PSY 3510 Exam 3 Study Guide
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Corporate Downsizing
Individual response: affects mid-level managers/professional staff & blue colllar workers
Terminated personnel are most directly affected (little time to search for new job, Marienthal case study)
Psychological effects: headaches, stomach problems, HBP
Learned helplessness, lower self-wowrth, inc in depression, feelings of betrayal, demoralization & cynicism
Survivng personnel has reduced trust & commitment b/c of violation of psychological contract (demotion, job-sharing, part-time/reduced hrs)
Organization may hire temporary workers (commonly young, female, minority); anti-social behavior
Psychology of Mergers & Acquisitions
Organizational merger - joining of 2 organizatons of equal status/power
Acquisition: procurement of property by another organization (dominance/hostile takeover)
Phases
Precombination: focus on financial issues: worth, taxes, return
Combination
Postcombination: potential culture clash, decline of employee morale & customer satisfaction
75% of mergers fail
Reactions to acquisitions are similar to bereavement (grief process)
Examples: Daimler-Benz & Chrysler, Google & Motorola
Antisocial Behavior in the Workplace
Types
Verbal, physical, sabotage, work-directed, workplace homicide
Frequency and severity of violence are escalating
Starting point to understanding violence is aggression
Three types of strategies in dealing with violence in the workplace
Display of sensitivity & concern; tolerate organizational violations of justice
Environmental Influences on Mental Health
Nine determinants (how the environment affects mental health)
Oppportunity for control: opportunity to choose own behavior/understanding relationship btwn behavior & consequences
Opportunity for skill use: environmental capacity to facilitate/inhibit skill use; lack of opportunity to use acquired skills/develop new ones
Externally generated goals: environment that creates challenges & goals; enhances mental health; non-stimulating environments lead to apathy
