Bio exam 1-5
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
Biology
the study of living things and their interactions with one another and their environments
Scientific Method
method of research with defined steps
Inductive
related observations to arrive at a general conclusion
Deductive
general principle or law to to forecast specific results
Scientific Method(steps)
observation
question
hypothesis
prediction
experiment
analyze
a Supported
b Not supported(try again)
Report results
Basic Science
seeks expand knowledge
Applied science
use science to solve immediate problems
Properties of life
Order/organization
Response to stimuli
Growth and development
Homeostasis/regulation
Energy processing
Adaptation/evolution
Reproduction
Levels of organization
Atom
Molecule
Macromolecule
Organelle
Cell
Tissue
Organs/organ system
Organism/population/communitie
Ecosystem
Biosphere
Phylogenetic tree of life
Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya
Bacteria/Archaea
prokaryotes: single celled with no intracellular organelles
Eukarya
Multicellular organisms
Four most common elements of living organisms
Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen
Atom
Smallest building block of life
Isotope
Form of an element with different # of neutrons
Reactants
Substances used at the beginning of reaction
Products
Substances formed at the end of reaction
Covalent bond
electrons are shared between atoms
Ionic bond
electrons are given up or gained by an atom
Polar covalent
electrons shared unequally(attracted to one nucleus more than the other)
Non-polar covalent
electrons shared equally
Hydrogen bonds
interaction between positively charged hydrogen atom and more electronegative negatively charged atom
Water important properties
Ions and polar molecules can dissolve
Can form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules/ions
Cohesion —> surface tension
Surface tension
capacity of a substance to withstand being ruptured when placed under tension
Adhesion
Attraction between water molecules and other molecules
Solution with high H+
acidic
Solution with high OH-
basic
pH
concentration of H+ ions in a solution
Buffer
