Animal Nutrition Exam III
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Roles of Digestive Tract
absorbing nutrients, rid the body of waste, break down food, and some immune responses like producing enzymes
roles of saliva
moisten food, produces salivary amylase (starch digestion, ruminants do not have amylase), buffers rumen pH
3 main salivary glands
parotid, sublingual, mandibular (PSM-Parker can Sub for spanish(lingual) with Mandi)
Deglutition
fancy word for swallowing
Peristalsis
movement of food down the esophagus (like a snake)
Regions of the stomach
cardiac: produces mucus for lubrication and protection, fundic: produces enzymes and hydrochloric acid, pyloric: secretes hormones and mucus
Parietal cells
produce HCl
chief cells
secrete pepsinogen
zymogen
non-activated hormone that must be activated by an enzyme
small intestine
major site of digestion and absorption
roles of small intestine
Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum
Duodenum
addition of digestive juices, pancreatic enzymes, bicarb, bile salts, enterocyte secretions
Jejunum
where most absorption occurs
Ileum
a major site of immune function, the transition from the small intestine to the large intestine, little absorption
villi
increase the surface area
Bile
stored in the gallbladder is secreted to aid in fat emulsification
areas of large intestine
cecum, colon, rectum (CeCoRe)
cecum
fermentation, large in hindgut fermenters
colon
some absorption of short-fatty acids
rectum
excretion of feces
what happens in large intestine?
microbial fermentation, synthesis of some water-soluble vitamins
enzymes
protease, lipase, amylase
protease
breaks down protein
lipase
breaks down fats
amylase
break down starch
Glucose Transportation
SGLT1, GLUT5, GLUT2
SGLT1
Sodium-Glucose Linked Transporter 1: brings glucose into the enterocyte from the intestinal Lumen
GLUT5
brings fructose into the enterocyte from the Lumen
GLUT2
Brings Glucose OUT of the enterocyte and into circulation
GI tract hormones
gastrin, ghrelin
gastrin
stimulates HCl and pepsin productions
ghrelin
increases hunger signaling
Incretins
secreted by the small intestine in the presence of food. They “prime” the pancreas for insulin secretion.
examples of Incretins
GLP-1, GLP-2
Gut Peptide Hormones
Cholecystokinin (CCK), peptide YY (PYY). Both decrease feed intake
cholecystokinin (CCK)
release of digestive enzymes and bile into the small intestine, decreases feed intake
Peptide YY (PYY)
increases retention in the intestine and water/electrolyte absorption, decreases feed intake
rumination
regurgitation and rechewing of cud (a bolus of food), and breaks down the food even more, increasing surface area for microbial digestion
cows digestive tract
rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum, papili
rumen
site of microbial fermentation and VFA absorption
reticulum
mixing and regurgitating feed
omasum
water absorption
Abomasum
“True stomach” secretes HCl and digestive enzymes to break down feed
papili
used to increase surface area
Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA)
produced by rumen
examples of VFAs
Acetate, Propionate, Butyrate
Acetate
Used as the primary source of acetyl-CoA for lipid synthesis
propionate
key substrate for glucose production
butyrate
oxidized in tissue for energy production
microbes in prokaryotes
bacteria, archaea
microbes in eukaryotes
Protozoa, fungi
Why can’t horses throw up?
esophagus only allows for one way peristaltic movement.(will drown)
Effect of Horses not having a gallbladder
will have less bile secretion, has a hard time breaking down fats
horses cecum
enlarged to aid in fiber digestion
Hindgut Acidosis
Significant increase in starch
increase in lactic acid in the hindgut
pH drops
decreasing in fiber-digesting bacteria and an increase in lactate-producing bacteria
death of bacteria
release endotoxins
causes inflammation
inflammation—> changes in laminae
Avians
Crop, Proventriculus, Gizzard, 2 Ceca, excretes nitrogen via uric acid mixed into feces
crop
regulates the flow of food to the lower GI tract. Allows breakdown by salivary amylase
proventriculus
production of HCl and pepsin
gizzard
mixing and grinding feed, CONTAINS GRIT
2 ceca
reabsorbs water
What is Energy measured in?
