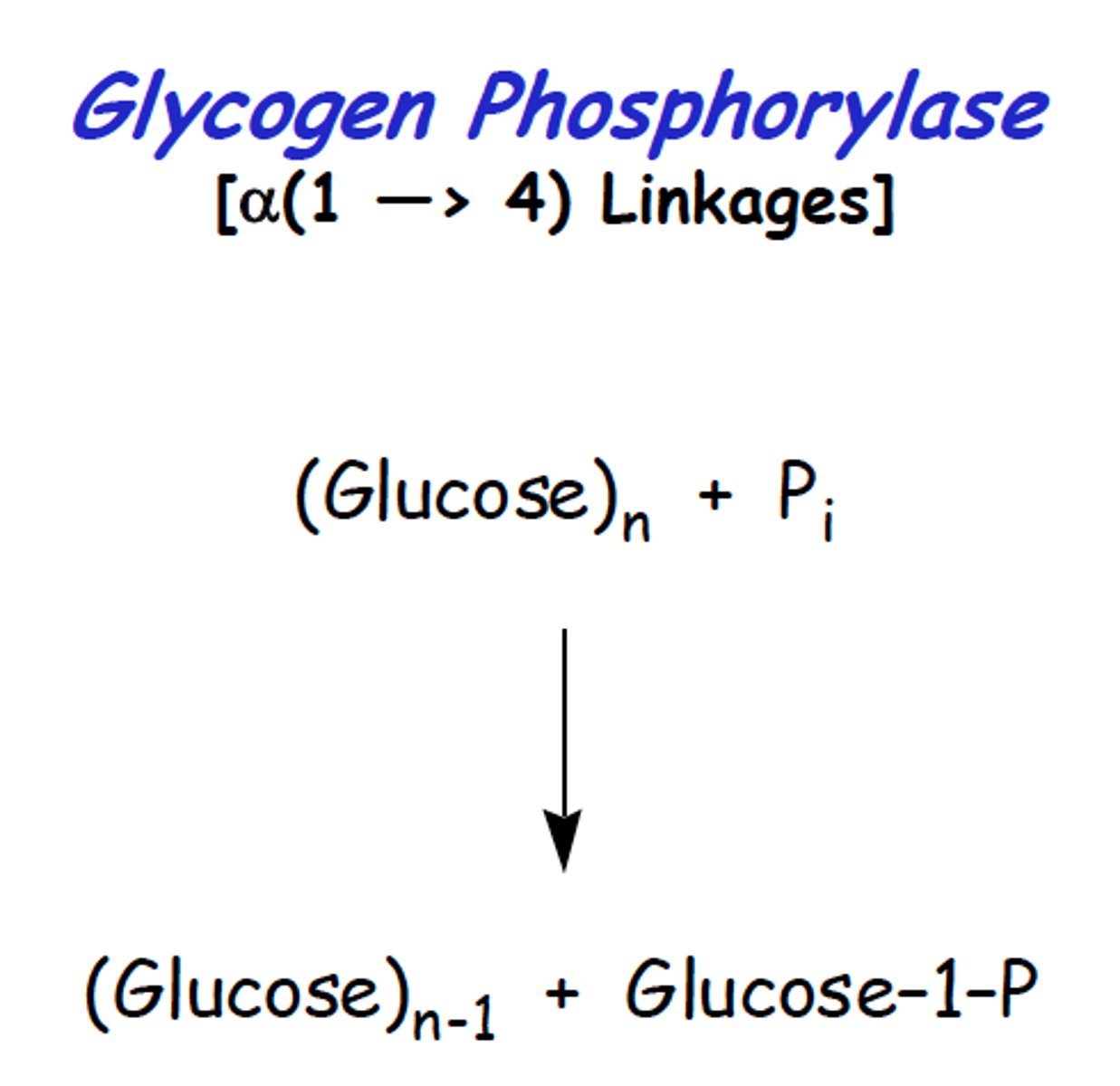
dephosphorylate
Remove phosphate from molecule
anaerobic pyruvate
turns into lactic acid
aerobic pyruvate
turns into acetyl CoA
Krebs cycle
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
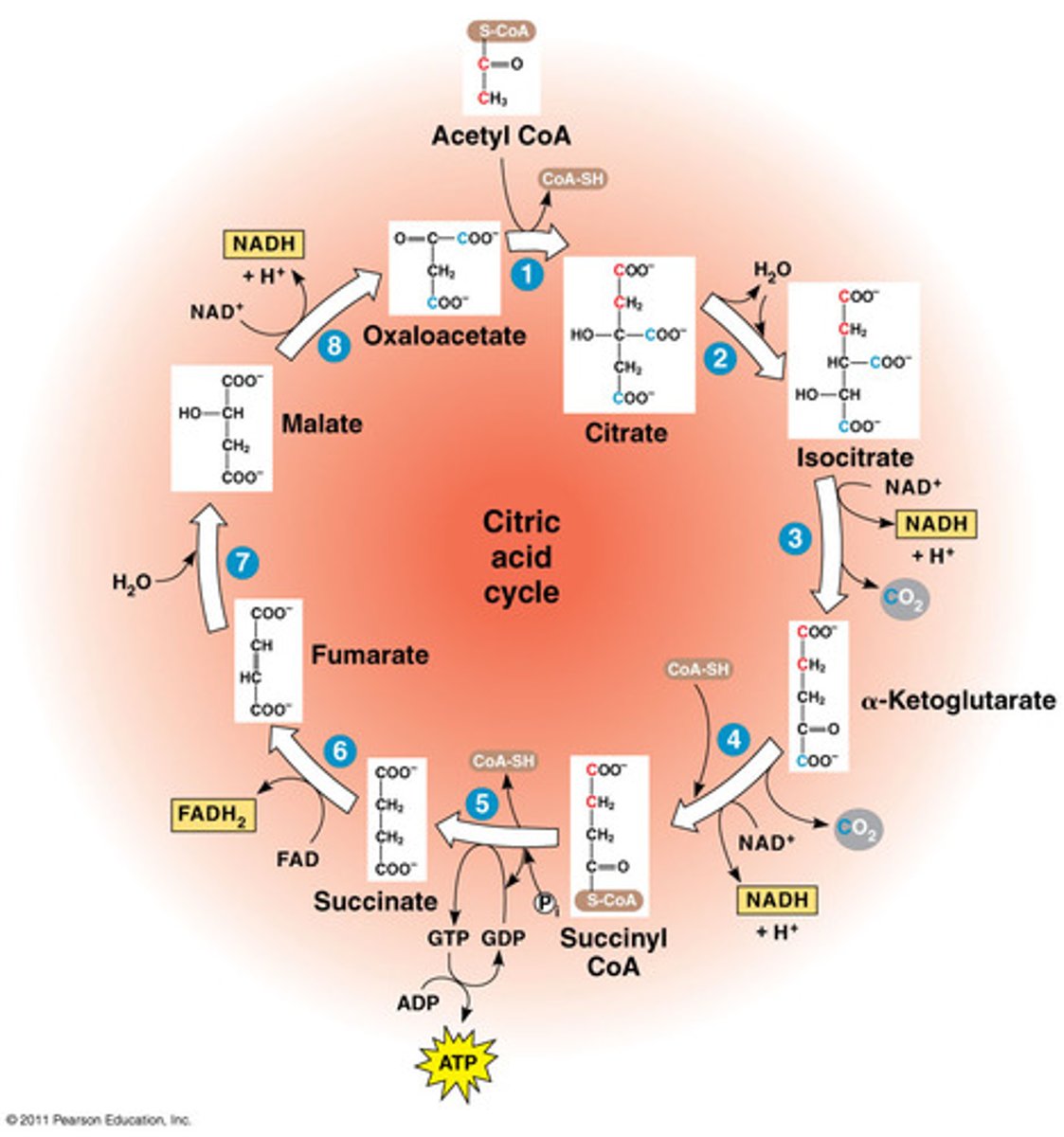
outcome of glycolysis/Krebs cycle/and electron transport chain
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH/NADH + H+ and FADH2/H2O and ATP
1st step of Krebs cycle
Acetyl CoA donates the acetyl group to
Oxaloacetic acid
to generate six-carbon molecule, Citric acid.
