Forensics final exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/242
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:37 AM on 5/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
243 Terms
1
New cards
whats the Bertillon method and why was it phased out
a method of taking 11 measurements and was phased out because some peoples measurements were identical
2
New cards
henry fauld
Suggested that skin ridge patterns could be important for identification of criminals.
3
New cards
william herschel
English civil servant, who had Indian citizens sign documents with handprints
4
New cards
francis galton
Discussed the anatomy of fingerprints, suggested method of classifying them (loops, arches, and whorls). No two fingerprints are alike and that prints remained unchanged from year to year.
5
New cards
Dr. Juan Vuctiech
Argentinian police officer, developed a workable system capable of filing thousands of prints in a logical and searchable system in 1891
6
New cards
Sir Edward Richard Henry
Developed another classification system adopted by Scotland yard, and is widely used in most English-speaking countries including the United States
7
New cards
what was the will west case of 1990 and how did it impact fingerprints in forensics
Two suspects were brought in with the same bertillion measurements but different fingerprints leading people to use fingerprints as a prefered identification method
8
New cards
what was the ruling in United States v. Byron C. Mitchell?
Fingerprint identification are admissible in court
9
New cards
what are the 3 major principals of fingerprints
1) no two fingerprints are the same
2) fingerprints do not change in an individuals life time
3) fingerprints have general ridge patterns that allow them to be identified
2) fingerprints do not change in an individuals life time
3) fingerprints have general ridge patterns that allow them to be identified
10
New cards
what are the 3 main ridge comparisons
identity, number, shape
11
New cards
epidermis
outermost layer of skin
12
New cards
dermis papille
barrier between epidermis and dermis, determins the ridges on the skin when they are a fetus
13
New cards
dermis
Inner skin
14
New cards
what are the 3 general cases of fingerprints, which is common and rare in the population
Loop 65% whorl 35% arch 5%
15
New cards
how to identify a loop / what are their subclasses
ridges entering \n from one side of the print, recurving, and \n exiting from the same side
Ulnar= the loop opens towards the pinkie
radial = the loop opens toward the index finger
Ulnar= the loop opens towards the pinkie
radial = the loop opens toward the index finger
16
New cards
how to identify a whorl / what are their subclasses
All whorls must have at least 2 deltas and a recurve in \n front of each \n Fundamental Principles of Fingerprints
Plain Whorl = imaginary line bwtween deltas
central pocket whorl = no imaginary line btween deltas
double loop = two seperate loop formations
accidental - any pattern that doesn’t fit into the ones listed
Plain Whorl = imaginary line bwtween deltas
central pocket whorl = no imaginary line btween deltas
double loop = two seperate loop formations
accidental - any pattern that doesn’t fit into the ones listed
17
New cards
how to identify arches / what are their subclasses
no deltas or cores
plain = simple rise or wave
tented = 90 degree or less
plain = simple rise or wave
tented = 90 degree or less
18
New cards
what does ACE-V stand for
Analysis, comparison, evaluation, verification
19
