Lab 8: Continental Crust & Passive Margins
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Passive margins
zones where oceanic crust and continental crust join within a single lithospheric plate
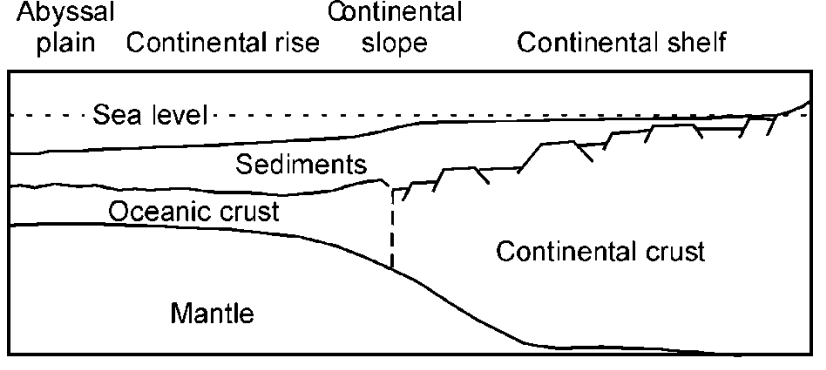
Cross-sectional diagram of a passive margin
Cobbles of granite and chert would indicate what?
The presence of granite and chert in the bedrock of the source area
Finding an arkose would indicate what?
suggest the dominance of granite or gneiss in the area from which the sand particles were derived
The presence of feldspar would indicate what?
indicate that the source area was not subjected to extensive chemical weathering and that erosion probably took place in an arid environment with high relief
Quartz arenite would indicate what?
probably represents repeated cycles of erosion , transportation and deposition of quartz grains that, although might have ultimately been sourced from igneous or metamorphic rocks, probably subsequently involved the reworking of previous sandstone deposits
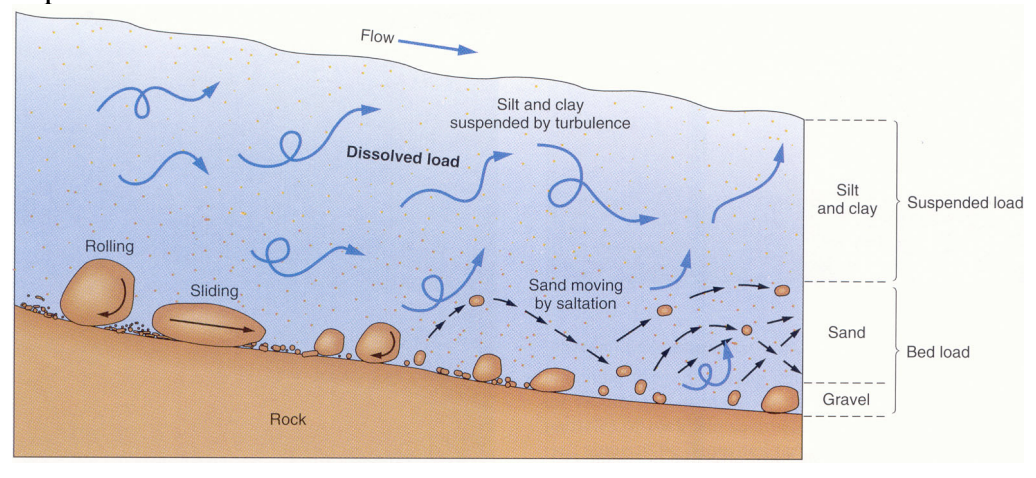
