Veterinary Ultrasound
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
B- mode scan zones
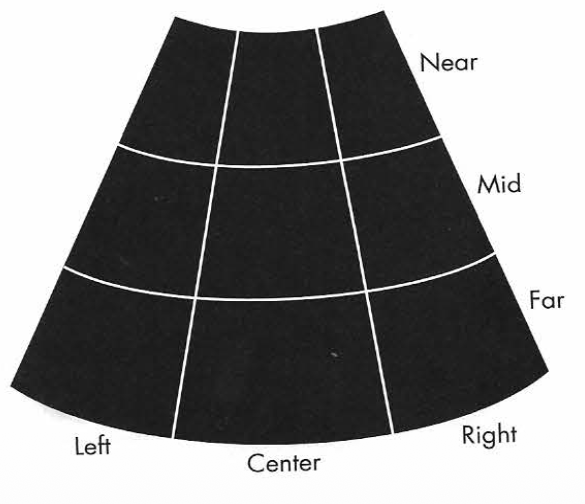
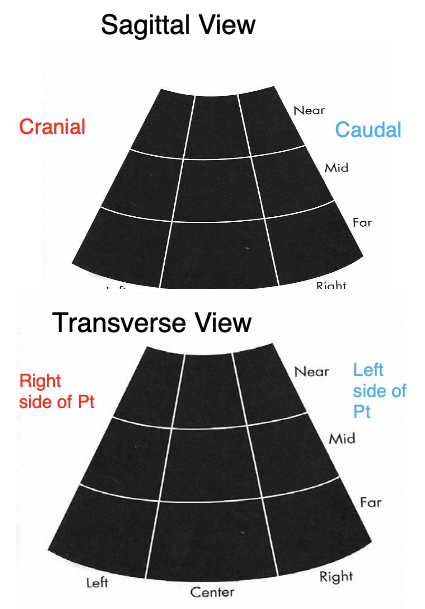
Transducer Marker
Sagittal view: marker faces cranially
Transverse view: marker faces right side of patient
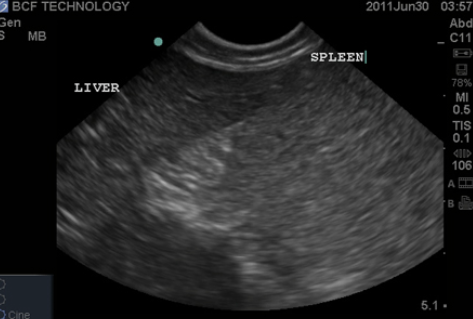
Echogenicity of common organs
spleen is hyperechoic to liver
liver is hyperechoic (or isochoeic) to renal cortex
renal cortex is hyperechoic to renal medulla
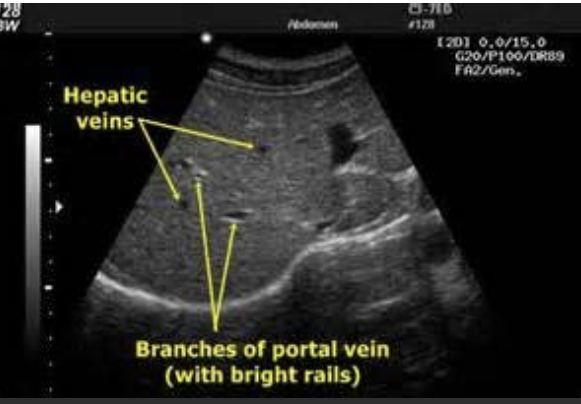
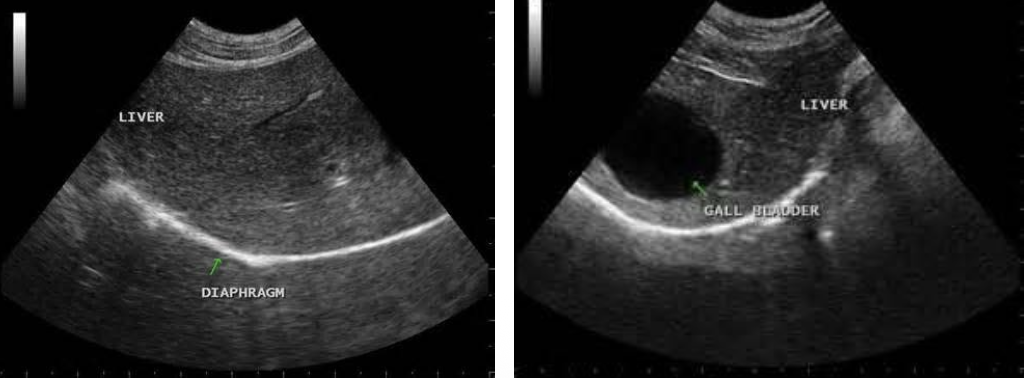
Liver
coarsely grained
large vessels, gallbladder is visible
diaphragm lies beneath the liver
portal veins have clearly defined, bright, hyperechoic walls