maintains neutral pH inside of an organism
Carbon unqieness
key component of macromolecules
can form covalent bond with 4 atoms
DNA structure
connected by hydrogen bonds
4 major macromolecules
Carbohydrate
Lipid
Protein
Nucleic acid
Monomer
individual subunits
Polymer
monomers linked together via covalent bonds
Hydrolysis
breaking down polymers into monomers using water
one monomer receives H+ other receives OH-
Dehydration synthesis
combination of two molecules by removing a water molecule from between them(removing OH- from one and H+ from the other)
Enzyme
biological molecules that speed up reaction
3 main subtypes of carbs
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides
Polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
Linear or ring shaped molecules
Disaccharides
two monosaccharides linked through a dehydration reaction
Polysaccharides
many monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages(glucose)
branched or unbranched
straight, 1 type of bond or branched out, 2 types of bonds
Lipids
non-polar hydrocarbons(hydrophobic)
Function of lipids
long-term energy storage
provide insulation
Building block for some hormones
important part of cellular membranes
Types of lipids
fats
oils
waxes
phospholipids
steroids
Fats and oils
two main components: glycerol and fatty acids
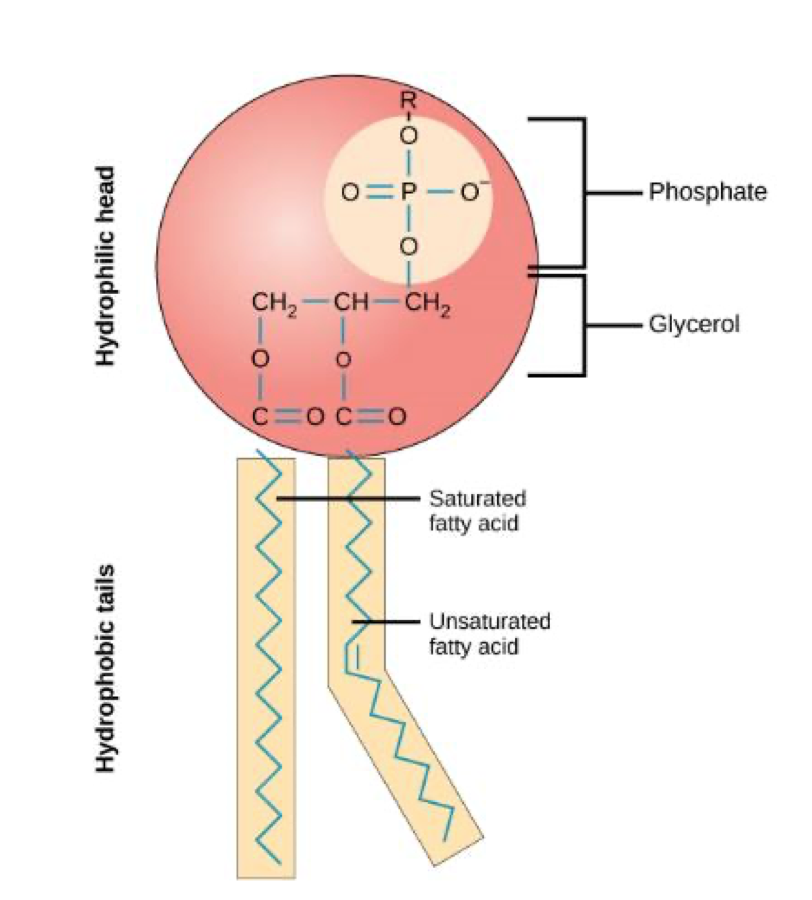
Saturated fats
no double bonds and solid at room temp
Unsaturated fats
contain double bonds and liquid at room temp
monounsaturated 1 double bond
polyunsaturated: 1< double bond
Phospholipid
two fatty acids + phosphate group attached to glycerol backbone
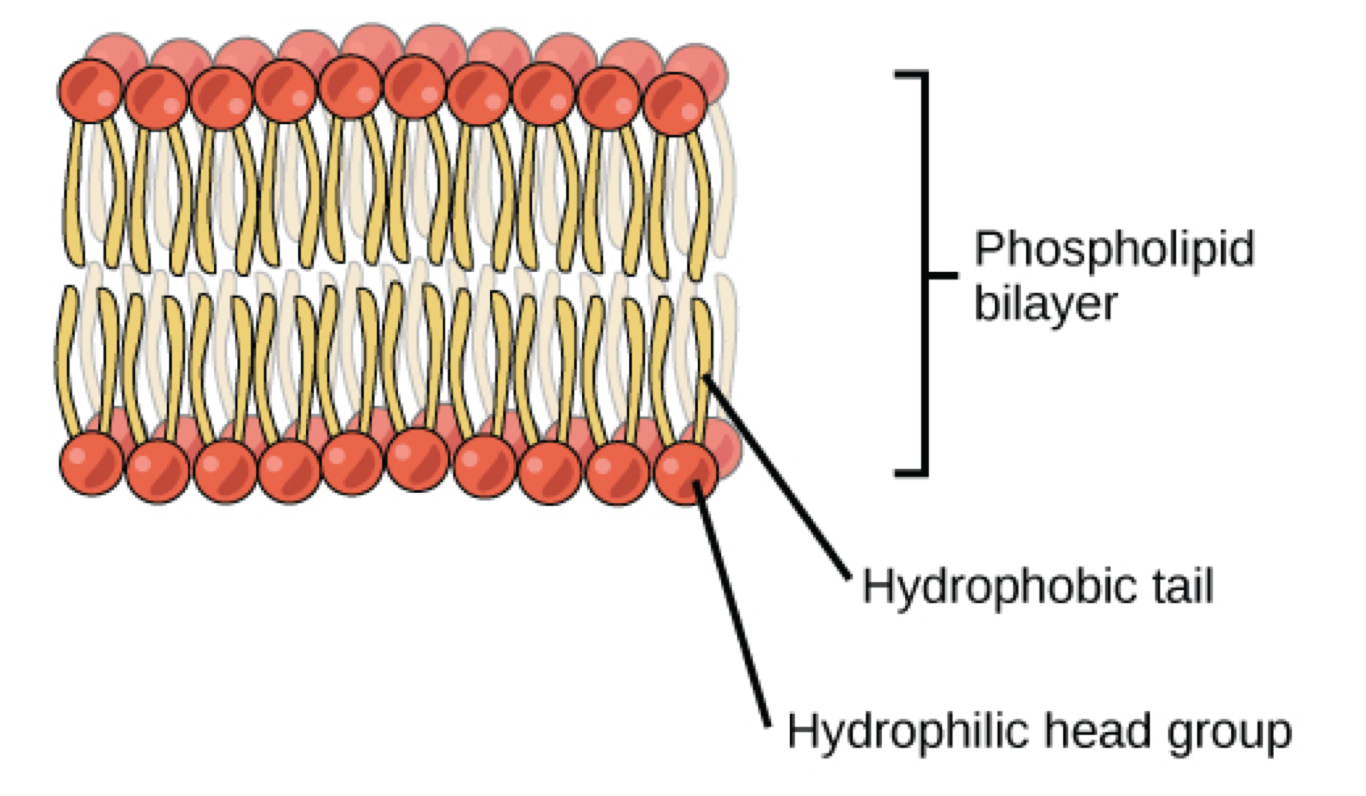
Phospholipid bilayer
Hydrophilic heads face aqueous solution(out)
Hydrophobic tails face in(middle of bilayer)
Steroids structure
closed ring structure with a short tail
Protein functions
Regulatory
Structural
Protective
Transport
Enzyme
Amino acids
monomers that make up proteins
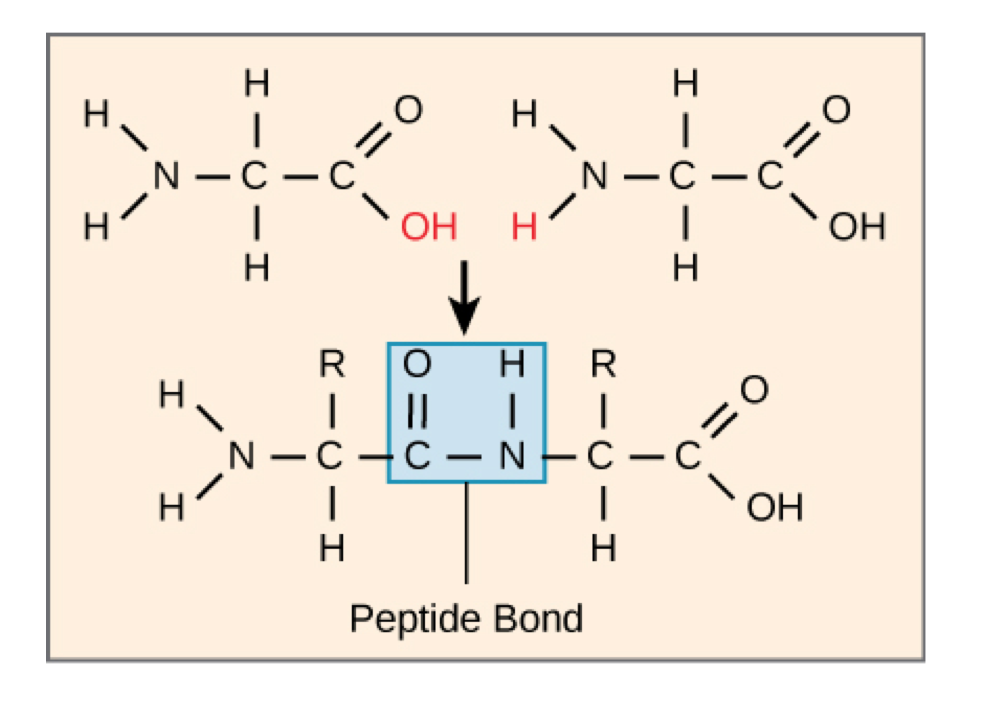
Peptide bond formation
amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds through dehydration synthesis
carboxyl group of one amino acid is linked to the amino group of the incoming amino acid