New cards
ACE-V (analysis)
look for distorations or surface patterns
20
New cards
ACE-V (Comparison)
Examiner compares print to known print at 3 levels
21
New cards
ACE-V (Evaluate)
Requires one decision of three of the examiner, Identification, Exclusion, and Inconclusive
22
New cards
ACE-V (verification)
Requires and independent examination of the questioned and known prints by a second examiner
23
New cards
Henry FBI identification system
Converts ridge patterns on all 10 fingers into a series of numbers and letters arranged in the form of a fraction
24
New cards
Class characteristics of finger prints
Types of ridge patterns
25
New cards
indivicual characteristics
Position of minutiae, Pores
26
New cards
what is AFIS how does IAFIS work
AFIS uses automatic scanning devices that convert the images the image of a fingerprint
27
New cards
what are the 3 types of prints found at a crime scene
Visible, plastic, latent
28
New cards
visible prints
Prints left by external substance like blood or paint
29
New cards
plastic prints
print imbeded into an object like playdough
30
New cards
latent prints
prints not so visible to the naked eye but shown through oil/ perspiraction left by yhe finger
31
New cards
what is RUVIS
Refelcted ultraviolet imaging system
can located prints in their natural state without chemicals or powders
can located prints in their natural state without chemicals or powders
32
New cards
Fingerprint powders
hard and nonabsortant surfaces, psticks to persiration and oils
33
New cards
Iodine Fuming
poruous surfaces, adheres to perspiraction and fatty oils
34
New cards
ninhindryn
porous and adheres to amino acids in perspiration
35
New cards
super glue and arodox
nonpours surfaces, adheres to perspiration
36
New cards
physical developer
porous surfaces adheres to fatty acids, ailver nitrate reagent
37
New cards
DFO / 1,2indenodine
DFO = porous amino acids and is more sensative to ninhindryun
1\.2indenodine= porous amino acids can replace the 2 step process of ninhyndryn and DFO
1\.2indenodine= porous amino acids can replace the 2 step process of ninhyndryn and DFO
38
New cards
how do you preserve fingerprints
take photos and if the item is small enough take the object, but if too large you can use tape to left a copryof the print
39
New cards
how are fingerprints processed on a computer and how is the quality improved
the picture is then converted to a digital file and then can be inproved in quality with the number of pixels, contrast to the background, qnd overall brgihtness
40
New cards
define fire arms
41
New cards
define ballistics
42
New cards
what are the 3 major types of hand guns
43
New cards
difference between single action and double action revolverr
44
New cards
characteristics of a single shot pistol
45
New cards
what are the 3 major types of revolvers / whats their differences
46
New cards
what are the characteristics of the semi automatic pistol
47
New cards
what are the two types of long gun / what are their differences
48
New cards
what is rifling and why is it done
49
New cards
what are the 3 types of rifling methods
50
New cards
what are the compnenets of amunition
51
New cards
what are the class characterisics of a bullet
52
New cards
what are the individual characterstics of the bullet
53
New cards
What are the past and current automated firearm searches?
54
New cards
What is gun shot residue? What is primer residue?
55
New cards
what are the 2 tests to run for GSR / what do they test for / what do positive and negative tests look like
