Unit A 16 Phys, Acid Base Homeostasis 2. Chemical Buffers
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Chemical buffers
pH homeostasis depends on three regulatory systems: _________________, Respiratory System, and Urinary System.
Urinary System
pH homeostasis depends on three regulatory systems: Chemical Buffers, Respiratory System, and ___________________.
Chemical buffers
In pH homeostasis, _____________________ are the 1st line of defense (react immediately) because they react the quickest.
Respiratory system
In pH homeostasis, the _____________________ is the 2nd line of defense (reacts within 1 to 3 minutes).
Urinary system
In pH homeostasis, the _____________________ is 3rd line of defense because it reacts in hours to days. However, it is the most powerful and lasts the longest but reacts the slowest.
Chemical buffers
_________________________ resist changes in pH by combining with H+ when H+ concentrations start to rise or releasing H+ when H+ concentrations start to fall. Buffers maintain the pH around 7.4 and are found within the blood, interstitial fluid, and cells
Decreasing
If an acidic solution is added, the chemical buffer will combine with the extra H+ ions to prevent the pH from ____________ (increasing or decreasing).
Increasing
If a basic solution is added or there is a loss of H+, the buffer will release H+ ions to prevent the pH from ___________ (increasing or decreasing).
Free
Remember the acidity of a solution reflects only the ________ hydrogen ions. Bound hydrogens do not affect pH.
Carbonic acid - bicarbonate
The body has three main chemical buffer systems:
1. The ________________________ buffer system.
2. The protein buffer system
3. The phosphate buffer system
Protein
The body has three main chemical buffer systems:
1. The carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer system.
2. The _________________ buffer system
3. The phosphate buffer system
Phosphate
The body has three main chemical buffer systems:
1. The carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer system.
2. The protein buffer system
3. The ____________________ buffer system
Weak
The carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer system consists of carbonic acid, a ____________ (weak or strong) acid, and bicarbonate, its conjugate base (weak base) and is the fastest acting buffering system in the body.
Aerobic respiration
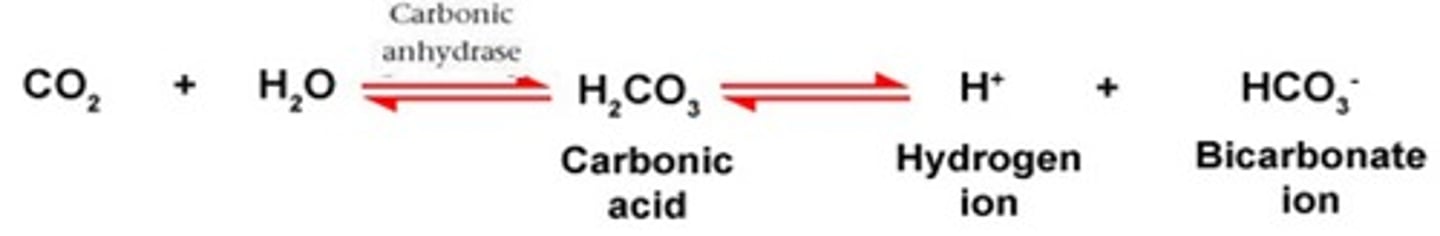
To form carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer, the carbon dioxide (CO2) produced from ______________________ by your cells combines with water (H2O) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), most of which rapidly dissociates to form hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate (HCO3) as shown in the equilibrium reaction.
Law of mass action
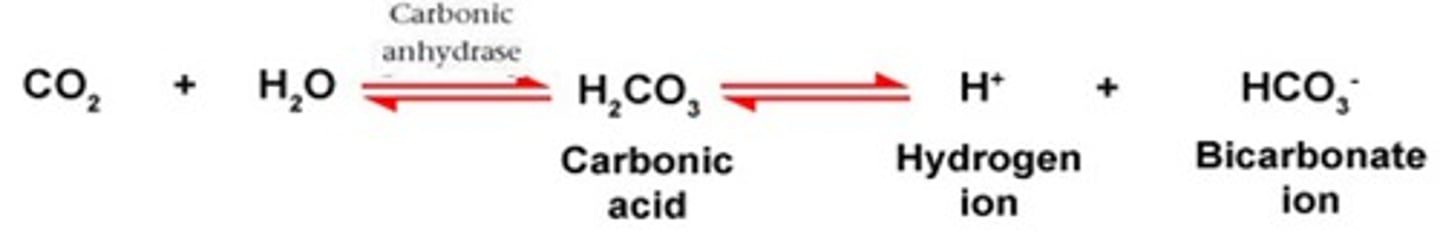
According to the _____________________, any change in the amount of CO2, H+, or HCO3− causes the reaction to shift until a new equilibrium is reached. See the equilibrium reaction.