(CoA released during this reaction can be recycled back)
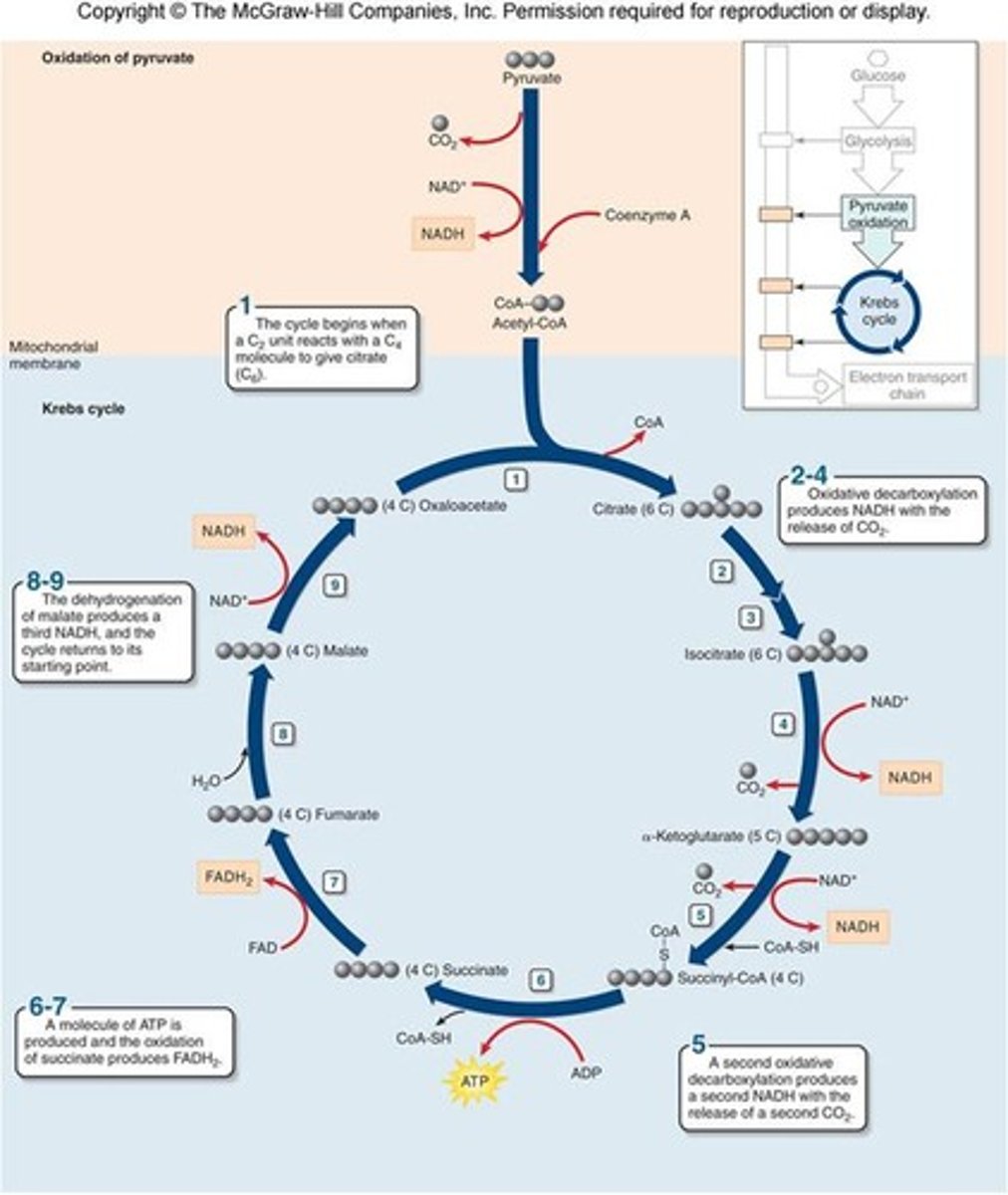
2nd step of krebs cycle
citric acid is isomerized to isocitrate acid
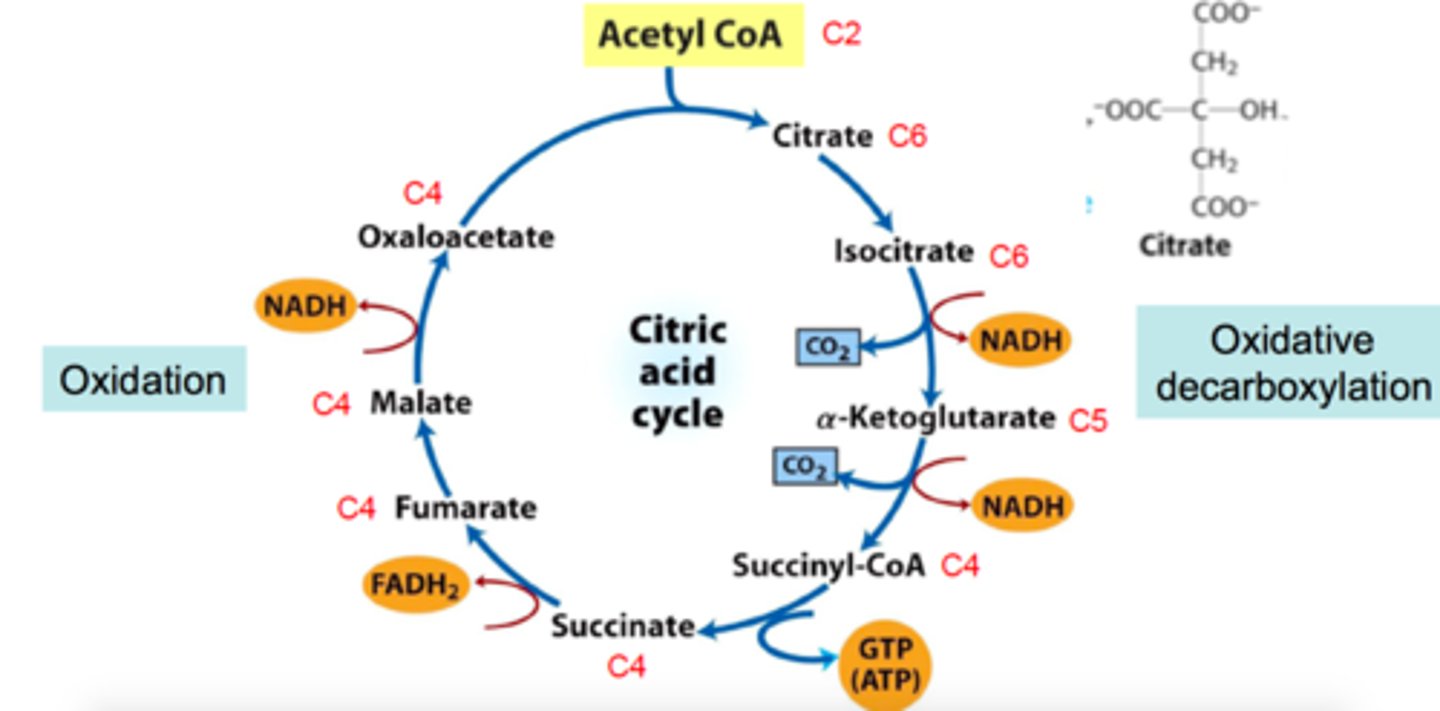
3rd step of krebs cycle
Isocitrate acid is oxidized oxidative hydroxylation reaction), it loses CO2 and also H ions are passed to NAD+ which makes NADH + H+
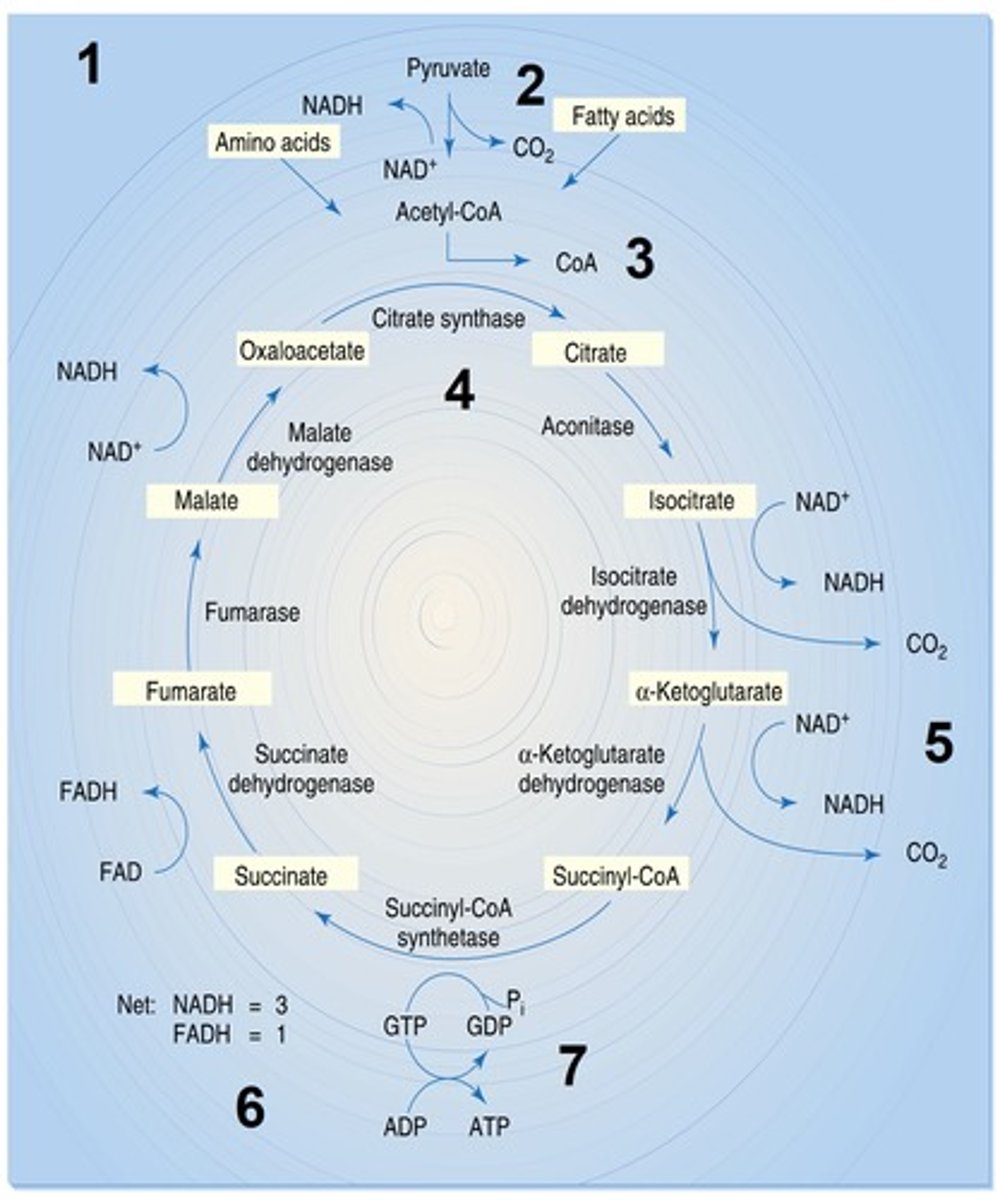
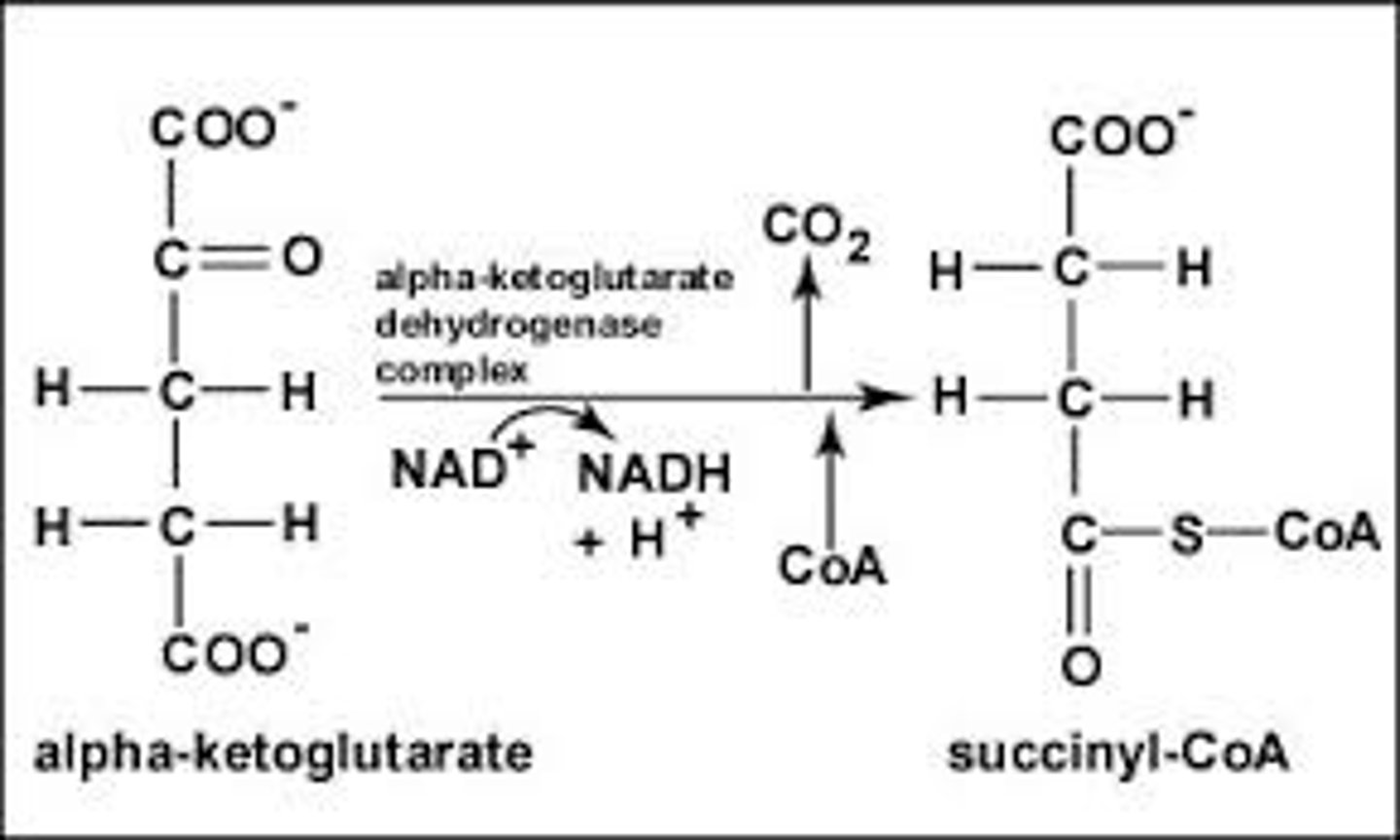
4th step of Krebs Cycle
alpha-ketoglutaric acid is oxidized and loses CO2, picks up CoA; H ions are passed to NAD+ which makes NADH + H+