hepatic veins have poorly defined walls
Function:
- digestion and absorption of nutrients
- synthesizing nutrients and regulating their release into the bloodstream
- excreting toxic substances
- producing most plasma proteins, cholesterol, and many of the blood coagulation factors
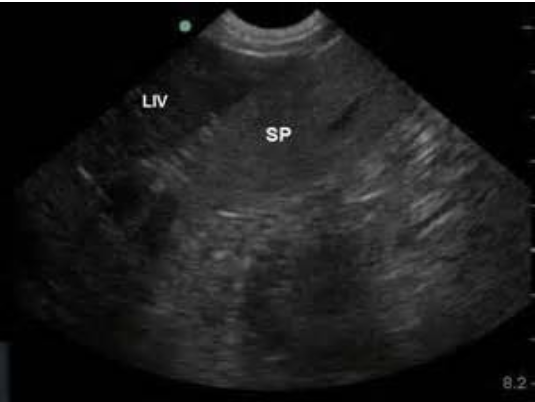
Spleen
elliptical, flat, with smooth contours
more echogenic than liver
may see splenic sinusoids
Function:
- stores RBC and produces RBC during fetal development
- filters the blood and lymph
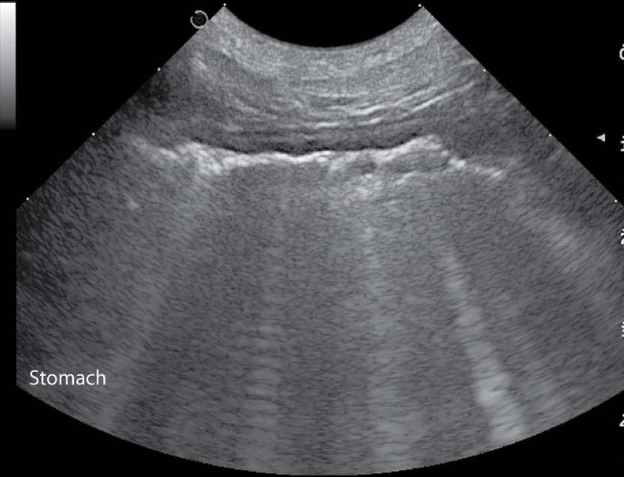
GI tract
stomach is caudal to liver on midline in canine and to the left in feline
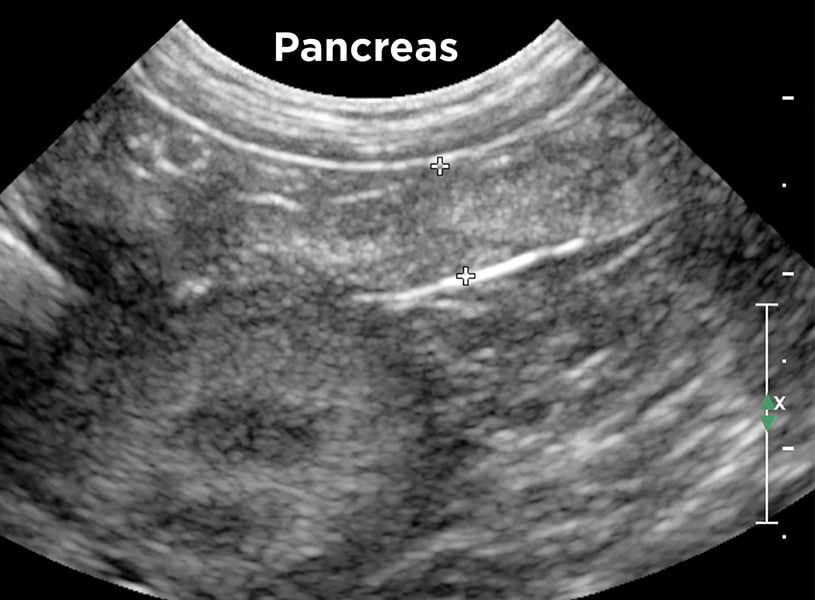
