Biology grade 12
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI4U Course
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
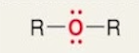
Ether
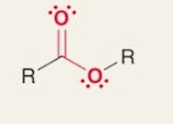
Ester
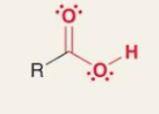
Carboxylic acid

Hydroxyl/alcohols
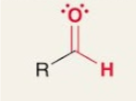
Aldehyde
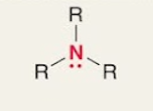
Amine
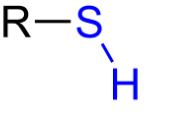
Sulflhydryl or Thiol
Hydrolisis
a chemical reaction in which water is used to break down the bonds of a particular substance
Dehydration synthesis
the process of joining 2 molecules or compounds together following the removal of water
Organic compounds
Always contain hydrogen and carbon
Always have covalent bonding between atoms
May be very large, with many atoms
Associated with living things
Inorganic compounds
Associated with non living things
Usually have ionic bonding between atoms
always contain a small number of atoms
usually contain metals and non metals
Functional groups
other atoms that are covalently bonded to the carbon backbone chain.
Are parts of molecules involved in chemical reactions
macromolecules
large complex molecules, usually composed of repeating units of smaller molecules linked by covalent bonds
polymer
a long molecule consisting of many similar smaller building blocks called monomers
monomer
one of the small repeating molecular units that make up a polymer
4 major macromolecules
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
Carbohydrates
biological molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Usually polar and has high number of hydroxyl groups
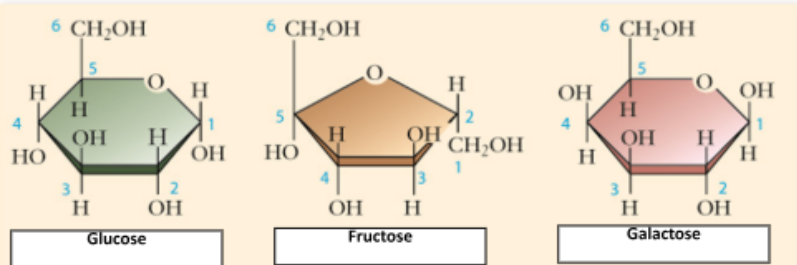
Monosaccharides
Composed of a single, carbon based monomer structure. They are simple sugars with 3-7 carbon atoms
Isomers
molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structures
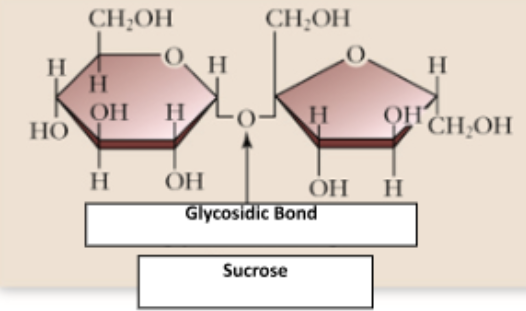
Disaccharides
Composed of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrate polymers of monosaccharides (usually glucose), joined covalently
3 arrangements of glucose produced polysaccharides
glucose, starch, cellulose
glycosidic linkage
the type of covalent bond that connects two monosaccharides together to form a disaccharide (or larger carbohydrate)
How polymers are built
Dehydration synthesis of two glucose (or other) monomers
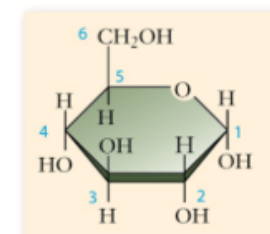
glucose
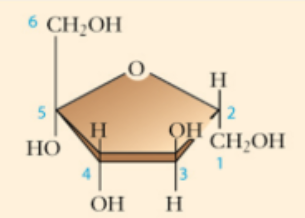
fructose
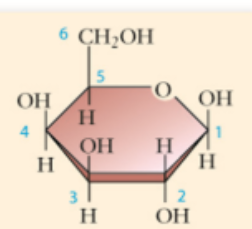
galactose
Lipids
Composed of C, H, and O and hydrophobic
Uses of lipids
Insulate against heat loss
Form protective cushion around major organs
major component of cell membranes
Types of lipids
Fatty Acids
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Steroids
Waxes
Saturated Fatty Acid
A hydrocarbon chain ending in a carboxyl group with no double bonds between carbon atoms
Monounsaturated fatty acids
A hydrocarbon chain ending in a carboxyl group with 1 double bond between carbon atoms
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
A hydrocarbon chain ending in a carboxyl group with more than 1 double bond between carbon atoms
Kinks
prevent unsaturated fatty acid chains from packing close together, so they stay liquid at room temp
Triglycerides
A lipid made of glycerol bonded to 3 fatty acids through ester linkages
Triglycerides containing saturated fatty acids
Are solid at room temperature
Triglycerides containing unsaturated fatty acids
liquid at room temperature
Hydrogenation
A food preservation process that adds hydrogen to unsaturated fats to make them saturated
Phospholipids
A lipid made of glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group; has a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails.