Polypeptide vs proteins
Polypeptide: chain of less than 100 amino acids
Protein: multiple polypeptides
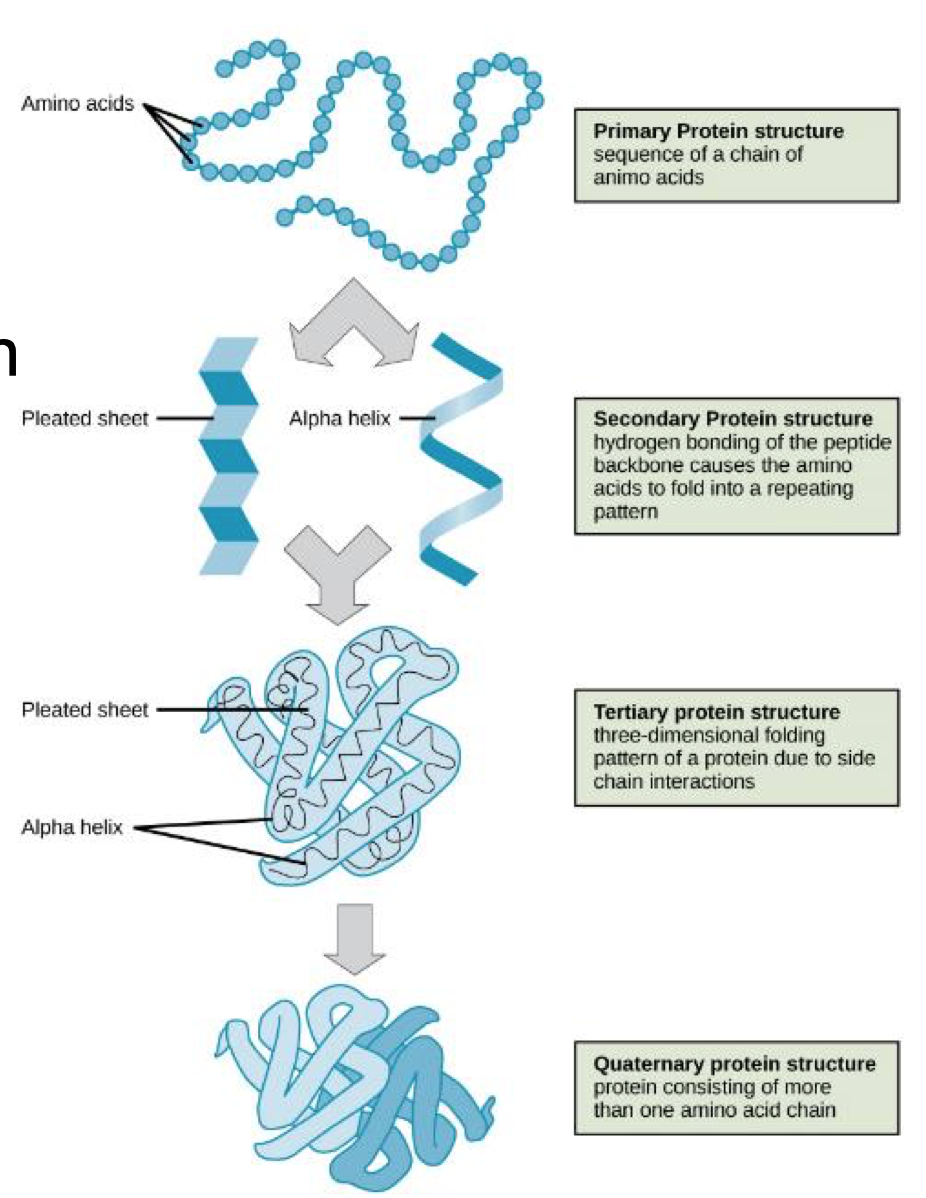
Protein structure levels
Primary: sequence of amino acids
Secondary: folding of polypeptide
Tertiary: 3D polypeptide structure
Quaternary: interaction between polypeptides
Denaturation
changes in protein structure that lead to changes in function
Nucleic acids
genetic material of living things
Two types of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
Location of nucleic acids
nucleus of eukaryotic cells
mitochondria
chloroplast
RNA role
protein synthesis
RNA types
mRNA
tRNA
rRNA
mRNA
leaves nucleus and contains blueprint for protein synthesis
Transcription
tRNA
bridge between nucleotides and amino acids
translation
mRNA
assists in protein synthesis
monomer for DNA/RNA
Nucleotides
Nucleotide structure
nitrogenous base
pentose sugar
1 or more phosphate group
Key features of DNA and RNA/differences between DNA and RNA
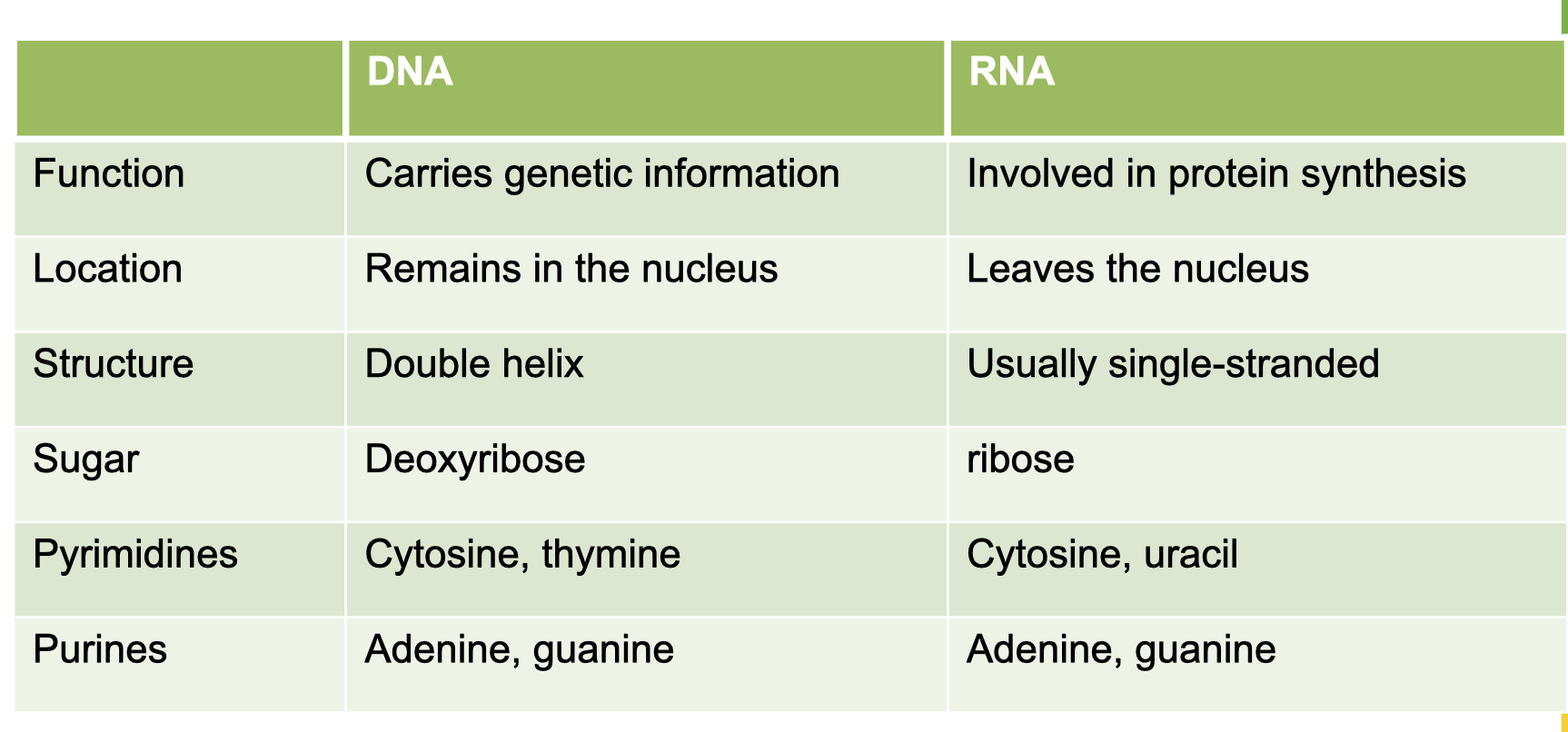
Central dogma of life
DNA can make copies of itself