Pancreas
medial to the duodenum on right side
echogenicity similar to liver
Function:
- has exocrine and endocrine functions
- produces important digestive enzymes (exocrine)
- produces hormones and deposits them directly into the bloodstream
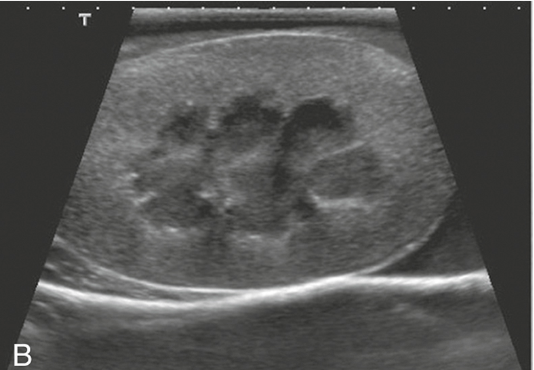
Kidneys
pelvis, cortex, and capsule are visible
adrenal glands are a dumbbell shape and are just cranial to the kidneys
Function:
- production of urine to facilitate the elimination of metabolic waste materials from the body
- helps maintain homeostasis by manipulating the composition of blood plasma
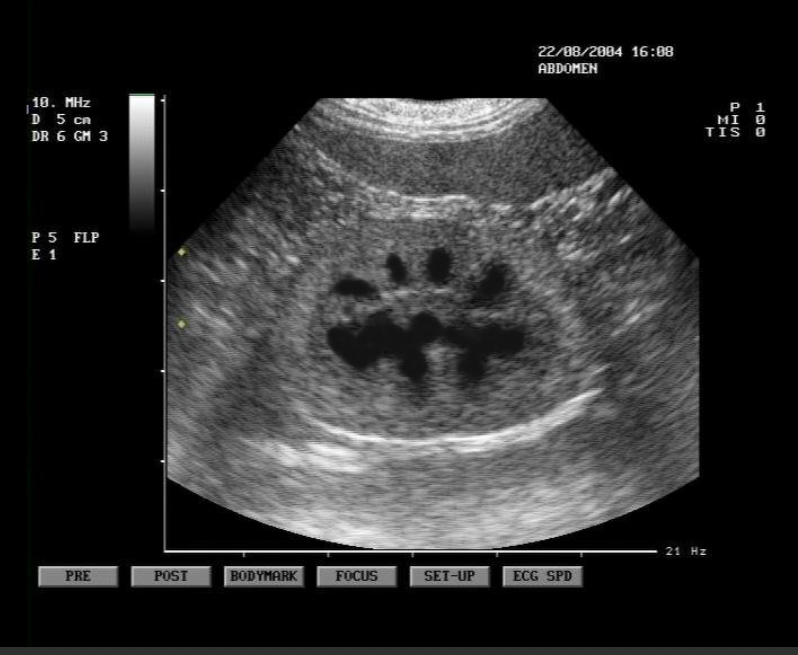
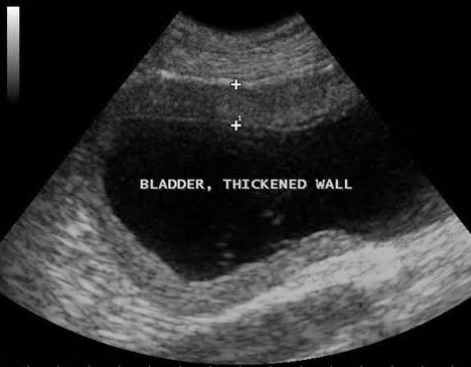
Urinary bladder