Joules and calorie & Calorie
Joules
standard international unit of energy. 1 cal=4.186 J
calorie (cal)
heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gallon of water 1 degree higher
Calorie
=1kcal=1000 calorie
Types of Energy
Kinetic, Potential, sound, light
Kinetic energy
thermal, mechanical, electrical, magnetic
potential energy
chemical, elastic, nuclear, gravitational
Energy Consumers
autotroph, heterotrophs, each time energy is transferred from one entity to another, some energy is lost as heat
Autotroph
can use atmospheric CO2
Phototrophs, and lithotrophs
phototrophs
uses light energy (photosynthetic bacteria and plants)
heterotrophs
cannot use atmospheric CO2
must obtain carbon from their environment from organic molecules (all animals fall in this category)
Positive energy balance
the animal will gain weight
Neutral energy balance
the animal will maintain its weight
negative energy balance
the animal will lose weight
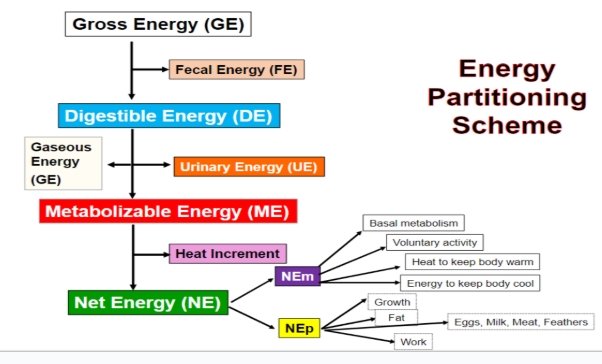
gross energy
the total chemical energy in feed
digestible energy
The amount of energy in the feed - the amount of energy lost in the feces
metabolizable energy
the amount of energy in the feed - the energy lost in heat
net energy
The amount of energy in the feed - the energy lost in the feces, urine, and heat production through digestive and metabolic processes
energy partitioning scheme
GEFEDEGUMHINE
%TDN: total digestible nutrients
digestible protein + digestible fiber + digestible nitrogen free extract + digestible (Fat x 2.25)
DE
GE-fecal
ME
DE - urine - gas
NE
ME - heat
Energetic Efficiency
(NE/GE) x 100
NE(L)
net energy for lactation. milk synthesis
NE(G)
net energy for growth. Tissue fat accretion
NE(M)
Net energy for Maintenance.
Basal metabolism, posture, movement, thermoregulation, and maintenance of homeostasis
energetic efficiency
metabolizable energy (ME)/Net energy (NE) x 100
Respiratory Quotient
can estimate an animal’s energy balance
it reflects the ratio of carbon dioxide produced to oxygen consumed during respiration (varies on the type of nutrient being used for E)
ATP
major form of cellular energy, 2 phosphoanhydride bonds (high E)
Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle
citric acid = krebs cycle, takes place in mitochondrial matrix
Oxidative Phosphorylation
links oxidation of high E molecules (NADH, FADH2) to the addition of a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP
Aerobic Respiration of Glucose
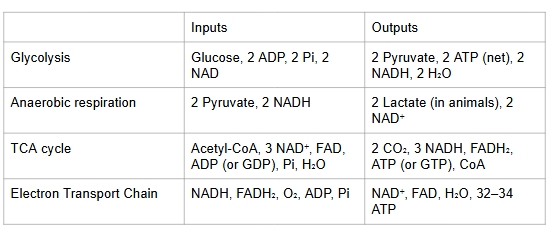
Gluconeogenesis
synthesis of glucose
substrates of Gluconeogenesis
glycerol, amino acids, lactate, propionate
beta-oxidation
conversion of fats to energy
Homeostasis
maintenance of physiological equilibrium
Homeohesis
orchestrated or coordinated in tissue metabolism necessary to support the priorites of a physiological state
homeohesis vs. homeostasis
changes a threshold based on changes in need vs. tries to maintain status quo