DNA can be transcribed into RNA
RNA can be translated to protein
Magnification
enlarging the appearance of an object
Resolution
clarity and detail of an image under a microscope
Cell theory
Cells are the basic unit of life
All living organisms made of cells
All cells made from preexisting cells
4 common components of cells
Enclosing plasma or cell membrane
Cytoplasm
DNA
Ribosomes
Prokaryotes charecteristics
lack organelles
cell wall containing peptidoglycan
similar to the first cells
organisms in Archaea and Bacteria domains
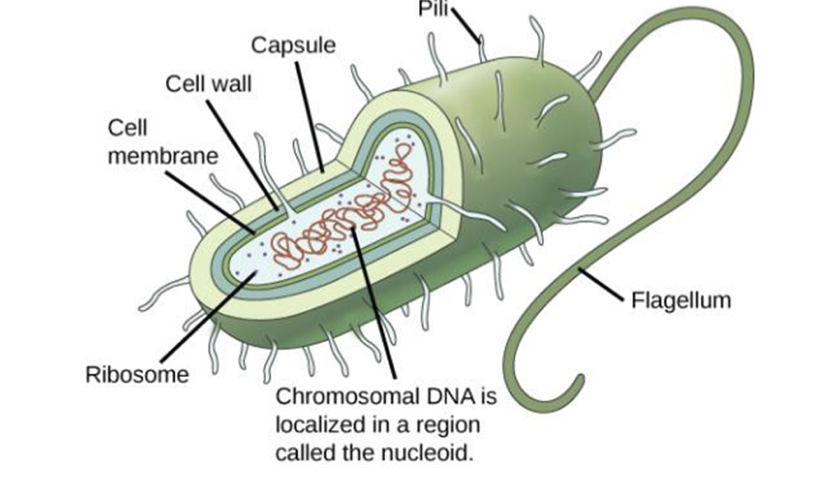
Prokaryote structure
chromosomal DNA in nucleoid
ribosome in cytoplasm
cell membrane surrounded by cell wall
Factors limiting cell growth
as cells get bigger volume increases faster than surface area
Parts of a eukaryotic cell
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
nucleus
ribosomes
ER
rough and smooth
golgi
lysosomes
mitochondria
peroxisomes
vacuole
Plasma membrane
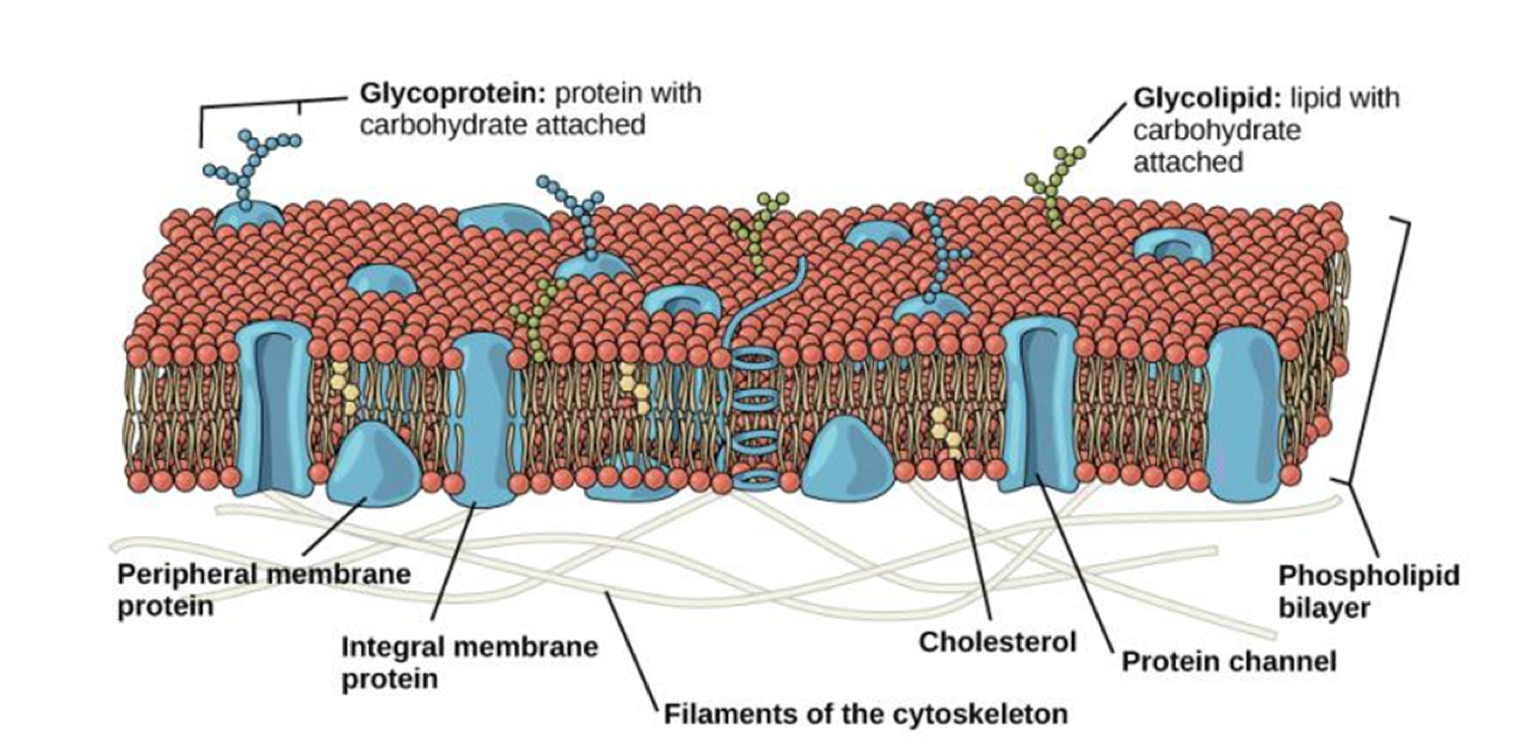
Cytoplasm
region between plasma membrane and nuclear envelope
Nucleus
