Intro to Risk Assessment
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
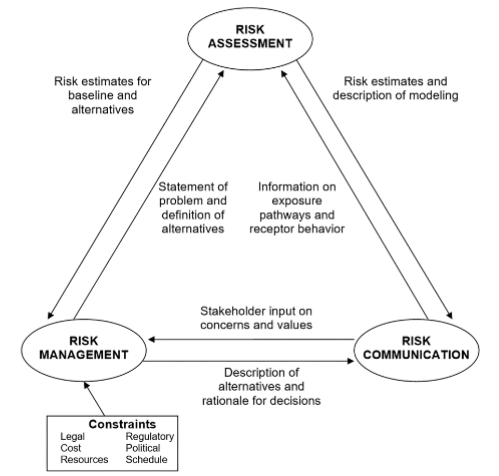
Risk Assessment Paradigm
What is risk?
the probability that a substance/situation will produce harm under specified conditions (probability that the event occurs AND consequences of event)
Exceedance probability vs risk
What are three uses/objectives for risk assessment?
ID hazards
Analyze/interpret risk
Determine/implement control measures
OR
meet regulation
meet cleanup criteria
meet the expected risk
Environmental risk assessment
process of making a quantitative estimate of human health risks resulting from release or potential release of contaminants to the environment
Problem statement
ask some type of question to lead to a scientific inquiry and hypothesis, can implicitly or explicitly mandate assumptions/methods
System description
qualitative and quantitative info about physical processes in system (timescale, geo and physical configuration), provides key info for risk calculation component
4 steps of environmental risk assessment calculation procedure with description
Release assessment (S_dot - contaminant emission rate) - ID of contaminants and quantitative estimation of release probabilities and rates
Transport assessment (C) - ID of pathways and estimation of contaminant concentration
Exposure assessment (D) - ID exposed populations and exposure routes and calc of rate/duration of exposure
Consequence assessment (risk) - adverse aesthetic, ecological, and human effects
Transport pathway vs exposure route
how contaminant moves through environment vs how contaminant moves through body
Aleatory uncertainty
related to chance
Epistemic uncertainty
related to knowledge
Assessment endpoint
valuable ecological or system characteristics you want to protect; all the way down to risk → more uncertainty
Measurement endpoint
measurable biological or physical indicators directly linked to those assessment endpoints that tell you if risk is present/changing; case study, stop and compare concentrations/values to literature
Conceptual model
abstraction of various physical, chemical, and biological processes that affect the behavior of the contaminant in the system
Mathematical model
mathematical representation of conceptual model which permits the calculation of assessment measures
Computational model
math model converted to this, usually identical to math model, calc of assessment involves substituting risk parameters into closed-form analytical expressions using rudimentary computational tool like calculator/spreadsheet
Verification
process of assuring that the math model is accurately translated into the computational model
Calibration
adjustment of risk parameters so that predictions of model match observations
Validation
comparison of predictions of computational model to actual field measurements
What are the appropriate units for radiological and chemical contaminant concentrations in air, soil, food, and water?
mass/time, activity/time