Biology first exam
1/255
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
256 Terms
What is science
A way of thinking
What can science NOT do
determine morally right from wrong, address god, explain feelings
5 steps of scientific method
observations, hypothesis, testable prediction, conduct experiment, conclusion
Observations are
description, measurement, 5 senses
Hypothesis
Informed logical and plausible explanation, statement, testable
Prediction
IF and THEN statement
How to conduct experiment
repeatable manipulation of one or more aspects of natural world
Elements of an experiment
control group, independent and dependent variables, treatment group, double blind, randomized
scientific literacy
understanding basics of science and scientific process
Correlation…
does not equal causation
Independent variable
manipulate variable from one group to another
Dependent Variable
responds to changes in independent variable
Treatment group
experimental group, same conditions as control, manipulated
Organisms are composed of
matter
chemical reactions occur to
move and grow
4 elements make up living things
hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen
Atom
Smallest element that has characteristic
atoms are broken into
subatomic particles
what are the 3 subatomic particles
protons, neutrons, and electrons
How many electrons are in 1st shell and 2nd and 3rd shell
2, 8
What happens with nuclei during chemical reaction
2 atoms do not come close together
Knowing how many electrons an atom has helps to
see how they interact
Chemical bond
attractive force that holds atoms together and link to molecule
What are types of chemical bonds between atoms
covalent polar and nonpolar and ionic
Electronegativity
atoms attraction for electrons in covalent bond
what does electronegativity determine
polar or nonpolar
The more electronegative…
stronger pulls electron toward itself
How to know by electronegativity if atoms are polar
if there is a greater than .4 difference
What would classify as equal sharing in a covalent bond?
.4 or less difference of electronegativity between the two atoms
What would classify as unequal sharing in a covalent bond?
greater than .4 difference in electronegativity
In covalent bonds, more time near oxygen means…
slightly negative charge
In covalent bonds, less time near hydrogen means
slightly positive charge
What type of molecule is water
polar covalent
Ionic bonds are when…
more than 1.7 difference in electronegativity
Ionic bonds result in
complete transfer to highly electronegative atoms
In ionic bonds, an atom that loses electron becomes
positively charged
In ionic bonds, an atom that gains electron becomes
negatively charged
A slight positive charge on hydrogen atom will attract…
negative charge on oxygen of neighboring water molecule
What gives water unique properties
hydrogen bonds that hold the water molecules together
cohesion
attraction between like molecules
adhesion
attraction between unlike molecules
What keeps water together
hydrogen bonds
What allows water to adhere to the surface
polar components
Surface tension
cohesive force caused by attraction between molecules at surface of liquid
Are molecules at surface weaker or stronger and why?
stronger bc of hydrogen bonding
What happens as water freezes
forms open crystal structure
Is ice more or less dense than liquid
less dense
Why is ice being less dense better
because it forms insulating blanket at top of body allowing animals to live underneath
Does water have high or low specific heat
high
High specific heat
amount of energy needed to raise temp of 1g of substance by 1C
What is the temperature of a substance measure
how quickly the molecules are moving
Hydrophillic
water loving
hydrophobic
water fearing
hydrophobic characteristics
uncharged, non polar, cant dissolve in water
How hydrophilic works
ions and polar molecules stay in solution due to their interactions with waters partial charges
What results when highly electronegative oxygen keeps electron
hydrogen ion
pH
negative logarithm of H+ concentration
Acid solutions have what kind of pH
low
Neutral solutions have pH of…
7
Neutral solutions have what ions
equal amt of OH- ions than H+ ions
Acid solutions have what ions
high H+
Basic solutions have what kind of pH
high
Basic solutions have what kind of ions
low H+ and more OH- than H+
organic molecule
molecule that contains carbon bonded to other elements linked in a chain or ring
almost all molecules found in organisms contain what element
carbon
What are the four classes of macromolecules
carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acid, lipids
All macromolecules aside from lipids are
polymers
Polymer
large macromolecules composed of many monomers linked together
Dehydration reactions do what
join monomers into polymers
does H2O go in or out during dehydr
Does H2O go in or out during hydrolysis
in
Hydrolysis
break polymers into monomers
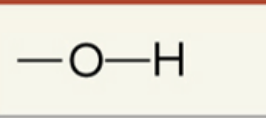
what function group is this
hydroxyl
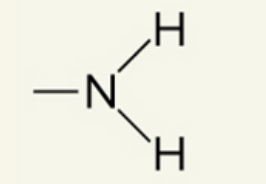
what functional group is this
amino
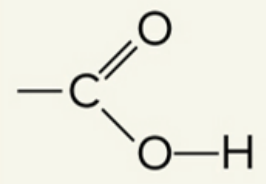
what functional group is this
carboxyl
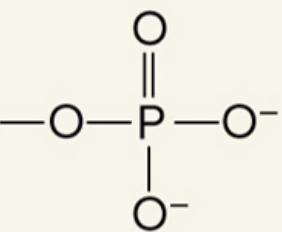
what functional group is this
phosphate
where are functional groups found
mono, di, and polysaccharides
monosaccharides are
one sugar monomers
disaccharides are
two sugars
polysaccharides are
many sugar polymers
Complex carbs are
long chains of glucose
Example of complex carb
polysaccharide
Examples of polysaccharides
cellulose, starch, glycogen
Cellulose
structure of plant cell walls, very solid
starch
energy storage in plants
starch has no
hydrogen bonds
How are starch polysaccharides assembled
made up of glucose
what does glucose molecule linkage allow for
branching and high solubility in water
How are glycogen polysaccharides assembled
with hydroxyl groups and molecules only face right side up
Are glycogen and starch polar or nonpolar and why
polar bc of hydroxal groups
Structure of cellulose and why
straight rodlike molecules held by hydrogen bonds and insoluble in water
Proteins are (3 things)
complex, highly versatile, polymers of amino acids
What do proteins do
carry out crucial bodily functions
monomer is an
amino acid
monomers have what 2 functional groups and do what in water
amino and carboxyl, ionize
ionization of water helps amino acid
stay dissolved and be highly reactive
How do amino acids differ
R groups (side chains)
What do the side chains traits help us know
how strands will interact with others
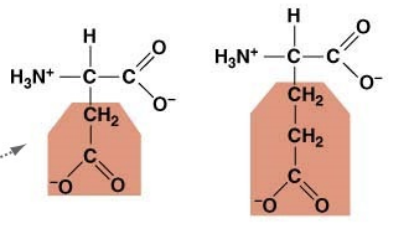
what characteristic and what do they attract
acidic, positive
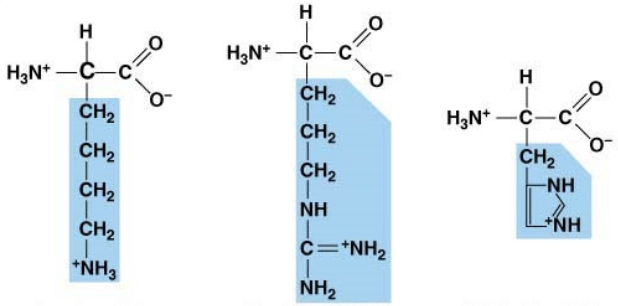
what characteristic and what do they attract
basic, negative