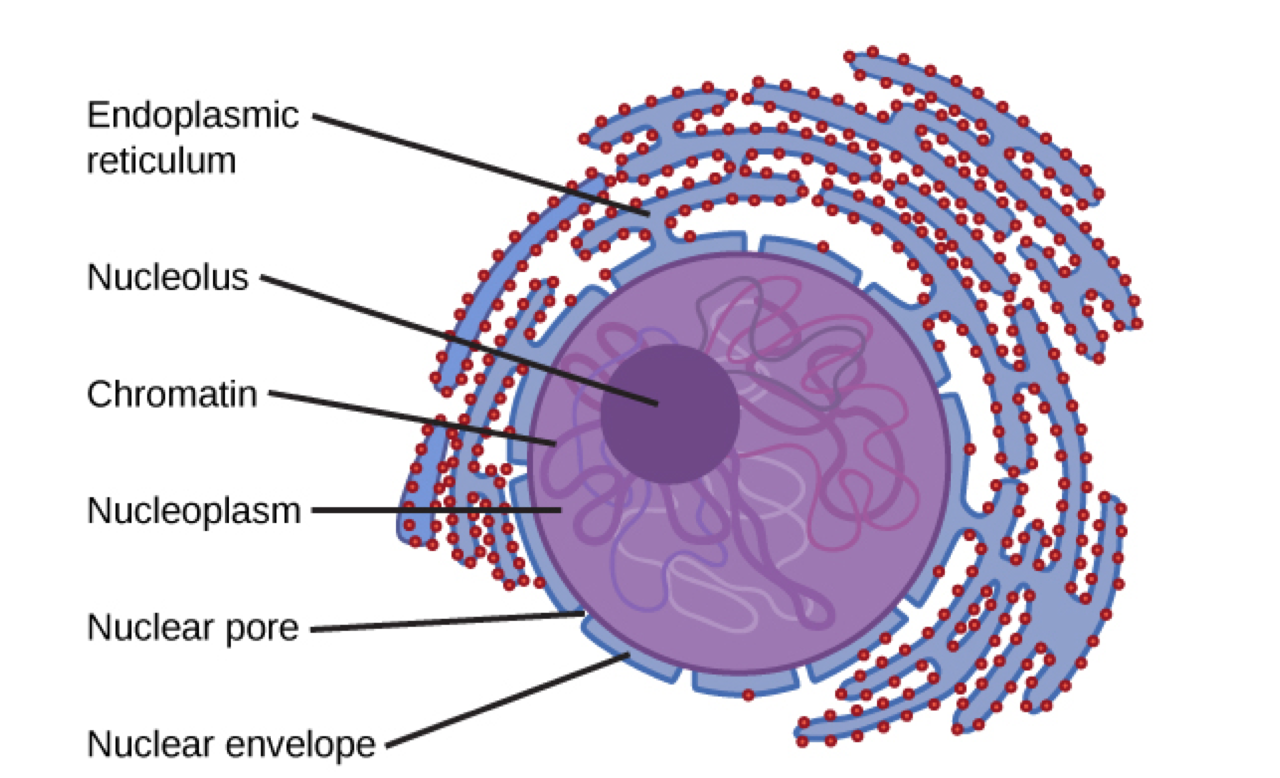
Nucleolus
where ribosomes are assembled from RNA and proteins
Mitochondria
conversion of stored energy to ATP
Endosymbiosis
hypothesis: mitochondria/chloroplasts originated as independent prokaryotic cells because they have their own DNA and ribosomes
Peroxisomes
break down fatty acids and amino acids here and detoxify poisons
Vacuole/vesicle
storage/transport container
vacuoles larger
Endomembrane system
organelles that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins
nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, ER, golgi, and plasma membrane
Endoplasmic reticulum(ER)
modifies proteins and synthesizes lipids
Rough ER
has ribosomes
proteins modified in lumen and sent to cellular membrane or secreted from cell
makes phospholipids for cellular membrane
Smooth ER
few/no ribosomes on surface
Synthesizes carbs, lipids and steroid hormones
Detox of meds and poison
Storage of Ca++
Golgi
proteins and lipids are sorted, packaged, and tagged here
Cytoskeleton componenets
microfilaments
actin
movement of cell
Intermediate filaments
fibrous protein
structure/shape
Microtubules
tubulin
movement of vesicles/chromosomes
Centrosome
2 centrioles that lie at right angles of each other
centrioles made of 9 microtubule triplets
Lysosome
contain digestive enzymes that break down large biomolecules and worn out organelles
Plant cell wall
made of cellulose and is outermost layer of cell
Chloroplasts
(similar to ribosomes that they have their own ribosome and DNA)
create energy through photosynthesis
Intercellular junctions
direct channels of communication between cells
Plasmodesmata
channels that connect between cell walls to connect cytoplasm and allow material to move
Tight Junctions
Watertight seals between animal cells that prevent material from leaking
in epithelial cells
Desmosomes
Join adjacent cells in tissues that stretch
short proteins in plasma membrane
only in animal cells
Gap junctions
Connect animal cells like plasmodesmata connect plant cells
create by 6 elongated proteins that align on on each side of the cell

Facilitated passive transport
moving substances down their concentration gradient