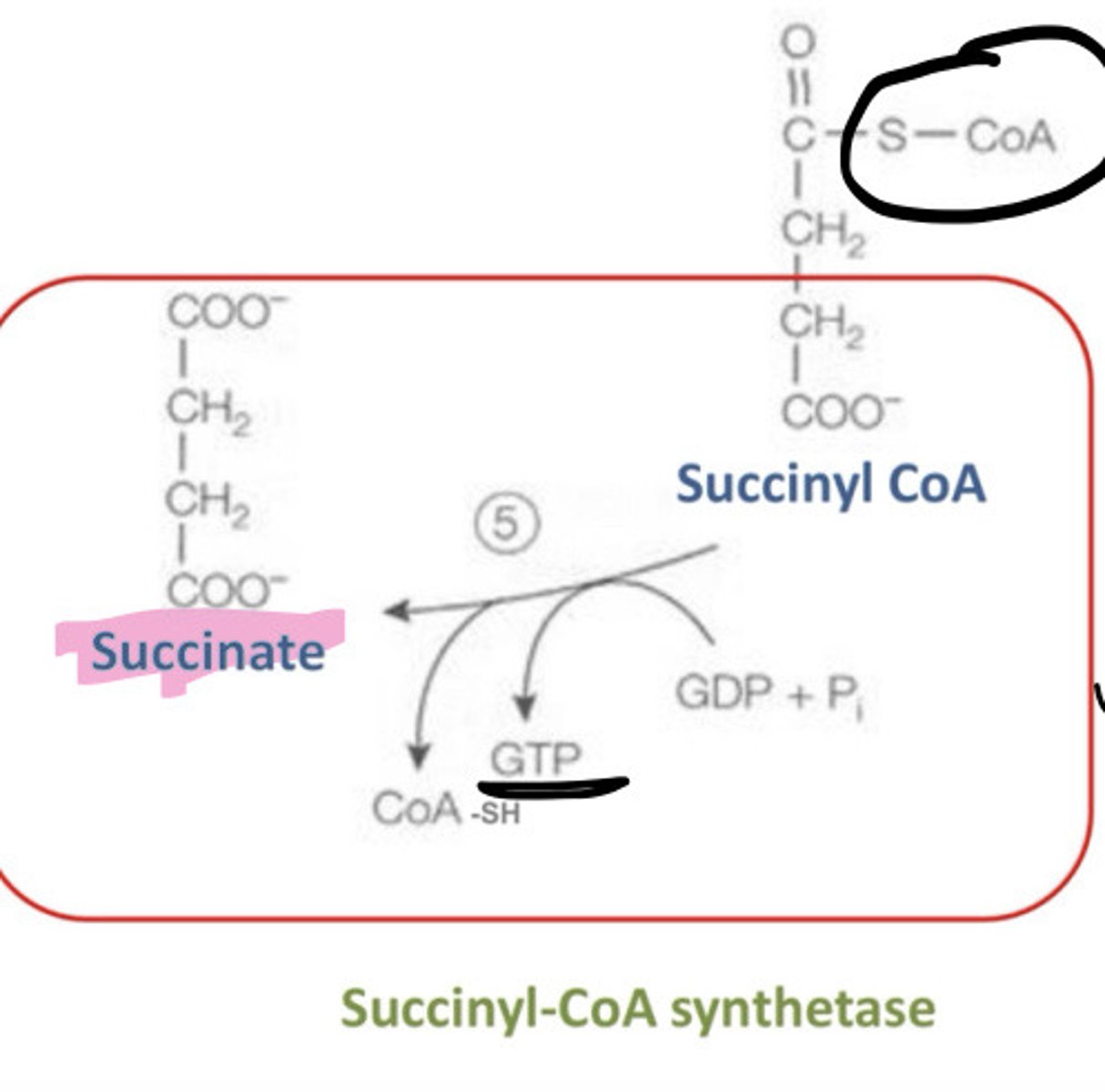
5th step of Krebs Cycle
succinyl CoA's CoA gets replaced with a PO4. It then transfers to GDP then GTP, then gives its PO4 to ADP which creates ATP
6th step of krebs cycle
succinate acid gets oxidizes, and 2 H go to FAD which reduces it to HADH2
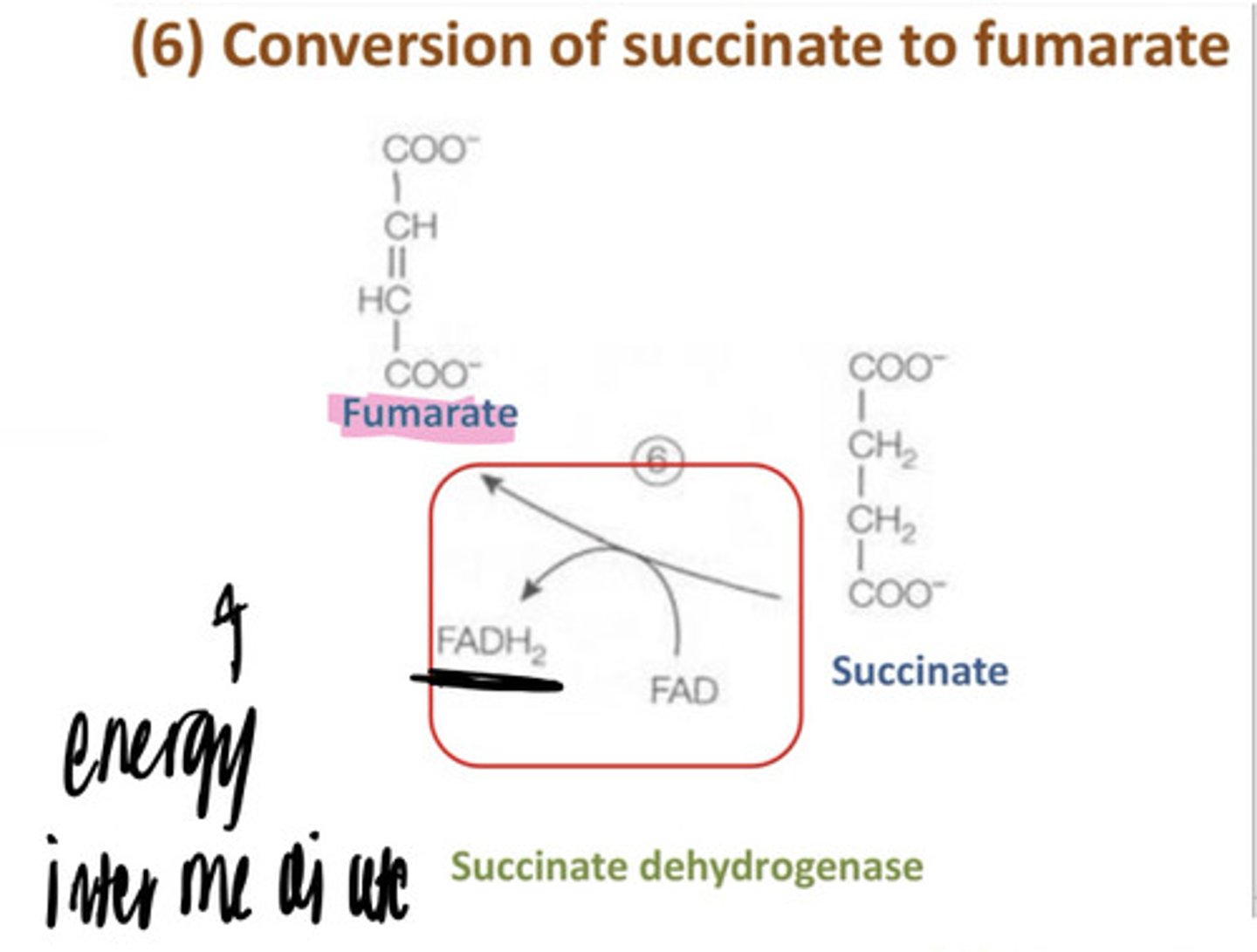
7th step of Krebs Cycle
fumarate gets water added to it to form malic acid
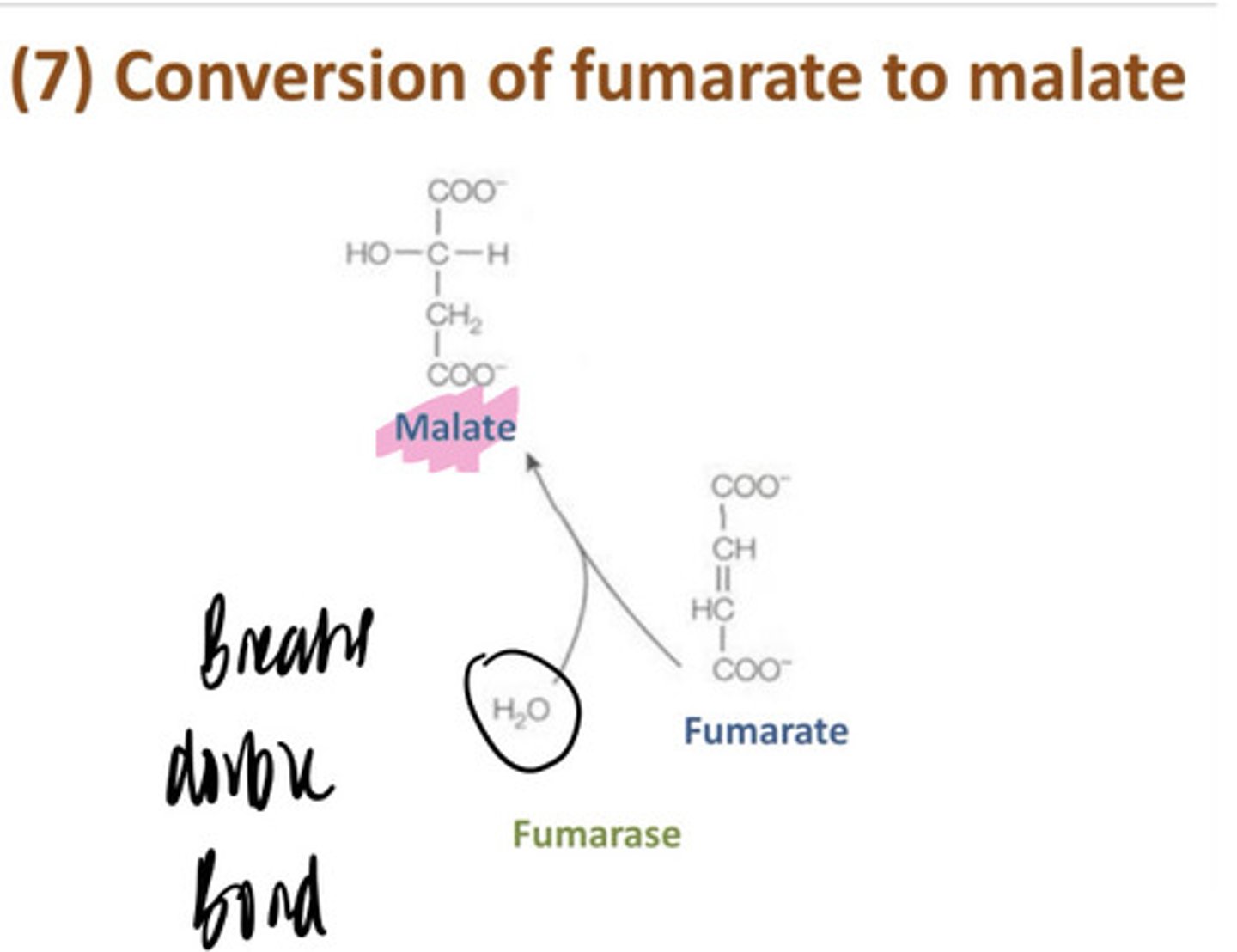
8th step of Krebs Cycle
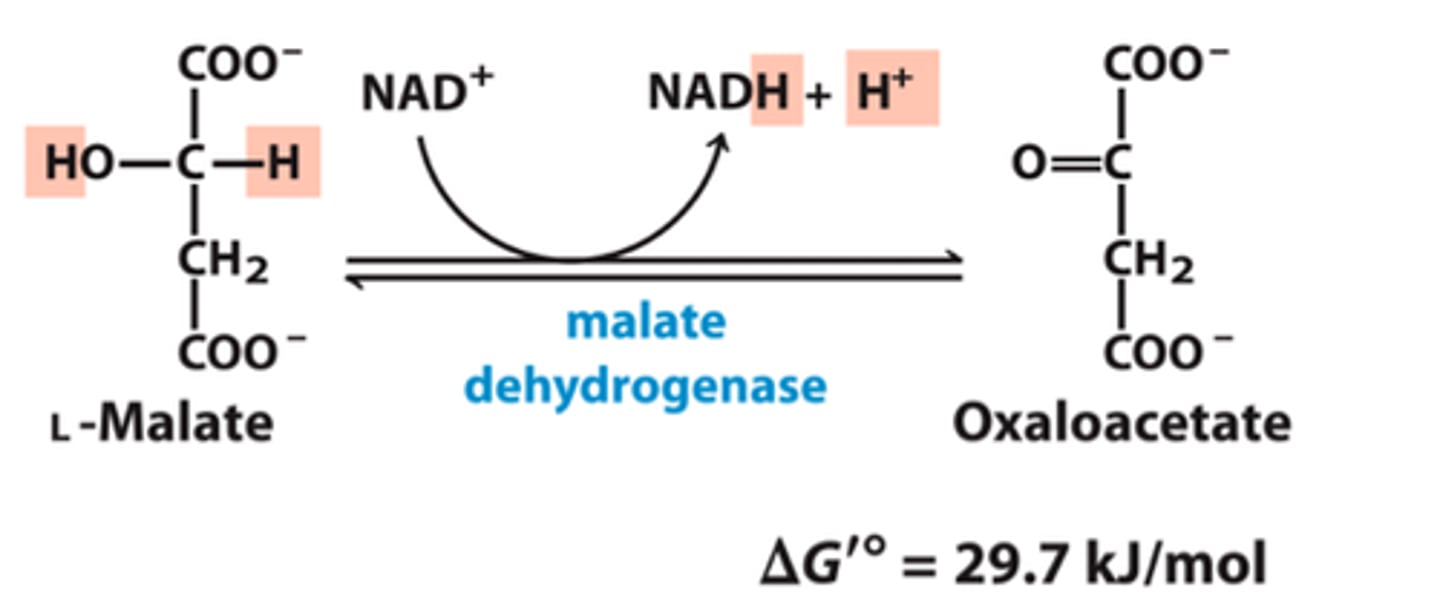
malic acid oxides to create oxaloacetic acid
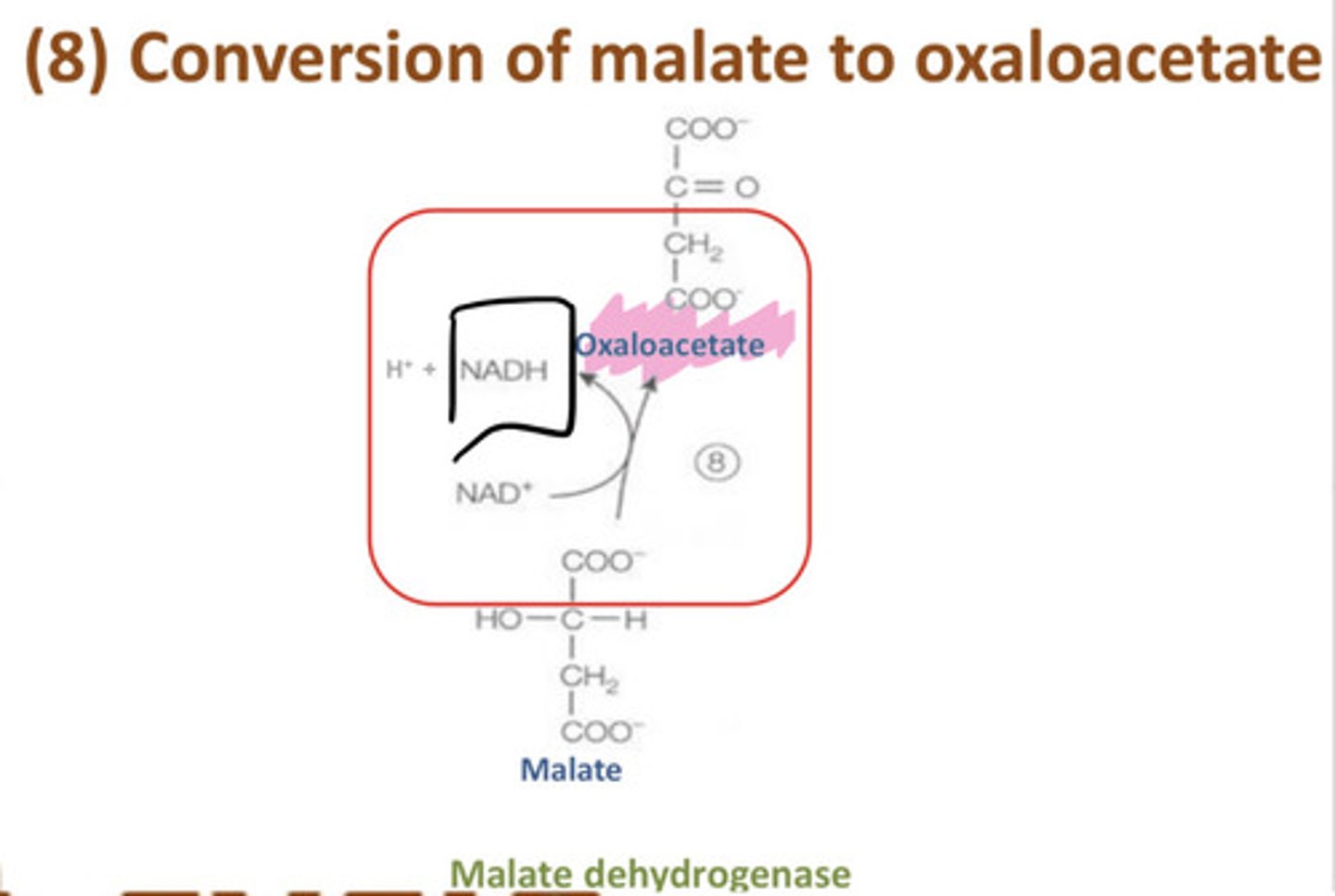