Sediment transport
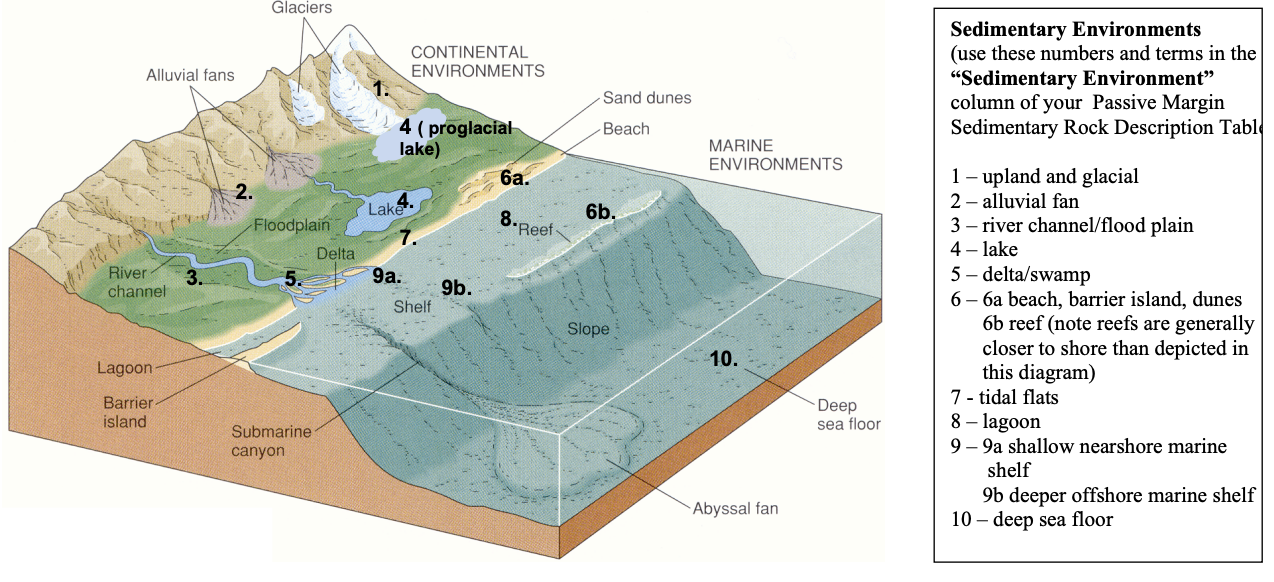
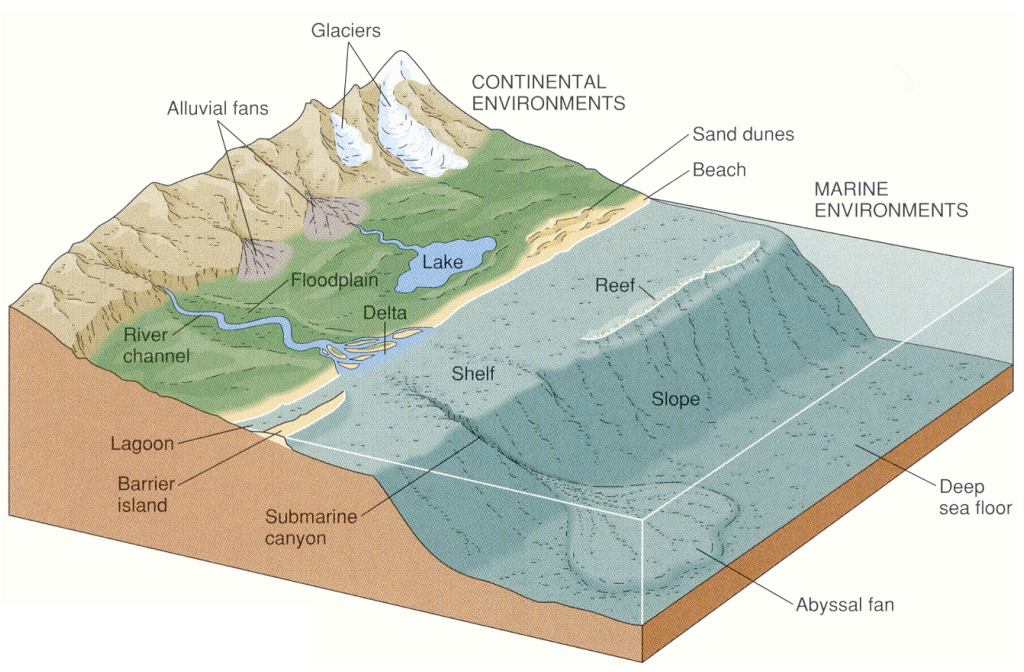
Environments of deposition
Alluvial fans
River channels
Floodplains
Lakes
Dunes
Delta
Beaches
Lagoons
Shelves
Reefs
Upland and Glacial environments
included together because their deposits closely resemble one another
Upland environment - sediments
sediments close to source area
contain abundant lithic (rock) fragments
very poorly sorted
Glacial environment - sediments
very poorly sorted and massive
large clasts “floating” in a mud matrix
sediment is called diamicton (rock - diamictite)
If scratches, rock - tillite
Alluvial fans - sediments
fan-shaped sediments
coarse, arkosic sandstones
conglomerates marked by coarse cross-bedding
abundance of potassium feldspar
points to arid climatic conditions
River channel & floodplains - river sediments
deposit elongate bars of conglomerate or sandstone
arkoses (feldspar, quartz, micas)
asymmetrical ripples and crossbedding provide evidence for the unidirectional current activity is streams
