Week 1 - BIOS 350
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Spontaneous Generation
the concept that life/living beings can come from non-living matter
What is pneuma?
the concept that moving air is required to sustain life
Miasma Theory
the idea that contaminated air from rotting organic matter causes illness
Germ Theory
the concept that microorganisms cause disease
Ignaz Semmelweis & Germ Theory
Semmelweis advocated for antiseptics, hand washing, and introduced these practices into obstetrics, reducing the mortality rate by 95%.
Joseph Lister & Germ Theory
advanced the antiseptics practices specifically in surgery, using phenol antiseptic.
Louis Pasteur & Germ Theory
conducted his flask and neck experiments to disprove spontaneous generation theory, pneuma, and miasma. theorized germ theory officially.
Robert Koch & Germ Theory
worked on the cattle disease Anthrax, was able to successfully isolate the bacteria causing the disease, proved that bacteria caused the disease
Negative Control
receives no treatment and nothing will happen to it. if anything happens to it it is due to external factors.
Positive Control
receives a treatment that will yield a known result. used to test the validity of the experimental factor
Koch’s Postulates
Association: the microorganism must be present in sick organisms but not present in healthy organisms
Isolation: must be able to be isolated from the diseased organism and grown in a pure culture
Inoculation: if the microorganism is isolated and injected into a healthy organism, it must cause the same disease
Re-Isolation: the microorganism must be reisolated from the infected host and identified as identical to the original microorganism
Pasteur’s Flask Experiment
Pasteur proved spontaneous generation theory wrong as the flask that was exposed to air grew bacteria, refuting the idea that life comes from nonliving things.
Structure of Prokaryotes
has a simple structure with a plasma membrane, genetic material floating around, does not have membrane bound organelles.
Structure of Eukaryotes
has a complex structure with a nucleus, and the organelles are membrane bound.
Structure of Viruses
not a cellular being (acellular), only contains genetic material
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
with circular genetic material, they reproduce via binary fission, allowing them to reproduce in large amounts in small amounts of time
How do eukaryotes reproduce?
has linear genetic material inside of a nucleus, reproduces via mitosis and meiosis
How do viruses reproduce?
they require a host’s cell and hijack the host cell to produce more viral particles
E.Coli is an example of a
prokaryote
Plants, yeast, and animals are examples of
eukaryotes
Influenza, HIV, and Hepatitis C are examples of
viruses
Why are prokaryotes important?
they have significant roles in ecosystems (as decomposers)
Why are eukaryotes important?
they form the basis of multicellular life, food chains, and human existance.
Why are viruses important?
they have a significant influence on human health, gene therapy, and biotechnology
Cocci Bacteria are
round in shape
Bacilli Bacteria are
shaped like rods
Spirillum Bacteria are
shaped like spirals
Coccus

Diplococci
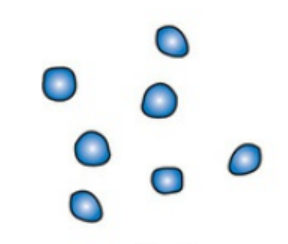
Staphylococci
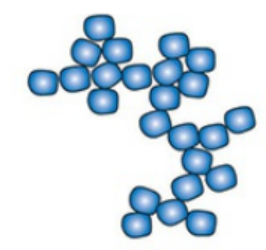
Streptococci

Bacillus

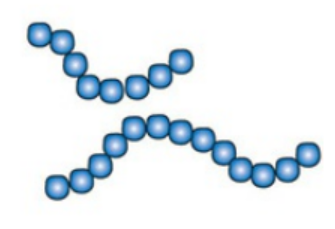
Diplobacilli
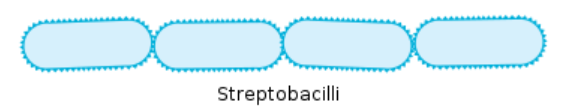
Streptobacilli
Spirillum
What is resolution in a microscope?
how clear the lens can make the object
What is magnification in a microscope?
the ability of the lens to enlarge the object
What was the outcome of John Needham’s experiments with broth?
He supported spontaneous generation by observing microbial growth in boiled broths