Envrionmental variety: environment provides choices & options; lack leads to reduction of skills & repetition leads to monotony/poorer health
Enviornmental clarity: how clear are the demands of the environment?
Unambiguous rules/standards for acceptable behavior
Accurate feedback regarding exhibited behavior
Availability of money: absence of $ leads to inc. mental, physical, & emotional impairment
Physical security: difficult to be mentally healthy if physically in danger; threat-free environment
Opportunity for personal contact: forming relationships for social/emotional fulfillment; isolation can cause mental/physical harm
Valued social postion: position in society held in high esteem; self esteem is derived from societal contribution; job loss associated w/ feelings of diminished role & poorer mental health
The Concept of Mental Health
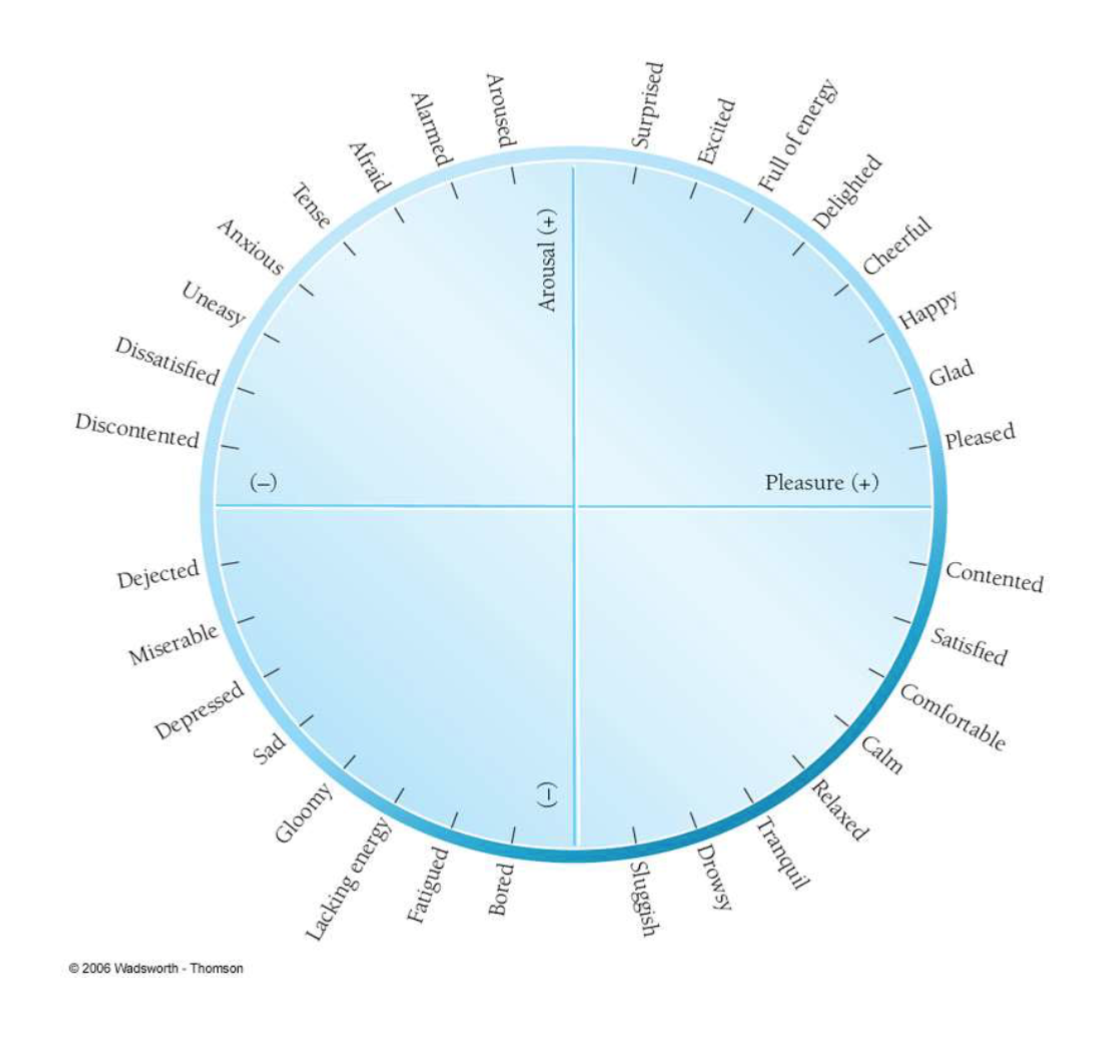
Affective well-being: pleasure/arousal; two-factorial model
Competence: success in various factors of life (relationship, employment, adaptability)
Autonomy: freedom to choose path of one’s own behavior based off of values; more emphasis in Western cultures
Aspiration: striving to achieve a more desirable outcome; low levels associated w/ resignation/acceptance
Integrated functioning: personal balance, harmoney, & inner relatedness; love/work; most difficult to achieve
Work Stress
No agreed-upon definition - good stress v. bad stress
Workplace stress among 10 work-related diseases/injuries in the US
Research focuses on caues, symptoms, consequences, & interventions
Physical, task-related, role, social, work-schedule, career-related, traumatic events, stressful change processes
Eustress (good stress)
Distress (bad stress)
A Model of Stress
Organizational antecedents to stress
Relationship btwn economic conditions & social indicators of health
Unemployment related to inc in psychosocial illness & absences
Stressors in organizational life (lead to ill health)