bladder wall should be smooth and uniform
routinely used to collect urine sample via cystocentesis
Function:
- collect, store, and release urine
Acoustic Shadowing
occurs at interfaces that reflect and/or absorb a significant portion of the U/S beam
common with mineral interfaces (bones, calculi, foreign bodies)
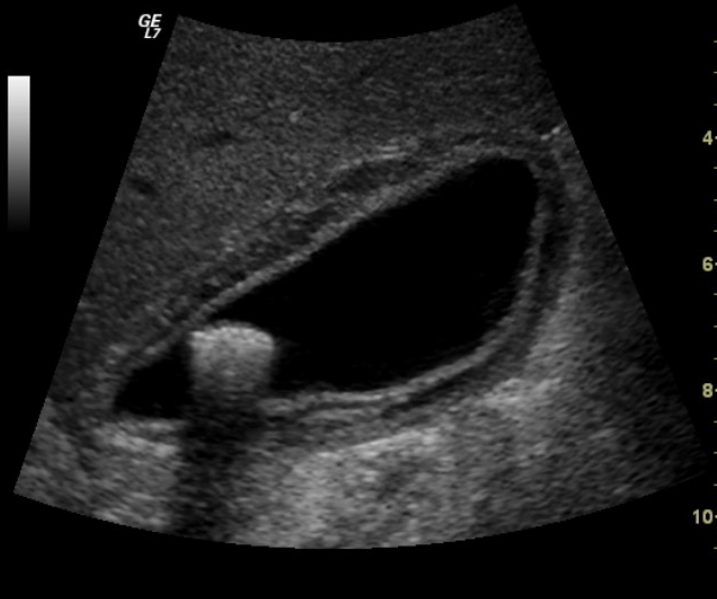
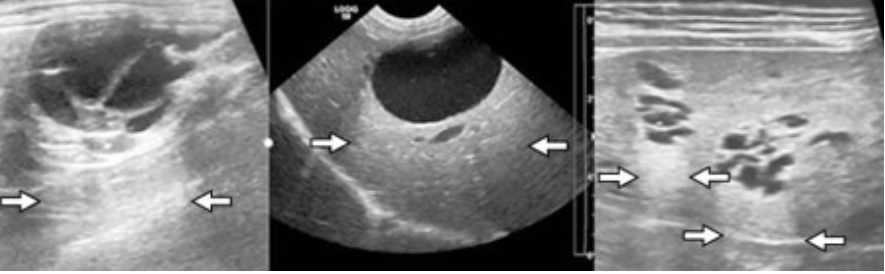
Edge Shadowing
most common with round fluid filled structures
occurs at edge parallel to the sound beam
causes a dark shadow from edge of structure
gallbladder, urinary bladder, cysts, and sometimes kidneys
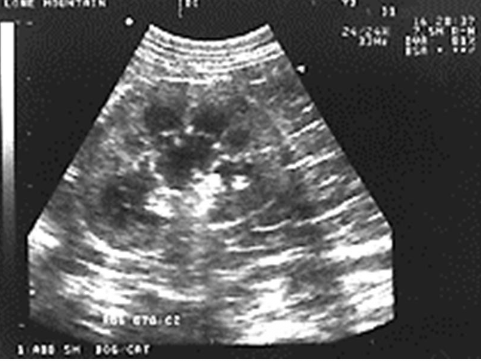
Reverberation (Ring Down)
highly reflective surfaces