9th step of Krebs Cycle
oxaloacetic acid loses 2 H and reduces NAD+ to NADH + H+
pantothenic acid
vitamin B that makes coenzyme A (CoA)
acetyl CoA
pantothenic acid converts to CoA + pyruvate dehydrogenase converts to pyruvic acid
Electric Transport Pump 1
FMN and 5+ iron-sulfur centers
- mobile carrier is mobile Q
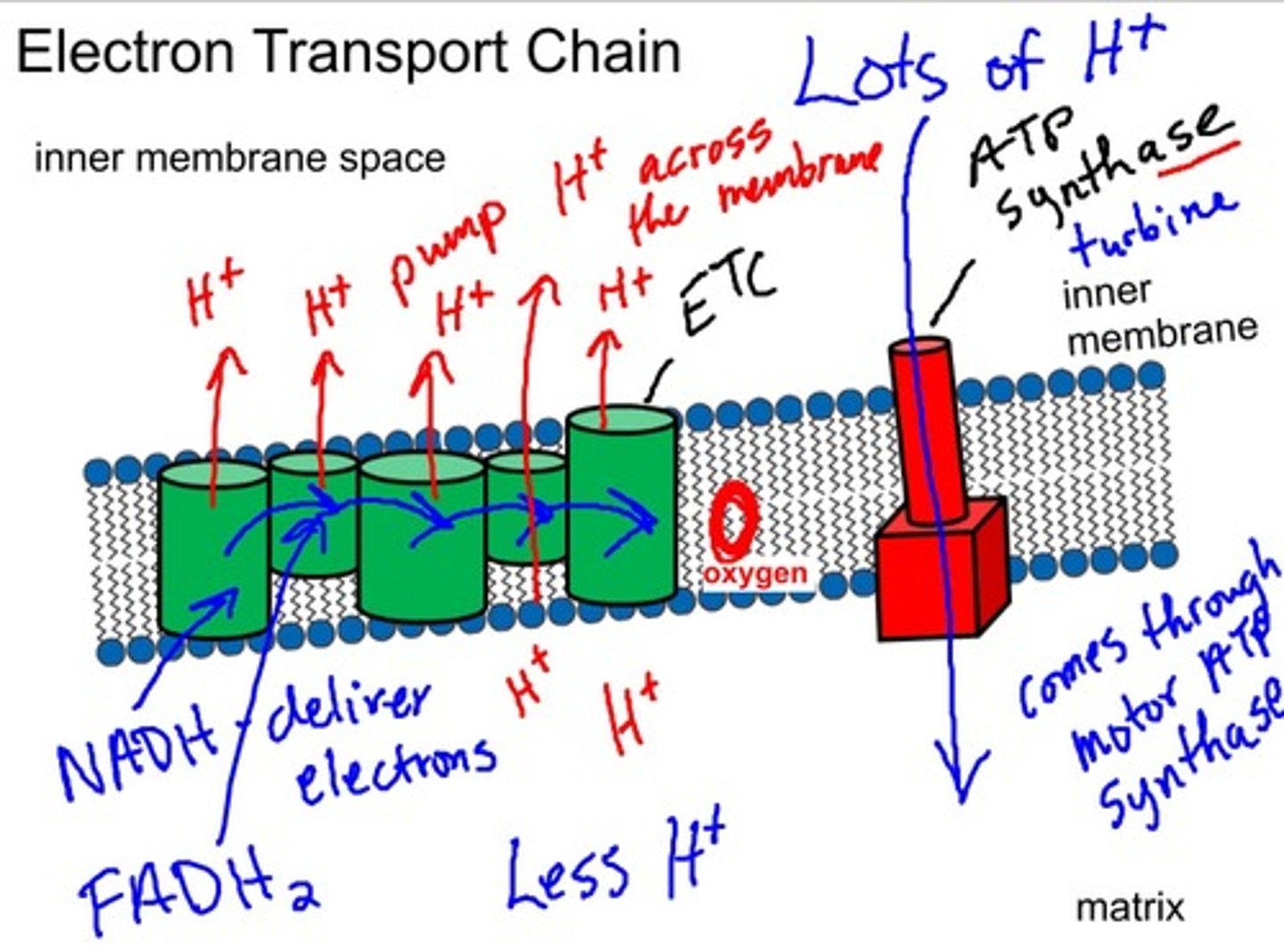
Electric Transport Pump 2
the cytochrome cb-c1 -> hands off electrons to cytochrome B -> B to Fe-S center ->Fe-s to cytochrome c1 -> cytochrome acts as mobile shuttle that moves electrons to the last pump
- mobile carrier is mobile C
