FRST 211- lecture 14 Floristics and Plant Associations
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
International Vegetation Classification (IVC)(
Classify existing natural vegetation
Basedd on physiognomy and floristics
Hierarchical classification
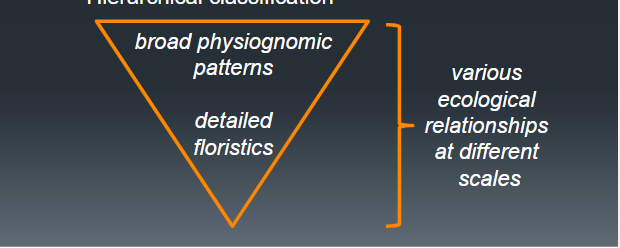
8 hierrchy Level for Natural Vegetation
Physiognomy
Dominant and diagnostic growth forms
Floristics
Diagnostic species, usually form multiple growth forms and/or strata
8 hierarchy levels for Natural Vegetation
Vegetation types:
Formation Class (Upper level) - Physiognomy
Formation Subclass (Upper level) - -Physiognomy
Formation (Upper level)- Physiognomy
Division(Middle level)-Physiognomy, Floristics
Macrogroup (Middle) - Physiognomy, Floristics
Group (Middle)- Physiognomy, Floristics
Alliance (Lower level) - Floristics
Association (Lower Level) -Floristics
what do formation class vegetation type
Temperature (Temperature and Moisture)
Formation subclasss
Latitude and continentality
Association
Local climate, site, disturbance
What is hierarchy based on in vegetation hierarchy levels?
“Diagnostic” growth forms and species and compositional similarity
Species and growth forms that exhibit patterns of fidelity, constancy, or dominance that differentiate one type from another
Diagnostic Growth Form
Any growth form or group of growth forms whose relative constancy or abundance differentiates one vegetation type from another. Diagnostic growth forms include dominant Growth Form and Indicator Growth Form.
Dominant Growth Form
A growth form with a high percent cover, usually in the uppermost canopy layer
Indicator Growth Form
Growth form whose presence, abundance, or vigor is considered to indicate certain climatic and site conditions
Dominant Species
Species with the highest percent of cover (or biomass or density or height, usually in the uppermost or dominant vegetation layer
Diagnostic Species
A plant species that is distinctly more widespread or successful in one of a pair of group of plant communities than int he other(s), although it may be still more successful in other communities not under discussion
Character species
As species that shows a distinct maximum concentration, quantitatively and by constancy, in one well-defined vegetation type; sometimes recognized at local, regional, and general geographic scales
Constant species
Species that are present in present in a high percentage of the plots that define a type, often defined as those species with at least 60% constancy

Which are the diagnostic species?
Community A
Community B: Hoary puccoon

Which is the dominant species?
Sage brush
Level 1-3 - CLimate
General similarities iin vegetation physiognomy at coarse scales
Level 8 - ORPT
Local-scale factor cause variation among sites in floristics at fine scales
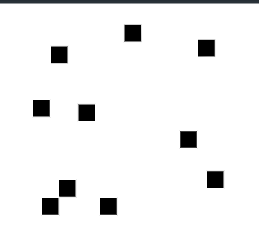
Completely Random
Statically unbiased
All samples independent
The location of one sample is not related to the locations of the other samples
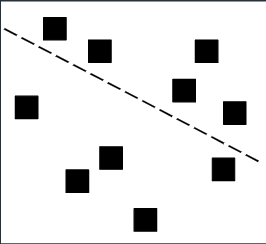
Stratified Random
Subdivide the area into homogenous units
To account for known differences in factors like soil or aspect
Randomly sample within units
Stratified Random Systematic
Subdivide the area into homogeneous units
Randomly select first sample
Starting from first sample, systematically sample along transects
Not statiscally optimal but allows for greater sample size in limited time
Collecting Fine-Scale Floristic Data
Stand selection and plot design
Species composition (floristics) of the plot
Vertical structure and physiognomy of the plot
Physical data of the plot
Geographic and metadata
What to do with vegetation plot data
A. Develop a new classification system
B. Determining Plant Association Using An Existing Classification System
C. Use Vegetation Plots to Verify Classification Maps