Types of tasks performed at job: simple-complex; repetitive-varied
Role properties
Other stressors related to ill health
AC buildings, sensory irritation; neurotoxic effects
Role conflicts; between-people & internal
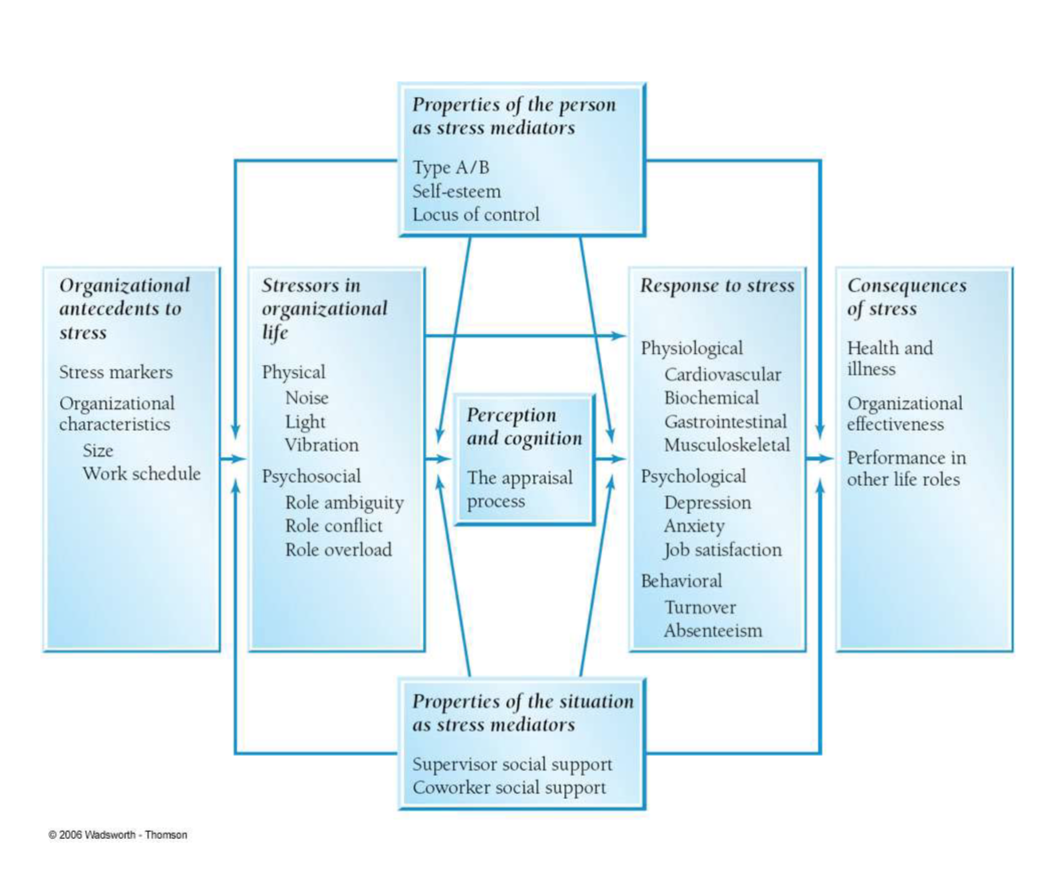
Perception and cognition
1. The (stress) appraisal process
Primary appraisal - initial assessment to whether stimulus is helpful, harmful, or no consequence
Secondary appraisal - determination of action taken to inc benefit or decrease potential harm
2. Response to stress
Physiological - BP, cholesterol, biochemical levels, gastrointestinal cond.
Psychological - Job dissatisfaction, inc in neg. emotions/mood; chronic stress associated w/ dec. in self-confidence & self-worth; numbness
Behavioral - job behavior, flight, antisocial behavior at/off work, self-abuse
3. Consequences of stress
Stress has impact on overall health & quality of life; non-work stress affects work attitudes & behavior
Properties Of The Person As Stress Moderators
Personalities:
Type A: walk, talk, eat rapidly, aggressive, competitive, under pressure
Type B: less concerned about time, play for fun/not to win, relax w/o guilt
Type A higher resting BPM; 2x as likely to develop heart disease; need for achievement
Locus of control:
Internal: belief that people are in control of their lives through skill, knowledge, effort, or decision-making
External: things happen due to external factors
People w/ high ego resilience endure stress effectively
Properties Of The Situation As Stress Moderators
Situational factors: social support to reduce stress effects; no relationship to boredom/job satisfaction
Unavoidable stress allows prediction of onset/offset
Prevention and intervention
Stress is preventable, or at least treatable
Prevention: physical fitness, exercise, meditation, time management
Intervention: counseling, social support groups, employee assistance programs
Work/family conflict
Understanding this conflict is a major role of I/O psychology