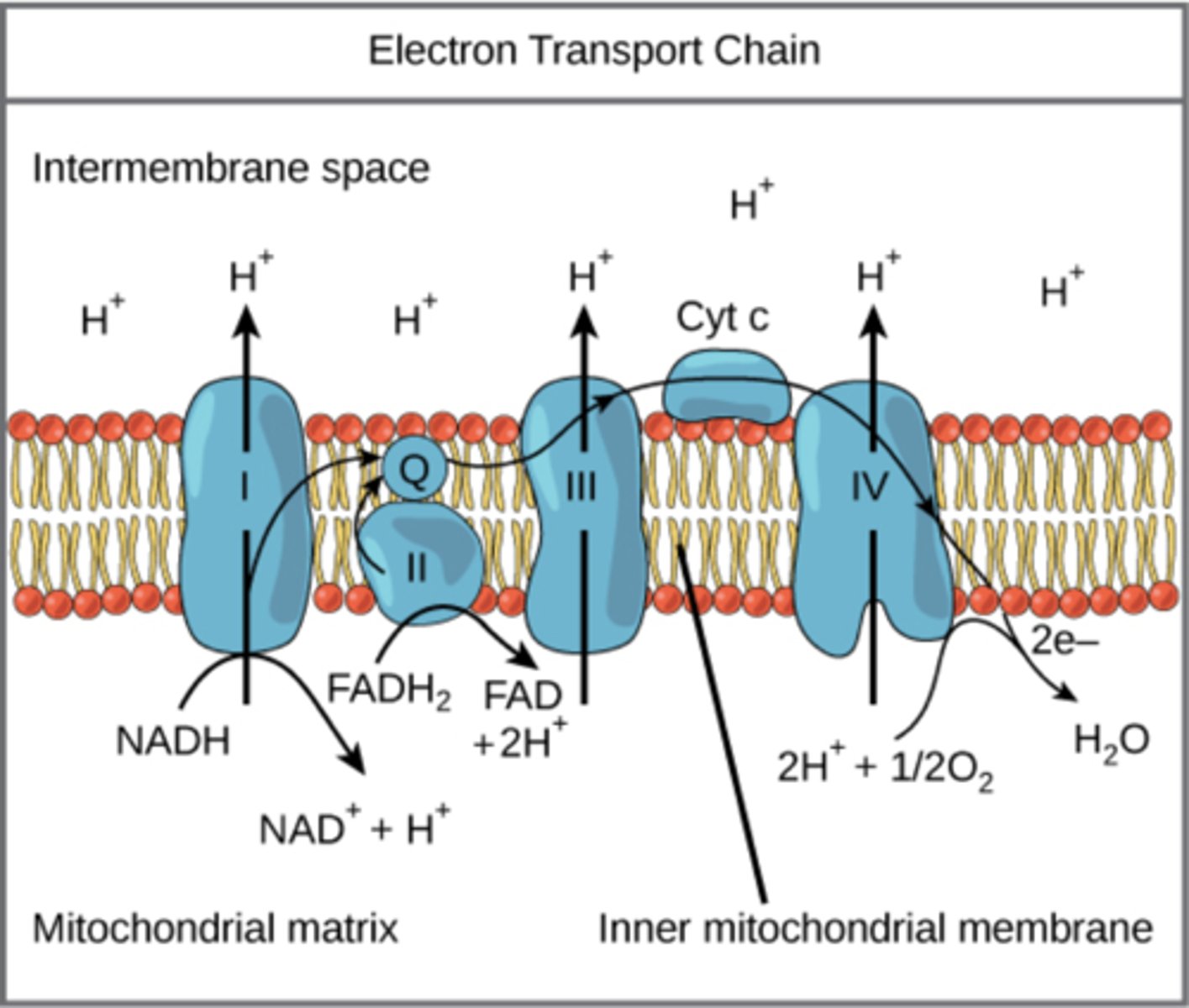
Electric Transport Pump 3
Cu, cytochome a, cytochrome a3, and oxygen
- makes water
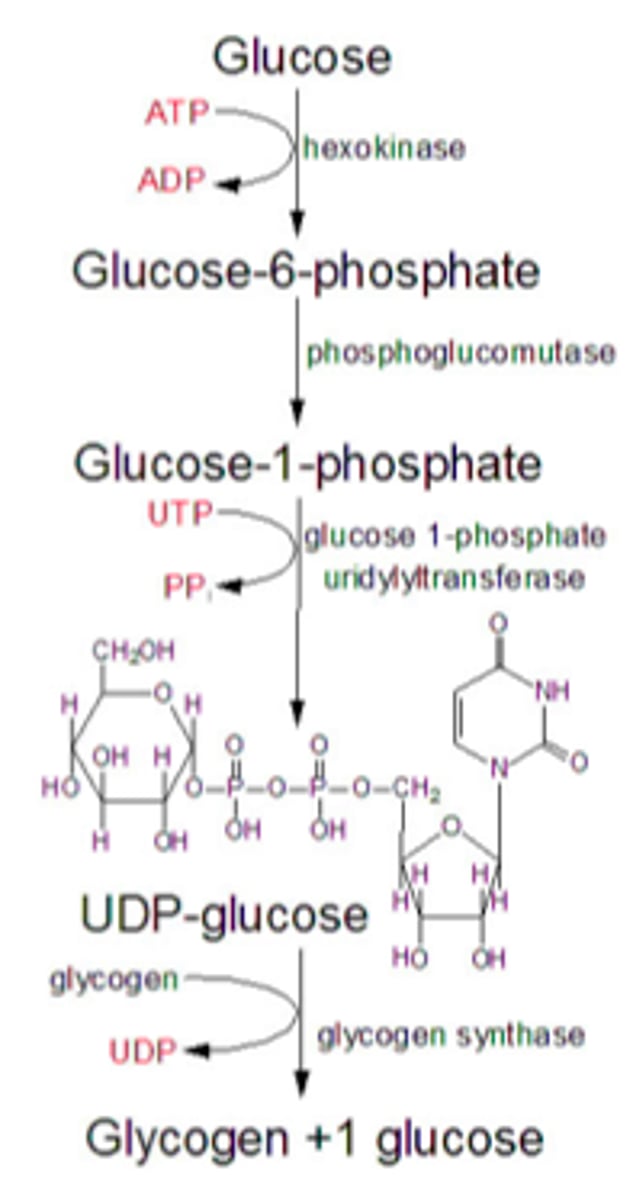
Glycogenesis
formation of glycogen from glucose; saving glycogen for a rainy day
- triggers: high blood sugar
- Phosphorylation of glucose -> glucose 6-phosphate -> glucose 1-phosphate -> uridine diphosphate glucose -> glycogen (not in normal glycolysis)
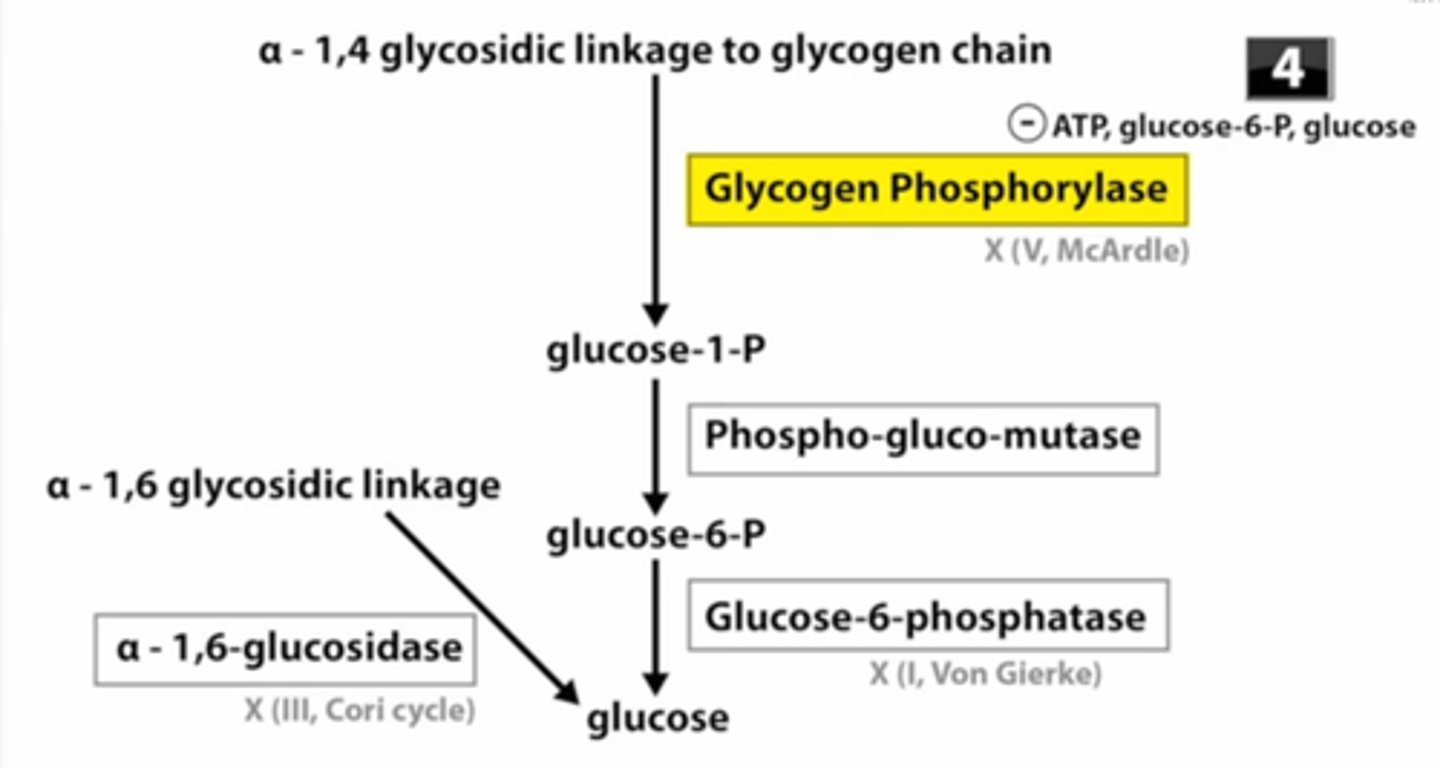
Glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen to glucose; withdrawl from rainy day fund
- triggers: low ATP and blood sugar