sound waves bounce back and forth - produce echoic lines at regular intervals
commonly caused by gas or free air
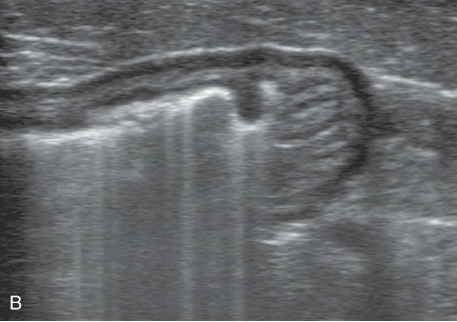
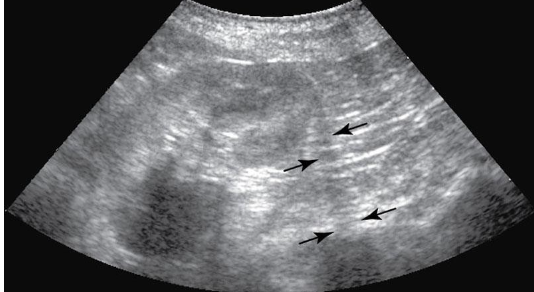
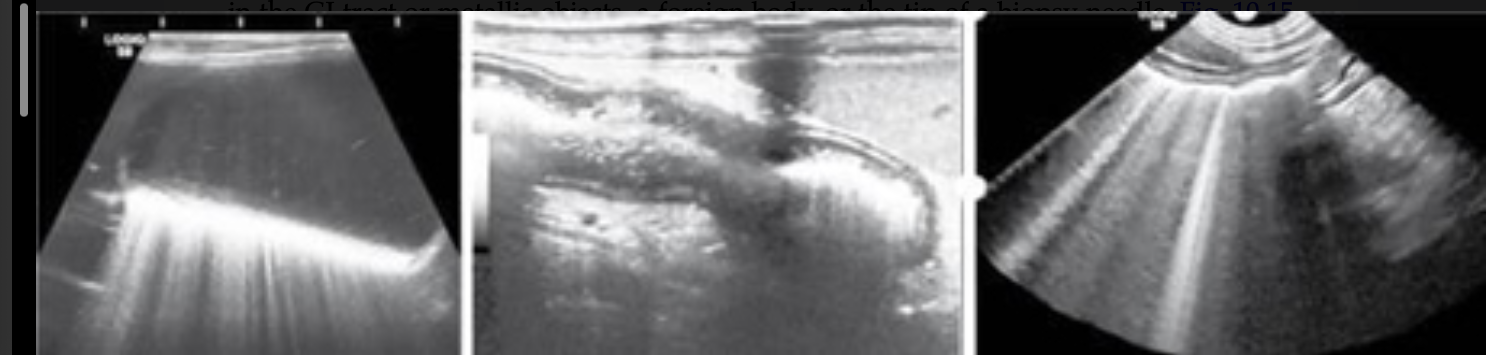
Comet Tails
type of reverberation artifact seen with gas interfaces
smaller width strong lines produced
air pockets in GI tract or metallic objects, a foreign body, or tip of a biopsy needle
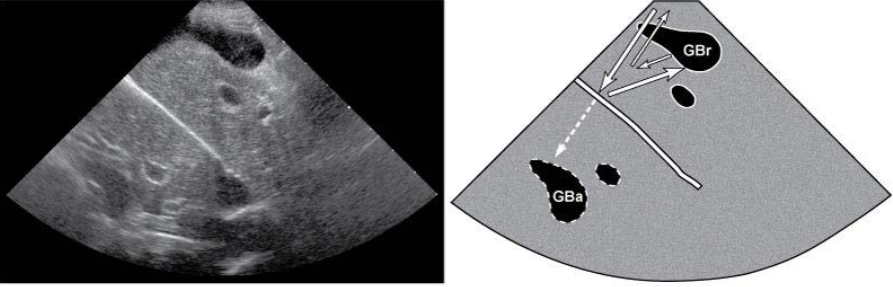
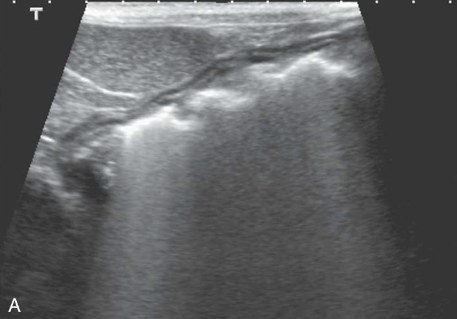
Mirror Image
caused by highly reflective curved surfaces
produces duplicate of structure deep to reflective surface
most common - liver will appear in thorax due to diaphragm
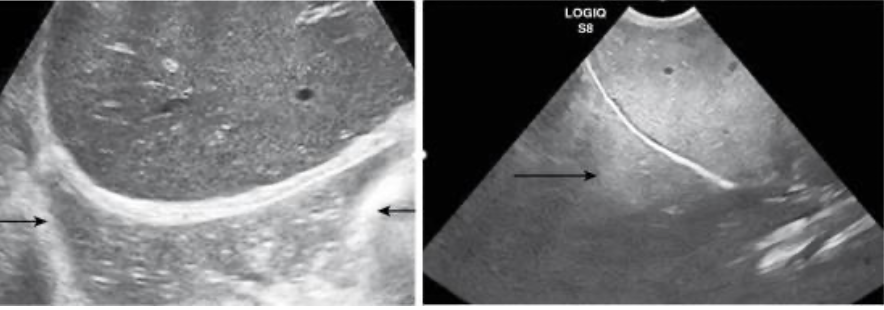