- Three topics that are research targets:
Effect of work on family
Effect of family on work
Family-work interaction
- Three conceptual models offered to explain work-family relationships:
Spillover model: similarity btwn work/family environment; work exp has influence over outside work exp; work attitudes spill over to family
Compensation model: inverse relationship btwn work & family; individuals make differential investments in these settings
Segmentation model: work/non-work are distinct; no influence from one to the other
- Other findings:
Work & family affect each other; are independent; are intertwined; overlap
Relationship btwn work & family changes; difference btwn families
2/3 of new workers female; ¾ of them eventually pregnant, sandwich generation; men have 60% spouses who work
- Ways to reduce work-home conflict
Additional skills besides time management
Accommodations to workers
Near-site childcare centers
Family leave
- Elder care is a growing concern

Dual-career families
Balancing demands of work/family
Mothers w/ young children work average 77 hrs/week
Most dual-career couples have work oriented lifestyle prior to birth of children
More women than men accommodate career to family; work environment does not adjust
Source of marital tension; agree on needed level of work success/family commitment
Lack of temporal control over time
Work schedules
- Shift Work
Common schedule 8-5 M-F
Police, physicians, nurses 24-hr services (3 8-hr shifts)
25% of working hrs in US are nontraditional
Issues in circadian rhythm, social life/relationships, fulfillment
- Flexible work hours
Variation = flextime
73% of US employers offer it
Everyone present during core time
Latitude in other hours (flexband)
Flexible work hrs alleviate outside-work problems
Mostlly benefits lower-level employees
Helpful for dual-career families, absenteeism, but inhibits g
- Compressed workweek
4 10-hr shifts
More free time; less costs
Fatigue, less productivity, accidents
Alcoholism And Drug Abuse In The Workplace