- Phosphorated branched glycogen -> glucose 1 phosphate -> glucose 6 phosphate (nonspecial cells stop here)-> glucose (only in special cells that have phosphatase)
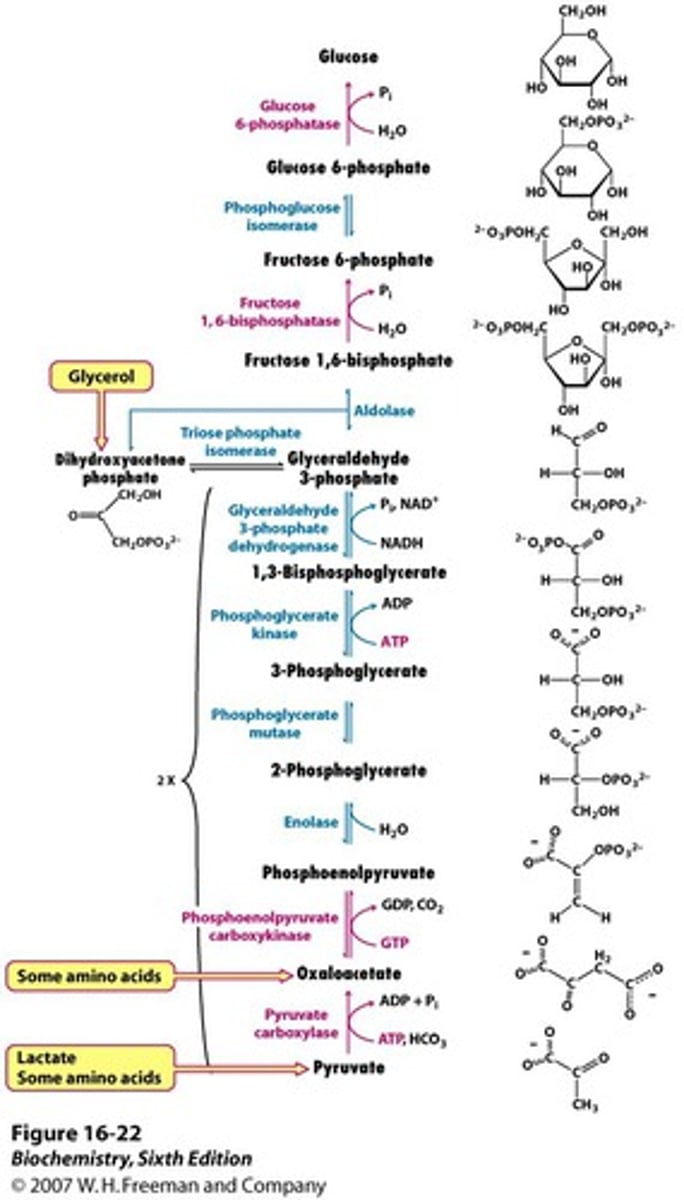
gluconeogenesis
additional sources of sugar when glycogen is exhausted; triglycerides (lipids); second choice
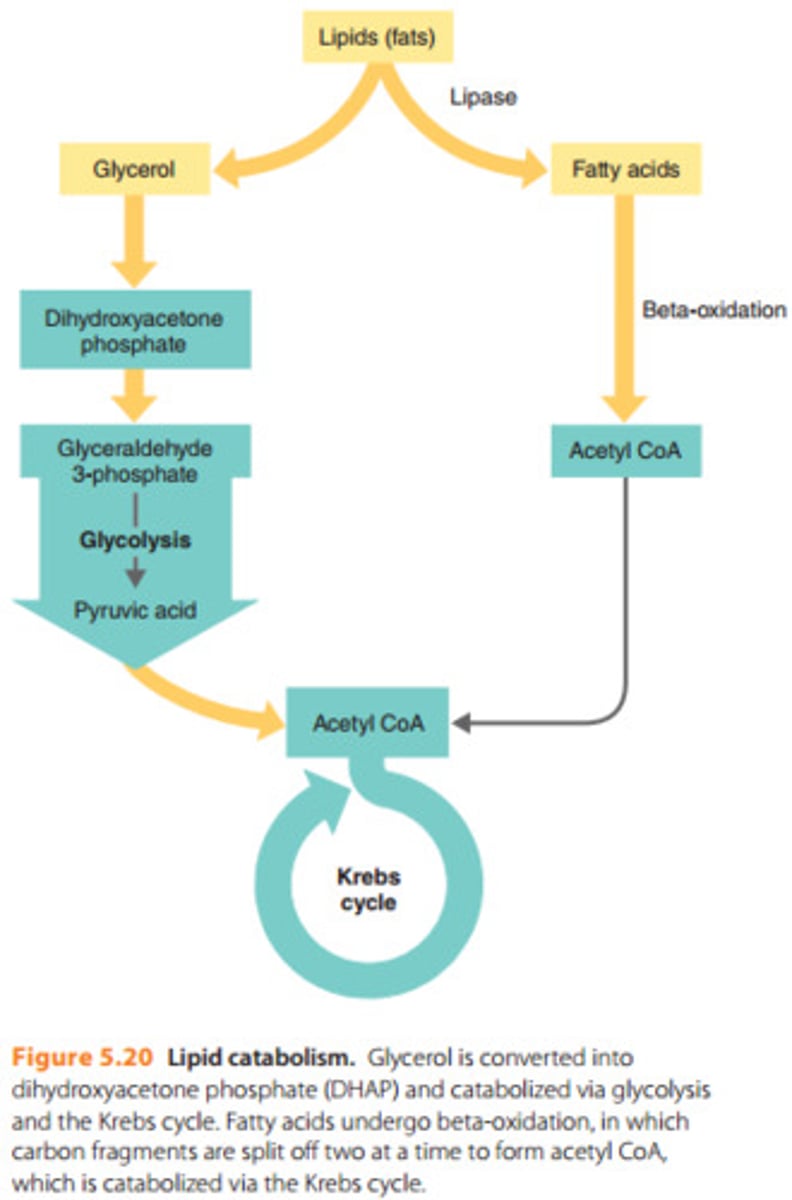
Lipolysis
the breakdown of fats and other lipids by hydrolysis to release fatty acids; goes to G3P from glycerol; goes from beta oxidation to acetyl CoA
- triggers: increase of SNS
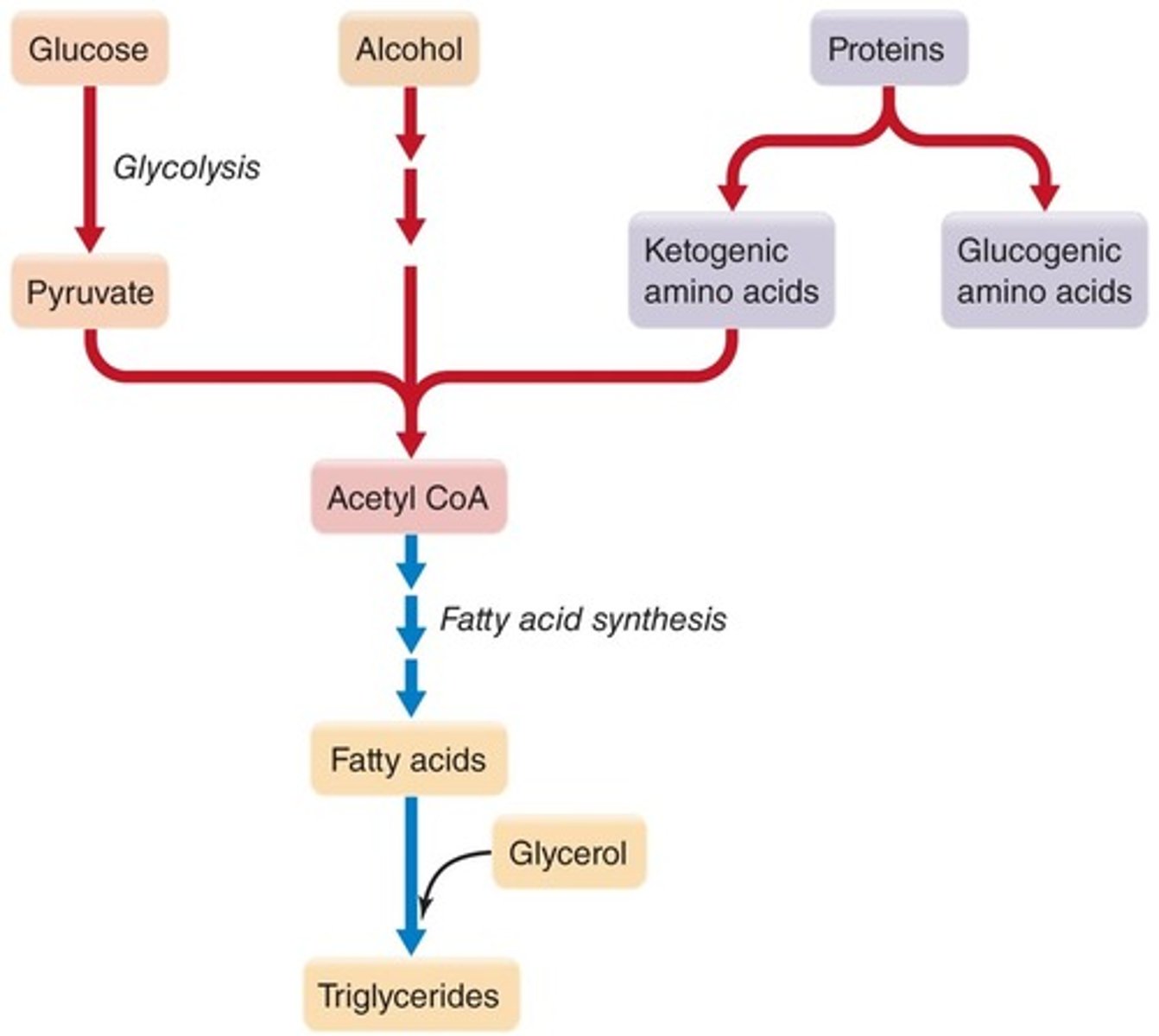
Lipogenesis