Right
In the carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffering system. If there is an increase in CO2, this would cause the equilibrium to shift to the ____________ (right or left)
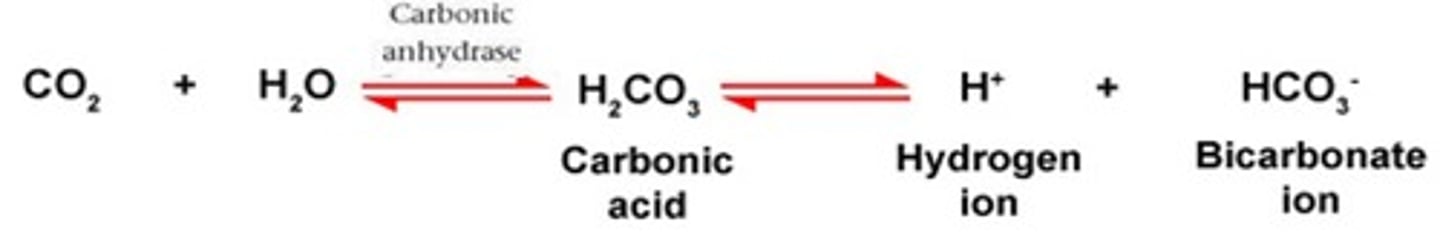
Left
In the carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffering system. If there is a decrease in CO2, this would cause the equilibrium to shift to the ____________ (right or left)
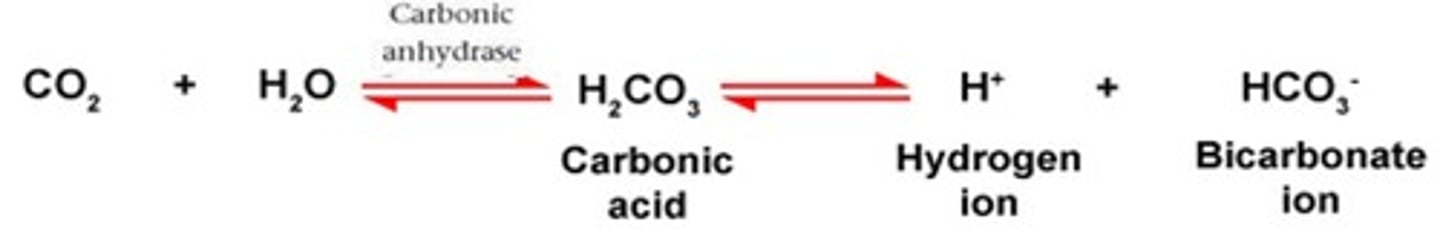
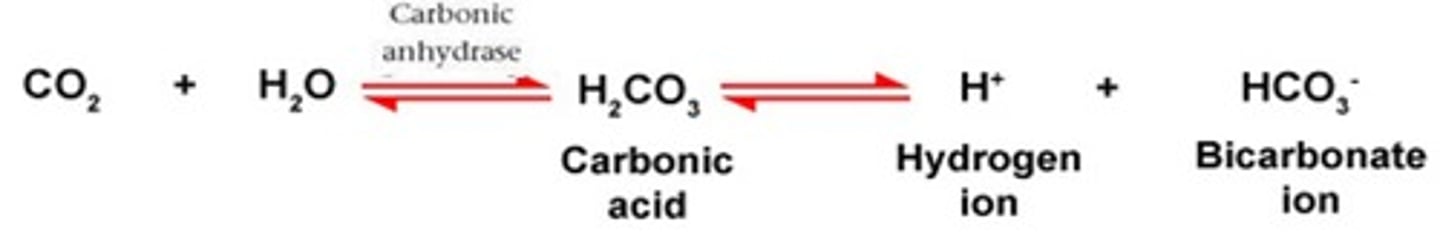
Right
In the carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffering system. If there is a decrease in H+, this would cause the equilibrium to shift to the ____________ (right or left)
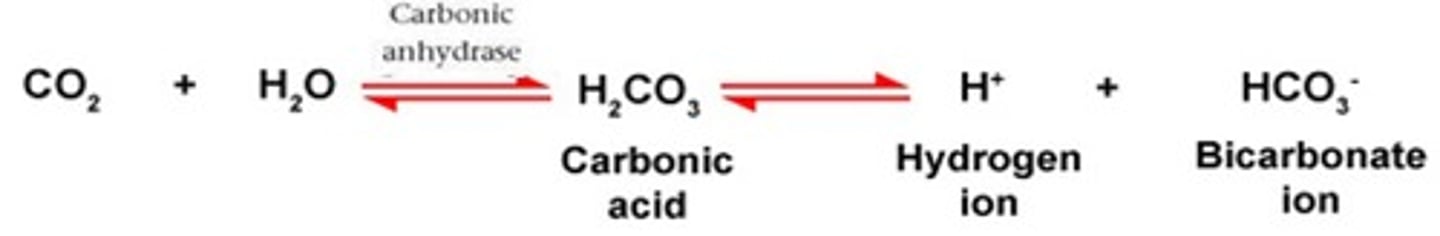
Left
In the carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffering system. If there is an increase in HCO3-, this would cause the equilibrium to shift to the ____________ (right or left)
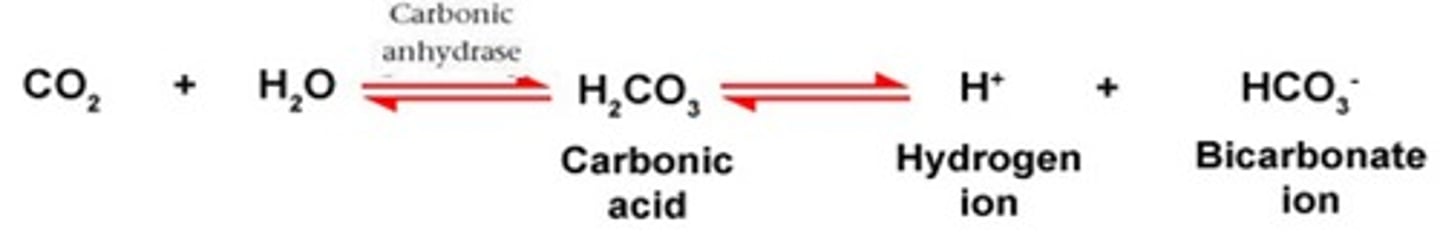
Right
In the carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffering system. If there is a decrease in HCO3-, this would cause the equilibrium to shift to the ____________ (right or left)