Substance abuse: includes alcohol, illegal and prescription drugs
- Performance impairment: negatively affect basic cognitive processes
- Issues of life-style and culture
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
- Addressing the problem of drug abuse: Two approaches:
Permissive norms about alcohold use
Acceptance by coworkers only by drinking more than them
- Staggering financial costs of $70 billion (based on four factors)
Costs of treatment
Lowered work productivity
Loss of income due to premature death
Crime-related costs
The Psychological Effects Of Unemployment
Unemployment is psychologically devastating
Research as to consequences of employment:
1. Jahoda: Intended and unintended
- Five latent consequences of employment
Impostion of time structure
Regular shared exp & contacts w/ people
Linking individuals to goals/purposes
Definition of aspects of personal status & identtiy
Enforcement of activity
2. Financial problems as the main cause (Fryer and Payne)
Loss of discrectionary control
Loss of income
Maintaining relationships, uncertainty, less freedom
3. Job-seeking has a negative affect on mental health (Wanberg)
Dealing w/ harsh judgment & rejection
Importance on promoting self-esteem, optimism, control
Less stability/confidence w/ repeated rejection
4. Strong link between employment and mental health (Warr)
Correlation of r=.54 between gaining employment and
improved mental well-beingCorrelation of r=.36 between losing employment and
decreased mental health
Child Labor And Exploitation
Economic activities carried out by persons >15 yrs
Most common in developing countries
Africa, Central America, & Asia
Interferes w/ healthy development & physical/psychological harm
Work Motivation
Defined with components of:
Direction: addresses choice of activities
Intensity: potential to exert various levels of effort
Duration: reflecting motivation over time
Five critical concepts in motivation
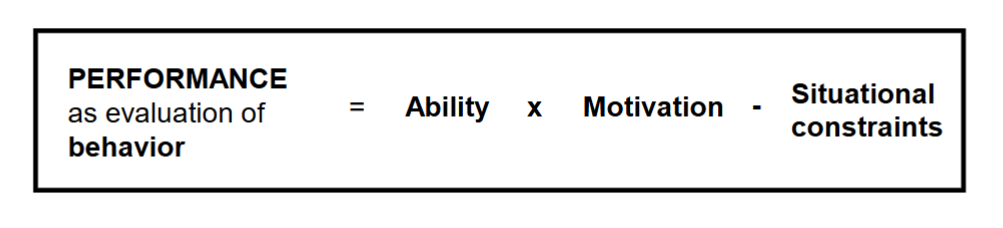
1. Behavior - action