River channel & floodplains - floodplains
lower velocity of rapids
finer sediments - fine sand and silt
thinly interbedded sandstones/siltstones and shales
evidence of exposure of the floodplain shows mud cracks, root traces or plants or footprints
Lakes - sediments
fine-grained
clastic mud (in humid climates)
preserve seasonal patters
dark clay, organic-rich layers (winter)
light, silt-rich layers (summer)
dropstones
Deltas - sediments
thickly interbedded sandstone/siltstone (with low-angle crossbedding) and shale cut coarser deposits
swamps - mud with abundant plant fossils
carbonaceous mudstone or shale
Beaches, barrier islands, dunes - sediments
well-sorted quartz sandstone
well-rounded grains
low-angle lamination, cross-bedding, and symmetrical ripples
quartz arenites
ooilitic limestone (tiny spherical carbonate grains)
Tidal flates - sediments
features such as mud cracks that indicate altering wet and dry periods
sandstone with mud cracks
Lagoons - sediments
fine-grained
finely laminated (reflecting quiet water conditions)
marine fossils
microbial mats can develop
when they dry out, they look crinkled
Marine shelves - sediments
sandstone, siltstone, mudstone/shale, carbonat mud (micrite)
thin-bedded sandstone with symmetrical ripple marks
oolitic limestone
mud with skeletal remains as thin shell beds (shells of marine organisms - brachiopods, trilobites, etc.)
Reefs - sediments
massive limestone
limestone breccia
sand-sized and finer-grained limestones
limestones full of skeletal fragments (coral, algae_
Deep marine environments - sediments
clay-rich mudrocks, shale, greywacke
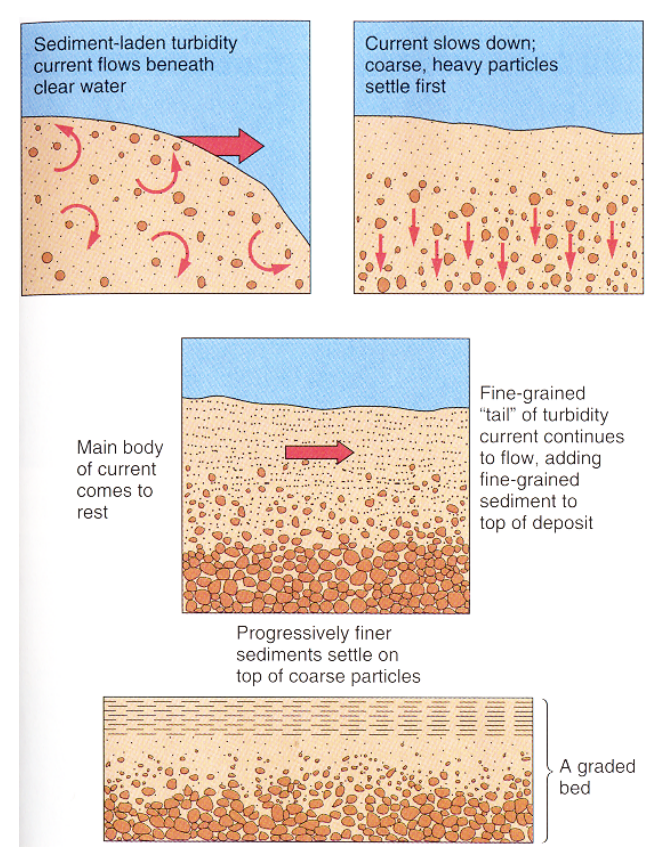
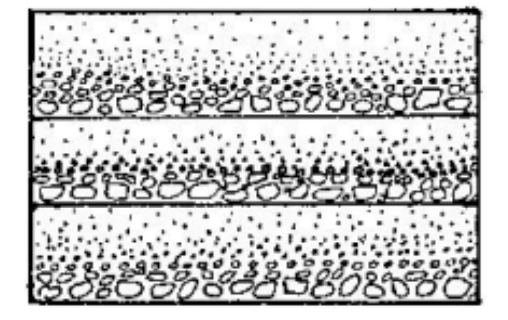
contain graded bedding
may preserve ripple marks
deep-water shales tend to preserve fossils of planktonic organisms
siliceous ooze (chert)
Graded bedding by a turbidity current
Ripples

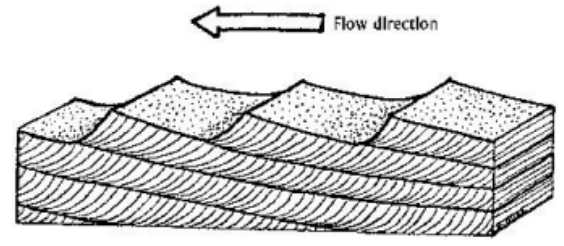
Cross-stratification / cross-bedding
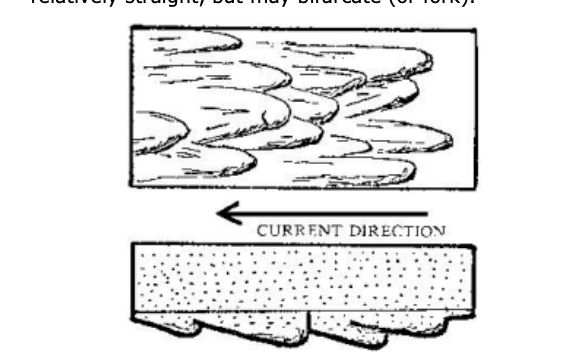
Flute marks
Graded bedding
Burrows
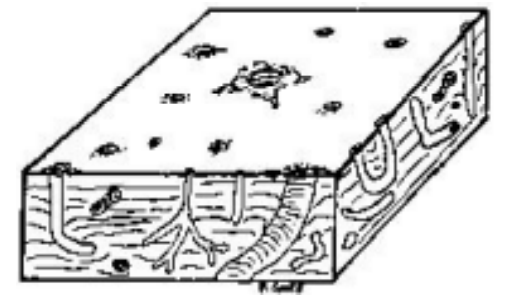
Stromatolites
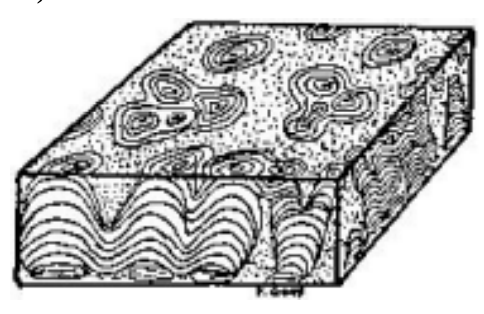
Sedimentary environments