the process of converting protein into fatty acids; G3P to glycerol; pyruvate to fatty acids and/or acetyl CoA
alternate sources of fuel for glycolysis/krebs/ETC
amino acids - pyruvic acid
lactic acid - pyruvic acid
glycerol - G3P
lipoproteins
transports fats in the blood, a hollow sphere with a outer shell of protein and inner shell of lipids
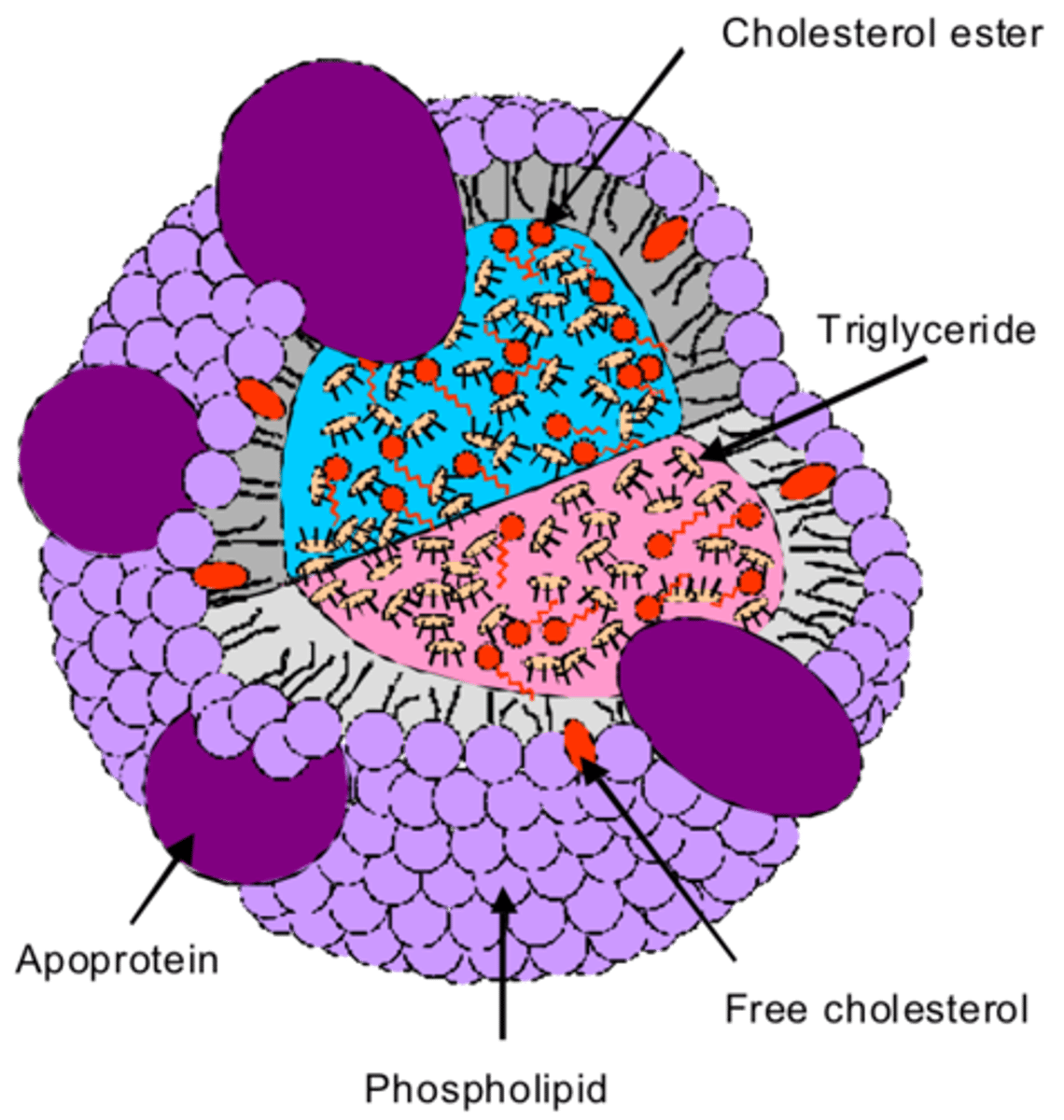
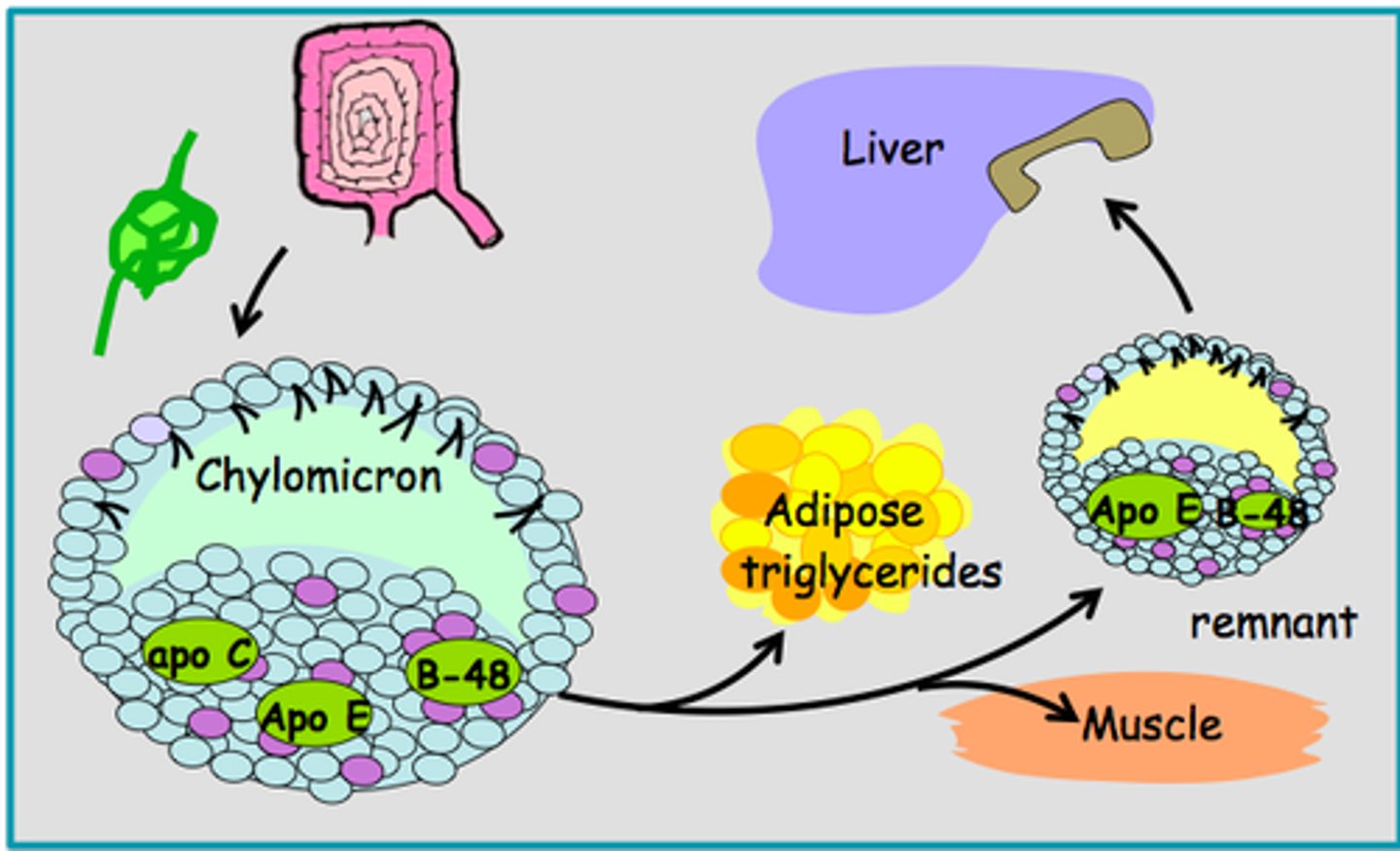
Chylomicrons
lightest and largest lipoprotein, on inner surface on the intestine
VLDL
-Very Low Density Lipoprotein
-Formed in the liver to carry lipids
TO the body