2. Performance - some evaluation/appraisal of the behavior
3. Ability - First determinant of behavior, relatively stable: what you can do
4. Situational constraints - Second determinant, beyond individual’s control
5. Motivation - The third determinant of behavior: what you will do
1. Need hierarchy theory: Abraham Maslow:
First Maslow identifies the needs
Physiological
Safety
Social
Self-esteem
Self-actualization
Maslow then discusses how the needs relate to each other:
Behavior is dominated & determined by unfilfilled needs
Individual will satisfy needs starting w/ the most basic needs
Basic needs take precedence over all those higher in the hierarchy
Implications for work:
W/ pay & security being poor employees focus on aspects of work necessary to fulfill basic needs
With improving conditions social relations become more important (w/ supervisor)
In a much improved environment work becomes important for self actualization
Evaluation of the theory
easy to dismiss
based on clinical insights
highly abstract about humans & more philosophical rather than empirical
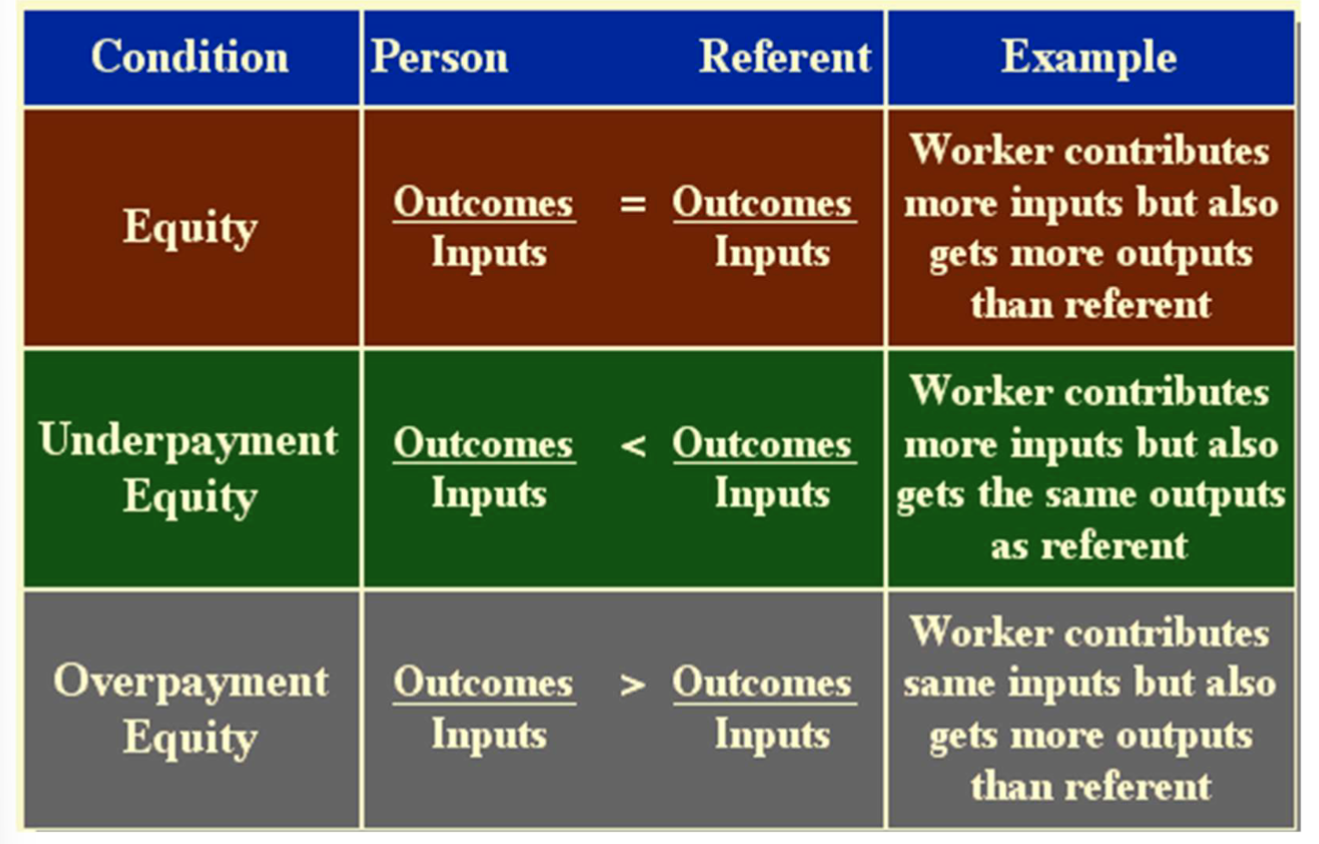
Equity theory (J. S. Adams)
Four parts: (drawn from the principles of social comparison)
Person percieves himself compared to others
Person compares himself w/ other individual
Person’s assets (input)
Person derives something from job (output)
Motivation described (it has a social rather than a biological origin)
Overpayment hourly - reduce inequity by inc input
Overpayment piece rate - inc effort; higher output; inc feeling of inequality
Underpayment hourly - decrease of effort to accommodate dec in outcome
Underpayment piece rate - participants produce more at lower quality
Empirical tests of the theory
Equity predictions held up best in underpayment conditions
Results of hourly payment stronger than in piece rate payment
Evaluation of the theory
financial compensations only one outcome
inequity → absenteeism & turnover
overpayment should result in working harder; high threshold
lower threshold for underpayment