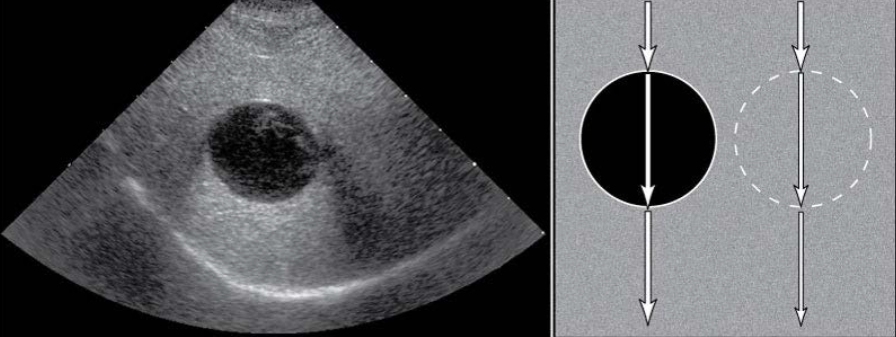
Acoustic Enhancement
increased echogenicty of tissue deep to an area or structure
often seen deep to fluid filled structures
AFAST
Abdominal Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma
rapidly identify free fluid in the peritoneal space
blunt trauma cases
performed ASAP and repeated PRN
4 specific areas in the abdomen examined
scoring system for abdominal fluid 0-5
TFAST
Thoracic Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma
used for detection of free air and free fluid
5 specific areas in thorax are assessed
emergency medicine, monitoring post surgery complications
used with suspected pneumothorax, hemothorax, pyothorax