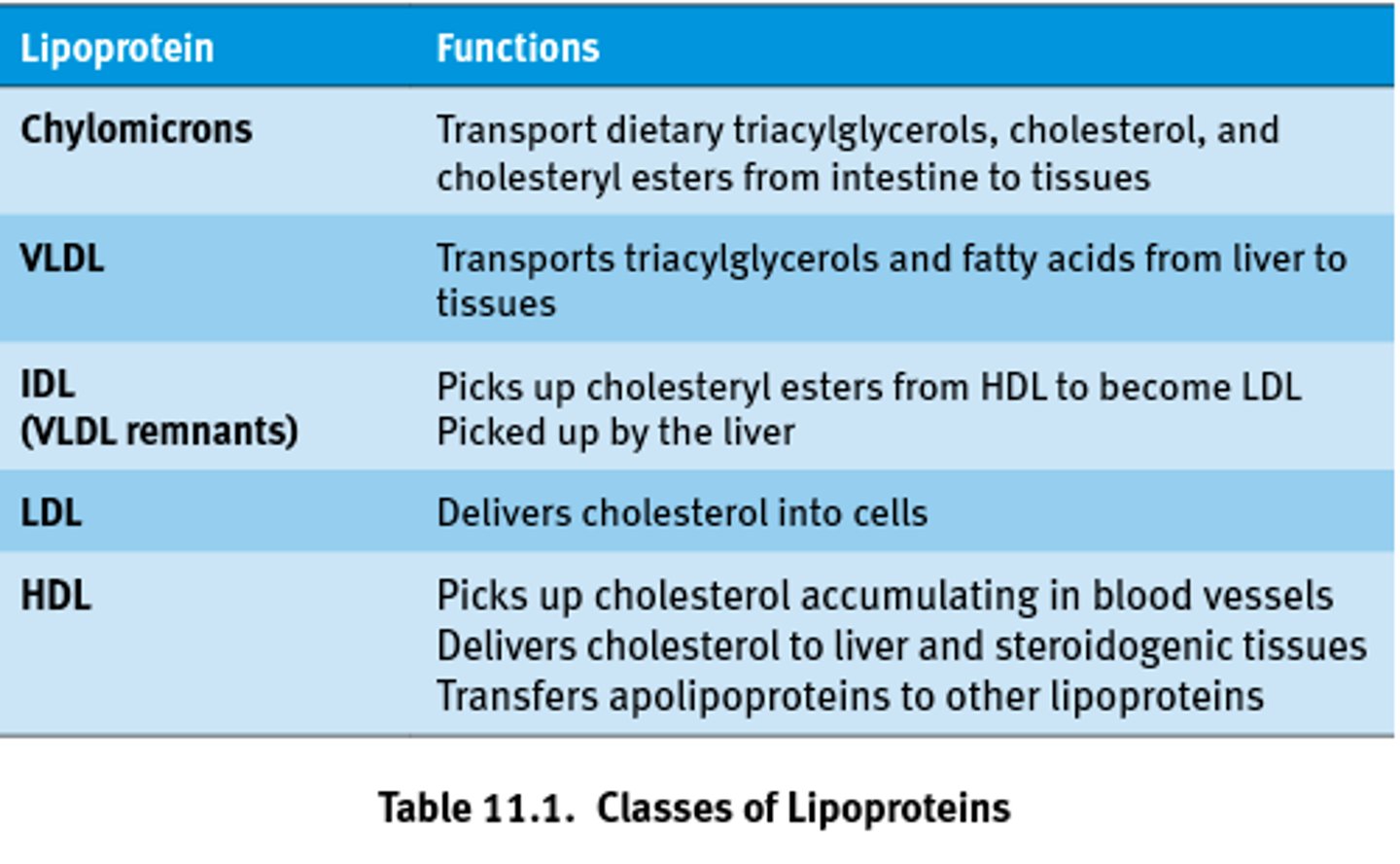
LDL
- low density lipoprotein
- unhealthy (depositing lipids in wrong place often that can cause buildup)
- carries 75% of total cholesterol
- repairs damage
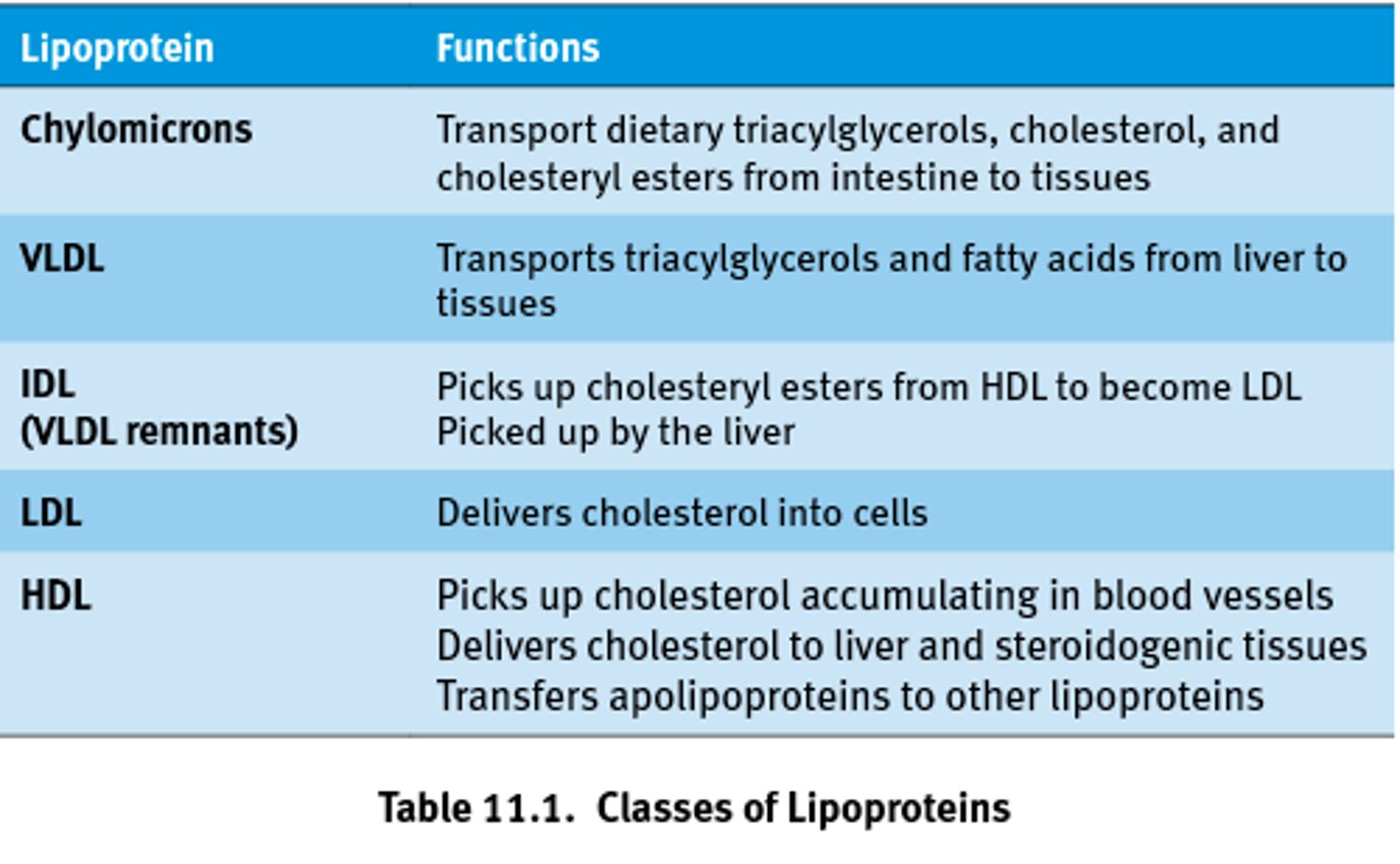
HDL
- high density lipoproteins
- healthy type of cholesterol (removes excess cholesterol)

sources of cholesterol in the blood
food and hepatocyte activity
Protien catabolism
triggered by adrenal cortex
- hepatocytes -> amino acids -> fatty acids -> glucose
- amino acids get R group taken off = produces ammonia
- third choice; because of ammonia