extends to status in organization
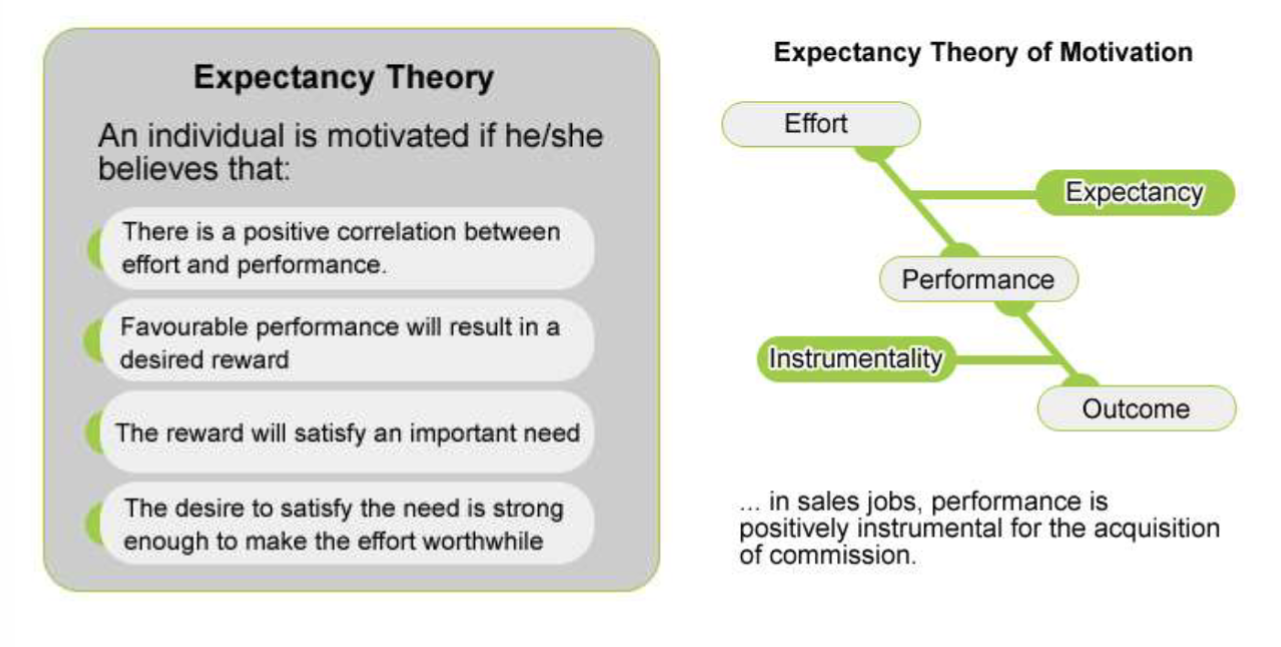
Expectancy theory (Vroom)
Cognitive theory: person is rational decision maker who perceives relationship
between effort expended and job performance
Five parts:
Job outcomes: pay, promotion, fired, transferred
Valences: feelings about outcomes (-10 to 10)
Instrumentality: degree of relationship btwn performance & outcome
Expectancy: perceived relationship btwn effort & performance
Force: effort/pressure to be motivated
Force score is a predictor of how motivated a person is (how much effort
Empirical tests of the theory
Across (btwn) subject design: most/least motivated in group
Within subject: prediction of effort for each task in set
Evaluation of the theory
Rational/conscious explanation
Used in occupation choice & tasks order
Reinforcement Theory (B. F. Skinner)
Operant conditioning; behaviorism
Three key variables
stimulus - any variable/condition that elicits behavioral response
response - some measure of job behavior
reward - something of value given in response to reinforce desired behavior
Motivate by manipulating one of four types of response reward connections
fixed interval, fixed ratio, variable interval, variable ratio
Empirical tests of the theory
ratio schedule more productive
contingent workers passed more than paid-by-hour
Evaluation of the theory
reinorcement does work but there are limits in organizational settings
Goal-setting theory (Locke and Latham)
Cognitive theory: people behave rationally
Relationship among goals, intentions, and task performance:
more difficult goals lead to higher performance
Goals (have two purposes)
basis for motivation
direct behavior
Goals are intended behaviors the person is consciously trying to attain
Theory’s emphasis is on the direction of behavior
Evaluation of the theory
effective; lies in the domain of purposefully directed action; improves performance
6. Self-regulation Theory (e.g. Self-efficacy theory and control theory)