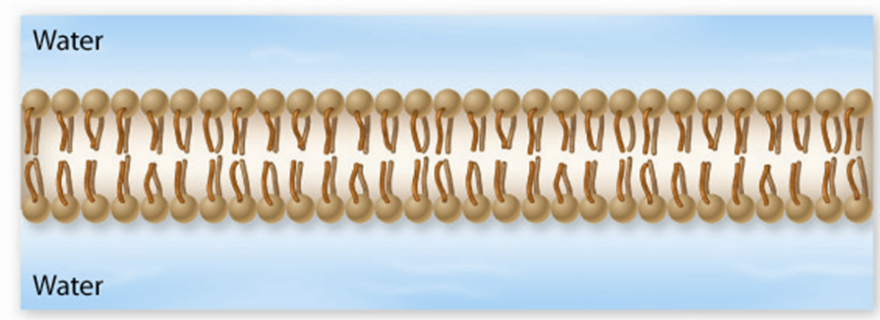
Lipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that forms the when in water, with hydrophilic heads facing water and hydrophobic tails inside.
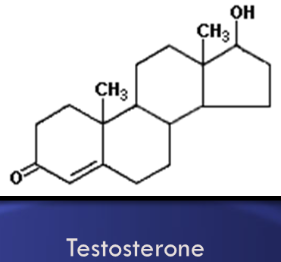
Sterols
Lipids made of four attached carbon rings. Examples include cholesterol, testosterone, and estrogen. Cholesterol is part of animal cell membranes and a precursor for other steroids, but high levels can lead to fatty deposits in blood vessels.
Use of sterols in medicine
Reduce inflammation
inhalers to treat asthma
Used to build muscle for patients with cancer of AIDS
Topical sterol ointments for skin conditions
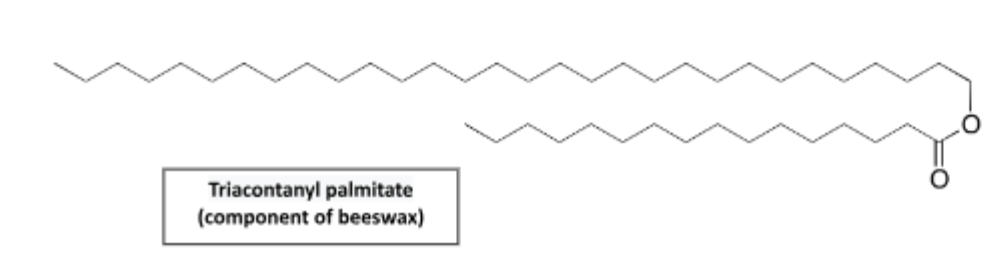
Waxes
Lipids composed of long, carbon-based chains. They are water repellent and solid at room temperature
Proteins
A polymer that has many different subunits folded into a 3-D structure that serves a certain purpose. Linked by covalent bonds
Functions of protein
catalyzing chemical reactions
providing structural support (bones, skin, hair, nails etc)
transporting substances (in blood, proteins transport O2
enabling organisms to move (muscle contraction)
regulating cellular processes (hormones, regulate genetic activity)
providing defense from disease (antibodies are proteins)
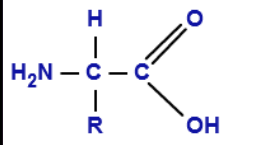
Amino acids
organic molecules composed of a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a hydrogen atom.
Peptide bond
A covalent bond that links amino acids together. It forms between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another through dehydration synthesis (water is released).
Polypeptides
Polymers composed of amino acids linked by covalent bonds. They fold into specific shapes to form proteins.
Denaturation of proteins
A structural change in a protein caused by factors like heat, pH, or chemicals. It causes the intermolecular bonds to break. Once a protein loses its 3d shape it can’t perform its function
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid and contains the genetic information for a cell (holds instruction for making proteins
RNA
ribonucleic acid. It assists the process of decoding DNA information into the amino acid sequences of proteins
Pyrimidine
A type of nitrogenous base with a single-ring structure found in nucleic acids. In DNA and RNA, the pyrimidines are cytosine (C), thymine (T, only in DNA), and uracil (U, only in RNA).
Purines
A type of nitrogenous base with a double-ring structure found in nucleic acids. In DNA and RNA, the purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G).
DNA Base pair rules
In DNA: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C).
RNA Base pair rules
In RNA: adenine (A) pairs with uracil (U), and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C).