56
New cards
what is a SEM spectrum and what is it used for
57
New cards
how does serial number restoration work and what are the chemicals
58
New cards
how are fire arms and amunition processed in a crime scene
59
New cards
what are the steps for calculating the height of the shooter given distance and angle of impact
60
New cards
what are the class and individual characteristics of tool marks
61
New cards
how are shoe impressions preserved at a crime scene
62
New cards
what is electrostatic lifting and how does it work
63
New cards
describe how to cast things chemically in two ways
64
New cards
describe the casting process normally and in snow
65
New cards
class and individual characteristics of a tire
66
New cards
what is sicar
67
New cards
whats the difference between a chemical and physical property
chemical = describes a substance in reletion to another substance
physical = describes a substance withput mentioning another substance
physical = describes a substance withput mentioning another substance
68
New cards
matter
anythong that has mass and ocupies space
69
New cards
element
simpliest sibstance, building blocks from which all matter is composed
70
New cards
atom
smallest particle in an element, protons, elextrons, nuetrons
71
New cards
compoud
pure substance composed of two or more elements
72
New cards
molecule
smallest unit of a compound
73
New cards
what are the 3 states of matter / what makes them unique
solid = has definite shape
liquid = occupies specific space
gas = no definite shape or space but will fill a container
liquid = occupies specific space
gas = no definite shape or space but will fill a container
74
New cards
what are the 3 phase changes
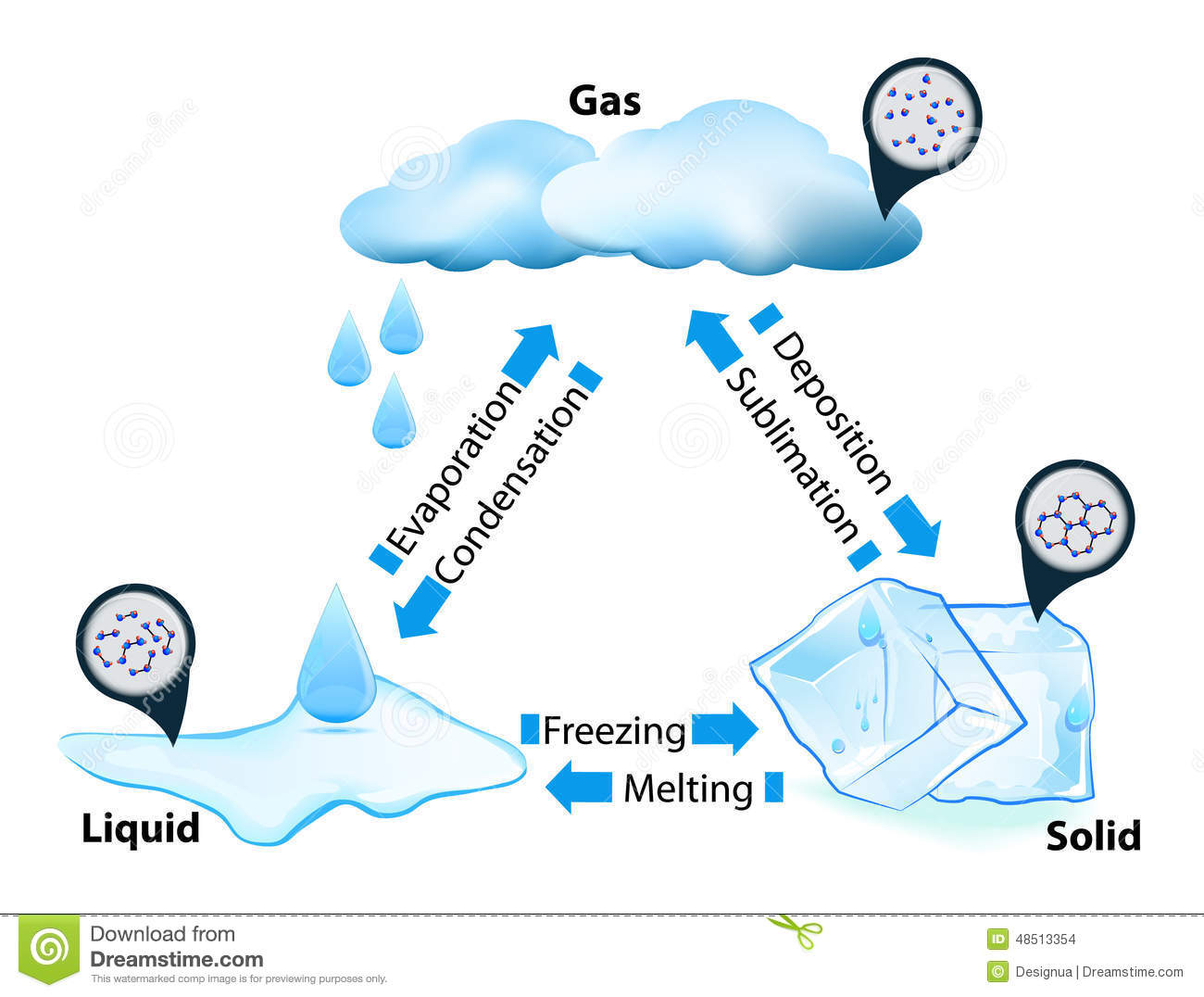
75
New cards
Metric conversions
kilo -> hecta →daka → basic unit → decit→ centi → mili
76
New cards
whats an intensive property
a property that is not dependent of on the size of the object
77
New cards
density calculation / what factors effect density
78
New cards
what is refraction and whats the refraction index
79
New cards
what are the two types of solids
80
New cards
what unique property do crystalline solids have
81
New cards
what is dispersion
82
New cards
true or false, light behaves like a wave AND a particle
true
83
New cards
what is frequency and wavelength / whats their reletionship
84
New cards
red vs violet wavelength, frequency, energy
85
New cards
radio waves vs gamma waves wavelength, frequency, energy
86
New cards
what is coherent and incoherent radiation
87
New cards
what are the 4 main types of glass and their properties
88
New cards
what are the class and individual characteristics of glass
89
New cards
3 ways to calculate density of glass
90
New cards
how to use snells law to calculate refractive index of a liquidi
91
New cards
How is the refractive index of a glass sample determined
92
New cards
what are becke lines
93
New cards
what are the two types of glass fractures
94
New cards
Know the unique properties to each of fracture type
95
New cards
What can be learned by studying glass fracture patterns?
96
New cards
which side the hole is wider on in a glass fracture
97
New cards
how chonchoidal Striations or wallner lines are used to determine directionality on radial and concentric edge of glass.
98
New cards
how velocity correlates to the shape of the hole in the class and to type of weapon
99
New cards
Given a fracture pattern, be able to determine the sequence of events
100
New cards
Know how to collect glass fragments