people play an active role in self-monitoring, seeking & responding to feedback, & forming ideas as to success of future actions
Family of theories with the core concept of goals
Goals at core
People self-monitor
People are self-regulating behavior
Evaluation of the theory
General pattern of results is very positive
Research provides rich conceptual basis to understanding how individual
becomes motivated to pursue a goal, and why they persevere
Self-efficacy adds utility to some of the other theories explains how
cognitive processes become activated in behavior; e.g. that people:
Work design theory (Hackman & Oldham)
Locus of control is within environment, not individuals
Proper design of jobs facilitates motivation
This process is called job enrichment
Four part model
Job Characteristics
skill variety
task identity
task significance
autonomy
task feedback
Critical psychological states
exp meaningfulness of work; responsibility for outcomes of work; knowledge of actual results of work activities
Motivating potential score
Employee gorwth need strength
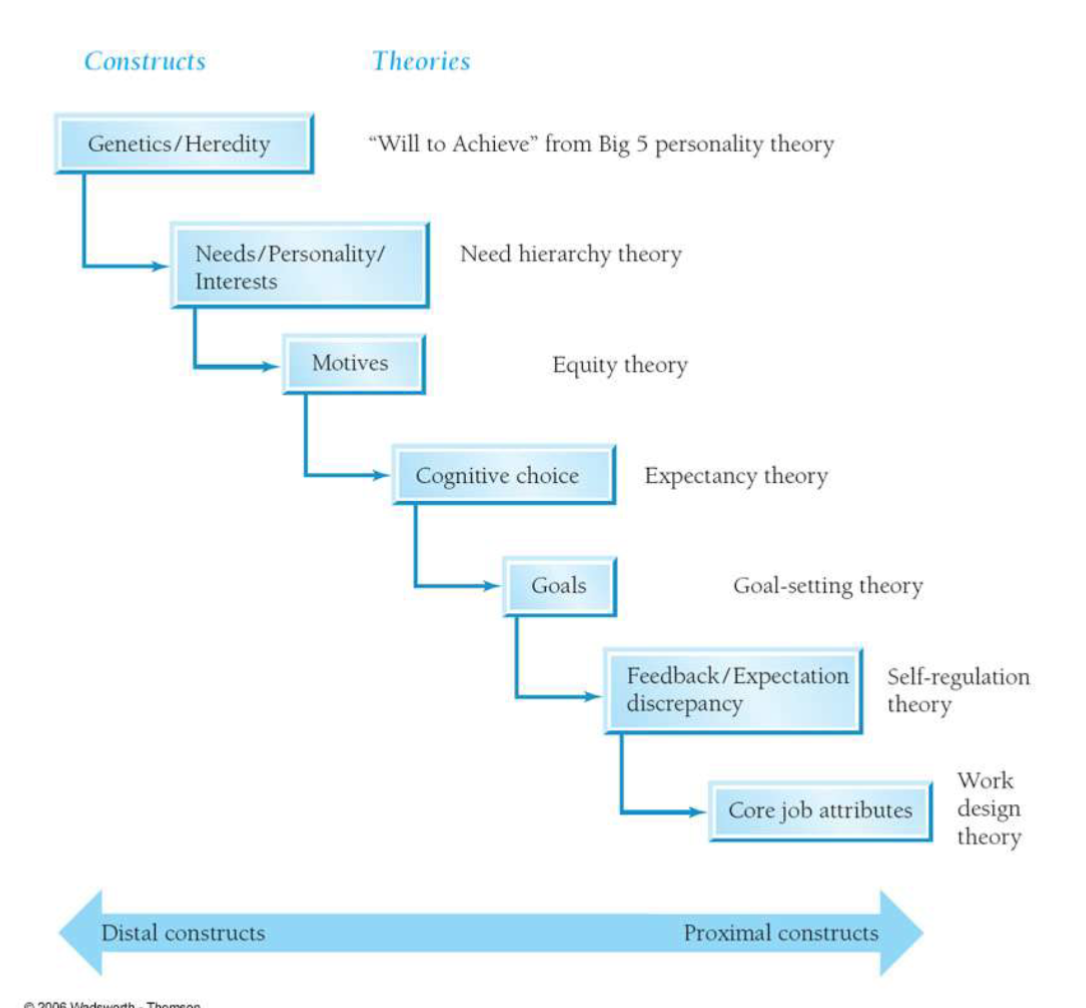
Overview and synthesis of work motivation theories
all include proximity to action
Distal constructs - exert indirect influence on behavior
Proximal constructs - goals & characteristics of workplace that directly influence behavior
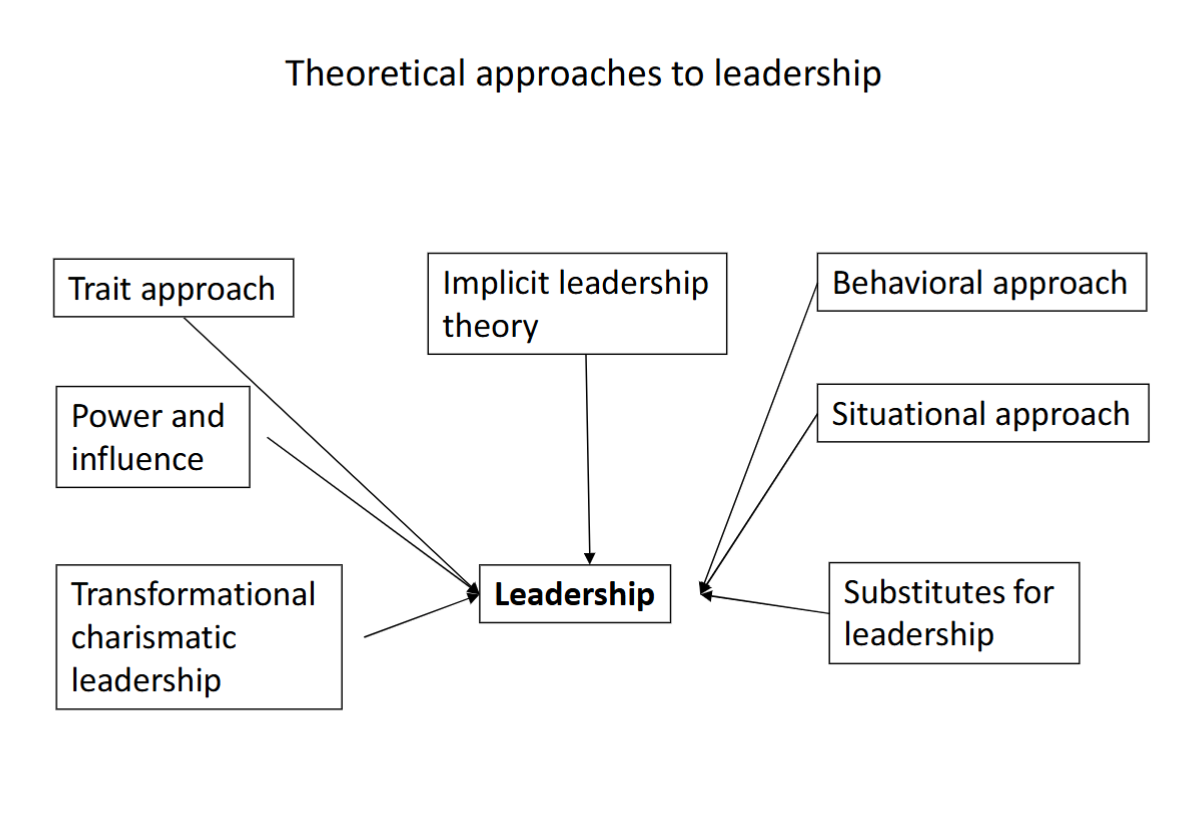
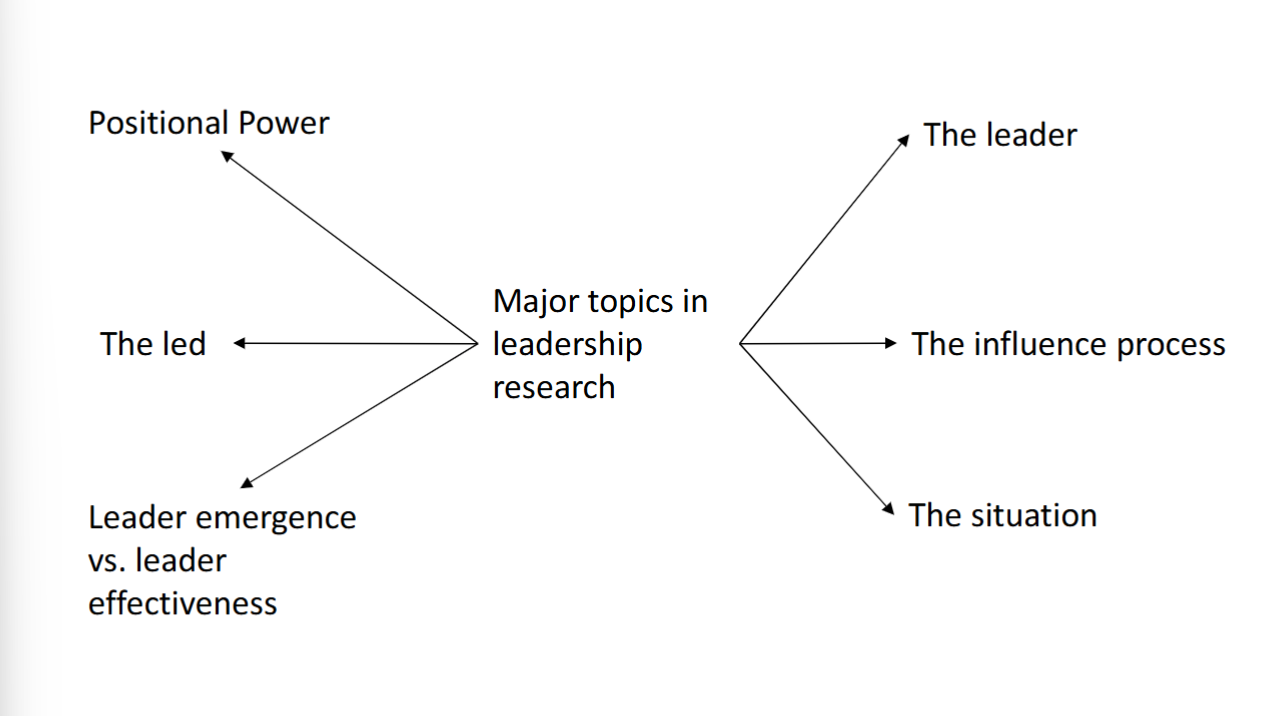
Major Topics in Leadership Research
Positional power
organizational roles/positions; influence tactics/use of power
The leader
individual leaders; personality characteristics/leader behavior
The led
work groups & subordinates; group size/exp of subordinates
The influence process
superior-subordinate interface; receptivity to influence/nature of influence attempts
The situation
environment or context of leadership; situational effects/factors defining favorable situations
Leader emergence vs effectiveness
individual & group; group dynamics/individual characteristics
Theoretical approaches to leadership